C++的STL简介(四)
目录
1.List
2.list 模拟实现
2.1基本框架
2.2 list_node
2.3 list
2.3.1 默认构造
2.3.2 析构函数
2.3.3 begin()
2.3.4 end()
2.3.5 size()
2.3.6 empty()
2.3.7 insert()
2.3.8 push_back()
2.3.9 push_front()
2.3.10 erase ()
2.3.11 pop_back()
2.3.12 pop_front()
2.4 list_iterator
2.4.1 - >
2.4.2 *
2.4.3 前置++
2.4.4 后置++
2.4.5 前置--
2.4.6 后置 --
2.4.7 !=
2.4.8 list_iterator完整代码
2.5 list_const_iterator
3.整个实现完整代码
1.List
-
List是连续的容器,而vector是非连续的容器,即list将元素存储在连续的存储器中,而vector存储在不连续的存储器中。
-
向量(vector)中间的插入和删除是非常昂贵的,因为它需要大量的时间来移动所有的元素。链表克服了这个问题,它是使用list容器实现的。
-
List支持双向,并为插入和删除操作提供了一种有效的方法。
-
在列表中遍历速度很慢,因为列表元素是按顺序访问的,而vector支持随机访问。
2.list 模拟实现
2.1基本框架
list_node来实现每个节点,list_iterator和list_const_iterator是两个不同版本的迭代器一个是普通迭代器一个是const类型的迭代器,名字上也有所区分,list本身就有迭代器的效果,这个是为了模拟这个,重载了一些基本运算符,而list是统一管理节点,具有增删查改等效果
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
#include <algorithm> // For std::reverseusing namespace std;namespace List
{// 节点类template<class T>class list_node{public:T _data;list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;list_node(const T& data = T()): _data(data), _next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr){}};//list迭代器template<class T>struct list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T> Self;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node): _node(node){ }};//const版本迭代器template<class T>struct list_const_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_const_iterator<T> Self;Node* _node;// 修正: list_const_iterator 的构造函数应该接受 Node* 类型list_const_iterator(Node* node): _node(node){ }};
//实现listtemplate<class T>class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef list_iterator<T> iterator;typedef list_const_iterator<T> const_iterator;list(){_head = new Node(T());_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}~list(){while (!empty()){pop_front();}delete _head;}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};}
2.2 list_node
定义节点
template<class T>class list_node{public:T _data;list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;list_node(const T& data = T()): _data(data), _next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr){}};2.3 list
维护节点
//实现listtemplate<class T>class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef list_iterator<T> iterator;typedef list_const_iterator<T> const_iterator;list(){_head = new Node(T());_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}~list(){while (!empty()){pop_front();}delete _head;}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};
2.3.1 默认构造
//默认构造list(){_head = new Node(T());_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}2.3.2 析构函数
//析构函数~list(){while (!empty()){pop_front();}delete _head;}2.3.3 begin()
开始位置的迭代器
//begin()iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}//const const_iterator begin() const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}
2.3.4 end()
结尾位置的迭代器
//普通版iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}//const版const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(_head);}2.3.5 size()
数据个数
size_t size() const{return _size;}2.3.6 empty()
判空
bool empty() const{return _size == 0;}2.3.7 insert()
指定位置插入
void insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);//prev newnode curnewnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;prev->_next = newnode;++_size;}2.3.8 push_back()
尾插
void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}2.3.9 push_front()
头插
void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}2.3.10 erase ()
指定位置删除
void erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;Node* next = pos._node->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete pos._node;--_size;}
2.3.11 pop_back()
尾删
void pop_back(){erase(--end());}2.3.12 pop_front()
头删
void pop_front(){erase(begin());}2.3.13 list完整代码
template<class T>class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef list_iterator<T> iterator;typedef list_const_iterator<T> const_iterator;list(){_head = new Node(T());_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}const_iterator begin() const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(_head);}size_t size() const{return _size;}bool empty() const{return _size == 0;}void insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);//prev newnode curnewnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;prev->_next = newnode;++_size;}void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;Node* next = pos._node->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete pos._node;--_size;}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}~list(){while (!empty()){pop_front();}delete _head;}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};2.4 list_iterator
为了支持list迭代器效果而模拟实现了一个迭代器
template<class T>struct list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T> Self;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node): _node(node){ }};2.4.1 - >
// 修正: 返回指向 _data 的指针,而不是引用T* operator->(){return &_node->_data;}
2.4.2 *
T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}2.4.3 前置++
Self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}2.4.4 后置++
Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}2.4.5 前置--
Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}
2.4.6 后置 --
Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}2.4.7 !=
bool operator!=(const Self& x) const{return _node != x._node;}
2.4.8 list_iterator完整代码
template<class T>struct list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T> Self;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node): _node(node){ }// 修正: 返回指向 _data 的指针,而不是引用T* operator->(){return &_node->_data;}T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}Self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& x) const{return _node != x._node;}};2.5 list_const_iterator
list_const_iterator和list_iterator实现原理一致,只是有些成员函数被const修饰,typedef了const
template<class T>struct list_const_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_const_iterator<T> Self;Node* _node;// 修正: list_const_iterator 的构造函数应该接受 Node* 类型list_const_iterator(Node* node): _node(node){ }// 修正: 返回指向 _data 的 const 指针,而不是引用const T* operator->() const{return &_node->_data;}const T& operator*() const{return _node->_data;}Self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& x) const{return _node != x._node;}};
3.整个实现完整代码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
#include <algorithm> // For std::reverseusing namespace std;namespace List
{// 节点类template<class T>class list_node{public:T _data;list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;list_node(const T& data = T()): _data(data), _next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr){}};template<class T>struct list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T> Self;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node): _node(node){ }// 修正: 返回指向 _data 的指针,而不是引用T* operator->(){return &_node->_data;}T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}Self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& x) const{return _node != x._node;}};template<class T>struct list_const_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_const_iterator<T> Self;Node* _node;// 修正: list_const_iterator 的构造函数应该接受 Node* 类型list_const_iterator(Node* node): _node(node){ }// 修正: 返回指向 _data 的 const 指针,而不是引用const T* operator->() const{return &_node->_data;}const T& operator*() const{return _node->_data;}Self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& x) const{return _node != x._node;}};template<class T>class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef list_iterator<T> iterator;typedef list_const_iterator<T> const_iterator;list(){_head = new Node(T());_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}const_iterator begin() const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(_head);}size_t size() const{return _size;}bool empty() const{return _size == 0;}void insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);//prev newnode curnewnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;prev->_next = newnode;++_size;}void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;Node* next = pos._node->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete pos._node;--_size;}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}~list(){while (!empty()){pop_front();}delete _head;}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};void test1(){list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;}
}
相关文章:
)
C++的STL简介(四)
目录 1.List 2.list 模拟实现 2.1基本框架 2.2 list_node 2.3 list 2.3.1 默认构造 2.3.2 析构函数 2.3.3 begin() 2.3.4 end() 2.3.5 size() 2.3.6 empty() 2.3.7 inser…...

NIO专题学习(一)
一、BIO/NIO/AIO介绍 1. 背景说明 在Java的软件设计开发中,通信架构是不可避免的。我们在进行不同系统或者不同进程之间的数据交互,或者在高并发的通信场景下都需要用到网络通信相关的技术。 对于一些经验丰富的程序员来说,Java早期的网络…...

Linux学习笔记:Linux基础知识汇总(个人复习版)
常用命令: 1、ls -a:显示所有文件(包括隐藏文件),简洁版 -l:显示所有文件,详细版 -R:显示所有文件以及子目录下文件,简洁版 可以搭配使用。 2、netstat -i&#x…...

MSR020/MSR040低温漂、低功耗电压基准
MSR020/MSR040 是低温漂、低功耗、高精度 CMOS 电压基准, 具有 0.05% 初始精度和低功耗的特点。 该器件的低输出电压迟滞和低长期输出电压漂移的 特性,可以进一步提高稳定性和系统可靠性。 此外,器 件的小尺寸和低工作电流的特性使其非…...

一个是生产打包的时候, 一个是本地测试启动的时候,maven如何配置?
在Maven项目中,使用两套不同的pom.xml配置分别用于生产打包和本地测试启动是常见需求,尤其当你需要调整依赖范围、插件配置或使用不同资源文件时。Maven通过profiles和activeProfiles提供了灵活的配置管理方案,允许你为不同的环境或构建场景定…...

公文字体包下载
https://zuzhibu.xaufe.edu.cn/info/1063/3421.htm 下载解压后,将相应字体文件粘贴至C:\Windows\Fonts 等待安装完成就可以了...

主从备份及安装准备
主从复制 学习内容 1. 备份的三种类型 1. 热备份 2. 逻辑备份 3. 物理备份 2. 情景 ⼊职企业,发现企业架构为⼀主多从,但是两台从服务器和主库不同 步,但是每天会全库北⽅主服务器上的数据到从服务器,由于数据量 不是很⼤&a…...

翻译英文的软件,分享3款翻译神器!
在这个全球化的时代,跨越语言障碍成为了我们连接世界的桥梁。无论你是旅行爱好者、国际商务人士,还是学习新语言的求知者,一款高效、准确的翻译软件都是不可或缺的伙伴。今天,就让我们一起探索那些让沟通无界限的翻译神器…...

软件测试解读——性能效率测试
一、性能效率测试概述 性能效率(efficiency)为GB/T 25000.51-2016标准中提及的软件产品的八大产品质量特征之一。性能效率测试用于评估待测系统与软件在给定的时间和其他资源限制下完成其指定功能的程度,也称作性能测试。 为完成系统与软件性能测试,…...

【PLC】子程序功能心得
博主用GX Works编程的时候用到子程序,这里给大家和自己强调一下,每个子程序一定要以SRET结束,尤其是有多个子程序的时候 博主吃了个大亏,由于有两个子程序,结果第一个子程序没有写SRET,结果两个子程序默认以…...

Iris for mac 好用的录屏软件
Iris 是一款高性能屏幕录像机,可录制到 h.264。Iris 在可用时利用板载 GPU 加速。它可以选择包括来自摄像头和最多两个麦克风的视频。 兼容性 所有功能在macOS 11.0-14上完全支持,包括macOS Sonoma。 简单编码 直接录制为h.264、h.265、ProRes或Motion…...

Transformers实战05-模型量化
文章目录 简介主要类型量化的优点量化的缺点量化过程量化过程反量化过程 精度和参数 量化实例bitsandbytes安装bitsandbytes4bit量化(加载)8bit量化(加载)验证效果 简介 模型量化(Model Quantization)是一种优化技术,旨在减少机器学习模型的…...

【Python】bytes 和 bytearray 到底是什么类型呢?
bytes和bytearray同属于二进制序列类型,是常见的数值类型的一种。 bytes多用在在文件的读写、网络通信、数据编码/解码等场景用的比较多。 而bytearray在二进制数据处理、图像处理、内存映射文件和网络通信等场景用的比较多。 其中这两部分的主要差别: …...

Windows10上安装SQL Server 2022 Express
Microsoft SQL Server 2022 Express是一个功能强大且可靠的免费数据管理系统,可为轻量级网站和桌面应用程序提供丰富可靠的数据存储,为关系数据库: (1).LocalDB(SqlLocalDB):是Express的一种轻型版本,该版本具备所有可…...

C++11 异常
目录 0.前言 1.C语言传统错误处理方式 1.1使用返回值 1.2使用全局变量 1.3使用断言 1.4优缺点 2.C异常的概念 3.异常的使用 3.1异常的抛出和捕获 3.1.1异常的抛出和匹配原则 3.1.2在函数调用链中异常栈展开匹配原则 3.2异常的重新抛出 3.3异常安全 3.4异常规范 4.自定义异常体系…...

pip下载lap失败
把pip install lap改为pip intsall lapx...

【Material-UI】Button 中的点击事件处理(Handling clicks)详解
文章目录 一、点击事件处理基础1. 基本用法2. 事件处理器的传递 二、实际应用中的注意事项1. 事件处理逻辑的优化2. 避免过多的状态更新3. 使用合适的事件类型 三、关于文档中未提及的原生属性四、最佳实践1. 无障碍性2. 视觉反馈3. 防止重复点击 五、总结 在现代前端开发中&am…...

Spring Cache框架(AOP思想)+ Redis实现数据缓存
文章目录 1 简介1.1 基本介绍1.2 为什么要用 Spring Cache? 2 使用方法2.1 依赖导入(Maven)2.2 常用注解2.3 使用步骤2.4 常用注解说明1)EnableCaching2)CachePut3)Cacheable4)CacheEvict 3 注意…...

在Windows编程中,MFC\C++中如何在OnCopyData中传递Vector类型数据?
我们在通过 WM_COPYDATA 消息实现进程间通信时,发送char 数组或其他类型数组与发送vector是有区别的。 1、发送基础类型时,直接发送指针。 typedef struct tagMYSTRUCT {int nTest;wchar_t cTest[40] {0}; } MYSTRUCT, *PMYSTRUCT;MYSTRUCT stSend; s…...

Java常见面试题-01-java基础
文章目录 面向对象的特征Java 的基本数据类型有哪些JDK、JRE、JVM 的区别重载和重写的区别Java 中和 equals 的区别String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder 三者之间的区别接口和抽象类的区别是什么string 常用的方法有哪些什么是单例模式?有几种?什么是反…...
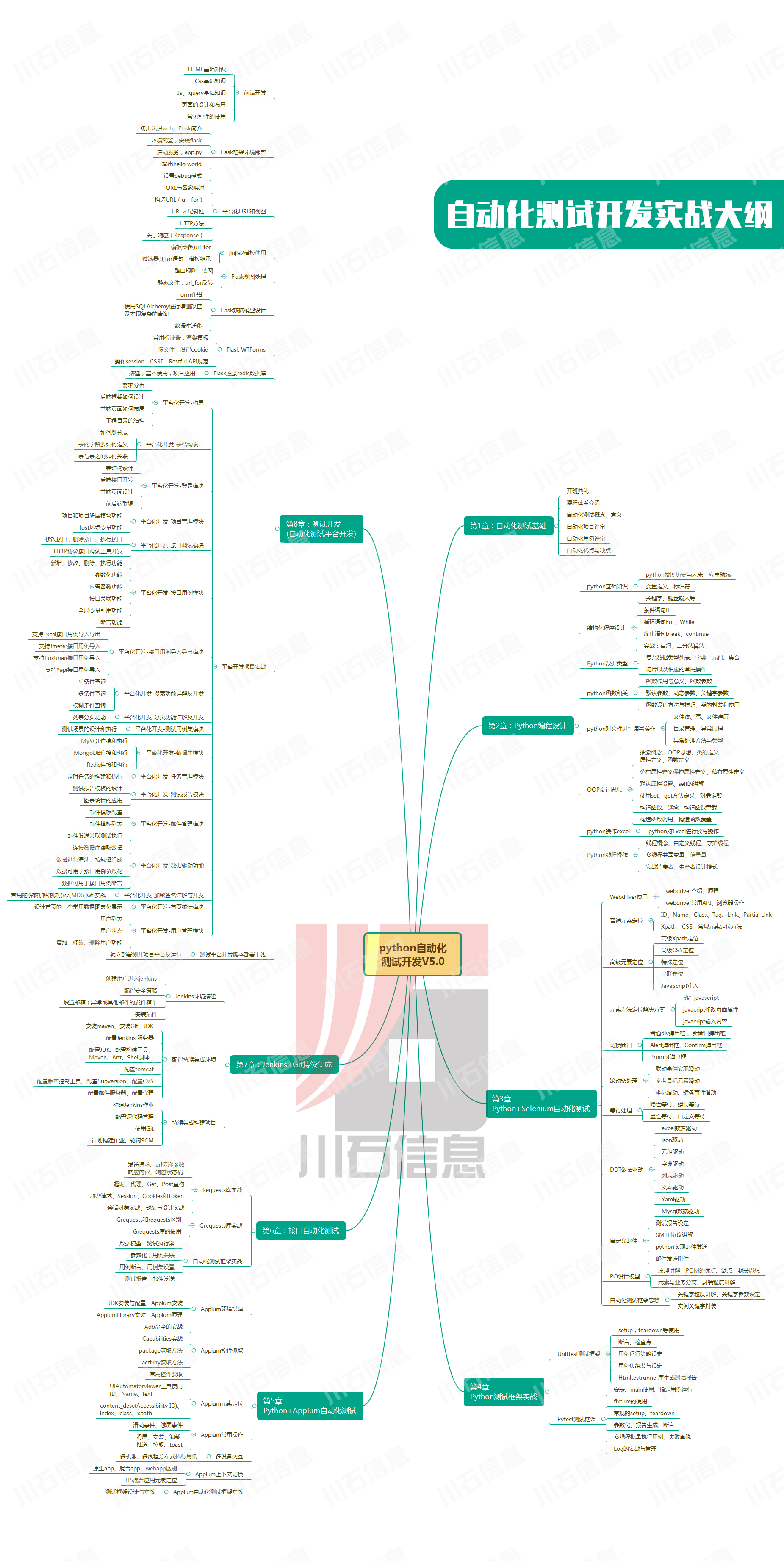
接口测试中缓存处理策略
在接口测试中,缓存处理策略是一个关键环节,直接影响测试结果的准确性和可靠性。合理的缓存处理策略能够确保测试环境的一致性,避免因缓存数据导致的测试偏差。以下是接口测试中常见的缓存处理策略及其详细说明: 一、缓存处理的核…...
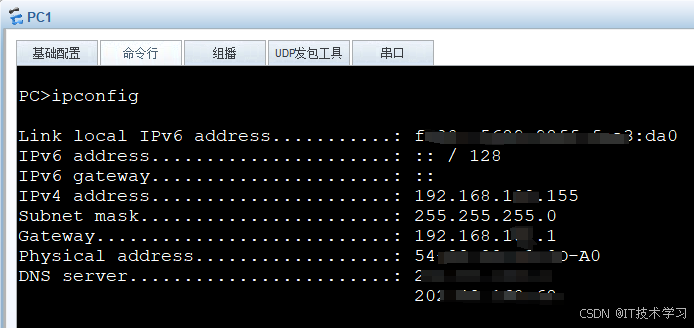
eNSP-Cloud(实现本地电脑与eNSP内设备之间通信)
说明: 想象一下,你正在用eNSP搭建一个虚拟的网络世界,里面有虚拟的路由器、交换机、电脑(PC)等等。这些设备都在你的电脑里面“运行”,它们之间可以互相通信,就像一个封闭的小王国。 但是&#…...
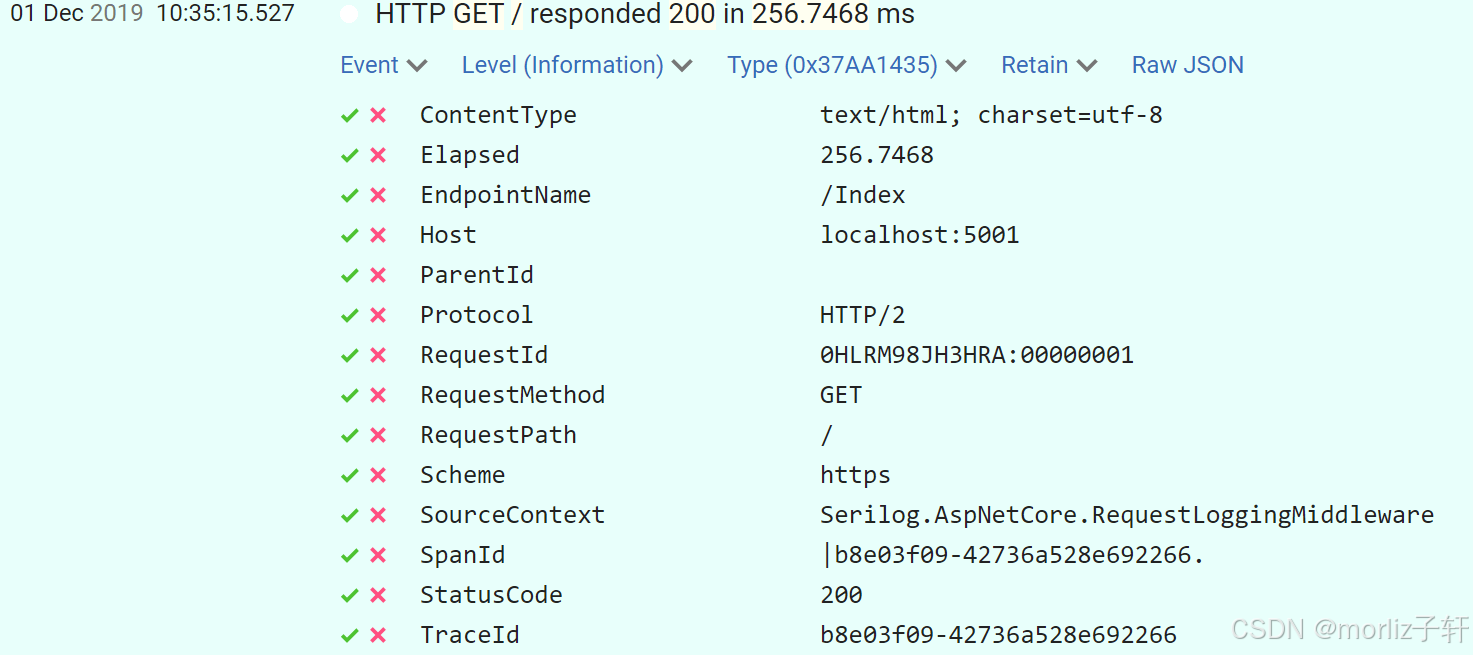
深入浅出Asp.Net Core MVC应用开发系列-AspNetCore中的日志记录
ASP.NET Core 是一个跨平台的开源框架,用于在 Windows、macOS 或 Linux 上生成基于云的新式 Web 应用。 ASP.NET Core 中的日志记录 .NET 通过 ILogger API 支持高性能结构化日志记录,以帮助监视应用程序行为和诊断问题。 可以通过配置不同的记录提供程…...

零门槛NAS搭建:WinNAS如何让普通电脑秒变私有云?
一、核心优势:专为Windows用户设计的极简NAS WinNAS由深圳耘想存储科技开发,是一款收费低廉但功能全面的Windows NAS工具,主打“无学习成本部署” 。与其他NAS软件相比,其优势在于: 无需硬件改造:将任意W…...
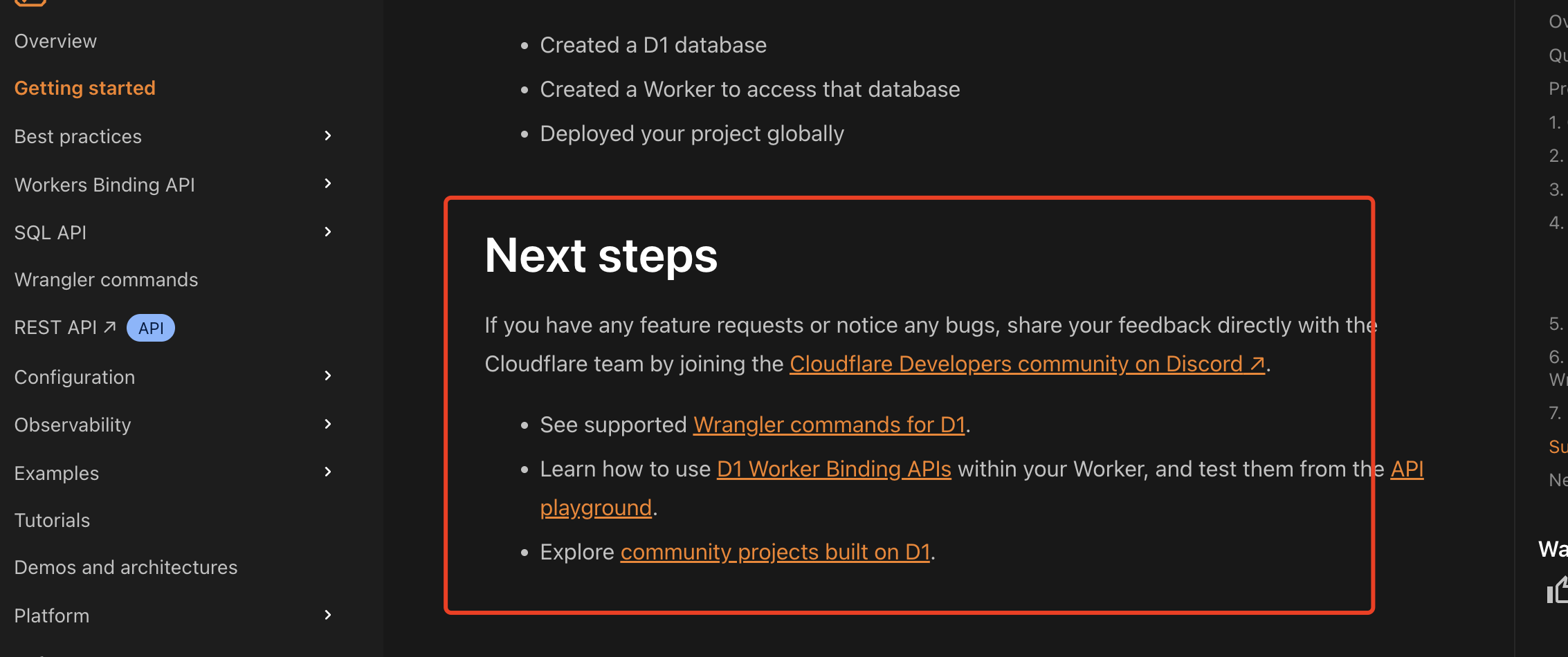
通过Wrangler CLI在worker中创建数据库和表
官方使用文档:Getting started Cloudflare D1 docs 创建数据库 在命令行中执行完成之后,会在本地和远程创建数据库: npx wranglerlatest d1 create prod-d1-tutorial 在cf中就可以看到数据库: 现在,您的Cloudfla…...
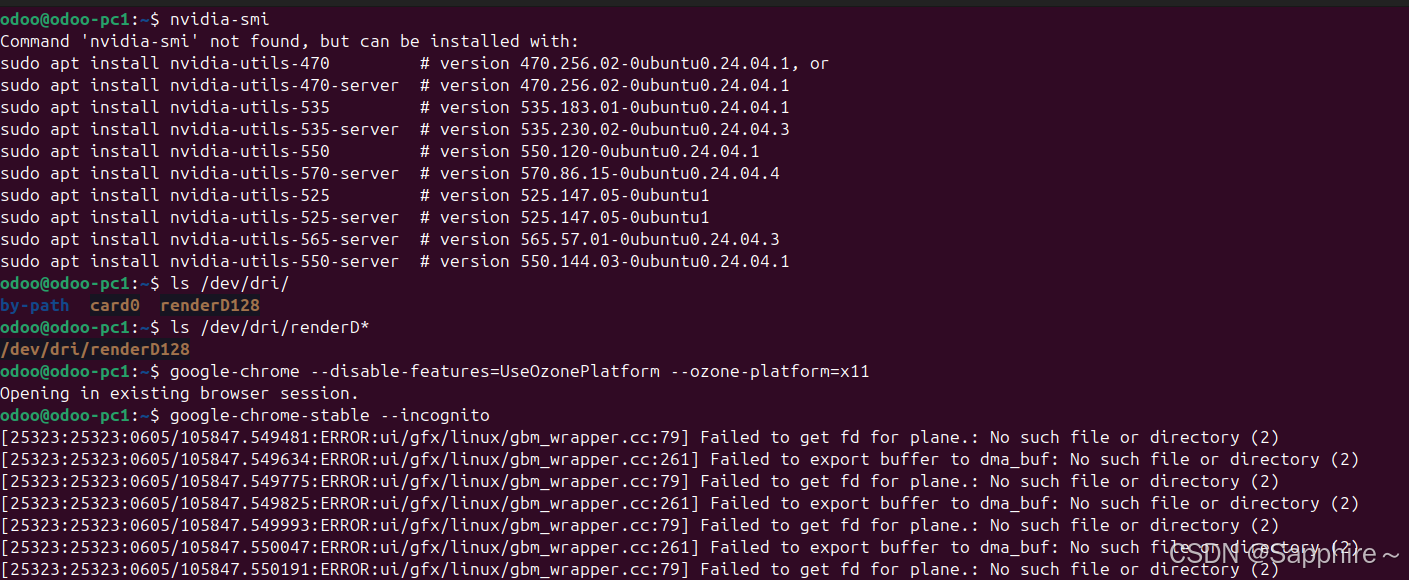
Linux-07 ubuntu 的 chrome 启动不了
文章目录 问题原因解决步骤一、卸载旧版chrome二、重新安装chorme三、启动不了,报错如下四、启动不了,解决如下 总结 问题原因 在应用中可以看到chrome,但是打不开(说明:原来的ubuntu系统出问题了,这个是备用的硬盘&a…...
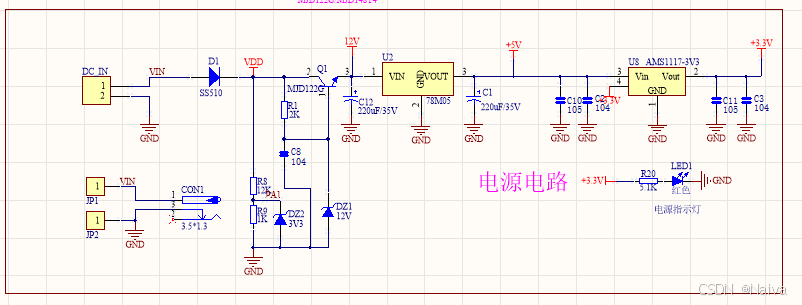
【电力电子】基于STM32F103C8T6单片机双极性SPWM逆变(硬件篇)
本项目是基于 STM32F103C8T6 微控制器的 SPWM(正弦脉宽调制)电源模块,能够生成可调频率和幅值的正弦波交流电源输出。该项目适用于逆变器、UPS电源、变频器等应用场景。 供电电源 输入电压采集 上图为本设计的电源电路,图中 D1 为二极管, 其目的是防止正负极电源反接, …...
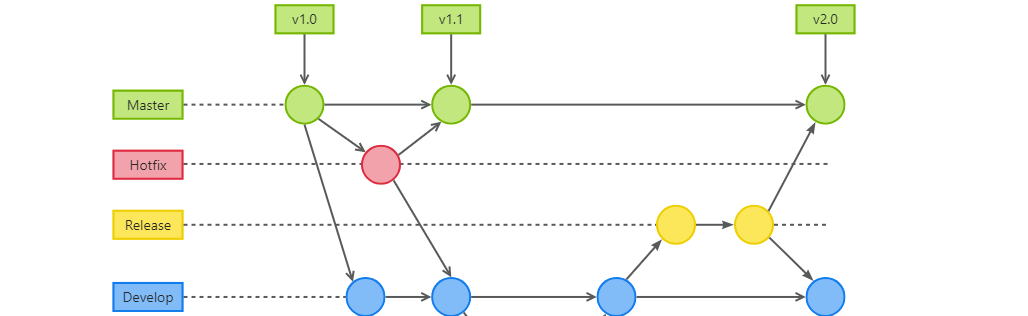
GitFlow 工作模式(详解)
今天再学项目的过程中遇到使用gitflow模式管理代码,因此进行学习并且发布关于gitflow的一些思考 Git与GitFlow模式 我们在写代码的时候通常会进行网上保存,无论是github还是gittee,都是一种基于git去保存代码的形式,这样保存代码…...
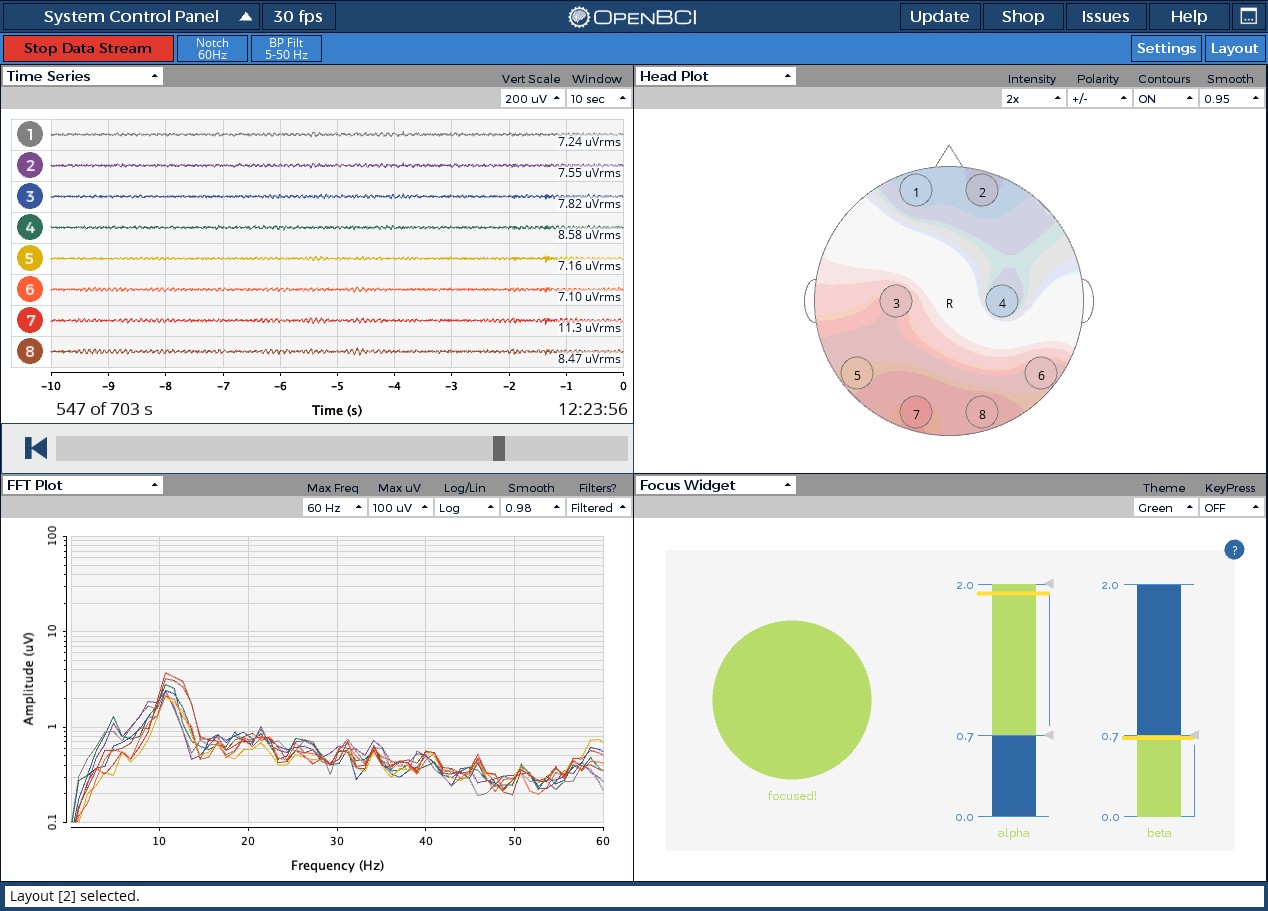
脑机新手指南(七):OpenBCI_GUI:从环境搭建到数据可视化(上)
一、OpenBCI_GUI 项目概述 (一)项目背景与目标 OpenBCI 是一个开源的脑电信号采集硬件平台,其配套的 OpenBCI_GUI 则是专为该硬件设计的图形化界面工具。对于研究人员、开发者和学生而言,首次接触 OpenBCI 设备时,往…...
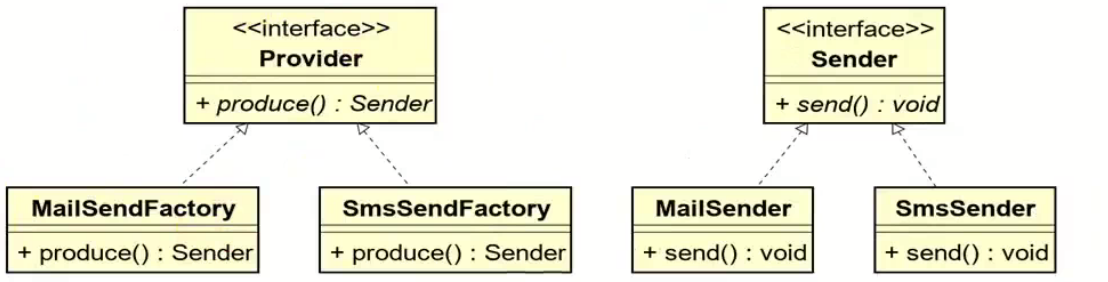
工厂方法模式和抽象工厂方法模式的battle
1.案例直接上手 在这个案例里面,我们会实现这个普通的工厂方法,并且对比这个普通工厂方法和我们直接创建对象的差别在哪里,为什么需要一个工厂: 下面的这个是我们的这个案例里面涉及到的接口和对应的实现类: 两个发…...
