Robot Operating System——深度解析单线程执行器(SingleThreadedExecutor)执行逻辑
大纲
- 创建SingleThreadedExecutor
- 新增Node
- add_node
- trigger_entity_recollect
- collect_entities
- 自旋等待
- get_next_executable
- wait_for_work
- get_next_ready_executable
- Timer
- Subscription
- Service
- Client
- Waitable
- AnyExecutable
- execute_any_executable
- 参考资料
在ROS2中,我们设置的各种回调都是在执行器(Executor)中执行的,所以它是整个系统非常核心的组件。

目前,rclcpp 提供了三种 Executor 类型,它们派生自同一个父类Executor。

本文我们将借用《Robot Operating System——单线程中启动多个Node》中的例子,将单线程执行器在最上层的使用方法总结如下
// Create an executor that will be responsible for execution of callbacks for a set of nodes.// With this version, all callbacks will be called from within this thread (the main one).rclcpp::executors::SingleThreadedExecutor exec;rclcpp::NodeOptions options;// Add some nodes to the executor which provide work for the executor during its "spin" function.// An example of available work is executing a subscription callback, or a timer callback.auto server = std::make_shared<composition::Server>(options);exec.add_node(server);// spin will block until work comes in, execute work as it becomes available, and keep blocking.// It will only be interrupted by Ctrl-C.exec.spin();
即:
- 创建SingleThreadedExecutor ;
- 新增Node;
- 自旋等待。
创建SingleThreadedExecutor
SingleThreadedExecutor的构造函数基本就是交给基类rclcpp::Executor的构造函数来实现。
// https://github.com/ros2/rclcpp/blob/jazzy/rclcpp/src/rclcpp/executors/single_threaded_executor.cpp
SingleThreadedExecutor::SingleThreadedExecutor(const rclcpp::ExecutorOptions & options)
: rclcpp::Executor(options) {}
在Executor的构造函数中,我们着重关注成员变量collector_。
Executor::Executor(const rclcpp::ExecutorOptions & options)
: spinning(false),interrupt_guard_condition_(std::make_shared<rclcpp::GuardCondition>(options.context)),shutdown_guard_condition_(std::make_shared<rclcpp::GuardCondition>(options.context)),context_(options.context),notify_waitable_(std::make_shared<rclcpp::executors::ExecutorNotifyWaitable>([this]() {this->entities_need_rebuild_.store(true);})),entities_need_rebuild_(true),collector_(notify_waitable_),wait_set_({}, {}, {}, {}, {}, {}, options.context),current_notify_waitable_(notify_waitable_),impl_(std::make_unique<rclcpp::ExecutorImplementation>())
{shutdown_callback_handle_ = context_->add_on_shutdown_callback([weak_gc = std::weak_ptr<rclcpp::GuardCondition>{shutdown_guard_condition_}]() {auto strong_gc = weak_gc.lock();if (strong_gc) {strong_gc->trigger();}});notify_waitable_->add_guard_condition(interrupt_guard_condition_);notify_waitable_->add_guard_condition(shutdown_guard_condition_);wait_set_.add_waitable(notify_waitable_);
}
collector_是一个集合,它保存了后续要执行的各个Node指针。
/// Collector used to associate executable entities from nodes and guard conditionsrclcpp::executors::ExecutorEntitiesCollector collector_;
新增Node
add_node
业务逻辑的Node会被添加到上面介绍的成员变量collector_中。
// https://github.com/ros2/rclcpp/blob/jazzy/rclcpp/src/rclcpp/executor.cpp
void
Executor::add_node(rclcpp::node_interfaces::NodeBaseInterface::SharedPtr node_ptr, bool notify)
{this->collector_.add_node(node_ptr);try {this->trigger_entity_recollect(notify);} catch (const rclcpp::exceptions::RCLError & ex) {throw std::runtime_error(std::string("Failed to trigger guard condition on node add: ") + ex.what());}
}
然后会调用trigger_entity_recollect方法。
trigger_entity_recollect
这个方法会做两件事:
- 修改std::atomic_bool类型变量entities_need_rebuild_的值为true,进而让collect_entities()被执行。
- 如果notify为true,则会通过interrupt_guard_condition_->trigger()唤醒一个处于等待状态的执行器。
// https://github.com/ros2/rclcpp/blob/jazzy/rclcpp/src/rclcpp/executor.cpp
void
Executor::trigger_entity_recollect(bool notify)
{this->entities_need_rebuild_.store(true);if (!spinning.load() && entities_need_rebuild_.exchange(false)) {std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(mutex_);this->collect_entities();}if (notify) {interrupt_guard_condition_->trigger();}
}
collect_entities
collect_entities主要做两件事:
- 过滤过期的Node以及相关回调函数。
// https://github.com/ros2/rclcpp/blob/jazzy/rclcpp/src/rclcpp/executor.cpp
void
Executor::collect_entities()
{// Updating the entity collection and waitset expires any active resultthis->wait_result_.reset();// Get the current list of available waitables from the collector.rclcpp::executors::ExecutorEntitiesCollection collection;this->collector_.update_collections();auto callback_groups = this->collector_.get_all_callback_groups();rclcpp::executors::build_entities_collection(callback_groups, collection);// We must remove expired entities here, so that we don't continue to use older entities.// See https://github.com/ros2/rclcpp/issues/2180 for more information.current_collection_.remove_expired_entities();
- 更新current_collection_和wait_set_。
// Update each of the groups of entities in the current collection, adding or removing// from the wait set as necessary.current_collection_.timers.update(collection.timers,[this](auto timer) {wait_set_.add_timer(timer);},[this](auto timer) {wait_set_.remove_timer(timer);});current_collection_.subscriptions.update(collection.subscriptions,[this](auto subscription) {wait_set_.add_subscription(subscription, kDefaultSubscriptionMask);},[this](auto subscription) {wait_set_.remove_subscription(subscription, kDefaultSubscriptionMask);});current_collection_.clients.update(collection.clients,[this](auto client) {wait_set_.add_client(client);},[this](auto client) {wait_set_.remove_client(client);});current_collection_.services.update(collection.services,[this](auto service) {wait_set_.add_service(service);},[this](auto service) {wait_set_.remove_service(service);});current_collection_.guard_conditions.update(collection.guard_conditions,[this](auto guard_condition) {wait_set_.add_guard_condition(guard_condition);},[this](auto guard_condition) {wait_set_.remove_guard_condition(guard_condition);});current_collection_.waitables.update(collection.waitables,[this](auto waitable) {wait_set_.add_waitable(waitable);},[this](auto waitable) {wait_set_.remove_waitable(waitable);});// In the case that an entity already has an expired weak pointer// before being removed from the waitset, additionally prune the waitset.this->wait_set_.prune_deleted_entities();
}
自旋等待
spin()内部核心是一个while循环。它会不停使用get_next_executable取出可以运行的Node的回调,然后让execute_any_executable将其执行。
// https://github.com/ros2/rclcpp/blob/jazzy/rclcpp/src/rclcpp/executors/single_threaded_executor.cpp
void
SingleThreadedExecutor::spin()
{if (spinning.exchange(true)) {throw std::runtime_error("spin() called while already spinning");}RCPPUTILS_SCOPE_EXIT(wait_result_.reset();this->spinning.store(false););// Clear any previous result and rebuild the waitsetthis->wait_result_.reset();this->entities_need_rebuild_ = true;while (rclcpp::ok(this->context_) && spinning.load()) {rclcpp::AnyExecutable any_executable;if (get_next_executable(any_executable)) {execute_any_executable(any_executable);}}
}
那么这个while循环会不会导致CPU一直空转呢?答案是:不是。我们可以看get_next_executable的实现。
get_next_executable
// https://github.com/ros2/rclcpp/blob/jazzy/rclcpp/src/rclcpp/executor.cpp
bool
Executor::get_next_executable(AnyExecutable & any_executable, std::chrono::nanoseconds timeout)
{bool success = false;// Check to see if there are any subscriptions or timers needing service// TODO(wjwwood): improve run to run efficiency of this functionsuccess = get_next_ready_executable(any_executable);// If there are noneif (!success) {// Wait for subscriptions or timers to work onwait_for_work(timeout);if (!spinning.load()) {return false;}// Try againsuccess = get_next_ready_executable(any_executable);}return success;
}
它会在底层调用wait_for_work。
wait_for_work
这个方法会一直阻塞到时间超时,或者有回调函数可以被调用。
// https://github.com/ros2/rclcpp/blob/jazzy/rclcpp/src/rclcpp/executor.cpp
void
Executor::wait_for_work(std::chrono::nanoseconds timeout)
{TRACETOOLS_TRACEPOINT(rclcpp_executor_wait_for_work, timeout.count());// Clear any previous wait resultthis->wait_result_.reset();{std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(mutex_);if (this->entities_need_rebuild_.exchange(false) || current_collection_.empty()) {this->collect_entities();}}this->wait_result_.emplace(wait_set_.wait(timeout));if (!this->wait_result_ || this->wait_result_->kind() == WaitResultKind::Empty) {RCUTILS_LOG_WARN_NAMED("rclcpp","empty wait set received in wait(). This should never happen.");} else {if (this->wait_result_->kind() == WaitResultKind::Ready && current_notify_waitable_) {auto & rcl_wait_set = this->wait_result_->get_wait_set().get_rcl_wait_set();if (current_notify_waitable_->is_ready(rcl_wait_set)) {current_notify_waitable_->execute(current_notify_waitable_->take_data());}}}
}
其中主要负责等待的是这句
wait_set_.wait(timeout)
在SingleThreadedExecutor中,由于调用get_next_executable没有传递时间,便采用了默认时间。这样get_next_executable会一直等到有回调可以被执行。这样就避免了CPU空转的问题。
/// Wait for executable in ready state and populate union structure./*** If an executable is ready, it will return immediately, otherwise* block based on the timeout for work to become ready.** \param[out] any_executable populated union structure of ready executable* \param[in] timeout duration of time to wait for work, a negative value* (the defualt behavior), will make this function block indefinitely* \return true if an executable was ready and any_executable was populated,* otherwise false*/RCLCPP_PUBLICboolget_next_executable(AnyExecutable & any_executable,std::chrono::nanoseconds timeout = std::chrono::nanoseconds(-1));
get_next_ready_executable
get_next_ready_executable会按顺序寻找Timer、Subscription、Service 、Client和Waitable中第一个处于可被回调状态的Node。
Timer
bool valid_executable = false;if (!wait_result_.has_value() || wait_result_->kind() != rclcpp::WaitResultKind::Ready) {return false;}if (!valid_executable) {size_t current_timer_index = 0;while (true) {auto [timer, timer_index] = wait_result_->peek_next_ready_timer(current_timer_index);if (nullptr == timer) {break;}current_timer_index = timer_index;auto entity_iter = current_collection_.timers.find(timer->get_timer_handle().get());if (entity_iter != current_collection_.timers.end()) {auto callback_group = entity_iter->second.callback_group.lock();if (!callback_group || !callback_group->can_be_taken_from()) {current_timer_index++;continue;}// At this point the timer is either ready for execution or was perhaps// it was canceled, based on the result of call(), but either way it// should not be checked again from peek_next_ready_timer(), so clear// it from the wait result.wait_result_->clear_timer_with_index(current_timer_index);// Check that the timer should be called still, i.e. it wasn't canceled.any_executable.data = timer->call();if (!any_executable.data) {current_timer_index++;continue;}any_executable.timer = timer;any_executable.callback_group = callback_group;valid_executable = true;break;}current_timer_index++;}}
Subscription
if (!valid_executable) {while (auto subscription = wait_result_->next_ready_subscription()) {auto entity_iter = current_collection_.subscriptions.find(subscription->get_subscription_handle().get());if (entity_iter != current_collection_.subscriptions.end()) {auto callback_group = entity_iter->second.callback_group.lock();if (!callback_group || !callback_group->can_be_taken_from()) {continue;}any_executable.subscription = subscription;any_executable.callback_group = callback_group;valid_executable = true;break;}}}
Service
if (!valid_executable) {while (auto service = wait_result_->next_ready_service()) {auto entity_iter = current_collection_.services.find(service->get_service_handle().get());if (entity_iter != current_collection_.services.end()) {auto callback_group = entity_iter->second.callback_group.lock();if (!callback_group || !callback_group->can_be_taken_from()) {continue;}any_executable.service = service;any_executable.callback_group = callback_group;valid_executable = true;break;}}}
Client
if (!valid_executable) {while (auto client = wait_result_->next_ready_client()) {auto entity_iter = current_collection_.clients.find(client->get_client_handle().get());if (entity_iter != current_collection_.clients.end()) {auto callback_group = entity_iter->second.callback_group.lock();if (!callback_group || !callback_group->can_be_taken_from()) {continue;}any_executable.client = client;any_executable.callback_group = callback_group;valid_executable = true;break;}}}
Waitable
if (!valid_executable) {while (auto waitable = wait_result_->next_ready_waitable()) {auto entity_iter = current_collection_.waitables.find(waitable.get());if (entity_iter != current_collection_.waitables.end()) {auto callback_group = entity_iter->second.callback_group.lock();if (!callback_group || !callback_group->can_be_taken_from()) {continue;}any_executable.waitable = waitable;any_executable.callback_group = callback_group;any_executable.data = waitable->take_data();valid_executable = true;break;}}}
AnyExecutable
// https://github.com/ros2/rclcpp/blob/jazzy/rclcpp/include/rclcpp/any_executable.hpp
struct AnyExecutable
{RCLCPP_PUBLICAnyExecutable();RCLCPP_PUBLICvirtual ~AnyExecutable();// Only one of the following pointers will be set.rclcpp::SubscriptionBase::SharedPtr subscription;rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer;rclcpp::ServiceBase::SharedPtr service;rclcpp::ClientBase::SharedPtr client;rclcpp::Waitable::SharedPtr waitable;// These are used to keep the scope on the containing itemsrclcpp::CallbackGroup::SharedPtr callback_group {nullptr};rclcpp::node_interfaces::NodeBaseInterface::SharedPtr node_base {nullptr};std::shared_ptr<void> data {nullptr};
};
execute_any_executable
找到可以执行的Node后,便可以调用execute_any_executable让其执行。
在execute_any_executable内部,我们看到它也是区分Timer、Subscription、Service 、Client和Waitable类型来执行的。
// https://github.com/ros2/rclcpp/blob/jazzy/rclcpp/src/rclcpp/executor.cpp
void
Executor::execute_any_executable(AnyExecutable & any_exec)
{if (!spinning.load()) {return;}assert((void("cannot execute an AnyExecutable without a valid callback group"),any_exec.callback_group));if (any_exec.timer) {TRACETOOLS_TRACEPOINT(rclcpp_executor_execute,static_cast<const void *>(any_exec.timer->get_timer_handle().get()));execute_timer(any_exec.timer, any_exec.data);}if (any_exec.subscription) {TRACETOOLS_TRACEPOINT(rclcpp_executor_execute,static_cast<const void *>(any_exec.subscription->get_subscription_handle().get()));execute_subscription(any_exec.subscription);}if (any_exec.service) {execute_service(any_exec.service);}if (any_exec.client) {execute_client(any_exec.client);}if (any_exec.waitable) {const std::shared_ptr<void> & const_data = any_exec.data;any_exec.waitable->execute(const_data);}// Reset the callback_group, regardless of typeany_exec.callback_group->can_be_taken_from().store(true);
}
参考资料
- https://docs.ros.org/en/rolling/Concepts/Intermediate/About-Executors.html#executors
相关文章:

Robot Operating System——深度解析单线程执行器(SingleThreadedExecutor)执行逻辑
大纲 创建SingleThreadedExecutor新增Nodeadd_nodetrigger_entity_recollectcollect_entities 自旋等待get_next_executablewait_for_workget_next_ready_executableTimerSubscriptionServiceClientWaitableAnyExecutable execute_any_executable 参考资料 在ROS2中,…...

【TS】使用npm全局安装typescript
查看npm安装 npm -v 安装typescript npm i -g typescript 查看安装 tsc 这就是标致着安装完成。...

安全用户角色权限
$PATH 搞系统设置设置⾥头path ⽬标包含mysql 可执⾏⽂件,那么就是由使⽤ 在终端使⽤ ./bin/mysql -h192.168.71.164 -P3306 -uroot -proot 1.远程登录前提条件是mysql.user表中的host属性为%,如果是 localhost就不允许远程登录,update…...

代理模式学习
代理模式 代理模式是常用的java设计模式,他的特征是代理类与委托类有同样的接口,代理类主要负责为委托类预处理消息、过滤消息、把消息转发给委托类,以及事后处理消息等。代理类与委托类之间通常会存在关联关系,一个代理类的对象…...

深入理解Go 语言信号量 Semaphore
1. 什么是信号量 信号量的概念是荷兰计算机科学家 1.1 P/V 操作 Dijkstra 在他的论文中为信号量定义了两个操作 : P 和 V 。 1.2 信号量和互斥锁的区别与联系 信号量有两种类型:二元信号量和计数信号量。 2. 信号量的 channel 实现 程序在运行时,…...

VisualStudio2019下载与安装
1.下载 通过百度网盘分享的文件:VisualStudio2019 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/16tqm0ZsOkmXTfGmi4LnGbA 提取码:wx60 --来自百度网盘超级会员V3的分享 2.安装...

李宏毅老师机器学习常见英语词汇
目录 1.Regression :回归2.Classification:分类3.local minima:局部最小值4.saddle point:鞍点5.ground truth:它是机器学习算法的参考标准,用于衡量模型的性的和判断模型的准确性6.optimization:优化 1.Regression :回归 2.Clas…...

人工智能时代,程序员如何保持核心竞争力?
人工智能时代,程序员如何保持核心竞争力? 随着AIGC(如chatgpt、midjourney、claude等)大语言模型接二连三的涌现,AI辅助编程工具日益普及,程序员的工作方式正在发生深刻变革。有人担心AI可能取代部分编程工…...

WiFi to Ethernet: 树莓派共享无线连接至有线网口,自动通过Captive Poartal网页登录认证
物联网开发系列:物联网开发之旅① WiFi to Ethernet: 树莓派共享无线连接至有线网口,自动通过Captive Poartal验证物联网开发番外篇之 Captive Portal验证原理 文章目录 背景实现工具实现细节一、将无线连接共享到以太网1. 配置静态IP地址2. 启用IP转发3…...

【神软大数据治理平台-高级动态SQL(接口开发)】
1、背景 业务部门需大数据平台按照所提需求提供企业数据接口,基于神软大数据治理平台-高级动态SQL功能,满足业务需求,如下: (1)业务系统需求: 输入: enterpriseName:…...

【Java数据结构】Map和Set超详细两万字讲解(内含搜索树+哈希表)
🔒文章目录: 1.❤️❤️前言~🥳🎉🎉🎉 2. Map和Set的基础概念 3.Map的基础使用 4.Set的基础使用 5. TreeMap的本质——红黑树 5.1二叉搜索树的概念 5.2二叉搜索树的模拟实现 二叉搜索树——查找 二…...

中国制造2025,会抛弃精益生产吗?
时至今日,“精益生产”模式依旧大行其道,它始终支持着中国制造业以最低的成本做出优质产品。我们认为,纵然是中国制造2025成为现实,精益生产模式也仍然是整个制造业的精髓之一。 首先,精益生产模式最重要的一根脊梁就是…...

Rust 循环
Rust 循环 在编程语言中,循环是一种重要的控制结构,它允许我们重复执行一段代码直到满足特定的条件。Rust 语言提供了多种循环方式,每种方式都有其特定的用途和语法。本文将详细介绍 Rust 中的循环,包括 loop、while、while let、…...

数据结构(其四)--特殊矩阵的存储
目录 11.特殊矩阵的压缩存储 (1).一维数组的储存结构 (2).二维数组的存储结构 (3).普通矩阵的存储 (4).特殊矩阵的压缩存储 i.对称矩阵 ii.三角矩阵 iii.三对角矩阵 iiii.稀疏矩…...

系统化学习 H264视频编码(06)哥伦布编码
说明:我们参考黄金圈学习法(什么是黄金圈法则?->模型 黄金圈法则,本文使用:why-what)来学习音H264视频编码。本系列文章侧重于理解视频编码的知识体系和实践方法,理论方面会更多地讲清楚 音视频中概念的…...

手机在网状态接口如何对接?(一)
一、什么是手机在网状态? 传入手机号码,查询该手机号的在网状态,返回内容有正常使用、停机、在网但不可用、不在网(销号/未启用/异常)、预销户等多种状态。 二、手机在网状态使用场景? 1.信贷审核&#…...

数据结构链表2(常考习题1)(C语言)
移除链表元素: . - 力扣(LeetCode) 题目: 给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。 解题思路: 情况1: 情…...

Rust的运行时多态
Rust的运行时多态 Rust的静态多态即编译时多态,通过**泛型特征约束(Generic Type Trait Constrait)**来实现; 那么动态多态(运行时多态)呢?答案是特征对象(Trait Objectÿ…...

sqllabs通关
sqllabs5:(报错注入) ?id1 回显You are in........... ?id2-1 回显You are in........... ?id1 回显 1 LIMIT 0,1 判断是字符型,闭合。?id1order by 3-- //页面显示正常我们试了4行得出是报错注入 我们先爆库名 http://127.0.0.1/sqli-labs-master/L…...
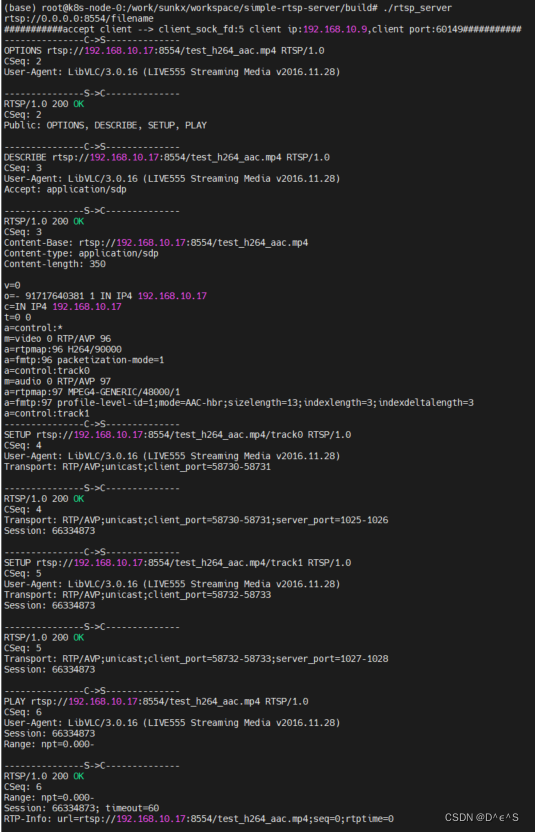
RTSP系列四:RTSP Server/Client实战项目
RTSP系列: RTSP系列一:RTSP协议介绍-CSDN博客 RTSP系列二:RTSP协议鉴权-CSDN博客 RTSP系列三:RTP协议介绍-CSDN博客 RTSP系列四:RTSP Server/Client实战项目-CSDN博客 目录 一、RTSP Server实战项目 1、准备 2、…...

应用升级/灾备测试时使用guarantee 闪回点迅速回退
1.场景 应用要升级,当升级失败时,数据库回退到升级前. 要测试系统,测试完成后,数据库要回退到测试前。 相对于RMAN恢复需要很长时间, 数据库闪回只需要几分钟。 2.技术实现 数据库设置 2个db_recovery参数 创建guarantee闪回点,不需要开启数据库闪回。…...
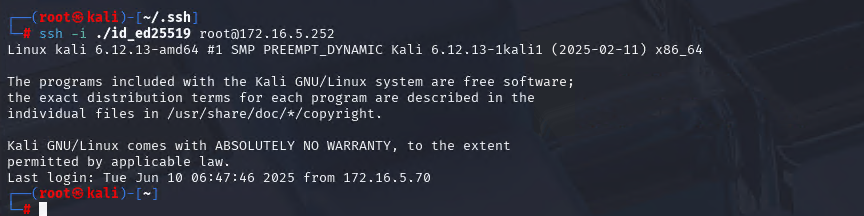
Xshell远程连接Kali(默认 | 私钥)Note版
前言:xshell远程连接,私钥连接和常规默认连接 任务一 开启ssh服务 service ssh status //查看ssh服务状态 service ssh start //开启ssh服务 update-rc.d ssh enable //开启自启动ssh服务 任务二 修改配置文件 vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config //第一…...

关于iview组件中使用 table , 绑定序号分页后序号从1开始的解决方案
问题描述:iview使用table 中type: "index",分页之后 ,索引还是从1开始,试过绑定后台返回数据的id, 这种方法可行,就是后台返回数据的每个页面id都不完全是按照从1开始的升序,因此百度了下,找到了…...

智能在线客服平台:数字化时代企业连接用户的 AI 中枢
随着互联网技术的飞速发展,消费者期望能够随时随地与企业进行交流。在线客服平台作为连接企业与客户的重要桥梁,不仅优化了客户体验,还提升了企业的服务效率和市场竞争力。本文将探讨在线客服平台的重要性、技术进展、实际应用,并…...

linux 错误码总结
1,错误码的概念与作用 在Linux系统中,错误码是系统调用或库函数在执行失败时返回的特定数值,用于指示具体的错误类型。这些错误码通过全局变量errno来存储和传递,errno由操作系统维护,保存最近一次发生的错误信息。值得注意的是,errno的值在每次系统调用或函数调用失败时…...

拉力测试cuda pytorch 把 4070显卡拉满
import torch import timedef stress_test_gpu(matrix_size16384, duration300):"""对GPU进行压力测试,通过持续的矩阵乘法来最大化GPU利用率参数:matrix_size: 矩阵维度大小,增大可提高计算复杂度duration: 测试持续时间(秒&…...

MySQL用户和授权
开放MySQL白名单 可以通过iptables-save命令确认对应客户端ip是否可以访问MySQL服务: test: # iptables-save | grep 3306 -A mp_srv_whitelist -s 172.16.14.102/32 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 3306 -j ACCEPT -A mp_srv_whitelist -s 172.16.4.16/32 -p tcp -m tcp -…...
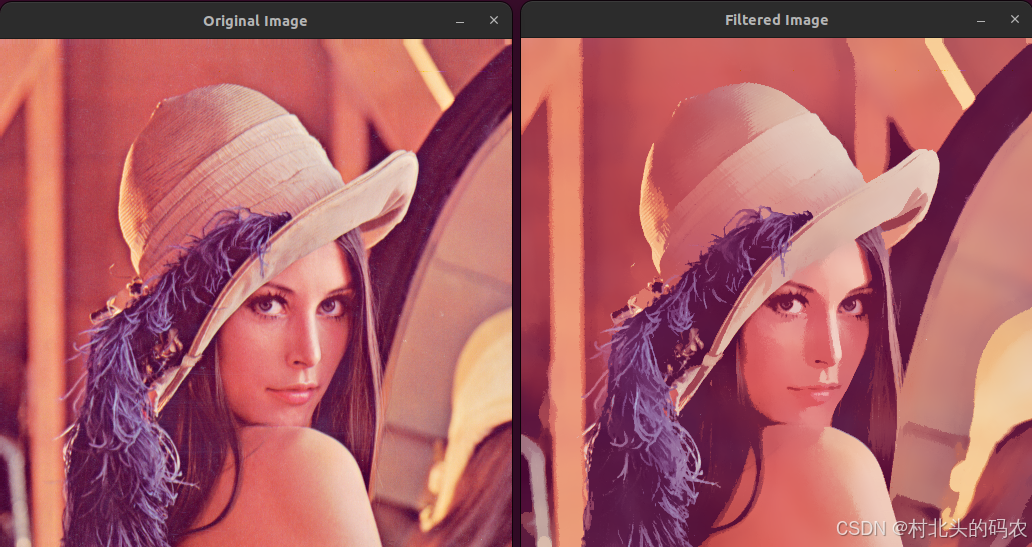
OPenCV CUDA模块图像处理-----对图像执行 均值漂移滤波(Mean Shift Filtering)函数meanShiftFiltering()
操作系统:ubuntu22.04 OpenCV版本:OpenCV4.9 IDE:Visual Studio Code 编程语言:C11 算法描述 在 GPU 上对图像执行 均值漂移滤波(Mean Shift Filtering),用于图像分割或平滑处理。 该函数将输入图像中的…...
)
安卓基础(aar)
重新设置java21的环境,临时设置 $env:JAVA_HOME "D:\Android Studio\jbr" 查看当前环境变量 JAVA_HOME 的值 echo $env:JAVA_HOME 构建ARR文件 ./gradlew :private-lib:assembleRelease 目录是这样的: MyApp/ ├── app/ …...

《C++ 模板》
目录 函数模板 类模板 非类型模板参数 模板特化 函数模板特化 类模板的特化 模板,就像一个模具,里面可以将不同类型的材料做成一个形状,其分为函数模板和类模板。 函数模板 函数模板可以简化函数重载的代码。格式:templa…...
