C++ STL 多线程库用法介绍
目录
一:Atomic:
二:Thread
1. 创建线程
2. 小心移动(std::move)线程
3. 如何创建带参数的线程
4. 线程参数是引用类型时,要小心谨慎。
5. 获取线程ID
6. jthread
7. 如何在线程中使用中断 stop_token
三:如何解决数据竞争
1.有问题的代码
2.使用互斥
3.预防死锁
4. 自动释放锁
5. 延迟锁
6. 共享锁
7. 线程安全的初始化
四:线程局部存储
五:线程通信
1.条件变量
2. 防止虚假唤醒
3. 防止唤醒丢失
4.信号量
5. std::latch
六:任务
1. std::promise, std::future
2. 用std::promise, std::future进行线程同步
3. std::async
4. std::package_task
一:Atomic:
#include <atomic>
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>using namespace std;std::atomic_int x, y;
int r1, r2;
void writeX() {x.store(1);r1 = y.load();
}
void writeY() {y.store(1);r2 = x.load();
} int main() {for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++){x = 0;y = 0;std::thread a(writeX);std::thread b(writeY);a.join();b.join();std::cout << r1 << r2 << std::endl;}return 0;
}
//可能的输出有三种情况:01, 10, 11
//01:先执行线程a, 再执行线程b
//10:先执行线程b,再执行线程a
//11:执行线程a一半后调度到线程b,然后再回来 二:Thread
1. 创建线程
#include <atomic>
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>using namespace std;void helloFunction() {cout << "function" << endl;
}class HelloFunctionObject {
public:void operator()() const {cout << "function object" << endl;}
};int main()
{thread t1(helloFunction); // functionHelloFunctionObject helloFunctionObject;thread t2(helloFunctionObject); // function objectthread t3([] { cout << "lambda function" << std::endl; }); // lambda functiont1.join(); //需要用join,否则可能会出现主线程退出时,t1线程还没有执行完的情况,引起异常t2.join();t3.join();return 0;
}
2. 小心移动(std::move)线程
#include <atomic>
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main()
{std::thread t([] { cout << "lambda function"; });std::thread t2;t2 = std::move(t);std::thread t3([] { cout << "lambda function"; });/*此处代码有问题,当t2 已经获得线程t后,它已经是callable和joinable,再赋值t3会terminate*/ t2 = std::move(t3); std::terminate
}3. 如何创建带参数的线程
#include <atomic>
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>using namespace std;//如何在线程中传递参数
void printStringCopy(string s) { cout << s; }
void printStringRef(const string& s) { cout << s; }int main()
{string s{ "C++" };thread tPerCopy([=] { cout << s; }); // C++thread tPerCopy2(printStringCopy, s); // C++tPerCopy.join();tPerCopy2.join();thread tPerReference([&] { cout << s; }); // C++thread tPerReference2(printStringRef, s); // C++tPerReference.join();tPerReference2.join();
}4. 线程参数是引用类型时,要小心谨慎。
#include <iostream>using namespace std;using std::this_thread::sleep_for;
using std::this_thread::get_id;struct Sleeper {Sleeper(int& i_) :i{ i_ } {};void operator() (int k) {for (unsigned int j = 0; j <= 5; ++j) {sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100));i += k;}std::cout << get_id(); // undefined behaviour}
private:int& i;
};int main()
{int valSleeper = 1000;//valSleeper 作为引用类型传给线程,如果主线程先退出,t线程使用valSleeper会产生未定义行为, 并且主线程和t线程共享varSleeper,产生数据竞争,std::thread t(Sleeper(valSleeper), 5); t.detach();std::cout << valSleeper; // undefined behaviour
}
5. 获取线程ID
using namespace std;
using std::this_thread::get_id;int main()
{std::cout << std::thread::hardware_concurrency() << std::endl; // 4std::thread t1([] { std::cout << get_id() << std::endl; }); // 139783038650112std::thread t2([] { std::cout << get_id() << std::endl; }); // 139783030257408std::cout << t1.get_id() << std::endl; // 139783038650112std::cout << t2.get_id() << std::endl; // 139783030257408t1.swap(t2);std::cout << t1.get_id() << std::endl; // 139783030257408std::cout << t2.get_id() << std::endl; // 139783038650112std::cout << get_id() << std::endl; // 140159896602432t1.join();t2.join();
}6. jthread
#include <atomic>
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
using std::this_thread::get_id;//jthread 自动join()的线程
int main()
{std::jthread thr{ [] { std::cout << "std::jthread" << "\n"; } }; // std::jthreadstd::cout << "thr.joinable(): " << thr.joinable() << "\n"; // thr.joinable(): true
}7. 如何在线程中使用中断 stop_token
#include <atomic>
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
using std::this_thread::get_id;
using namespace::std::literals;//字面量,比如0.2s, C++20能识别这种写法std::jthread nonInterruptable([] { // (1) 创建非中断线程int counter{ 0 };
while (counter < 10) {std::this_thread::sleep_for(0.2s);std::cerr << "nonInterruptable: " << counter << std::endl;++counter;
}});
std::jthread interruptable([](std::stop_token stoken) { // (2) 创建可中断线程int counter{ 0 };
while (counter < 10) {std::this_thread::sleep_for(0.2s);if (stoken.stop_requested()) return; // (3) 检查线程是否被中断std::cerr << "interruptable: " << counter << std::endl;++counter;
}});int main()
{std::this_thread::sleep_for(1s);std::cerr << "Main thread interrupts both jthreads" << std::endl;nonInterruptable.request_stop(); // (4)//请求中断,非中断线程不理会interruptable.request_stop();//请求中断,中断线程会响应
}三:如何解决数据竞争
1.有问题的代码
#include <atomic>
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>using namespace std;struct Worker {Worker(string n) :name(n) {};void operator() () {for (int i = 1; i <= 3; ++i) {this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(200));//流本身是线程安全的,但是cout是共享变量,它会独占流,多个线程访问cout时会引起数据竞争 cout << name << ": " << "Work " << i << endl;}}
private:string name;
};int main()
{thread herb = thread(Worker("Herb"));thread andrei = thread(Worker(" Andrei"));thread scott = thread(Worker(" Scott"));thread bjarne = thread(Worker(" Bjarne"));herb.join();andrei.join();scott.join();bjarne.join();}2.使用互斥
#include <atomic>
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>
#include <mutex>using namespace std;std::mutex mutexCout;struct Worker {Worker(string n) :name(n) {};void operator() () {for (int i = 1; i <= 3; ++i) {this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(200));mutexCout.lock();cout << name << ": " << "Work " << i << endl;mutexCout.unlock();}}
private:string name;
};int main()
{thread herb = thread(Worker("Herb"));thread andrei = thread(Worker("Andrei"));thread scott = thread(Worker("Scott"));thread bjarne = thread(Worker("Bjarne"));herb.join();andrei.join();scott.join();bjarne.join();}3.预防死锁
m.lock();
sharedVar= getVar(); //如果此处抛出异常,会导致m.unlock未调用,锁不能被释放,其他线程无法得到锁,进而可能产生死锁
m.unlock()#include <iostream>
#include <mutex>using namespace std;struct CriticalData {std::mutex mut;
};
void deadLock(CriticalData& a, CriticalData& b) {a.mut.lock();std::cout << "get the first mutex\n";std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1));b.mut.lock();std::cout << "get the second mutex\n";a.mut.unlock(), b.mut.unlock();
}int main()
{CriticalData c1;CriticalData c2;//t1, t2在拿到锁后都在等对方释放锁std::thread t1([&] { deadLock(c1, c2); });std::thread t2([&] { deadLock(c2, c1); });t1.join();t2.join();
}4. 自动释放锁
#include <atomic>
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>
#include <mutex>using namespace std;std::mutex mutexCout;
struct Worker {Worker(std::string n) :name(n) {};void operator() () {for (int i = 1; i <= 3; ++i) {std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(200));std::lock_guard<std::mutex> myLock(mutexCout);//自动释放锁std::cout << name << ": " << "Work " << i << std::endl;}}
private:std::string name;
};int main()
{thread herb = thread(Worker("Herb"));thread andrei = thread(Worker("Andrei"));thread scott = thread(Worker("Scott"));thread bjarne = thread(Worker("Bjarne"));herb.join();andrei.join();scott.join();bjarne.join();
}5. 延迟锁
#include <atomic>
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>
#include <mutex>using namespace std;using namespace std;
struct CriticalData {mutex mut;
};
void deadLockResolved(CriticalData& a, CriticalData& b) {unique_lock<mutex>guard1(a.mut, defer_lock);cout << this_thread::get_id() << ": get the first lock" << endl;this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(1));unique_lock<mutex>guard2(b.mut, defer_lock);cout << this_thread::get_id() << ": get the second lock" << endl;cout << this_thread::get_id() << ": atomic locking" << endl;lock(guard1, guard2);
}int main()
{CriticalData c1;CriticalData c2;thread t1([&] { deadLockResolved(c1, c2); });thread t2([&] { deadLockResolved(c2, c1); });t1.join();t2.join();
}6. 共享锁
#include <mutex>
...
std::shared_timed_mutex sharedMutex;
std::unique_lock<std::shared_timed_mutex> writerLock(sharedMutex);
std::shared_lock<std::shared_time_mutex> readerLock(sharedMutex);
std::shared_lock<std::shared_time_mutex> readerLock2(sharedMutex);7. 线程安全的初始化
//常量表达式是线程安全的
struct MyDouble{
constexpr MyDouble(double v):val(v){};
constexpr double getValue(){ return val; }
private:
double val
};
constexpr MyDouble myDouble(10.5);
std::cout << myDouble.getValue(); // 10.5//块内静态变量
void blockScope(){
static int MySharedDataInt= 2011;
}//once_flag, call_once
#include <mutex>
...
using namespace std;
once_flag onceFlag;
void do_once(){
call_once(onceFlag, []{ cout << "Only once." << endl; });
}
thread t1(do_once);
thread t2(do_once);四:线程局部存储
std::mutex coutMutex;
thread_local std::string s("hello from ");
void addThreadLocal(std::string const& s2){
s+= s2;
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(coutMutex);
std::cout << s << std::endl;
std::cout << "&s: " << &s << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::thread t1(addThreadLocal, "t1");
std::thread t2(addThreadLocal, "t2");
std::thread t3(addThreadLocal, "t3");
std::thread t4(addThreadLocal, "t4");五:线程通信
1.条件变量
#include <atomic>
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>using namespace std;std::mutex mutex_;
std::condition_variable condVar;
bool dataReady = false;
void doTheWork() {std::cout << "Processing shared data." << std::endl;
}
void waitingForWork() {std::cout << "Worker: Waiting for work." << std::endl;std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lck(mutex_);condVar.wait(lck, [] { return dataReady; });doTheWork();std::cout << "Work done." << std::endl;
}
void setDataReady() {std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lck(mutex_);dataReady = true;std::cout << "Sender: Data is ready." << std::endl;condVar.notify_one();
}int main()
{std::thread t1(waitingForWork);std::thread t2(setDataReady);t1.join();t2.join();
}2. 防止虚假唤醒
//为了防止虚假唤醒,在唤醒前应进行条件检查,且发送方应将条件置为true。
//dataReady = true; //发送方设置条件满足
//[] { return dataReady; } //接收方进行条件检查3. 防止唤醒丢失
//如果发送方在接收方等待之前,就发送了唤醒,可能会导致唤醒丢失,因此要做两件事:
//1: 要先等待,后发送唤醒
//2: 在接收方的等待函数中要检查是否满足条件 [] { return dataReady; };
4.信号量
#include <atomic>
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <semaphore>
#include <vector>using namespace std;std::vector<int> myVec;std::counting_semaphore<1> prepareSignal(0); // (1)
void prepareWork() {myVec.insert(myVec.end(), { 0, 1, 0, 3 });std::cout << "Sender: Data prepared." << '\n';prepareSignal.release(); // (2)
}void completeWork() {std::cout << "Waiter: Waiting for data." << '\n';prepareSignal.acquire(); // (3)myVec[2] = 2;std::cout << "Waiter: Complete the work." << '\n';for (auto i : myVec) std::cout << i << " ";std::cout << '\n';
}int main()
{std::thread t1(prepareWork);std::thread t2(completeWork);t1.join();t2.join();
}5. std::latch
#include <atomic>
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <semaphore>
#include <vector>
#include <latch>using namespace std;std::mutex coutMutex;std::latch workDone(2);
std::latch goHome(1); // (5)
void synchronizedOut(const std::string s) {std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lo(coutMutex);std::cout << s;
}class Worker {
public:Worker(std::string n) : name(n) { };void operator() () {// notify the boss when work is donesynchronizedOut(name + ": " + "Work done!\n");workDone.count_down(); // (3) 完成工作// waiting before going homegoHome.wait();//等待老板发命令让他们回家synchronizedOut(name + ": " + "Good bye!\n");}
private:std::string name;
};int main()
{std::cout << "BOSS: START WORKING! " << '\n';Worker herb(" Herb"); // (1) 工人1std::thread herbWork(herb); //工人1必须完成自己的工作Worker scott(" Scott"); // (2) 工人2std::thread scottWork(scott);//工人2必须完成自己的工作workDone.wait(); // (4) 完成工作后等待std::cout << '\n';goHome.count_down();//老板发命令回家std::cout << "BOSS: GO HOME!" << '\n';herbWork.join();scottWork.join();
}6. std::barrier
#include <barrier>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <syncstream>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>int main()
{const auto workers = { "Anil", "Busara", "Carl" };auto on_completion = []() noexcept{// locking not needed herestatic auto phase ="... done\n""Cleaning up...\n";std::cout << phase;phase = "... done\n";};std::barrier sync_point(std::ssize(workers), on_completion);auto work = [&](std::string name){std::string product = " " + name + " worked\n";std::osyncstream(std::cout) << product; // ok, op<< call is atomicsync_point.arrive_and_wait();product = " " + name + " cleaned\n";std::osyncstream(std::cout) << product;sync_point.arrive_and_wait();};std::cout << "Starting...\n";std::vector<std::jthread> threads;threads.reserve(std::size(workers));for (auto const& worker : workers)threads.emplace_back(work, worker);
}
六:任务

1. std::promise, std::future
#include <future>
#include <iostream>void product(std::promise<int>&& intPromise, int a, int b) {intPromise.set_value(a * b);
}
int main()
{int a = 20;int b = 10;std::promise<int> prodPromise;std::future<int> prodResult = prodPromise.get_future();std::jthread prodThread(product, std::move(prodPromise), a, b);std::cout << "20*10= " << prodResult.get(); // 20*10= 200
}2. 用std::promise, std::future进行线程同步
#include <future>
#include <iostream>void doTheWork() {std::cout << "Processing shared data." << std::endl;
}
void waitingForWork(std::future<void>&& fut) {std::cout << "Worker: Waiting for work." <<std::endl;fut.wait();doTheWork();std::cout << "Work done." << std::endl;
}
void setDataReady(std::promise<void>&& prom) {std::cout << "Sender: Data is ready." <<std::endl;prom.set_value();
}int main()
{std::promise<void> sendReady;auto fut = sendReady.get_future();std::jthread t1(waitingForWork, std::move(fut));std::jthread t2(setDataReady, std::move(sendReady));}3. std::async
#include <future>
#include <iostream>using std::chrono::duration;
using std::chrono::system_clock;
using std::launch;int main()
{auto begin = system_clock::now();auto asyncLazy = std::async(launch::deferred, [] { return system_clock::now(); });auto asyncEager = std::async(launch::async, [] { return system_clock::now(); });std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));auto lazyStart = asyncLazy.get() - begin;auto eagerStart = asyncEager.get() - begin;auto lazyDuration = duration<double>(lazyStart).count();auto eagerDuration = duration<double>(eagerStart).count();std::cout << lazyDuration << " sec"; // 1.00018 sec.std::cout << eagerDuration << " sec"; // 0.00015489 sec.
}#include <future>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>using std::chrono::duration;
using std::chrono::system_clock;
using std::launch;int main()
{int res;std::thread t([&] { res = 2000 + 11; });t.join();std::cout << res << std::endl; // 2011auto fut = std::async([] { return 2000 + 11; });//异步调用std::cout << fut.get() << std::endl; // 2011
}4. std::package_task
#include <future>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <thread>using namespace std;
using std::chrono::duration;
using std::chrono::system_clock;
using std::launch;struct SumUp {int operator()(int beg, int end) {for (int i = beg; i < end; ++i) sum += i;return sum;}
private:int beg;int end;int sum{ 0 };
};int main()
{SumUp sumUp1, sumUp2;packaged_task<int(int, int)> sumTask1(sumUp1);//任务1packaged_task<int(int, int)> sumTask2(sumUp2);//任务2future<int> sum1 = sumTask1.get_future(); //任务1的结果future<int> sum2 = sumTask2.get_future(); //任务2的结果deque< packaged_task<int(int, int)>> allTasks; //存储所有的任务allTasks.push_back(move(sumTask1));//将任务1加入队列allTasks.push_back(move(sumTask2));//将任务2加入队列int begin{ 1 };int increment{ 5000 };int end = begin + increment;while (not allTasks.empty()) {packaged_task<int(int, int)> myTask = move(allTasks.front());//取出1个任务allTasks.pop_front();thread sumThread(move(myTask), begin, end);//执行这个任务begin = end;end += increment;sumThread.detach();}auto sum = sum1.get() + sum2.get();//查询任务的结果cout << sum;}相关文章:

C++ STL 多线程库用法介绍
目录 一:Atomic: 二:Thread 1. 创建线程 2. 小心移动(std::move)线程 3. 如何创建带参数的线程 4. 线程参数是引用类型时,要小心谨慎。 5. 获取线程ID 6. jthread 7. 如何在线程中使用中断 stop_token 三:如何…...
Jmeter实现接口自动化
自动化测试理论知识 什么是自动化测试? 让程序或工具代替人为执行测试用例什么样的项目适合做自动化? 1、项目周期长 --多长算长?(自己公司运营项目) 2、需求稳定(更多具体功能/模块) 3、需要…...

【大模型】多模型在大模型中的调度艺术:解锁效率与协同的新境界
多模型在大模型中的调度艺术:解锁效率与协同的新境界 引言一、多模型与大模型的概念解析二、多模型调度的必要性三、多模型调度的关键技术3.1 负载均衡与动态分配3.2 模型间通信与协作3.3 模型选择与优化 四、多模型运行优化策略4.1 异构计算平台的利用4.2 模型压缩…...

LeetCode 704, 290, 200
目录 704. 二分查找题目链接标签思路代码 290. 单词规律题目链接标签思路代码 200. 岛屿数量题目链接标签思路代码 704. 二分查找 题目链接 704. 二分查找 标签 数组 二分查找 思路 这道题是 二分查找 最经典的一道题,掌握了本题的思想就进入了 二分 思想的大…...

如何利用Java进行大数据处理?
如何利用Java进行大数据处理? 大家好,我是微赚淘客系统3.0的小编,也是冬天不穿秋裤,天冷也要风度的程序猿! 1. 引言 在当今信息爆炸的时代,处理大数据是许多应用程序和系统的核心需求之一。Java作为一种…...
【论文通读】GUICourse: From General Vision Language Model to Versatile GUI Agent
GUICourse: From General Vision Language Model to Versatile GUI Agent 前言AbstractMotivationSolutionGUICourseGUIEnvGUIEnv-globalGUIEnv-local GUIActGUIAct (web-single)GUIAct (web-multi)GUIAct (smartphone) GUIChat ExperimentsMain ResultAblation Study Conclusi…...

王道考研数据机构:中缀表达式转为后缀表达式
实现方法: 初始化一个栈,用于保存暂时还不能确定运算顺序的运算符。从左到右处理各个元素,直到末尾。可能遇到三种情况: 遇到操作数。直接加入后缀表达式遇到界限符。遇到“(”直接入栈;遇到“)”则依次弹出栈内运算符并加入后缀表达式&…...

PL/SQL安装+汉化教程
PL/SQL安装教程 一、安装: 登陆官网:PL/SQL Developer - Allround Automations下载 下载PL/SQL稳定版本12.0.7 根据自己计算机版本安装相适配的版本。我这里安装X64-bit版本 进行安装: 根据情况去更改安装,我这里全部下一步…...

Qt | Qt 线程相关类概述和举例
Qt 是一个广泛用于跨平台应用开发的框架。在 Qt 中,多线程支持是其核心特性之一,它允许开发者在不同平台上创建并发应用。以下是 Qt 中与线程相关的类概述及其使用示例。 Qt 中的线程相关类 QThread QThread 是 Qt 中用于创建和管理线程的基类。通过派生并重写 run() 函数…...

Linux 复现Docker NAT网络
Linux 复现Docker NAT网络 docker 网络的构成分为宿主机docker0网桥和为容器创建的veth 对构成。这个默认网络命名空间就是我们登陆后日常使用的命名空间 使用ifconfig命令查看到的就是默认网络命名空间,docker0就是网桥,容器会把docker0当成路由&…...

HBuilder X 小白日记03-用css制作简单的交互动画
:hover选择器,用于选择鼠标指针浮动在上面的元素。 :hover选择器可用于所有元素,不只是链接 :link选择器 设置指向未被访问页面的链接的样式 :visited选择器 用于设置指向已被访问的页面的链接 :active选择器 用于活动链接...

【深度学习练习】心脏病预测
🍨 本文为🔗365天深度学习训练营 中的学习记录博客🍖 原作者:K同学啊 一、什么是RNN RNN与传统神经网络最大的区别在于,每次都会将前一次的输出结果,带到下一隐藏层中一起训练。如下图所示: …...

创建react的脚手架
Create React App 中文文档 (bootcss.com) 网址:creat-react-app.bootcss.com 主流的脚手架:creat-react-app 创建脚手架的方法: 方法一(JS默认): 1. npx create-react-app my-app 2. cd my-app 3. …...

用例导图CMind
突然有一些觉悟,程序猿不能只会吭哧吭哧的低头做事,应该学会怎么去展示自己,怎么去宣传自己,怎么把自己想做的事表述清楚。 于是,这两天一直在整理自己的作品,也为接下来的找工作多做点准备。接下来…...
C++ 仿函数
一、介绍 CSTL中的仿函数,又被称为函数对象,其实就是:重载了()运算符的类。 因为在使用重载的operator()时,类似于函数调用,因此被称为仿函数。 ※注意※:仿函数本质上是一个类,不是函数。 二…...
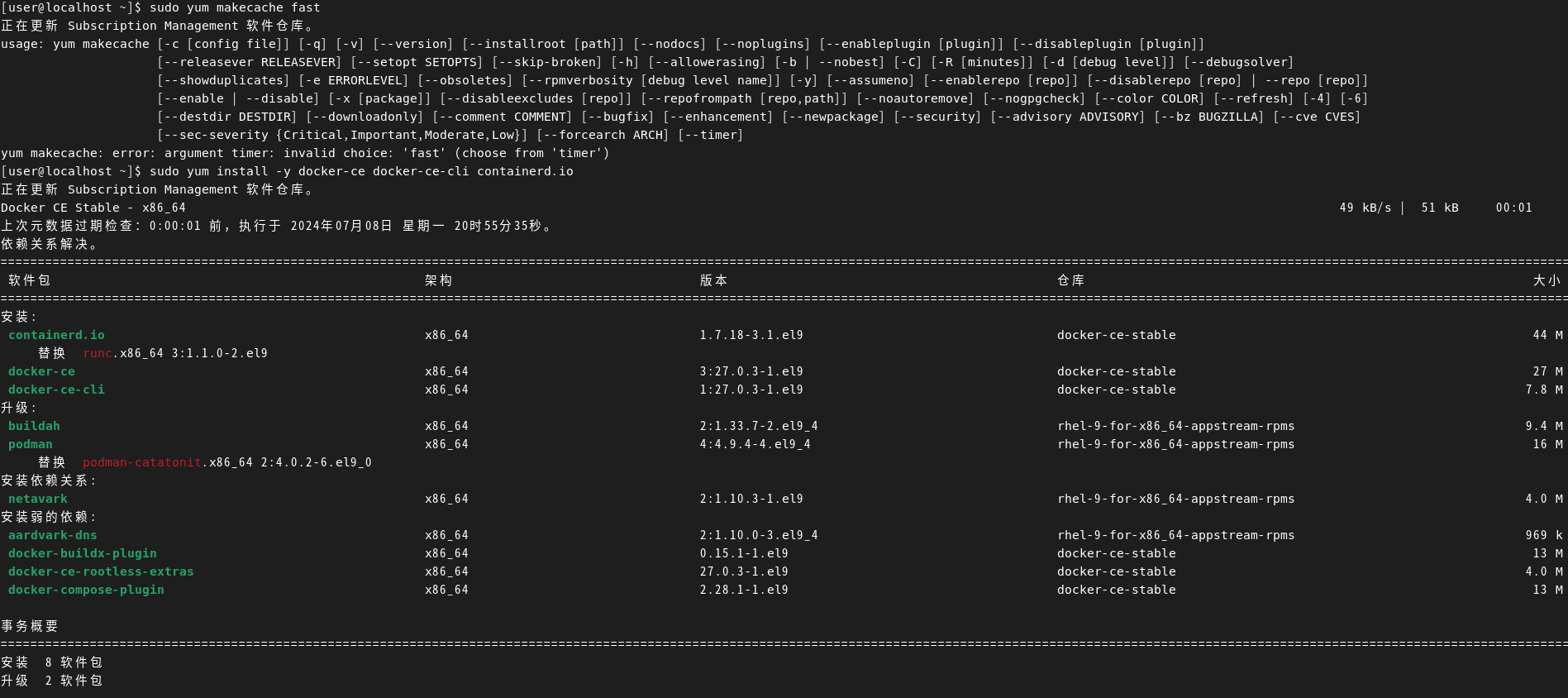
Redhat 安装 docker 网络连接超时问题
目录 添加阿里云的Docker CE仓库 更新YUM缓存 安装 Docker Engine 启动并设置Docker自启动 验证 Docker 安装 [userlocalhost ~]$ sudo yum-config-manager --add-repohttps://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo 正在更新 Subscription Management 软件仓库…...

Java面试题:undo log和redo log
undo log和redo log的区别 缓冲池(buffer pool): 主内存中的一个区域,可以缓存磁盘上经常被操作的数据,在执行crud时先操作缓冲池的数据以减少磁盘io 数据页(page): InnoDB存储引擎管理的最小单元,每页大小为16kb,页中存储的是行数据 redo log 重做日志,用来实现任务的持…...

【Scrapy】Scrapy 中间件等级设置规则
准我快乐地重饰演某段美丽故事主人 饰演你旧年共寻梦的恋人 再去做没流着情泪的伊人 假装再有从前演过的戏份 重饰演某段美丽故事主人 饰演你旧年共寻梦的恋人 你纵是未明白仍夜深一人 穿起你那无言毛衣当跟你接近 🎵 陈慧娴《傻女》 Scrapy 是…...

SDK环境的安装(测试使用)
1、安装 将文件解压至目录,我的目录为:D:\Program Files\Android 解压后如下: 下载链接如下: sdk下载 提取码见文章最后: 2、配置环境 1、在环境变量中,选择系统变量,点击新建。 变量名:ANDROID_HOME 变量值:“你自己的android-sdk安装路径” (例如我的:D:\Pro…...
【matlab】【python】爬虫实战
目录 引言 具体步骤 1.设置请求选项 2.发送请求并获取响应 3.设置正则表达式 4.执行正则表达式匹配 matlab完整代码 python代码示例 引言 在当今这个信息爆炸的时代,数据已成为推动社会进步和企业发展的核心动力之一。随着互联网的普及和技术的飞速发展&am…...
: K8s 核心概念白话解读(上):Pod 和 Deployment 究竟是什么?)
云原生核心技术 (7/12): K8s 核心概念白话解读(上):Pod 和 Deployment 究竟是什么?
大家好,欢迎来到《云原生核心技术》系列的第七篇! 在上一篇,我们成功地使用 Minikube 或 kind 在自己的电脑上搭建起了一个迷你但功能完备的 Kubernetes 集群。现在,我们就像一个拥有了一块崭新数字土地的农场主,是时…...
7.4.分块查找
一.分块查找的算法思想: 1.实例: 以上述图片的顺序表为例, 该顺序表的数据元素从整体来看是乱序的,但如果把这些数据元素分成一块一块的小区间, 第一个区间[0,1]索引上的数据元素都是小于等于10的, 第二…...
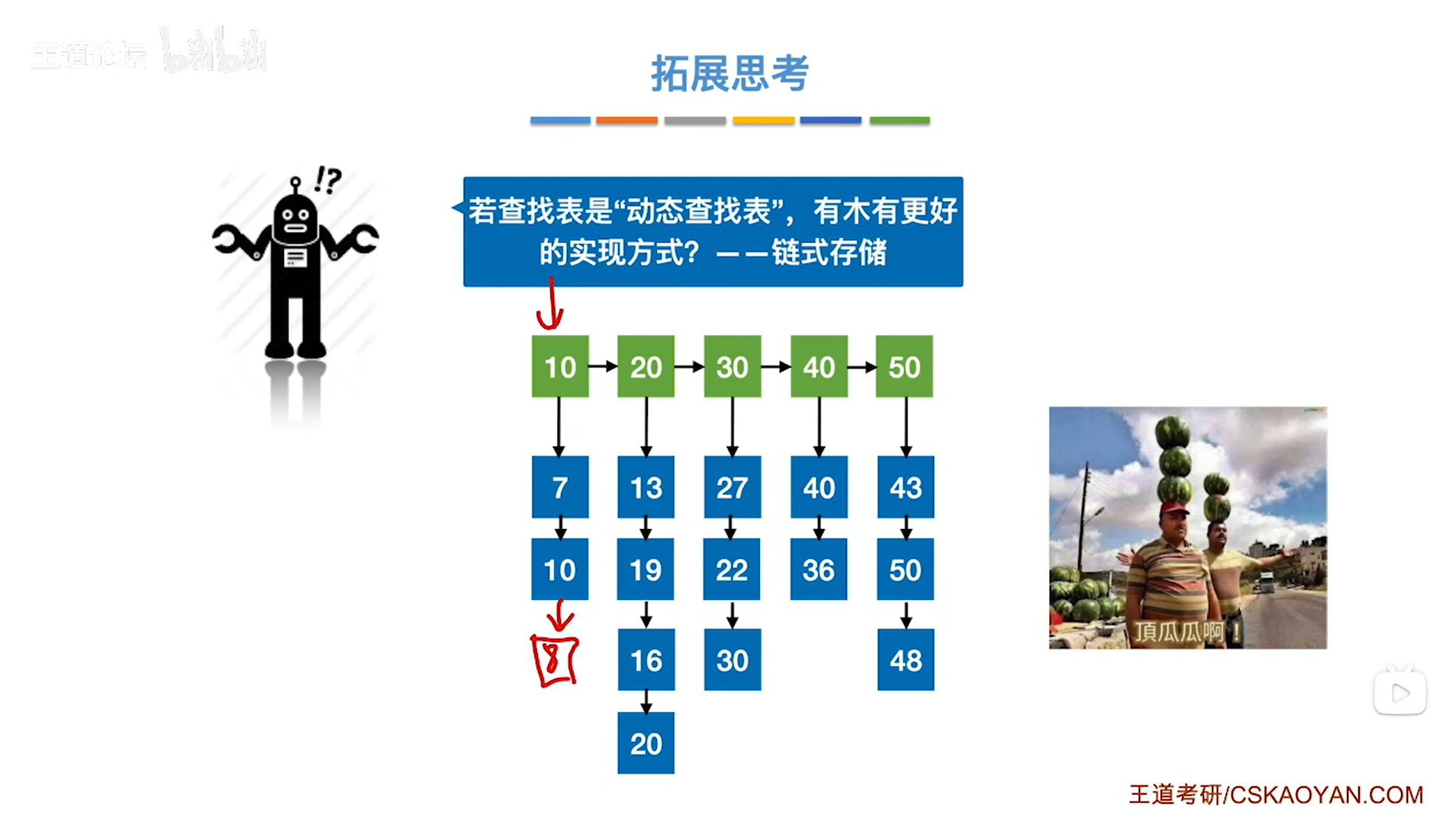
python打卡day49
知识点回顾: 通道注意力模块复习空间注意力模块CBAM的定义 作业:尝试对今天的模型检查参数数目,并用tensorboard查看训练过程 import torch import torch.nn as nn# 定义通道注意力 class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):def __init__(self,…...
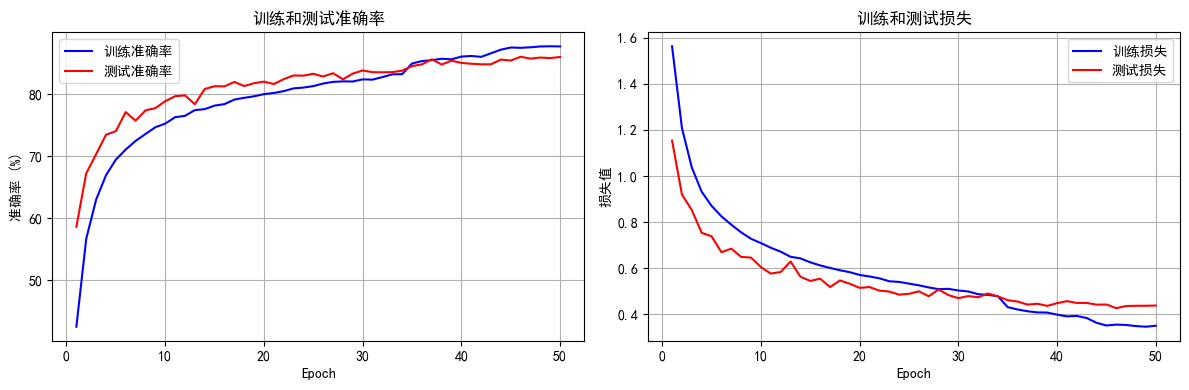
遍历 Map 类型集合的方法汇总
1 方法一 先用方法 keySet() 获取集合中的所有键。再通过 gey(key) 方法用对应键获取值 import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Set;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {HashMap hashMap new HashMap();hashMap.put("语文",99);has…...

系统设计 --- MongoDB亿级数据查询优化策略
系统设计 --- MongoDB亿级数据查询分表策略 背景Solution --- 分表 背景 使用audit log实现Audi Trail功能 Audit Trail范围: 六个月数据量: 每秒5-7条audi log,共计7千万 – 1亿条数据需要实现全文检索按照时间倒序因为license问题,不能使用ELK只能使用…...

Java多线程实现之Callable接口深度解析
Java多线程实现之Callable接口深度解析 一、Callable接口概述1.1 接口定义1.2 与Runnable接口的对比1.3 Future接口与FutureTask类 二、Callable接口的基本使用方法2.1 传统方式实现Callable接口2.2 使用Lambda表达式简化Callable实现2.3 使用FutureTask类执行Callable任务 三、…...
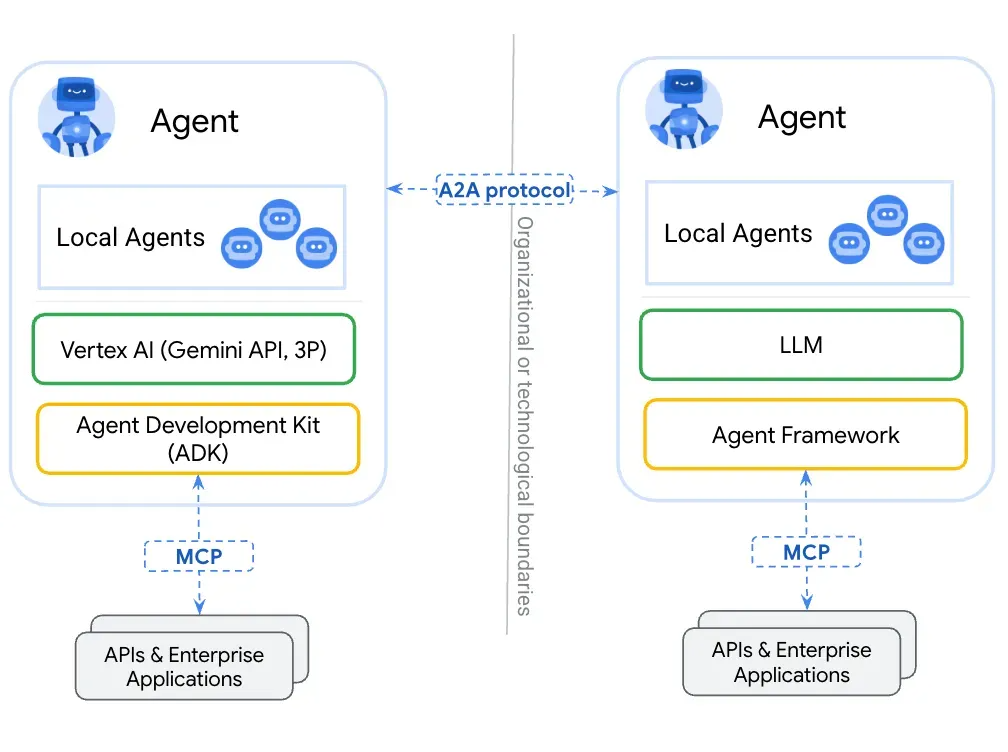
第一篇:Agent2Agent (A2A) 协议——协作式人工智能的黎明
AI 领域的快速发展正在催生一个新时代,智能代理(agents)不再是孤立的个体,而是能够像一个数字团队一样协作。然而,当前 AI 生态系统的碎片化阻碍了这一愿景的实现,导致了“AI 巴别塔问题”——不同代理之间…...
 自用)
css3笔记 (1) 自用
outline: none 用于移除元素获得焦点时默认的轮廓线 broder:0 用于移除边框 font-size:0 用于设置字体不显示 list-style: none 消除<li> 标签默认样式 margin: xx auto 版心居中 width:100% 通栏 vertical-align 作用于行内元素 / 表格单元格ÿ…...
保姆级教程:在无网络无显卡的Windows电脑的vscode本地部署deepseek
文章目录 1 前言2 部署流程2.1 准备工作2.2 Ollama2.2.1 使用有网络的电脑下载Ollama2.2.2 安装Ollama(有网络的电脑)2.2.3 安装Ollama(无网络的电脑)2.2.4 安装验证2.2.5 修改大模型安装位置2.2.6 下载Deepseek模型 2.3 将deepse…...
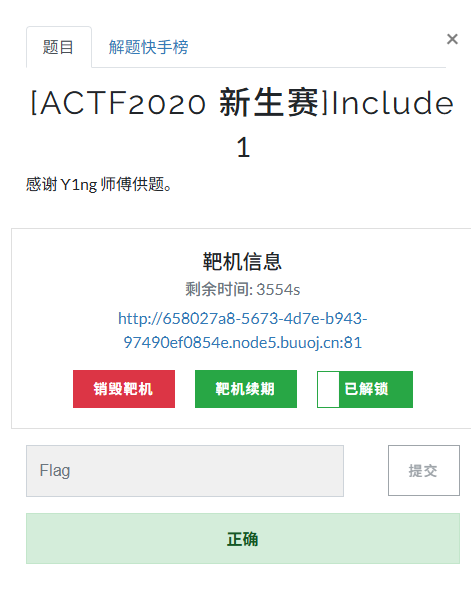
[ACTF2020 新生赛]Include 1(php://filter伪协议)
题目 做法 启动靶机,点进去 点进去 查看URL,有 ?fileflag.php说明存在文件包含,原理是php://filter 协议 当它与包含函数结合时,php://filter流会被当作php文件执行。 用php://filter加编码,能让PHP把文件内容…...
