大模型笔记5 Extractive QA任务评估
目录
Extractive QA任务评估
Extractive QA评测指标
precision, recall, f1
ROUGE
划分训练与评估数据集
token位置评估
单个token位置评估
输入label的token位置
预测token位置
评估
Wandb
共享机器同时登录
样本类别平衡
标记token label时对窗口进行筛选
训练输入json数据格式调整
GPU内存不足
服务器远程连接断开后进程停止运行
Extractive QA任务评估
Extractive QA评测指标
Extractive QA Evaluation Metrics:
参考:
Evaluating Question Answering Evaluation
Evaluating Question Answering Evaluation - ACL Anthology
现有指标(BLEU、ROUGE、METEOR 和 F1)是使用 n-gram 相似性计算的
how-to-evaluate-question-answering代码
How to Evaluate a Question Answering System | deepset
Evaluation of a QA System | Haystack
slides:
https://anthonywchen.github.io/Papers/evaluatingqa/mrqa_slides.pdf
QAEval:
https://direct.mit.edu/tacl/article/doi/10.1162/tacl_a_00397/106792/Towards-Question-Answering-as-an-Automatic-Metric
代码:
https://github.com/CogComp/qaeval-experiments
precision:candidate中匹配reference的内容占candidate比例
recall:candidate中匹配reference的内容占reference比例
| Reference: I work on machine learning. Candidate A: I work. Candidate B: He works on machine learning. |
Precision A>B, recall B>A
F1
| import evaluate metric = evaluate.load("squad") |
| metric.compute(predictions=predicted_answers, references=theoretical_answers) |
| {'exact_match': 83.0, 'f1': 88.25} |
ROUGE (Recall Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation)
https://aclanthology.org/W04-1013/
分类:ROUGE-N(常用其中的ROUGE-1和ROUGE-2), ROUGE-L,ROUGE-W,ROUGE-S(后两种不常用) 原版论文中ROUGE主要关注recall值,但事实上在用的时候可以用precision、recall和F值。
ROUGE-N:基于n-grams,如ROUGE-1计算基于匹配unigrams的recall,以此类推。 ROUGE-L:基于longest common subsequence (LCS)
BLUE
precision用modified n-gram precision估计,recall用best match length估计。
Modified n-gram precision:
n-gram precision是candidate中与reference匹配的n-grams占candidates的比例
| Reference: I work on machine learning. Candidate 1: He works on machine learning. |
Precision=60%(3/5)
best match length
precision, recall, f1
数据集标签labels_texts中一篇文章的数据集描述为一个字符串list,
模型输出prediction_strings中一篇文章的数据集描述为连在一起的字符串.
示例数据:
| labels_texts = [["description1 in paper1", "description2 in paper1"], ["description1 in paper2"]] prediction_strings = ["description1 in paper1. description2 in paper1", "description1 in paper2"] |
使用 F1 分数来评估模型的输出
1. 将 labels_texts 转化为 token 级别的标签。
2. 训练模型并生成预测结果 prediction_strings。
3. 比较预测的 token 和参考的 token,并基于它们的交集计算评估指标。
| # 评估模型输出 def evaluate(predictions, references): y_true = [] y_pred = [] for ref, pred in zip(references, predictions): ref_tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(" ".join(ref)) pred_tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(pred) common = set(ref_tokens) & set(pred_tokens)
y_true.extend([1] * len(common) + [0] * (len(ref_tokens) - len(common))) y_pred.extend([1] * len(common) + [0] * (len(pred_tokens) - len(common)))
precision, recall, f1, _ = precision_recall_fscore_support(y_true, y_pred, average='binary') return precision, recall, f1 precision, recall, f1 = evaluate(prediction_strings, labels_texts) print(f"Precision: {precision:.4f}, Recall: {recall:.4f}, F1 Score: {f1:.4f}") |
precision, recall, f1, _ = precision_recall_fscore_support(y_true, y_pred, average='binary')这一句报错ValueError: Found input variables with inconsistent numbers of samples: [40, 42]
这是因为生成的句子比参考的句子更长
常见的处理方法包括
截断生成的句子:将生成的句子截断到与参考句子相同的长度。
填充参考句子:将参考句子填充到与生成句子相同的长度。
对齐比较:在评估时只比较重叠部分,并忽略多出的部分。
截断比较
| # 两个字符串长度不一样, 会报错, 截断比较 min_len = min(len(ref_tokens), len(pred_tokens)) ref_tokens = ref_tokens[:min_len] pred_tokens = pred_tokens[:min_len] |
得到输出
| Prediction Strings: ['impossible. In this paper, we aim to solve this problem by introducing FAR-Trans, the first public dataset for FAR, containing pricing in- formation and retail investor transactions acquired from a large European financial institution.'] Precision: 1.0000, Recall: 0.9750, F1 Score: 0.9873 |
ROUGE
(Recall Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation)
ROUGE: A Package for Automatic Evaluation of Summaries - ACL Anthology
文本生成评估指标简单介绍BLEU+ROUGE+Perplexity+Meteor 代码实现_meteor指标-CSDN博客
简介:主要用于评估机器翻译、文本摘要(或其他自然语言处理任务)的质量,即:衡量目标文本与生成文本之间的匹配程度,此外还考虑生成文本的召回率,BLEU则相对更看重生成文本的准确率,着重于涵盖参考摘要的内容和信息的完整性。
主要有两种形式:
ROUGE-N(N = 1, 2, 3, …)
ROUGE-L
ROUGE-N计算方式为:
| ROUGE-N = Candidate ∩ Reference l e n ( Reference ) \text{ROUGE-N} = \frac{\text{Candidate} \cap \text{Reference}}{len(\text{Reference})} |
这里的分子交集不像ROUGE-L的最长公共子串一样,这里的交集不考虑顺序。
交集主要考虑n-gram
参考:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/647310970
n代表连续的n个词的组合。"n"可以是1、2、3,或者更高。
- 1-gram:也称为unigram,是指单个的词语。例如,在句子 "我喜欢学习自然语言处理。" 中的1-gram为:["我", "喜欢", "学习", "自然语言处理", "。"]
- 2-gram:也称为bigram,是指两个连续的词语组合。例如,在句子 "我喜欢学习自然语言处理。" 中的2-gram为:["我喜欢", "喜欢学习", "学习自然语言处理", "自然语言处理。"]
ROUGE-L
考虑最长公共子串(是区分顺序的)
单句ROUGE-L
| ROUGE-L = 最长公共子串 ( Candidate , Reference ) l e n ( Reference ) \text{ROUGE-L} = \frac{\text{最长公共子串}(\text{Candidate}, \text{Reference})}{len(\text{Reference})} |

Rouge库:
rouge · PyPI
https://www.cnblogs.com/bonelee/p/18152511
发现环境中已经按照了rouge-score
rouge-score · PyPI
| from rouge_score import rouge_scorer scorer = rouge_scorer.RougeScorer(['rouge1','rouge2', 'rougeL'], use_stemmer=True) scores = scorer.score('The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog', 'The quick brown dog jumps on the log.') print(scores["rouge1"]) print(scores["rouge2"]) print(scores["rougeL"]) |
看看多组不能直接预测, 要拆开每一个样本对比预测.
这样多个样本时候如何计算呢, 查到一个例子, 是把列表中所有字符串拼接在一起
自然语言处理评估指标_自然语言处理结果-CSDN博客
文本摘要教程
https://github.com/hellotransformers/Natural_Language_Processing_with_Transformers/blob/main/chapter6.md
多个样本例子:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/67390427/rouge-score-append-a-list
| #同一个文档拼接到同一个字符串 ==================rouge==================== from nltk.translate.bleu_score import sentence_bleu from nltk.translate.rouge_score import rouge_n, rouge_scorer def gouge(evaluated_sentences, reference_sentences): """ :param evaluated_sentences: 生成的摘要句子列表 :param reference_sentences: 参考摘要句子列表 :return: GOUGE指标 """ scorer = rouge_scorer.RougeScorer(['rouge1', 'rouge2', 'rouge 3', 'rouge4']) scores = scorer.score(' '.join(evaluated_sentences), ' '.join(reference_sentences)) rouge_n_scores = [scores[f'rouge{i}'].precision for i in range(1, 5)] return np.exp(np.mean(np.log(rouge_n_scores))) |
| # 不同文档分别计算评估指标 # importing the native rouge library from rouge_score import rouge_scorer # a list of the hypothesis documents hyp = ['This is the first sample', 'This is another example'] # a list of the references documents ref = ['This is the first sentence', 'It is one more sentence'] # make a RougeScorer object with rouge_types=['rouge1'] scorer = rouge_scorer.RougeScorer(['rouge1']) # a dictionary that will contain the results results = {'precision': [], 'recall': [], 'fmeasure': []} # for each of the hypothesis and reference documents pair for (h, r) in zip(hyp, ref): # computing the ROUGE score = scorer.score(h, r) # separating the measurements precision, recall, fmeasure = score['rouge1'] # add them to the proper list in the dictionary results['precision'].append(precision) results['recall'].append(recall) results['fmeasure'].append(fmeasure) print(results) |
| {'precision': [0.8, 0.2], 'recall': [0.8, 0.25], 'fmeasure': [0.8000000000000002, 0.22222222222222224]} |
但是拼接不同样本为同一个字符串再一起计算rouge的方式在含义上不太合适, 所以每个样本分别计算, 然后对所有样本取均值.
pip安装rouge_score
计算评估指标
| def rouge_evaluate(predictions, refs): scorer = rouge_scorer.RougeScorer(['rouge1', 'rouge2', 'rougeL'], use_stemmer=True) rouge_scores = {'rouge1': [], 'rouge2': [], 'rougeL': []}
for ref, pred in zip(refs, predictions): score = scorer.score(" ".join(ref), pred) for key in rouge_scores: rouge_scores[key].append(score[key].fmeasure)
avg_rouge_scores = {key: sum(scores) / len(scores) for key, scores in rouge_scores.items()} #指标直接储存在文件中 with open('output/evaluation_rouge.txt', 'w') as eval_file: # eval_file.write(f"rouge1: {precision:.4f}\n") # eval_file.write(f"rouge2: {recall:.4f}\n") # eval_file.write(f"rougeL: {f1:.4f}\n") eval_file.write(f"ROUGE Scores:\n") for key, score in avg_rouge_scores.items(): eval_file.write(f"{key}: {score:.4f}\n") return avg_rouge_scores rouge_results = rouge_evaluate(dataset_descriptions, labels_texts) |
此处只计算f值的均值, 若有需要, 后续再补充其它值.
划分训练与评估数据集
| from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split |
在分割完token label后
| # Split the dataset into training and evaluation sets train_size = 0.8 train_indices, val_indices = train_test_split(list(range(len(inputs["input_ids"]))), train_size=train_size, random_state=42) train_inputs = {key: val[train_indices] for key, val in inputs.items()} val_inputs = {key: val[val_indices] for key, val in inputs.items()} train_dataset = TensorDataset(train_inputs["input_ids"], train_inputs["attention_mask"], train_inputs["labels"]) val_dataset = TensorDataset(val_inputs["input_ids"], val_inputs["attention_mask"], val_inputs["labels"]) train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=True) val_dataloader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=False) |
| #训练时 for batch in train_dataloader: … avg_epoch_loss = epoch_loss / len(train_dataloader) |
| #评估时 # Evaluate on the validation set val_predictions, val_labels = evaluate(model, val_dataloader, tokenizer) … precision, recall, f1, rouge_scores = calculate_metrics(val_predictions, val_labels, tokenizer) |
检查batch中是否有paper_idx
注意DataLoader中的key和修改后的输入的key对齐
["input_ids"]["attention_mask"]["labels"]["paper_idx"]
| val_dataset = TensorDataset(val_inputs["input_ids"], val_inputs["attention_mask"], val_inputs["labels"], val_inputs["paper_idx"]) |
还有一个问题, 抽样的时候把不同样本的滑窗分开了怎么办
为了确保从同一样本生成的滑动窗口保持在一起,我们需要修改数据拆分过程。我们不会在标记化后拆分数据集,而是拆分原始数据,然后分别对每个子集进行标记。这样,滑动窗口将保留在相同的训练或验证拆分中。
Tokenize前拆分
| # Split the original data into training and evaluation subsets train_sentences, val_sentences, train_labels_texts, val_labels_texts, train_titles, val_titles = train_test_split( sentences, labels_texts, titles, train_size=0.8, random_state=42 ) |
分别tokenize, 创建dataloder
| # Tokenize the training and validation data separately train_inputs = tokenize_and_align_labels(train_sentences, train_labels_texts, train_titles, tokenizer) val_inputs = tokenize_and_align_labels(val_sentences, val_labels_texts, val_titles, tokenizer) model.to(device) train_inputs = {key: val.to(device) for key, val in train_inputs.items()} val_inputs = {key: val.to(device) for key, val in val_inputs.items()} train_dataset = TensorDataset(train_inputs["input_ids"], train_inputs["attention_mask"], train_inputs["labels"]) val_dataset = TensorDataset(val_inputs["input_ids"], val_inputs["attention_mask"], val_inputs["labels"]) train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=True) val_dataloader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=False)#防止生成的同一篇文章断开 |
评估时的label也更换
| precision, recall, f1 = token_evaluate(dataset_descriptions, val_labels_texts) |
| rouge_results = rouge_evaluate(dataset_descriptions, val_labels_texts) |
输出时
| dataset_descriptions = get_extracted_description(val_predictions, val_inputs["input_ids"], val_inputs["paper_idx"]) |
token位置评估
常见方法:
- 准确率 (Accuracy):衡量模型预测的答案是否完全正确,适用于答案只有一个标准的情况。
- 精确率 (Precision), 召回率 (Recall) 和 F1 分数:这些指标常用于衡量模型在预测多个可能答案时的表现。精确率衡量正确预测的答案在所有预测答案中的比例,召回率衡量正确预测的答案在所有正确答案中的比例,F1 分数是精确率和召回率的调和平均数。
- EM (Exact Match):衡量模型预测的答案与参考答案完全匹配的比例。
- ROUGE (Recall-Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation):衡量模型生成的答案与参考答案之间的重叠情况,常用于评估生成任务。ROUGE-1 和 ROUGE-L 常用于评估答案的词汇和序列匹配度。
- BLEU (Bilingual Evaluation Understudy):衡量模型生成答案与参考答案之间的 n-gram 重叠情况,常用于机器翻译任务,但在 QA 任务中也可作为辅助指标。
使用输出 token 的位置作为评估指标是合适的,特别是在以下情况中:
- 开始和结束位置的准确性:对于 Extractive QA 任务,模型通常预测答案在文本中的开始和结束位置。这可以直接用于评估模型是否准确地定位了答案的位置。
- 重叠率:评估预测答案的起止位置与真实答案的起止位置之间的重叠情况,可以使用 Intersection over Union (IoU) 或者其他重叠率指标。
单个token位置评估
此处模型输出不是单个连续序列, 因此使用label中每个token的位置与预测token位置对比进行评估
输入label的token位置
1.利用label_text构建token_label时同时保存token位置(匹配成功的每一个token在该滑窗中的下标), 保存在tokenized_inputs中
添加了一个名为 token_positions 的键,用于保存每个匹配成功的 token 在滑窗中的下标。
| tokenized_inputs = {"input_ids": [], "attention_mask": [], "labels": [], "paper_idx": [], "token_positions": []} |
token_positions 列表只包含与 token_label 值为 1 的部分对应的下标
同一篇文章中的每一个滑窗, 其中每一个滑窗是一个数组, 有的label在这个滑窗中, 有的不在, 所以会出现部分滑窗token位置中为空的情况
| for j in range(len(input_ids)):#同一篇文章中的每一个滑窗 tokenized_sentence = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(input_ids[j]) token_label = [0] * len(tokenized_sentence) main_body_start=find_main_body(tokenized_sentence) token_positions = [] for label_text in labels_text: # print("label_text:",label_text) tokenized_label = tokenizer.tokenize(label_text) # print("label_text:",label_text) tokenized_label = [token for token in tokenized_label if token != '<pad>']#删除pad label_length = len(tokenized_label) # print("tokenized_label:",tokenized_label) # 处理label跨滑窗 for k in range(main_body_start,len(tokenized_sentence)-1):#从正文部分开始匹配 # print("tokenized_sentence:",tokenized_sentence[k:k + label_length]) end_position=min(len(tokenized_sentence)-1, k + label_length) if tokenized_sentence[k:end_position] == tokenized_label[0:end_position]:#后半部分没有的情况 print("matched tokenized_label:", tokenized_sentence[k:end_position]) # print("matched tokenized_label:",tokenized_label,"\n",tokenized_sentence[k:end_position]) token_label[k:end_position] = [1] * (end_position-k) # print("matched clsfy_label:",token_label[k:len(tokenized_sentence)-1]) for pos in range(k, end_position): token_positions.append(pos) for label_start in range(label_length-1):#前半部分没有的情况 # print("tokenized_sentence:",tokenized_sentence[k:k + label_length]) if tokenized_sentence[main_body_start:label_length-label_start] == tokenized_label[label_start:]:#后半部分没有的情况 print("matched tokenized_label:",tokenized_sentence[main_body_start:label_length-label_start]) # print("matched tokenized_label:",tokenized_sentence[main_body_start:label_length-label_start],"\n",tokenized_label[label_start:]) token_label[main_body_start:label_length-label_start] = [1] * (label_length-label_start) # print("matched clsfy_label:",token_label[k:len(tokenized_sentence)-1]) for pos in range(main_body_start, label_length - label_start): token_positions.append(pos) |
| tokenized_inputs["token_positions"].append(token_positions) |
因为tokenized_inputs["token_positions"]中的数组不等长, 无法转换成tensor使用torch.stack(), 无法和其它key一起转到gpu中, 所以, 转到gpu的操作只在分批之后的其它key上进行
预测token位置
2.输出token分类转换成句子时候, 同时输出token预测位置
将get_prediction_string中predicted_tokens_classes的类别预测为'Dataset description'的token位置也记录下来并一起返回
新增一个pre_token_positions列表用于记录预测类别为 'Dataset description' 的 token 的位置。函数最后返回 dataset_description_string 和pre_token_positions
| pre_token_positions = [] |
| for idx, (token, pred_class) in enumerate(zip(tokenized_sub_sentence, predicted_tokens_classes)): is_descrp=(pred_class == 'Dataset description') if(is_descrp): pre_token_positions.append(idx) |
| return dataset_description_string, pre_token_positions |
| dataset_description, pre_token_positions=get_prediction_string(prediction_class, predicted_input_id, is_same_paper) |
不同窗口的token位置分别评测, 避免不同窗口的token位置计算混乱
Token位置不需要拼接吧, 毕竟不是输出包含句意的内容, 放在一个大列表中分开不同窗口评测更好, 拼接之后不同窗口的位置反而容易串了
每一个pre_token_positions列表作为一个元素存入papers_pre_token_positions中
| papers_pre_token_positions=[] |
| dataset_description, pre_token_positions=get_prediction_string(prediction_class, predicted_input_id, is_same_paper) papers_pre_token_positions.append(pre_token_positions) |
| return dataset_descriptions, papers_pre_token_positions |
| dataset_descriptions,papers_pre_token_positions = get_extracted_description(val_predictions, val_inputs["input_ids"], val_inputs["paper_idx"]) |
评估
评估时的label与预测中token数量可能不同
其中label, 预测分别为papers_pre_token_positions, val_inputs["token_positions"]
准确率(Precision):P=TP/(TP+FP)。通俗地讲,就是预测正确的正例数据占预测为正例数据的比例。
召回率(Recall):R=TP/(TP+FN)。通俗地讲,就是预测为正例的数据占实际为正例数据的比
F1=(2*P*R)/(P+R)
true_positive 表示预测正确的 token 位置的数量,false_positive 表示错误预测的 token 位置的数量,false_negative 表示遗漏的实际 token 位置的数量。通过遍历每个滑窗的预测位置和实际位置,计算这些指标并最终得到 precision, recall 和 F1-score
| def token_evaluate(pre_token_positions, label_token_positions): true_positive = 0 false_positive = 0 false_negative = 0
for pred_positions, label_positions in zip(pre_token_positions, label_token_positions): pred_positions_set = set(pred_positions) label_positions_set = set(label_positions)
true_positive += len(pred_positions_set & label_positions_set) false_positive += len(pred_positions_set - label_positions_set) false_negative += len(label_positions_set - pred_positions_set)
precision = true_positive / (true_positive + false_positive) if (true_positive + false_positive) > 0 else 0 recall = true_positive / (true_positive + false_negative) if (true_positive + false_negative) > 0 else 0 f1 = 2 * (precision * recall) / (precision + recall) if (precision + recall) > 0 else 0
return precision, recall, f1 |
| # 例子 pre_token_positions = [[], [2], []] label_token_positions = [[1], [2], [3]] precision, recall, f1 = token_evaluate(pre_token_positions, label_token_positions) print(f"Precision: {precision}") print(f"Recall: {recall}") print(f"F1-score: {f1}") |
Wandb
Wandb是一个模型训练日志自动记录工具, 配置好后可以比较方便地在wandb.ai的网页查看每一次训练记录的plot和每条曲线的中的值
使用Wandb记录训练日志
安装wandb
| pip install wandb |
在命令行登录
| wandb login |
输入注册后生成的key, 登录成功
运行测试样例
| import wandb import random # start a new wandb run to track this script wandb.init( # set the wandb project where this run will be logged project="my-awesome-project", # track hyperparameters and run metadata config={ "learning_rate": 0.02, "architecture": "CNN", "dataset": "CIFAR-100", "epochs": 10, } ) # simulate training epochs = 10 offset = random.random() / 5 for epoch in range(2, epochs): acc = 1 - 2 ** -epoch - random.random() / epoch - offset loss = 2 ** -epoch + random.random() / epoch + offset # log metrics to wandb wandb.log({"acc": acc, "loss": loss}) # [optional] finish the wandb run, necessary in notebooks wandb.finish() |
获得提示
| wandb: Run data is saved locally in D:\Projects\longformer\wandb\run-20240805_204153-4hznct2i wandb: Run `wandb offline` to turn off syncing. wandb: Syncing run hearty-eon-1 wandb: View project at https://wandb.ai/lalagoon-north-china-electric-power-university/test-project wandb: View run at https://wandb.ai/lalagoon-north-china-electric-power-university/test-project/runs/4hznct2i |
打开网址可以看到生成的图像, 说明成功了
在自己的项目中加入
| import wandb |
| # start a new wandb run to track this script wandb.init( # set the wandb project where this run will be logged project="extract-dataset-description-project", # track hyperparameters and run metadata config={ "learning_rate": 5e-5, "architecture": "Longformer", "dataset": "Description-500", "epochs": 100, } ) |
运行过程中的epoch进行记录
| # 记录损失到 wandb wandb.log({"loss": avg_epoch_loss}) |
完事关掉
| wandb.finish() |
得到loss图在
https://wandb.ai/lalagoon-north-china-electric-power-university/extract-dataset-description-project
共享机器同时登录
服务器上有另一个wandb账号已经登录了, 则在命令行用这个代替login
| export WANDB_API_KEY='xxxx' |
样本类别平衡
标记token label时对窗口进行筛选
如果窗口中没有正例则不输入进行训练
在标记label时, 传入一个flag判断是否标记的是训练集, 训练集中判断token_positions, 如果是空数组, 则不在tokenized_inputs加入这个滑窗.
如果要过滤且没有label在滑窗, 则打断这个滑窗的循环, 不把值加入inputs
| if(filter_empty_window and len(token_positions)==0): continue |
在训练集中开启
| train_inputs = tokenize_and_align_labels(train_papers, tokenizer,filter_empty_window=True) |
训练输入json数据格式调整
将输入格式由字符串数组调整为json数组, 同一篇文章的不同信息放在一起方便对比
从json数组中读取
| descri_file_path='input/papers_and_datasets.json' def read_json(file_path): with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file: data = json.load(file) return data papers_info = read_json(descri_file_path) |
之后所有的循环改成从papers_info中读取
| sentences = data['paper_texts'] labels_texts = data['dataset_descriptions'] titles= data['titles'] |
训练集测试集划分, 改为划分paper_info
| train_papers, val_papers = train_test_split( papers_info, train_size=0.8, random_state=42 ) |
输入tokenize_and_align_labels匹配token label时使用paper_info,
| train_inputs = tokenize_and_align_labels(train_papers, tokenizer) val_inputs = tokenize_and_align_labels(val_papers, tokenizer) |
| def tokenize_and_align_labels(papers, tokenizer, max_length=4096, stride=256): |
使用tokenizer时循环paper_info, 并取出其中各项.
| for i, paper in enumerate(papers_info): sentence=paper.get("paper_text") labels_text = paper.get("dataset_descriptions") title = paper.get("title") |
在评估时候也循环取出
1.token评估
| def token_evaluate(predictions, val_papers, tokenizer): |
| for paper, pred in zip(val_papers, predictions):#ref_tokens中是一篇文章的label, y_true.extend后是所有样本的输出 ref=paper.get("dataset_descriptions") |
| precision, recall, f1 = token_evaluate(dataset_descriptions, val_papers, tokenizer) |
2.rouge
| def rouge_evaluate(predictions, val_papers): |
| for paper, pred in zip(val_papers, predictions): ref=paper.get("dataset_descriptions") |
| rouge_results = rouge_evaluate(dataset_descriptions, val_papers) |
同时, 为方便不同设备路径修改, 将使用到的路径统一汇总到开头
| descri_file_path='input/papers_and_datasets.json' loss_log_path='output/training_loss.txt' loss_fig_path='output/training_loss.png' model_save_path="output/trained_model" eval_token_path='output/evaluation_token.txt' eval_rouge_path='output/evaluation_rouge.txt' |
GPU内存不足
Colab上分批训练时将输入转移到GPU
| input_ids, attention_mask, labels = input_ids.to(device), attention_mask.to(device), labels.to(device) |
报错
| # OutOfMemoryError: CUDA out of memory. Tried to allocate 24.00 MiB. GPU |
注释了移GPU的, RAM又不够, 换了个号一样说不够用, 之后完善一下代码放华为卡上试试吧
华为卡跑多了也报错:
| RuntimeError: NPU out of memory. Tried to allocate 578.00 MiB (NPU 0; 60.97 GiB total capacity; 8.23 GiB already allocated; 8.23 GiB current active; 362.04 MiB free; 8.95 GiB reserved in total by PyTorch) If reserved memory is >> allocated memory try setting max_split_size_mb to avoid fragmentation. |
清除缓存和减少batch size, 参考
python - How to avoid "CUDA out of memory" in PyTorch - Stack Overflow
| import torch torch.cuda.empty_cache() |
| torch_npu.npu.empty_cache() |
设置max_split_size_mb, 参考:
环境变量方法:
| export 'PYTORCH_NPU_ALLOC_CONF=max_split_size_mb:512' |
代码方法:
| torch._C._debug_set_max_split_size_mb(512) torch_npu._C._debug_set_max_split_size_mb(512) |
华为卡查看剩余NPU资源
| npu-smi info |
可以看到有人在跑
| +---------------------------+---------------+----------------------------------------------------+ | NPU Chip | Process id | Process name | Process memory(MB) | +===========================+===============+====================================================+ | 0 0 | 1349884 | python | 30216 | +===========================+===============+====================================================+ |
指定一块GPU运行python程序, 参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/tyty-Somnuspoppy/p/10071716.html
| os.environ["NPU_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "1,2,3" |
| device = torch.device("npu:1" if torch.npu.is_available() else "npu:2") |
检查每个设备的可用内存是否足够:
| def select_available_npu(required_memory_mb): if torch.npu.is_available(): for i in range(1, 8): props = torch.npu.get_device_properties(f"npu:{i}") if props.total_memory - props.reserved_memory >= required_memory_mb * 1024 * 1024: return torch.device(f"npu:{i}") return torch.device("cpu") |
| 查看总内存 torch_npu.npu.get_device_properties("npu:1").total_memory |
| 设置特定npu, 注意这里查询要用torch_npu.npu, 不然取不到 device = torch.device("npu:1" if torch_npu.npu.is_available() else "npu:2") |
longformer的输入序列长, 4096也很大
不像现在的infini transformer这种先分割在分块处理
Longformer不支持多卡训练, 只能把batchsize设置小一点,显存会下降一点
batch_size=8
能跑起来了
| ----+ | NPU Chip | Process id | Process name | Process memory(MB) | +===========================+===============+====================================================+ | 0 0 | 47784 | python | 52657 | +===========================+===============+================================================ |
服务器远程连接断开后进程停止运行
Nohup参考:
在Linux系统的ECS实例内,当断开SSH客户端后,如何保持进程继续运行的解决方案_云服务器 ECS(ECS)-阿里云帮助中心
Linux服务器SSH客户端断开后保持程序继续运行的方法_ssh退出后如何保持程序继续运行-CSDN博客
SSH 断开后使进程仍在后台运行 — Linux latest 文档
| nohup ping www.baidu.com & |
| ls |
| cat nohup.out |
| ps -ef | grep ping |
| kill [$PID] |
[$PID]为之前nohup命令输出的值
| [1] 1255914 nohup: ignoring input and appending output to 'nohup.out' |
用于执行程序
| nohup python tkn_clsfy.py & |
| ps -ef | grep python |
得到输出
| [1] 27308 root 27308 27285 99 13:19 pts/14 00:01:49 python tkn_clsfy.py |
相关文章:

大模型笔记5 Extractive QA任务评估
目录 Extractive QA任务评估 Extractive QA评测指标 precision, recall, f1 ROUGE 划分训练与评估数据集 token位置评估 单个token位置评估 输入label的token位置 预测token位置 评估 Wandb 共享机器同时登录 样本类别平衡 标记token label时对窗口进行筛选 训练…...

RCE绕过方式
目录 小于8个字符突破限制 无字母数字执行 php7的做法 php5的思考 PHP5shell 深入理解glob通配符 构造POC,执行任意命令 无参数读文件和RCE总结 代码解读 构造. 另一种构造方法 小于8个字符突破限制 但也只能执行一些非常短的命令,没有什么意义…...

Flutter 电视投屏模块
前言 村里的老人说:“珍爱生命,远离低头族。“ 之前开发的一个 DIM 项目 Tarsier,里面有一个分享视频的功能,同时包含在线视频播放、电视直播等。 考虑到用户在手机上看视频的体验问题,需要增加一个投屏功能,以便用户可以电影、电视直播等投到电视上用大屏幕观看。 用…...

【机器学习】卷积神经网络简介
🌈个人主页: 鑫宝Code 🔥热门专栏: 闲话杂谈| 炫酷HTML | JavaScript基础 💫个人格言: "如无必要,勿增实体" 文章目录 卷积神经网络简介1. 引言2. CNN的基本概念2.1 什么是卷积神经网络2.2 CNN与传统…...

时间函数链接函数等
1. 2.top相当于windows任务管理器 3.命令模式下不加冒号20G直接跳转行数 4. 相当于strcat 5.:13,15y 13行到15行复制 6. Ctrl 右 】是追踪命令 7. vi off_t -t看类型 8. qa关闭所有 9.gg 移动最前面 GG移动到最后面 10.终端中的全选命令1. 使用快捷键&…...

Android控件(示例)
在Android应用程序中,界面由布局和组件组成。布局相当于框架,而控件则是框架里面的内容。了解过Android布局后,如果要设计ui界面,还需要了解和掌握各个控件的应用。 一个界面的设计,先从创建容器开始,再向…...

图论------贝尔曼-福德(Bellman-Ford)算法
算法概述: Bellman-Ford算法核心代码如下 for(int i 1;i<n-1;i) for(int j 1;j<m;j) if(dic[v[j]]> dic[u[j]] w[j]] dic[v[j]] dic[u[j]] w[j]; 首先我们要了解一个点就是我们这次不再使用邻接矩阵来存储图的信息,而是定义三个一维数组来…...

带你彻底搞懂useLayoutEffect的使用场景
开篇第一句: useLayoutEffect 可能会影响性能。尽可能使用 useEffect。 useLayoutEffect 是 useEffect 的一个版本,在浏览器重新绘制屏幕之前触发。 使用方法 useLayoutEffect(setup, dependencies?)调用 useLayoutEffect 在浏览器重新绘制屏幕之前进行布局测量&…...

大厂进阶之二:React高级用法HOC、Hooks对比、异步组件
本文分文三部分: HOC高阶组件 higher order componentHooks 16.8版本后新增的钩子API异步组件使用lazy和suspense两个api实现组件代码打包分割和异步加载 一、HOC高阶组件 1、定义 高阶组件不是组件而是函数,是react中用于复用组件逻辑的高级技巧&am…...

【扒代码】ope.py
文件目录: 引用方式 if not self.zero_shot: # 非零样本情况下,计算边界框的宽度和高度 box_hw torch.zeros(bboxes.size(0), bboxes.size(1), 2).to(bboxes.device) box_hw[:, :, 0] bboxes[:, :, 2] - bboxes[:, :, 0] # 宽度 box_hw[:, :, 1] bbox…...

【Rust光年纪】探索Rust终端编程:从跨平台操作到用户界面设计
构建跨平台终端应用的完美选择:Rust 库综述 前言 随着终端应用程序的发展,越来越多的开发者开始寻找跨平台的、易于使用的库来构建终端用户界面和执行终端操作。本文将介绍几个流行的 Rust 库,它们提供了丰富的功能和灵活的 API 来满足不同…...

67、ceph
一、ceph 1.1、ceph概念 ceph是一个开源的,用c语言写的分布式的存储系统。存储文件数据。 /dev/sdb fdisk /dev/sdb gdisk /dev/sdb lvm 逻辑卷 可以扩容 raid 磁盘阵列 高可用 基于物理意义上的单机的存储系统。 分布式有多台物理磁盘组成一个集群&…...

最大正方形[中等]
优质博文:IT-BLOG-CN 一、题目 在一个由0和1组成的二维矩阵内,找到只包含1的最大正方形,并返回其面积。 示例 1: 输入:matrix [["1","0","1","0","0"],[&quo…...

JavaScript 浅谈观察者模式 前端设计模式
2、观察者模式 2.1、观察者模式 2.1.1、前言 定义一种一对多的依赖关系,当一个对象发生变化时,所有依赖于它的对象都会自动收到通知并更新。 两个角色: Subject(主题/被观察者) Observer(观察者&…...

【自动驾驶】自定义消息格式的话题通信(C++版本)
目录 新建消息文件更改包xml文件中的依赖关系更改cmakelist文件中的配置执行时依赖改变cmakelist编译顺序发布者程序调用者程序新建launch文件程序测试 新建消息文件 在功能包目录下,新建msg文件夹,下面新建mymsg.msg文件,其内容为 string …...

提升前端性能的JavaScript技巧
1. 前端JavaScript性能问题 前端JavaScript的性能问题可以显著影响Web应用的用户体验和整体性能。以下是一些常见的前端JavaScript性能问题: 1.1. 频繁的DOM操作 问题描述:JavaScript经常需要与DOM(文档对象模型)交互来更新页面内容。然而,每次DOM操作都可能触发浏览器的…...

“服务之巅:Spring Cloud中SLA监控与管理的艺术“
标题:“服务之巅:Spring Cloud中SLA监控与管理的艺术” 在微服务架构中,服务调用的可靠性和性能是至关重要的。服务级别协议(Service Level Agreement,简称SLA)是衡量服务性能的关键指标,它定义…...

ChatGPT角色定位提问提示词和指令完整版
角色定位提问 在与ChatGPT的对话中,角色定位提问是一种有效的策略,通过为ChatGPT和自己设定特定的角色或身份,可以引导对话朝着更加具体、有针对性的方向发展。这种提问方式不仅有助于ChatGPT更好地理解问题的背景和需求,还能使回…...

docker之我不会的命令
docker命令之我不会的 保存镜像(打包) docker save 镜像名或镜像id -o 保存路径和镜像名字例子: docker save tomcat -o /home/my_tomcat.tar加载保存的镜像 docker load -i 镜像保存的位置例子 在/home/路径下 docker load -i my_tomca…...

Together规则引擎 金融解决方案
目录 1.金融法规和期望正在发生变化,快速跟踪您的金融数字化变革!2.抵押贷款功能集(MFS)3.MFS 示例模型4.MFS 知识特点5.MFS特定功能 1.金融法规和期望正在发生变化,快速跟踪您的金融数字化变革! ogether规则引擎使金融机构能够简…...
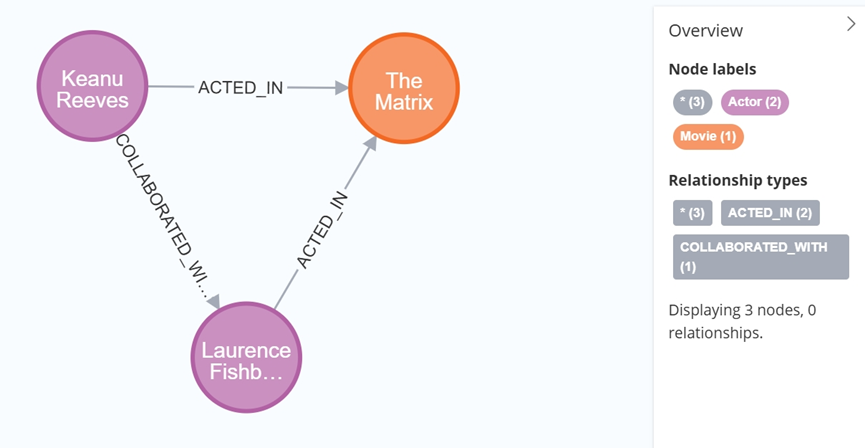
大数据学习栈记——Neo4j的安装与使用
本文介绍图数据库Neofj的安装与使用,操作系统:Ubuntu24.04,Neofj版本:2025.04.0。 Apt安装 Neofj可以进行官网安装:Neo4j Deployment Center - Graph Database & Analytics 我这里安装是添加软件源的方法 最新版…...
label-studio的使用教程(导入本地路径)
文章目录 1. 准备环境2. 脚本启动2.1 Windows2.2 Linux 3. 安装label-studio机器学习后端3.1 pip安装(推荐)3.2 GitHub仓库安装 4. 后端配置4.1 yolo环境4.2 引入后端模型4.3 修改脚本4.4 启动后端 5. 标注工程5.1 创建工程5.2 配置图片路径5.3 配置工程类型标签5.4 配置模型5.…...

反向工程与模型迁移:打造未来商品详情API的可持续创新体系
在电商行业蓬勃发展的当下,商品详情API作为连接电商平台与开发者、商家及用户的关键纽带,其重要性日益凸显。传统商品详情API主要聚焦于商品基本信息(如名称、价格、库存等)的获取与展示,已难以满足市场对个性化、智能…...

前端倒计时误差!
提示:记录工作中遇到的需求及解决办法 文章目录 前言一、误差从何而来?二、五大解决方案1. 动态校准法(基础版)2. Web Worker 计时3. 服务器时间同步4. Performance API 高精度计时5. 页面可见性API优化三、生产环境最佳实践四、终极解决方案架构前言 前几天听说公司某个项…...

智能分布式爬虫的数据处理流水线优化:基于深度强化学习的数据质量控制
在数字化浪潮席卷全球的今天,数据已成为企业和研究机构的核心资产。智能分布式爬虫作为高效的数据采集工具,在大规模数据获取中发挥着关键作用。然而,传统的数据处理流水线在面对复杂多变的网络环境和海量异构数据时,常出现数据质…...

稳定币的深度剖析与展望
一、引言 在当今数字化浪潮席卷全球的时代,加密货币作为一种新兴的金融现象,正以前所未有的速度改变着我们对传统货币和金融体系的认知。然而,加密货币市场的高度波动性却成为了其广泛应用和普及的一大障碍。在这样的背景下,稳定…...
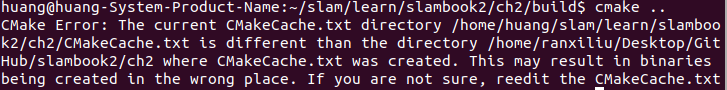
视觉slam十四讲实践部分记录——ch2、ch3
ch2 一、使用g++编译.cpp为可执行文件并运行(P30) g++ helloSLAM.cpp ./a.out运行 二、使用cmake编译 mkdir build cd build cmake .. makeCMakeCache.txt 文件仍然指向旧的目录。这表明在源代码目录中可能还存在旧的 CMakeCache.txt 文件,或者在构建过程中仍然引用了旧的路…...

音视频——I2S 协议详解
I2S 协议详解 I2S (Inter-IC Sound) 协议是一种串行总线协议,专门用于在数字音频设备之间传输数字音频数据。它由飞利浦(Philips)公司开发,以其简单、高效和广泛的兼容性而闻名。 1. 信号线 I2S 协议通常使用三根或四根信号线&a…...

4. TypeScript 类型推断与类型组合
一、类型推断 (一) 什么是类型推断 TypeScript 的类型推断会根据变量、函数返回值、对象和数组的赋值和使用方式,自动确定它们的类型。 这一特性减少了显式类型注解的需要,在保持类型安全的同时简化了代码。通过分析上下文和初始值,TypeSc…...
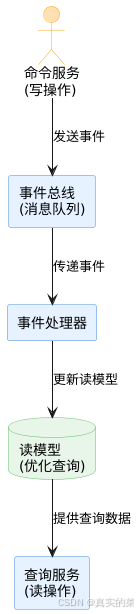
消息队列系统设计与实践全解析
文章目录 🚀 消息队列系统设计与实践全解析🔍 一、消息队列选型1.1 业务场景匹配矩阵1.2 吞吐量/延迟/可靠性权衡💡 权衡决策框架 1.3 运维复杂度评估🔧 运维成本降低策略 🏗️ 二、典型架构设计2.1 分布式事务最终一致…...
