GNU/Linux - 是否可以多次打开同一个设备文件
使用设备/dev/ttyS1举例来说明。
一个设备文件打开多次
在 Linux 中,多次打开 /dev/ttyS1 以读取数据通常是可以接受的。多次打开 /dev/ttyS1 并向 /dev/ttyS1 发送数据时,所有打开的文件描述符都能接收数据。每个打开的文件描述符都代表与串行端口的独立连接,发送到 /dev/ttyS1 的数据将被所有打开的文件描述符接收。从多个文件描述符读取 /dev/ttyS1 中的数据本身不会导致数据丢失。不过,在某些情况下,如果处理不当也会造成数据丢失。
有一些注意事项需要牢记:
1. 并发性: 每个打开的文件描述符在内核中都代表一个独立的文件对象。从同一个串行端口(本例中为 /dev/ttyS1)同时读取多个文件描述符是可能的。不过,如果多个进程或线程同时从同一设备读取数据,则应注意潜在的竞赛条件。如有必要,应采用适当的同步机制来避免冲突。
竞赛条件: 如果多个进程或线程在没有适当同步的情况下同时从 /dev/ttyS1 读取数据,就可能出现竞赛条件。例如,一个进程可能会读取原本打算给另一个进程使用的数据,从而导致数据丢失或损坏。
2. 缓冲: 内核通常会对从串行端口读取的数据进行缓冲。多次打开 /dev/ttyS1 时,每个文件描述符都有自己的缓冲区。这意味着从一个文件描述符读取的数据不会影响从另一个文件描述符读取的数据。不过,缓冲区的大小是有限的,如果一个文件描述符读取数据的速度比另一个文件描述符快,缓冲区溢出时可能会丢失数据。
每个文件描述符在内核中都有自己的缓冲区,用于存放从串行端口接收到的数据。如果接收数据的速度超过从缓冲区读取数据的速度,缓冲区可能会被填满,导致后续数据被丢弃。这会导致数据丢失。
3. 资源消耗: 每个打开的文件描述符都会消耗系统资源。多次打开 /dev/ttyS1 会增加资源使用量,包括用于缓冲区的文件描述符和内核内存。请注意资源限制,尤其是在资源有限的环境中。
4. 共享配置: 所有打开的文件描述符共享相同的串行端口配置,如波特率、奇偶校验和流量控制设置。通过一个文件描述符对配置所做的更改将影响所有其他文件描述符所看到的串行端口行为。
5、顺序传输: 虽然所有打开的文件描述符都能接收数据,但向 /dev/ttyS1 的数据传输是按顺序进行的。数据写入串行端口时,会按照驱动程序接收数据的顺序发送出去。因此,如果多个进程或线程同时向 /dev/ttyS1 写入数据,数据将按顺序而不是并发地发送出去。
6、数据丢失
从多个文件描述符读取 /dev/ttyS1 的数据时,要降低数据丢失的风险,请考虑以下几点:
* 缓冲区大小: 确保内核为每个文件描述符分配的缓冲区大小足以处理预期的数据速率。
* 流量控制: 使用硬件或软件流量控制机制来控制串行端口和应用程序之间的数据流。流量控制可在缓冲区满时暂停数据传输,有助于防止缓冲区溢出。
* 同步: 如果多个进程或线程同时从 /dev/ttyS1 读取数据,则应使用适当的同步机制(如互斥、semaphores)来协调对串行端口和共享数据结构的访问。
* 错误处理: 实施稳健的错误处理,以检测和恢复可能导致数据丢失的情况,如缓冲区溢出或通信错误。
通过仔细管理缓冲区大小、实施流量控制、同步访问串行端口并适当处理错误,可以最大限度地降低从多个文件描述符读取 /dev/ttyS1 数据时丢失数据的风险。
总之,在 Linux 中多次打开 /dev/ttyS1 读取数据一般是没问题的,但应考虑并发、缓冲、资源使用和串行端口配置,以确保正确高效的操作,尤其是在多线程或多进程环境中。
内核如何向多个文件描述符分发数据
当你向/dev/ttyS1 发送数据时,内核会处理将数据分发到每个打开的文件描述符。每个打开的文件描述符都代表与串行端口的独立连接,内核会确保写入 /dev/ttyS1 的数据被所有打开的文件描述符接收。
下面是该过程的一般工作方式:
1. 数据传输: 向 /dev/ttyS1 写入数据时,数据会被发送到内核中的串口驱动程序进行传输。
2. 缓冲: 内核会为与 /dev/ttyS1 相关联的每个打开的文件描述符维护一个缓冲区。从串行端口驱动程序接收数据时,数据会被复制到每个打开的文件描述符的缓冲区中。
3. 读取操作: 当进程从与 /dev/ttyS1 关联的打开文件描述符中读取数据时,会从其缓冲区中读取数据。每个进程都有自己的缓冲区,因此从一个文件描述符读取数据不会影响从其他文件描述符读取数据。
4. 顺序传输: 发送到 /dev/ttyS1 的数据是按顺序传输的,这意味着如果多个进程或线程同时向 /dev/ttyS1 写入数据,数据将按照驱动程序接收到的顺序发送出去。这就确保了数据完整性,不同进程的数据不会交错。
总之,在向 /dev/ttyS1 发送数据时,内核会确保将数据分发给与 /dev/ttyS1 相关的所有打开的文件描述符。每个文件描述符都有自己的缓冲区用于接收数据,数据传输按顺序进行,以保持数据的完整性。
============= 分割线 =============
英文版:
Open one device file multiple times
Opening /dev/ttyS1 multiple times to read data in Linux is generally acceptable. When you open /dev/ttyS1 multiple times and send data to /dev/ttyS1, all open file descriptors can receive data. Each open file descriptor represents an independent connection to the serial port, and data sent to /dev/ttyS1 will be received by all open file descriptors. Reading data from /dev/ttyS1 from multiple file descriptors should not inherently cause data loss. However, there are scenarios where data loss can occur if not handled properly.
There are some considerations to keep in mind:
1. Concurrency: Each open file descriptor represents an independent file object in the kernel. Reading from the same serial port (/dev/ttyS1 in this case) from multiple file descriptors concurrently is possible. However, you should be aware of potential race conditions if multiple processes or threads are reading from the same device simultaneously. Proper synchronization mechanisms should be employed if needed to avoid conflicts.
Race Conditions: If multiple processes or threads are reading from /dev/ttyS1 concurrently without proper synchronization, race conditions can occur. For example, one process may read data that was intended for another process, leading to data loss or corruption.
2. Buffering: The kernel typically buffers data read from the serial port. When you open /dev/ttyS1 multiple times, each file descriptor has its own buffer. This means that data read from one file descriptor will not affect the data available for reading from another file descriptor. However, the size of the buffer is limited, and if one file descriptor reads data faster than another, data may be lost if the buffer overflows.
Each file descriptor has its own buffer in the kernel for data received from the serial port. If the rate at which data is received exceeds the rate at which it is read from the buffer, the buffer may fill up, causing subsequent data to be discarded. This can lead to data loss.
3. Resource Usage: Each open file descriptor consumes system resources. Opening /dev/ttyS1 multiple times increases resource usage, including file descriptors and kernel memory for buffers. Be mindful of resource limits, especially in resource-constrained environments.
4. Shared Configuration: All open file descriptors share the same serial port configuration, such as baud rate, parity, and flow control settings. Changes made to the configuration via one file descriptor will affect the behavior of the serial port as seen by all other file descriptors.
5, Sequential Transmission: While all open file descriptors can receive data, data transmission to /dev/ttyS1 occurs sequentially. When data is written to the serial port, it is sent out in the order it was received by the driver. Therefore, if multiple processes or threads are concurrently writing data to /dev/ttyS1, the data will be sent out sequentially, not concurrently.
6, Data loss
To mitigate the risk of data loss when reading from /dev/ttyS1 from multiple file descriptors, consider the following:
* Buffer Size: Ensure that the buffer size allocated by the kernel for each file descriptor is sufficient to handle the expected data rate.
* Flow Control: Use hardware or software flow control mechanisms to control the flow of data between the serial port and the application. Flow control can help prevent buffer overflows by pausing data transmission when the buffer is full.
* Synchronization: If multiple processes or threads are reading from /dev/ttyS1 concurrently, use appropriate synchronization mechanisms (e.g., mutexes, semaphores) to coordinate access to the serial port and shared data structures.
* Error Handling: Implement robust error handling to detect and recover from conditions that may lead to data loss, such as buffer overflows or communication errors.
By carefully managing buffer sizes, implementing flow control, synchronizing access to the serial port, and handling errors appropriately, you can minimize the risk of data loss when reading from /dev/ttyS1 from multiple file descriptors.
In summary, while it's generally okay to open /dev/ttyS1 multiple times to read data in Linux, you should consider concurrency, buffering, resource usage, and serial port configuration to ensure correct and efficient operation, especially in multi-threaded or multi-process environments.
How kernel distribute the data to more file descriptor
When you send data to /dev/ttyS1, which is open for multiple file descriptors, the kernel handles distributing the data to each open file descriptor. Each open file descriptor represents an independent connection to the serial port, and the kernel ensures that data written to /dev/ttyS1 is received by all open file descriptors.
Here's how the process generally works:
1. Data Transmission: When you write data to /dev/ttyS1, the data is sent to the serial port driver in the kernel for transmission.
2. Buffering: The kernel maintains a buffer for each open file descriptor associated with /dev/ttyS1. When data is received from the serial port driver, it is copied into the buffer of each open file descriptor.
3. Read Operation: When a process reads data from an open file descriptor associated with /dev/ttyS1, it reads from its buffer. Each process has its own buffer, so reading data from one file descriptor does not affect the data available for reading from other file descriptors.
4. Sequential Transmission: Data sent to /dev/ttyS1 is transmitted sequentially, meaning that if multiple processes or threads are concurrently writing data to /dev/ttyS1, the data will be sent out in the order it was received by the driver. This ensures that data integrity is maintained, and data from different processes does not get interleaved.
In summary, when sending data to /dev/ttyS1, the kernel ensures that the data is distributed to all open file descriptors associated with /dev/ttyS1. Each file descriptor has its own buffer for receiving data, and data transmission occurs sequentially to maintain data integrity.
注意:上面的分析和说明仅是书面,我还没有实际操作和验证过。
相关文章:

GNU/Linux - 是否可以多次打开同一个设备文件
使用设备/dev/ttyS1举例来说明。 一个设备文件打开多次 在 Linux 中,多次打开 /dev/ttyS1 以读取数据通常是可以接受的。多次打开 /dev/ttyS1 并向 /dev/ttyS1 发送数据时,所有打开的文件描述符都能接收数据。每个打开的文件描述符都代表与串行端口的独立…...
Visual Studio的使用方法
目录 1. 下载软件 2. 软件安装 3. 软件使用 4. VS工具的字体背景美化 5. 程序调试 1. 下载软件 官网地址:Visual Studio 2022 IDE - 适用于软件开发人员的编程工具 (microsoft.com) 2. 软件安装 1.选中vs_Professional,鼠标右击选择“以管理员身份…...

【35分钟掌握金融风控策略18】贷前风控策略详解-3
目录 编辑 贷前风控数据源 第三方数据 贷前风控数据源 第三方数据 在金融风控过程中,金融机构通常会引入一些第三方的风控数据(或第三方金融技术)来辅助识别贷款个人或贷款企业的风险状况,帮助金融机构进行风控决策&#x…...

秋招后端开发面试题 - MySQL事务
目录 MySQL事务前言面试题什么是数据库事务为什么要有事务呢?项目中遇到的事务事务的传播机制事务的特性?事务并发存在的问题四大隔离级别四大隔离级别,都会存在哪些并发问题呢数据库是如何保证事务的隔离性的呢?如何解决加锁后的…...
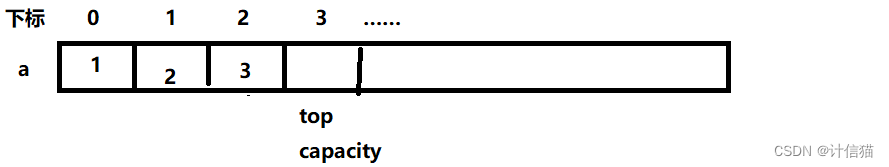
C语言栈的含义与栈数据操作代码详解!
引言:在本篇博客中,我们将学到数据结构——栈,讲到栈的含义与关于栈的数据操作代码。栈可以在顺序表、双向链表以及单链表的基础上实现,而于本篇博客中,我们选择在顺序表的基础上实现栈。 更多有关C语言和数据结构知识…...
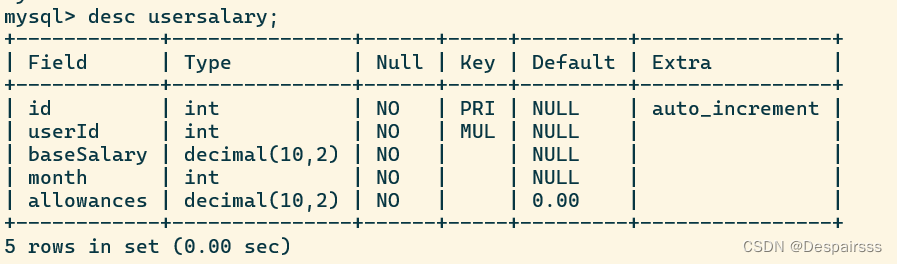
数据库基础语法二
一、数据库 1、登陆数据库 2、创建数据库zoo 3、修改数据库zoo字符集为gbk 4、选择当前数据库为zoo 5、查看创建数据库zoo信息 6、删除数据库zoo mysql -uroot -p #登陆数据库 create database zoo; #创建数据库zoo alter database zoo character set gbk collate gbk_…...

数据库的一些知识点
在Sno between列上创建约束,要求Sno的值在18至22岁之间,约束名Sno_CK。请写出对应的完整性命名子句constraint Sno_CK primary key check and。 本题得分: 0分 正确答案: 填空1 : 学号填空2 : snobetween18and22 2.单选题 (12分) 下述SQL命令的短语中…...
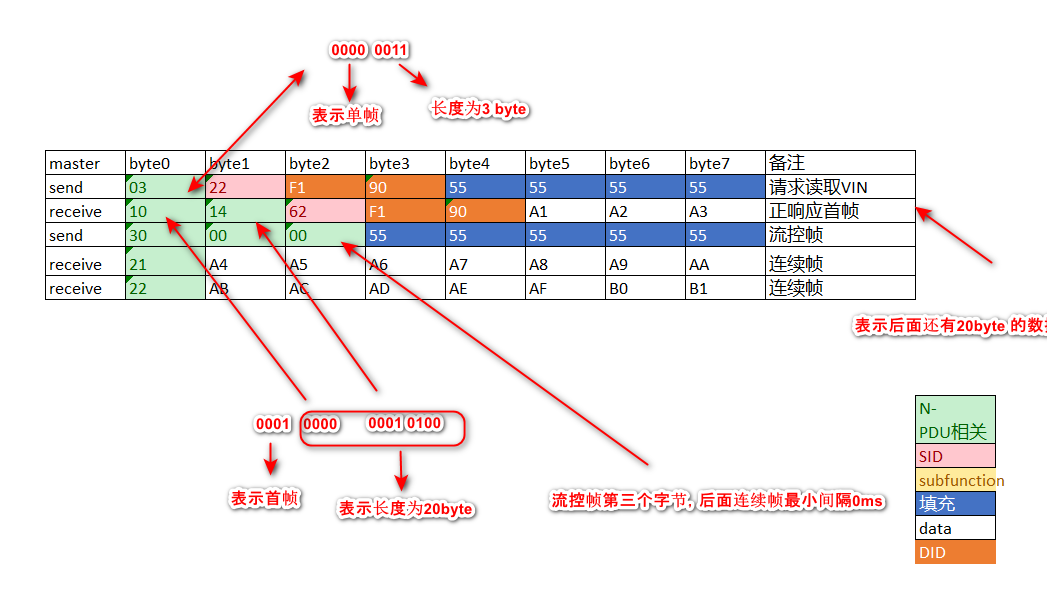
[AutoSar]BSW_Com021单帧 首帧 流控帧 连续帧 详解
目录 关键词平台说明一、N_PDU和N_PCI二、单帧三、首帧四、流控帧五、连续帧六、case 关键词 嵌入式、C语言、autosar、OS、BSW、UDS、diagnostic 平台说明 项目ValueOSautosar OSautosar厂商vector , EB芯片厂商TI 英飞凌编程语言C,C编译器HighTec (…...

CSS学习笔记之中级教程(一)
1、CSS 布局 - display 属性 1.1 display 属性 display 属性是用于控制布局的最重要的 CSS 属性。 display 属性规定是否/如何显示元素。 每个 HTML 元素都有一个默认的 display 值,具体取决于它的元素类型。大多数元素的默认 display 值为 block 或 inline。 …...
Spring Cloud Alibaba 网关 Gateway 集成(7)
项目的源码地址 Spring Cloud Alibaba 工程搭建(1) Spring Cloud Alibaba 工程搭建连接数据库(2) Spring Cloud Alibaba 集成 nacos 以及整合 Ribbon 与 Feign 实现负载调用(3) Spring Cloud Alibaba Ribbo…...

低代码技术赋能未来乡村建设:创新与实践
引言 随着我国新型城镇化进程的推进,乡村建设正面临着前所未有的挑战。如何在有限的人力、物力、财力资源下,高效推动乡村建设,实现城乡一体化发展,成为当下亟待解决的问题。低代码技术作为一种创新性的解决方案,为未来…...

基于Springboot的房屋租赁管理系统(有报告)。Javaee项目,springboot项目。
演示视频: 基于Springboot的房屋租赁管理系统(有报告)。Javaee项目,springboot项目。 项目介绍: 采用M(model)V(view)C(controller)三层体系结构…...

跨平台移动应用开发指南:打造跨越iOS和Android的移动应用
跨平台移动应用开发已经成为许多开发者的首选,因为它可以节省时间、成本和精力,同时使得应用能够覆盖更广泛的用户群体。本指南将介绍跨平台移动应用开发的基本概念、流行的跨平台框架以及一些最佳实践,帮助您快速入门并打造出高质量的跨平台…...

QT+多线程编程
QT的多线程编程有两种 1、自定义类继承QThread 第一种是自定义一个类继承于QThread,重写run()方法来实现。然后当需要使用线程的时候你就新建一个自定义对象,然后调用start方法开始运行。 下面的例子是widget里面创建一个线程,然后调用sta…...
)
设计模式——迭代器模式(Iterator)
迭代器模式(Iterator Pattern)是一种行为设计模式,它使得我们能够顺序地访问一个聚合对象中的各个元素,而又不需要暴露该对象的内部表示。迭代器模式为遍历不同的聚合结构提供了一个统一的接口,使得客户端代码可以独立…...
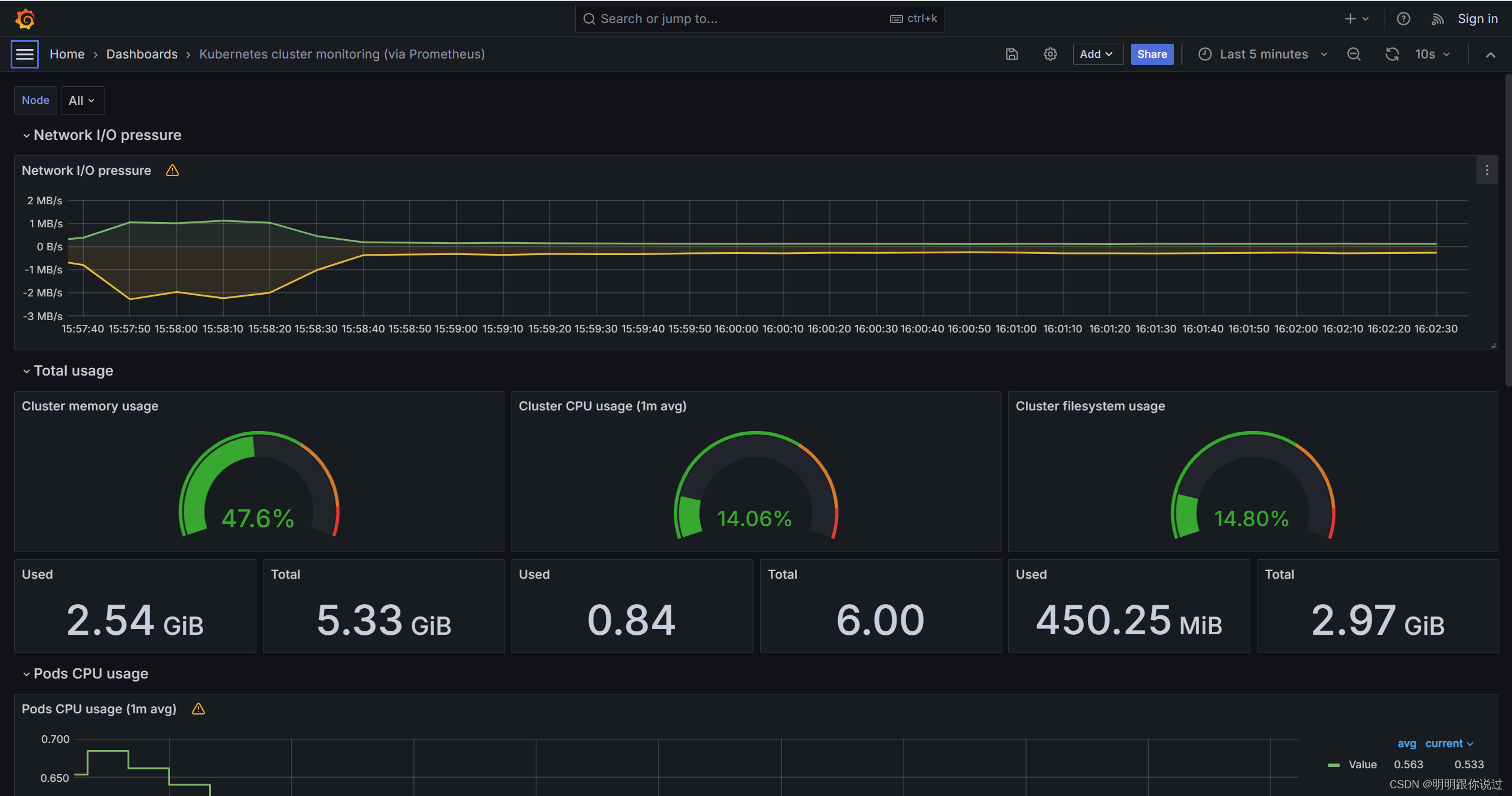
在k8s中安装Grafana并对接Prometheus,实现k8s集群监控数据的展示
🐇明明跟你说过:个人主页 🏅个人专栏:《Grafana:让数据说话的魔术师》 🏅 🔖行路有良友,便是天堂🔖 目录 一、引言 1、Grafana简介 2、Grafana的重要性与影响力 …...
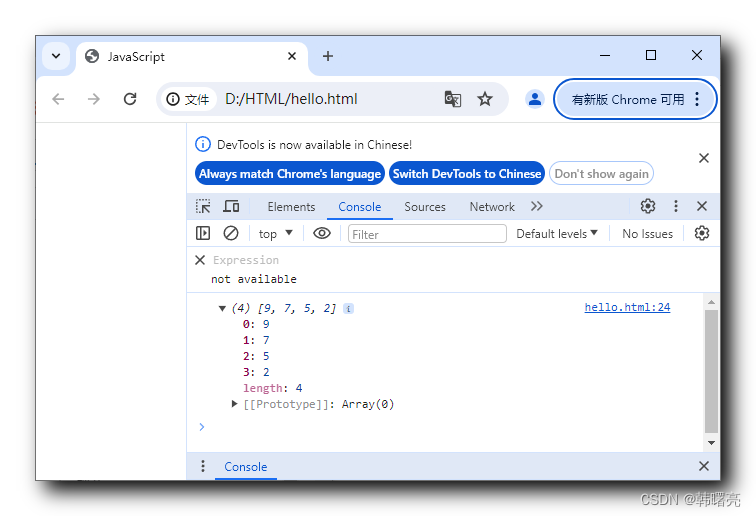
【JavaScript】内置对象 - 数组对象 ③ ( 数组反转 - reverse 方法 | 数组排序 - sort 方法 | 自定义数组排序规则 )
文章目录 一、数组排序1、翻转数组元素 - reverse()2、数组元素排序 - sort() 默认从小到大排序3、数组元素排序 - sort() 自定义排序规则4、数组元素排序 - sort() 自定义降序排序简化写法 Array 数组对象参考文档 : https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript…...

ctfshow web入门 php反序列化 web267--web270
web267 查看源代码发现这三个页面 然后发现登录页面直接admin/admin登录成功 然后看到了 ///backdoor/shell unserialize(base64_decode($_GET[code]))EXP <?php namespace yii\rest{class IndexAction{public $checkAccess;public $id;public function __construct(){…...

智慧公厕解决什么问题?实现了什么样的价值?
公共厕所一直是城市管理的难题,常常面临着卫生条件不佳、管理不善以及使用体验差等问题。为了解决这些困扰城市的难题,智慧公厕应运而生。智慧公厕不仅应用了信息化和数字化技术,还通过全方位的智能化应用,彻底改变了传统公厕的面…...

IATF16949认证是什么?
IATF16949认证是一项国际质量管理体系的认证标准,由国际汽车行业联合会(IATF)开发,旨在提高汽车行业的质量管理水平,满足客户对汽车部件和零部件的要求。该标准是在ISO/TS 16949标准的基础上,专门为汽车行业…...
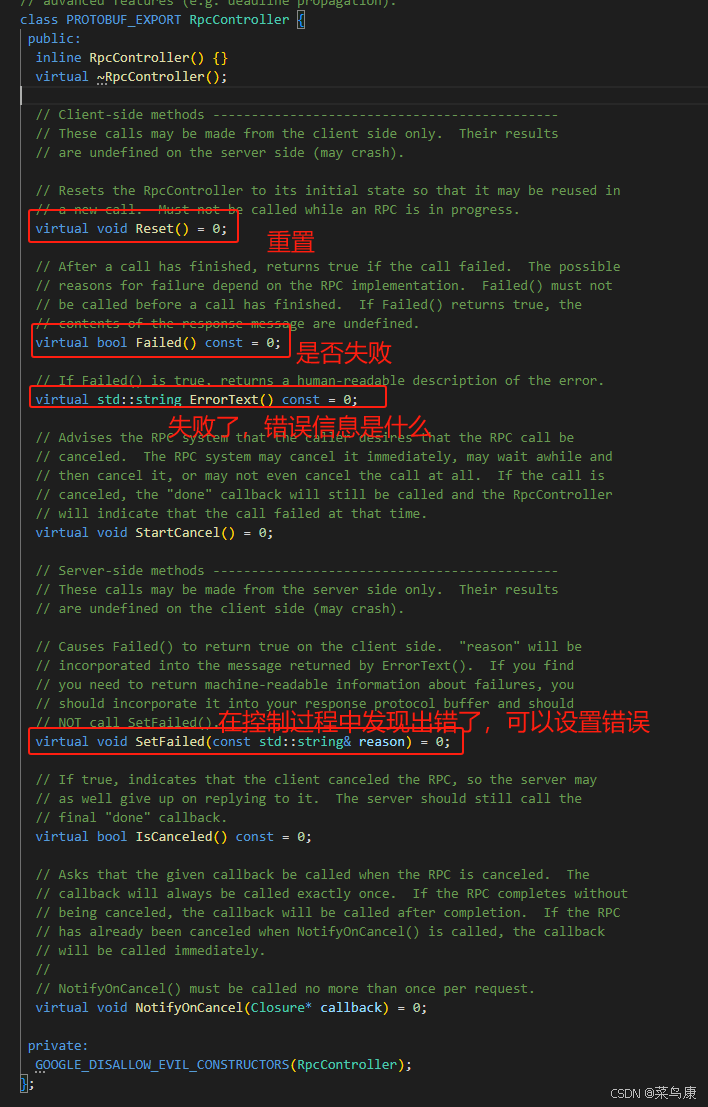
C++实现分布式网络通信框架RPC(3)--rpc调用端
目录 一、前言 二、UserServiceRpc_Stub 三、 CallMethod方法的重写 头文件 实现 四、rpc调用端的调用 实现 五、 google::protobuf::RpcController *controller 头文件 实现 六、总结 一、前言 在前边的文章中,我们已经大致实现了rpc服务端的各项功能代…...
)
进程地址空间(比特课总结)
一、进程地址空间 1. 环境变量 1 )⽤户级环境变量与系统级环境变量 全局属性:环境变量具有全局属性,会被⼦进程继承。例如当bash启动⼦进程时,环 境变量会⾃动传递给⼦进程。 本地变量限制:本地变量只在当前进程(ba…...

【磁盘】每天掌握一个Linux命令 - iostat
目录 【磁盘】每天掌握一个Linux命令 - iostat工具概述安装方式核心功能基础用法进阶操作实战案例面试题场景生产场景 注意事项 【磁盘】每天掌握一个Linux命令 - iostat 工具概述 iostat(I/O Statistics)是Linux系统下用于监视系统输入输出设备和CPU使…...

【AI学习】三、AI算法中的向量
在人工智能(AI)算法中,向量(Vector)是一种将现实世界中的数据(如图像、文本、音频等)转化为计算机可处理的数值型特征表示的工具。它是连接人类认知(如语义、视觉特征)与…...
)
论文解读:交大港大上海AI Lab开源论文 | 宇树机器人多姿态起立控制强化学习框架(一)
宇树机器人多姿态起立控制强化学习框架论文解析 论文解读:交大&港大&上海AI Lab开源论文 | 宇树机器人多姿态起立控制强化学习框架(一) 论文解读:交大&港大&上海AI Lab开源论文 | 宇树机器人多姿态起立控制强化…...
python执行测试用例,allure报乱码且未成功生成报告
allure执行测试用例时显示乱码:‘allure’ �����ڲ����ⲿ���Ҳ���ǿ�&am…...

Java线上CPU飙高问题排查全指南
一、引言 在Java应用的线上运行环境中,CPU飙高是一个常见且棘手的性能问题。当系统出现CPU飙高时,通常会导致应用响应缓慢,甚至服务不可用,严重影响用户体验和业务运行。因此,掌握一套科学有效的CPU飙高问题排查方法&…...

三分算法与DeepSeek辅助证明是单峰函数
前置 单峰函数有唯一的最大值,最大值左侧的数值严格单调递增,最大值右侧的数值严格单调递减。 单谷函数有唯一的最小值,最小值左侧的数值严格单调递减,最小值右侧的数值严格单调递增。 三分的本质 三分和二分一样都是通过不断缩…...
 + 力扣解决)
LRU 缓存机制详解与实现(Java版) + 力扣解决
📌 LRU 缓存机制详解与实现(Java版) 一、📖 问题背景 在日常开发中,我们经常会使用 缓存(Cache) 来提升性能。但由于内存有限,缓存不可能无限增长,于是需要策略决定&am…...

Linux系统部署KES
1、安装准备 1.版本说明V008R006C009B0014 V008:是version产品的大版本。 R006:是release产品特性版本。 C009:是通用版 B0014:是build开发过程中的构建版本2.硬件要求 #安全版和企业版 内存:1GB 以上 硬盘…...
