RTX3060 FP64测试与猜想
RTX3060 FP64测试与猜想
- 一.小结
- 二.查看FP64的峰值性能
- 三.打满FP64、FP32的利用率,对比差异
- 四.进一步证明pipe_fp64_cycles_active并不是2个fp64 core的metrics
RTX3060 FP64测试与猜想
一.小结
- RTX3060 compute capability为8.6,每个SM有2个FP64 core。每个cycle可输出2个fp64的结果
- RTX3060 有4个subcore,这2个core怎么给4个sub_core分呢
- 执行FP64 DADD指令时,MIO PQ利用率超20%(FADD指令不存在该现象),且fp64 pipe的利用率最多为84%
- 每个smsp 执行一条DADD warp指令 pipe_fp64_cycles_active 增加16个cycle,4个smsp一起运行一条DADD warp指令仍是16个cycle
- 猜测:
- smsp按 1DADD/cycle 交替发送给2个FP64 core,一个warp需要16个cycle(32inst/16cycle->2inst/cycle)
- 如果4个sub core同时按这个速度发,则超过了FP64的处理能力(8inst/cycle > 2inst/cycle),但pipe_fp64_cycles_active没有增加
- 说明,在发射FP64指令之前会检测资源的可用性,如果不足,则不发射,pipe_fp64_cycles_active也就不会增加
- 也就解释了4个sub core一起执行时,pipe_fp64_cycles_active.max还是16个cycle
- 执行FP64指令时,4个subcore通过MIO共享FP64实际的执行单元
二.查看FP64的峰值性能
tee fp64_peak_sustained.cu<<-'EOF'
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <cuda.h>
__global__ void fake_kernel(){}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{fake_kernel<<<1, 1>>>();cudaDeviceSynchronize();
}
EOF
/usr/local/cuda/bin/nvcc -std=c++17 -arch=sm_86 -lineinfo -o fp64_peak_sustained fp64_peak_sustained.cu \-I /usr/local/cuda/include -L /usr/local/cuda/lib64 -lcuda
/usr/local/NVIDIA-Nsight-Compute/ncu --metrics \
sm__sass_thread_inst_executed_op_fp64_pred_on.avg.peak_sustained,\
sm__sass_thread_inst_executed_op_fp64_pred_on.sum.peak_sustained ./fp64_peak_sustained输出
fake_kernel() (1, 1, 1)x(1, 1, 1), Context 1, Stream 7, Device 0, CC 8.6
Section: Command line profiler metrics
---------------------------------------------------------------- ----------- ------------
Metric Name Metric Unit Metric Value
---------------------------------------------------------------- ----------- ------------
sm__sass_thread_inst_executed_op_fp64_pred_on.avg.peak_sustained inst/cycle 2 #每个sm的峰值性能
sm__sass_thread_inst_executed_op_fp64_pred_on.sum.peak_sustained inst/cycle 56 #28个sm
---------------------------------------------------------------- ----------- ------------
- 2 FP64 cores in devices of compute capability 8.6, 8.7 and 8.9
- 问题:这2个core怎么给4个sub_core分呢?
三.打满FP64、FP32的利用率,对比差异
tee fp64_test.cu<<-'EOF'
#include <iostream>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cuda.h>__global__ void kernel_add_float(volatile float *input,volatile float *output)
{unsigned int tid = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;float l=input[tid];float r=output[tid];for(int i=0;i<256;i++){l-=r;} input[tid]=l;
}
__global__ void kernel_add_double(volatile double *input,volatile double *output)
{unsigned int tid = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;double left=input[tid];double right=output[tid];for(int i=0;i<256;i++){left+=right;} output[tid]=left;
}
EOF/usr/local/cuda/bin/nvcc -std=c++17 -dc -lineinfo -arch=sm_86 -ptx fp64_test.cu -o fp64_test.ptx
/usr/local/cuda/bin/nvcc -arch=sm_86 fp64_test.ptx -cubin -o fp64_test.cubin
/usr/local/cuda/bin/nvcc -arch=sm_86 fp64_test.cubin -fatbin -o fp64_test.fatbin
cat fp64_test.ptx
/usr/local/cuda/bin/cuobjdump --dump-sass fp64_test.fatbin# 删掉除DADD、FADD以外的指令
cuasm.py fp64_test.cubin fp64_test.cuasm
sed '/MOV/d' -i fp64_test.cuasm
sed '/S2R/d' -i fp64_test.cuasm
sed '/ULDC/d' -i fp64_test.cuasm
sed '/IMAD/d' -i fp64_test.cuasm
sed '/LDG/d' -i fp64_test.cuasm
sed '/STG/d' -i fp64_test.cuasm
sed '/F2F/d' -i fp64_test.cuasmcuasm.py fp64_test.cuasm
/usr/local/cuda/bin/nvcc -arch=sm_86 fp64_test.cubin -fatbin -o fp64_test.fatbin
/usr/local/cuda/bin/cuobjdump --dump-sass fp64_test.fatbin
/usr/local/cuda/bin/cuobjdump --dump-resource-usage fp64_test.fatbintee fp64_test_main.cpp<<-'EOF'
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <cuda.h>int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{CUresult error;CUdevice cuDevice;cuInit(0);int deviceCount = 0;error = cuDeviceGetCount(&deviceCount);error = cuDeviceGet(&cuDevice, 0);if(error!=CUDA_SUCCESS){printf("Error happened in get device!\n");}CUcontext cuContext;error = cuCtxCreate(&cuContext, 0, cuDevice);if(error!=CUDA_SUCCESS){printf("Error happened in create context!\n");}int block_count=28*1000;int block_size=32*4*4;int thread_size=block_count*block_size;int data_size=sizeof(double)*thread_size;double *output_ptr=nullptr;double *input_ptr=nullptr;int cudaStatus=0;cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&input_ptr, data_size);cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&output_ptr, data_size);void *kernelParams[]= {(void*)&output_ptr, (void*)&input_ptr};CUmodule module;CUfunction double_function;CUfunction float_function;const char* module_file = "fp64_test.fatbin";const char* double_kernel_name = "_Z17kernel_add_doublePVdS0_";const char* float_kernel_name = "_Z16kernel_add_floatPVfS0_";error = cuModuleLoad(&module, module_file);if(error!=CUDA_SUCCESS){printf("Error happened in load moudle %d!\n",error);}error = cuModuleGetFunction(&double_function, module, double_kernel_name);if(error!=CUDA_SUCCESS){printf("get double_function error!\n");}error = cuModuleGetFunction(&float_function, module, float_kernel_name);if(error!=CUDA_SUCCESS){printf("get float_kernel_name error!\n");} cuLaunchKernel(double_function,block_count, 1, 1,block_size, 1, 1,0,0,kernelParams, 0);cuLaunchKernel(float_function,block_count, 1, 1,block_size, 1, 1,0,0,kernelParams, 0);cudaFree(output_ptr);cudaFree(input_ptr);cuModuleUnload(module);cuCtxDestroy(cuContext);return 0;
}
EOF
g++ fp64_test_main.cpp -o fp64_test_main -I /usr/local/cuda/include -L /usr/local/cuda/lib64 -lcudart -lcuda
/usr/local/NVIDIA-Nsight-Compute/ncu --metrics \
sm__inst_executed.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed,\
smsp__inst_issued.sum,\
sm__issue_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed,\
sm__pipe_fma_cycles_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed,\
sm__pipe_fmaheavy_cycles_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed,\
sm__inst_executed_pipe_cbu_pred_on_any.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed,\
sm__mio_inst_issued.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed,\
sm__mio_pq_read_cycles_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed,\
sm__mio_pq_write_cycles_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed,\
sm__mio_pq_write_cycles_active_pipe_lsu.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed,\
sm__mio_pq_write_cycles_active_pipe_tex.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed,\
sm__mioc_inst_issued.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed,\
sm__mio_inst_issued.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed,\
sm__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed ./fp64_test_main
输出
kernel_add_double(volatile double *, volatile double *) (28000, 1, 1)x(512, 1, 1), Context 1, Stream 7, Device 0, CC 8.6
Section: Command line profiler metrics
------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------- ------------
Metric Name Metric Unit Metric Value
------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------- ------------
sm__inst_executed.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 1.32
sm__inst_executed_pipe_cbu_pred_on_any.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 0.02
sm__issue_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 1.32
sm__mio_inst_issued.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 3.51
sm__mio_pq_read_cycles_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 0
sm__mio_pq_write_cycles_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 21.05
sm__mio_pq_write_cycles_active_pipe_lsu.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 0
sm__mio_pq_write_cycles_active_pipe_tex.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 21.05 # of cycles where register operands from the register file werewritten to MIO PQ, for the tex pipe
sm__mioc_inst_issued.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 1.32
sm__pipe_fma_cycles_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 0
sm__pipe_fmaheavy_cycles_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 0
sm__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 84.21 #利用率打不满
smsp__inst_issued.sum inst 115,136,000 #跟fp32相同的指令条数
------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------- ------------kernel_add_float(volatile float *, volatile float *) (28000, 1, 1)x(512, 1, 1), Context 1, Stream 7, Device 0, CC 8.6
Section: Command line profiler metrics
------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------- ------------
Metric Name Metric Unit Metric Value
------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------- ------------
sm__inst_executed.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 99.76
sm__inst_executed_pipe_cbu_pred_on_any.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 1.55
sm__issue_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 99.76
sm__mio_inst_issued.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 0
sm__mio_pq_read_cycles_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 0
sm__mio_pq_write_cycles_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 0
sm__mio_pq_write_cycles_active_pipe_lsu.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 0
sm__mio_pq_write_cycles_active_pipe_tex.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 0
sm__mioc_inst_issued.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 0.39
sm__pipe_fma_cycles_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 99.37
sm__pipe_fmaheavy_cycles_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 99.37
sm__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.avg.pct_of_peak_sustained_elapsed % 0
smsp__inst_issued.sum inst 115,136,000
------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------- ------------
*猜测,sm__pipe_fp64_cycles_active并不是那2个FP64 core的metrics,而是smsp里通往fp64 core的接口模块的活动cycle数
*4个subcore里的fp64接口模块,连接到2个fp64 core,并且经过了mio模块.因此,无法打满fp64的利用率
四.进一步证明pipe_fp64_cycles_active并不是2个fp64 core的metrics
tee fp64_test.cu<<-'EOF'
#include <iostream>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cuda.h>__global__ void kernel_add_double(volatile double *input,volatile double *output)
{unsigned int tid = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;double left=input[tid];double right=output[tid];for(int i=0;i<1;i++){left+=right;} output[tid]=left;
}
EOF/usr/local/cuda/bin/nvcc -std=c++17 -dc -lineinfo -arch=sm_86 -ptx fp64_test.cu -o fp64_test.ptx
/usr/local/cuda/bin/nvcc -arch=sm_86 fp64_test.ptx -cubin -o fp64_test.cubin
/usr/local/cuda/bin/nvcc -arch=sm_86 fp64_test.cubin -fatbin -o fp64_test.fatbin
cat fp64_test.ptx
/usr/local/cuda/bin/cuobjdump --dump-sass fp64_test.fatbincuasm.py fp64_test.cubin fp64_test.cuasm
sed '/MOV/d' -i fp64_test.cuasm
sed '/S2R/d' -i fp64_test.cuasm
sed '/ULDC/d' -i fp64_test.cuasm
sed '/IMAD/d' -i fp64_test.cuasm
sed '/LDG/d' -i fp64_test.cuasm
sed '/STG/d' -i fp64_test.cuasm
sed '/F2F/d' -i fp64_test.cuasmcuasm.py fp64_test.cuasm
/usr/local/cuda/bin/nvcc -arch=sm_86 fp64_test.cubin -fatbin -o fp64_test.fatbin
/usr/local/cuda/bin/cuobjdump --dump-sass fp64_test.fatbin
/usr/local/cuda/bin/cuobjdump --dump-resource-usage fp64_test.fatbintee fp64_test_main.cpp<<-'EOF'
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <cuda.h>int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{CUresult error;CUdevice cuDevice;cuInit(0);int deviceCount = 0;error = cuDeviceGetCount(&deviceCount);error = cuDeviceGet(&cuDevice, 0);if(error!=CUDA_SUCCESS){printf("Error happened in get device!\n");}CUcontext cuContext;error = cuCtxCreate(&cuContext, 0, cuDevice);if(error!=CUDA_SUCCESS){printf("Error happened in create context!\n");}int block_count=1;int block_size=32*4*4;int thread_size=block_count*block_size;int data_size=sizeof(double)*thread_size;double *output_ptr=nullptr;double *input_ptr=nullptr;int cudaStatus=0;cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&input_ptr, data_size);cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&output_ptr, data_size);void *kernelParams[]= {(void*)&output_ptr, (void*)&input_ptr};CUmodule module;CUfunction double_function;const char* module_file = "fp64_test.fatbin";const char* double_kernel_name = "_Z17kernel_add_doublePVdS0_";error = cuModuleLoad(&module, module_file);if(error!=CUDA_SUCCESS){printf("Error happened in load moudle %d!\n",error);}error = cuModuleGetFunction(&double_function, module, double_kernel_name);if(error!=CUDA_SUCCESS){printf("get float_kernel_name error!\n");} cuLaunchKernel(double_function,block_count, 1, 1,8, 1, 1,0,0,kernelParams, 0);cuLaunchKernel(double_function,block_count, 1, 1,16, 1, 1,0,0,kernelParams, 0);cuLaunchKernel(double_function,block_count, 1, 1,32, 1, 1,0,0,kernelParams, 0);cuLaunchKernel(double_function,block_count, 1, 1,32*2, 1, 1,0,0,kernelParams, 0);cuLaunchKernel(double_function,block_count, 1, 1,32*4, 1, 1,0,0,kernelParams, 0);cuLaunchKernel(double_function,block_count, 1, 1,32*5, 1, 1,0,0,kernelParams, 0);cuLaunchKernel(double_function,block_count, 1, 1,32*4*8, 1, 1,0,0,kernelParams, 0);cudaFree(output_ptr);cudaFree(input_ptr);cuModuleUnload(module);cuCtxDestroy(cuContext);return 0;
}
EOF
g++ fp64_test_main.cpp -o fp64_test_main -I /usr/local/cuda/include -L /usr/local/cuda/lib64 -lcudart -lcuda/usr/local/NVIDIA-Nsight-Compute/ncu --metrics smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active ./fp64_test_main
输出
kernel_add_double(volatile double *, volatile double *) (1, 1, 1)x(8, 1, 1), Context 1, Stream 7, Device 0, CC 8.6
Section: Command line profiler metrics
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------
Metric Name Metric Unit Metric Value
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.avg cycle 0.14
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.max cycle 16
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.min cycle 0
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.sum cycle 16
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------kernel_add_double(volatile double *, volatile double *) (1, 1, 1)x(16, 1, 1), Context 1, Stream 7, Device 0, CC 8.6
Section: Command line profiler metrics
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------
Metric Name Metric Unit Metric Value
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.avg cycle 0.14
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.max cycle 16 #不足一个warp跟一个warp 的pipe_fp64_cycles_active一样,说明存在无效计算
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.min cycle 0
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.sum cycle 16
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------kernel_add_double(volatile double *, volatile double *) (1, 1, 1)x(32, 1, 1), Context 1, Stream 7, Device 0, CC 8.6
Section: Command line profiler metrics
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------
Metric Name Metric Unit Metric Value
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.avg cycle 0.14
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.max cycle 16
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.min cycle 0
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.sum cycle 16
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------kernel_add_double(volatile double *, volatile double *) (1, 1, 1)x(64, 1, 1), Context 1, Stream 7, Device 0, CC 8.6
Section: Command line profiler metrics
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------
Metric Name Metric Unit Metric Value
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.avg cycle 0.29
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.max cycle 16
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.min cycle 0
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.sum cycle 32
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------kernel_add_double(volatile double *, volatile double *) (1, 1, 1)x(128, 1, 1), Context 1, Stream 7, Device 0, CC 8.6
Section: Command line profiler metrics
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------
Metric Name Metric Unit Metric Value
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.avg cycle 0.57
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.max cycle 16
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.min cycle 0
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.sum cycle 64
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------kernel_add_double(volatile double *, volatile double *) (1, 1, 1)x(160, 1, 1), Context 1, Stream 7, Device 0, CC 8.6
Section: Command line profiler metrics
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------
Metric Name Metric Unit Metric Value
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.avg cycle 0.71
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.max cycle 32
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.min cycle 0
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.sum cycle 80
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------kernel_add_double(volatile double *, volatile double *) (1, 1, 1)x(1024, 1, 1), Context 1, Stream 7, Device 0, CC 8.6
Section: Command line profiler metrics
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------
Metric Name Metric Unit Metric Value
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.avg cycle 4.57
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.max cycle 128
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.min cycle 0
smsp__pipe_fp64_cycles_active.sum cycle 512 #每个smsp 执行一个warp的fp64需要16个pipe_fp64_cycles_active
--------------------------------- ----------- ------------
- 如果是2个fp64 cores的metrics,不会出现这样的现象
相关文章:

RTX3060 FP64测试与猜想
RTX3060 FP64测试与猜想 一.小结二.查看FP64的峰值性能三.打满FP64、FP32的利用率,对比差异四.进一步证明pipe_fp64_cycles_active并不是2个fp64 core的metrics RTX3060 FP64测试与猜想 一.小结 RTX3060 compute capability为8.6,每个SM有2个FP64 core。每个cycle可输出2个fp…...

uniapp写移动端常见问题汇总
1. 手机顶部状态栏遮挡 写在需要的地方 <view class"status_bar" style"height: var(--status-bar-height); width: 100%;">2. 手机顶部状态栏字体颜色 // pages.json "statusBarStyle": "light",3. 背景覆盖全屏 page{widt…...
Linux运维排查常见故障_在tmp目录下有大量包含picture_ 的临时文件,每天晚上2 30需要对一天前的文件进行
echo“”>>/etc/security/limits.conf echo“*softnproc65535″>>/etc/security/limits.conf echo“*hardnproc65535″>>/etc/security/limits.conf echo“*softnofile65535″>>/etc/security/limits.conf echo“*hardnofile65535″>>/etc/secur…...
基于SpringBoot的智能制造云平台系统的设计与实现计算机毕设
一、选题背景与意义(300字左右) 根据工业4.0智能制造生态链中云工厂在实际生产当中的工作流程进行充分调研和整理出来的,描述最终用户在本系统中对于生产订单的处理、排产、以及生产的完整在线处理流程和业务需求的文档。 针对制造业而言&a…...
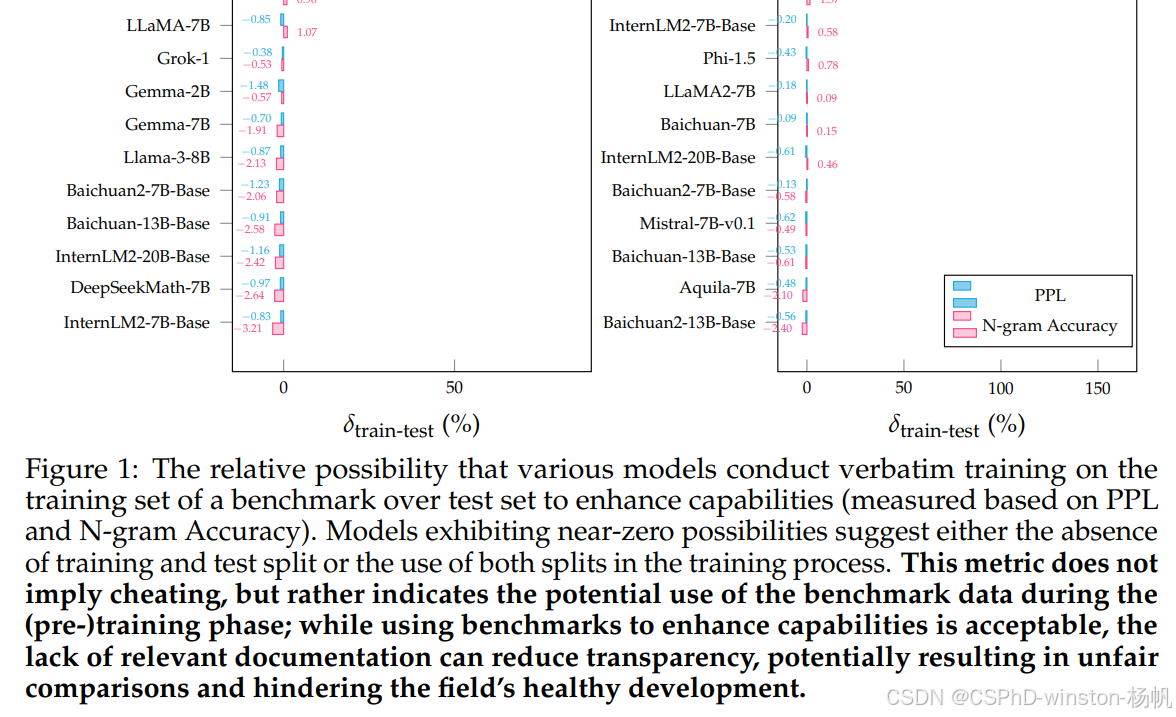
论文翻译:arxiv-2024 Benchmarking Benchmark Leakage in Large Language Models
Benchmarking Benchmark Leakage in Large Language Models https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.18824 在大型语言模型中基准测试泄露的基准测试 文章目录 在大型语言模型中基准测试泄露的基准测试摘要1 引言 图1:不同模型在基准测试的训练集上进行逐字训练相对于测试集以…...
十二、新版UI
一、UI Toolkit 这个组件是新版的UI系统 创建了一个新的UIBuild,在单独的场景中打开 未来Unity会以这个为基准。 缺点:目前没有Animator,做不了动画;没法加shader...
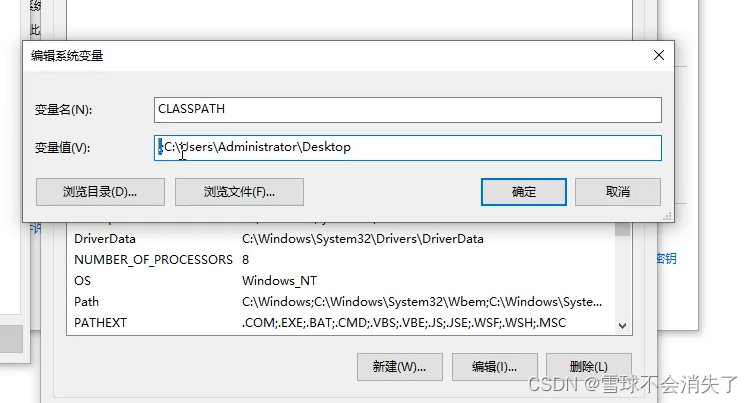
Path系统环境变量和CLASSPATH环境变量
Path系统环境变量 概述:Path环境变量不是java的,它隶属于windows操作系统 作用: PATH环境变量实际上就是给windows操作系统指路的。 在Path环境变量中有很多路径,路径和路径之间采用 分号(;) 隔开在DOS命令窗口中输入一条DOS命…...

自然语言处理系列六十六》对话机器人项目实战》对话机器人原理与介绍
注:此文章内容均节选自充电了么创始人,CEO兼CTO陈敬雷老师的新书《自然语言处理原理与实战》(人工智能科学与技术丛书)【陈敬雷编著】【清华大学出版社】 文章目录 自然语言处理系列六十六对话机器人项目实战》对话机器人原理与介…...
解码数字化转型顶层规划(附236页PPT:xx企业数字化转型项目顶层规划方案)
写在前面:PPT分享见后文~ 企业数字化转型顶层规划的制定是一个系统性的过程,需要综合考虑多个方面。以下是制定企业数字化转型顶层规划的一些关键步骤和要点,以供参考: 1、明确数字化转型战略定位: 将数字化转型作为…...

无需温度修正,测值准确可靠 GEO ACxxxx型振弦式锚索测力计
无需温度修正,测值准确可靠 GEO ACxxxx型振弦式锚索测力计 精准稳定的振弦式传感器,ACxxxx型振弦式锚索测力计,是长期监测预应力锚索压力的不二选择。采用特制应变计作为传感部件,无需温度修正,测值准确可靠。该传感器…...

shell脚本【一、 特殊变量/子串/特殊扩展变量/父子shell/内置命令、外置命令】
特殊变量 位置参数的获取 $0 获取shell脚本文件名,以及脚本路径;$n 获取shell脚本的第n个参数,n在1~9之间,如$1$2$9,大于9则需要写 ${10};$# 获取执行的shell脚本后面的参数总个数;$* 获取she…...
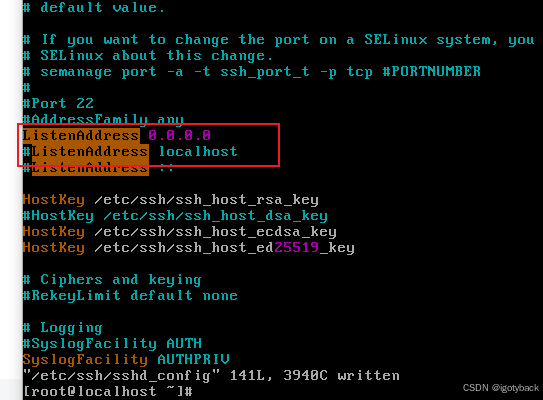
服务器禁用远程(22)
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config 修改 ListenAddress 0.0.0.0 为ListenAddress localhost 修改完后 重启一下sshd systemctl restart sshd 修改就生效了...

Docker 进阶构建:镜像、网络与仓库管理
目录 三. docker镜像构建 1. docker镜像结构 2. 镜像运行的基本原理 3. 镜像获得方式 4. 镜像构建 5. Dockerfile实例 6. 镜像优化方案 6.1. 镜像优化策略 6.2. 镜像优化示例:缩减镜像层 6.3. 镜像优化示例:多阶段构建 6.4. 镜像优化示例:使用最精简镜像 四. docke…...

opencv学习:图像轮廓识别及代码实现
图像轮廓 1.获取图像轮廓 cv2.findContours() 函数是 OpenCV 库中用于检测图像中轮廓的函数。它可以检测到图像中所有连通区域的边界,并返回这些轮廓的列表。从 OpenCV 3.4 版本开始,这个函数的返回值和参数有所变化,以下是详细的参数说明&…...
)
存储课程学习笔记2_借助内核插入一个文件系统,用文件夹下测试文件系统(mount文件系统到目录下是入口)
裸盘是如何能达到我们日常操作目录那样,按目录依次访问文件等,实际上就是基于裸盘上,用文件系统进行控制。 0:总结。 0:mount是入口,一个裸盘先赋予文件系统,然后mount后才可以用。 1…...

chunk-vendors.js 文件过大导致页面加载缓慢解决方案
1、路由懒加载 在 Webpack 中,我们可以使用动态 import语法来定义代码分块点 (split point): import(./Foo.vue) // 返回 Promise如果您使用的是 Babel,你将需要添加 syntax-dynamic-import 插件,才能使 Babel 可以正确地解析语…...
【Postgresql】地理空间数据的存储与查询,查询效率优化策略,数据类型与查询速度的影响
注:使用postgresql数据库会用到PostGIS 扩展。 一、安装PostGIS 扩展 在 PostgreSQL 中遇到错误 “type geography does not exist” 通常意味着你的 PostgreSQL 数据库还没有安装 PostGIS 扩展,或者 PostGIS 扩展没有被正确地安装在你的数据库中。geo…...

设计模式应用
单例模式 RunTime类是单例模式的体现,getRunTime()方法会返回一个唯一的实例。确保程序中只有一个唯一的RunTime类对象建造者模式 StringBuilder和StringBuffer是建造者模式的体现工厂模式 Calender类中Calender.getInstance()方法 DriverManager.getConnection()方…...

Android开机启动流程
Android开机启动流程 systemReady启动"added application" frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java mainnew SystemServer().run();startBootstrapServicesmActivityManagerService ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.startService(…...
数据结构基本知识
一、什么是数据结构 1.1、组织存储数据 ---------》内存(存储) 1.2、研究目的 如何存储数据(变量,数组....)程序数据结构算法 1.3、常见保存数据的方法 数组:保存自己的数据指针:是间接访问已经存在的…...

变量 varablie 声明- Rust 变量 let mut 声明与 C/C++ 变量声明对比分析
一、变量声明设计:let 与 mut 的哲学解析 Rust 采用 let 声明变量并通过 mut 显式标记可变性,这种设计体现了语言的核心哲学。以下是深度解析: 1.1 设计理念剖析 安全优先原则:默认不可变强制开发者明确声明意图 let x 5; …...

Linux应用开发之网络套接字编程(实例篇)
服务端与客户端单连接 服务端代码 #include <sys/socket.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <pthread.h> …...
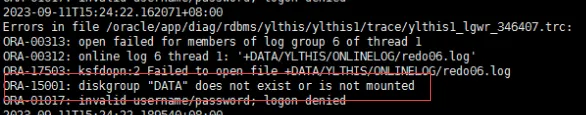
19c补丁后oracle属主变化,导致不能识别磁盘组
补丁后服务器重启,数据库再次无法启动 ORA01017: invalid username/password; logon denied Oracle 19c 在打上 19.23 或以上补丁版本后,存在与用户组权限相关的问题。具体表现为,Oracle 实例的运行用户(oracle)和集…...
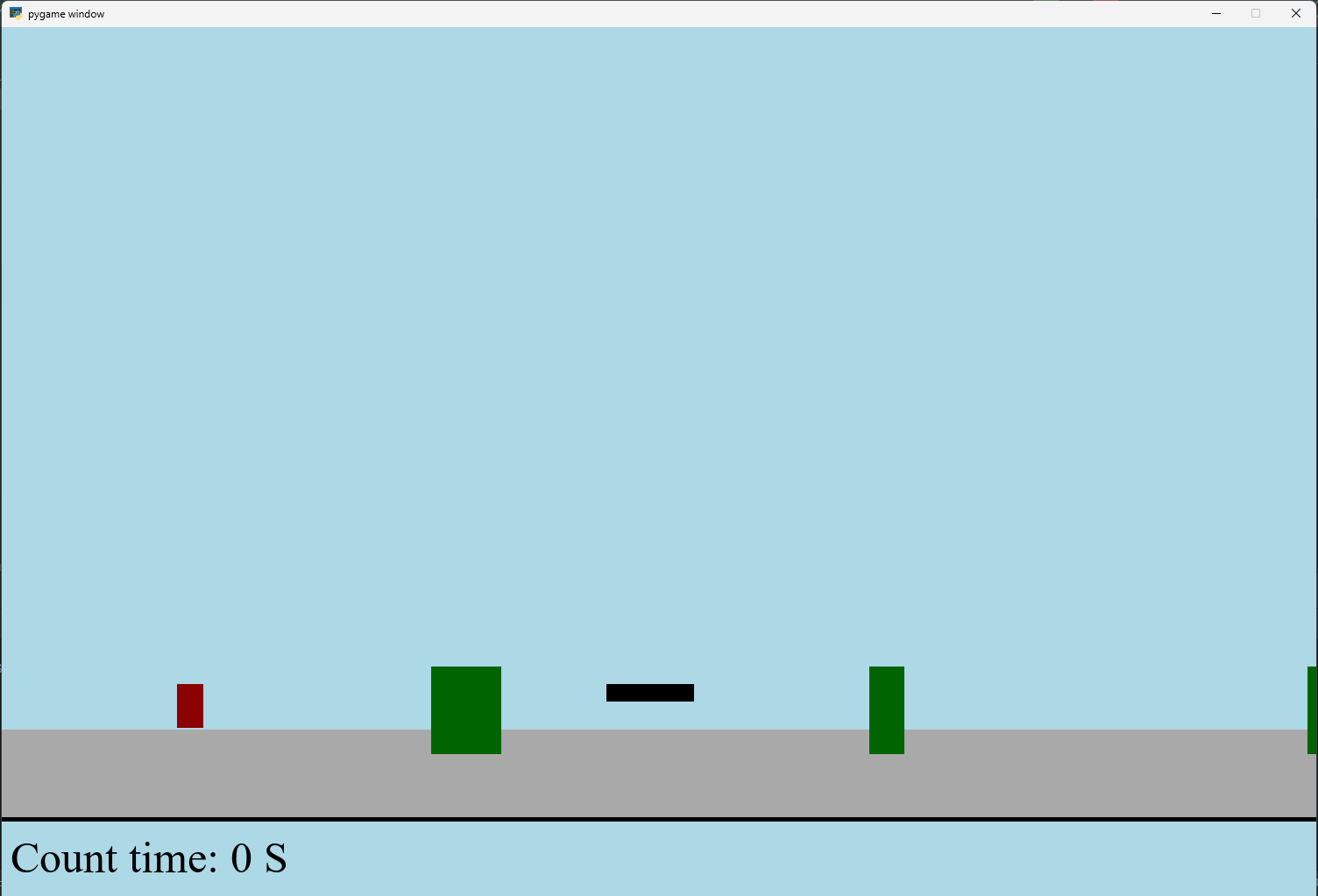
【Python】 -- 趣味代码 - 小恐龙游戏
文章目录 文章目录 00 小恐龙游戏程序设计框架代码结构和功能游戏流程总结01 小恐龙游戏程序设计02 百度网盘地址00 小恐龙游戏程序设计框架 这段代码是一个基于 Pygame 的简易跑酷游戏的完整实现,玩家控制一个角色(龙)躲避障碍物(仙人掌和乌鸦)。以下是代码的详细介绍:…...

iPhone密码忘记了办?iPhoneUnlocker,iPhone解锁工具Aiseesoft iPhone Unlocker 高级注册版分享
平时用 iPhone 的时候,难免会碰到解锁的麻烦事。比如密码忘了、人脸识别 / 指纹识别突然不灵,或者买了二手 iPhone 却被原来的 iCloud 账号锁住,这时候就需要靠谱的解锁工具来帮忙了。Aiseesoft iPhone Unlocker 就是专门解决这些问题的软件&…...
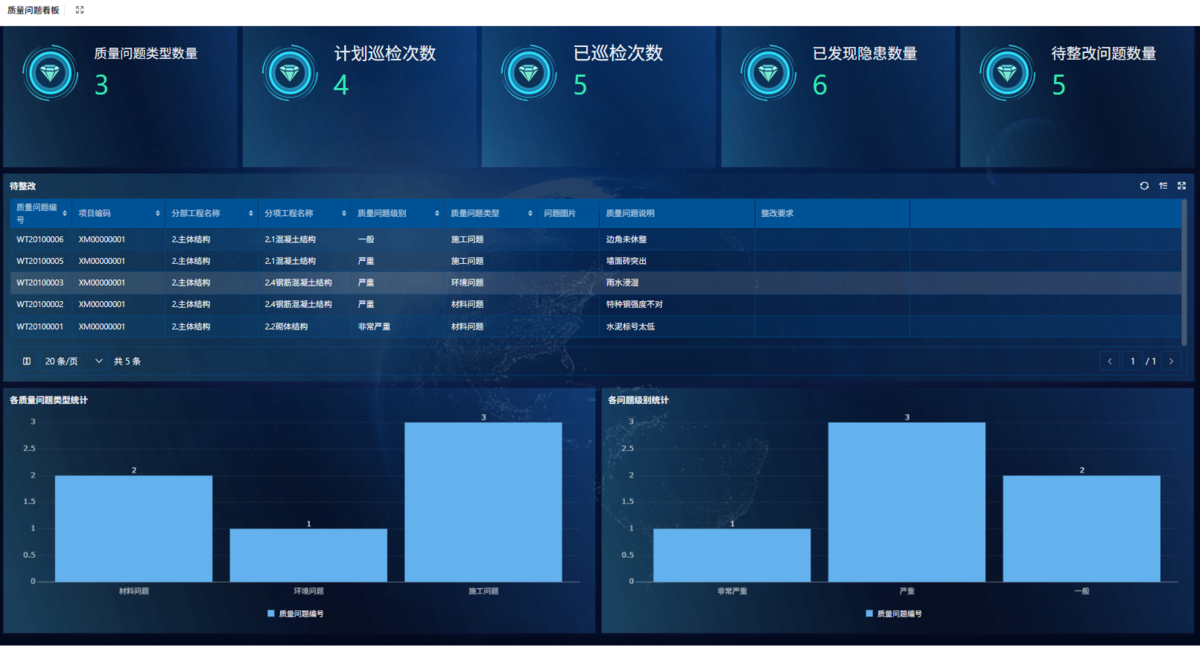
为什么需要建设工程项目管理?工程项目管理有哪些亮点功能?
在建筑行业,项目管理的重要性不言而喻。随着工程规模的扩大、技术复杂度的提升,传统的管理模式已经难以满足现代工程的需求。过去,许多企业依赖手工记录、口头沟通和分散的信息管理,导致效率低下、成本失控、风险频发。例如&#…...

蓝牙 BLE 扫描面试题大全(2):进阶面试题与实战演练
前文覆盖了 BLE 扫描的基础概念与经典问题蓝牙 BLE 扫描面试题大全(1):从基础到实战的深度解析-CSDN博客,但实际面试中,企业更关注候选人对复杂场景的应对能力(如多设备并发扫描、低功耗与高发现率的平衡)和前沿技术的…...
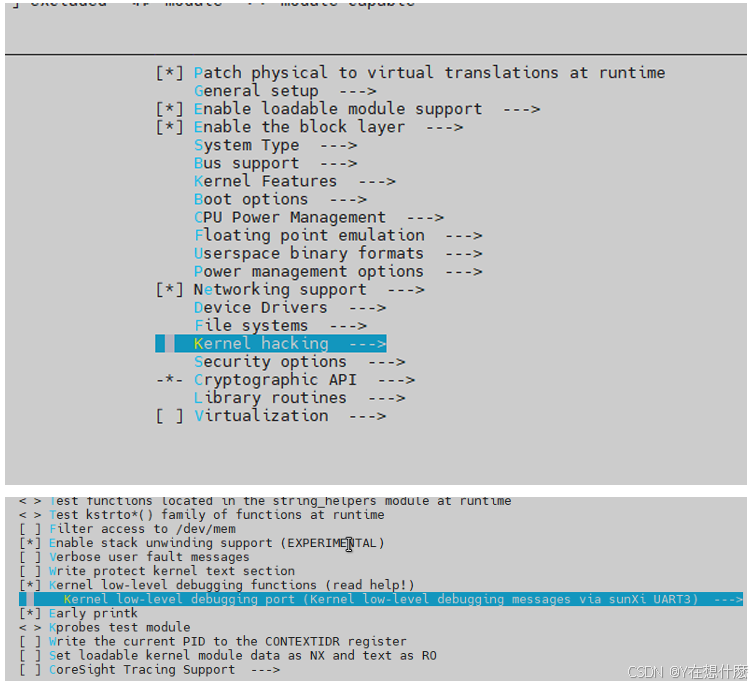
全志A40i android7.1 调试信息打印串口由uart0改为uart3
一,概述 1. 目的 将调试信息打印串口由uart0改为uart3。 2. 版本信息 Uboot版本:2014.07; Kernel版本:Linux-3.10; 二,Uboot 1. sys_config.fex改动 使能uart3(TX:PH00 RX:PH01),并让boo…...

Mac下Android Studio扫描根目录卡死问题记录
环境信息 操作系统: macOS 15.5 (Apple M2芯片)Android Studio版本: Meerkat Feature Drop | 2024.3.2 Patch 1 (Build #AI-243.26053.27.2432.13536105, 2025年5月22日构建) 问题现象 在项目开发过程中,提示一个依赖外部头文件的cpp源文件需要同步,点…...
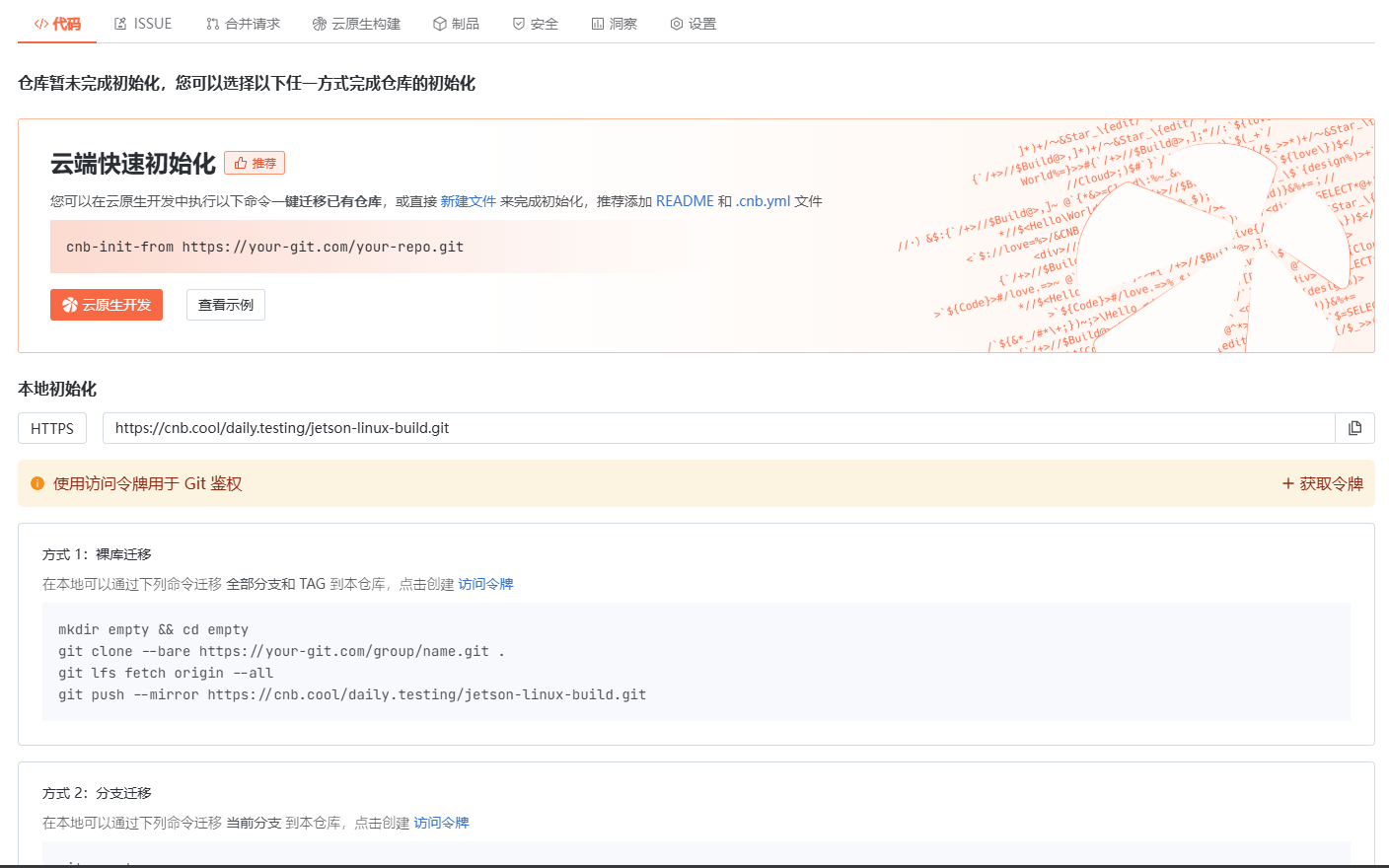
云原生玩法三问:构建自定义开发环境
云原生玩法三问:构建自定义开发环境 引言 临时运维一个古董项目,无文档,无环境,无交接人,俗称三无。 运行设备的环境老,本地环境版本高,ssh不过去。正好最近对 腾讯出品的云原生 cnb 感兴趣&…...
