C++三剑客之std::any(二) : 源码剖析
目录
1.引言
2.std::any的存储分析
3._Any_big_RTTI与_Any_small_RTTI
4.std::any的构造函数
4.1.从std::any构造
4.2.可变参数模板构造函数
4.3.赋值构造与emplace函数
5.reset函数
6._Cast函数
7.make_any模版函数
8.std::any_cast函数
9.总结
1.引言
C++三剑客之std::any(一) : 使用详解_c++ std::any-CSDN博客
在前面详细的讲解了std::any的用法,std::any能够容纳任何可拷贝构造类型的数据,我们不禁会想它是怎么做到的呢?不同类型怎么做到巧妙的构造与转换的?多种构造函数如何实现?内部数据怎么储存?为什么分Big,Samll,trivial?
下面就以vs2019的std::any实现为例进行具体分析它的实现。
2.std::any的存储分析
std::any 将保存内容的内存形式分为了三种:_Small、_Trivial、_Big
划分规则代码为:
// size in pointers of std::function and std::any (roughly 3 pointers larger than std::string when building debug)
constexpr int _Small_object_num_ptrs = 6 + 16 / sizeof(void*); //64位系统: 8//64位系统:_Any_trivial_space_size = 56
inline constexpr size_t _Any_trivial_space_size = (_Small_object_num_ptrs - 1) * sizeof(void*);template <class _Ty>
inline constexpr bool _Any_is_trivial = alignof(_Ty) <= alignof(max_align_t)&& is_trivially_copyable_v<_Ty> && sizeof(_Ty) <= _Any_trivial_space_size;//64位系统:_Any_small_space_size = 48
inline constexpr size_t _Any_small_space_size = (_Small_object_num_ptrs - 2) * sizeof(void*);template <class _Ty>
inline constexpr bool _Any_is_small = alignof(_Ty) <= alignof(max_align_t)&& is_nothrow_move_constructible_v<_Ty> && sizeof(_Ty) <= _Any_small_space_size;简单来说,满足 _Any_is_trivial 则为 Trivial 类型内存,满足 _Any_is_small 则为 Small 类型内存,其余的则为 Big 类型内存。
在 64 位系统下,划分规则可以解释为:
_Any_is_small:类型长度小于等于 48 字节,内存对齐长度小于等于 8 字节,拥有具备 nothrow 声明的移动构造_Any_is_trivial:类型长度小于等于 56 字节,内存对齐长度小于等于 8 字节,可平凡拷贝(基本数据类型、可平凡拷贝的聚合类型、以上类型的数组等)
下面是一些 _Any_is_small 和 _Any_is_trivial 判断的实测值:
struct Test1 {char a[48];
};struct Test2 {char a[56];
};struct Test3 {Test3(Test3&& other){memcpy(a, other.a, sizeof(Test3));}char a[48] {};
};struct Test4 {int& a;
};struct Test5 {virtual void a() = 0;
};// 1
std::cout << std::_Any_is_small<char> << std::endl;
// 1
std::cout << std::_Any_is_small<int> << std::endl;
// 1
std::cout << std::_Any_is_small<double> << std::endl;
// 1
std::cout << std::_Any_is_small<Test1> << std::endl;
// 0, sizeof(Test2) > _Any_trivial_space_size
std::cout << std::_Any_is_small<Test2> << std::endl;
// 0, is_nothrow_move_constructible_v<_Ty> == false
std::cout << std::_Any_is_small<Test3> << std::endl;
// 1
std::cout << std::_Any_is_small<Test4> << std::endl;
// 0, is_nothrow_move_constructible_v<_Ty> == false
std::cout << std::_Any_is_small<Test5> << std::endl;// 1
std::cout << std::_Any_is_trivial<char> << std::endl;
// 1
std::cout << std::_Any_is_trivial<int> << std::endl;
// 1
std::cout << std::_Any_is_trivial<double> << std::endl;
// 1
std::cout << std::_Any_is_trivial<Test1> << std::endl;
// 1
std::cout << std::_Any_is_trivial<Test2> << std::endl;
// 0, is_trivially_copyable_v == false
std::cout << std::_Any_is_trivial<Test3> << std::endl;
// 1
std::cout << std::_Any_is_trivial<Test4> << std::endl;
// 0, is_trivially_copyable_v == false
std::cout << std::_Any_is_trivial<Test5> << std::endl;下面看看3中模型的数据存储结构:
//【1】struct _Small_storage_t {unsigned char _Data[_Any_small_space_size];const _Any_small_RTTI* _RTTI;};static_assert(sizeof(_Small_storage_t) == _Any_trivial_space_size);//【2】struct _Big_storage_t {// Pad so that _Ptr and _RTTI might share _TypeData's cache lineunsigned char _Padding[_Any_small_space_size - sizeof(void*)];void* _Ptr;const _Any_big_RTTI* _RTTI;};static_assert(sizeof(_Big_storage_t) == _Any_trivial_space_size);//【3】struct _Storage_t {union {unsigned char _TrivialData[_Any_trivial_space_size];_Small_storage_t _SmallStorage;_Big_storage_t _BigStorage;};uintptr_t _TypeData;};static_assert(sizeof(_Storage_t) == _Any_trivial_space_size + sizeof(void*));static_assert(is_standard_layout_v<_Storage_t>);union {_Storage_t _Storage{};max_align_t _Dummy;};我们可以看出_Storage_t本身由于一个联合体加上uintptr_t类型的_TypeData,在64位下uintptr_t就是unsigned long long,32位 unsigned int;
- _TypeData,这个实际是MSVC自己实现的,为了方便类型区分,借助了编译器内部类型信息。其什为:
_Storage._TypeData = reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(&typeid(_Decayed)) | static_cast<uintptr_t>(_Any_representation::_Trivial);其中_Decayed为any要储存类型的模板退化类型,然后用typeid求出std::type_info全局静态类型再取地址,用reinterpret_cast强转,说来说去就是为了类型得到一个类似hash后的数值,这里只是地址,然后再|上_Any_representation枚举值,为了后面来区分类型。enum class _Any_representation : uintptr_t { _Trivial, _Big, _Small };类型也比较容易,平凡类对应数值0,大类1,小类2- typeid返回type_info这个实现,实际上没有编译器内部实现也可以自己模板实现,模板类有个int型静态常量成员,对类型进行特化,最后也是取地址即可。
- 为什么_TypeData敢直接或上枚举,因为type_info的大小肯定大于3,两个type_info就算连续存储地址差肯定大于4,所以就算|2的话,从hash角度够用,也不会引发错误。
- _TrivialData[_Any_trivial_space_size];为char数组,其中
inline constexpr size_t _Any_trivial_space_size = (_Small_object_num_ptrs - 1) * sizeof(void*);,编译器常量,只要求_Small_object_num_ptrs即可,_Small_object_num_ptrs它又是typeinfo文件中的编译期常量,constexpr int _Small_object_num_ptrs = 6 + 16 / sizeof(void*);,对于64位也就是8,那么可以得出_Any_trivial_space_size为56,所以就是大小为char[56] - _Small_storage_t;是一个结构体,先是char数组且大小为_Any_small_space_size,这个也是编译期常理,
inline constexpr size_t _Any_small_space_size = (_Small_object_num_ptrs - 2) * sizeof(void*);由上面可以就是6* 8 = 48;然后接一个_Any_small_RTTI指针,也是8,大小总共一起还是56 - _Big_storage_t;也是一个结构体,先是char数组且大小为_Any_small_space_size - sizeof(void*),这由上面可以就是48 - 8 = 40;再接一个8字节void*指针,最后接一个_Any_big_RTTI指针,也是8,大小总共一起还是56
综上可以看出:_Storage_t就是56+8 = 64字节大小,我们对any进行sizeof得到的结果也是64,印证分析,只不过具体一个any的对象是union中三个类型中的一个。
3._Any_big_RTTI与_Any_small_RTTI
Trivial 类型的内存是直接对拷的,对于这种内存无需再添加额外的生命周期指针。按照 Small 内存的定义,对于 Small 内存要添加 in_place 的销毁、拷贝、移动函数指针,而 Big 则需要保存堆内存的拷贝与销毁函数指针。源码中定义了 _Any_small_RTTI 和 _Any_big_RTTI 结构体,来存储这些指针:
struct _Any_big_RTTI { // Hand-rolled vtable for types that must be heap allocated in an anyusing _Destroy_fn = void __CLRCALL_PURE_OR_CDECL(void*) _NOEXCEPT_FNPTR;using _Copy_fn = void* __CLRCALL_PURE_OR_CDECL(const void*);template <class _Ty>static void __CLRCALL_PURE_OR_CDECL _Destroy_impl(void* const _Target) noexcept {::delete static_cast<_Ty*>(_Target);}template <class _Ty>_NODISCARD static void* __CLRCALL_PURE_OR_CDECL _Copy_impl(const void* const _Source) {return ::new _Ty(*static_cast<const _Ty*>(_Source));}_Destroy_fn* _Destroy;_Copy_fn* _Copy;
};struct _Any_small_RTTI { // Hand-rolled vtable for nontrivial types that can be stored internally in an anyusing _Destroy_fn = void __CLRCALL_PURE_OR_CDECL(void*) _NOEXCEPT_FNPTR;using _Copy_fn = void __CLRCALL_PURE_OR_CDECL(void*, const void*);using _Move_fn = void __CLRCALL_PURE_OR_CDECL(void*, void*) _NOEXCEPT_FNPTR;template <class _Ty>static void __CLRCALL_PURE_OR_CDECL _Destroy_impl(void* const _Target) noexcept {_Destroy_in_place(*static_cast<_Ty*>(_Target));}template <class _Ty>static void __CLRCALL_PURE_OR_CDECL _Copy_impl(void* const _Target, const void* const _Source) {_Construct_in_place(*static_cast<_Ty*>(_Target), *static_cast<const _Ty*>(_Source));}template <class _Ty>static void __CLRCALL_PURE_OR_CDECL _Move_impl(void* const _Target, void* const _Source) noexcept {_Construct_in_place(*static_cast<_Ty*>(_Target), _STD move(*static_cast<_Ty*>(_Source)));}_Destroy_fn* _Destroy;_Copy_fn* _Copy;_Move_fn* _Move;
};- 先看big,先用using重定义了两个函数指针类型_Destroy_fn和_Copy_fn,现在写法都流行用using而不是typedef,不过本身using功能也更强大一些,这个结构体成员是这两个函数指针。再定义两个静态的模板函数,用来创建和释放内存,都是调用系统命名空间::下new与delete,不过new实际调用的是一个拷贝构造的函数。其都是重新申请和释放的内存,只是得到的结果是指针而已。
- 再看small,结构基本等同big,只不过多了一个move的函数,支持移动语义。但仔细看它的三个静态成员函数,其并没有直接实现,而是利用了xutility文件中提供的标准模板函数_Construct_in_place与xmemory文件中的_Destroy_in_place标准模板函数。里面也没做什么,调用palcement new进构造函数调用与最后析构函数,也就是没有真正参与内存分配与释放,只是走了内存池那套流程,在已经分配好的内存上玩一圈。可以提供一下代码,其中_Construct_in_place还是可变模板参数的。
// FUNCTION TEMPLATE _Construct_in_place
template <class _Ty, class... _Types>
_CONSTEXPR20_DYNALLOC void _Construct_in_place(_Ty& _Obj, _Types&&... _Args) noexcept(is_nothrow_constructible_v<_Ty, _Types...>) {
#ifdef __cpp_lib_constexpr_dynamic_allocif (_STD is_constant_evaluated()) {_STD construct_at(_STD addressof(_Obj), _STD forward<_Types>(_Args)...);} else
#endif // __cpp_lib_constexpr_dynamic_alloc{::new (_Voidify_iter(_STD addressof(_Obj))) _Ty(_STD forward<_Types>(_Args)...);}
}template <class _Ty>
_CONSTEXPR20_DYNALLOC void _Destroy_in_place(_Ty& _Obj) noexcept {if constexpr (is_array_v<_Ty>) {_Destroy_range(_Obj, _Obj + extent_v<_Ty>);} else {_Obj.~_Ty();}
}结构体中首先有对应的函数指针,另外,还提供了带模板的静态实现方法,实际用法是定义模板变量来保存 RTTI 结构体实例,实例中保存对应模板静态方法的指针,来为不同的类型提供 RTTI 功能:
template <class _Ty>
inline constexpr _Any_big_RTTI _Any_big_RTTI_obj = {&_Any_big_RTTI::_Destroy_impl<_Ty>, &_Any_big_RTTI::_Copy_impl<_Ty>};template <class _Ty>
inline constexpr _Any_small_RTTI _Any_small_RTTI_obj = {&_Any_small_RTTI::_Destroy_impl<_Ty>, &_Any_small_RTTI::_Copy_impl<_Ty>, &_Any_small_RTTI::_Move_impl<_Ty>};4.std::any的构造函数
4.1.从std::any构造
constexpr any() noexcept {}any(const any& _That) {_Storage._TypeData = _That._Storage._TypeData;switch (_Rep()) {case _Any_representation::_Small:_Storage._SmallStorage._RTTI = _That._Storage._SmallStorage._RTTI;_Storage._SmallStorage._RTTI->_Copy(&_Storage._SmallStorage._Data, &_That._Storage._SmallStorage._Data);break;case _Any_representation::_Big:_Storage._BigStorage._RTTI = _That._Storage._BigStorage._RTTI;_Storage._BigStorage._Ptr = _Storage._BigStorage._RTTI->_Copy(_That._Storage._BigStorage._Ptr);break;case _Any_representation::_Trivial:default:_CSTD memcpy(_Storage._TrivialData, _That._Storage._TrivialData, sizeof(_Storage._TrivialData));break;}}any(any&& _That) noexcept {_Move_from(_That);}- 无参普通构造什么也没做
- 拷贝构造先拷贝_TypeData,再处理_Storage的联合体,也就是处理对应的类型_Rep()直接返回类型,其原理也很简单,
static_cast<_Any_representation>(_Storage._TypeData & _Rep_mask);,_Rep_mask前面提过是3,就这么轻松把类型提取出来了。再接着就是RTTI指针的拷贝,对于真正的数据,small型栈上move操作,并不真正分配内存,big型是真正new一下内存拷贝构造,trivial更是简单,只需要直接拷贝内存就可以了。 - 移动语义拷贝构造,调用_Move_from,这个其实也简单,相比普通拷贝,small型调用move操作,big型拷贝内存指针,不重新申请内存,平凡性当然移动语义在这意义不大,直接还是内存拷贝。参见代码:
void _Move_from(any& _That) noexcept {_Storage._TypeData = _That._Storage._TypeData;switch (_Rep()) {case _Any_representation::_Small:_Storage._SmallStorage._RTTI = _That._Storage._SmallStorage._RTTI;_Storage._SmallStorage._RTTI->_Move(&_Storage._SmallStorage._Data, &_That._Storage._SmallStorage._Data);break;case _Any_representation::_Big:_Storage._BigStorage._RTTI = _That._Storage._BigStorage._RTTI;_Storage._BigStorage._Ptr = _That._Storage._BigStorage._Ptr;_That._Storage._TypeData = 0;break;case _Any_representation::_Trivial:default:_CSTD memcpy(_Storage._TrivialData, _That._Storage._TrivialData, sizeof(_Storage._TrivialData));break;}}4.2.可变参数模板构造函数
template <class _ValueType, enable_if_t<conjunction_v<negation<is_same<decay_t<_ValueType>, any>>,is_copy_constructible<decay_t<_ValueType>>>,int> = 0>any& operator=(_ValueType&& _Value) {// replace contained value with an object of type decay_t<_ValueType> initialized from _Value*this = any{_STD forward<_ValueType>(_Value)};return *this;}// Modifiers [any.modifiers]template <class _ValueType, class... _Types,enable_if_t<conjunction_v<is_constructible<decay_t<_ValueType>, _Types...>, is_copy_constructible<decay_t<_ValueType>>>,int> = 0>decay_t<_ValueType>& emplace(_Types&&... _Args) {// replace contained value with an object of type decay_t<_ValueType> initialized from _Args...reset();return _Emplace<decay_t<_ValueType>>(_STD forward<_Types>(_Args)...);}template <class _ValueType, class _Elem, class... _Types,enable_if_t<conjunction_v<is_constructible<decay_t<_ValueType>, initializer_list<_Elem>&, _Types...>,is_copy_constructible<decay_t<_ValueType>>>,int> = 0>decay_t<_ValueType>& emplace(initializer_list<_Elem> _Ilist, _Types&&... _Args) {// replace contained value with an object of type decay_t<_ValueType> initialized from _Ilist and _Args...reset();return _Emplace<decay_t<_ValueType>>(_Ilist, _STD forward<_Types>(_Args)...);}- 一个参数的构造,enable_if_t在以前的文长说过了,主要为了借助SFINAE编译期判断,假设条件不通过,返回并没有定义type,否则返回int,并初始值为0,假如不能通过设为0为报错的,也就是匹配不成功,所有都失败,才会编译错误。就是能用一个参数进行构造,会走这里。
- 可变参数的构造,结构基本同前面分析。注意一下,这个是explicit显式的函数,第一个参数传占位符,后面根构造用的参数。
- 带初始化列表的构造,结构基本同前面分析。注意一下,这个是explicit显式的函数,第一个参数传占位符,第二个是初始化列表,后面跟具体的的参数。
三者的重点其实都落到了,_Emplace函数上了,我们看看具体实现
template <class _Decayed, class... _Types>_Decayed& _Emplace(_Types&&... _Args) { // emplace construct _Decayedif constexpr (_Any_is_trivial<_Decayed>) {// using the _Trivial representationauto& _Obj = reinterpret_cast<_Decayed&>(_Storage._TrivialData);_Construct_in_place(_Obj, _STD forward<_Types>(_Args)...);_Storage._TypeData =reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(&typeid(_Decayed)) | static_cast<uintptr_t>(_Any_representation::_Trivial);return _Obj;} else if constexpr (_Any_is_small<_Decayed>) {// using the _Small representationauto& _Obj = reinterpret_cast<_Decayed&>(_Storage._SmallStorage._Data);_Construct_in_place(_Obj, _STD forward<_Types>(_Args)...);_Storage._SmallStorage._RTTI = &_Any_small_RTTI_obj<_Decayed>;_Storage._TypeData =reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(&typeid(_Decayed)) | static_cast<uintptr_t>(_Any_representation::_Small);return _Obj;} else {// using the _Big representation_Decayed* const _Ptr = ::new _Decayed(_STD forward<_Types>(_Args)...);_Storage._BigStorage._Ptr = _Ptr;_Storage._BigStorage._RTTI = &_Any_big_RTTI_obj<_Decayed>;_Storage._TypeData =reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(&typeid(_Decayed)) | static_cast<uintptr_t>(_Any_representation::_Big);return *_Ptr;}}可以看出_Emplace是any与真正的类型转换实现,这个模板第一个参数作了返回值,是无法推断的,必显示的传入,我们也看到都是显示传入T的退化类型的。有了前部分的分析,也是非常的容易了,先判断是trivial还是small还是big类型,方法已经说过。
- trivial:这种来说,真接内存强转,然后_Construct_in_place实质是STL的方法,就是调用placement new进行构造的,再设置_TypeData,这些都是容易处理的。
- small这里和trivial没有本质上的区别,只是内存变成48字节内了,然后多了一个RTTI指针获取,构造函数也真正起作用,不像tirival
- big类型更是容易,直接new内存进行显示的T(args...)构造,模板参数包展开,他们都是万能引用与完美转发,然后将申请并初始化的内存地址交给了_Storage._BigStorage._Ptr
总结:small型与trivial型都是没有直接进行堆内存再申请,,在any已经有的64个字节内强转操作,不同的small会真正处理调用构造函数,big型来说是进行再次堆内存申请,然后存其指针。
4.3.赋值构造与emplace函数
这个没什么好说的,实际还是调用前面说的拷贝构造与带参的构造,包装过一层而已。
// Assignment [any.assign]any& operator=(const any& _That) {*this = any{_That};return *this;}any& operator=(any&& _That) noexcept {reset();_Move_from(_That);return *this;}template <class _ValueType, enable_if_t<conjunction_v<negation<is_same<decay_t<_ValueType>, any>>,is_copy_constructible<decay_t<_ValueType>>>,int> = 0>any& operator=(_ValueType&& _Value) {// replace contained value with an object of type decay_t<_ValueType> initialized from _Value*this = any{_STD forward<_ValueType>(_Value)};return *this;}// Modifiers [any.modifiers]template <class _ValueType, class... _Types,enable_if_t<conjunction_v<is_constructible<decay_t<_ValueType>, _Types...>, is_copy_constructible<decay_t<_ValueType>>>,int> = 0>decay_t<_ValueType>& emplace(_Types&&... _Args) {// replace contained value with an object of type decay_t<_ValueType> initialized from _Args...reset();return _Emplace<decay_t<_ValueType>>(_STD forward<_Types>(_Args)...);}template <class _ValueType, class _Elem, class... _Types,enable_if_t<conjunction_v<is_constructible<decay_t<_ValueType>, initializer_list<_Elem>&, _Types...>,is_copy_constructible<decay_t<_ValueType>>>,int> = 0>decay_t<_ValueType>& emplace(initializer_list<_Elem> _Ilist, _Types&&... _Args) {// replace contained value with an object of type decay_t<_ValueType> initialized from _Ilist and _Args...reset();return _Emplace<decay_t<_ValueType>>(_Ilist, _STD forward<_Types>(_Args)...);}从中可以看出,operator=、emplace内部都是调用的_Emplace。
5.reset函数
void reset() noexcept { // transition to the empty stateswitch (_Rep()) {case _Any_representation::_Small:_Storage._SmallStorage._RTTI->_Destroy(&_Storage._SmallStorage._Data);break;case _Any_representation::_Big:_Storage._BigStorage._RTTI->_Destroy(_Storage._BigStorage._Ptr);break;case _Any_representation::_Trivial:default:break;}_Storage._TypeData = 0;}reset就是调用析构和释放内存的,对于small来说,不用释放内存,内部直接调用析构,对于big来说,其实际是delete,即析构还释放内存,对trivial来说,不用处理内存相关,最后都将_TypeData清零。
6._Cast函数
template <class _Decayed>_NODISCARD const _Decayed* _Cast() const noexcept {// if *this contains a value of type _Decayed, return a pointer to itconst type_info* const _Info = _TypeInfo();if (!_Info || *_Info != typeid(_Decayed)) {return nullptr;}if constexpr (_Any_is_trivial<_Decayed>) {// get a pointer to the contained _Trivial value of type _Decayedreturn reinterpret_cast<const _Decayed*>(&_Storage._TrivialData);} else if constexpr (_Any_is_small<_Decayed>) {// get a pointer to the contained _Small value of type _Decayedreturn reinterpret_cast<const _Decayed*>(&_Storage._SmallStorage._Data);} else {// get a pointer to the contained _Big value of type _Decayedreturn static_cast<const _Decayed*>(_Storage._BigStorage._Ptr);}}template <class _Decayed>_NODISCARD _Decayed* _Cast() noexcept { // if *this contains a value of type _Decayed, return a pointer to itreturn const_cast<_Decayed*>(static_cast<const any*>(this)->_Cast<_Decayed>());}_Cast是类型转换,提供const与非const两个版本,也是内存地址强转,big用的_Storage._BigStorage._Ptr,samll用&_Storage._SmallStorage._Data,当然trivial用的是&_Storage._TrivialData。
7.make_any模版函数
template <class _ValueType, class... _Types>
_NODISCARD any make_any(_Types&&... _Args) { // construct an any containing a _ValueType initialized with _Args...return any{in_place_type<_ValueType>, _STD forward<_Types>(_Args)...};
}
template <class _ValueType, class _Elem, class... _Types>
_NODISCARD any make_any(initializer_list<_Elem> _Ilist, _Types&&... _Args) {// construct an any containing a _ValueType initialized with _Ilist and _Args...return any{in_place_type<_ValueType>, _Ilist, _STD forward<_Types>(_Args)...};
}就是将参数透传到 std::any 的初始化列表构造并执行。
8.std::any_cast函数
template <class _ValueType>
_NODISCARD const _ValueType* any_cast(const any* const _Any) noexcept {// retrieve a pointer to the _ValueType contained in _Any, or nullstatic_assert(!is_void_v<_ValueType>, "std::any cannot contain void.");if constexpr (is_function_v<_ValueType> || is_array_v<_ValueType>) {return nullptr;} else {if (!_Any) {return nullptr;}return _Any->_Cast<_Remove_cvref_t<_ValueType>>();}
}
template <class _ValueType>
_NODISCARD _ValueType* any_cast(any* const _Any) noexcept {// retrieve a pointer to the _ValueType contained in _Any, or nullstatic_assert(!is_void_v<_ValueType>, "std::any cannot contain void.");if constexpr (is_function_v<_ValueType> || is_array_v<_ValueType>) {return nullptr;} else {if (!_Any) {return nullptr;}return _Any->_Cast<_Remove_cvref_t<_ValueType>>();}
}template <class _Ty>
_NODISCARD remove_cv_t<_Ty> any_cast(const any& _Any) {static_assert(is_constructible_v<remove_cv_t<_Ty>, const _Remove_cvref_t<_Ty>&>,"any_cast<T>(const any&) requires remove_cv_t<T> to be constructible from ""const remove_cv_t<remove_reference_t<T>>&");const auto _Ptr = _STD any_cast<_Remove_cvref_t<_Ty>>(&_Any);if (!_Ptr) {_Throw_bad_any_cast();}return static_cast<remove_cv_t<_Ty>>(*_Ptr);
}
template <class _Ty>
_NODISCARD remove_cv_t<_Ty> any_cast(any& _Any) {static_assert(is_constructible_v<remove_cv_t<_Ty>, _Remove_cvref_t<_Ty>&>,"any_cast<T>(any&) requires remove_cv_t<T> to be constructible from remove_cv_t<remove_reference_t<T>>&");const auto _Ptr = _STD any_cast<_Remove_cvref_t<_Ty>>(&_Any);if (!_Ptr) {_Throw_bad_any_cast();}return static_cast<remove_cv_t<_Ty>>(*_Ptr);
}
template <class _Ty>
_NODISCARD remove_cv_t<_Ty> any_cast(any&& _Any) {static_assert(is_constructible_v<remove_cv_t<_Ty>, _Remove_cvref_t<_Ty>>,"any_cast<T>(any&&) requires remove_cv_t<T> to be constructible from remove_cv_t<remove_reference_t<T>>");const auto _Ptr = _STD any_cast<_Remove_cvref_t<_Ty>>(&_Any);if (!_Ptr) {_Throw_bad_any_cast();}return static_cast<remove_cv_t<_Ty>>(_STD move(*_Ptr));
}所有 std::any_cast 最终都会先取保存的 std::type_info 然后与目标类型相比较,失败则抛出 std::bad_any_cast,否则则返回 value。这里要注意的是返回的类型会根据 std::any_cast 的入参产生变化:
const any* const->const _ValueType*any* const _Any->_ValueType*const any& _Any->remove_cv_t<_Ty>any& _Any->remove_cv_t<_Ty>any&& _Any->remove_cv_t<_Ty>
总结起来就是入参的 std::any 为指针时,返回指针,否则返回 remove_cv_t<_Ty>,所以使用时如果对应的是结构体 / 类,应该尽量获取指针或者引用来保持高效,避免内存拷贝降低性能(例子可以看前面的介绍)。
9.总结
到此我们已经全部分析完毕,任何做技术的都是要知其然,更好知其所以然。只要这样,才能把这些设计手法运用到我们平时的项目当中,只有你能熟练的运用了才是真正的掌握了。还是那句话,纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行。
相关推荐阅读
 std::is_trivially_copyable
std::is_trivially_copyable
 std::is_move_constructible
std::is_move_constructible
 C++内存分配策略
C++内存分配策略
相关文章:

C++三剑客之std::any(二) : 源码剖析
目录 1.引言 2.std::any的存储分析 3._Any_big_RTTI与_Any_small_RTTI 4.std::any的构造函数 4.1.从std::any构造 4.2.可变参数模板构造函数 4.3.赋值构造与emplace函数 5.reset函数 6._Cast函数 7.make_any模版函数 8.std::any_cast函数 9.总结 1.引言 C三剑客之s…...
)
【C语言】8.C语言操作符详解(2)
文章目录 6.单⽬操作符7.逗号表达式8.下标访问[]、函数调⽤()8.1 [ ] 下标引⽤操作符8.2 函数调⽤操作符 9.结构成员访问操作符9.1 结构体9.1.1 结构的声明9.1.2 结构体变量的定义和初始化 9.2 结构成员访问操作符9.2.1 结构体成员的直接访问9.2.2 结构体成员的间接访问 6.单⽬…...

vivado 物理约束KEEP_HIERARCHY
KEEP_HIERARCHY Applied To Cells Constraint Values • TRUE • FALSE • YES • NO UCF Example INST u1 KEEP_HIERARCHY TRUE; XDC Example set_property DONT_TOUCH true [get_cells u1] IOB Applied To Cells Constraint Values IOB_XnYn UCF Examp…...

Linux 三十六章
🐶博主主页:ᰔᩚ. 一怀明月ꦿ ❤️🔥专栏系列:线性代数,C初学者入门训练,题解C,C的使用文章,「初学」C,linux 🔥座右铭:“不要…...

ntsd用法+安装包
ntsd是一个强大的进程终止软件,除了少数系统进程之外一律杀掉 用法 1.ntsd -c q -p 进程的pid 2.ntsd -c q -pn 进程名 记得解压到System32里面 当然,资源管理器的进程是可以杀的所以也可以让电脑黑屏 同样可以让电脑黑屏的还有taskkill /f /im 进程…...

Nacos 微服务管理
Nacos 本教程将为您提供Nacos的基本介绍,并带您完成Nacos的安装、服务注册与发现、配置管理等功能。在这个过程中,您将学到如何使用Nacos进行微服务管理。下方是官方文档: Nacos官方文档 1. Nacos 简介 Nacos(Naming and Confi…...
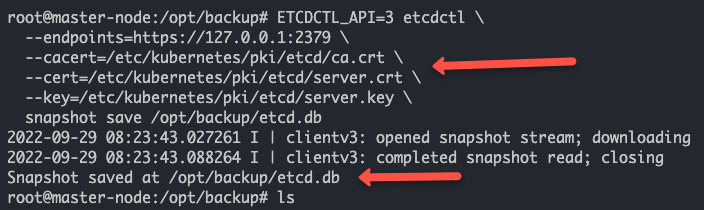
Kubernetes集群上的Etcd备份和恢复
在本教程中,您将学习如何在Kubernetes集群上使用etcd快照进行etcd备份和恢复。 在Kubernetes架构中,etcd是集群的重要组成部分。所有集群对象及其状态都存储在etcd中。为了更好地理解Kubernetes,有几点关于etcd的信息是您需要了解的。 它是…...
)
创建型模式 (Python版)
单例模式 懒汉式 class SingleTon:# 类属性_obj None # 用来存储对象# 创造对象def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):# 如果对象不存在,就创造一个对象if cls._obj is None:cls._obj super().__new__(cls, *args, *kwargs)# 返回对象return cls._objif __name__…...

【收录 Hello 算法】9.4 小结
目录 9.4 小结 1. 重点回顾 2. Q & A 9.4 小结 1. 重点回顾 图由顶点和边组成,可以表示为一组顶点和一组边构成的集合。相较于线性关系(链表)和分治关系(树),网络关系(图&am…...

MYSQL数据库基础语法
目录 友情提醒第一章:数据库简述1)数据库简述2)常见的数据库软件3)MySQL数据库安装和连接4)SQL语句分类①DDL(Data Definition)②DML(Data Manipulation)③DQL࿰…...
)
R实验 参数检验(二)
实验目的:掌握正态分布和二项分布中,功效与样本容量之间的关系;学会利用R软件完成一个正态总体方差和两个正态总体方差比的区间估计和检验。 实验内容: (习题5.28)一种药物可治疗眼内高压,目的…...

【Linux】进程信号及相关函数/系统调用的简单认识与使用
文章目录 前言一、相关函数/系统调用1. signal2. kill3. abort (库函数)4. raise (库函数)5. alarm 前言 现实生活中, 存在着诸多信号, 比如红绿灯, 上下课铃声…我们在接收到信号时, 就会做出相应的动作. 对于进程也是如此的, 进程也会收到来自 OS 发出的信号, 根据信号的不同…...
什么是Spring Boot)
Spring (14)什么是Spring Boot
Spring Boot是一个开源的Java基础框架,旨在简化Spring应用的创建和开发过程。Spring Boot通过提供一套默认配置(convention over configuration),自动配置和启动器(starters)来减少开发者的开发工作量和配置…...

区间预测 | Matlab实现CNN-KDE卷积神经网络结合核密度估计多置信区间多变量回归区间预测
区间预测 | Matlab实现CNN-KDE卷积神经网络结合核密度估计多置信区间多变量回归区间预测 目录 区间预测 | Matlab实现CNN-KDE卷积神经网络结合核密度估计多置信区间多变量回归区间预测效果一览基本介绍程序设计参考资料 效果一览 基本介绍 1.Matlab实现CNN-KDE卷积神经网络结合…...

Java集合框架全景解读:从源码到实践精通指南
1. Java集合框架简介 在Java中,集合框架是用于存储和处理数据集合的一组类和接口。它提供了一系列的数据结构,比如列表(List)、集(Set)和映射(Map)。这些数据结构为开发者处理数据提…...

Python | Leetcode Python题解之第107题二叉树的层序遍历II
题目: 题解: class Solution:def levelOrderBottom(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:levelOrder list()if not root:return levelOrderq collections.deque([root])while q:level list()size len(q)for _ in range(size):node q.popl…...
H4vdo 台湾APT-27视频投放工具
地址:https://github.com/MartinxMax/H4vdo 视频 关于 H4vdo RTMP lock 屏播放视频工具,可以向目标发送有效载荷,播放目标的屏幕内容。目标无法曹作计算机 使用方法 安装依赖 根据你的操作系统选择一个安装程序 RTMP 服务端 ./rtsp-simple-server.…...

数据结构(树)
1.树的概念和结构 树,顾名思义,它看起来像一棵树,是由n个结点组成的非线性的数据结构。 下面就是一颗树: 树的一些基本概念: 结点的度:一个结点含有的子树的个数称为该结点的度; 如上图&#…...

HTML静态网页成品作业(HTML+CSS)——川西旅游介绍网页(2个页面)
🎉不定期分享源码,关注不丢失哦 文章目录 一、作品介绍二、作品演示三、代码目录四、网站代码HTML部分代码 五、源码获取 一、作品介绍 🏷️本套采用HTMLCSS,未使用Javacsript代码,共有2个页面。 二、作品演示 三、代…...
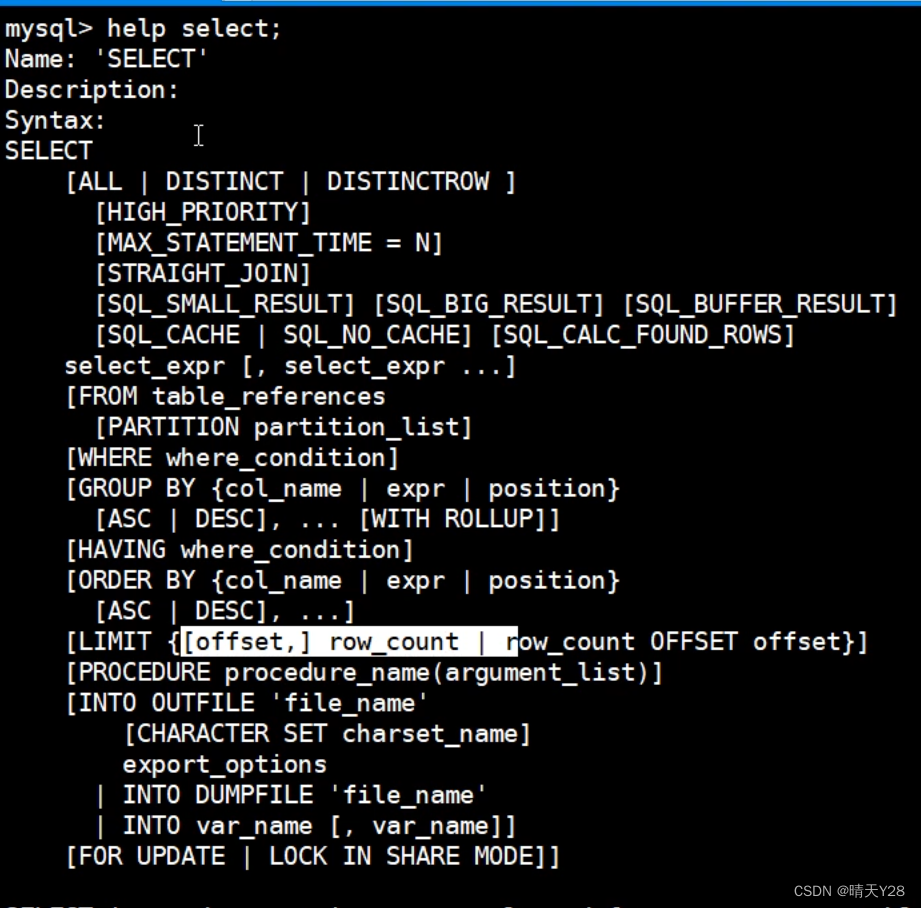
MySQL数据库单表查询中查询条件的写法
1.使用比较运算符作为查询条件 ; !; >; >; <; <; 如上图所示,可以使用命令select 字段,字段 from 表名 where Gender “M”; 即挑选出Gender “M” 的教师, 如上图所示,可以使用命令select 字段,…...

Python爬虫实战:研究feedparser库相关技术
1. 引言 1.1 研究背景与意义 在当今信息爆炸的时代,互联网上存在着海量的信息资源。RSS(Really Simple Syndication)作为一种标准化的信息聚合技术,被广泛用于网站内容的发布和订阅。通过 RSS,用户可以方便地获取网站更新的内容,而无需频繁访问各个网站。 然而,互联网…...

页面渲染流程与性能优化
页面渲染流程与性能优化详解(完整版) 一、现代浏览器渲染流程(详细说明) 1. 构建DOM树 浏览器接收到HTML文档后,会逐步解析并构建DOM(Document Object Model)树。具体过程如下: (…...

PL0语法,分析器实现!
简介 PL/0 是一种简单的编程语言,通常用于教学编译原理。它的语法结构清晰,功能包括常量定义、变量声明、过程(子程序)定义以及基本的控制结构(如条件语句和循环语句)。 PL/0 语法规范 PL/0 是一种教学用的小型编程语言,由 Niklaus Wirth 设计,用于展示编译原理的核…...
 自用)
css3笔记 (1) 自用
outline: none 用于移除元素获得焦点时默认的轮廓线 broder:0 用于移除边框 font-size:0 用于设置字体不显示 list-style: none 消除<li> 标签默认样式 margin: xx auto 版心居中 width:100% 通栏 vertical-align 作用于行内元素 / 表格单元格ÿ…...

【C++从零实现Json-Rpc框架】第六弹 —— 服务端模块划分
一、项目背景回顾 前五弹完成了Json-Rpc协议解析、请求处理、客户端调用等基础模块搭建。 本弹重点聚焦于服务端的模块划分与架构设计,提升代码结构的可维护性与扩展性。 二、服务端模块设计目标 高内聚低耦合:各模块职责清晰,便于独立开发…...
关键领域软件测试的突围之路:如何破解安全与效率的平衡难题
在数字化浪潮席卷全球的今天,软件系统已成为国家关键领域的核心战斗力。不同于普通商业软件,这些承载着国家安全使命的软件系统面临着前所未有的质量挑战——如何在确保绝对安全的前提下,实现高效测试与快速迭代?这一命题正考验着…...
安装docker)
Linux离线(zip方式)安装docker
目录 基础信息操作系统信息docker信息 安装实例安装步骤示例 遇到的问题问题1:修改默认工作路径启动失败问题2 找不到对应组 基础信息 操作系统信息 OS版本:CentOS 7 64位 内核版本:3.10.0 相关命令: uname -rcat /etc/os-rele…...

处理vxe-table 表尾数据是单独一个接口,表格tableData数据更新后,需要点击两下,表尾才是正确的
修改bug思路: 分别把 tabledata 和 表尾相关数据 console.log() 发现 更新数据先后顺序不对 settimeout延迟查询表格接口 ——测试可行 升级↑:async await 等接口返回后再开始下一个接口查询 ________________________________________________________…...
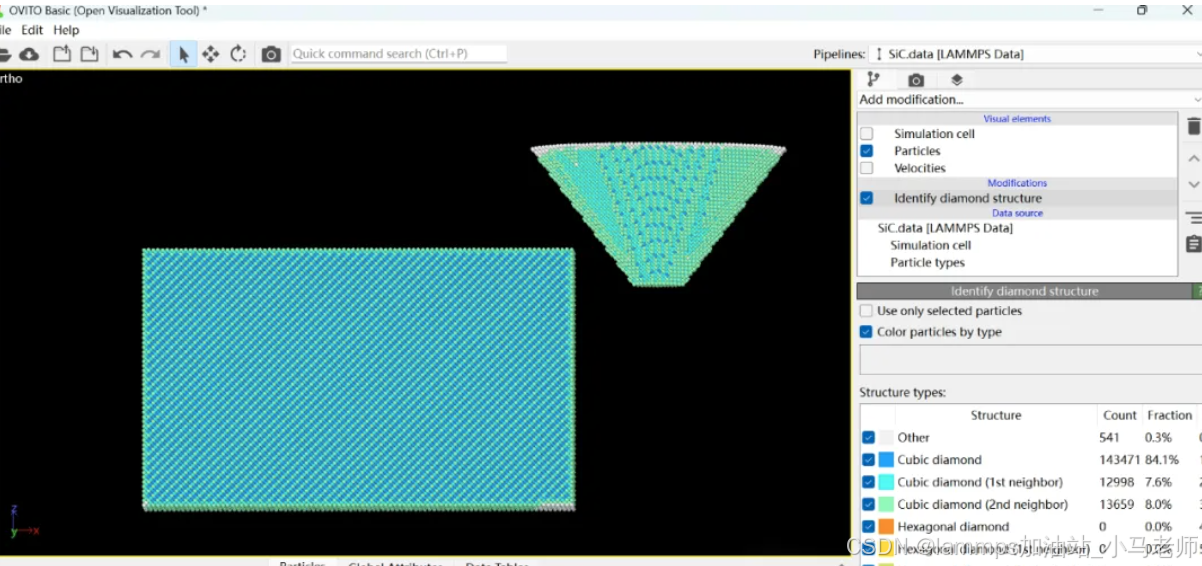
Python Ovito统计金刚石结构数量
大家好,我是小马老师。 本文介绍python ovito方法统计金刚石结构的方法。 Ovito Identify diamond structure命令可以识别和统计金刚石结构,但是无法直接输出结构的变化情况。 本文使用python调用ovito包的方法,可以持续统计各步的金刚石结构,具体代码如下: from ovito…...
HybridVLA——让单一LLM同时具备扩散和自回归动作预测能力:训练时既扩散也回归,但推理时则扩散
前言 如上一篇文章《dexcap升级版之DexWild》中的前言部分所说,在叠衣服的过程中,我会带着团队对比各种模型、方法、策略,毕竟针对各个场景始终寻找更优的解决方案,是我个人和我司「七月在线」的职责之一 且个人认为,…...
