rust一些通用编程的概念
rust一些通用编程的概念
官网文档数据类型 - Rust 程序设计语言 中文版 (rustwiki.org)
变量,数据类型,条件判断,循环
-
变量
rust中变量的可变性是值得注意的
例如:
fn main(){let number = 1;number = 2;println!("the number is {}",number); }let关键字定义的变量默认无法改变,上述的方式会导致运行报错
使用cargo run运行时得到以下结果
PS D:\rust_project\demo2> cargo runCompiling demo2 v0.1.0 (D:\rust_project\demo2) warning: value assigned to `number` is never read--> src/main.rs:2:9| 2 | let number = 1;| ^^^^^^|= help: maybe it is overwritten before being read?= note: `#[warn(unused_assignments)]` on by defaulterror[E0384]: cannot assign twice to immutable variable `number`--> src/main.rs:3:5| 2 | let number = 1;| ------ first assignment to `number` 3 | number = 2;| ^^^^^^^^^^ cannot assign twice to immutable variable| help: consider making this binding mutable| 2 | let mut number = 1;| +++For more information about this error, try `rustc --explain E0384`. warning: `demo2` (bin "demo2") generated 1 warning error: could not compile `demo2` (bin "demo2") due to 1 previous error; 1 warning emitted因为这里let直接定义的属于不可变变量,如果你需要定义一个可变变量需要使用mut关键字
fn main(){let mut number = 1;number = 2;println!("the number is {}",number); }结果就可以正常运行,不过会有相对应的warnning
warning: value assigned to `number` is never read--> src/main.rs:2:13| 2 | let mut number = 1;| ^^^^^^|= help: maybe it is overwritten before being read?= note: `#[warn(unused_assignments)]` on by defaultwarning: `demo2` (bin "demo2") generated 1 warningFinished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.47sRunning `target\debug\demo2.exe` the number is 2再引入一个概念
常量
常量和不可变变量类似,用于绑定到一个常量名且不允许更改的值,但是常量和变量之间存在一定差异,常量不允许使用mut关键字
且自始至终无法改变,使用const关键字定义常量,同时必须标注数据类型,常量可以在任意作用域中声明,包括全局作用域,且无法为函数调用结果或只能在运算时得到的值
fn main(){const THREE_HOURS_IN_SECONDS: u32 = 60 * 60 * 3;println!("the time is {}",THREE_HOURS_IN_SECONDS);}D:\rust_project\demo2>cargo runCompiling demo2 v0.1.0 (D:\rust_project\demo2)Finished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.35sRunning `target\debug\demo2.exe` the time is 10800遮掩
可以通过声明相同的变量名称来遮盖前面一个变量
fn main() {let x = 5;let x = x + 1;{let x = x * 2;println!("The value of x in the inner scope is: {}", x);}println!("The value of x is: {}", x); }The value of x in the inner scope is: 12 The value of x is: 6遮掩与mut区别在于
- 遮掩需要重新使用let定义新变量来遮盖达到修改原先变量的值,而mut不需要
- 遮掩是创建一个新变量所以可以改变原先变量的数据类型,但是mut始终一个变量类型
fn main() {let spaces = " ";let spaces = spaces.len(); }这其中第一个spaces为字符串类型,第二个为数字类型
fn main() {let mut spaces = " ";spaces = spaces.len(); }而这样编译器则会报错
Compiling demo2 v0.1.0 (D:\rust_project\demo2) error: format argument must be a string literal--> src/main.rs:4:14| 4 | println!(spaces)| ^^^^^^| help: you might be missing a string literal to format with| 4 | println!("{}", spaces)| +++++error: could not compile `demo2` (bin "demo2") due to 1 previous error -
数据类型
rust是一种静态类型语言,因此它在编译期必须知道所有变量的类型,rust每一个值都有确切的数据类型
一般可以在变量名称后面使用英文冒号加数据类型的方式进行标注
eg.
let guess: u32 = "42".parse().expect("Not a number!");: u32表示guess是一个无符号的32位整型数据
同时这段代码必须加上对应的:u32数据标注,因为等式的右边采用parse()方法将String类型转为数值类型时,必须显性的声明变量的数据类型
否则报错
error[E0282]: type annotations needed--> src/main.rs:2:9| 2 | let guess = "42".parse().expect("Not a number!");| ^^^^^ consider giving `guess` a typeFor more information about this error, try `rustc --explain E0282`. error: could not compile `no_type_annotations` due to previous error标量类型
标量类型表示单个值。Rust有4个基本的标量类型:整型、浮点型、布尔型和字符
-
整数类型
长度 有符号类型 无符号类型 8位 i8 u8 16 位 i16 u16 32 位 i32 u32 64 位 i64 u64 128 位 i128 u128 arch isize usize 有无符号表示是否取负数,每个有符号类型规定的数字范围是 -(2n - 1) ~ 2n - 1 - 1,其中
n是该定义形式的位长度。所以i8可存储数字范围是 -(27) ~ 27 - 1,即 -128 ~ 127。无符号类型可以存储的数字范围是 0 ~ 2n - 1,所以u8能够存储的数字为 0 ~ 28 - 1,即 0 ~ 255。此外,
isize和usize类型取决于程序运行的计算机体系结构,在表中表示为“arch”:若使用 64 位架构系统则为 64 位,若使用 32 位架构系统则为 32 位。可能属于多种数字类型的数字字面量允许使用类型后缀来指定类型,例如
57u8。数字字面量还可以使用_作为可视分隔符以方便读数,如1_000,此值和1000相同。数字字面量 示例 十进制 98_222 十六进制 0xff 八进制 0o77 二进制 0b1111_0000 字节 (仅限于 u8)b’A’ 同时如果不确定整数类型,rust通常会默认i32
-
浮点数
带有小数的数字
浮点数按照 IEEE-754 标准表示。
f32类型是单精度浮点型,f64为双精度浮点型。Rust 的所有数字类型都支持基本数学运算:加法、减法、乘法、除法和取模运算。整数除法会向下取整。下面代码演示了各使用一条
let语句来说明相应数字运算的用法:fn main() {// additionlet sum = 5 + 10;// subtractionlet difference = 95.5 - 4.3;// multiplicationlet product = 4 * 30;// divisionlet quotient = 56.7 / 32.2;let floored = 2 / 3; // Results in 0// remainderlet remainder = 43 % 5; } -
布尔类型
表示是否,和大多数编程语言一样
fn main() {let t = true;let f: bool = false; // with explicit type annotation } -
字符类型
Rust 的
char(字符)类型是该语言最基本的字母类型,且为4个字节支持Unicode编码下面是一些声明char值的例子:fn main() {let c = 'z';let z = 'ℤ';let heart_eyed_cat = '😻'; } -
复合类型
-
元组
和python中的元组概念类似
可以将多种类型的值组合到一个复合类型中
fn main() {let tup: (i32, f64, u8) = (500, 6.4, 1); }同时可以使用模式解构的方式获取元组中的某个值
fn main() {let tup: (i32,u32,f64,bool) = (-1,1121,3.1415926,true);let (x,y,z,w) = tup;println!("The value of x is: {}",x); }D:\rust_project\demo2>cargo runCompiling demo2 v0.1.0 (D:\rust_project\demo2) warning: unused variable: `y`--> src/main.rs:3:12| 3 | let (x,y,z,w) = tup;| ^ help: if this is intentional, prefix it with an underscore: `_y`|= note: `#[warn(unused_variables)]` on by defaultwarning: unused variable: `z`--> src/main.rs:3:14| 3 | let (x,y,z,w) = tup;| ^ help: if this is intentional, prefix it with an underscore: `_z`warning: unused variable: `w`--> src/main.rs:3:16| 3 | let (x,y,z,w) = tup;| ^ help: if this is intentional, prefix it with an underscore: `_w`warning: `demo2` (bin "demo2") generated 3 warningsFinished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.35sRunning `target\debug\demo2.exe` The value of x is: -1也可以利用.运算符来获取元组中的某个值,同时索引从0开始
warning: unused variable: `x`--> src/main.rs:3:10| 3 | let (x,y,z,w) = tup;| ^ help: if this is intentional, prefix it with an underscore: `_x`|= note: `#[warn(unused_variables)]` on by defaultwarning: unused variable: `y`--> src/main.rs:3:12| 3 | let (x,y,z,w) = tup;| ^ help: if this is intentional, prefix it with an underscore: `_y`warning: unused variable: `z`--> src/main.rs:3:14| 3 | let (x,y,z,w) = tup;| ^ help: if this is intentional, prefix it with an underscore: `_z`warning: unused variable: `w`--> src/main.rs:3:16| 3 | let (x,y,z,w) = tup;| ^ help: if this is intentional, prefix it with an underscore: `_w`warning: `demo2` (bin "demo2") generated 4 warningsFinished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.35sRunning `target\debug\demo2.exe` The value of x is: -1 -
数组类型
写法上等同于python中的列表,但是概念等同于c语言
fn main() {let array = [1,2,3];println!("{}", array[0]) }D:\rust_project\demo2>cargo runCompiling demo2 v0.1.0 (D:\rust_project\demo2)Finished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.35sRunning `target\debug\demo2.exe` 1但是数组长度不可变,数组中的数据类型必须一致
显示写法
fn main() { let a: [i32; 5] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; }这里,
i32是每个元素的类型。分号之后,数字5表明该数组包含 5 个元素。如果要为每个元素创建包含相同值的数组,可以指定初始值,后跟分号,然后在方括号中指定数组的长度,如下所示:
fn main() { let a = [3; 5]; }
-
-
-
函数
其实很类似与python的显示函数声明
通过关键字fn自定义函数
main函数便是rust程序的启动入口
fn main() {println!("Hello, world!");another_function(); }fn another_function() {println!("Another function."); }$ cargo runCompiling functions v0.1.0 (file:///projects/functions)Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.28sRunning `target/debug/functions` Hello, world! Another function.参数
函数也可以被定义为拥有参数(parameter),参数是特殊变量,是函数签名的一部分。当函数拥有参数(形参)时,可以为这些参数提供具体的值(实参)。技术上讲,这些具体值被称为实参(argument),但是在日常交流中,人们倾向于不区分使用 parameter 和 argument 来表示函数定义中的变量或调用函数时传入的具体值。
在函数签名中,必须声明每个参数的类型。这是一个 Rust 设计中经过慎重考虑的决定:要求在函数定义中提供类型标注,意味着编译器几乎从不需要你在代码的其他地方注明类型来指出你的意图。
当一个函数有多个参数时,使用逗号分隔,像这样:
fn main() {print_labeled_measurement(5, 'h'); }fn print_labeled_measurement(value: i32, unit_label: char) {println!("The measurement is: {}{}", value, unit_label); }这个例子创建了一个有两个参数的名为
print_labeled_measurement的函数。第一个参数名为value, 类型是i32。第二个参数是unit_label,类型是char。接着该函数打印包含value和unit_label的文本。语句和表达式
函数体由一系列语句组成,也可选择以表达式结尾。目前为止,我们介绍的函数还没有包含结尾表达式,不过你已经看到了表达式作为语句的一部分。因为 Rust 是一门基于表达式(expression-based)的语言,所以这是一个需要理解的重要区别。其他语言没有这样的区别,所以让我们看看语句和表达式分别是什么,以及它们的区别如何影响函数体。
语句(statement)是执行一些操作但不返回值的指令。表达式(expression)计算并产生一个值。让我们看一些例子:
实际上,我们已经使用过语句和表达式。使用
let关键字创建变量并绑定一个值是一个语句。在示例中,let y = 6;是一个语句。fn main() {let y = 6; }函数定义也是语句,上面整个例子本身就是一个语句。
语句不返回值。因此,不能把
let语句赋值给另一个变量,就像下面的代码尝试做的那样,会产生一个错误:fn main() {let x = (let y = 6); }$ cargo runCompiling functions v0.1.0 (file:///projects/functions) error: expected expression, found statement (`let`)--> src/main.rs:2:14| 2 | let x = (let y = 6);| ^^^^^^^^^|= note: variable declaration using `let` is a statementerror[E0658]: `let` expressions in this position are experimental--> src/main.rs:2:14| 2 | let x = (let y = 6);| ^^^^^^^^^|= note: see issue #53667 <https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/53667> for more information= help: you can write `matches!(<expr>, <pattern>)` instead of `let <pattern> = <expr>`warning: unnecessary parentheses around assigned value--> src/main.rs:2:13| 2 | let x = (let y = 6);| ^ ^|= note: `#[warn(unused_parens)]` on by default help: remove these parentheses| 2 - let x = (let y = 6); 2 + let x = let y = 6;| For more information about this error, try `rustc --explain E0658`. warning: `functions` (bin "functions") generated 1 warning error: could not compile `functions` due to 2 previous errors; 1 warning emitted表达式会计算出一个值,考虑一个数学运算,比如
5 + 6,这是一个表达式并计算出值11。表达式可以是语句的一部分语句
let y = 6;中的6是一个表达式,它计算出的值是6。函数调用是一个表达式。宏调用是一个表达式。我们用来创建新作用域的大括号(代码块){}也是一个表达式,例如fn main() {let y = {let x = 3;x + 1};println!("The value of y is: {}", y); }中这个就是表达式
{let x = 3;x + 1 }是一个代码块,在这个例子中计算结果是
4。这个值作为let语句的一部分被绑定到y上。注意,x + 1行的末尾没有分号,这与你目前见过的大部分代码行不同。表达式的结尾没有分号。如果在表达式的末尾加上分号,那么它就转换为语句,而语句不会返回值。在接下来探讨函数返回值和表达式时带有返回值的函数
函数可以向调用它的代码返回值。我们并不对返回值命名,但要在箭头(
->)后声明它的类型。在 Rust 中,函数的返回值等同于函数体最后一个表达式的值。使用return关键字和指定值,可以从函数中提前返回;但大部分函数隐式返回最后一个表达式。这是一个有返回值函数的例子:fn five() -> i32 {5 }fn main() {let x = five();println!("The value of x is: {}", x); }在
five函数中没有函数调用、宏,甚至没有let语句——只有数字5本身。这在 Rust 中是一个完全有效的函数。注意,函数返回值的类型也被指定好,即-> i32。尝试运行代码;输出应如下所示:$ cargo runCompiling functions v0.1.0 (file:///projects/functions)Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.30sRunning `target/debug/functions` The value of x is: 5five函数的返回值是5,所以返回值类型是i32。让我们仔细检查一下这段代码。有两个重要的部分:首先,let x = five();这一行表明我们使用函数的返回值初始化一个变量。因为five函数返回5,这一行与如下代码相同:#![allow(unused)] fn main() { let x = 5; }其次,
five函数没有参数并定义了返回值类型,不过函数体只有单单一个5也没有分号,因为这是一个表达式,正是我们想要返回的值。让我们看看另一个例子:
fn main() {let x = plus_one(5);println!("The value of x is: {}", x); }fn plus_one(x: i32) -> i32 {x + 1 }运行代码会打印出
The value of x is: 6。但如果在包含x + 1的行尾加上一个分号,把它从表达式变成语句,我们将得到一个错误。fn main() {let x = plus_one(5);println!("The value of x is: {}", x); }fn plus_one(x: i32) -> i32 {x + 1; }$ cargo runCompiling functions v0.1.0 (file:///projects/functions) error[E0308]: mismatched types--> src/main.rs:7:24| 7 | fn plus_one(x: i32) -> i32 {| -------- ^^^ expected `i32`, found `()`| || implicitly returns `()` as its body has no tail or `return` expression 8 | x + 1;| - help: consider removing this semicolonFor more information about this error, try `rustc --explain E0308`. error: could not compile `functions` due to previous error主要的错误信息 “mismatched types”(类型不匹配)揭示了这段代码的核心问题。函数
plus_one的定义说明它要返回一个i32类型的值,不过语句并不会返回值,此值由单元类型()表示,表示不返回值。因为不返回值与函数定义相矛盾,从而出现一个错误。在输出中,Rust 提供了一条信息,可能有助于纠正这个错误:它建议删除分号,这将修复错误。不过使用return也可以正常返回
fn main() {let res = add(1,2);println!("{}", res);} fn add(value_first: i32, value_second: i32)->i32{return value_first + value_second; }D:\rust_project\demo2>cargo runCompiling demo2 v0.1.0 (D:\rust_project\demo2)Finished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.34sRunning `target\debug\demo2.exe` 3 -
注释
和c语言一样,//和/**/
还有一种文档注释后期说明
-
控制流
根据条件是否为真来决定是否执行某些代码,或根据条件是否为真来重复运行一段代码,是大部分编程语言的基本组成部分。Rust 代码中最常见的用来控制执行流的结构是
if表达式和循环。if表达式if表达式允许根据条件执行不同的代码分支。你提供一个条件并表示 “如果条件满足,运行这段代码;如果条件不满足,不运行这段代码。fn main() {let number = 3;if number < 5 {println!("condition was true");} else {println!("condition was false");} }$ cargo runCompiling branches v0.1.0 (file:///projects/branches)Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.31sRunning `target/debug/branches` condition was true值得注意的是代码中的条件必须是
bool值。如果条件不是bool值,我们将得到一个错误。例如fn main() {let number = 3;if number {println!("number was three");} }$ cargo runCompiling branches v0.1.0 (file:///projects/branches) error[E0308]: mismatched types--> src/main.rs:4:8| 4 | if number {| ^^^^^^ expected `bool`, found integerFor more information about this error, try `rustc --explain E0308`. error: could not compile `branches` due to previous error必须自始至终显式地使用布尔值作为
if的条件使用
else if处理多重条件可以将
if和else组成的else if表达式来实现多重条件。例如:fn main() {let number = 6;if number % 4 == 0 {println!("number is divisible by 4");} else if number % 3 == 0 {println!("number is divisible by 3");} else if number % 2 == 0 {println!("number is divisible by 2");} else {println!("number is not divisible by 4, 3, or 2");} }在
let语句中使用if因为
if是一个表达式,我们可以在let语句的右侧使用它来将结果赋值给一个变量,例如:fn main() {let condition = true;let number = if condition { 5 } else { 6 };println!("The value of number is: {}", number); }其实就是三元运算符
但是记住,代码块的值是其最后一个表达式的值,而数字本身就是一个表达式。在这个例子中,整个
if表达式的值取决于哪个代码块被执行。这意味着if的每个分支的可能的返回值都必须是相同类型;在示例中,if分支和else分支的结果都是i32整型。如果它们的类型不匹配,如下面这个例子,则会产生一个错误:fn main() {let condition = true;let number = if condition { 5 } else { "six" };println!("The value of number is: {}", number); }$ cargo runCompiling branches v0.1.0 (file:///projects/branches) error[E0308]: `if` and `else` have incompatible types--> src/main.rs:4:44| 4 | let number = if condition { 5 } else { "six" };| - ^^^^^ expected integer, found `&str`| || expected because of thisFor more information about this error, try `rustc --explain E0308`. error: could not compile `branches` due to previous error循环控制流
在 Rust 中,循环控制流主要包括三种类型的循环:
loop、while和for。它们的区别在于使用场景、语法以及控制流的特点。以下是对这三种循环的详细论述:1.
loop循环loop是 Rust 中的无限循环语句。它会无限执行其内部的代码块,直到明确使用break退出循环。适用于需要无限循环的场景,比如服务的事件循环。示例:
let mut count = 0; loop {count += 1;if count == 10 {break;}println!("Count: {}", count); }-
特点:
- 无条件循环,需要手动使用
break来退出。 - 可以通过
continue跳过当前循环并进入下一次循环。 - 适用于无法确定循环次数或者需要手动控制的循环场景。
- 无条件循环,需要手动使用
-
返回值:
loop循环可以返回值,通常与break结合使用。
let result = loop {count += 1;if count == 10 {break count * 2; // 返回值为 20} };
2.
while循环while是基于条件判断的循环,在条件为true时重复执行代码块,条件为false时退出循环。示例:
let mut number = 3; while number != 0 {println!("{}!", number);number -= 1; } println!("Liftoff!");-
特点:
- 依赖布尔条件的判断,当条件为
false时自动结束。 - 适用于条件驱动的循环场景。
- 依赖布尔条件的判断,当条件为
-
优点:
- 比
loop更灵活和安全,因为它不需要显式地使用break。
- 比
3.
for循环for循环用于遍历集合(如数组、迭代器、范围等)。它是 Rust 中最常用的循环形式。示例:
let a = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]; for element in a.iter() {println!("The value is: {}", element); }-
特点:
- 适合遍历固定范围或者集合类型(如数组、切片等)。
- 语法简洁,自动处理索引范围,不容易出现越界错误。
-
使用范围语法:
for number in 1..4 {println!("{}!", number); // 输出 1, 2, 3 } -
迭代器结合:
for循环与迭代器结合非常方便,可以利用 Rust 提供的强大迭代器机制来简化循环操作。
小结:
loop:无限循环,适用于需要手动控制退出的场景。while:条件驱动的循环,适合在满足某个条件时执行的操作。for:集合或范围遍历,最常用的循环形式,安全且简洁。
-
相关文章:

rust一些通用编程的概念
rust一些通用编程的概念 官网文档数据类型 - Rust 程序设计语言 中文版 (rustwiki.org) 变量,数据类型,条件判断,循环 变量 rust中变量的可变性是值得注意的 例如: fn main(){let number 1;number 2;println!("the number is {}&quo…...

SpringBoot基础知识
谈一谈你对SpringBoot的理解,它有哪些特性(优点)? SpringBoot用来快速开发Spring应用的一个脚手架,其目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。 优点: 简化配置:提供了很多内置的…...

ubuntu配置libtorch CPU版本
配置环境:Ubuntu 20.04Date:2024 / 08 1、下载最新版本的libtorch wget https://download.pytorch.org/libtorch/nightly/cpu/libtorch-shared-with-deps-latest.zip unzip libtorch-shared-with-deps-latest.zip2、创建一个C工程文件夹,目…...

Docker MySql 数据备份、恢复
docker-compose.yaml实例 version: 3.8 services:db:image: mysql:9.0.1environment:MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: 123456MYSQL_DATABASE: dataMYSQL_USER: dataMYSQL_PASSWORD: 123456MYSQL_ROOT_HOST: % 1、备份 docker exec -it <容器名称> /usr/bin/mysqldump -u root -p12…...

django项目添加测试数据的三种方式
文章目录 自定义终端命令Faker添加模拟数据基于终端脚本来完成数据的添加编写python脚本编写shell脚本执行脚本需要权限使用shell命令来完成测试数据的添加 添加测试数据在工作中一共有三种方式: 可以根据django的manage.py指令进行[自定义终端命令]可以采用第三方…...

用Python提取PDF表格到Excel文件
在对PDF中的表格进行再利用时,除了直接将PDF文档转换为Excel文件,我们还可以提取PDF文档中的表格数据并写入Excel工作表。这样做可以避免一些不必要的文本和格式带来的干扰,获得更易于分析和处理的表格数据,并方便进行更多的格式设…...

Java基础|多线程:多线程分页拉取
前言: 通常我们都会遇到分页拉取的需求,比如与第三方系统同步数据,定时拉取全量数据做缓存,下面我们简单介绍下多线程分页写法 需求: 全量同步第三方系统数据,并在全部数据同步完后,统一做缓存…...
Android RecyclerView 实现 GridView ,并实现点击效果及方向位置的显示
效果图 一、引入 implementation com.github.CymChad:BaseRecyclerViewAdapterHelper:2.9.30 二、使用步骤 1.Adapter public class UnAdapter extends BaseQuickAdapter<UnBean.ResultBean, BaseViewHolder> {private int selectedPosition RecyclerView.NO_POSITIO…...

Centos中dnf和yum区别对比
dnf和yum是两种不同的包管理工具,它们各自具有独特的特点和优势,主要用于在Linux系统上安装、更新和卸载软件包。以下是dnf和yum之间的主要区别: 1. 依赖关系解决 dnf:dnf在处理依赖关系方面表现出更强的能力。它能够更高效地解…...

CVPT: Cross-Attention help Visual Prompt Tuning adapt visual task
论文汇总 当前的问题 图1:在VTAB-1k基准测试上,使用预训练的ViT-B/16模型,VPT和我们的CVPT之间的性能和Flops比较。我们将提示的数量分别设置为1、10、20、50,100,150,200。 如图1所示,当给出大量提示时,VPT显示了性能的显著下降…...

基于双向 LSTM 和 CRF 的序列标注模型
基于双向 LSTM 和 CRF 的序列标注模型 在自然语言处理中,序列标注是一项重要的任务,例如命名实体识别、词性标注等。本文将介绍如何使用 Keras 构建一个基于双向 LSTM 和 CRF 的序列标注模型。 一、引言 序列标注任务要求为输入序列中的每个元素分配一个标签。传统的方法可…...

为何美国与加拿大边界看似那么随意?
我们在《日本移民巴西超200万,会成第二个“巴勒斯坦”吗?》一文中探讨了日本移民巴西的历史,以及移民对巴西的风险与挑战。 今天我们来探讨美国与加拿大边界为什么那么随意,并整理了加拿大和美国的国界、省界、市界行政边界数据分享给大家&a…...
?触发器何时会被触发?)
什么是触发器(Trigger)?触发器何时会被触发?
在数据库管理系统中,触发器是一种特殊的存储过程,它会在特定的表上执行插入、更新或删除操作时自动触发。 触发器的主要用途是维护数据的一致性和完整性,以及实现一些复杂的业务逻辑。 触发器何时会被触发? 触发器可以在以下几…...

一步一步优化一套生成式语言模型系统
以下是这套生成式语言模型解决任务的流程图概述: #mermaid-svg-keXg8yGoCyObKDtu {font-family:"trebuchet ms",verdana,arial,sans-serif;font-size:16px;fill:#333;}#mermaid-svg-keXg8yGoCyObKDtu .error-icon{fill:#552222;}#mermaid-svg-keXg8yGoCyO…...

Q必达任务脚本
文章目录 1.购买服务器地址2.部署教程3. 代码如下4. 如何联系我 1.购买服务器地址 服务器购买地址 https://t.aliyun.com/U/rUHk58 若失效,可用地址 https://www.aliyun.com/activity/wuying/dj?source5176.29345612&userCode49hts92d 2.部署教程 2024年最…...

问请问请问2312123213123
📢博客主页:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_779549673 📢欢迎点赞 👍 收藏 ⭐留言 📝 如有错误敬请指正! 📢本文由 JohnKi 原创,首发于 CSDN🙉 📢未来很长&#…...

Vue3:快速生成模板代码
目录 一.模板代码 1.提供基础结构 2.定义组件名称 3.初始化数据和方法 4.应用样式 5.提高开发效率 二.操作 1.点击右下角设置按钮选择代码片段 2.输入vue.json,打开vue.json文件 3.构造模板 4.模板代码 5.使用 6.效果 一.模板代码 Vue3快速生成模板代…...

文件上传-php
查找方式 ***(1) 黑盒 查找(upload) 扫描 (2) 应用型 窗口 上传中心或者后台中心 上传 Ps:后台是后台 权限是权限 (3) 会员中心 (4) 白盒 基本函数定义 写前端的 Enctype 上传类型Method 提交方式Onsubmit 鼠标的时间Action"放在指定文件"Php 接受表单数据 isset(…...

C++设计模式(更新中)
文章目录 1、创建型模式1.1 简单工厂(Simple Factory)(1)示例(2)总结 1.2 工厂方法(Factory Method)(1)示例(2)总结 1.3 抽象工厂&…...

Kali crunsh字典工具
查看自带密码字典 vim /usr/share/wordlists 使用 crunch 字典工具 随机组成6位纯数字密码 crunch 6 6 0123456789 -o test1.txt 由 Abc1234 随机组成的 6~8 位密码 crunch 6 8 Abc1234 -o test2.txt 以A开头后面跟3位数字组成的4位密码 crunch 4 4 -t A%%% -o test3.txt...

日语AI面试高效通关秘籍:专业解读与青柚面试智能助攻
在如今就业市场竞争日益激烈的背景下,越来越多的求职者将目光投向了日本及中日双语岗位。但是,一场日语面试往往让许多人感到步履维艰。你是否也曾因为面试官抛出的“刁钻问题”而心生畏惧?面对生疏的日语交流环境,即便提前恶补了…...
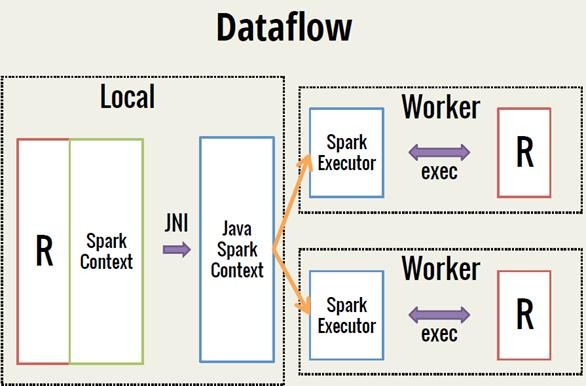
Spark 之 入门讲解详细版(1)
1、简介 1.1 Spark简介 Spark是加州大学伯克利分校AMP实验室(Algorithms, Machines, and People Lab)开发通用内存并行计算框架。Spark在2013年6月进入Apache成为孵化项目,8个月后成为Apache顶级项目,速度之快足见过人之处&…...
从深圳崛起的“机器之眼”:赴港乐动机器人的万亿赛道赶考路
进入2025年以来,尽管围绕人形机器人、具身智能等机器人赛道的质疑声不断,但全球市场热度依然高涨,入局者持续增加。 以国内市场为例,天眼查专业版数据显示,截至5月底,我国现存在业、存续状态的机器人相关企…...
)
python爬虫:Newspaper3k 的详细使用(好用的新闻网站文章抓取和解析的Python库)
更多内容请见: 爬虫和逆向教程-专栏介绍和目录 文章目录 一、Newspaper3k 概述1.1 Newspaper3k 介绍1.2 主要功能1.3 典型应用场景1.4 安装二、基本用法2.2 提取单篇文章的内容2.2 处理多篇文档三、高级选项3.1 自定义配置3.2 分析文章情感四、实战案例4.1 构建新闻摘要聚合器…...
python执行测试用例,allure报乱码且未成功生成报告
allure执行测试用例时显示乱码:‘allure’ �����ڲ����ⲿ���Ҳ���ǿ�&am…...
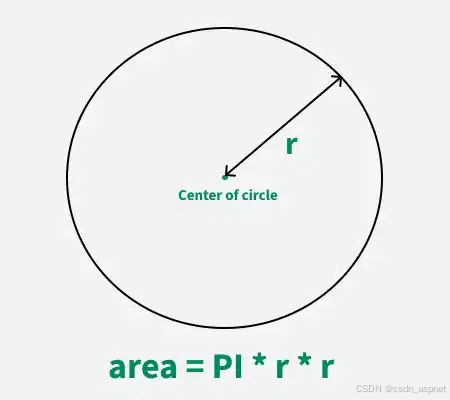
C# 求圆面积的程序(Program to find area of a circle)
给定半径r,求圆的面积。圆的面积应精确到小数点后5位。 例子: 输入:r 5 输出:78.53982 解释:由于面积 PI * r * r 3.14159265358979323846 * 5 * 5 78.53982,因为我们只保留小数点后 5 位数字。 输…...
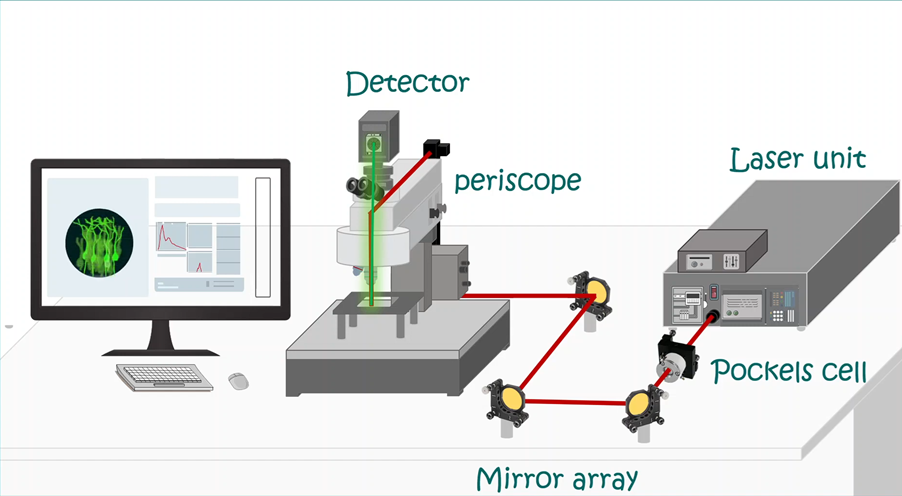
LabVIEW双光子成像系统技术
双光子成像技术的核心特性 双光子成像通过双低能量光子协同激发机制,展现出显著的技术优势: 深层组织穿透能力:适用于活体组织深度成像 高分辨率观测性能:满足微观结构的精细研究需求 低光毒性特点:减少对样本的损伤…...
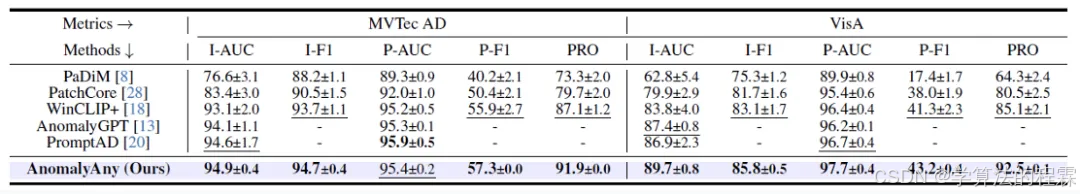
CVPR2025重磅突破:AnomalyAny框架实现单样本生成逼真异常数据,破解视觉检测瓶颈!
本文介绍了一种名为AnomalyAny的创新框架,该方法利用Stable Diffusion的强大生成能力,仅需单个正常样本和文本描述,即可生成逼真且多样化的异常样本,有效解决了视觉异常检测中异常样本稀缺的难题,为工业质检、医疗影像…...
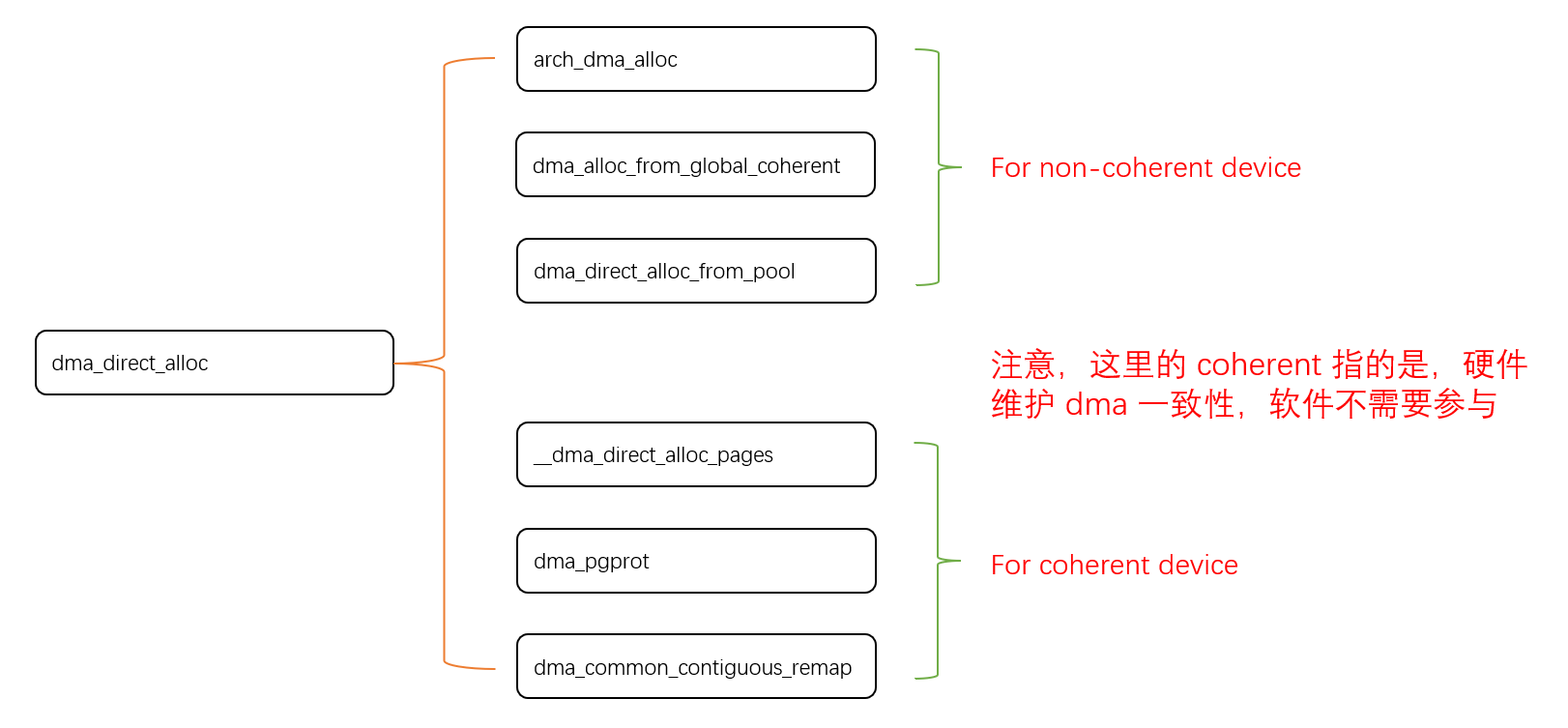
Linux 下 DMA 内存映射浅析
序 系统 I/O 设备驱动程序通常调用其特定子系统的接口为 DMA 分配内存,但最终会调到 DMA 子系统的dma_alloc_coherent()/dma_alloc_attrs() 等接口。 关于 dma_alloc_coherent 接口详细的代码讲解、调用流程,可以参考这篇文章,我觉得写的非常…...

6️⃣Go 语言中的哈希、加密与序列化:通往区块链世界的钥匙
Go 语言中的哈希、加密与序列化:通往区块链世界的钥匙 一、前言:离区块链还有多远? 区块链听起来可能遥不可及,似乎是只有密码学专家和资深工程师才能涉足的领域。但事实上,构建一个区块链的核心并不复杂,尤其当你已经掌握了一门系统编程语言,比如 Go。 要真正理解区…...
