C++编程:实现一个基于原始指针的环形缓冲区(RingBuffer)缓存串口数据
文章目录
- 0. 引言
- 1. 使用示例
- 2. 流程图
- 2.1 追加数据流程
- 2.2 获取空闲块流程
- 2.3 处理特殊字符流程
- 2.4 释放块流程
- 2.5 获取下一个使用块流程
- 3. 代码详解
- 3.1 Block 结构体
- 3.2 RingBuffer 类
- 3.3 主要方法解析
- append 方法
- currentUsed 和 currentUsing 方法
- release 方法
- nextUsed 方法
- 3.4 私有方法解析
- nextFree 方法
- checkSpecial 方法
- 4. 内存管理与拷贝控制
- 5. 完整代码
0. 引言
本文将介绍一个解析串口数据的环形缓冲区,使用’$‘或者’#'分割串口消息。
主要设计考虑包括:
- 内存管理:选用内存块数组,而不是选用一整块的内存+读写指针的方式,以减少读写数据时的资源竞争。使用原始指针手动分配和释放内存,确保每个
Block管理自己的缓冲区。
确保资源的安全转移。 - 状态管理:每个
Block通过status成员变量表示其当前状态(空闲、使用中或已使用)。
1. 使用示例
以下是一个简单的使用示例,展示如何创建 RingBuffer 实例、追加数据、访问当前使用的 Block 以及释放 Block。
#include "ring_buffer.hpp"int main()
{try{// 创建一个包含10个Block的RingBufferRingBuffer ringBuffer(10);// 追加数据1const char* data1 = "Hello, World!";if (!ringBuffer.append(reinterpret_cast<const uint8_t*>(data1), std::strlen(data1))){std::cerr << "Failed to append data1.\n";}// 追加数据2,包含特殊字符const char* data2 = "Special#Character";if (!ringBuffer.append(reinterpret_cast<const uint8_t*>(data2), std::strlen(data2))){std::cerr << "Failed to append data2.\n";}// 访问当前使用的Blockconst RingBuffer::Block& usedBlock = ringBuffer.currentUsed();std::cout << "Used Block Index: " << usedBlock.index << ", Written: " << usedBlock.written << "\n";// 访问当前正在写入的Blockconst RingBuffer::Block& usingBlock = ringBuffer.currentUsing();std::cout << "Using Block Index: " << usingBlock.index << ", Written: " << usingBlock.written << "\n";// 释放第一个BlockringBuffer.release(0);}catch (const std::exception& ex){std::cerr << "Exception: " << ex.what() << "\n";}return 0;
}
解析:
- 创建 RingBuffer:初始化一个包含10个
Block的RingBuffer实例。 - 追加数据:
- 追加字符串
"Hello, World!"。 - 追加包含特殊字符
"#"的字符串"Special#Character",触发数据分割逻辑。
- 追加字符串
- 访问 Block:
- 获取并打印当前使用的
Block的索引和已写入字节数。 - 获取并打印当前正在写入的
Block的索引和已写入字节数。
- 获取并打印当前使用的
- 释放 Block:释放第一个
Block,将其状态标记为BufFree并重置已写入字节数。 - 异常处理:使用
try-catch块捕获并处理可能抛出的异常,确保程序的稳定性。
2. 流程图
2.1 追加数据流程
首先,我们来看一下追加数据的整体流程。这是环形缓冲区的核心功能,负责将新数据添加到缓冲区中。
流程图解析
- 开始:数据追加操作的起点。
- 验证数据长度:检查待追加的数据是否超过单个块的大小(
BlockSize)。- 长度超过:输出错误信息,终止操作。
- 长度合适:继续下一步。
- 检查当前块空间和状态:判断当前块是否有足够的空间且状态为
BufUsing(使用中)。- 有足够空间且状态正确:将数据复制到当前块。
- 无足够空间或状态不符:尝试获取下一个空闲块。
- 尝试获取下一个空闲块:
- 获取成功:设置新块的状态为
BufUsing,继续数据追加。 - 获取失败:输出错误信息,终止操作。
- 获取成功:设置新块的状态为
- 结束:数据追加流程结束。
2.2 获取空闲块流程
当当前块空间不足或状态不符时,需要获取下一个空闲块。以下流程图展示了获取空闲块的具体步骤。
flowchart TDA[开始] --> B[检查当前块状态]B --> |状态为BufFree| C[可以使用当前块]B --> |状态不为BufFree| D[检查是否允许重试]D --> |允许重试| E[返回失败]D --> |不允许重试| F[标记当前块为BufUsed]F --> G[检查是否到达缓冲区末尾]G --> |是| H[回绕到第一个块]G --> |否| I[移动到下一个块]H --> J[检查块是否为空]I --> JJ --> |块为空| K[成功获取空闲块]J --> |块不为空| L[输出警告,返回失败]C --> KK --> M[结束]L --> ME --> M
流程图解析
- 开始:获取空闲块操作的起点。
- 检查当前块状态:判断当前块是否为空闲状态(
BufFree)。- 状态为BufFree:可以直接使用当前块。
- 状态不为BufFree:进一步检查是否允许重试。
- 检查是否允许重试:
- 允许重试:直接返回失败,不进行进一步操作。
- 不允许重试:将当前块标记为
BufUsed,表示已被使用。
- 标记当前块为BufUsed:更新当前块的状态。
- 检查是否到达缓冲区末尾:
- 是:回绕到缓冲区的第一个块。
- 否:移动到下一个块。
- 检查块是否为空:判断目标块是否为空闲状态。
- 块为空:成功获取空闲块。
- 块不为空:输出警告信息,返回失败。
- 结束:获取空闲块流程结束。
2.3 处理特殊字符流程
在追加数据过程中,如果数据中包含特殊字符(如#或$),需要对数据进行分割处理。以下流程图展示了处理特殊字符的具体步骤。
流程图解析
- 开始:处理特殊字符操作的起点。
- 检查数据中是否包含特殊字符:扫描数据是否包含
#或$。- 不包含:直接将整个数据复制到当前块。
- 包含:将特殊字符前的数据复制到当前块。
- 复制特殊字符前的数据到当前块:部分数据复制到当前块。
- 尝试获取新块:
- 获取成功:设置新块状态为
BufUsing。 - 获取失败:输出错误信息,终止操作。
- 获取成功:设置新块状态为
- 设置新块状态为BufUsing:更新新块的状态。
- 复制特殊字符到新块:将特殊字符复制到新块。
- 检查是否有剩余数据:
- 有:将剩余数据复制到新块。
- 无:结束操作。
- 结束:处理特殊字符流程结束。
2.4 释放块流程
当某个块的数据被处理完毕后,需要将其释放,以便后续数据的追加。以下流程图展示了释放块的具体步骤。
流程图解析
- 开始:释放块操作的起点。
- 检查块索引是否有效:验证要释放的块索引是否在有效范围内。
- 有效:继续释放流程。
- 无效:输出错误信息,终止操作。
- 重置写入字节数:将块中的
written成员变量重置为0。 - 设置块状态为BufFree:将块的状态更新为
BufFree,表示该块已空闲。 - 结束:释放块流程结束。
2.5 获取下一个使用块流程
在某些情况下,需要获取下一个已经使用的块。以下流程图展示了获取下一个使用块的具体步骤。
流程图解析
- 开始:获取下一个使用块操作的起点。
- 检查当前使用块的状态:判断当前
indexUsed_指向的块是否为BufUsed状态。- 状态为BufUsed:返回当前使用块的索引。
- 状态不为BufUsed:继续检查是否需要回绕。
- 检查是否到达缓冲区末尾:
- 是:检查第一个块的状态。
- 否:检查下一个块的状态。
- 检查第一个块的状态:
- 状态为BufUsed:更新
indexUsed_为0,返回索引。 - 状态不为BufUsed:返回
-1,表示没有找到下一个使用块。
- 状态为BufUsed:更新
- 检查下一个块的状态:
- 状态为BufUsed:更新
indexUsed_为下一个块的索引,返回索引。 - 状态不为BufUsed:返回
-1,表示没有找到下一个使用块。
- 状态为BufUsed:更新
- 结束:获取下一个使用块流程结束。
3. 代码详解
下面我们将逐步解析 RingBuffer 类的实现,理解其内部工作机制。
3.1 Block 结构体
struct Block
{uint8_t* buf; ///< Buffer to store data.int8_t status; ///< Status of the block (free, using, or used).int32_t index; ///< Index of the block within the ring buffer.uint32_t written; ///< Number of bytes written to the block./*** @brief Constructs a Block with a pre-allocated buffer.** Initializes the buffer and sets default values for other members.*/Block() : buf(new uint8_t[BlockSize]), status(BufFree), index(-1), written(0){// Initialize buffer to zero (optional)std::memset(buf, 0, BlockSize);}/*** @brief Destructor to deallocate the buffer.*/~Block() { delete[] buf; }// Delete copy constructor and copy assignment operator to prevent shallow copies.Block(const Block&) = delete;Block& operator=(const Block&) = delete;// Define move constructor and move assignment operator for safe transfers.Block(Block&& other) noexcept : buf(other.buf), status(other.status), index(other.index), written(other.written){other.buf = nullptr;other.status = BufFree;other.index = -1;other.written = 0;}Block& operator=(Block&& other) noexcept{if (this != &other){delete[] buf;buf = other.buf;status = other.status;index = other.index;written = other.written;other.buf = nullptr;other.status = BufFree;other.index = -1;other.written = 0;}return *this;}static constexpr uint32_t BlockSize = 256; ///< Size of each block in bytes.static constexpr int8_t BufFree = 0; ///< Indicates the block is free.static constexpr int8_t BufUsing = 1; ///< Indicates the block is currently in use.static constexpr int8_t BufUsed = 2; ///< Indicates the block has been used.
};
解析:
-
成员变量:
uint8_t* buf:指向数据缓冲区的原始指针。int8_t status:表示Block的当前状态,BufFree(空闲)、BufUsing(使用中)、BufUsed(已使用)。int32_t index:Block在RingBuffer中的索引。uint32_t written:已写入Block的字节数。
-
构造函数与析构函数:
- 构造函数中,使用
new分配固定大小的缓冲区,并初始化其他成员变量。 - 析构函数中,使用
delete[]释放缓冲区内存。
- 构造函数中,使用
-
拷贝控制:
- 拷贝构造函数和拷贝赋值运算符被删除,防止浅拷贝带来的内存管理问题。
- 移动构造函数和移动赋值运算符 被定义,允许
Block实例的资源安全转移。
3.2 RingBuffer 类
class RingBuffer
{public:// Block 结构体定义.../*** @brief Constructs a RingBuffer with a specified number of blocks.** @param num The number of blocks in the ring buffer. Defaults to 1000.*/explicit RingBuffer(uint32_t num = 1000) : blocks_(num), blockNum_(num), index_(0), indexUsed_(-1){// Initialize each block's index.for (uint32_t i = 0; i < blocks_.size(); ++i){blocks_[i].index = static_cast<int32_t>(i);}// Set the first block's status to 'using'.if (!blocks_.empty()){blocks_[0].status = Block::BufUsing;}}/*** @brief Destructor to deallocate all blocks.*/~RingBuffer() = default; // Blocks are automatically destroyed, and their destructors handle buffer deallocation.// Delete copy constructor and copy assignment operator to prevent shallow copies.RingBuffer(const RingBuffer&) = delete;RingBuffer& operator=(const RingBuffer&) = delete;// Define move constructor and move assignment operator for safe transfers.RingBuffer(RingBuffer&& other) noexcept: blocks_(std::move(other.blocks_)),blockNum_(other.blockNum_),index_(other.index_),indexUsed_(other.indexUsed_){other.blockNum_ = 0;other.index_ = 0;other.indexUsed_ = -1;}RingBuffer& operator=(RingBuffer&& other) noexcept{if (this != &other){blocks_ = std::move(other.blocks_);blockNum_ = other.blockNum_;index_ = other.index_;indexUsed_ = other.indexUsed_;other.blockNum_ = 0;other.index_ = 0;other.indexUsed_ = -1;}return *this;}// append 方法定义...// currentUsed 和 currentUsing 方法定义...// release 方法定义...// nextUsed 方法定义...private:// nextFree 和 checkSpecial 方法定义...std::vector<Block> blocks_; ///< Vector of blocks managed by the ring buffer.int32_t index_ = 0; ///< Current index for writing data.int32_t blockNum_ = 0; ///< Total number of blocks in the ring buffer.int32_t indexUsed_ = -1; ///< Index of the currently used block.
};
解析:
-
成员变量:
std::vector<Block> blocks_:存储所有Block的容器。int32_t index_:当前用于写入数据的Block索引。int32_t blockNum_:环形缓冲区中Block的总数。int32_t indexUsed_:当前正在使用的Block索引,初始化为-1表示无Block被使用。
-
构造函数与析构函数:
- 构造函数中,初始化
blocks_向量,并为每个Block设置其索引。默认情况下,第一个Block的状态设置为BufUsing,表示其已被使用。 - 析构函数使用默认实现,依赖于
Block的析构函数自动释放内存。
- 构造函数中,初始化
-
拷贝控制:
- 拷贝构造函数和拷贝赋值运算符被删除,防止浅拷贝导致的资源管理问题。
- 移动构造函数和移动赋值运算符 被定义,允许
RingBuffer实例的资源安全转移。
3.3 主要方法解析
append 方法
/*** @brief Appends data to the ring buffer.** This method attempts to append the provided data to the current block.* If there's insufficient space or a retry is requested, it tries to acquire the next free block.* It also handles splitting data when special characters are encountered.** @param buf Pointer to the data to append.* @param length Length of the data in bytes.* @param retry Flag indicating whether to retry acquiring a free block.* @return True if the data was successfully appended; false otherwise.*/
bool append(const uint8_t* buf, uint32_t length, bool retry = false)
{// Validate that the data length does not exceed block size.if (length > Block::BlockSize){std::cerr << "Error: Length " << length << " exceeds block size " << Block::BlockSize << ".\n";return false;}// Check if the current block has enough space and is in the correct status.if (!retry && blocks_[index_].written + length <= Block::BlockSize){if (blocks_[index_].status != Block::BufUsing){std::cerr << "Error: Current block status is not BufUsing.\n";return false;}}else{// Attempt to acquire the next free block.if (!nextFree(retry)){// If acquiring a free block fails, ensure the current block status is correct.if (blocks_[index_].status != Block::BufUsed){std::cerr << "Error: Current block status is not BufUsed.\n";}return false;}// Update the status of the newly acquired block.blocks_[index_].status = Block::BufUsing;}// If the current block is empty, copy the entire buffer.if (blocks_[index_].written == 0){std::memcpy(blocks_[index_].buf + blocks_[index_].written, buf, length);blocks_[index_].written += length;}else{// Check for special characters in the buffer.int specialIdx = checkSpecial(buf, length);if (specialIdx == -1){// No special characters found; attempt to copy the entire buffer.if (blocks_[index_].written + length > Block::BlockSize){std::cerr << "Error: Not enough space to append data without special character.\n";return false;}std::memcpy(blocks_[index_].buf + blocks_[index_].written, buf, length);blocks_[index_].written += length;}else{// Special character found; split the data at the special character.if (blocks_[index_].written + specialIdx > Block::BlockSize){std::cerr << "Error: Not enough space to copy data before special character.\n";return false;}// Copy data up to the special character.std::memcpy(blocks_[index_].buf + blocks_[index_].written, buf, specialIdx);blocks_[index_].written += specialIdx;// Attempt to acquire a new free block for the special character.if (!nextFree(retry)){if (blocks_[index_].status != Block::BufUsed){std::cerr << "Error: Current block status is not BufUsed after finding special character.\n";}return false;}// Update the status and reset the write position for the new block.blocks_[index_].status = Block::BufUsing;blocks_[index_].written = 0;// Copy the special character to the new block.blocks_[index_].buf[blocks_[index_].written++] = buf[specialIdx];// If there is remaining data after the special character, copy it to the new block.if (static_cast<uint32_t>(specialIdx + 1) < length){uint32_t remainingLength = length - specialIdx - 1;if (remainingLength > Block::BlockSize - blocks_[index_].written){std::cerr << "Error: Not enough space to copy remaining data after special character.\n";return false;}std::memcpy(blocks_[index_].buf + blocks_[index_].written, buf + specialIdx + 1, remainingLength);blocks_[index_].written += remainingLength;}}}return true;
}
解析:
- 功能:向环形缓冲区追加数据。
- 步骤:
- 长度校验:确保待追加的数据长度不超过单个
Block的大小。 - 空间与状态检查:检查当前
Block是否有足够的空间以及其状态是否为BufUsing。 - 获取新块:如果当前块空间不足或请求重试,尝试获取下一个空闲块。
- 数据复制:
- 如果当前块为空,直接复制整个数据。
- 如果当前块已有数据,检查数据中是否包含特殊字符(
#或$)。- 无特殊字符:直接复制数据。
- 有特殊字符:在特殊字符处分割数据,分别复制到当前块和新获取的块中。
- 长度校验:确保待追加的数据长度不超过单个
currentUsed 和 currentUsing 方法
/*** @brief Retrieves the currently used block.** @return A constant reference to the currently used block.* @throws std::out_of_range if the indexUsed_ is invalid.*/
const Block& currentUsed() const
{if (indexUsed_ >= 0 && static_cast<size_t>(indexUsed_) < blocks_.size()){return blocks_[indexUsed_];}throw std::out_of_range("currentUsed(): indexUsed_ is out of range.");
}/*** @brief Retrieves the block that is currently being used for writing.** @return A constant reference to the block currently in use.* @throws std::out_of_range if the index_ is invalid.*/
const Block& currentUsing() const
{if (static_cast<size_t>(index_) < blocks_.size()){return blocks_[index_];}throw std::out_of_range("currentUsing(): index_ is out of range.");
}
解析:
- 功能:
currentUsed():获取当前正在使用的Block。currentUsing():获取当前用于写入的Block。
- 实现:
- 通过索引
indexUsed_和index_访问blocks_向量中的相应Block。 - 添加了边界检查,若索引无效,抛出
std::out_of_range异常,防止访问越界。
- 通过索引
release 方法
/*** @brief Releases a block, marking it as free and resetting its written bytes.** @param idx The index of the block to release.*/
void release(uint32_t idx)
{if (idx < blocks_.size()){blocks_[idx].written = 0;blocks_[idx].status = Block::BufFree;}else{std::cerr << "Error: Release index " << idx << " is out of bounds.\n";}
}
解析:
- 功能:释放指定索引的
Block,将其状态标记为BufFree并重置已写入字节数。 - 实现:
- 检查索引是否在有效范围内。
- 更新
Block的written和status成员。
nextUsed 方法
/*** @brief Retrieves the next used block's index.** @return The index of the next used block, or -1 if no such block exists.*/
int32_t nextUsed()
{// Check if the current used index is valid and marked as used.if (indexUsed_ >= 0 && static_cast<size_t>(indexUsed_) < blocks_.size() &&blocks_[indexUsed_].status == Block::BufUsed){return indexUsed_;}// Handle wrapping around to the beginning of the ring buffer.if (indexUsed_ == static_cast<int32_t>(blockNum_) - 1){if (!blocks_.empty() && blocks_[0].status == Block::BufUsed){indexUsed_ = 0;return indexUsed_;}else{return -1;}}else{// Check the next block in sequence.if ((indexUsed_ + 1) < static_cast<int32_t>(blockNum_) && blocks_[indexUsed_ + 1].status == Block::BufUsed){indexUsed_ += 1;return indexUsed_;}else{return -1;}}
}
解析:
- 功能:获取下一个已使用的
Block的索引。 - 实现:
- 检查当前
indexUsed_是否指向一个已使用的Block。 - 如果在缓冲区末尾,尝试回绕到起始位置。
- 否则,检查下一个
Block是否已使用。 - 若未找到,则返回
-1。
- 检查当前
3.4 私有方法解析
nextFree 方法
/*** @brief Attempts to acquire the next free block in the ring buffer.** @param retry Flag indicating whether to retry acquiring a free block.* @return True if a free block was successfully acquired; false otherwise.*/
bool nextFree(bool retry = false)
{// If the current block is free, it can be used.if (blocks_[index_].status == Block::BufFree){return true;}else{// If retry is requested and the block is not free, do not attempt further.if (retry){return false;}}// Mark the current block as used since it cannot be reused immediately.blocks_[index_].status = Block::BufUsed;// Handle wrapping around to the first block.if (index_ == static_cast<int32_t>(blockNum_) - 1){index_ = 0;if (blocks_[index_].status != Block::BufFree){std::cerr << "Warning: Block 0 is not free.\n";return false;}}else{// Move to the next block in the sequence.index_ += 1;if (index_ >= static_cast<int32_t>(blockNum_)){std::cerr << "Error: Index exceeded block number.\n";return false;}if (blocks_[index_].status != Block::BufFree){std::cerr << "Warning: Block " << index_ << " is not free.\n";return false;}}return true;
}
解析:
- 功能:尝试获取下一个空闲的
Block。 - 实现:
- 检查当前
Block是否为空闲状态。 - 若不为空闲且不允许重试,标记当前
Block为已使用,并尝试下一个Block。 - 添加了回绕逻辑,确保环形缓冲区的循环特性。
- 在获取失败时,输出警告或错误信息。
- 检查当前
checkSpecial 方法
/*** @brief Checks for the presence of special characters in the buffer.** This method scans the buffer for '#' or '$' characters.** @param buf Pointer to the buffer to check.* @param length Length of the buffer in bytes.* @return The index of the first special character found; -1 if none are found.*/
int checkSpecial(const uint8_t* buf, uint32_t length) const
{for (uint32_t i = 0; i < length; ++i){if (buf[i] == '#' || buf[i] == '$'){return static_cast<int>(i);}}return -1;
}
解析:
- 功能:检查缓冲区中是否存在特殊字符(
#或$)。 - 实现:
- 遍历缓冲区数据,查找特殊字符。
- 若找到,返回其索引;否则,返回
-1。
4. 内存管理与拷贝控制
在本实现中,内存管理 和 拷贝控制 是确保 RingBuffer 类安全高效运行的关键因素。
-
原始指针管理内存:
- 每个
Block使用new分配固定大小的缓冲区,并在析构函数中使用delete[]释放。 - 这种手动管理内存的方法需要开发者确保在所有情况下都正确分配和释放资源,避免内存泄漏或重复释放。
- 每个
-
拷贝控制:
- 通过 删除拷贝构造函数和拷贝赋值运算符,防止
Block和RingBuffer实例被浅拷贝,避免多个实例指向同一内存区域。 - 移动构造函数和移动赋值运算符 的实现,允许资源的安全转移,提高类的灵活性。
- 通过 删除拷贝构造函数和拷贝赋值运算符,防止
5. 完整代码
/*** @brief A ring buffer implementation for managing fixed-size memory blocks without using smart pointers.*/
class RingBuffer
{public:/*** @brief Represents a single block within the ring buffer.*/struct Block{uint8_t* buf; ///< Buffer to store data.int8_t status; ///< Status of the block (free, using, or used).int32_t index; ///< Index of the block within the ring buffer.uint32_t written; ///< Number of bytes written to the block./*** @brief Constructs a Block with a pre-allocated buffer.** Initializes the buffer and sets default values for other members.*/Block() : buf(new uint8_t[BlockSize]), status(BufFree), index(-1), written(0){// Initialize buffer to zero (optional)std::memset(buf, 0, BlockSize);}/*** @brief Destructor to deallocate the buffer.*/~Block() { delete[] buf; }// Delete copy constructor and copy assignment operator to prevent shallow copies.Block(const Block&) = delete;Block& operator=(const Block&) = delete;// Define move constructor and move assignment operator for safe transfers.Block(Block&& other) noexcept : buf(other.buf), status(other.status), index(other.index), written(other.written){other.buf = nullptr;other.status = BufFree;other.index = -1;other.written = 0;}Block& operator=(Block&& other) noexcept{if (this != &other){delete[] buf;buf = other.buf;status = other.status;index = other.index;written = other.written;other.buf = nullptr;other.status = BufFree;other.index = -1;other.written = 0;}return *this;}static constexpr uint32_t BlockSize = 256; ///< Size of each block in bytes.static constexpr int8_t BufFree = 0; ///< Indicates the block is free.static constexpr int8_t BufUsing = 1; ///< Indicates the block is currently in use.static constexpr int8_t BufUsed = 2; ///< Indicates the block has been used.};/*** @brief Constructs a RingBuffer with a specified number of blocks.** @param num The number of blocks in the ring buffer. Defaults to 1000.*/explicit RingBuffer(uint32_t num = 1000) : blocks_(num), blockNum_(num), index_(0), indexUsed_(-1){// Initialize each block's index.for (uint32_t i = 0; i < blocks_.size(); ++i){blocks_[i].index = static_cast<int32_t>(i);}// Set the first block's status to 'using'.if (!blocks_.empty()){blocks_[0].status = Block::BufUsing;}}/*** @brief Destructor to deallocate all blocks.*/~RingBuffer() = default; // Blocks are automatically destroyed, and their destructors handle buffer deallocation.// Delete copy constructor and copy assignment operator to prevent shallow copies.RingBuffer(const RingBuffer&) = delete;RingBuffer& operator=(const RingBuffer&) = delete;// Define move constructor and move assignment operator for safe transfers.RingBuffer(RingBuffer&& other) noexcept: blocks_(std::move(other.blocks_)),blockNum_(other.blockNum_),index_(other.index_),indexUsed_(other.indexUsed_){other.blockNum_ = 0;other.index_ = 0;other.indexUsed_ = -1;}RingBuffer& operator=(RingBuffer&& other) noexcept{if (this != &other){blocks_ = std::move(other.blocks_);blockNum_ = other.blockNum_;index_ = other.index_;indexUsed_ = other.indexUsed_;other.blockNum_ = 0;other.index_ = 0;other.indexUsed_ = -1;}return *this;}/*** @brief Appends data to the ring buffer.** This method attempts to append the provided data to the current block.* If there's insufficient space or a retry is requested, it tries to acquire the next free block.* It also handles splitting data when special characters are encountered.** @param buf Pointer to the data to append.* @param length Length of the data in bytes.* @param retry Flag indicating whether to retry acquiring a free block.* @return True if the data was successfully appended; false otherwise.*/bool append(const uint8_t* buf, uint32_t length, bool retry = false){// Validate that the data length does not exceed block size.if (length > Block::BlockSize){std::cerr << "Error: Length " << length << " exceeds block size " << Block::BlockSize << ".\n";return false;}// Check if the current block has enough space and is in the correct status.if (!retry && blocks_[index_].written + length <= Block::BlockSize){if (blocks_[index_].status != Block::BufUsing){std::cerr << "Error: Current block status is not BufUsing.\n";return false;}}else{// Attempt to acquire the next free block.if (!nextFree(retry)){// If acquiring a free block fails, ensure the current block status is correct.if (blocks_[index_].status != Block::BufUsed){std::cerr << "Error: Current block status is not BufUsed.\n";}return false;}// Update the status of the newly acquired block.blocks_[index_].status = Block::BufUsing;}// If the current block is empty, copy the entire buffer.if (blocks_[index_].written == 0){std::memcpy(blocks_[index_].buf + blocks_[index_].written, buf, length);blocks_[index_].written += length;}else{// Check for special characters in the buffer.int specialIdx = checkSpecial(buf, length);if (specialIdx == -1){// No special characters found; attempt to copy the entire buffer.if (blocks_[index_].written + length > Block::BlockSize){std::cerr << "Error: Not enough space to append data without special character.\n";return false;}std::memcpy(blocks_[index_].buf + blocks_[index_].written, buf, length);blocks_[index_].written += length;}else{// Special character found; split the data at the special character.if (blocks_[index_].written + specialIdx > Block::BlockSize){std::cerr << "Error: Not enough space to copy data before special character.\n";return false;}// Copy data up to the special character.std::memcpy(blocks_[index_].buf + blocks_[index_].written, buf, specialIdx);blocks_[index_].written += specialIdx;// Attempt to acquire a new free block for the special character.if (!nextFree(retry)){if (blocks_[index_].status != Block::BufUsed){std::cerr << "Error: Current block status is not BufUsed after finding special character.\n";}return false;}// Update the status and reset the write position for the new block.blocks_[index_].status = Block::BufUsing;blocks_[index_].written = 0;// Copy the special character to the new block.blocks_[index_].buf[blocks_[index_].written++] = buf[specialIdx];// If there is remaining data after the special character, copy it to the new block.if (static_cast<uint32_t>(specialIdx + 1) < length){uint32_t remainingLength = length - specialIdx - 1;if (remainingLength > Block::BlockSize - blocks_[index_].written){std::cerr << "Error: Not enough space to copy remaining data after special character.\n";return false;}std::memcpy(blocks_[index_].buf + blocks_[index_].written, buf + specialIdx + 1, remainingLength);blocks_[index_].written += remainingLength;}}}return true;}/*** @brief Retrieves the currently used block.** @return A constant reference to the currently used block.* @throws std::out_of_range if the indexUsed_ is invalid.*/const Block& currentUsed() const{if (indexUsed_ >= 0 && static_cast<size_t>(indexUsed_) < blocks_.size()){return blocks_[indexUsed_];}throw std::out_of_range("currentUsed(): indexUsed_ is out of range.");}/*** @brief Retrieves the block that is currently being used for writing.** @return A constant reference to the block currently in use.* @throws std::out_of_range if the index_ is invalid.*/const Block& currentUsing() const{if (static_cast<size_t>(index_) < blocks_.size()){return blocks_[index_];}throw std::out_of_range("currentUsing(): index_ is out of range.");}/*** @brief Releases a block, marking it as free and resetting its written bytes.** @param idx The index of the block to release.*/void release(uint32_t idx){if (idx < blocks_.size()){blocks_[idx].written = 0;blocks_[idx].status = Block::BufFree;}else{std::cerr << "Error: Release index " << idx << " is out of bounds.\n";}}/*** @brief Retrieves the next used block's index.** @return The index of the next used block, or -1 if no such block exists.*/int32_t nextUsed(){// Check if the current used index is valid and marked as used.if (indexUsed_ >= 0 && static_cast<size_t>(indexUsed_) < blocks_.size() &&blocks_[indexUsed_].status == Block::BufUsed){return indexUsed_;}// Handle wrapping around to the beginning of the ring buffer.if (indexUsed_ == static_cast<int32_t>(blockNum_) - 1){if (!blocks_.empty() && blocks_[0].status == Block::BufUsed){indexUsed_ = 0;return indexUsed_;}else{return -1;}}else{// Check the next block in sequence.if ((indexUsed_ + 1) < static_cast<int32_t>(blockNum_) && blocks_[indexUsed_ + 1].status == Block::BufUsed){indexUsed_ += 1;return indexUsed_;}else{return -1;}}}private:/*** @brief Attempts to acquire the next free block in the ring buffer.** @param retry Flag indicating whether to retry acquiring a free block.* @return True if a free block was successfully acquired; false otherwise.*/bool nextFree(bool retry = false){// If the current block is free, it can be used.if (blocks_[index_].status == Block::BufFree){return true;}else{// If retry is requested and the block is not free, do not attempt further.if (retry){return false;}}// Mark the current block as used since it cannot be reused immediately.blocks_[index_].status = Block::BufUsed;// Handle wrapping around to the first block.if (index_ == static_cast<int32_t>(blockNum_) - 1){index_ = 0;if (blocks_[index_].status != Block::BufFree){std::cerr << "Warning: Block 0 is not free.\n";return false;}}else{// Move to the next block in the sequence.index_ += 1;if (index_ >= static_cast<int32_t>(blockNum_)){std::cerr << "Error: Index exceeded block number.\n";return false;}if (blocks_[index_].status != Block::BufFree){std::cerr << "Warning: Block " << index_ << " is not free.\n";return false;}}return true;}/*** @brief Checks for the presence of special characters in the buffer.** This method scans the buffer for '#' or '$' characters.** @param buf Pointer to the buffer to check.* @param length Length of the buffer in bytes.* @return The index of the first special character found; -1 if none are found.*/int checkSpecial(const uint8_t* buf, uint32_t length) const{for (uint32_t i = 0; i < length; ++i){if (buf[i] == '#' || buf[i] == '$'){return static_cast<int>(i);}}return -1;}std::vector<Block> blocks_; ///< Vector of blocks managed by the ring buffer.int32_t index_ = 0; ///< Current index for writing data.int32_t blockNum_ = 0; ///< Total number of blocks in the ring buffer.int32_t indexUsed_ = -1; ///< Index of the currently used block.
};相关文章:
缓存串口数据)
C++编程:实现一个基于原始指针的环形缓冲区(RingBuffer)缓存串口数据
文章目录 0. 引言1. 使用示例2. 流程图2.1 追加数据流程2.2 获取空闲块流程2.3 处理特殊字符流程2.4 释放块流程2.5 获取下一个使用块流程 3. 代码详解3.1 Block 结构体3.2 RingBuffer 类3.3 主要方法解析append 方法currentUsed 和 currentUsing 方法release 方法nextUsed 方法…...

LangChain 创始人万字科普:手把手教你设计 Agent 用户交互
LangChain 可以算是 LLM 时代做 AI 应用开发必备的框架和平台,从模型选择、数据库链接与各种 Agent 搭建等,AI 应用的搭建、运行和管理都可以在 LangChain 上进行。 某种意义上,LangChain 可能是最了解 Agent(智能体)…...

Docker 用例:15 种最常见的 Docker 使用方法
容器化应用程序而不是将它们托管在虚拟机上是过去几年一直流行的概念,使容器管理流行起来。Docker 处于这一转变的核心,帮助组织无缝地采用容器化技术。最近,Docker 用例遍布所有行业,无论规模大小和性质如何。 什么是Docker&…...
若依 RuoYi4.6.0 代码审计
环境布置: 到官网下载源码:https://github.com/yangzongzhuan/RuoYi 采用phpstudy集成数据库,5.7版本。JDK1.8。 IDEA打开项目,等待自动加载,修改application-druid.yml配置文件:数据库名,账…...

C语言入门-选择结构
在编程中,我们经常需要根据不同的条件执行不同的操作。C语言为此提供了几种非常实用的选择结构:条件运算符、逻辑运算、if语句和switch语句。接下来,让我们深入探讨这些重要的知识点,帮助你更好地理解和掌握C语言的选择结构。 1.…...

Legion拯救者 刃7000K-26IAB联想台式机T5 26IAB7(90SU,90SV,90SW,90SX)原厂Windows11系统镜像下载
适用机型:【90SW、90SX、90SU、90SV】 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1gJ4ZwWW2orlGYoPk37M-cg?pwd4mvv 提取码:4mvv lenovo联想原装WIN系统自带所有驱动、出厂主题专用壁纸、系统属性联机支持标志、系统属性专属LOGO标志、Office办公软…...

代码随想录算法训练营第二十四天|Day24 回溯算法
93.复原IP地址 题目链接/文章讲解:https://programmercarl.com/0093.%E5%A4%8D%E5%8E%9FIP%E5%9C%B0%E5%9D%80.html 视频讲解:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1XP4y1U73i/ 思路 char** result; int resultTop; int segments[3]; int isValid(char* s…...

vue elementui table编辑表单时,弹框增加编辑明细数据
需求: 前端进行新增表单时,同时增加表单的明细数据。明细数据部分,通过弹框方式增加或者编辑。 效果图: 代码: <!-- 新增主表弹窗 Begin --><el-dialog:title"titleInfo"top"5vh"centerwidth"…...

springboot集成Redisson做分布式消息队列
这里演示Redisson做分布式消息队列。首先引入 Redisson依赖,官方github <dependency><groupId>org.redisson</groupId><artifactId>redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId><version>3.17.6</version> </dependen…...

如何通过Lua语言请求接口拿到数据
文章目录 概要http客户端通过请求下载数据 概要 当某个需求是需要在模块内请求接口拿到数据,需要使用http客户端调用接口 http客户端 LuaSOC请求接口官方文档 调用:http.request(method,url,headers,body,opts,ca_file,client_ca, client_key, clien…...

Android 13 SystemUI 隐藏下拉快捷面板部分模块(wifi,bt,nfc等)入口
frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/qs/tileimpl/QSFactoryImpl.java createTileInternal(tileSpec)方法注释想隐藏的模块即可。...

自由学习记录(14)
unity操作问题 位置:子物体的位置是相对于父物体的。如果你移动父物体,子物体会保持相对于父物体的相对位置,跟着一起移动。 旋转:子物体的旋转也是相对于父物体的。旋转父物体会导致子物体围绕父物体的原点旋转。 缩放…...

疯狂Spring Boot讲义[推荐1]
《疯狂Spring Boot讲义》是2021年电子工业出版社出版的图书,作者是李刚 《疯狂Spring Boot终极讲义》不是一本介绍类似于PathVariable、MatrixVariable、RequestBody、ResponseBody这些基础注解的图书,它是真正讲解Spring Boot的图书。Spring Boot的核心…...

vue中$nextTick的作用是什么,什么时候使用
$nextTick 是 Vue 提供的一个方法,用于在下一次 DOM 更新周期之后执行回调函数。它通常用于在 Vue 完成数据更新后,需要访问更新后的 DOM 状态时,保证操作的是更新后的 DOM。 工作原理: Vue 是异步更新 DOM 的,当数据…...

Redis实现全局ID生成器
全局ID生成器 为什么要用全局ID生成器 1.当我们使用数据库自增来实现id的生成时,规律过于明显,会给用户暴露很多信息 2.当我们订单量过大时无法用数据库的一张表来存放订单,如果两张表的id都是自增的话,id就会出现重复 什么是全局ID生成器 全局ID生成器,是一种在分布式系统…...

Xshell远程连接工具详解
Xshell是一款在Windows平台上运行的远程连接工具,它支持SSH1、SSH2以及Microsoft Windows平台的TELNET协议。Xshell通过互联网实现对远程主机的安全连接,帮助用户在复杂的网络环境中享受他们的工作。本文将详细介绍Xshell的溯源、最新版本以及它的优势。…...
的切换?)
如何在verilog设计的磁盘阵列控制器中实现不同RAID级别(如RAID 0、RAID 1等)的切换?
以下是一种在Verilog设计的磁盘阵列控制器中实现不同RAID级别(以RAID 0和RAID 1为例)切换的方法: 添加控制信号 在磁盘阵列控制器模块中添加一个输入信号,例如raid_mode,用于选择RAID模式。假设raid_mode = 0表示RAID 0模式,raid_mode = 1表示RAID 1模式。module raid_co…...

基于元神操作系统实现NTFS文件操作(十)
1. 背景 本文补充介绍文件遍历操作的部分附加内容,譬如,过滤掉系统元文件、过滤掉重复的文件项、过滤掉隐藏文件等,并提供了基于元神操作系统的部分实现代码。 2. 方法 (1)过滤掉系统元文件 NTFS文件系统的前16个元…...

Qt的几个函数方法
void receiveInfo1() {// 假设这是从串口接收到的字符串QString receivedString "23.5C,45%,1012hPa";// 使用逗号分隔符分割字符串QStringList parts receivedString.split(,);// 检查分割后的列表是否有足够的部分if (parts.size() > 3) {QString part1 part…...

openpnp - bug - 散料飞达至少定义2个物料
文章目录 openpnp - bug - 散料飞达至少定义2个物料笔记END openpnp - bug - 散料飞达至少定义2个物料 笔记 散料飞达上定义的物料个数用完了,现在只需要一个料就可以。 用顶部相机去找编带上是否还有一个单独的料,找到了。 定义散料飞达的料为1个&…...

NFT模式:数字资产确权与链游经济系统构建
NFT模式:数字资产确权与链游经济系统构建 ——从技术架构到可持续生态的范式革命 一、确权技术革新:构建可信数字资产基石 1. 区块链底层架构的进化 跨链互操作协议:基于LayerZero协议实现以太坊、Solana等公链资产互通,通过零知…...
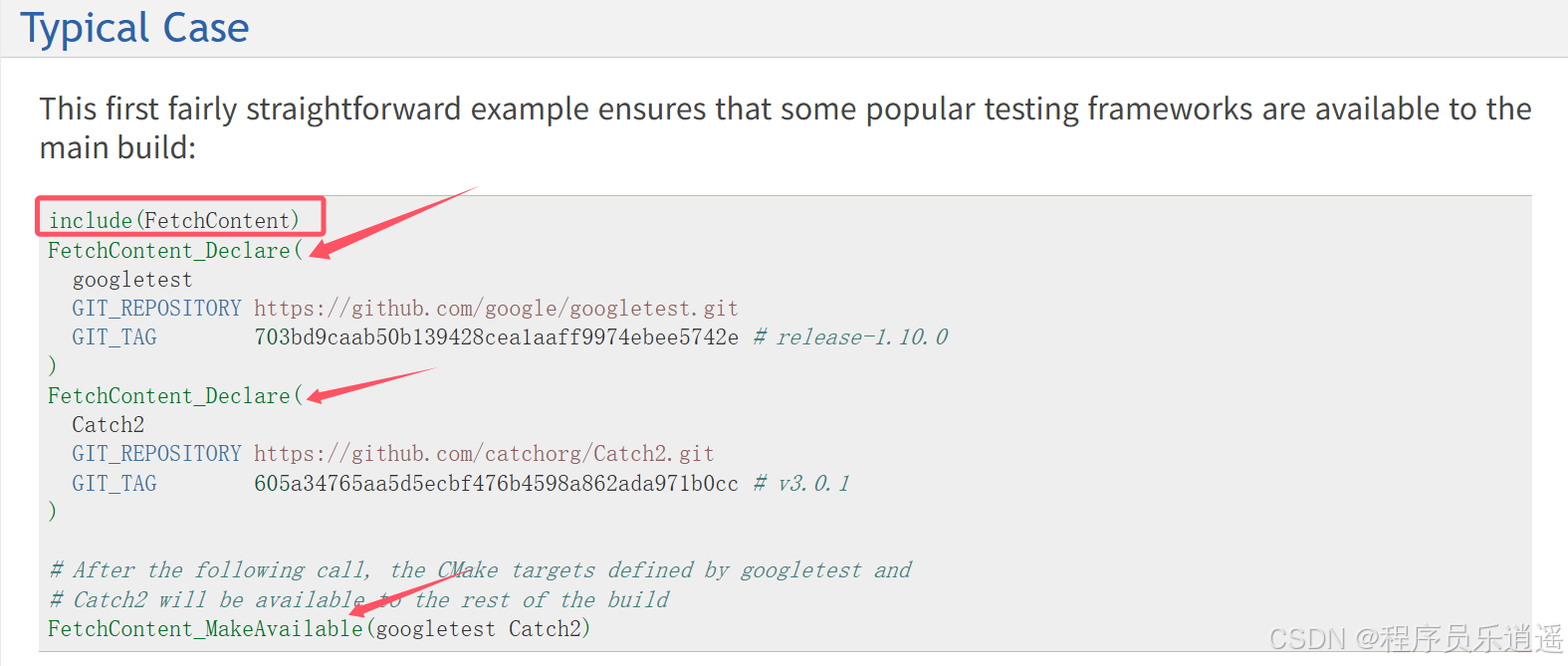
CMake 从 GitHub 下载第三方库并使用
有时我们希望直接使用 GitHub 上的开源库,而不想手动下载、编译和安装。 可以利用 CMake 提供的 FetchContent 模块来实现自动下载、构建和链接第三方库。 FetchContent 命令官方文档✅ 示例代码 我们将以 fmt 这个流行的格式化库为例,演示如何: 使用 FetchContent 从 GitH…...
springboot整合VUE之在线教育管理系统简介
可以学习到的技能 学会常用技术栈的使用 独立开发项目 学会前端的开发流程 学会后端的开发流程 学会数据库的设计 学会前后端接口调用方式 学会多模块之间的关联 学会数据的处理 适用人群 在校学生,小白用户,想学习知识的 有点基础,想要通过项…...

Python 高效图像帧提取与视频编码:实战指南
Python 高效图像帧提取与视频编码:实战指南 在音视频处理领域,图像帧提取与视频编码是基础但极具挑战性的任务。Python 结合强大的第三方库(如 OpenCV、FFmpeg、PyAV),可以高效处理视频流,实现快速帧提取、压缩编码等关键功能。本文将深入介绍如何优化这些流程,提高处理…...

Axure 下拉框联动
实现选省、选完省之后选对应省份下的市区...

【Java多线程从青铜到王者】单例设计模式(八)
wait和sleep的区别 我们的wait也是提供了一个还有超时时间的版本,sleep也是可以指定时间的,也就是说时间一到就会解除阻塞,继续执行 wait和sleep都能被提前唤醒(虽然时间还没有到也可以提前唤醒),wait能被notify提前唤醒…...

Excel 怎么让透视表以正常Excel表格形式显示
目录 1、创建数据透视表 2、设计 》报表布局 》以表格形式显示 3、设计 》分类汇总 》不显示分类汇总 1、创建数据透视表 2、设计 》报表布局 》以表格形式显示 3、设计 》分类汇总 》不显示分类汇总...

ubuntu清理垃圾
windows和ubuntu 双系统,ubuntu 150GB,开发用,基本不装太多软件。但是磁盘基本用完。 1、查看home目录 sudo du -h -d 1 $HOME | grep -v K 上面的命令查看$HOME一级目录大小,发现 .cache 有26GB,.local 有几个GB&am…...

宠物车载安全座椅市场报告:解读行业趋势与投资前景
一、什么是宠物车载安全座椅? 宠物车载安全座椅是一种专为宠物设计的车内固定装置,旨在保障宠物在乘车过程中的安全性与舒适性。它通常由高强度材料制成,具备良好的缓冲性能,并可通过安全带或ISOFIX接口固定于车内。 近年来&…...
)
Spring Boot 与 Kafka 的深度集成实践(二)
3. 生产者实现 3.1 生产者配置 在 Spring Boot 项目中,配置 Kafka 生产者主要是配置生产者工厂(ProducerFactory)和 KafkaTemplate 。生产者工厂负责创建 Kafka 生产者实例,而 KafkaTemplate 则是用于发送消息的核心组件&#x…...
