C++笔记(体系结构与内核分析)
1.OOP面向对象编程 vs. GP泛型编程
- OOP将data和method放在一起,目的是通过封装、继承、多态提高软件的可维护性和可扩展性
- GP将data和method分开,可以将任何容器与任何算法结合使用,只要容器满足塞饭所需的迭代器类型
2.算法与仿函数的区别
bool strLonger(const string &s1, const string &s2)
{return s1.size() < s2.size();
}// 算法
cout << "max of zoo and hello:" << max(string("zoo"), string("hello")) << endl;
// 仿函数
cout << "max of zoo and hello:" << max(string("zoo"), string("hello"), strLonger) << endl;
3.泛化、特化、偏特化
- 泛化:支持广泛的数据类型和情况,而不是针对特定类型
- 特化:为特定类型或一组类型提供特定的实现
#include <iostream>// General template
template <typename T>
void print(T arg) {std::cout << "General print: " << arg << std::endl;
}// Specialization for const char*
template <>
void print<const char*>(const char* arg) {std::cout << "Specialized print for const char*: " << arg << std::endl;
}int main() {print(123); // Uses general templateprint("Hello, world"); // Uses specialized template
}
- 偏特化:针对特定类型组合提供优化的行为或特殊实现。完全特化需要指定模板的所有参数,偏特化只需指定部分参数,或对参数施加某些约束。
- 第一种偏特化处理第二个模板参数为
int的情况。 - 第二种偏特化处理两个模板参数相同的情况。
- 第一种偏特化处理第二个模板参数为
#include <iostream>// 基本模板
template <typename T, typename U>
class MyClass {
public:void print() {std::cout << "Base template\\n";}
};// 偏特化:特化第二个类型为 int 的情况
template <typename T>
class MyClass<T, int> {
public:void print() {std::cout << "Partially specialized template for T and int\\n";}
};// 偏特化:特化两个类型都为相同类型的情况
template <typename T>
class MyClass<T, T> {
public:void print() {std::cout << "Partially specialized template for T, T\\n";}
};int main() {MyClass<double, double> myClass1; // 会匹配 MyClass<T, T>MyClass<double, int> myClass2; // 会匹配 MyClass<T, int>MyClass<double, char> myClass3; // 会匹配基本模板 MyClass<T, U>myClass1.print(); // 输出: Partially specialized template for T, TmyClass2.print(); // 输出: Partially specialized template for T and intmyClass3.print(); // 输出: Base template
}
4.分配器allocates
分配器(allocators)是用来管理内存分配和回收的对象。
- 在 VC6 中,
operator new()通常通过调用malloc()实现,malloc()函数不仅会开辟用户请求的内存外,还会引入额外的内存开销:
void* operator new(size_t size) {void* p = malloc(size);if (p == 0) // 如果malloc失败,则抛出std::bad_alloc异常throw std::bad_alloc();return p;
}
- 例如:当我们需要分配512个整型数据时
int *p = allocator<int>().allocate(512,(int *)0);
allocator<int>().deallocate(p,512);
- 在 VC6 / BC++ / G++中,
allocator类都是使用operator new来分配内存,并使用operator delete来释放内存。其中,operator new()通常通过调用malloc()实现开辟内存,operator delete()通常通过调用free()实现回收内存:
// VC6 STL中容器对allocator的使用
template<class _Ty, class _A=allocator<_Ty>> // 调用allocator类
class vector
{ ...
};
template <typename T>
class allocator {
public:typedef size_t size_type; // size_t是一个无符合整型数据类型typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; // 表示同一个数组中任意两个元素之间的差异typedef T* pointer;typedef T value_type;pointer allocate(size_type n, const void* hint = 0) {return (pointer) (::operator new(n * sizeof(value_type)));}void deallocate(pointer p, size_type n) {::operator delete(p);}
}
- 在GCC2.9中
// VC6 STL中容器对allocator的使用
template<class T, class Alloc = alloc> // 调用allocator类
class vector
{ ...
};

①内存池:由一系列内存块组成,每块预分配一定数量的内存。
②自由列表:每个固定大小的内存块都有自己的自由列表。
③大小分类:根据内存请求的大小被分类到不同的自由列表。
-
GCC4.9所附的标准库,其中**__pool_alloc就是GCC2.9中的alloc**
// 使用方法 vector<string, __gnn_cxx::__pool_alloc<string>> vec;
5.容器的分类
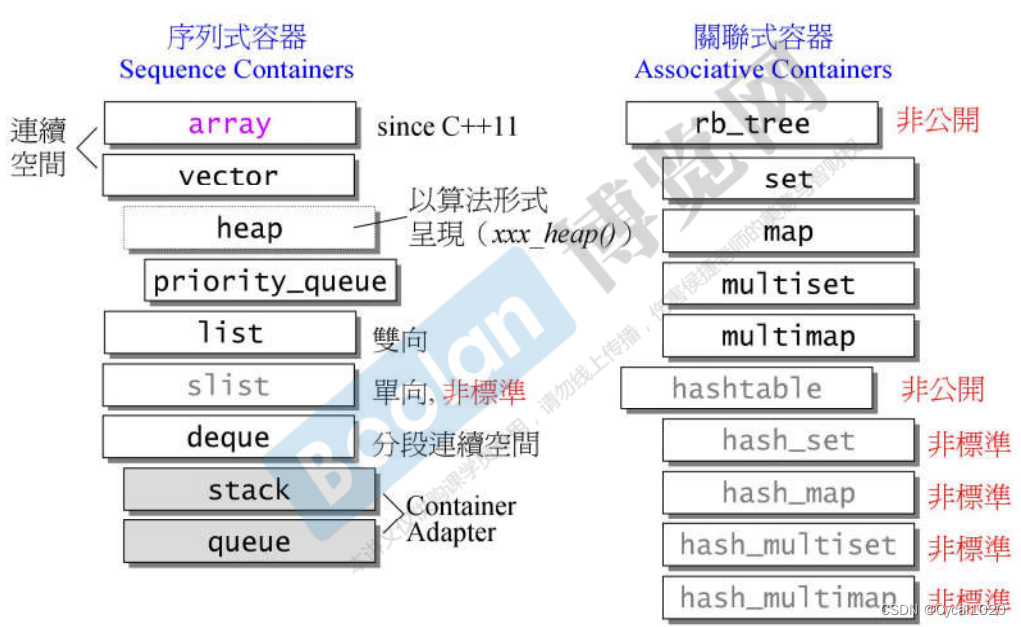
6.容器list
G2.9版本:
template <class T, class Alloc = alloc>
class list{
protected:typeof __list_node<T> list_node; // 1号代码块
public:typeof list_node* link_type;typeof __list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator; // 2号代码块
protected:link_type node;
}
// 1号代码块
template <class T>
struct __list_node {void* prev;void* next;T data;
};
// 2号代码块
template <class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator{typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category; // (1)typedef T value_type; // (2)typedef Ptr pointer; // (3)typedef Ref reference; // (4)typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; // (5)typedef __list_node<T> list_node;typedef list_node* list_type;typedef __list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> self;link_type node;reference operator*() const{ return (*node).data; } // 返回引用pointer operator->() const{ return &(operator *());} // 返回指针。获得该对象的内存地址,即一个指向该对象的指针self& operator++() // i++{ node = (link_type) ((*node).next); return *this; // 返回自身的引用}// (*node).next是一个 __list_node<T>* 类型的值,加上(list_type)是显式类型转换// (*node).next 等价于 node->next 等价于 (&(*node))->next;// node只是一个迭代器的指针,不是迭代器本身// self&表示返回迭代器的引用self operator++(int) // ++i{ self tmp = *this; ++*this; return tmp;}
};
- 前缀递增 (
operator++()) 将迭代器向前移动到下一个元素 - 后缀递增 (
operator++(int)) 返回迭代器的一个临时副本(在递增前的状态),然后再递增迭代器。 - 内置
->操作符 用于直接从指针访问对象成员。 - 重载的
operator->()提供了一种方式,通过迭代器对象模拟原生指针的行为,允许通过迭代器间接访问对象成员。 (*node).next等价于node->next等价于(&(*node))->next
G4.9版本:
template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc=std::allocator<_Tp>>
class list:protected_List_base<_Tp,_Alloc>
{
public:typedef _List_iterator<_Tp> iterator;
}
template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc = std::allocator<_Tp>>- 这是一个类模板,接受两个模板参数。
_Tp表示列表中要存储的数据类型。_Alloc是分配器类型,用于控制链表中元素的内存分配。这个参数有一个默认值,即std::allocator<_Tp>,这是 C++ 标准库提供的一种通用内存分配器。
: protected _List_base<_Tp, _Alloc>list类从_List_base类继承而来,使用保护(protected)继承。这意味着_List_base中的公共和保护成员在list类中将变为保护成员。_List_base是一个实现链表基础功能的类
template<typename _Tp>
struct _List_iterator
{typedef _Tp* pointer;typedef _Tp& reference;...
};
// 自身类型的指针使得可以从任何一个节点开始
// 沿着链表向前或向后移动,这对于双向遍历和双向操作非常重要。
struct _List_node_base
{_List_node_base* _M_next;_List_node_base* _M_prev;
};
template<typename _Tp>
struct _List_node:public _List_node_base
{_Tp _M_data;
};
7.Iterator必须提供5中associated types
算法提问:
template<typename T>
incline void
algorithm(T first, T last) // 迭代器
{...T::iterator_categoryT::value_typeT::pointerT::referenceT::difference_type...
};
迭代器回答:
template <class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator{typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category; // (1)typedef T value_type; // (2)typedef Ptr pointer; // (3)typedef Ref reference; // (4)typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; // (5)...
};
8. iterator_traits 类型萃取
但当我们向算法中传入的是指针,而不是迭代器时,就需要用到traits。也就是说,iterator_traits 为所有类型的迭代器(包括原生指针)提供统一的方式来访问迭代器的属性,是在 <iterator> 头文件中定义的。
作用:
std::iterator_traits 模板用于提取迭代器相关的类型信息。
举例:
#include<iostream>
#include<iterator>
#include<vector>template<typename Iterator>
void print_vector(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{// using关键字用来定义类型的别名// typename关键字告诉编译器这是一个依赖于模版参数Iterator的类型,而不是变量using ValueType = typename iterator_traits<Iterator>::value_type;
}int main()
{vector<int> v = {1,2,3,4,5};print_vector(v.begin(), v.end());
}
// 当Iterator是一个类时
template<class Iterator>
struct iterator_traits
{typedef typename Iterator::value_type value_type;
};// 两种偏特化情况
// 当Iterator是一个普通指针时
// 如int*,那么T为int,得到value_type就被定义为“int”
template<class T>
struct iterator_traits<T*>
{typedef T value_type;
};// 当Iterator是一个常量指针(指针的指向可以修改,指针指向的值不能修改)
template<class T>
struct iterator_traits<const T*>
{typedef T value_type;
};
- Iterator若是int*,ValueType 就是 int
- Iterator若是const int*,ValueType 还是 int
- 因为如果 ValueType 是 const int,后续再使用ValueType创建其他容器时,就会受到限制。因为标准库中的容器(如 std::vector)不能存储常量类型的元素,它们需要能被赋值和移动。
完整的iterator_traits:
template<class Iterator>
struct iterator_traits
{typedef typename Iterator::iterator_category iterator_category;typedef typename Iterator::value_type value_type;typedef typename Iterator::pointer iterator_category;typedef typename Iterator::reference reference;typedef typename Iterator::difference_type difference_type;
};template<class T>
struct iterator_traits<T*>
{typedef random_access_iterator_tag iterator_category;typedef T value_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;typedef T* pointer;typedef T& reference;
};template<class T>
struct iterator_traits<const T*>
{typedef random_access_iterator_tag iterator_category;typedef T value_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;typedef const T* pointer;typedef const T& reference;
};9.容器vector
定义:
template <class T, class Alloc = std::allocator<T>>
class vector
{
public:typedef T value_type;typedef T* pointer;typedef &T reference;typedef size_t size_type;
protected:iterator **start**;iterator **finish**;iterator **end_of_range**;Allocator alloc;
public:iterator begin() { return **start**;}iterator end() { return **finish**;}size_type size const { return size_type(end() - start());}size_type capacity() const{ return size_type(**end_of_storage** - begin());}bool empty() const { return begin() == end();}reference operator[](size_type n}{return *(begin()+n);referebce front() {return *begin();}reference back() {return *(end()-1);}
};
push_back操作源码:
template <class T, class Alloc=std::allocator<T>>
void push_back(const T& value)
{if(finish == end_of_storage) // 原始空间不足{size_type old_size = size();// old_size == 0:当前vector中没有任何元素,新分配的存储空间至少有一个元素的容量// old_size != 0:分配新的容量将是当前大小的两倍, 称为指数增长size_type new_capacity = old_size == 0 ? 1 : 2 * old_size;iterator new_start = alloc.allocator(new_capacity);iterator new_finsih = new_start;try{// 将原数据移动到新空间for(iterator old_iter = start; old_iter != finish; ){alloc.construct(new_finish++, *old_iter);alloc.destroy(old_iter++);}// 添加新元素alloc.construct(new_finish++, value);}catch(...){// 如果构造失败,释放已分配的内存for(iterator it=new_start; it!=new_finish; ++it){alloc.destory(it);}alloc.deallocate(new_start, new_capacity);throw; // 重新抛出当前异常}// 释放旧空间if (start) {alloc.deallocate(start, end_of_storage - start);}// 更新指针start = new_start;finish = new_finish;end_of_storage = start + new_capacity;} else {alloc.construct(finish++, value); // 有足够空间,直接构造新元素}
}
vector的迭代器iterator:
template <class T, class Alloc = alloc>
class vector
{
public:typedef T value_type;typedef T* iterator;
};// 调用方法
vectot<int> v;
vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();
10.容器deque
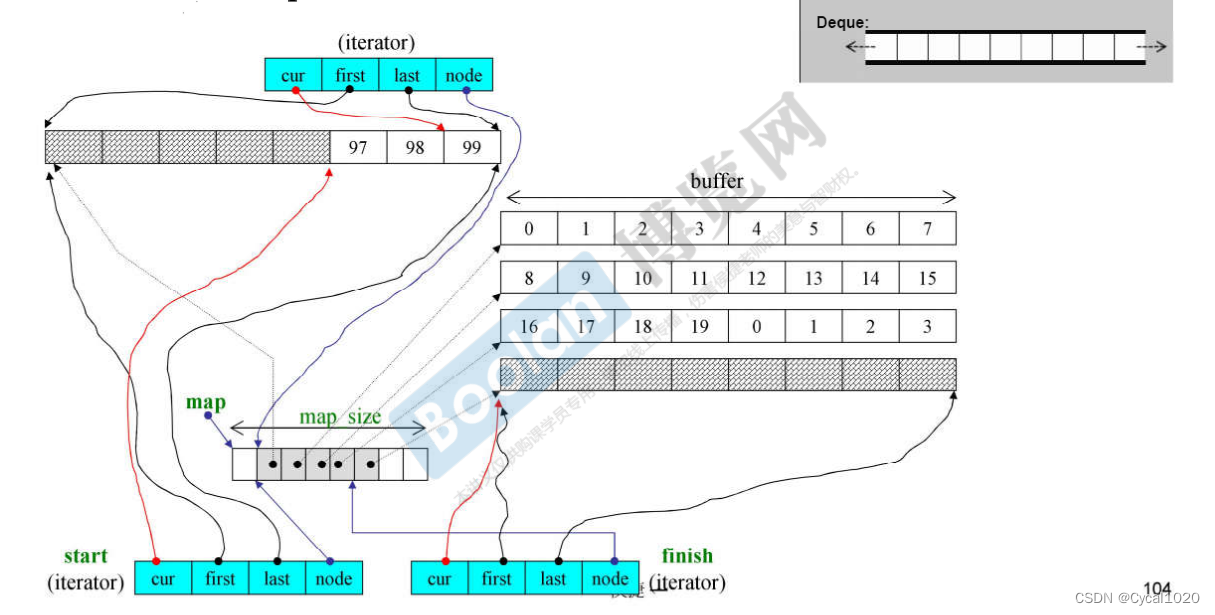
// BufSize是指缓冲区buffer的长度
template<class T,class Alloc = alloc, size_t BufSize=0>
class deque
{
public:typedef T value_type;typedef size_t size_type;typedef __deque_iterator<T,T&,T*,BufSiz> iterator;
protected:typedef T** map_pointer; // 指向指针数组的指针
protected:iterator start;iterator finish;map_point map; // 指向指针数组的指针,每一个都指向一个缓冲区size_type map_size;
public:iterator begin() {return start;}iterator end() {return finish;}size_type size() {return finish - start;}...
};
deque的迭代器iterator:
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr, size_t BufSize>
struct __deque_iterator
{typedef random_access_iterator_tag iterator_category;typedef T value_type;typedef Ref reference; // T&typedef Ptr pointer; // T*typedef size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;typedef T** map_pointer;typedef __deque_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr,BufSiz> self;T* **cur**;T* **first**;T* **last**;map_point **node**;
};
相关文章:

C++笔记(体系结构与内核分析)
1.OOP面向对象编程 vs. GP泛型编程 OOP将data和method放在一起,目的是通过封装、继承、多态提高软件的可维护性和可扩展性GP将data和method分开,可以将任何容器与任何算法结合使用,只要容器满足塞饭所需的迭代器类型 2.算法与仿函数的区别 …...

c++ 唤醒指定线程
在C中,直接唤醒一个特定的线程并不像在Java的Thread类中有interrupt()方法或者某些操作系统特定的API(如POSIX的pthread_cond_signal或Windows的SetEvent)那样简单。C标准库没有提供一个直接的方法来"唤醒"一个正在等待的线程。然而…...
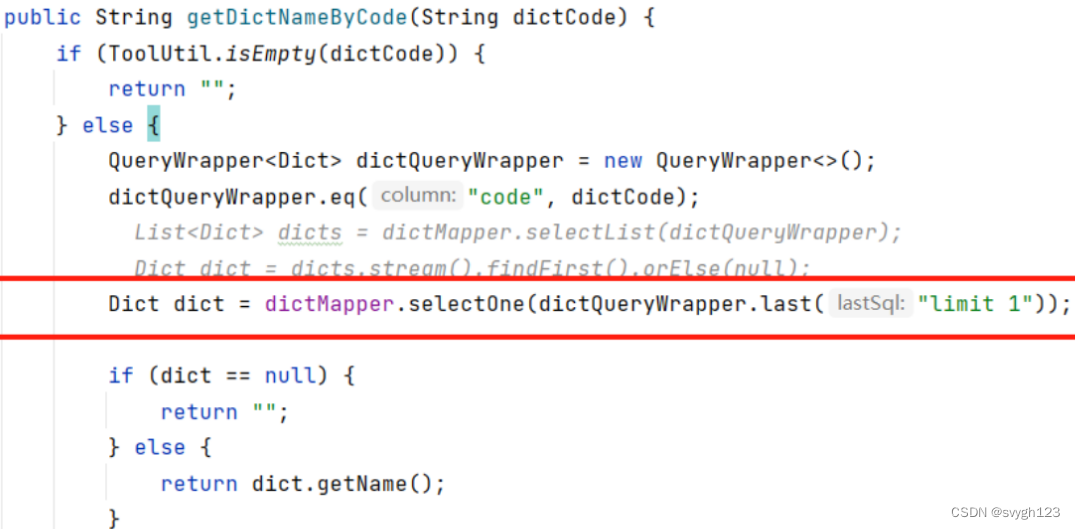
java报错:使用mybatis plus查询一个只返回一条数据的sql,却报错返回了1000多条
今天遇到一个问题 系统线上问题,经常出现这样的问题,刚重启系统时不报错了,可是运行一段时间又会出现。sql已经写了limit 1,mybatis的debug日志也返回total为1,可是却报错返回了1805条数据 乍一看,感觉太不…...

AI图书推荐:利用生成式AI实现业务流程超自动化
《利用生成式AI实现业务流程超自动化》(Hyperautomation with Generative AI)这本书探索了广泛的用例和示例,展示了超自动化在不同行业、领域和特定部门的多样化应用, 让您熟悉UiPath、Automation Anywhere和IBM等流行工具和平台&…...

什么事防抖和节流,有什么区别,如何实现
防抖和节流,本质上是优化高频率执行代码的一种手段,比如:resize、scroll、keypress、mousemove这些事件在触发的时候,会不断调用绑定在事件上的回调函数,这样极大浪费资源,降低前端性能。 为了优化体验&am…...

PanguSync大数据量初始化脚本
由于数据库增量同步软件PanguSync初始化最大超时时间为600s,如果初始数据量很大,第一次部署时可能会超时,可以先停止任务,使用以下Sql语句进行初始化,以下语句可以分步执行,初始化完成后,后续无需再执行耗时…...
DELL T630服务器iDRAC分辨率调整办法
对于Dell T630服务器的iDRAC分辨率调整,您需要登录到iDRAC的Web界面。以下是详细的步骤: 登录iDRAC:在浏览器中输入iDRAC的IP地址,然后使用用户名(通常是“root”)和密码登录。 导航到虚拟控制台ÿ…...

您真的会高效使用 Mac 吗?
文章目录 屏幕的保养快捷键预览修改文件名查看文件属性搜索编辑复制,粘贴,剪切,撤销删除 跳转窗口屏幕截图声音Dock强制退出查字典神奇的Option键鼠标与触控板切换桌面与应用程序打开通知中心打开Mission Control 安装与卸载Mac应用程序压缩和…...

Vue11 Vue3完结撒花
shallowRef和shallowReactive shallowRef 作用:创建一个响应式数据,但只对顶层属性进行响应式处理 用法 let myVar shallowRef(initialValue)特点:只跟踪引用值变化,不关心值内部的属性变化 案例 <template><div c…...
)
CodeTop 高频笔试题总结(持续更新)
🏆 频率从高到低排序 👨🏫 参考的频率数据:CodeTop 👨🏫 力扣hot100 无重复字符的最长子串 双指针 滑动窗口 哈希👨🏫 力扣hot100 反转链表 指针 递归 一题多解👨…...

类和对象一(从封装开始讲述)
目录: 一.封装 二.封装扩展之包,自定义包 三.访问限定符 四.static成员 一.封装:封装:将数据和操作数据的方法进行有机结合,隐藏对象的属性和实现细节,仅对外公开接口来和对象进行 交互。面向对象…...

LeetCode100题总结
LeetCode100题总结 前言LeetCode100题总结题型梳理双指针11. 盛最多水的容器234.回文链表75.颜色分类206.反转链表142.环形链表215.三数之和 滑动窗口3. 无重复字符的最长子串209. 长度最小的子数组438. 找到字符串中所有字母异位词 广搜102. 二叉树的层序遍历200. 岛屿数量617…...

基于截断傅里叶级数展开的抖动波形生成
1、背景 抖动是影响信号完整性的重要因素。随着信号速率的不断提高,抖动的影响日益显著。仿真生成抖动时钟或抖动信号,对系统极限性能验证具有重要意义。抖动是定义在时域上的概念,它表征真实跳变位置(如跳边沿或过零点)与理想跳变位…...
——支持撤销的画线行为)
图片标注编辑平台搭建系列教程(9)——支持撤销的画线行为
文章目录 背景渲染行为mouseDownmouseMovemouseDbclick总结背景 编辑器中的绘制,要想做的足够好,是需要支持撤销形点的,因为作业员在绘制过程中,可能会点错位置,需要及时撤销,否则影响编辑效率。撤销我们知道,需要通过ID编辑器的history的undo来实现,那么意味着,每一…...
)
赶紧收藏!2024 年最常见 100道 Java 基础面试题(四十一)
上一篇地址:赶紧收藏!2024 年最常见 100道 Java 基础面试题(四十)-CSDN博客 八十一、tcp为什么要三次握手,两次不行吗?为什么? TCP(传输控制协议)使用三次握手…...

使用自关联方法处理多表关系
使用自关联方法处理多表关系 这里通过省市区之间的关系来解释自关联的情况 在设置地址的过程中 , 不可避免的需要设置 , 省份 ,市以及区 而省市区三者之间的具有一定的关联关系 一个省份对应多个市 一个市对应多个区 如果通过设置主表从表关系则需要设置三张标分别对应省…...

annaconda详细解读换源文件
annaconda换源详细解读文件 annaconda换源详细解读文件 annaconda换源详细解读文件 #踩坑/annaconda换源详细解读通道问题 如何准确使用国内源高效安装GPU版本的Pytorch - 知乎 文件中的custom通道,需要自己手动添加到默认通道里面,记得后面更上/包名…...
的实践技巧)
AI大模型系列:编写高质量提示(prompt)的实践技巧
AI大模型系列专栏 文章收录于AI大模型系列专栏 文明基石,文字与数字的起源与演变自然语言处理,从规则到统计的演变AI魔法师,提示工程的力量编写高质量提示(prompt)的小技巧编写高质量提示(prompt…...
汽车EDI:安通林Antolin EDI 项目案例
安通林(Antolin)是一家全球性的汽车零部件制造商,专注于汽车内饰系统和零部件的生产,致力于创新和采用先进的技术。近年来 安通林Antolin 推动其供应商部署EDI系统,使得双方能够通过EDI传输业务单据,极大提…...

今日arXiv最热NLP大模型论文:揭露大语言模型短板,北京大学提出事件推理测试基准
人工智能领域又一里程碑时刻!北京大学、北京智源人工智能研究院等机构联合推出大型事件推理评测基准 。这是首个同时在知识和推理层面全面评估大模型事件推理能力的数据集。 总所周知,事件推理需要丰富的事件知识和强大的推理能力,涉及多种推…...

Toasty最佳实践指南:10个避免常见陷阱的开发者经验分享
Toasty最佳实践指南:10个避免常见陷阱的开发者经验分享 【免费下载链接】Toasty The usual Toast, but with steroids 💪 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/to/Toasty Toasty是一款为Android应用提供增强型Toast通知的开源库,…...

FinalBurn Neo代码架构解析:从C++03合规性看跨平台兼容性设计
FinalBurn Neo代码架构解析:从C03合规性看跨平台兼容性设计 【免费下载链接】FBNeo FinalBurn Neo - We are Team FBNeo. 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/fb/FBNeo FinalBurn Neo(FBNeo)作为一款经典的多平台街机模拟器&am…...

谷歌浏览器插件
项目中有时候会用到插件 sync-cookie-extension1.0.0:开发环境同步测试 cookie 至 localhost,便于本地请求服务携带 cookie 参考地址:https://juejin.cn/post/7139354571712757767 里面有源码下载下来,加在到扩展即可使用FeHelp…...

CTF show Web 红包题第六弹
提示 1.不是SQL注入 2.需要找关键源码 思路 进入页面发现是一个登录框,很难让人不联想到SQL注入,但提示都说了不是SQL注入,所以就不往这方面想了 先查看一下网页源码,发现一段JavaScript代码,有一个关键类ctfs…...
相机Camera日志实例分析之二:相机Camx【专业模式开启直方图拍照】单帧流程日志详解
【关注我,后续持续新增专题博文,谢谢!!!】 上一篇我们讲了: 这一篇我们开始讲: 目录 一、场景操作步骤 二、日志基础关键字分级如下 三、场景日志如下: 一、场景操作步骤 操作步…...
)
postgresql|数据库|只读用户的创建和删除(备忘)
CREATE USER read_only WITH PASSWORD 密码 -- 连接到xxx数据库 \c xxx -- 授予对xxx数据库的只读权限 GRANT CONNECT ON DATABASE xxx TO read_only; GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA public TO read_only; GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO read_only; GRANT EXECUTE O…...

Java 加密常用的各种算法及其选择
在数字化时代,数据安全至关重要,Java 作为广泛应用的编程语言,提供了丰富的加密算法来保障数据的保密性、完整性和真实性。了解这些常用加密算法及其适用场景,有助于开发者在不同的业务需求中做出正确的选择。 一、对称加密算法…...

Spring Boot面试题精选汇总
🤟致敬读者 🟩感谢阅读🟦笑口常开🟪生日快乐⬛早点睡觉 📘博主相关 🟧博主信息🟨博客首页🟫专栏推荐🟥活动信息 文章目录 Spring Boot面试题精选汇总⚙️ **一、核心概…...

Spring AI与Spring Modulith核心技术解析
Spring AI核心架构解析 Spring AI(https://spring.io/projects/spring-ai)作为Spring生态中的AI集成框架,其核心设计理念是通过模块化架构降低AI应用的开发复杂度。与Python生态中的LangChain/LlamaIndex等工具类似,但特别为多语…...

OPENCV形态学基础之二腐蚀
一.腐蚀的原理 (图1) 数学表达式:dst(x,y) erode(src(x,y)) min(x,y)src(xx,yy) 腐蚀也是图像形态学的基本功能之一,腐蚀跟膨胀属于反向操作,膨胀是把图像图像变大,而腐蚀就是把图像变小。腐蚀后的图像变小变暗淡。 腐蚀…...
