python 字符串驻留机制

偶然发现一个python字符串的现象:
>>> a = '123_abc'
>>> b = '123_abc'
>>> a is b
True
>>> c = 'abc#123'
>>> d = 'abc#123'
>>> c is d
False
这是为什么呢,原来它们的id不一样。
>>> id(a) == id(b)
True
>>> id(c) == id(d)
False
那为什么它们的地址有的相同,有的不同呢?查询后得知这是一种 Python 的字符串驻留机制。
字符串驻留机制
也称为字符串常量优化(string interning),是一种在 Python 解释器中自动进行的优化过程。它主要目的是减少内存的使用,提高程序的运行效率。
工作原理
- 小字符串:Python 只会对短小的字符串进行驻留。但是,这个长度并不是固定的,它可能会因 Python 的不同版本或实现而有所不同。
- 字符串池(String Pool):Python 解释器维护一个字符串池,用于存储所有已经出现过的字符串常量。
- 驻留(Interning):当解释器遇到一个新的字符串字面量时,它会首先检查这个字符串是否已经存在于字符串池中。如果存在,则直接使用池中的引用;如果不存在,就将这个字符串添加到池中,并返回这个字符串的引用。
- 内存节省:由于相同的字符串字面量在程序中可能被多次使用,通过字符串驻留机制,可以确保这些重复的字符串只存储一次,从而节省内存。
- 性能提升:字符串比较操作可以通过比较它们的引用地址来完成,这比逐字符比较要快得多。因此,字符串驻留可以提高字符串比较的性能。
- 自动和透明:字符串驻留是自动进行的,程序员不需要显式地进行任何操作。Python 解释器会在后台处理这一过程。
- 不可变类型:字符串驻留机制只适用于不可变类型,因为可变类型的对象内容可能会改变,这会使得引用地址比较失去意义。如果字符串可以修改,那么驻留机制可能会导致意外的副作用。
- 限制:字符串驻留机制虽然有诸多好处,但也存在一些限制。例如,如果程序中使用了大量的动态生成的字符串,那么字符串驻留可能不会带来太大的好处,因为这些字符串可能不会被重复使用。
- 字符串字面量:只有当字符串是字面量时,Python 才会尝试进行驻留。通过其他方式(如 str() 函数、字符串拼接等)创建的字符串通常不会被驻留。
- 编译时驻留:字符串驻留是在 Python 源代码编译成字节码时进行的,而不是在运行时。这意味着在运行时动态生成的字符串通常不会被驻留。
显式驻留
Python 提供了一个sys库函数 intern(),允许程序员显式地将一个字符串驻留。使用这个函数可以手动控制字符串的驻留过程:
>>> from sys import intern
>>> s = intern('abc#123')
>>> t = intern('abc#123')
>>> s is t
True
>>> s = 'abc#123'
>>> t = 'abc#123'
>>> s is t
False
>>> a = intern('abc_123')
>>> b = 'abc_123'
>>> a is b
True
字符串长短的分界
小字符串才进行驻留,具体多少长度是界线也没有细查,大概用二分法也能枚举出来。
>>> x = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'*100
>>> y = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'*100
>>> x is y
True
>>> x = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'*200
>>> y = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'*200
>>> x is y
False
>>> x = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'*150
>>> y = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'*150
>>> x is y
True
>>> x = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'*175
>>> y = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'*175
>>> x is y
False
......
附:字符串方法
(版本python 3.12)
capitalize(self, /)
Return a capitalized version of the string.
More specifically, make the first character have upper case and the rest lower
case.
casefold(self, /)
Return a version of the string suitable for caseless comparisons.
center(self, width, fillchar=' ', /)
Return a centered string of length width.
Padding is done using the specified fill character (default is a space).
count(...)
S.count(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
Return the number of non-overlapping occurrences of substring sub in
string S[start:end]. Optional arguments start and end are
interpreted as in slice notation.
encode(self, /, encoding='utf-8', errors='strict')
Encode the string using the codec registered for encoding.
encoding
The encoding in which to encode the string.
errors
The error handling scheme to use for encoding errors.
The default is 'strict' meaning that encoding errors raise a
UnicodeEncodeError. Other possible values are 'ignore', 'replace' and
'xmlcharrefreplace' as well as any other name registered with
codecs.register_error that can handle UnicodeEncodeErrors.
endswith(...)
S.endswith(suffix[, start[, end]]) -> bool
Return True if S ends with the specified suffix, False otherwise.
With optional start, test S beginning at that position.
With optional end, stop comparing S at that position.
suffix can also be a tuple of strings to try.
expandtabs(self, /, tabsize=8)
Return a copy where all tab characters are expanded using spaces.
If tabsize is not given, a tab size of 8 characters is assumed.
find(...)
S.find(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
Return the lowest index in S where substring sub is found,
such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
Return -1 on failure.
format(...)
S.format(*args, **kwargs) -> str
Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from args and kwargs.
The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}').
format_map(...)
S.format_map(mapping) -> str
Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from mapping.
The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}').
index(...)
S.index(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
Return the lowest index in S where substring sub is found,
such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
Raises ValueError when the substring is not found.
isalnum(self, /)
Return True if the string is an alpha-numeric string, False otherwise.
A string is alpha-numeric if all characters in the string are alpha-numeric and
there is at least one character in the string.
isalpha(self, /)
Return True if the string is an alphabetic string, False otherwise.
A string is alphabetic if all characters in the string are alphabetic and there
is at least one character in the string.
isascii(self, /)
Return True if all characters in the string are ASCII, False otherwise.
ASCII characters have code points in the range U+0000-U+007F.
Empty string is ASCII too.
isdecimal(self, /)
Return True if the string is a decimal string, False otherwise.
A string is a decimal string if all characters in the string are decimal and
there is at least one character in the string.
isdigit(self, /)
Return True if the string is a digit string, False otherwise.
A string is a digit string if all characters in the string are digits and there
is at least one character in the string.
isidentifier(self, /)
Return True if the string is a valid Python identifier, False otherwise.
Call keyword.iskeyword(s) to test whether string s is a reserved identifier,
such as "def" or "class".
islower(self, /)
Return True if the string is a lowercase string, False otherwise.
A string is lowercase if all cased characters in the string are lowercase and
there is at least one cased character in the string.
isnumeric(self, /)
Return True if the string is a numeric string, False otherwise.
A string is numeric if all characters in the string are numeric and there is at
least one character in the string.
isprintable(self, /)
Return True if the string is printable, False otherwise.
A string is printable if all of its characters are considered printable in
repr() or if it is empty.
isspace(self, /)
Return True if the string is a whitespace string, False otherwise.
A string is whitespace if all characters in the string are whitespace and there
is at least one character in the string.
istitle(self, /)
Return True if the string is a title-cased string, False otherwise.
In a title-cased string, upper- and title-case characters may only
follow uncased characters and lowercase characters only cased ones.
isupper(self, /)
Return True if the string is an uppercase string, False otherwise.
A string is uppercase if all cased characters in the string are uppercase and
there is at least one cased character in the string.
join(self, iterable, /)
Concatenate any number of strings.
The string whose method is called is inserted in between each given string.
The result is returned as a new string.
Example: '.'.join(['ab', 'pq', 'rs']) -> 'ab.pq.rs'
ljust(self, width, fillchar=' ', /)
Return a left-justified string of length width.
Padding is done using the specified fill character (default is a space).
lower(self, /)
Return a copy of the string converted to lowercase.
lstrip(self, chars=None, /)
Return a copy of the string with leading whitespace removed.
If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
partition(self, sep, /)
Partition the string into three parts using the given separator.
This will search for the separator in the string. If the separator is found,
returns a 3-tuple containing the part before the separator, the separator
itself, and the part after it.
If the separator is not found, returns a 3-tuple containing the original string
and two empty strings.
removeprefix(self, prefix, /)
Return a str with the given prefix string removed if present.
If the string starts with the prefix string, return string[len(prefix):].
Otherwise, return a copy of the original string.
removesuffix(self, suffix, /)
Return a str with the given suffix string removed if present.
If the string ends with the suffix string and that suffix is not empty,
return string[:-len(suffix)]. Otherwise, return a copy of the original
string.
replace(self, old, new, count=-1, /)
Return a copy with all occurrences of substring old replaced by new.
count
Maximum number of occurrences to replace.
-1 (the default value) means replace all occurrences.
If the optional argument count is given, only the first count occurrences are
replaced.
rfind(...)
S.rfind(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
Return the highest index in S where substring sub is found,
such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
Return -1 on failure.
rindex(...)
S.rindex(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
Return the highest index in S where substring sub is found,
such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
Raises ValueError when the substring is not found.
rjust(self, width, fillchar=' ', /)
Return a right-justified string of length width.
Padding is done using the specified fill character (default is a space).
rpartition(self, sep, /)
Partition the string into three parts using the given separator.
This will search for the separator in the string, starting at the end. If
the separator is found, returns a 3-tuple containing the part before the
separator, the separator itself, and the part after it.
If the separator is not found, returns a 3-tuple containing two empty strings
and the original string.
rsplit(self, /, sep=None, maxsplit=-1)
Return a list of the substrings in the string, using sep as the separator string.
sep
The separator used to split the string.
When set to None (the default value), will split on any whitespace
character (including \n \r \t \f and spaces) and will discard
empty strings from the result.
maxsplit
Maximum number of splits (starting from the left).
-1 (the default value) means no limit.
Splitting starts at the end of the string and works to the front.
rstrip(self, chars=None, /)
Return a copy of the string with trailing whitespace removed.
If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
split(self, /, sep=None, maxsplit=-1)
Return a list of the substrings in the string, using sep as the separator string.
sep
The separator used to split the string.
When set to None (the default value), will split on any whitespace
character (including \n \r \t \f and spaces) and will discard
empty strings from the result.
maxsplit
Maximum number of splits (starting from the left).
-1 (the default value) means no limit.
Note, str.split() is mainly useful for data that has been intentionally
delimited. With natural text that includes punctuation, consider using
the regular expression module.
splitlines(self, /, keepends=False)
Return a list of the lines in the string, breaking at line boundaries.
Line breaks are not included in the resulting list unless keepends is given and
true.
startswith(...)
S.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]]) -> bool
Return True if S starts with the specified prefix, False otherwise.
With optional start, test S beginning at that position.
With optional end, stop comparing S at that position.
prefix can also be a tuple of strings to try.
strip(self, chars=None, /)
Return a copy of the string with leading and trailing whitespace removed.
If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
swapcase(self, /)
Convert uppercase characters to lowercase and lowercase characters to uppercase.
title(self, /)
Return a version of the string where each word is titlecased.
More specifically, words start with uppercased characters and all remaining
cased characters have lower case.
translate(self, table, /)
Replace each character in the string using the given translation table.
table
Translation table, which must be a mapping of Unicode ordinals to
Unicode ordinals, strings, or None.
The table must implement lookup/indexing via __getitem__, for instance a
dictionary or list. If this operation raises LookupError, the character is
left untouched. Characters mapped to None are deleted.
upper(self, /)
Return a copy of the string converted to uppercase.
zfill(self, width, /)
Pad a numeric string with zeros on the left, to fill a field of the given width.
The string is never truncated.
目录
字符串驻留机制
工作原理
显式驻留
字符串长短的分界
附:字符串方法
完
相关文章:

python 字符串驻留机制
偶然发现一个python字符串的现象: >>> a 123_abc >>> b 123_abc >>> a is b True >>> c abc#123 >>> d abc#123 >>> c is d False 这是为什么呢,原来它们的id不一样。 >>> id(a)…...
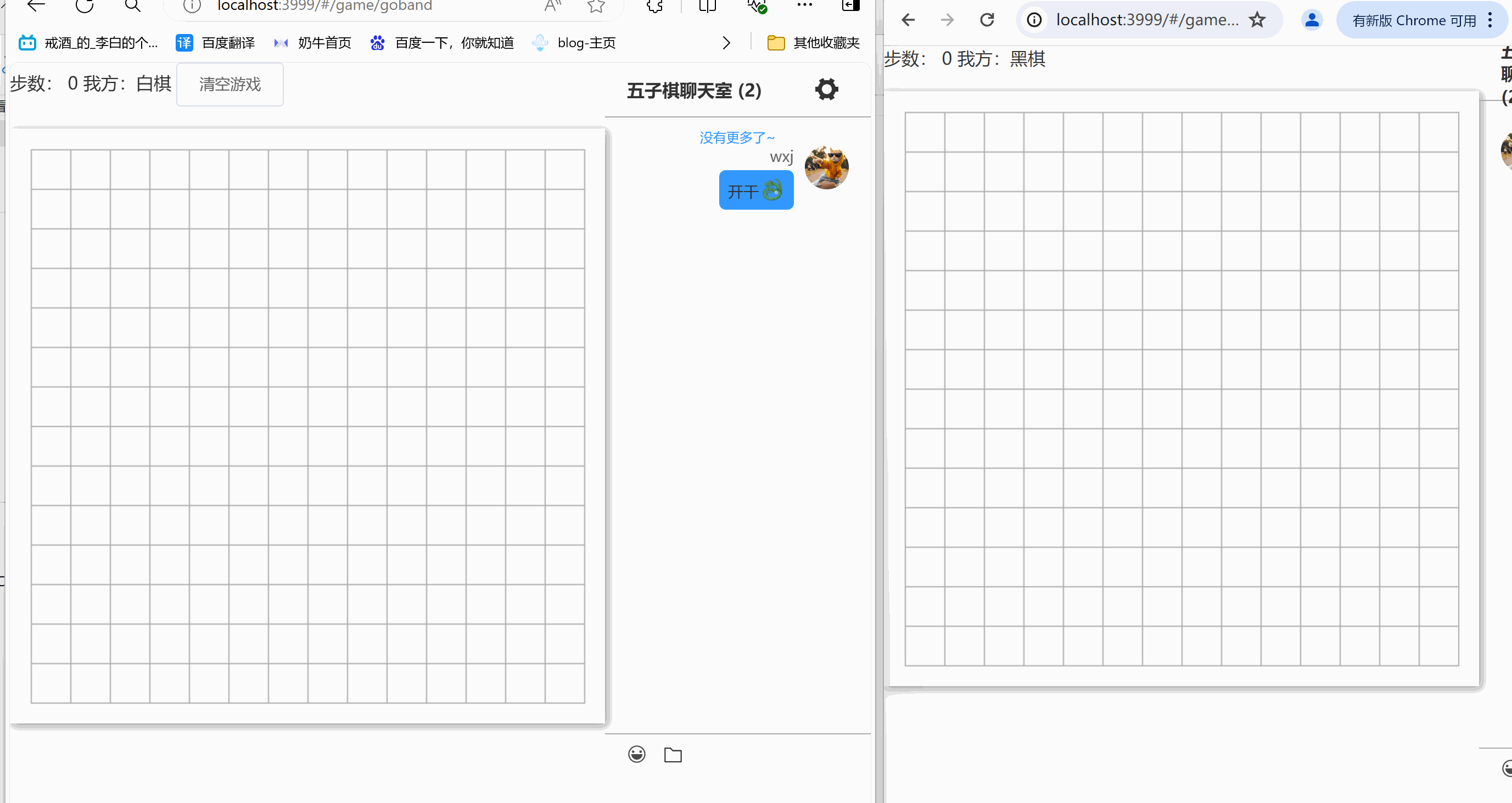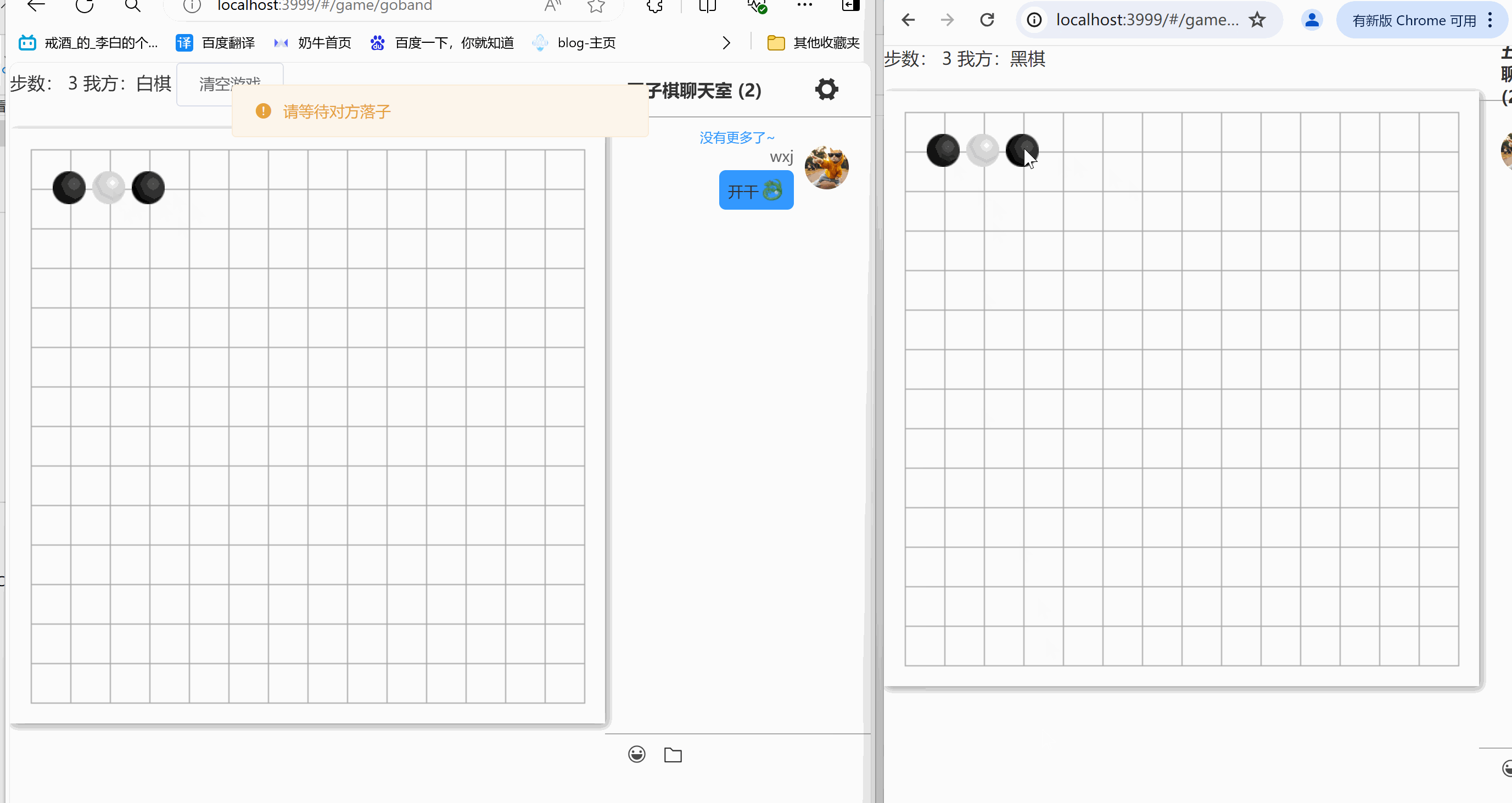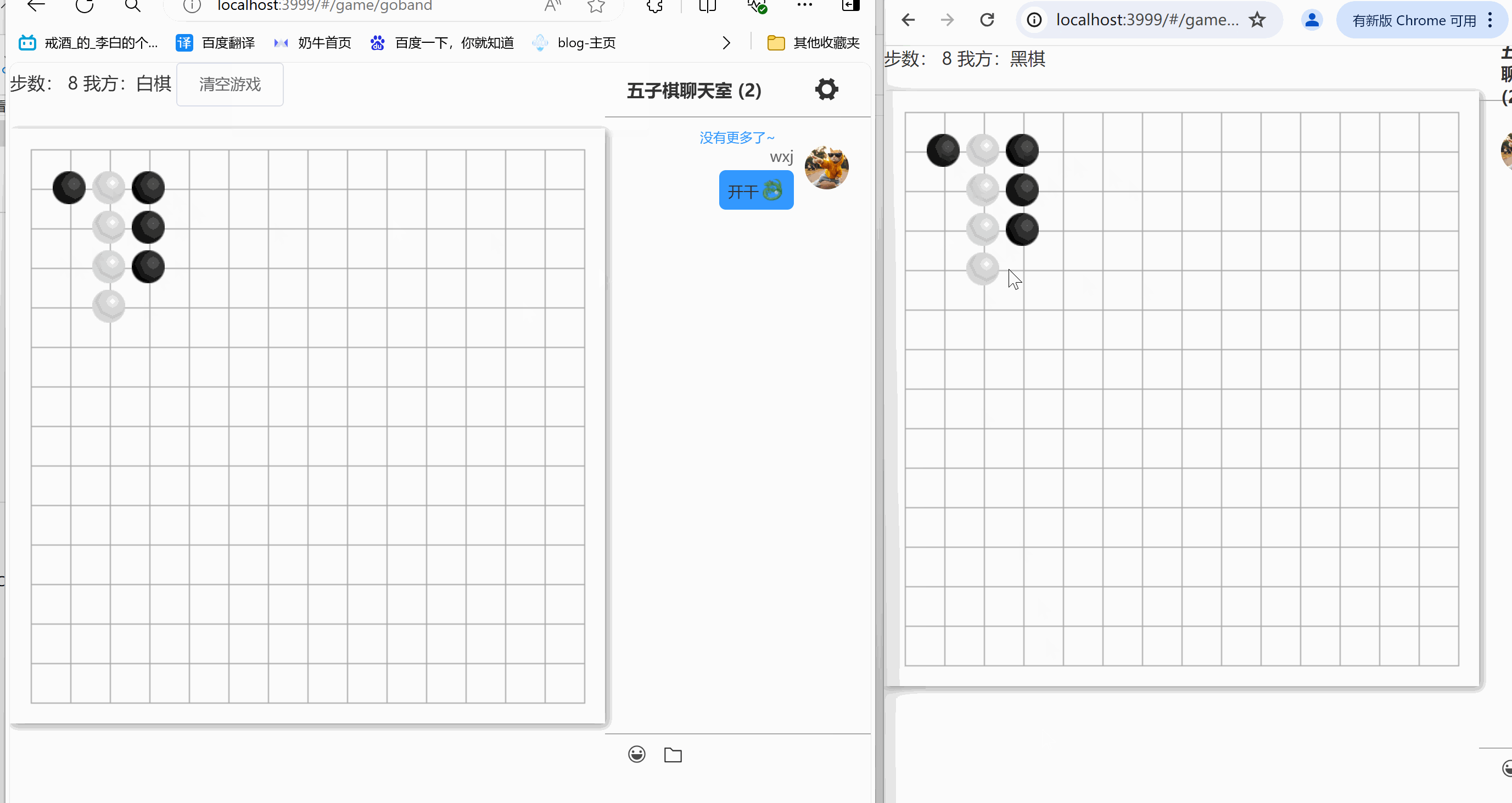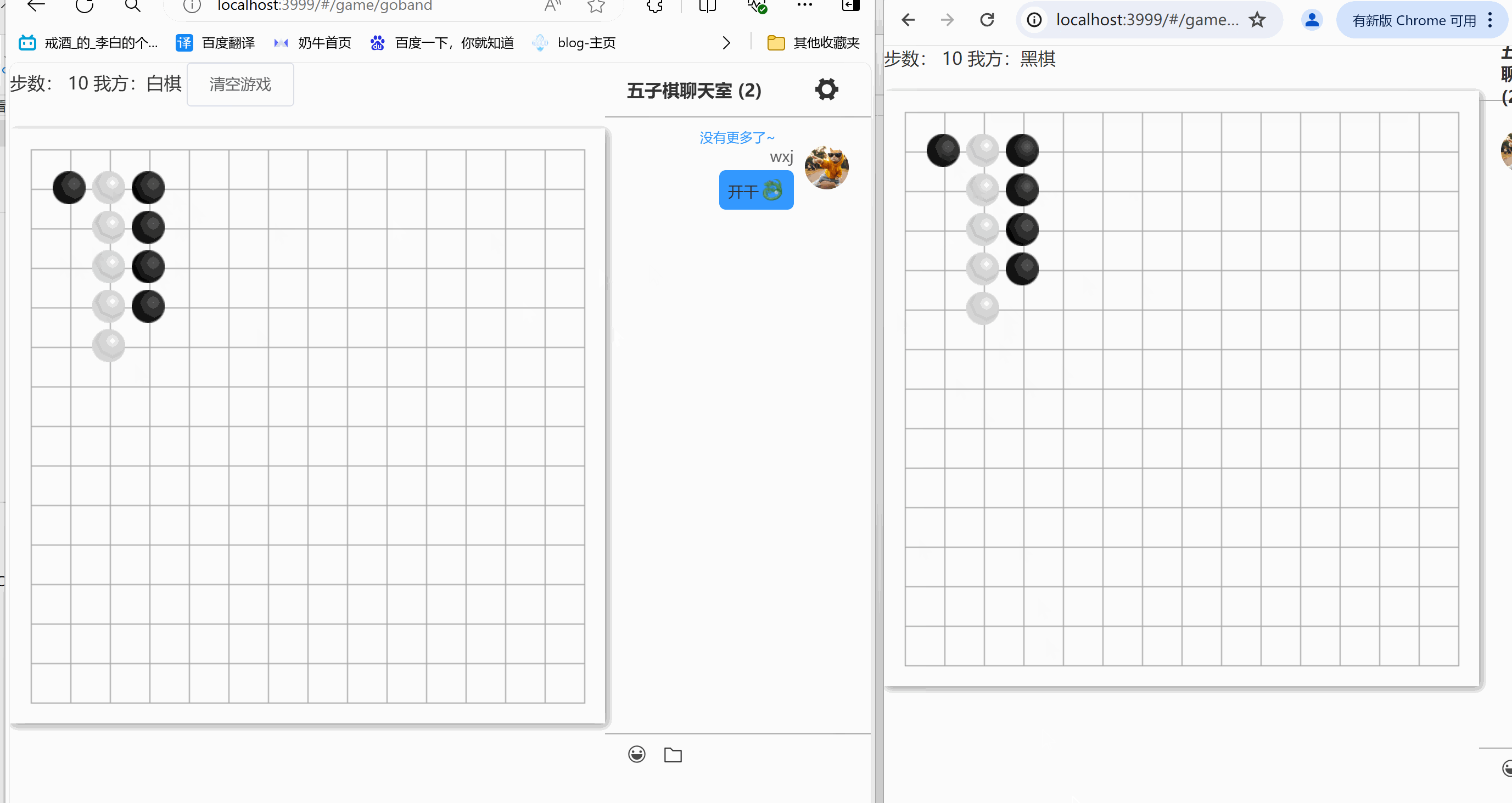
express+vue 在线五子棋(一)
示例 在线体验地址五子棋,记得一定要再拉个人才能对战 本期难点 1、完成了五子棋的布局,判断游戏结束 2、基本的在线对战 3、游戏配套im(这个im的实现,请移步在线im) 下期安排 1、每步的倒计时设置 2、黑白棋分配由玩家自定义 3、新增旁观…...
AI 大模型企业应用实战(06)-初识LangChain
LLM大模型与AI应用的粘合剂。 1 langchain是什么以及发展过程 LangChain是一个开源框架,旨在简化使用大型语言模型构建端到端应用程序的过程,也是ReAct(reasonact)论文的落地实现。 2022年10月25日开源 54K star 种子轮一周1000万美金,A轮2…...
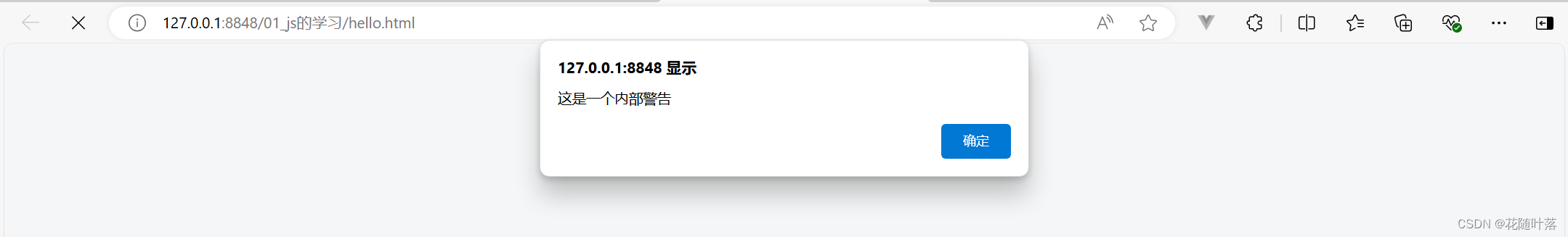
JavaScript的学习之旅之初始JS
目录 一、认识三个常见的js代码 二、js写入的第二种方式 三、js里内外部文件 一、认识三个常见的js代码 <script>//写入js位置的第一个地方// 控制浏览器弹出一个警告框alert("这是一个警告");// 在计算机页面输入一个内容(写入body中ÿ…...

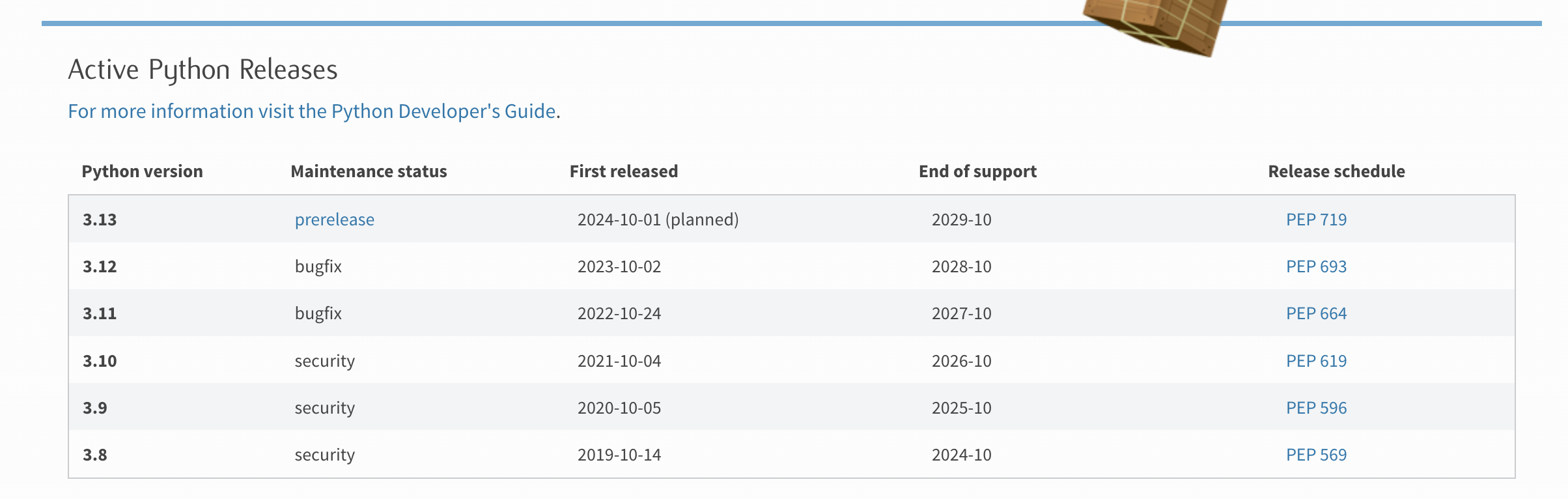
DataStructure.时间和空间复杂度
时间和空间复杂度 【本节目标】1. 如何衡量一个算法的好坏2. 算法效率3. 时间复杂度3.1 时间复杂度的概念3.2 大O的渐进表示法3.3 推导大O阶方法3.4 常见时间复杂度计算举例3.4.1 示例13.4.2 示例23.4.3 示例33.4.4 示例43.4.5 示例53.4.6 示例63.4.7 示例7 4.空间复杂度4.1 示…...

[Spring Boot]Netty-UDP客户端
文章目录 简述Netty-UDP集成pom引入ClientHandler调用 消息发送与接收在线UDP服务系统调用 简述 最近在一些场景中需要使用UDP客户端进行,所以开始集成新的东西。本文集成了一个基于netty的SpringBoot的简单的应用场景。 Netty-UDP集成 pom引入 <!-- netty --…...

基础C语言知识串串香11☞宏定义与预处理、函数和函数库
六、C语言宏定义与预处理、函数和函数库 6.1 编译工具链 源码.c ——> (预处理)——>预处理过的.i文件——>(编译)——>汇编文件.S——>(汇编)——>目标文件.o->(链接)——>elf可执行程序 预处理用预处理器,编译用编译器,…...

Python 3 函数
Python 3 函数 引言 Python 是一种高级编程语言,以其简洁明了的语法和强大的功能而闻名。在 Python 中,函数是一等公民,扮演着至关重要的角色。它们是组织代码、提高代码复用性和模块化编程的关键。本文将深入探讨 Python 3 中的函数,包括其定义、特性、类型以及最佳实践…...

【Linux详解】冯诺依曼架构 | 操作系统设计 | 斯坦福经典项目Pintos
目录 一. 冯诺依曼体系结构 (Von Neumann Architecture) 注意事项 存储器的意义:缓冲 数据流动示例 二. 操作系统 (Operating System) 操作系统的概念 操作系统的定位与目的 操作系统的管理 系统调用和库函数 操作系统的管理: sum 三. 系统调…...
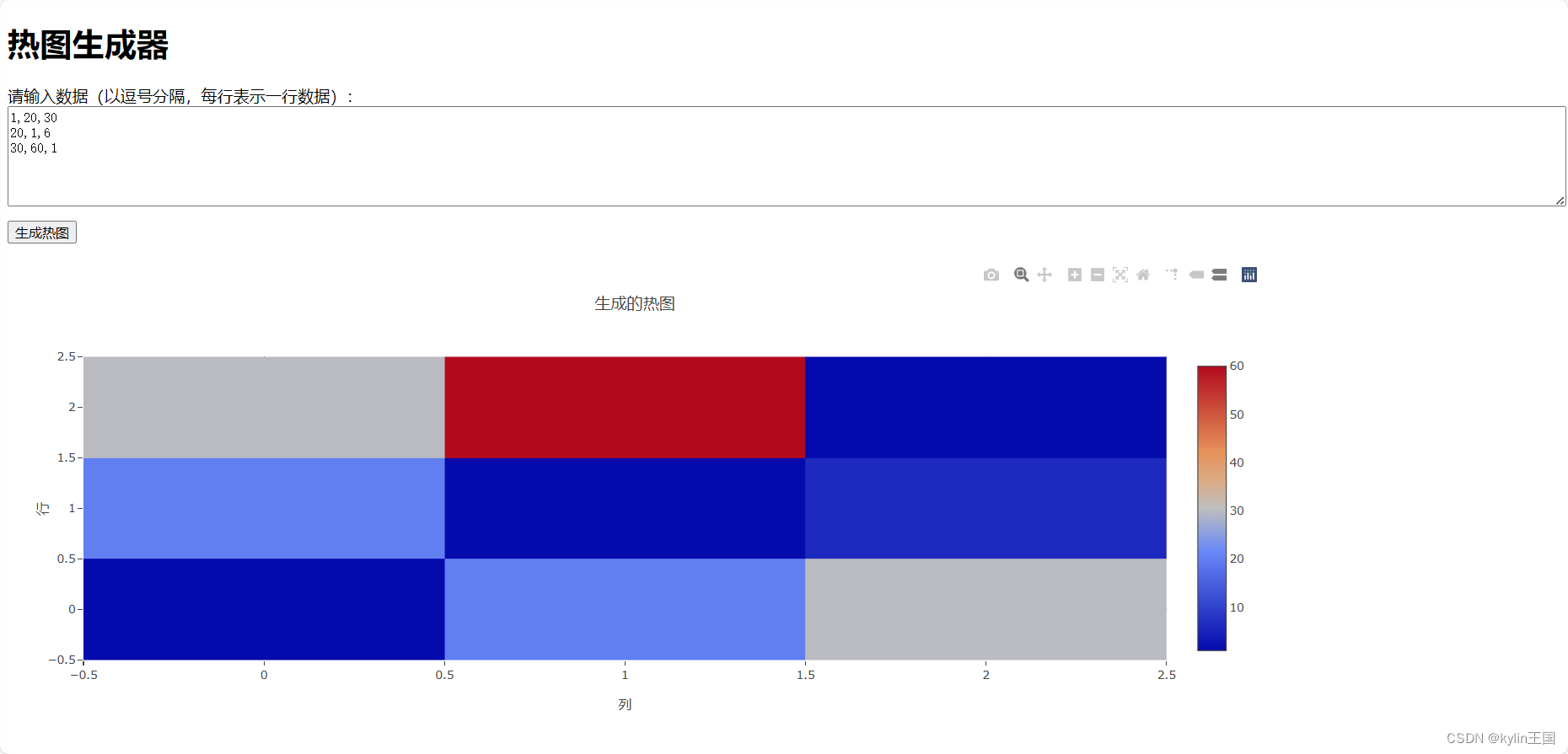
html做一个画热图的软件
完整示例 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang"zh-CN"> <head><meta charset"UTF-8"><title>热图生成器</title><script src"https://cdn.plot.ly/plotly-latest.min.js"></script><style>body …...
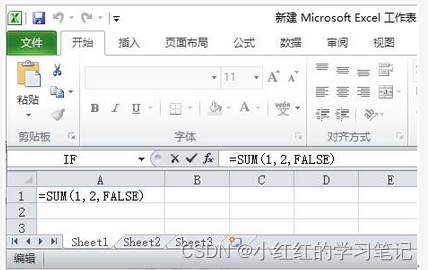
软考初级网络管理员__软件单选题
1.在Excel 中,设单元格F1的值为56.323,若在单元格F2中输入公式"TEXT(F1,"¥0.00”)”,则单元格F2的值为()。 ¥56 ¥56.323 ¥56.32 ¥56.00 2.要使Word 能自动提醒英文单…...

数据库新技术【分布式数据库】
文章目录 第一章 概述1.1 基本概念1.1.1 分布式数据库1.1.2 数据管理的透明性1.1.3 可靠性1.1.4 分布式数据库与集中式数据库的区别 1.2 体系结构1.3 全局目录1.4 关系代数1.4.1 基操1.4.2 关系表达式1.4.3 查询树 第二章 分布式数据库的设计2.1 设计策略2.2 分布设计的目标2.3…...

关于运用人工智能帮助自己实现英语能力的有效提升?
# 实验报告 ## 实验目的 - 描述实验的目标:自己可以知道,自己的ai学习方法是否可以有效帮助自己实现自己的学习提升。 预期结果:在自己利用科技对于自己进行学习的过程中,自己的成长速度应该是一个幂指数的增长 ## 文献回顾 根据…...
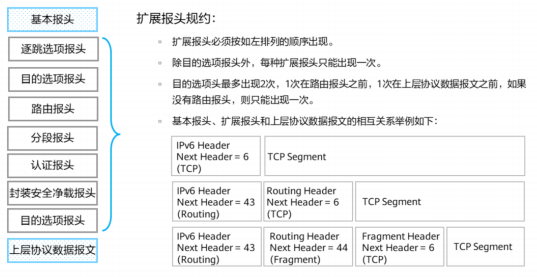
IPv6知识点整理
IPv6:是英文“Internet Protocol Version 6”(互联网协议第6版)的缩写,是互联网工程任务组(IETF)设计的用于替代IPv4的下一代IP协议,其地址数量号称可以为全世界的每一粒沙子编上一个地址 。 国…...
——体系:数据标准化——概述、关注焦点)
数据赋能(127)——体系:数据标准化——概述、关注焦点
概述 数据标准化是指将数据按照一定的规范和标准进行处理的过程。 数据标准化是属于数据整理过程。 数据标准化的目的在于提高数据的质量、促进数据的共享和交互、降低数据管理的成本,并增强数据的安全性。通过数据标准化,可以使得数据具有统一的格式…...

【 ARMv8/ARMv9 硬件加速系列 3.5.1 -- SVE 谓词寄存器有多少位?】
文章目录 SVE 谓词寄存器(predicate registers)简介SVE 谓词寄存器的位数SVE 谓词寄存器对向量寄存器的控制SVE 谓词寄存器位数计算SVE 谓词寄存器小结 SVE 谓词寄存器(predicate registers)简介 ARMv9的Scalable Vector Extension (SVE) 引入了谓词寄存器(Predica…...

Python - 调用函数时检查参数的类型是否合规
前言 阅读本文大概需要3分钟 说明 在python中,即使加入了类型注解,使用注解之外的类型也是不报错的 def test(uid: int):print(uid)test("999")但是我就想要类型不对就直接报错确实可以另辟蹊径,实现报错,似乎有强…...

Python基础面试题解答
Python基础面试题解答 基础语法 1. Python中的变量是如何管理内存的? Python中的变量通过引用计数来管理内存。当一个变量被创建时,会分配一个内存地址,并记录引用次数。当引用次数变为0时,垃圾回收机制会自动释放该内存。 2.…...
MATLAB直方图中bin中心与bin边界之间的转换
要将 bin 中心转换为 bin 边界,请计算 centers 中各连续值之间的中点。 d diff(centers)/2; edges [centers(1)-d(1), centers(1:end-1)d, centers(end)d(end)];要将 bin 边界转换为bin 中心 bincenters binedges(1:end-1)diff(binedges)/2;...
Chromium 开发指南2024 Mac篇-开始编译Chromium(五)
1.引言 在之前的指南中,我们已经详细介绍了在 macOS 上编译和开发 Chromium 的准备工作。您学会了如何安装和配置 Xcode,如何下载和配置 depot_tools,以及如何获取 Chromium 的源代码。通过这些步骤,您的开发环境已经搭建完毕&am…...
)
Java 语言特性(面试系列2)
一、SQL 基础 1. 复杂查询 (1)连接查询(JOIN) 内连接(INNER JOIN):返回两表匹配的记录。 SELECT e.name, d.dept_name FROM employees e INNER JOIN departments d ON e.dept_id d.dept_id; 左…...
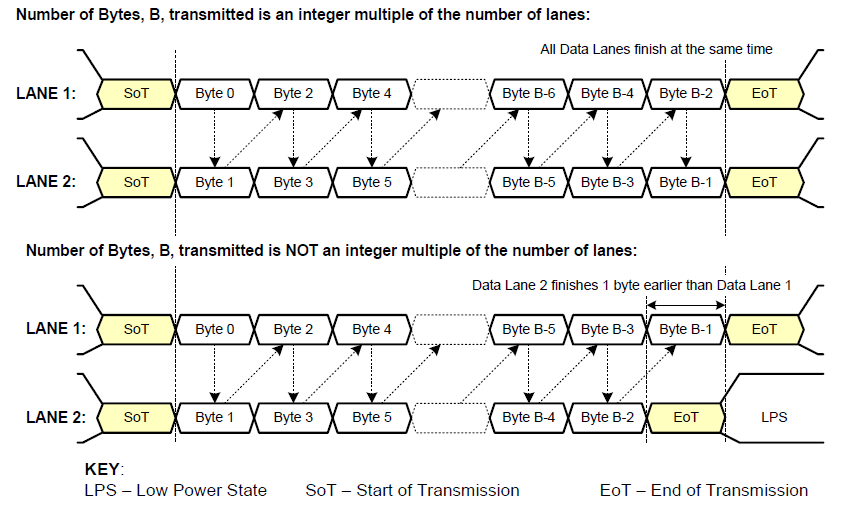
《从零掌握MIPI CSI-2: 协议精解与FPGA摄像头开发实战》-- CSI-2 协议详细解析 (一)
CSI-2 协议详细解析 (一) 1. CSI-2层定义(CSI-2 Layer Definitions) 分层结构 :CSI-2协议分为6层: 物理层(PHY Layer) : 定义电气特性、时钟机制和传输介质(导线&#…...
)
【位运算】消失的两个数字(hard)
消失的两个数字(hard) 题⽬描述:解法(位运算):Java 算法代码:更简便代码 题⽬链接:⾯试题 17.19. 消失的两个数字 题⽬描述: 给定⼀个数组,包含从 1 到 N 所有…...

FastAPI 教程:从入门到实践
FastAPI 是一个现代、快速(高性能)的 Web 框架,用于构建 API,支持 Python 3.6。它基于标准 Python 类型提示,易于学习且功能强大。以下是一个完整的 FastAPI 入门教程,涵盖从环境搭建到创建并运行一个简单的…...
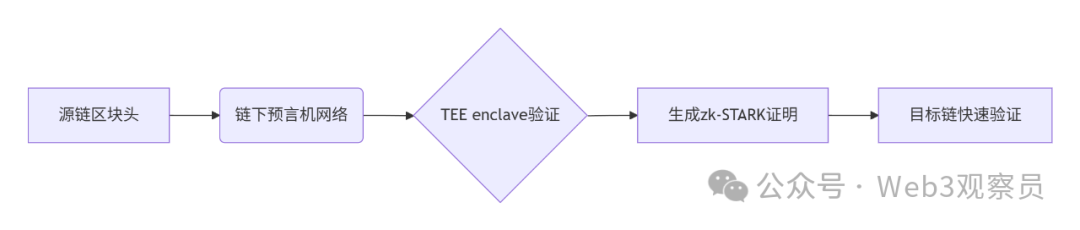
跨链模式:多链互操作架构与性能扩展方案
跨链模式:多链互操作架构与性能扩展方案 ——构建下一代区块链互联网的技术基石 一、跨链架构的核心范式演进 1. 分层协议栈:模块化解耦设计 现代跨链系统采用分层协议栈实现灵活扩展(H2Cross架构): 适配层…...
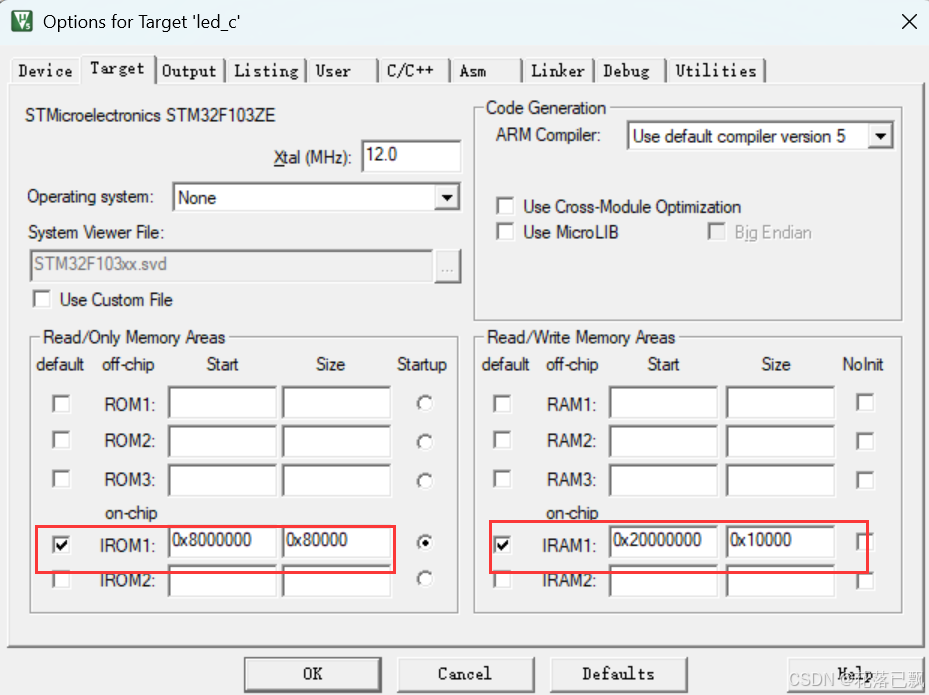
Keil 中设置 STM32 Flash 和 RAM 地址详解
文章目录 Keil 中设置 STM32 Flash 和 RAM 地址详解一、Flash 和 RAM 配置界面(Target 选项卡)1. IROM1(用于配置 Flash)2. IRAM1(用于配置 RAM)二、链接器设置界面(Linker 选项卡)1. 勾选“Use Memory Layout from Target Dialog”2. 查看链接器参数(如果没有勾选上面…...

unix/linux,sudo,其发展历程详细时间线、由来、历史背景
sudo 的诞生和演化,本身就是一部 Unix/Linux 系统管理哲学变迁的微缩史。来,让我们拨开时间的迷雾,一同探寻 sudo 那波澜壮阔(也颇为实用主义)的发展历程。 历史背景:su的时代与困境 ( 20 世纪 70 年代 - 80 年代初) 在 sudo 出现之前,Unix 系统管理员和需要特权操作的…...

多种风格导航菜单 HTML 实现(附源码)
下面我将为您展示 6 种不同风格的导航菜单实现,每种都包含完整 HTML、CSS 和 JavaScript 代码。 1. 简约水平导航栏 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang"zh-CN"> <head><meta charset"UTF-8"><meta name"viewport&qu…...

CSS设置元素的宽度根据其内容自动调整
width: fit-content 是 CSS 中的一个属性值,用于设置元素的宽度根据其内容自动调整,确保宽度刚好容纳内容而不会超出。 效果对比 默认情况(width: auto): 块级元素(如 <div>)会占满父容器…...
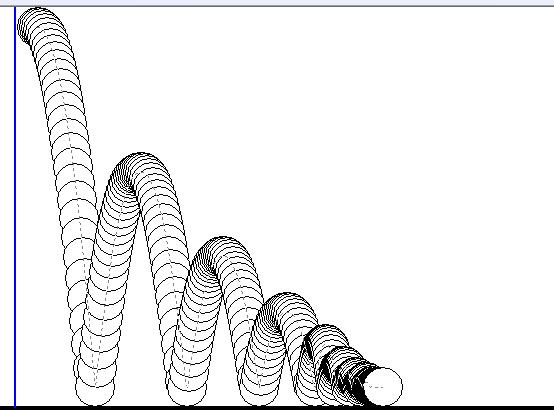
MFC 抛体运动模拟:常见问题解决与界面美化
在 MFC 中开发抛体运动模拟程序时,我们常遇到 轨迹残留、无效刷新、视觉单调、物理逻辑瑕疵 等问题。本文将针对这些痛点,详细解析原因并提供解决方案,同时兼顾界面美化,让模拟效果更专业、更高效。 问题一:历史轨迹与小球残影残留 现象 小球运动后,历史位置的 “残影”…...
