Halcon深度学习分类模型
1.Halcon20之后深度学习支持CPU训练模型,没有money买显卡的小伙伴有福了。但是缺点也很明显,就是训练速度超级慢,推理效果也没有GPU好,不过学习用足够。
2.分类模型是Halcon深度学习最简单的模型,可以用在物品分类,缺陷检测等项目。
3.图像预处理和训练代码
*分类网络
dev_update_off ()
dev_close_window ()
WindowWidth := 800
WindowHeight := 600
dev_open_window_fit_size (0, 0, WindowWidth, WindowHeight, -1, -1, WindowHandle)
set_display_font (WindowHandle, 16, ‘mono’, ‘true’, ‘false’)
*训练原图路径
RawImageBaseFolder :=‘D:/训练图/’+ [‘U’,‘SR’,‘MR’,‘BR’,‘C’,‘D’,‘NG’]
*预处理数据存储路径
ExampleDataDir := ‘D:/classify_pill_defects_data’
-
Dataset directory basename for any outputs written by preprocess_dl_dataset.
DataDirectoryBaseName := ExampleDataDir + ‘/dldataset_pill’
- ** Set parameters ***
- LabelSource for reading in the dataset.
LabelSource := ‘last_folder’ - Percentages for splitting the dataset.
TrainingPercent := 70
ValidationPercent := 15 - Image dimensions the images are rescaled to during preprocessing.
ImageWidth := 300
ImageHeight := 300
ImageNumChannels := 3 - Further parameters for image preprocessing.
NormalizationType := ‘none’
DomainHandling := ‘full_domain’ - In order to get a reproducible split we set a random seed.
- This means that re-running the script results in the same split of DLDataset.
SeedRand := 42
- ** Read the labeled data and split it into train, validation and test ***
- Set the random seed.
set_system (‘seed_rand’, SeedRand) - Read the dataset with the procedure read_dl_dataset_classification.
- Alternatively, you can read a DLDataset dictionary
- as created by e.g., the MVTec Deep Learning Tool using read_dict().
read_dl_dataset_classification (RawImageBaseFolder, LabelSource, DLDataset) - Generate the split.
split_dl_dataset (DLDataset, TrainingPercent, ValidationPercent, [])
- ** Preprocess the dataset ***
- Create the output directory if it does not exist yet.
file_exists (ExampleDataDir, FileExists)
if (not FileExists)
make_dir (ExampleDataDir)
endif - Create preprocess parameters.
create_dl_preprocess_param (‘classification’, ImageWidth, ImageHeight, ImageNumChannels, -127, 128, NormalizationType, DomainHandling, [], [], [], [], DLPreprocessParam) - Dataset directory for any outputs written by preprocess_dl_dataset.
DataDirectory := DataDirectoryBaseName + ‘_’ + ImageWidth + ‘x’ + ImageHeight - Preprocess the dataset. This might take a few seconds.
create_dict (GenParam)
set_dict_tuple (GenParam, ‘overwrite_files’, true)
preprocess_dl_dataset (DLDataset, DataDirectory, DLPreprocessParam, GenParam, DLDatasetFileName) - Store preprocess params separately in order to use it e.g. during inference.
PreprocessParamFileBaseName := DataDirectory + ‘/dl_preprocess_param.hdict’
write_dict (DLPreprocessParam, PreprocessParamFileBaseName, [], [])
- ** Preview the preprocessed dataset ***
- Before moving on to training, it is recommended to check the preprocessed dataset.
- Display the DLSamples for 10 randomly selected train images.
get_dict_tuple (DLDataset, ‘samples’, DatasetSamples)
find_dl_samples (DatasetSamples, ‘split’, ‘train’, ‘match’, SampleIndices)
tuple_shuffle (SampleIndices, ShuffledIndices)
read_dl_samples (DLDataset, ShuffledIndices[0:9], DLSampleBatchDisplay)
create_dict (WindowHandleDict)
for Index := 0 to |DLSampleBatchDisplay| - 1 by 1
* Loop over samples in DLSampleBatchDisplay.
dev_display_dl_data (DLSampleBatchDisplay[Index], [], DLDataset, ‘classification_ground_truth’, [], WindowHandleDict)
Text := ‘Press Run (F5) to continue’
dev_disp_text (Text, ‘window’, ‘bottom’, ‘right’, ‘black’, [], [])
stop ()
endfor
*
- Close windows that have been used for visualization.
dev_close_window_dict (WindowHandleDict)
*检测电脑是否有GPU,如果无GPU则使用CPU训练
query_available_dl_devices ([‘runtime’,‘runtime’], [‘gpu’,‘cpu’], DLDeviceHandles)
if (|DLDeviceHandles| == 0)
throw (‘No supported device found to continue this example.’)
endif
- Due to the filter used in query_available_dl_devices, the first device is a GPU, if available.
DLDevice := DLDeviceHandles[0]
get_dl_device_param (DLDevice, ‘type’, DLDeviceType)
if (DLDeviceType == ‘cpu’)- The number of used threads may have an impact
- on the training duration.
NumThreadsTraining := 4
set_system (‘thread_num’, NumThreadsTraining)
endif
- ** Set input and output paths ***
-
File path of the initialized model.
ModelFileName := ‘pretrained_dl_classifier_compact.hdl’ -
File path of the preprocessed DLDataset.
-
Note: Adapt DataDirectory after preprocessing with another image size.
DataDirectory := ExampleDataDir + ‘/dldataset_pill_300x300’
DLDatasetFileName := DataDirectory + ‘/dl_dataset.hdict’
DLPreprocessParamFileName := DataDirectory + ‘/dl_preprocess_param.hdict’ -
Output path of the best evaluated model.
BestModelBaseName := ExampleDataDir + ‘/best_dl_model_classification’ -
Output path for the final trained model.
FinalModelBaseName := ExampleDataDir + ‘/final_dl_model_classification’
- ** Set basic parameters ***
- The following parameters need to be adapted frequently.
- Model parameters.
- Batch size. In case this example is run on a GPU,
- you can set BatchSize to ‘maximum’ and it will be
- determined automatically.
BatchSize := 64 - Initial learning rate.
InitialLearningRate := 0.001 - Momentum should be high if batch size is small.
Momentum := 0.9 - Parameters used by train_dl_model.
- Number of epochs to train the model.
NumEpochs := 16 - Evaluation interval (in epochs) to calculate evaluation measures on the validation split.
EvaluationIntervalEpochs := 1 - Change the learning rate in the following epochs, e.g. [4, 8, 12].
- Set it to [] if the learning rate should not be changed.
ChangeLearningRateEpochs := [4,8,12] - Change the learning rate to the following values, e.g. InitialLearningRate * [0.1, 0.01, 0.001].
- The tuple has to be of the same length as ChangeLearningRateEpochs.
ChangeLearningRateValues := InitialLearningRate * [0.1,0.01,0.001]
- ** Set advanced parameters ***
- The following parameters might need to be changed in rare cases.
- Model parameter.
- Set the weight prior.
WeightPrior := 0.0005 - Parameters used by train_dl_model.
- Control whether training progress is displayed (true/false).
EnableDisplay := true - Set a random seed for training.
RandomSeed := 42
set_system (‘seed_rand’, RandomSeed) - In order to obtain nearly deterministic training results on the same GPU
- (system, driver, cuda-version) you could specify “cudnn_deterministic” as
- “true”. Note, that this could slow down training a bit.
- set_system (‘cudnn_deterministic’, ‘true’)
- Set generic parameters of create_dl_train_param.
- Please see the documentation of create_dl_train_param for an overview on all available parameters.
GenParamName := []
GenParamValue := [] - Augmentation parameters.
- If samples should be augmented during training, create the dict required by augment_dl_samples.
- Here, we set the augmentation percentage and method.
create_dict (AugmentationParam) - Percentage of samples to be augmented.
set_dict_tuple (AugmentationParam, ‘augmentation_percentage’, 50) - Mirror images along row and column.
set_dict_tuple (AugmentationParam, ‘mirror’, ‘rc’)
GenParamName := [GenParamName,‘augment’]
GenParamValue := [GenParamValue,AugmentationParam] - Change strategies.
- It is possible to change model parameters during training.
- Here, we change the learning rate if specified above.
if (|ChangeLearningRateEpochs| > 0)
create_dict (ChangeStrategy)- Specify the model parameter to be changed, here the learning rate.
set_dict_tuple (ChangeStrategy, ‘model_param’, ‘learning_rate’) - Start the parameter value at ‘initial_value’.
set_dict_tuple (ChangeStrategy, ‘initial_value’, InitialLearningRate) - Reduce the learning rate in the following epochs.
set_dict_tuple (ChangeStrategy, ‘epochs’, ChangeLearningRateEpochs) - Reduce the learning rate to the following values.
set_dict_tuple (ChangeStrategy, ‘values’, ChangeLearningRateValues) - Collect all change strategies as input.
GenParamName := [GenParamName,‘change’]
GenParamValue := [GenParamValue,ChangeStrategy]
endif
- Specify the model parameter to be changed, here the learning rate.
- Serialization strategies.
- There are several options for saving intermediate models to disk (see create_dl_train_param).
- Here, we save the best and the final model to the paths set above.
create_dict (SerializationStrategy)
set_dict_tuple (SerializationStrategy, ‘type’, ‘best’)
set_dict_tuple (SerializationStrategy, ‘basename’, BestModelBaseName)
GenParamName := [GenParamName,‘serialize’]
GenParamValue := [GenParamValue,SerializationStrategy]
create_dict (SerializationStrategy)
set_dict_tuple (SerializationStrategy, ‘type’, ‘final’)
set_dict_tuple (SerializationStrategy, ‘basename’, FinalModelBaseName)
GenParamName := [GenParamName,‘serialize’]
GenParamValue := [GenParamValue,SerializationStrategy] - Display parameters.
- In this example, 20% of the training split are selected to display the
- evaluation measure for the reduced training split during the training. A lower percentage
- helps to speed up the evaluation/training. If the evaluation measure for the training split
- shall not be displayed, set this value to 0 (default).
SelectedPercentageTrainSamples := 20 - Set the x-axis argument of the training plots.
XAxisLabel := ‘epochs’
create_dict (DisplayParam)
set_dict_tuple (DisplayParam, ‘selected_percentage_train_samples’, SelectedPercentageTrainSamples)
set_dict_tuple (DisplayParam, ‘x_axis_label’, XAxisLabel)
GenParamName := [GenParamName,‘display’]
GenParamValue := [GenParamValue,DisplayParam]
- ** Read initial model and dataset ***
- Check if all necessary files exist.
check_data_availability (ExampleDataDir, DLDatasetFileName, DLPreprocessParamFileName) - Read in the model that was initialized during preprocessing.
read_dl_model (ModelFileName, DLModelHandle) - Read in the preprocessed DLDataset file.
read_dict (DLDatasetFileName, [], [], DLDataset)
- ** Set model parameters ***
- Set model hyper-parameters as specified in the settings above.
set_dl_model_param (DLModelHandle, ‘learning_rate’, InitialLearningRate)
set_dl_model_param (DLModelHandle, ‘momentum’, Momentum) - Set the class names for the model.
get_dict_tuple (DLDataset, ‘class_names’, ClassNames)
set_dl_model_param (DLModelHandle, ‘class_names’, ClassNames) - Get image dimensions from preprocess parameters and set them for the model.
read_dict (DLPreprocessParamFileName, [], [], DLPreprocessParam)
get_dict_tuple (DLPreprocessParam, ‘image_width’, ImageWidth)
get_dict_tuple (DLPreprocessParam, ‘image_height’, ImageHeight)
get_dict_tuple (DLPreprocessParam, ‘image_num_channels’, ImageNumChannels)
set_dl_model_param (DLModelHandle, ‘image_dimensions’, [ImageWidth,ImageHeight,ImageNumChannels])
if (BatchSize == ‘maximum’ and DLDeviceType == ‘gpu’)
set_dl_model_param_max_gpu_batch_size (DLModelHandle, 100)
else
set_dl_model_param (DLModelHandle, ‘batch_size’, BatchSize)
endif - When the batch size is determined, set the device.
set_dl_model_param (DLModelHandle, ‘device’, DLDevice)
if (|WeightPrior| > 0)
set_dl_model_param (DLModelHandle, ‘weight_prior’, WeightPrior)
endif - Set class weights to counteract unbalanced training data. In this example
- we choose the default values, since the classes are evenly distributed in the dataset.
tuple_gen_const (|ClassNames|, 1.0, ClassWeights)
set_dl_model_param (DLModelHandle, ‘class_weights’, ClassWeights)
- ** Train the model ***
- Create training parameters.
create_dl_train_param (DLModelHandle, NumEpochs, EvaluationIntervalEpochs, EnableDisplay, RandomSeed, GenParamName, GenParamValue, TrainParam) - Start the training by calling the training operator
- train_dl_model_batch () within the following procedure.
train_dl_model (DLDataset, DLModelHandle, TrainParam, 0, TrainResults, TrainInfos, EvaluationInfos) - Stop after the training has finished, before closing the windows.
dev_disp_text (‘Press Run (F5) to continue’, ‘window’, ‘bottom’, ‘right’, ‘black’, [], [])
stop () - Close training windows.
dev_close_window ()
4.推理代码
dev_update_off ()
dev_close_window ()
WindowWidth := 800
WindowHeight := 600
dev_open_window_fit_size (0, 0, WindowWidth, WindowHeight, -1, -1, WindowHandle)
set_display_font (WindowHandle, 16, ‘mono’, ‘true’, ‘false’) - ** INFERENCE **
*检测电脑是否有GPU,如果无GPU则使用CPU推理
query_available_dl_devices ([‘runtime’,‘runtime’], [‘gpu’,‘cpu’], DLDeviceHandles)
if (|DLDeviceHandles| == 0)
throw (‘No supported device found to continue this example.’)
endif
- Due to the filter used in query_available_dl_devices, the first device is a GPU, if available.
DLDevice := DLDeviceHandles[0]
*总路径
ExampleDataDir := ‘D:/classify_pill_defects_data’
-
Dataset directory basename for any outputs written by preprocess_dl_dataset.
DataDirectoryBaseName := ExampleDataDir + ‘/dldataset_pill’ -
File name of the dict containing parameters used for preprocessing.
-
Note: Adapt DataDirectory after preprocessing with another image size.
DataDirectory := ExampleDataDir + ‘/dldataset_pill_300x300’
PreprocessParamFileName := DataDirectory + ‘/dl_preprocess_param.hdict’ -
File name of the finetuned object detection model.
RetrainedModelFileName := ExampleDataDir + ‘/best_dl_model_classification.hdl’ -
Batch Size used during inference.
BatchSizeInference := 1
- ** Inference ***
- Check if all necessary files exist.
check_data_availability (ExampleDataDir, PreprocessParamFileName, RetrainedModelFileName, false) - Read in the retrained model.
read_dl_model (RetrainedModelFileName, DLModelHandle) - Set the batch size.
set_dl_model_param (DLModelHandle, ‘batch_size’, BatchSizeInference) - Initialize the model for inference.
set_dl_model_param (DLModelHandle, ‘device’, DLDevice) - Get the class names and IDs from the model.
get_dl_model_param (DLModelHandle, ‘class_names’, ClassNames)
get_dl_model_param (DLModelHandle, ‘class_ids’, ClassIDs) - Get the parameters used for preprocessing.
read_dict (PreprocessParamFileName, [], [], DLPreprocessParam) - Create window dictionary for displaying results.
create_dict (WindowHandleDict) - Create dictionary with dataset parameters necessary for displaying.
create_dict (DLDataInfo)
set_dict_tuple (DLDataInfo, ‘class_names’, ClassNames)
set_dict_tuple (DLDataInfo, ‘class_ids’, ClassIDs) - Set generic parameters for visualization.
create_dict (GenParam)
set_dict_tuple (GenParam, ‘scale_windows’, 1.1)
list_files (‘E:/NG’, [‘files’,‘follow_links’], ImageFiles)
tuple_regexp_select (ImageFiles, [‘\.(tif|tiff|gif|bmp|jpg|jpeg|jp2|png|pcx|pgm|ppm|pbm|xwd|ima|hobj)$’,‘ignore_case’], ImageFiles)
for Index := 0 to |ImageFiles| - 1 by 1
read_image (ImageBatch, ImageFiles[Index])
gen_dl_samples_from_images (ImageBatch, DLSampleBatch)
preprocess_dl_samples (DLSampleBatch, DLPreprocessParam)
apply_dl_model (DLModelHandle, DLSampleBatch, [], DLResultBatch)
DLSample := DLSampleBatch[0]
DLResult := DLResultBatch[0]
*获取识别结果 参数:分类的结果,批处理中图像的索引,通用参数的名称,通用参数的值
get_dict_tuple (DLResult, ‘classification_class_ids’, ClassificationClassID)
get_dict_tuple (DLResult, ‘classification_class_names’, ClassificationClassName)
get_dict_tuple (DLResult, ‘classification_confidences’, ClassificationClassConfidence)
dev_display (ImageBatch)
Text := ‘预测类为: ’ + ClassificationClassName[0] + ’ 置信度:’+ClassificationClassConfidence[0]
dev_disp_text (Text, ‘window’, ‘top’, ‘left’, ‘red’, ‘box’, ‘false’)
stop ()
endfor
dev_close_window_dict (WindowHandleDict)
相关文章:

Halcon深度学习分类模型
1.Halcon20之后深度学习支持CPU训练模型,没有money买显卡的小伙伴有福了。但是缺点也很明显,就是训练速度超级慢,推理效果也没有GPU好,不过学习用足够。 2.分类模型是Halcon深度学习最简单的模型,可以用在物品分类&…...

洗地机哪种牌子好?洗地机排行榜前十名公布
洗地机市场上品牌琳琅满目,每个品牌都有其独特的魅力和优势。消费者在选择时,往往会根据自己的实际需求、预算以及对产品性能的期望来做出决策。因此,无论是哪个品牌的洗地机,只要能够满足用户的清洁需求,提供便捷的操…...

C++中的虚函数与多态机制如何工作?
在C中,虚函数和多态机制是实现面向对象编程的重要概念。 虚函数是在基类中声明的函数,可以在派生类中进行重写。当基类的指针或引用指向派生类的对象时,通过调用虚函数可以实现动态绑定,即在运行时确定要调用的函数。 多态是指通…...

《LeetCode热题100》---<哈希三道>
本篇博客讲解 LeetCode热题100道中的哈希篇中的三道题。分别是 1.第一道:两数之和(简单) 2.第二道:字母异位词分组(中等) 3.第三道:最长连续序列(中等) 第一道࿱…...
秒懂C++之string类(下)
目录 一.接口说明 1.1 erase 1.2 replace(最好别用) 1.3 find 1.4 substr 1.5 rfind 1.6 find_first_of 1.7 find_last_of 二.string类的模拟实现 2.1 构造 2.2 无参构造 2.3 析构 2.4.【】运算符 2.5 迭代器 2.6 打印 2.7 reserve扩容 …...
github简单地操作
1.调节字体大小 选择options 选择text 选择select 选择你需要的参数就可以了。 2.配置用户名和邮箱 桌面右键,选择git Bash Here git config --global user.name 用户名 git config --global user.email 邮箱名 3.用git实现代码管理的过程 下载别人的项目 git …...
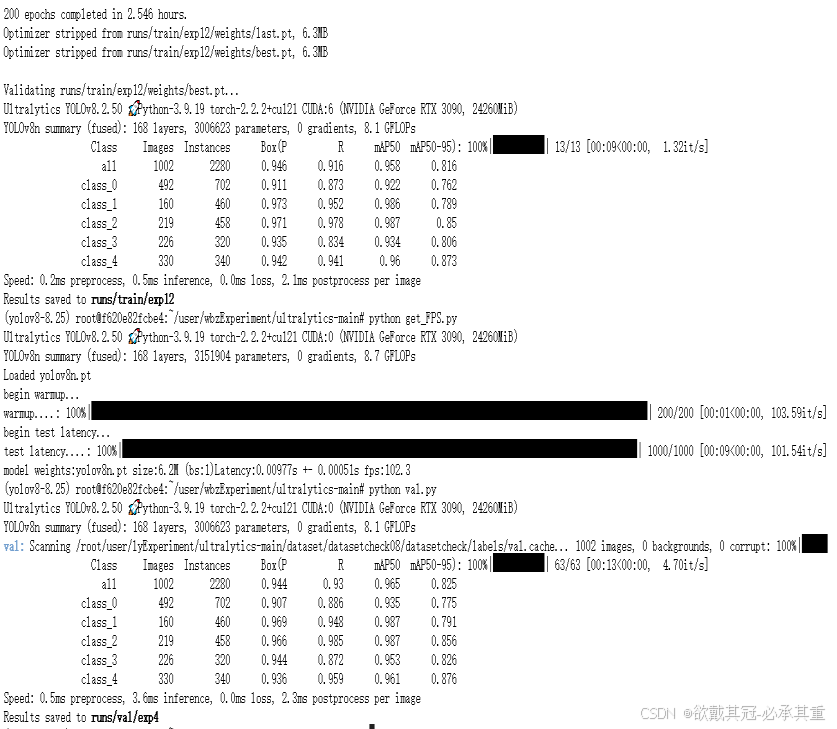
模型改进-损失函数合集
模版 第一步在哪些地方做出修改: 228行 self.use_wiseiouTrue 230行 self.wiou_loss WiseIouLoss(ltypeMPDIoU, monotonousFalse, inner_iouTrue, focaler_iouFalse) 238行 wiou self.wiou_loss(pred_bboxes[fg_mask], target_bboxes[fg_mask], ret_iouFalse…...
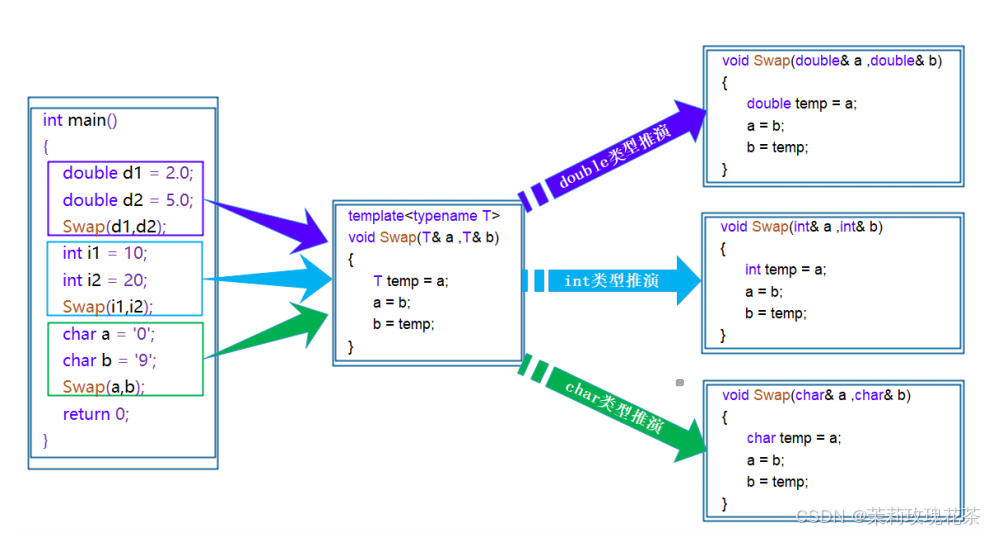
C++模板(初阶)
1.引入 在之前的笔记中有提到:函数重载(特别是交换函数(Swap)的实现) void Swap(int& left, int& right) {int temp left;left right;right temp; } void Swap(double& left, double& right) {do…...

下面关于Date类的描述错误的一项是?
下面关于Date类的描述错误的一项是? A. java.util.Date类下有三个子类:java.sql.Date、java.sql.Timestamp、java.sql.Time; B. 利用SimpleDateFormat类可以对java.util.Date类进行格式化显示; C. 直接输出Date类对象就可以取得日…...
【Python面试题收录】Python编程基础练习题①(数据类型+函数+文件操作)
本文所有代码打包在Gitee仓库中https://gitee.com/wx114/Python-Interview-Questions 一、数据类型 第一题(str) 请编写一个Python程序,完成以下任务: 去除字符串开头和结尾的空格。使用逗号(","&#…...
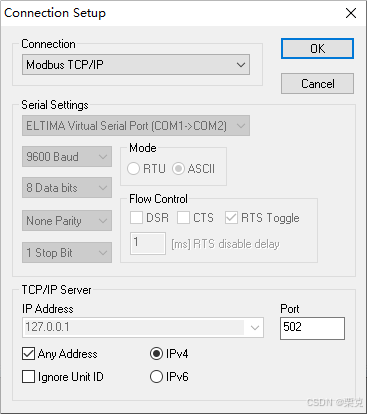
C# Nmodbus,EasyModbusTCP读写操作
Nmodbus读写 两个Button控件分别为 读取和写入 分别使用控件的点击方法 ①引用第三方《NModbus4》2.1.0版本 全局 public SerialPort port new SerialPort("COM2", 9600, Parity.None, 8, (StopBits)1); ModbusSerialMaster master; public Form1() port.Open();…...

spark常用参数调优
目录 1.set spark.grouping.sets.reference.hivetrue;2.set spark.locality.wait.rack0s3.set spark.locality.wait0s;4.set spark.executor.memoryOverhead 2G;5.set spark.sql.shuffle.partitions 1000;6.set spark.shuffle.file.buffer 256k7. set spark.reducer.maxSizeInF…...
C#/WinFrom TCP通信+ 网线插拔检测+客服端异常掉线检测
Winfor Tcp通信(服务端) 今天给大家讲一下C# 关于Tcp 通信部分,这一块的教程网上一大堆,不过关于掉网,异常断开连接的这部分到是到是没有多少说明,有方法 不过基本上最多的两种方式(1.设置一个超时时间,2.…...

一篇文章掌握Python爬虫的80%
转载:一篇文章掌握Python爬虫的80% Python爬虫 Python 爬虫技术在数据采集和信息获取中有着广泛的应用。本文将带你掌握Python爬虫的核心知识,帮助你迅速成为一名爬虫高手。以下内容将涵盖爬虫的基本概念、常用库、核心技术和实战案例。 一、Python 爬虫…...

【用户会话信息在异步事件/线程池的传递】
用户会话信息在异步事件/线程池的传递 author:shengfq date:2024-07-29 version:1.0 背景: 同事写的一个代码功能,是在一个主线程中通过如下代码进行异步任务的执行,结果遇到了问题. 1.ThreadPool.execute(Runnable)启动一个子线程执行异步任务 2.applicationContext.publis…...

Java8: BigDecimal
Java8:BigDecimal 转两位小数的百分数-CSDN博客 BigDecimal 先做除法 然后取绝对值 在Java 8中,如果你想要对一个BigDecimal值进行除法操作,并随后取其绝对值,你可以通过组合divide方法和abs方法来实现这一目的。不过,需要注意的…...

苹果推送iOS 18.1带来Apple Intelligence预览
🦉 AI新闻 🚀 苹果推送iOS 18.1带来Apple Intelligence预览 摘要:苹果向iPhone和iPad用户推送iOS 18.1和iPadOS 18.1开发者预览版Beta更新,带来“Apple Intelligence”预览。目前仅支持M1芯片或更高版本的设备。Apple Intellige…...

testRigor-基于人工智能驱动的无代码自动化测试平台
1、testRigor介绍 简单来说,testRigor是一款基于人工智能驱动的无代码自动化测试平台,它能够通过分析应用的行为模式,智能地生成测试用例,并自动执行这些测试,无需人工编写测试脚本。可以用于Web、移动、API和本机桌面…...

hadoop学习(一)
一.hadoop概述 1.1hadoop优势 1)高可靠性:Hadoop底层维护多个数据副本,即使Hadoop某个计算元素或存储出现故障,也不会导致数据的丢失。 2)高扩展性:在集群间分配任务数据,可方便扩展数以千计…...
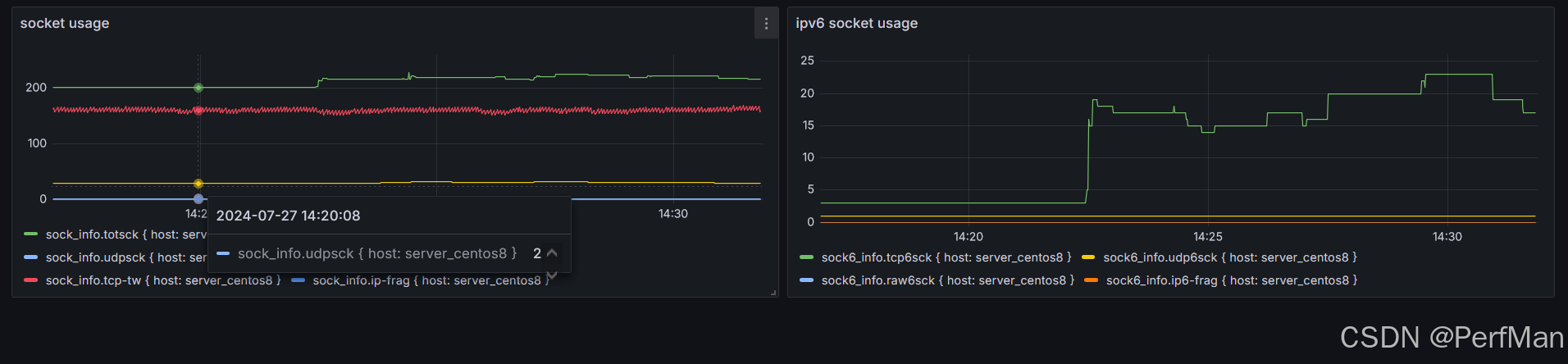
Linux性能监控:sar的可视化方案
在当今的IT环境中,系统性能监控是确保应用程序稳定运行和快速响应问题的关键。Linux作为一种广泛使用的操作系统,拥有多种性能监控工具,其中sar(System Activity Reporter)因其全面性和灵活性被广泛采用。然而…...

零门槛NAS搭建:WinNAS如何让普通电脑秒变私有云?
一、核心优势:专为Windows用户设计的极简NAS WinNAS由深圳耘想存储科技开发,是一款收费低廉但功能全面的Windows NAS工具,主打“无学习成本部署” 。与其他NAS软件相比,其优势在于: 无需硬件改造:将任意W…...
linux之kylin系统nginx的安装
一、nginx的作用 1.可做高性能的web服务器 直接处理静态资源(HTML/CSS/图片等),响应速度远超传统服务器类似apache支持高并发连接 2.反向代理服务器 隐藏后端服务器IP地址,提高安全性 3.负载均衡服务器 支持多种策略分发流量…...
Linux 文件类型,目录与路径,文件与目录管理
文件类型 后面的字符表示文件类型标志 普通文件:-(纯文本文件,二进制文件,数据格式文件) 如文本文件、图片、程序文件等。 目录文件:d(directory) 用来存放其他文件或子目录。 设备…...

React---day11
14.4 react-redux第三方库 提供connect、thunk之类的函数 以获取一个banner数据为例子 store: 我们在使用异步的时候理应是要使用中间件的,但是configureStore 已经自动集成了 redux-thunk,注意action里面要返回函数 import { configureS…...
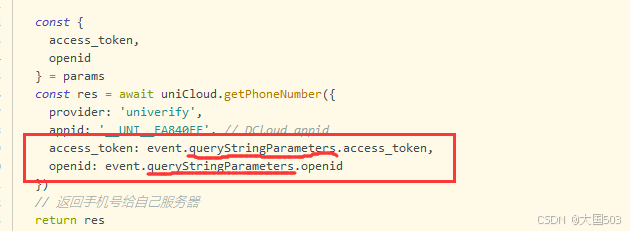
uniapp手机号一键登录保姆级教程(包含前端和后端)
目录 前置条件创建uniapp项目并关联uniClound云空间开启一键登录模块并开通一键登录服务编写云函数并上传部署获取手机号流程(第一种) 前端直接调用云函数获取手机号(第三种)后台调用云函数获取手机号 错误码常见问题 前置条件 手机安装有sim卡手机开启…...

CRMEB 中 PHP 短信扩展开发:涵盖一号通、阿里云、腾讯云、创蓝
目前已有一号通短信、阿里云短信、腾讯云短信扩展 扩展入口文件 文件目录 crmeb\services\sms\Sms.php 默认驱动类型为:一号通 namespace crmeb\services\sms;use crmeb\basic\BaseManager; use crmeb\services\AccessTokenServeService; use crmeb\services\sms\…...
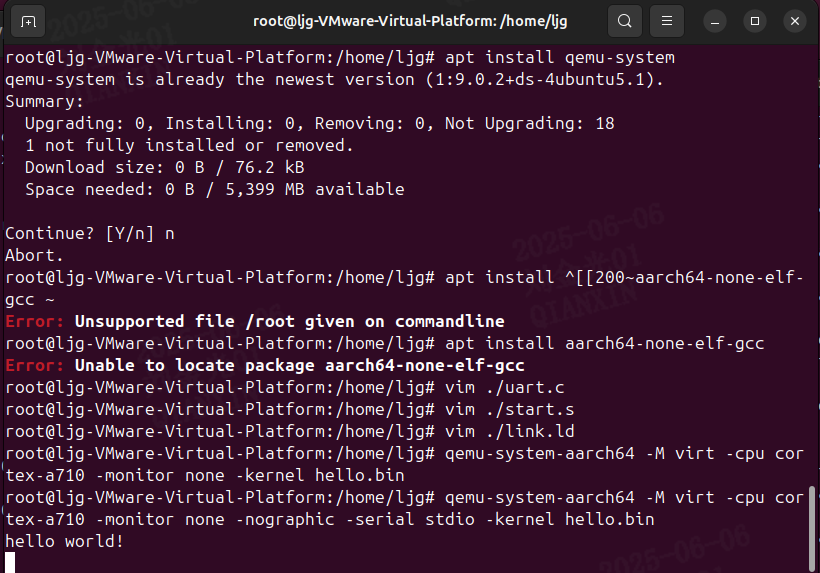
Qemu arm操作系统开发环境
使用qemu虚拟arm硬件比较合适。 步骤如下: 安装qemu apt install qemu-system安装aarch64-none-elf-gcc 需要手动下载,下载地址:https://developer.arm.com/-/media/Files/downloads/gnu/13.2.rel1/binrel/arm-gnu-toolchain-13.2.rel1-x…...
)
安卓基础(Java 和 Gradle 版本)
1. 设置项目的 JDK 版本 方法1:通过 Project Structure File → Project Structure... (或按 CtrlAltShiftS) 左侧选择 SDK Location 在 Gradle Settings 部分,设置 Gradle JDK 方法2:通过 Settings File → Settings... (或 CtrlAltS)…...

Qt的学习(二)
1. 创建Hello Word 两种方式,实现helloworld: 1.通过图形化的方式,在界面上创建出一个控件,显示helloworld 2.通过纯代码的方式,通过编写代码,在界面上创建控件, 显示hello world; …...

Axure Rp 11 安装、汉化、授权
Axure Rp 11 安装、汉化、授权 1、前言2、汉化2.1、汉化文件下载2.2、windows汉化流程2.3、 macOs汉化流程 3、授权 1、前言 Axure Rp 11官方下载链接:https://www.axure.com/downloadthanks 2、汉化 2.1、汉化文件下载 链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/18Clf…...
