Java SE入门及基础(54) 函数式接口
目录
1. 什么是函数式接口
函数式接口
示例
示例
2. 函数式编程
示例
3. Lambda 表达式延迟执行
应用场景
示例
4. Consumer 接口
解释说明
示例
5. BiConsumer 接口
解释说明
示例
6. Predicate 接口
解释说明
示例
练习
7. Function 接口
解释说明
示例
练习
1. 什么是函数式接口
函数式接口
A functional interface is any interface that contains only one abstract method. (A functional interface may contain one or more default methods or static methods.) Because a functional interface contains only one abstract method, you can omit the name of that method when you implement it.函数式接口是仅包含一种抽象方法的任何接口。 (一个函数式接口可能包含一个或多个默认方法或静态方法。)由于一个函数式接口仅包含一个抽象方法,因此在实现该方法时可以省略该方法的名称。
示例
public interface Hello {void sayHello ( String name );static void show (){}default void print (){}private void test (){}}
示例
@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface Hello {void sayHello ( String name );static void show (){}default void print (){}private void test (){}}
2. 函数式编程
示例
@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface Hello {void sayHello ( String name );static void show (){}default void print (){}// private void test(){}}package com . wq . functional ;public class HelloTest {public static void main ( String [] args ) {// Hello hello = name -> System.out.println(name);Hello hello = System . out :: println ;hello . sayHello ( "Marry" );}}
3. Lambda 表达式延迟执行
应用场景
示例
package com . wq . lambda . lazy ;public interface MsgBuilder {String buildMsg ( String ... infos );}package com . wq . lambda . lazy ;public class PrintUtil {public static void print ( boolean valid , String msg ){if ( valid ){System . out . println ( msg );}}private static String build ( String ... infos ){StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder ();for ( String info : infos ){builder . append ( info );}return builder . toString ();}public static void print ( boolean valid , String ... infos ){if ( valid ){// MsgBuilder builder = new MsgBuilder() {// @Override// public String buildMsg(String... infos) {// return PrintUtil.build(infos);// }// };// MsgBuilder builder = (String... arr) -> {// return PrintUtil.build(arr);// };// MsgBuilder builder = arr -> PrintUtil.build(arr);MsgBuilder builder = PrintUtil :: build ;System . out . println ( builder . buildMsg ( infos ));}}}package com . wq . lambda . lazy ;public class PrintTest {public static void main ( String [] args ) {String name = "Marry" ;String desc = " is friendly" ;//不会打印任何信息,但是此时已经完成了字符串的组装,这是属于性能上的浪费PrintUtil . print ( false , name + desc );//不会打印任何信息,但是也未构建字符串PrintUtil . print ( false , name , desc );//会打印信息时才会构建字符串PrintUtil . print ( true , name , desc );}}
4. Consumer 接口
void accept ( T t ); // 接收一个被消费的数据
解释说明
示例
package com . wq . consumer ;import java . util . Arrays ;import java . util . HashSet ;import java . util . List ;import java . util . Set ;import java . util . function . Consumer ;public class ConsumerTest {public static void main ( String [] args ) {// Consumer<String> c1 = new Consumer<String>() {// @Override// public void accept(String s) {// System.out.println(s);// }// };// Consumer<String> c1 = (String s) -> {// System.out.println(s);// };// Consumer<String> c1 = s -> System.out.println(s);Consumer < String > c1 = System . out :: println ;c1 . accept ( " 这是被消费的信息 " );// Consumer<String> c2 = new Consumer<String>() {// @Override// public void accept(String s) {// System.out.println(s.charAt(0));// }// };Consumer < String > c2 = s -> System . out . println ( s . charAt ( 0 ));c2 . accept ( "This is a consumer" );Consumer < String > c3 = c1 . andThen ( c2 );c3 . accept ( " 先打印再取第一个字符 " );//将数组转换为集合List < Integer > numbers = Arrays . asList ( 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 );// numbers.forEach(new Consumer<Integer>() {// @Override// public void accept(Integer integer) {// System.out.println(integer);// }// });//// numbers.forEach(integer -> System.out.println(integer));numbers . forEach ( System . out :: println );Set < String > names = new HashSet <> ();names . add ( "admin" );names . add ( "test" );names . add ( "developer" );// names.forEach(new Consumer<String>() {// @Override// public void accept(String s) {// System.out.println(s);// }// });names . forEach ( System . out :: println );}}
5. BiConsumer 接口
void accept ( T t , U u ); // 接收两个被消费的数据
解释说明
示例
package com . wq . consumer ;import java . util . HashMap ;import java . util . Map ;import java . util . function . BiConsumer ;public class BiConsumerTest {public static void main ( String [] args ) {// BiConsumer<String,Integer> bc = new BiConsumer<String, Integer>() {// @Override// public void accept(String s, Integer integer) {// System.out.println(s + "=>" + integer);// }// };BiConsumer < String , Integer > bc = ( s , i ) -> System . out . println ( s + "=>" + i );bc . accept ( "a" , 1 );Map < String , String > counties = new HashMap <> ();counties . put ( "CN" , " 中国 " );counties . put ( "EN" , " 英国 " );counties . put ( "US" , " 美国 " );// counties.forEach(new BiConsumer<String, String>() {// @Override// public void accept(String s1, String s2) {// System.out.println(s1 + "=>" + s2);// }// });counties . forEach (( s1 , s2 ) -> System . out . println ( s1 + "=>" + s2 ));}}
6. Predicate 接口
boolean test ( T t ); // 检测是否满足条件default Predicate < T > and ( Predicate <? super T > other ); // 条件之间的逻辑与衔接default Predicate < T > negate (); // 条件取反default Predicate < T > or ( Predicate <? super T > other ); // 条件之间的逻辑或衔接
解释说明
示例
import java . util . function . Predicate ;public class PredicateTest {public static void main ( String [] args ) {// Predicate<String> p1 = new Predicate<String>() {// @Override// public boolean test(String s) {// return s.contains("中国");// }// };Predicate < String > p1 = s -> s . contains ( " 中 " );boolean result1 = p1 . test ( " 中华人民共和国 " );System . out . println ( result1 );Predicate < String > p2 = s -> s . indexOf ( " 啊 " ) > 0 ;boolean result2 = p2 . test ( " 中华人民共和国 " );System . out . println ( result2 );Predicate < String > p3 = p1 . negate (); // 取反System . out . println ( p3 . test ( " 中华人民共和国 " ));Predicate < String > p4 = p1 . and ( p2 ); // 逻辑与衔接System . out . println ( p4 . test ( " 中华人民共和国 " ));Predicate < String > p5 = p1 . or ( p2 ); // 逻辑或衔接System . out . println ( p5 . test ( " 中华人民共和国 " ));}}
练习
package com . wq . predicate ;public class Student {private String name ;private String sex ;private int age ;public Student ( String name , String sex , int age ) {this . name = name ;this . sex = sex ;this . age = age ;}public String getName () {return name ;}public void setName ( String name ) {this . name = name ;}public String getSex () {return sex ;}public void setSex ( String sex ) {this . sex = sex ;}public int getAge () {return age ;}public void setAge ( int age ) {this . age = age ;}@Overridepublic String toString () {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", sex='" + sex + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}' ;}}package com . wq . predicate ;import java . util . Arrays ;import java . util . List ;import java . util . function . Consumer ;import java . util . function . Predicate ;public class Exercise {public static void main ( String [] args ) {List < Integer > numbers = Arrays . asList ( 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 );List < Student > students = Arrays . asList (new Student ( " 管理员 1" , " 男 " , 20 ),new Student ( " 管理员 2" , " 女 " , 21 ),new Student ( " 管理员 3" , " 男 " , 22 ),new Student ( " 管理员 4" , " 女 " , 23 ),new Student ( " 管理员 5" , " 男 " , 24 ),new Student ( " 管理员 6" , " 女 " , 18 ),new Student ( " 管理员 7" , " 男 " , 16 ),new Student ( " 管理员 8" , " 女 " , 19 ),new Student ( " 管理员 9" , " 男 " , 20 ),new Student ( " 管理员 0" , " 女 " , 23 ));// Predicate<Student> p1 = new Predicate<Student>() {// @Override// public boolean test(Student student) {// return "男".equals(student.getSex());// }// };Predicate < Student > p1 = stu -> " 男 " . equals ( stu . getSex ());Predicate < Student > p2 = stu -> stu . getAge () > 20 ;Predicate < Student > p3 = p1 . and ( p2 );// students.forEach(new Consumer<Student>() {// @Override// public void accept(Student student) {// if(p3.test(student)){// System.out.println(student);// }// }// });students . forEach ( student -> {if ( p3 . test ( student )){System . out . println ( student );}});}}
7. Function 接口
R apply ( T t ); // 将一个对象转换为另一种数据类型的对象default < V > Function < T , V > andThen ( Function <? super R , ? extends V >after ); // 复合转换
解释说明
示例
import java . util . function . Function ;public class FunctionTest {public static void main ( String [] args ) {// Function<String,Integer> f1 = new Function<String, Integer>() {// @Override// public Integer apply(String s) {// return Integer.parseInt(s);// }// };// Function<String,Integer> f1 = s -> Integer.parseInt(s);Function < String , Integer > f1 = Integer :: parseInt ;Integer i = f1 . apply ( "123" );System . out . println ( i );// Function<Integer,Double> f2 = new Function<Integer, Double>() {// @Override// public Double apply(Integer integer) {// return integer * 10.0;// }// };Function < Integer , Double > f2 = integer -> integer * 10.0 ;System . out . println ( f2 . apply ( i ));Function < String , Double > f3 = f1 . andThen ( f2 );double d = f3 . apply ( "5" );System . out . println ( d );}}
练习
谢霆锋 , 男 ,37刘德华 , 男 ,52郭富城 , 男 ,46张学友 , 男 ,40
import java . io . BufferedReader ;import java . io . FileNotFoundException ;import java . io . FileReader ;import java . io . IOException ;import java . util . ArrayList ;import java . util . List ;import java . util . function . Function ;public class Exercise {public static void main ( String [] args ) {String path = "F:/stu.txt" ;// Function<String, Student> function = new Function<String, Student>() {// @Override// public Student apply(String s) {// return new Student(s.split(","));// }// };Function < String , Student > function = s -> newStudent ( s . split ( "," ));List < Student > students = readStudent ( path , function );students . forEach ( System . out :: println );System . out . println ( "========================" );// Function<String[], Student> f = new Function<String[], Student> () {// @Override// public Student apply(String[] strings) {// return new Student(strings);// }// };// Function<String[], Student> f = strings -> new Student(strings);Function < String [], Student > f = Student :: new ;List < Student > stus = readStudent1 ( path , f );stus . forEach ( System . out :: println );}public static List < Student > readStudent1 ( String path ,Function < String [], Student > function ){List < Student > students = new ArrayList <> ();try ( FileReader reader = new FileReader ( path );BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader ( reader )) {String line ;while (( line = br . readLine ()) != null ){String [] arr = line . split ( "," );Student stu = function . apply ( arr );students . add ( stu );}} catch ( FileNotFoundException e ) {e . printStackTrace ();} catch ( IOException e ) {e . printStackTrace ();}return students ;}public static List < Student > readStudent ( String path , Function < String , Student > function ){List < Student > students = new ArrayList <> ();try ( FileReader reader = new FileReader ( path );BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader ( reader )) { String line ;while (( line = br . readLine ()) != null ){Student stu = function . apply ( line );students . add ( stu );}} catch ( FileNotFoundException e ) {e . printStackTrace ();} catch ( IOException e ) {e . printStackTrace ();}return students ;}private static class Student {private String name ;private String sex ;private int age ;public Student ( String [] arr ) {this . name = arr [ 0 ];this . sex = arr [ 1 ];this . age = Integer . parseInt ( arr [ 2 ]);}public String getName () {return name ;}public void setName ( String name ) {this . name = name ;}public String getSex () {return sex ;}public void setSex ( String sex ) {this . sex = sex ;}public int getAge () {return age ;}public void setAge ( int age ) {this . age = age ;}@Overridepublic String toString () {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", sex='" + sex + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}' ;}}}
相关文章:
 函数式接口)
Java SE入门及基础(54) 函数式接口
目录 1. 什么是函数式接口 函数式接口 示例 示例 2. 函数式编程 示例 3. Lambda 表达式延迟执行 应用场景 示例 4. Consumer 接口 解释说明 示例 5. BiConsumer 接口 解释说明 示例 6. Predicate 接口 解释说明 示例 练习 7. Function 接口 解释说明 示例…...
轻松同步:将照片从三星手机传输到iPad的简便方法
概括 想要在新 iPad 上查看三星照片吗?但是,如果您不知道如何将照片从三星手机传输到 iPad,则无法在 iPad 上查看图片。为此,本文分享了 7 个有用的方法,以便您可以使用它们在不同操作系统之间轻松发送照片。现在&…...

MySQL查询某个字段含有字母数字的值
在MySQL中,要查询某个字段含有字母和数字的值,可以使用正则表达式配合REGEXP操作符。以下是一个详细的示例,说明如何编写这样的查询。 假设我们有一个名为my_table的表,其中有一个名为my_column的字段,我们想要查询这…...

通关!游戏设计之道Day14
力量与你同在 所有类型的游戏里,赛车类,解谜类,动作冒险类和射击类你都能找到强化道具。 强化道具 设计强化道具时,设计师应该开动脑筋琢磨下面几个问题 1.强化道具有什么用? 2.他长什么样子,在整个游戏…...

实现一个自定义 hook,用于强制刷新当前组件
写在前面 在 react 中,如果 state 数据发生变化,我们知道,会重新渲染该组件。 但是这个前提是我们需要依赖 state 数据的变化,那比如我们并不想定义 state,又或者说我们的操作不能引起 state 的变化,此时…...

牛客热题:滑动窗口的最大值
📟作者主页:慢热的陕西人 🌴专栏链接:力扣刷题日记 📣欢迎各位大佬👍点赞🔥关注🚓收藏,🍉留言 文章目录 牛客热题:滑动窗口的最大值题目链接方法一…...

Adobe产品安装目录修改
进入安装包目录,进入到products文件夹 编辑driver.xml文件 将“InstallDir”修改为你需要安装的软件的目录,我这里是修改到D:\Adobe目录 <DriverInfo> <ProductInfo> xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx </ProductInfo> 拷贝RequestInfo这部分…...
时间(空间)复杂度(结构篇)
目录 前言: 一、时间复杂度 1.1 时间复杂度的定义 1.2 时间复杂度的分析 表示方法: 1.3 常见的时间复杂度 1.4 时间复杂度的计算以及简单的分析 冒泡排序 折半查找(二分查找) 斐波那契数列(递归)…...

react记录部署
导语 React中的核心概念 1 虚拟DOM(Virtual DOM) 2 Diff算法(虚拟DOM的加速器,提升React性能的法宝) React主要的原理 Virtual DOM 虚拟DOM; 提供了一种不同的而又强大的方式来更新DOM, 代替直接的DOM操…...
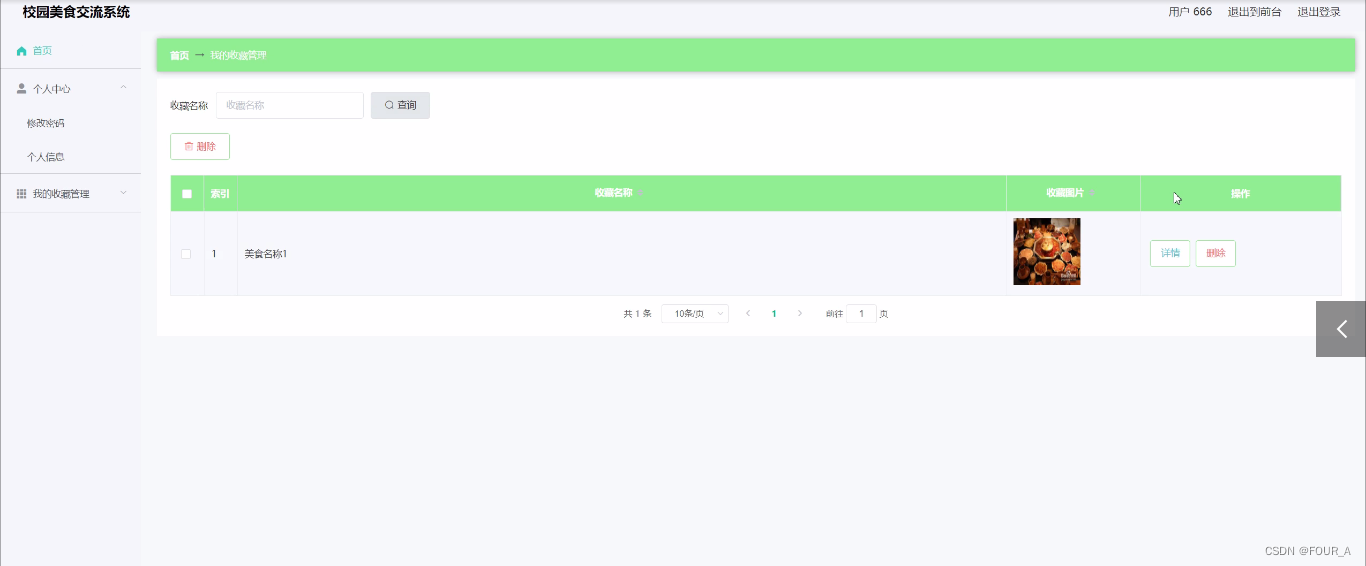
【计算机毕业设计】基于SSM+Vue的校园美食交流系统【源码+lw+部署文档】
目录 前 言 第1章 概述 1.1 研究背景 1.2 研究目的 1.3 研究内容 第二章 开发技术介绍 2.1 Java技术 2.2 Mysql数据库 2.3 B/S结构 2.4 SSM框架 第三章 系统分析 3.1 可行性分析 3.1.1 技术可行性 3.1.2 经济可行性 3.1.3 操作可行性 3.2 系统性能分析 3.3 系…...
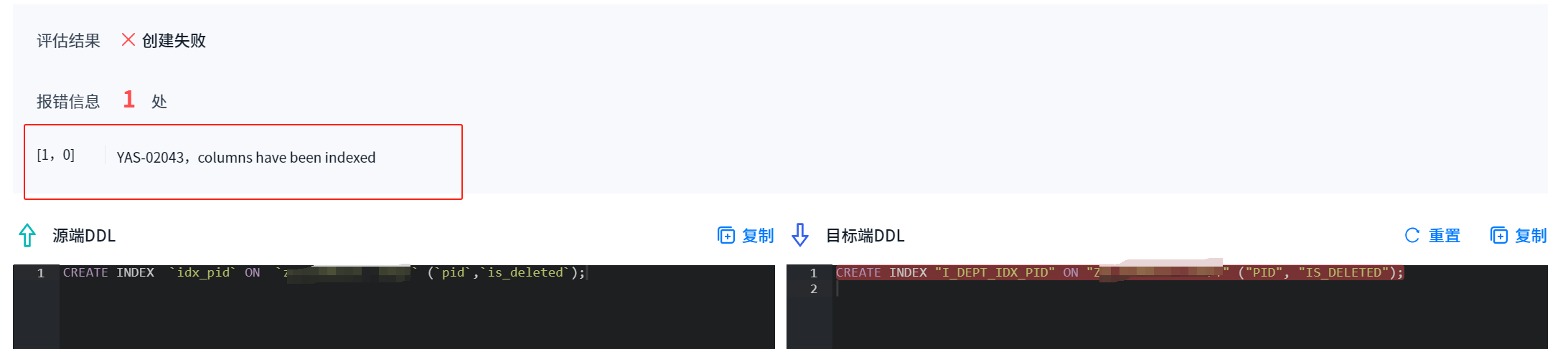
「YashanDB迁移体验官」Mysql生产环境迁移至YashanDB数据库深度体验
「YashanDB迁移体验官」Mysql生产环境迁移至YashanDB数据库深度体验 1. 前言1.1 产品介绍1.2 产品架构1.3 产品规格1.3.1 数据库版本支持1.3.2 数据类型支持 2. YMP安装2.1 环境说明2.2 执行安装2.3 访问YMP2.3.1 YMP登录界面2.3.2 YMP迁移流程 3. YMP数据迁移3.1 创建数据源3.…...

qmt量化交易策略小白学习笔记第4期【qmt如何获取获取行情数据--内置python使用方法】
内置python使用方法 qmt更加详细的教程方法,会持续慢慢梳理。 也可找寻博主的历史文章,搜索关键词查看解决方案 ! 感谢关注,需免费开通量化回测与咨询实盘权限,可以和博主联系! 获取历史行情与实时行情…...

XXE(XML外部实体注入)
1、XXE原理 XXE(XML外部实体注入,XML External Entity) ,在应用程序解析XML输入时,当允许引用外部实体时,可构造恶意内容,导致读取任意文件、探测内网端口、攻击内网网站、发起DoS拒绝服务攻击、执行系统命…...

kafka 案例
kafka 案例 目录概述需求: 设计思路实现思路分析1.kafka案例_API 带回调函数的生产者2.kafka案例_API生产者分区策略测试3.kafka案例_自定义分区的生产者4.kafka案例_API同步发送生产者5.kafka案例_API简单消费者5.kafka案例_API消费者重置offset 参考资料和推荐阅读…...

别被“涨价“带跑,性价比才是消费真理
文章来源:全食在线 “再不好好赚钱,连方便面也吃不起了。”这是昨天在热搜下,一位网友的留言。而热搜的内容,正是康师傅方便面即将涨价的消息。 01 传闻初现 昨天上午,朋友圈就有人放出康师傅方便面要涨价的消息&am…...

GEE深度学习——使用Tensorflow进行神经网络DNN土地分类
Tensorflow TensorFlow是一个开源的深度学习框架,由Google开发和维护。它提供了一个灵活的框架来构建和训练各种机器学习模型,尤其是深度神经网络模型。 TensorFlow的主要特点包括: 1. 它具有高度的灵活性,可以用于训练和部署各种类型的机器学习模型,包括分类、回归、聚…...
)
死锁示例(python、go)
Thread 1首先获取了资源A,然后尝试获取资源B,但此时资源B已经被Thread 2获取,因此Thread 1会一直等待。而Thread 2也类似,首先获取资源B,然后尝试获取资源A,但此时资源A已经被Thread 1获取,因此…...
)
Spring Cloud 面试题(五)
1. Eureka的自我保护模式是什么? Eureka的自我保护模式是一种应对网络异常的安全保护措施,旨在防止因网络分区或其他异常情况导致服务实例被错误地注销。当Eureka Server在短时间内丢失过多的客户端心跳时,会触发自我保护机制。以下是自我保…...
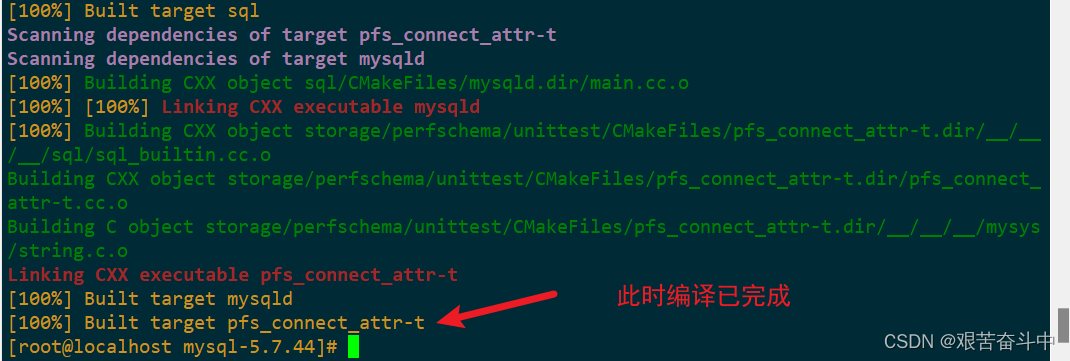
源码编译安装LAMP
1.LAMP介绍 LAMP架构是目前成熟的企业网站应用模式之一,指的是协同工作的一整套系统和相关软件,能够提供动态Web站点服务及其应用开发环境。LAMP是一个缩写词,具体包括Linux操作系统、Apache网站服务器、MySQL数据库服务器、PHP(…...
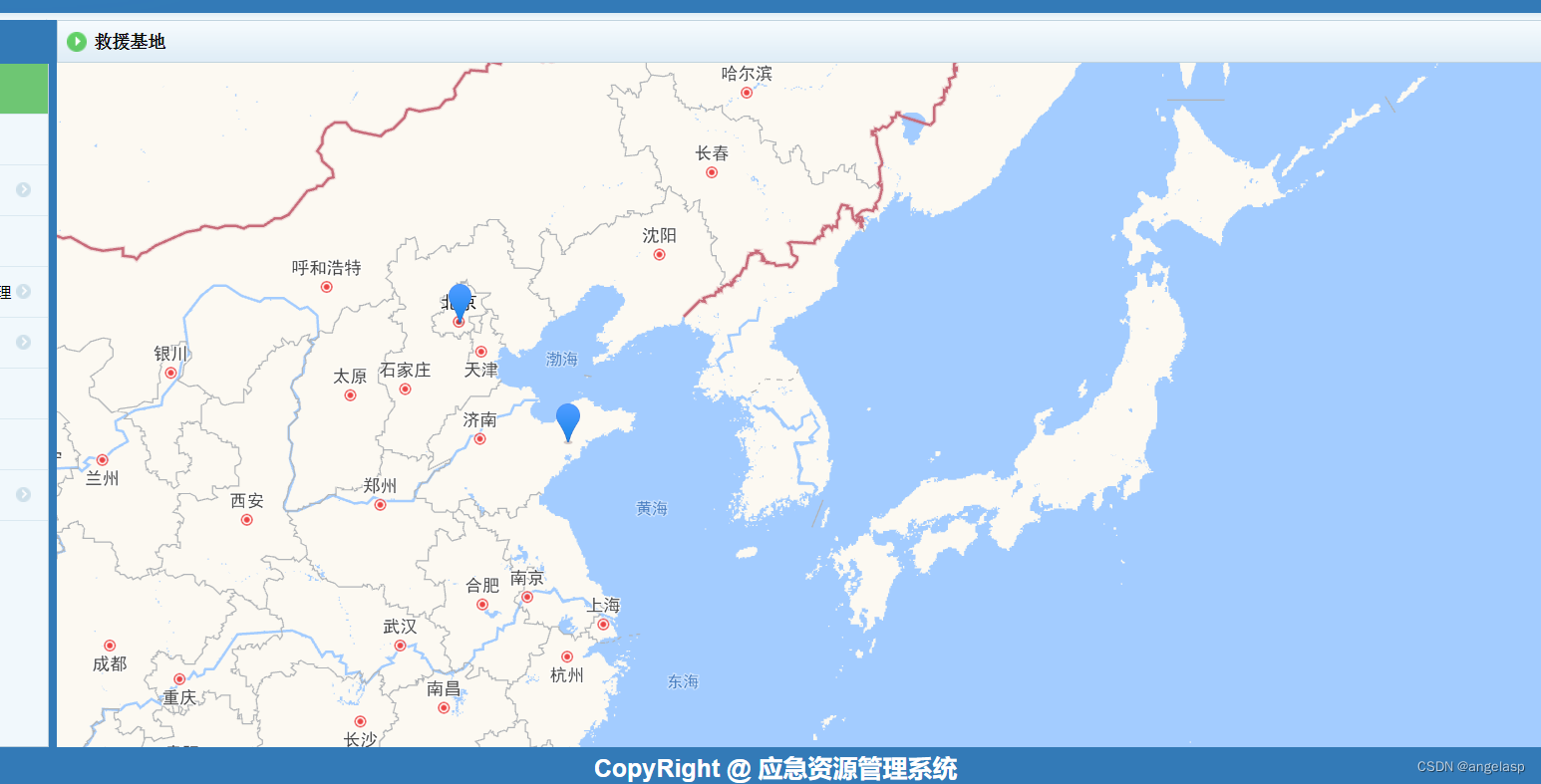
html5网页-浏览器中实现高德地图定位功能
介绍 HTML5是当前Web开发中最常用的技术之一,而地图应用又是其中一个非常常见的需求。高德地图是国内最受欢迎的地图服务提供商之一,他们提供了一系列的API,方便开发者在自己的网站或应用中集成地图功能。 接下来我们如何使用HTML5浏览器和高…...

RestClient
什么是RestClient RestClient 是 Elasticsearch 官方提供的 Java 低级 REST 客户端,它允许HTTP与Elasticsearch 集群通信,而无需处理 JSON 序列化/反序列化等底层细节。它是 Elasticsearch Java API 客户端的基础。 RestClient 主要特点 轻量级ÿ…...
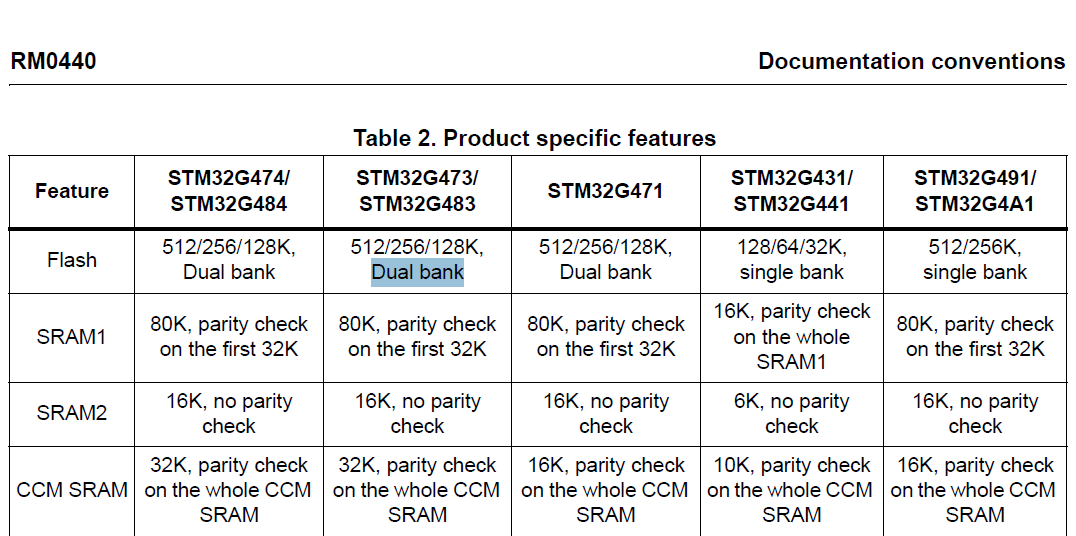
stm32G473的flash模式是单bank还是双bank?
今天突然有人stm32G473的flash模式是单bank还是双bank?由于时间太久,我真忘记了。搜搜发现,还真有人和我一样。见下面的链接:https://shequ.stmicroelectronics.cn/forum.php?modviewthread&tid644563 根据STM32G4系列参考手…...
)
进程地址空间(比特课总结)
一、进程地址空间 1. 环境变量 1 )⽤户级环境变量与系统级环境变量 全局属性:环境变量具有全局属性,会被⼦进程继承。例如当bash启动⼦进程时,环 境变量会⾃动传递给⼦进程。 本地变量限制:本地变量只在当前进程(ba…...
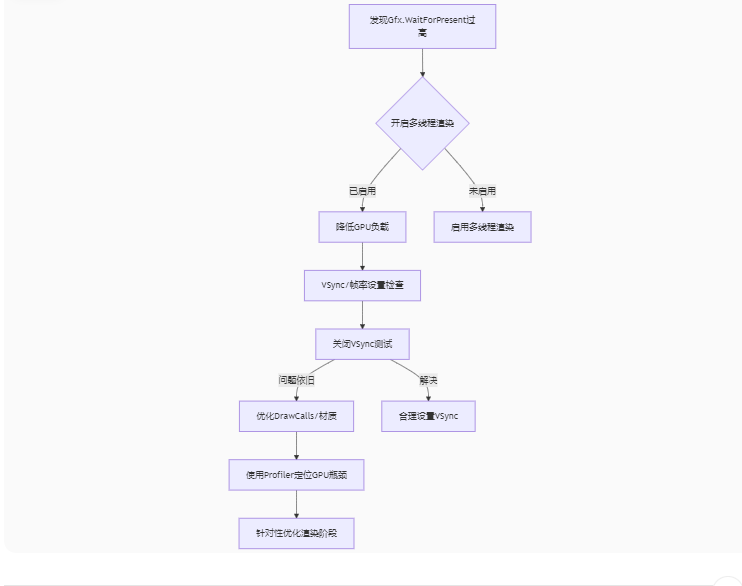
Unity3D中Gfx.WaitForPresent优化方案
前言 在Unity中,Gfx.WaitForPresent占用CPU过高通常表示主线程在等待GPU完成渲染(即CPU被阻塞),这表明存在GPU瓶颈或垂直同步/帧率设置问题。以下是系统的优化方案: 对惹,这里有一个游戏开发交流小组&…...

Python:操作 Excel 折叠
💖亲爱的技术爱好者们,热烈欢迎来到 Kant2048 的博客!我是 Thomas Kant,很开心能在CSDN上与你们相遇~💖 本博客的精华专栏: 【自动化测试】 【测试经验】 【人工智能】 【Python】 Python 操作 Excel 系列 读取单元格数据按行写入设置行高和列宽自动调整行高和列宽水平…...

FastAPI 教程:从入门到实践
FastAPI 是一个现代、快速(高性能)的 Web 框架,用于构建 API,支持 Python 3.6。它基于标准 Python 类型提示,易于学习且功能强大。以下是一个完整的 FastAPI 入门教程,涵盖从环境搭建到创建并运行一个简单的…...

浅谈不同二分算法的查找情况
二分算法原理比较简单,但是实际的算法模板却有很多,这一切都源于二分查找问题中的复杂情况和二分算法的边界处理,以下是博主对一些二分算法查找的情况分析。 需要说明的是,以下二分算法都是基于有序序列为升序有序的情况…...

蓝桥杯3498 01串的熵
问题描述 对于一个长度为 23333333的 01 串, 如果其信息熵为 11625907.5798, 且 0 出现次数比 1 少, 那么这个 01 串中 0 出现了多少次? #include<iostream> #include<cmath> using namespace std;int n 23333333;int main() {//枚举 0 出现的次数//因…...
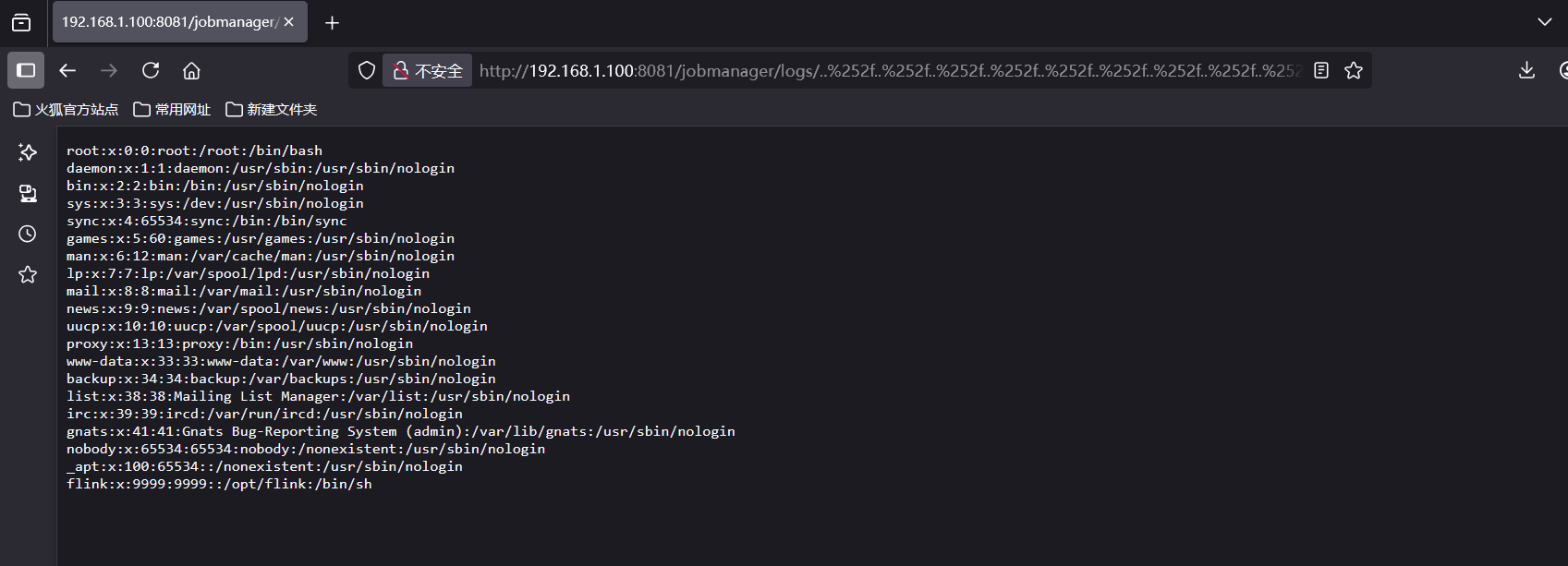
CVE-2020-17519源码分析与漏洞复现(Flink 任意文件读取)
漏洞概览 漏洞名称:Apache Flink REST API 任意文件读取漏洞CVE编号:CVE-2020-17519CVSS评分:7.5影响版本:Apache Flink 1.11.0、1.11.1、1.11.2修复版本:≥ 1.11.3 或 ≥ 1.12.0漏洞类型:路径遍历&#x…...

2025年渗透测试面试题总结-腾讯[实习]科恩实验室-安全工程师(题目+回答)
安全领域各种资源,学习文档,以及工具分享、前沿信息分享、POC、EXP分享。不定期分享各种好玩的项目及好用的工具,欢迎关注。 目录 腾讯[实习]科恩实验室-安全工程师 一、网络与协议 1. TCP三次握手 2. SYN扫描原理 3. HTTPS证书机制 二…...
