informer中的indexer机制的实现分析与源码解读
1. 背景
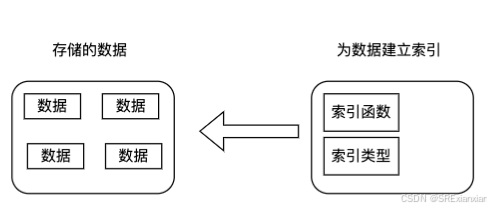
2. indexer的源码分析
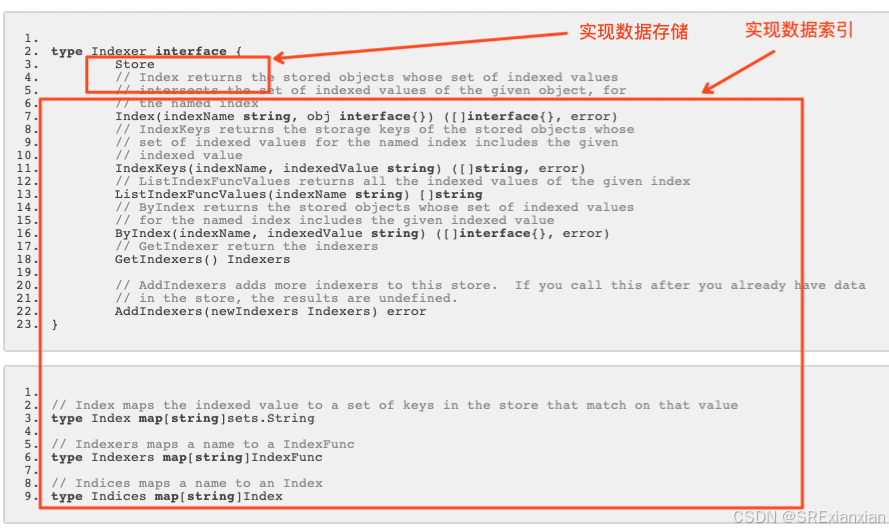
type Indexer interface {Store// Index returns the stored objects whose set of indexed values// intersects the set of indexed values of the given object, for// the named indexIndex(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error)// IndexKeys returns the storage keys of the stored objects whose// set of indexed values for the named index includes the given// indexed valueIndexKeys(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]string, error)// ListIndexFuncValues returns all the indexed values of the given indexListIndexFuncValues(indexName string) []string// ByIndex returns the stored objects whose set of indexed values// for the named index includes the given indexed valueByIndex(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]interface{}, error)// GetIndexer return the indexersGetIndexers() Indexers// AddIndexers adds more indexers to this store. If you call this after you already have data// in the store, the results are undefined.AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error
}
// Index maps the indexed value to a set of keys in the store that match on that value
type Index map[string]sets.String
// Indexers maps a name to a IndexFunc
type Indexers map[string]IndexFunc
// Indices maps a name to an Index
type Indices map[string]Indexfunc cityIndexFunc(obj interface{}) ([]string, error) {pod := obj.(*corev1.Pod)psaId := pod.Labels["city"]return []string{psaId}, nil
}
3. store.go 源码分析
type Store interface {Add(obj interface{}) error // 往存储里面添加一个对象Update(obj interface{}) error // 更新存储里面的一个对象Delete(obj interface{}) error // 删除存储里面的一个对象List() []interface{} // 提取存储里面所有对象ListKeys() []string // 提取存储里面所有对象的keyGet(obj interface{}) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error) // 获取存储里面的一个对象GetByKey(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error) // 通过key来获取存储里面的一个对象// Replace will delete the contents of the store, using instead the// given list. Store takes ownership of the list, you should not reference// it after calling this function.Replace([]interface{}, string) error // 替换存储里面的所有对象Resync() error
}
// NewStore returns a Store implemented simply with a map and a lock.
func NewStore(keyFunc KeyFunc) Store {return &cache{cacheStorage: NewThreadSafeStore(Indexers{}, Indices{}),keyFunc: keyFunc,}
}
// NewIndexer returns an Indexer implemented simply with a map and a lock.
func NewIndexer(keyFunc KeyFunc, indexers Indexers) Indexer {return &cache{cacheStorage: NewThreadSafeStore(indexers, Indices{}),keyFunc: keyFunc,}
}
// cache responsibilities are limited to:
// 1. Computing keys for objects via keyFunc
// 2. Invoking methods of a ThreadSafeStorage interface
type cache struct {// cacheStorage bears the burden of thread safety for the cachecacheStorage ThreadSafeStore // ThreadSafeStore 是存数据的地方// keyFunc is used to make the key for objects stored in and retrieved from items, and// should be deterministic.keyFunc KeyFunc // 作用把一个object计算出一个key出来
}
var _ Store = &cache{}// MetaNamespaceKeyFunc is a convenient default KeyFunc which knows how to make
// keys for API objects which implement meta.Interface.
// The key uses the format <namespace>/<name> unless <namespace> is empty, then
// it's just <name>.
//
// TODO: replace key-as-string with a key-as-struct so that this
// packing/unpacking won't be necessary.
func MetaNamespaceKeyFunc(obj interface{}) (string, error) {if key, ok := obj.(ExplicitKey); ok {return string(key), nil}meta, err := meta.Accessor(obj)if err != nil {return "", fmt.Errorf("object has no meta: %v", err)}if len(meta.GetNamespace()) > 0 {return meta.GetNamespace() + "/" + meta.GetName(), nil // 如果有namespace的资源类型,返回ns+name,比如pod,configmap等}return meta.GetName(), nil // 如果没有namespace的资源类型,返回ns,比如node,pv等
}4. ThreadSafeStore.go 源码分析
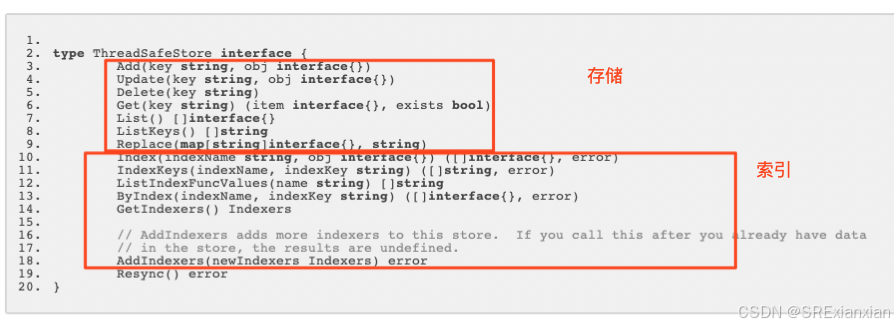
type ThreadSafeStore interface {Add(key string, obj interface{})Update(key string, obj interface{})Delete(key string)Get(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool)List() []interface{}ListKeys() []stringReplace(map[string]interface{}, string)Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error)IndexKeys(indexName, indexKey string) ([]string, error)ListIndexFuncValues(name string) []stringByIndex(indexName, indexKey string) ([]interface{}, error)GetIndexers() Indexers// AddIndexers adds more indexers to this store. If you call this after you already have data// in the store, the results are undefined.AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) errorResync() error
}
// threadSafeMap implements ThreadSafeStore
type threadSafeMap struct {lock sync.RWMutex // 保证对items map表操作的线程安全items map[string]interface{} // 真正存储数据的map表结构// indexers maps a name to an IndexFuncindexers Indexers // 保存IndexFunc索引函数的map结构// indices maps a name to an Indexindices Indices // 保存Index索引表的map结构
}

5. 举例说明
func cityIndexFunc(obj interface{}) ([]string, error) {pod := obj.(*corev1.Pod)psaId := pod.Labels["city"]return []string{psaId}, nil
}
func TestIndexer(t *testing.T) {// 用NewIndexer构造函数,创建一个indexer对象indexer := cache.NewIndexer(cache.MetaNamespaceKeyFunc, cache.Indexers{"cityIndex": cityIndexFunc,})// 造数据,添加pods到indexer中pod1 := &corev1.Pod{ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{Name: "one", Namespace: "public", Labels: map[string]string{"city": "shenzhen"}}}pod2 := &corev1.Pod{ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{Name: "two", Namespace: "public", Labels: map[string]string{"city": "chengdu"}}}pod3 := &corev1.Pod{ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{Name: "tre", Namespace: "public", Labels: map[string]string{"city": "beijing"}}}pod4 := &corev1.Pod{ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{Name: "for", Namespace: "public", Labels: map[string]string{"city": "shenzhen"}}}indexer.Add(pod1)indexer.Add(pod2)indexer.Add(pod3)indexer.Add(pod4)fmt.Println("显示索引表的所有数据: ")for k, v := range indexer.List() {fmt.Println(k, v.(*corev1.Pod).Name, v.(*corev1.Pod).Labels)}// 显示indexer中的所有索引值values := indexer.ListIndexFuncValues("cityIndex")fmt.Println("values: ", values) // values: [chengdu beijing shenzhen]// 查询索引值为shenzhen的pod// ByIndex 根据索引函数名与索引值,检索出匹配的obj对象foundPods2, err := indexer.ByIndex("cityIndex", "shenzhen")if err != nil {fmt.Printf("unexpected error: %v\n", err)}fmt.Println("pod have label shenzhen: ")for _, pod2 := range foundPods2 {fmt.Println(pod2.(*corev1.Pod).Namespace, pod2.(*corev1.Pod).Name) // 结果是 public for; public one}// IndexKeys 根据索引名与索引值,检索出匹配的obj的key(key是由ns/name组成)keys, err := indexer.IndexKeys("cityIndex", "shenzhen")if err != nil {t.Error(err)}for _, key := range keys {fmt.Println("key: ", key) // 结果是: public/one;public/for}// 查询所有obj中,用索引函数匹配的索引值ss := indexer.ListIndexFuncValues("cityIndex")fmt.Println("indexFuncValue: ", ss) // indexFuncValue: [chengdu beijing shenzhen]// 返回与输入obj有同样索引的objress, err := indexer.Index("cityIndex", pod1)if err != nil {return}fmt.Println(len(ress))for _, pod := range ress {fmt.Println(pod.(*corev1.Pod).Name, pod.(*corev1.Pod).Namespace) // one public,for public}
}func cityIndexFunc(obj interface{}) ([]string, error) {pod := obj.(*corev1.Pod)psaId := pod.Labels["city"]return []string{psaId}, nil
}
indexer := cache.NewIndexer(cache.MetaNamespaceKeyFunc, cache.Indexers{"cityIndex": cityIndexFunc,})
func NewIndexer(keyFunc KeyFunc, indexers Indexers) Indexer {return &cache{cacheStorage: NewThreadSafeStore(indexers, Indices{}),keyFunc: keyFunc,}
}
// NewThreadSafeStore creates a new instance of ThreadSafeStore.
func NewThreadSafeStore(indexers Indexers, indices Indices) ThreadSafeStore {return &threadSafeMap{items: map[string]interface{}{},indexers: indexers,indices: indices,}
}
// 造数据,添加pods到indexer中pod1 := &corev1.Pod{ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{Name: "one", Namespace: "public", Labels: map[string]string{"city": "shenzhen"}}}pod2 := &corev1.Pod{ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{Name: "two", Namespace: "public", Labels: map[string]string{"city": "chengdu"}}}pod3 := &corev1.Pod{ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{Name: "tre", Namespace: "public", Labels: map[string]string{"city": "beijing"}}}pod4 := &corev1.Pod{ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{Name: "for", Namespace: "public", Labels: map[string]string{"city": "shenzhen"}}}indexer.Add(pod1)indexer.Add(pod2)indexer.Add(pod3)indexer.Add(pod4)
// Add inserts an item into the cache.
func (c *cache) Add(obj interface{}) error {key, err := c.keyFunc(obj) // 现有keyFunc也就是MetaNamespaceKeyFunc方法,计算出obj的key(由<ns>/<name>表示)if err != nil {return KeyError{obj, err}}c.cacheStorage.Add(key, obj) // 再调用ThreadSafeStore接口类型的Add()方法return nil
}
func (c *threadSafeMap) Add(key string, obj interface{}) {c.lock.Lock()defer c.lock.Unlock()oldObject := c.items[key] // 通过key获取存储内原来的obj对象即oldObjectc.items[key] = obj // 新的obj存到items表中c.updateIndices(oldObject, obj, key) // 使用updateIndices()更新索引
}
// updateIndices modifies the objects location in the managed indexes, if this is an update, you must provide an oldObj
// updateIndices must be called from a function that already has a lock on the cache
func (c *threadSafeMap) updateIndices(oldObj interface{}, newObj interface{}, key string) {// if we got an old object, we need to remove it before we add it againif oldObj != nil {c.deleteFromIndices(oldObj, key) // 如存储里面,已经有obj的老数据,先把老数据的索引删除}for name, indexFunc := range c.indexers {indexValues, err := indexFunc(newObj) // 通过indexFunc获取到newObj的索引值indexValuesif err != nil {panic(fmt.Errorf("unable to calculate an index entry for key %q on index %q: %v", key, name, err))}index := c.indices[name] // 通过indexName索引函数名,找到对应index索引表if index == nil { // 如果indexName索引函数名,还没有对应的索引表Index,就index{}新创建一个索引表index = Index{}c.indices[name] = index // 把新创建的索引表index,加到indices表中}for _, indexValue := range indexValues {set := index[indexValue] // 在index索引表中,用indexValue值找对应的值,值是一个set.string{}类型if set == nil { // 如果在index索引表,没有找到indexValue值时,就新建一个set.string{}类型set = sets.String{} index[indexValue] = set // indexValue与set对应的数据,存放到index索引表}set.Insert(key) // 如果index表中,已经有indexValue值的set.string{}数据,就将key加到这个set.string{}集合中去}}
}// sets.String is a set of strings, implemented via map[string]struct{} for minimal memory consumption.
type String map[string]Empty
type Empty struct{}fmt.Println("显示索引表的所有数据: ")for k, v := range indexer.List() {fmt.Println(k, v.(*corev1.Pod).Name, v.(*corev1.Pod).Labels)}
// 显示indexer中的所有索引值
values := indexer.ListIndexFuncValues("cityIndex")
fmt.Println("values: ", values) // values: [chengdu beijing shenzhen]
// 查询索引值为shenzhen的pod
// ByIndex 根据索引函数名与索引值,检索出匹配的obj对象
foundPods2, err := indexer.ByIndex("cityIndex", "shenzhen")
if err != nil {fmt.Printf("unexpected error: %v\n", err)
}
fmt.Println("pod have label shenzhen: ")
for _, pod2 := range foundPods2 {fmt.Println(pod2.(*corev1.Pod).Namespace, pod2.(*corev1.Pod).Name) // 结果是 public for; public one
}
// IndexKeys 根据索引名与索引值,检索出匹配的obj的key(key是由ns/name组成)
keys, err := indexer.IndexKeys("cityIndex", "shenzhen")
if err != nil {t.Error(err)
}
for _, key := range keys {fmt.Println("key: ", key) // 结果是: public/one;public/for
}
// 返回与输入obj有同样索引的obj
ress, err := indexer.Index("cityIndex", pod1)
if err != nil {return
}
fmt.Println(len(ress))
for _, pod := range ress {fmt.Println(pod.(*corev1.Pod).Name, pod.(*corev1.Pod).Namespace) // one public,for public
}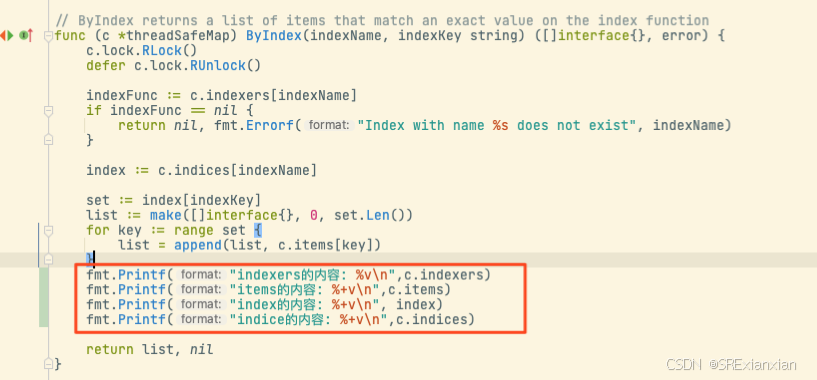
map["public/for": &pod{},"public/one": &pod{},"public/tre": &pod{},"public/two": &pod{},
]
map["shenzhen": map["public/for": {},"public/one": {}]"beijing": map["public/tre":{}]"chengdu": map["public/two":{}]
]map["cityIndex": index]map["cityIndex": map["beijing": map["public/tre": {}]"chengdu": map["public/two": {}]"shenzhen": map["public/for":{} "public/one":{}]
]相关文章:

informer中的indexer机制的实现分析与源码解读
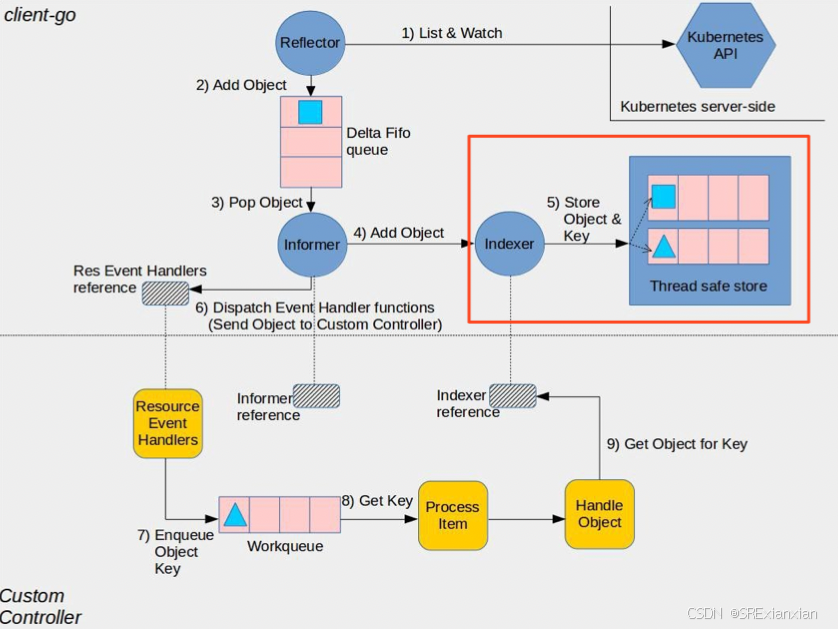
1. 背景 client-go工具下的tools/cache.indexer为informer提供缓存与索引的能力。可以实现快速通过索引找到对应的对象(pod, deployment,secret,configmap等)。 indexer再informer机制中的使用图示: indexer包括2部分: 一部分是store用于实际数据的存储,…...

英特尔宣布针对对Llama 3.1进行优化 以提升所有产品的性能
日前Meta正式发布了Llama 3.1开源大模型,以其庞大的参数量和卓越性能,首次在多项基准测试中击败了GPT-4o等业界领先的闭源模型。允许开发者自由地进行微调、蒸馏,甚至在任何地方部署,这种开放性为AI技术的普及和创新提供了无限可能…...
Python3网络爬虫开发实战(1)爬虫基础
一、URL 基础 URL也就是网络资源地址,其满足如下格式规范 scheme://[username:password]hostname[:port][/path][;parameters][?query][#fragment] scheme:协议,常用的协议有 Http,https,ftp等等;usern…...

Redis的五种数据类型与命令
目录 引言 一 Redis的特性 二 Redis的安装 三 Redis的优点 四 Redis的五种数据类型与命令 五 Redis的配置文件 引言 Redis是什么? Remote Dictionary Service(远程字典服务器) Redis 是一个开源的(BSD许可)的,C语言编写的,高性能的数…...

RocketMQ的详细讲解(四种mq的对比(activeMq、rabbitmq、rocketmq、kafka))
20240729 RocketMQ1 mq的三大作用 异步、削峰限流、解耦合2. 四种mq的对比(activeMq、rabbitmq、rocketmq、kafka)3 rocketmq特点1. 平台无关2. 能提供什么样的功能 4 rocketMq4.1 broker中的标题,来约束读和写4.2 rocketmq的结构4.3 读和写的…...

除了GPT,还有哪些好用的AI工具?
最强AI视频生成:小说文案智能分镜智能识别角色和场景批量Ai绘图自动配音添加音乐一键合成视频百万播放量https://aitools.jurilu.com/ 多得很,这20个免费的国产AI工具,打工人必备,除了比chatGPT好用,甚至还可以用来变现…...

04 | 深入浅出索引(上)
此系列文章为极客时间课程《MySQL 实战 45 讲》的学习笔记! 索引的常见模型 可以提供查询效率的数据结构有很多,常见的有三种:哈希表、有序数组、搜索数。 哈希表是一种以 key-value 形式存储的数据结构。输入一个 key,通过固定…...
Linux的yum源安装MySQL5.7
linux的yum源安装MySQL5.7 一、MySQL 1、简介 MySQL 是一种流行的关系型数据库管理系统(RDBMS),由瑞典公司 MySQL AB 开发,后来被 Oracle Corporation 收购。它是一个开源软件,提供了高效、稳定和可靠的数据管理解决…...

基于深度学习的音频自监督学习
基于深度学习的音频自监督学习(Self-Supervised Learning, SSL)是一种利用未标注的音频数据,通过设计自监督任务进行特征学习的方法。这种方法在需要大量标注数据的音频处理任务(如语音识别、情感分析等)中,…...

用uniapp 及socket.io做一个简单聊天app1
####相关的表结构,用的是mysql 用户表(Users) 存储用户的基本信息。 CREATE TABLE Users (id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,username VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL UNIQUE,password VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE,created_a…...

在Postman中引用JS库
前言 在做接口测试时,出于安全因素,请求参数需要做加密或者加上签名才能正常请求,例如:根据填写的请求参数进行hash计算进行签名。postman作为主流的接口调试工具也是支持请求预处理的,即在请求前使用JavaScript脚本对…...

学习笔记-系统框图简化求传递函数公式例题
简化系统结构图求系统传递函数例题 基础知识回顾 第四讲 控制系统的方框图 (zhihu.com) 「自控原理」2.3 方框图的绘制及化简_方框图化简-CSDN博客 自动控制原理笔记-结构图及其等效变换_结构图等效变换-CSDN博客 例子一 「自控原理」2.3 方框图的绘制及化简_方框图化简-CS…...

postgrsql——事务概述
事务概述 事务的特性 原子性(Atomicity): 事务被视为一个整体,其中的操作要么全部执行成功,要么全部不执行,即不存在部分执行的情况。这确保了事务的完整性和一致性。一致性(Consistency&…...
)
1.Spring Boot 简介(Spring MVC+Mybatis-plus)
文章目录 一,Spring Boot 简介二,搭建springboot项目并整合mybatis-plus框架1.pom导依赖2.添加启动项3.配置文件.yml 三,springboot集成 Spring MVC1.springmvc定义2.应用注解 一,Spring Boot 简介 SpringBoot是Spring的子工程(或…...

《计算机网络》(学习笔记)
目录 一、计算机网络体系结构 1.1 计算机网络概述 1.1.1 计算机网络的概念 1.1.2 计算机网络的组成 1.1.3 计算机网络的功能 1.1.4 电流交换、报文交换和分组交换 1.1.5 计算机网络的分类 1.1.6 计算机网络的性能指标 1.2 计算机网络体系结构与参考模型 1.2.1 计算机…...

指针函数和函数指针
函数名在表达式中应该如何被解读?答:函数名可以在表达式中被解读成“指向该函数的指针”。 函数指针和指针函数有什么区别?答:函数指针是一个指向函数的指针;指针函数是一个返回指针变量的函数。 一个函数能否有时候…...

Elasticsearch跨集群搜索
Elasticsearch(简称ES)是一种基于Lucene的搜索引擎,以其高性能、可扩展性和实时搜索能力而广受欢迎。在大型分布式系统中,跨集群搜索成为了一个重要的需求,它允许用户从多个Elasticsearch集群中联合查询数据࿰…...
基于FPGA的数字信号处理(19)--行波进位加法器
1、10进制加法是如何实现的? 10进制加法是大家在小学就学过的内容,不过在这里我还是帮大家回忆一下。考虑2个2位数的10进制加法,例如:15 28 43,它的运算过程如下: 个位两数相加,结果为5 8 1…...

树莓派下,centos7操作系统, TensorFlow java版实现植物分类功能
在树莓派上运行CentOS 7,并使用TensorFlow Java版本实现植物分类功能可以通过以下步骤实现。以下是详细的指导: 一、安装和设置环境 1. 更新系统并安装基本工具 确保你的CentOS 7系统是最新的,并安装必要的工具: sudo yum update -y sudo yum install -y wget unzip gi…...

开源一个react路由缓存库
Github仓库 背景 产品希望可以像浏览器那样每打开一个路由,会多一个tab,用户可以切换tab访问之前加载过的页面,且不会重新加载。真就产品一句话…… Github上有轮子了吗 Github上开箱即用的轮子是基于react-router-dom V5实现的ÿ…...

手游刚开服就被攻击怎么办?如何防御DDoS?
开服初期是手游最脆弱的阶段,极易成为DDoS攻击的目标。一旦遭遇攻击,可能导致服务器瘫痪、玩家流失,甚至造成巨大经济损失。本文为开发者提供一套简洁有效的应急与防御方案,帮助快速应对并构建长期防护体系。 一、遭遇攻击的紧急应…...

工业安全零事故的智能守护者:一体化AI智能安防平台
前言: 通过AI视觉技术,为船厂提供全面的安全监控解决方案,涵盖交通违规检测、起重机轨道安全、非法入侵检测、盗窃防范、安全规范执行监控等多个方面,能够实现对应负责人反馈机制,并最终实现数据的统计报表。提升船厂…...

HTML 列表、表格、表单
1 列表标签 作用:布局内容排列整齐的区域 列表分类:无序列表、有序列表、定义列表。 例如: 1.1 无序列表 标签:ul 嵌套 li,ul是无序列表,li是列表条目。 注意事项: ul 标签里面只能包裹 li…...

【Go】3、Go语言进阶与依赖管理
前言 本系列文章参考自稀土掘金上的 【字节内部课】公开课,做自我学习总结整理。 Go语言并发编程 Go语言原生支持并发编程,它的核心机制是 Goroutine 协程、Channel 通道,并基于CSP(Communicating Sequential Processes࿰…...

linux 下常用变更-8
1、删除普通用户 查询用户初始UID和GIDls -l /home/ ###家目录中查看UID cat /etc/group ###此文件查看GID删除用户1.编辑文件 /etc/passwd 找到对应的行,YW343:x:0:0::/home/YW343:/bin/bash 2.将标红的位置修改为用户对应初始UID和GID: YW3…...

在鸿蒙HarmonyOS 5中使用DevEco Studio实现录音机应用
1. 项目配置与权限设置 1.1 配置module.json5 {"module": {"requestPermissions": [{"name": "ohos.permission.MICROPHONE","reason": "录音需要麦克风权限"},{"name": "ohos.permission.WRITE…...
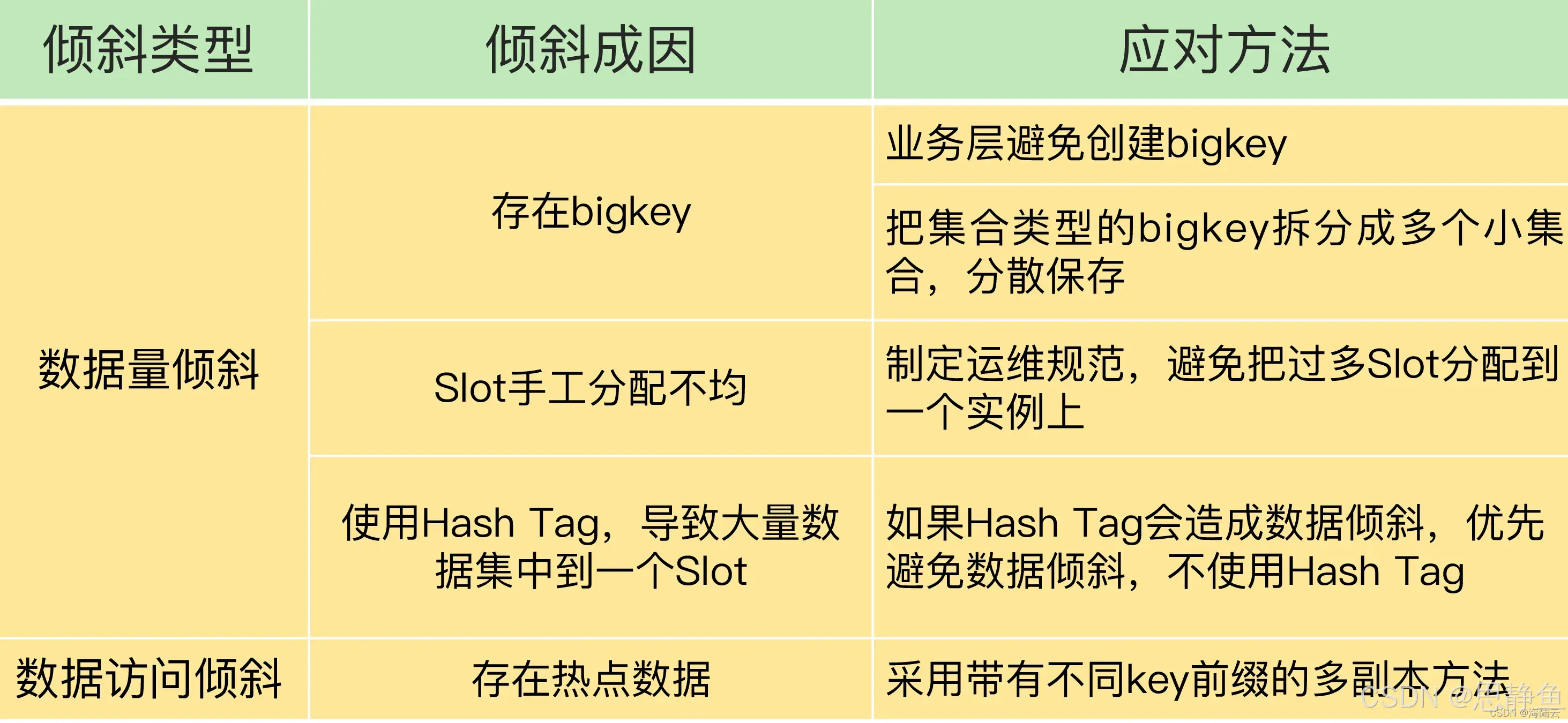
Redis数据倾斜问题解决
Redis 数据倾斜问题解析与解决方案 什么是 Redis 数据倾斜 Redis 数据倾斜指的是在 Redis 集群中,部分节点存储的数据量或访问量远高于其他节点,导致这些节点负载过高,影响整体性能。 数据倾斜的主要表现 部分节点内存使用率远高于其他节…...

[免费]微信小程序问卷调查系统(SpringBoot后端+Vue管理端)【论文+源码+SQL脚本】
大家好,我是java1234_小锋老师,看到一个不错的微信小程序问卷调查系统(SpringBoot后端Vue管理端)【论文源码SQL脚本】,分享下哈。 项目视频演示 【免费】微信小程序问卷调查系统(SpringBoot后端Vue管理端) Java毕业设计_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 项…...
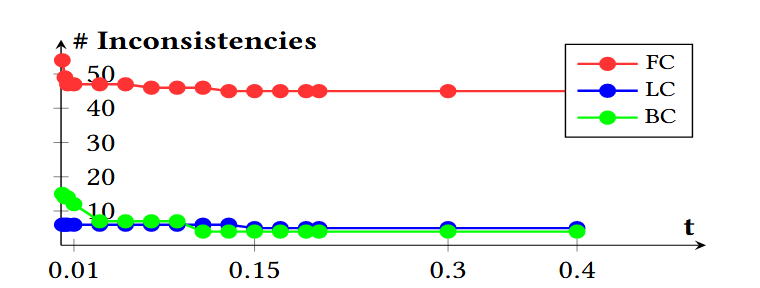
论文阅读笔记——Muffin: Testing Deep Learning Libraries via Neural Architecture Fuzzing
Muffin 论文 现有方法 CRADLE 和 LEMON,依赖模型推理阶段输出进行差分测试,但在训练阶段是不可行的,因为训练阶段直到最后才有固定输出,中间过程是不断变化的。API 库覆盖低,因为各个 API 都是在各种具体场景下使用。…...

算术操作符与类型转换:从基础到精通
目录 前言:从基础到实践——探索运算符与类型转换的奥秘 算术操作符超级详解 算术操作符:、-、*、/、% 赋值操作符:和复合赋值 单⽬操作符:、--、、- 前言:从基础到实践——探索运算符与类型转换的奥秘 在先前的文…...
