PostgreSQL技术内幕17:PG分区表
文章目录
- 0.简介
- 1.概念介绍
- 2.分区表技术产生的背景
- 3.分区类型及使用方式
- 4.实现原理
- 4.1 分区表创建
- 4.2 分区表查询
- 4.3 分区表写入
- 4.4 分区表删除
0.简介
本文主要介绍PG中分区表的概念,产生分区表技术的原因,使用方式和其内部实现原理,旨在能对PG分区表技术有一个系统的说明。
1.概念介绍
分区表是数据库用于管理大量数据的一种技术,它允许将一个大表分割成多个小表,这些小表在物理上是独立的,但在逻辑上作为一个整体被查询和更新。分区表的主要优势在于提高查询性能,特别是当查询集中在少数几个分区时。此外,分区表还可以简化数据的批量删除和加载,以及将不常用的数据迁移到成本较低的存储介质上实现冷热分离。

1)主表/父表/Master Table:该表是创建子表的模板。它是一个正常的普通表,但正常情况下它并不储存任何数据。
2)子表/分区表/Child Table/Partition Table:这些表继承并属于一个主表。子表中存储所有的数据。主表与分区表属于一对多的关系,也就是说,一个主表包含多个分区表,而一个分区表只从属于一个主表
2.分区表技术产生的背景
在使用数据库过程中,随着时间的推移,每张表数据量会不断增加,造成查询速度越来越慢,在分区表之前有很多查询的技术去优化它,比如添加特殊的索引,将磁盘分区(把日志文件放到单独的磁盘分区),调整参数等等。这些优化技术都能对查询性能做出或多或少的提升,但其并没有对于表特点以及局部性的原理进行合理应用,因为对于很多应用来说,许多历史数据对于查询可能并没有太多用处,或者是某一列是特定值时是更为关系的数据,如果能够将不常用数据进行隐藏,就能大大提高查询速度,分区表就是为了解决这个问题而产生的。比如可以按照时间作为分区键进行分区将新老数据分离。
3.分区类型及使用方式
PG 10以后支持三种分区,以下都使用主流的使用方式声明式分区(还有表继承)进行说明:
1)范围(Range)分区
CREATE TABLE students (grade INTEGER) PARTITION BY RANGE(grade);
CREATE TABLE stu_fail PARTITION OF students FOR VALUES FROM (MINVALUE) TO (60);
CREATE TABLE stu_pass PARTITION OF students FOR VALUES FROM (60) TO (MAXVALUE);\d+ studentsTable "public.students"Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description
--------+---------+-----------+----------+---------+---------+--------------+-------------grade | integer | | | | plain | |
Partition key: RANGE (grade)
Partitions: stu_fail FOR VALUES FROM (MINVALUE) TO (60),stu_pass FOR VALUES FROM (60) TO (MAXVALUE)\d+ stu_failTable "public.stu_fail"Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description
--------+---------+-----------+----------+---------+---------+--------------+-------------grade | integer | | | | plain | |
Partition of: students FOR VALUES FROM (MINVALUE) TO (60)
Partition constraint: ((grade IS NOT NULL) AND (grade < 60))
可以看出,其中最大值是小于关系,不是小于等于关系。
2)列表(List)分区
列表分区明确指定根据某字段的某个具体值进行分区,默认分区(可选值)保存不属于任何指定分区的列表值。
CREATE TABLE students (status character varying(30)) PARTITION BY LIST(status);
CREATE TABLE stu_active PARTITION OF students FOR VALUES IN ('ACTIVE');
CREATE TABLE stu_exp PARTITION OF students FOR VALUES IN ('EXPIRED');
CREATE TABLE stu_others PARTITION OF students DEFAULT;\d+ studentsTable "public.students"Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description
--------+-----------------------+-----------+----------+---------+----------+--------------+-------------status | character varying(30) | | | | extended | |
Partition key: LIST (status)
Partitions: stu_active FOR VALUES IN ('ACTIVE'),stu_exp FOR VALUES IN ('EXPIRED'),stu_others DEFAULT\d+ stu_others;Table "public.stu_others"Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description
--------+-----------------------+-----------+----------+---------+----------+--------------+-------------status | character varying(30) | | | | extended | |
Partition of: students DEFAULT
Partition constraint: (NOT ((status IS NOT NULL) AND ((status)::text = ANY (ARRAY['ACTIVE'::character varying(30), 'EXPIRED'::character varying(30)]))))
3)哈希(Hash)分区
通过对每个分区使用取模和余数来创建hash分区,modulus指定了对N取模,而remainder指定了除完后的余数。
CREATE TABLE students (id INTEGER) PARTITION BY HASH(id);
CREATE TABLE stu_part1 PARTITION OF students FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 3, remainder 0);
CREATE TABLE stu_part2 PARTITION OF students FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 3, remainder 1);
CREATE TABLE stu_part3 PARTITION OF students FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 3, remainder 2);\d+ students;Table "public.students"Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description
--------+---------+-----------+----------+---------+---------+--------------+-------------id | integer | | | | plain | |
Partition key: HASH (id)
Partitions: stu_part1 FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 3, remainder 0),stu_part2 FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 3, remainder 1),stu_part3 FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 3, remainder 2)\d+ stu_part1;Table "public.stu_part1"Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description
--------+---------+-----------+----------+---------+---------+--------------+-------------id | integer | | | | plain | |
Partition of: students FOR VALUES WITH (modulus 3, remainder 0)
Partition constraint: satisfies_hash_partition('16439'::oid, 3, 0, id)
PG分区还支持创建子分区:LIST-LIST,LIST-RANGE,LIST-HASH,RANGE-RANGE,RANGE-LIST,RANGE-HASH,HASH-HASH,HASH-LIST和HASH-RANGE;以及和普通表之间互相转换,DETACH PARTITION可以将分区表转换为普通表,而attach partition可以将普通表附加到分区表上。
4.实现原理
4.1 分区表创建
分区表创建相对简单,对PG来说实际是一张逻辑表对应多张物理表,下面简单看创建时其分区表相关的调用流程。
--> transformPartitionBound --> RelationGetPartitionKey--> get_partition_strategy--> transformPartitionBoundValue--> transformPartitionRangeBounds--> validateInfiniteBounds--> check_new_partition_bound--> StorePartitionBound // Update pg_class tuple of rel to store the partition bound and set relispartition to true--> StoreCatalogInheritance // 向系统表pg_inherits插入信息// 处理stmt->partspec--> transformPartitionSpec--> ComputePartitionAttrs--> StorePartitionKey // 向pg_partitioned_table中插入分区键等信息
4.2 分区表查询
分区表查询是要根据条件查询一定数量的子表然后进行返回,其主要分为三步:
1)识别分区表并找到所有的分区子表
/** expand_inherited_tables* Expand each rangetable entry that represents an inheritance set* into an "append relation". At the conclusion of this process,* the "inh" flag is set in all and only those RTEs that are append* relation parents.*/
void
expand_inherited_tables(PlannerInfo *root)
{Index nrtes;Index rti;ListCell *rl;/** expand_inherited_rtentry may add RTEs to parse->rtable. The function is* expected to recursively handle any RTEs that it creates with inh=true.* So just scan as far as the original end of the rtable list.*/nrtes = list_length(root->parse->rtable);rl = list_head(root->parse->rtable);for (rti = 1; rti <= nrtes; rti++){RangeTblEntry *rte = (RangeTblEntry *) lfirst(rl);expand_inherited_rtentry(root, rte, rti);rl = lnext(rl);}
}
2)根据约束条件识别需要查询的分区,也就是分区裁剪,只读取需要的分区;
prune_append_rel_partitions* Process rel's baserestrictinfo and make use of quals which can be* evaluated during query planning in order to determine the minimum set* of partitions which must be scanned to satisfy these quals. Returns* the matching partitions in the form of a Relids set containing the* partitions' RT indexes.** Callers must ensure that 'rel' is a partitioned table.*/
Relids
prune_append_rel_partitions(RelOptInfo *rel)
{Relids result;List *clauses = rel->baserestrictinfo;List *pruning_steps;GeneratePruningStepsContext gcontext;PartitionPruneContext context;Bitmapset *partindexes;int i;Assert(clauses != NIL);Assert(rel->part_scheme != NULL);/* If there are no partitions, return the empty set */if (rel->nparts == 0)return NULL;/** Process clauses to extract pruning steps that are usable at plan time.* If the clauses are found to be contradictory, we can return the empty* set.*/gen_partprune_steps(rel, clauses, PARTTARGET_PLANNER,&gcontext);if (gcontext.contradictory)return NULL;pruning_steps = gcontext.steps;/* Set up PartitionPruneContext */context.strategy = rel->part_scheme->strategy;context.partnatts = rel->part_scheme->partnatts;context.nparts = rel->nparts;context.boundinfo = rel->boundinfo;context.partcollation = rel->part_scheme->partcollation;context.partsupfunc = rel->part_scheme->partsupfunc;context.stepcmpfuncs = (FmgrInfo *) palloc0(sizeof(FmgrInfo) *context.partnatts *list_length(pruning_steps));context.ppccontext = CurrentMemoryContext;/* These are not valid when being called from the planner */context.partrel = NULL;context.planstate = NULL;context.exprstates = NULL;/* Actual pruning happens here. */partindexes = get_matching_partitions(&context, pruning_steps);/* Add selected partitions' RT indexes to result. */i = -1;result = NULL;while ((i = bms_next_member(partindexes, i)) >= 0)result = bms_add_member(result, rel->part_rels[i]->relid);return result;
}
3)对结果集执行APPEND,作为最终结果输出,这和其他表append操作一致,使用ExecInitAppend和ExecAppend函数。
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------* ExecAppend** Handles iteration over multiple subplans.* ----------------------------------------------------------------*/
static TupleTableSlot *
ExecAppend(PlanState *pstate)
{AppendState *node = castNode(AppendState, pstate);if (node->as_whichplan < 0){/** If no subplan has been chosen, we must choose one before* proceeding.*/if (node->as_whichplan == INVALID_SUBPLAN_INDEX &&!node->choose_next_subplan(node))return ExecClearTuple(node->ps.ps_ResultTupleSlot);/* Nothing to do if there are no matching subplans */else if (node->as_whichplan == NO_MATCHING_SUBPLANS)return ExecClearTuple(node->ps.ps_ResultTupleSlot);}for (;;){PlanState *subnode;TupleTableSlot *result;CHECK_FOR_INTERRUPTS();/** figure out which subplan we are currently processing*/Assert(node->as_whichplan >= 0 && node->as_whichplan < node->as_nplans);subnode = node->appendplans[node->as_whichplan];/** get a tuple from the subplan*/result = ExecProcNode(subnode);if (!TupIsNull(result)){/** If the subplan gave us something then return it as-is. We do* NOT make use of the result slot that was set up in* ExecInitAppend; there's no need for it.*/return result;}/* choose new subplan; if none, we're done */if (!node->choose_next_subplan(node))return ExecClearTuple(node->ps.ps_ResultTupleSlot);}
}
4.3 分区表写入
分区表写入分为两个阶段,一个是查找到要写入的分区,然后就是正常去做写入,下面来看查找分区的函数。
/** ExecPrepareTupleRouting --- prepare for routing one tuple** Determine the partition in which the tuple in slot is to be inserted,* and modify mtstate and estate to prepare for it.** Caller must revert the estate changes after executing the insertion!* In mtstate, transition capture changes may also need to be reverted.** Returns a slot holding the tuple of the partition rowtype.*/
static TupleTableSlot *
ExecPrepareTupleRouting(ModifyTableState *mtstate,EState *estate,PartitionTupleRouting *proute,ResultRelInfo *targetRelInfo,TupleTableSlot *slot)
{ModifyTable *node;int partidx;ResultRelInfo *partrel;HeapTuple tuple;/** Determine the target partition. If ExecFindPartition does not find a* partition after all, it doesn't return here; otherwise, the returned* value is to be used as an index into the arrays for the ResultRelInfo* and TupleConversionMap for the partition.*/partidx = ExecFindPartition(targetRelInfo,proute->partition_dispatch_info,slot,estate);Assert(partidx >= 0 && partidx < proute->num_partitions);/** Get the ResultRelInfo corresponding to the selected partition; if not* yet there, initialize it.*/partrel = proute->partitions[partidx];if (partrel == NULL)partrel = ExecInitPartitionInfo(mtstate, targetRelInfo,proute, estate,partidx);/** Check whether the partition is routable if we didn't yet** Note: an UPDATE of a partition key invokes an INSERT that moves the* tuple to a new partition. This check would be applied to a subplan* partition of such an UPDATE that is chosen as the partition to route* the tuple to. The reason we do this check here rather than in* ExecSetupPartitionTupleRouting is to avoid aborting such an UPDATE* unnecessarily due to non-routable subplan partitions that may not be* chosen for update tuple movement after all.*/if (!partrel->ri_PartitionReadyForRouting){/* Verify the partition is a valid target for INSERT. */CheckValidResultRel(partrel, CMD_INSERT);/* Set up information needed for routing tuples to the partition. */ExecInitRoutingInfo(mtstate, estate, proute, partrel, partidx);}/** Make it look like we are inserting into the partition.*/estate->es_result_relation_info = partrel;/* Get the heap tuple out of the given slot. */tuple = ExecMaterializeSlot(slot);/** If we're capturing transition tuples, we might need to convert from the* partition rowtype to parent rowtype.*/if (mtstate->mt_transition_capture != NULL){if (partrel->ri_TrigDesc &&partrel->ri_TrigDesc->trig_insert_before_row){/** If there are any BEFORE triggers on the partition, we'll have* to be ready to convert their result back to tuplestore format.*/mtstate->mt_transition_capture->tcs_original_insert_tuple = NULL;mtstate->mt_transition_capture->tcs_map =TupConvMapForLeaf(proute, targetRelInfo, partidx);}else{/** Otherwise, just remember the original unconverted tuple, to* avoid a needless round trip conversion.*/mtstate->mt_transition_capture->tcs_original_insert_tuple = tuple;mtstate->mt_transition_capture->tcs_map = NULL;}}if (mtstate->mt_oc_transition_capture != NULL){mtstate->mt_oc_transition_capture->tcs_map =TupConvMapForLeaf(proute, targetRelInfo, partidx);}/** Convert the tuple, if necessary.*/ConvertPartitionTupleSlot(proute->parent_child_tupconv_maps[partidx],tuple,proute->partition_tuple_slot,&slot);/* Initialize information needed to handle ON CONFLICT DO UPDATE. */Assert(mtstate != NULL);node = (ModifyTable *) mtstate->ps.plan;if (node->onConflictAction == ONCONFLICT_UPDATE){Assert(mtstate->mt_existing != NULL);ExecSetSlotDescriptor(mtstate->mt_existing,RelationGetDescr(partrel->ri_RelationDesc));Assert(mtstate->mt_conflproj != NULL);ExecSetSlotDescriptor(mtstate->mt_conflproj,partrel->ri_onConflict->oc_ProjTupdesc);}return slot;
}
4.4 分区表删除
分区表的删除即为先删除其分区,然后整体删除。
相关文章:

PostgreSQL技术内幕17:PG分区表
文章目录 0.简介1.概念介绍2.分区表技术产生的背景3.分区类型及使用方式4.实现原理4.1 分区表创建4.2 分区表查询4.3 分区表写入4.4 分区表删除 0.简介 本文主要介绍PG中分区表的概念,产生分区表技术的原因,使用方式和其内部实现原理,旨在能…...

群控系统服务端开发模式-应用开发-上传工厂开发
现在的文件、图片等上传基本都在使用oss存储。而现在常用的oss存储有阿里云、腾讯云、七牛云、华为云等,但是用的最多的还是前三种。而我主要封装的是本地存储、阿里云存储、腾讯云存储、七牛云存储。废话不多说,直接上传设计图及说明,就一目…...

【Docker系列】指定系统平台拉取 openjdk:8 镜像
💝💝💝欢迎来到我的博客,很高兴能够在这里和您见面!希望您在这里可以感受到一份轻松愉快的氛围,不仅可以获得有趣的内容和知识,也可以畅所欲言、分享您的想法和见解。 推荐:kwan 的首页,持续学…...

语音识别:docker部署FunASR以及springboot集成funasr
内容摘选自: https://github.com/modelscope/FunASR/blob/main/runtime/docs/SDK_advanced_guide_offline_zh.md FunASR FunASR是一个基础语音识别工具包,提供多种功能,包括语音识别(ASR)、语音端点检测(VAD…...

Rust项目结构
文章目录 一、module模块1.文件内的module 二、模块化项目结构1.关于module2.各个模块之间互相引用 三、推荐项目结构1.实例 参考 一、module模块 1.文件内的module 关键字:mod 引入模块中的方法 usemod名字:方法名usemod名字.*写全路径 二、模块化项…...

计算并联电阻的阻值
计算并联电阻的阻值 C语言代码C代码Java代码Python代码 💐The Begin💐点点关注,收藏不迷路💐 对于阻值为r1和r2的电阻,其并联电阻阻值公式计算如下: R1/(1/r11/r2) 输入 两个电阻阻抗大小,浮…...
)
MySQL符号类型(详细)
在 MySQL 中,符号可以分为几种主要类型,以下是所有符号类型的小写分类: 1. 占位符 ?:用于准备语句中的占位符,表示将来要替换的值。 2. 分隔符 ;:表示 sql 语句的结束。 ,:用于分隔列、值或…...

Angular引用控件类
说明: angular 在一个控件类里面,引入另外一个控件类,这样做的好处,就是代码分离,当你一个页面存在多少类似于独立的界面时,可以使用这种方式,分离代码 更好维护程序 效果图: step…...

stm32 踩坑笔记
串口问题: 问题:会改变接收缓冲的下一个字节 串口的初始化如下,位长度选择了9位。因为要奇偶校验,要选择9位。但是接收有用数据只用到1个字节。 问题原因: 所以串口接收时会把下一个数据更改...

文件上传和文件包含
声明: 本文章只是适用于网络安全教学,请自觉遵守网络安全法,严禁用于非法途径,若读者做出来任何危害网络安全的行为,后果自负,均与本人无关. 文件上传: 大部分的网站和应用系统都有上传的功能,如用户头像上传,图片上传,文档上传…...
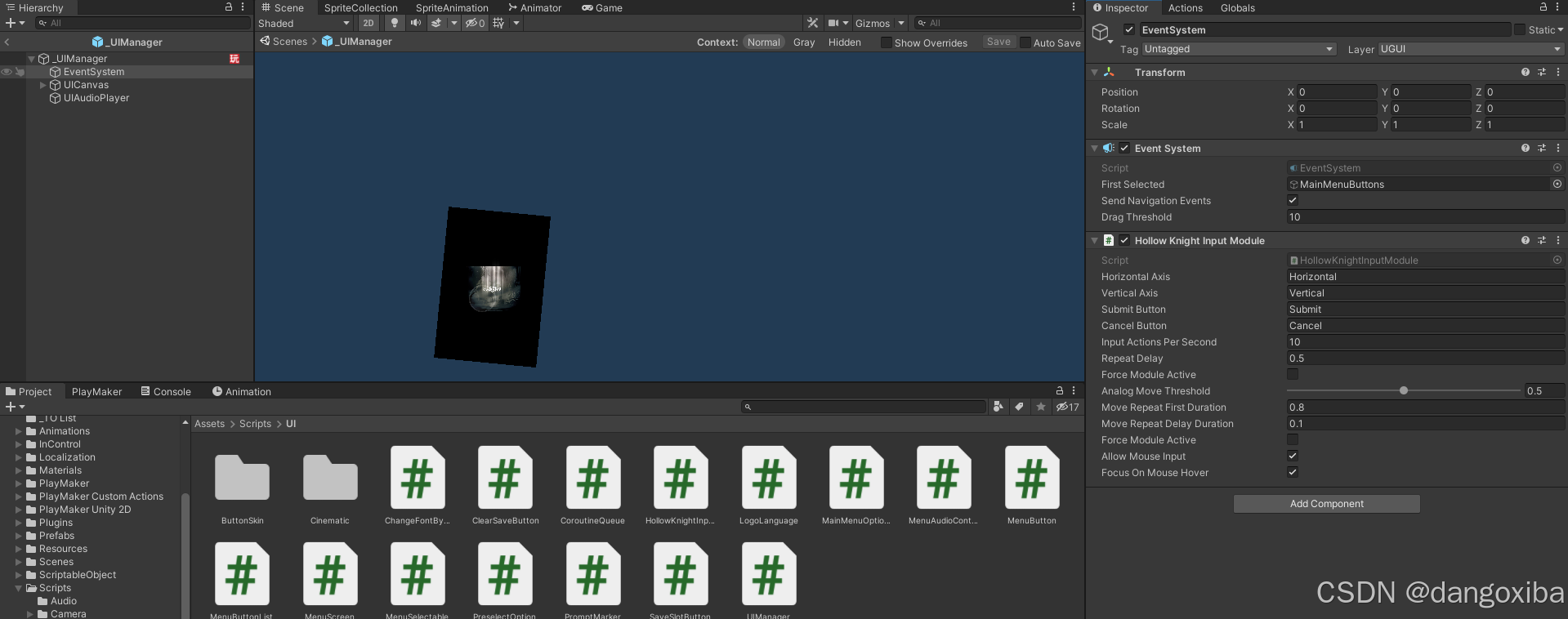
[Unity Demo]从零开始制作空洞骑士Hollow Knight第十八集补充:制作空洞骑士独有的EventSystem和InputModule
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档 文章目录 前言一、制作空洞骑士独有的EventSystem和InputModule总结 前言 hello大家好久没见,之所以隔了这么久才更新并不是因为我又放弃了这个项目,而…...

yelp数据集上试验SVD,SVDPP,PMF,NMF 推荐算法
SVD、SVD、PMF 和 NMF 是几种常见的推荐算法,它们主要用于协同过滤和矩阵分解方法来生成个性化推荐。下面是对每种算法的简要介绍: 1. SVD(Singular Value Decomposition) 用途:SVD 是一种矩阵分解技术,通…...

计算机视觉常用数据集Cityscapes的介绍、下载、转为YOLO格式进行训练
我在寻找Cityscapes数据集的时候花了一番功夫,因为官网下载需要用公司或学校邮箱邮箱注册账号,等待审核通过后才能进行下载数据集。并且一开始我也并不了解Cityscapes的格式和内容是什么样的,现在我弄明白后写下这篇文章,用于记录…...

Flink和Spark在实时计算方面有何异同
Flink和Spark在实时计算方面既有相似之处,也存在显著的差异。以下是对它们之间异同的详细分析: 一、设计理念与世界观 Flink: 专注于流处理,认为批是流的特例。数据流分为有限流(Bounded)和无限流…...

纵然千万数据流逝,唯独vector长存
公主请阅 1.vector的一些方法1vector和stringpush_back 插入以及三种遍历数组的方式一些方法vector中的一些常见的方法1. push_back()2. pop_back()3. size()4. clear()5. empty()6. resize()7. insert()8. erase()9. at()10. front和 back()11. data()12. capacity()13. shrin…...

【LeetCode】【算法】739. 每日温度
LeetCode 739. 每日温度 题目描述 给定一个整数数组 temperatures ,表示每天的温度,返回一个数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 是指对于第 i 天,下一个更高温度出现在几天后。如果气温在这之后都不会升高,请在该位置用 0…...
2025年知识管理新方案:十款前沿知识库搭建工具详解
随着企业信息化和智能化的发展,知识管理已成为提升企业竞争力的关键要素。一个高效的知识库不仅能促进内部沟通,还能展示企业的专业形象。以下是2025年十款前沿知识库搭建工具的详解。 1. HelpLook AI知识库 HelpLook AI知识库是一款专注于为企业提供高…...

WebSocket实现消息实时推送
文章目录 websocket介绍特点工作原理 用websocket实现实时推送引入依赖WebSocket 函数定义变量声明初始化 WebSocket 连接WebSocket 连接的初始化和事件处理连接打开事件接收消息处理连接关闭和重连机制心跳机制使用 WebSocket代码完整显示 websocket介绍 WebSocket 是一种网络…...

flink 内存配置(三):设置JobManager内存
flink 内存配置(一):设置Flink进程内存 flink 内存配置(二):设置TaskManager内存 flink 内存配置(三):设置JobManager内存 flink 内存配置(四)…...
)
蓝桥杯 Python组-神奇闹钟(datetime库)
神奇闹钟 传送门: 0神奇闹钟 - 蓝桥云课 问题描述 小蓝发现了一个神奇的闹钟,从纪元时间(1970 年 11 日 00:00:00)开始,每经过 x 分钟,这个闹钟便会触发一次闹铃 (…...

(LeetCode 每日一题) 3442. 奇偶频次间的最大差值 I (哈希、字符串)
题目:3442. 奇偶频次间的最大差值 I 思路 :哈希,时间复杂度0(n)。 用哈希表来记录每个字符串中字符的分布情况,哈希表这里用数组即可实现。 C版本: class Solution { public:int maxDifference(string s) {int a[26]…...

设计模式和设计原则回顾
设计模式和设计原则回顾 23种设计模式是设计原则的完美体现,设计原则设计原则是设计模式的理论基石, 设计模式 在经典的设计模式分类中(如《设计模式:可复用面向对象软件的基础》一书中),总共有23种设计模式,分为三大类: 一、创建型模式(5种) 1. 单例模式(Sing…...
51c自动驾驶~合集58
我自己的原文哦~ https://blog.51cto.com/whaosoft/13967107 #CCA-Attention 全局池化局部保留,CCA-Attention为LLM长文本建模带来突破性进展 琶洲实验室、华南理工大学联合推出关键上下文感知注意力机制(CCA-Attention),…...
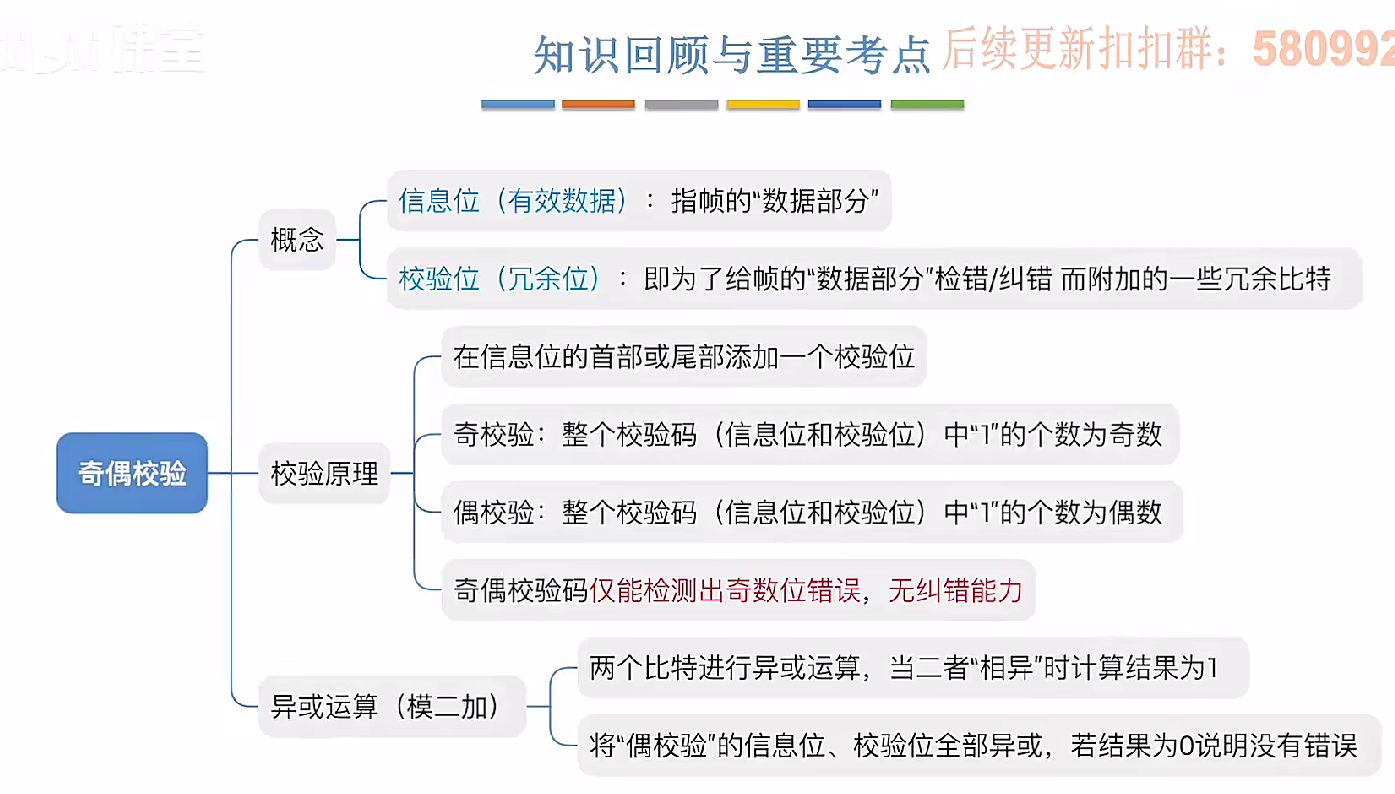
3.3.1_1 检错编码(奇偶校验码)
从这节课开始,我们会探讨数据链路层的差错控制功能,差错控制功能的主要目标是要发现并且解决一个帧内部的位错误,我们需要使用特殊的编码技术去发现帧内部的位错误,当我们发现位错误之后,通常来说有两种解决方案。第一…...

PAN/FPN
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import mathclass LowResQueryHighResKVAttention(nn.Module):"""方案 1: 低分辨率特征 (Query) 查询高分辨率特征 (Key, Value).输出分辨率与低分辨率输入相同。"""def __…...
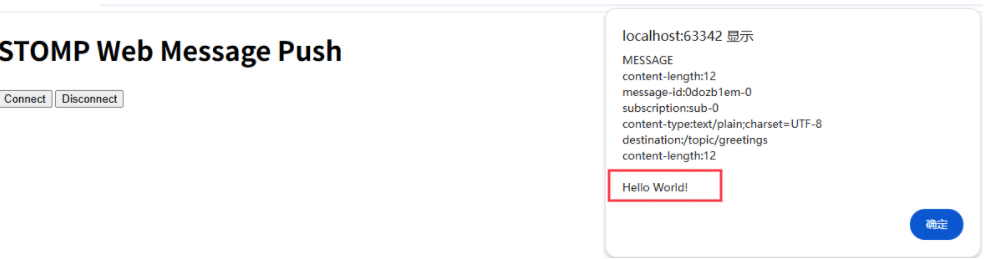
RabbitMQ入门4.1.0版本(基于java、SpringBoot操作)
RabbitMQ 一、RabbitMQ概述 RabbitMQ RabbitMQ最初由LShift和CohesiveFT于2007年开发,后来由Pivotal Software Inc.(现为VMware子公司)接管。RabbitMQ 是一个开源的消息代理和队列服务器,用 Erlang 语言编写。广泛应用于各种分布…...
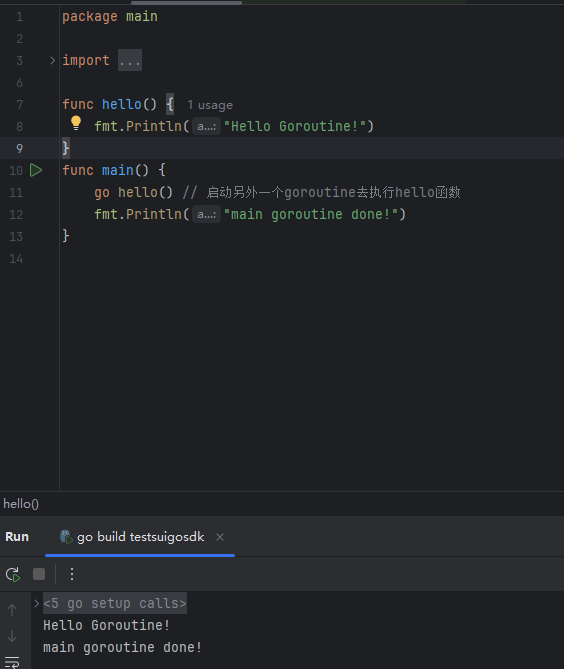
GO协程(Goroutine)问题总结
在使用Go语言来编写代码时,遇到的一些问题总结一下 [参考文档]:https://www.topgoer.com/%E5%B9%B6%E5%8F%91%E7%BC%96%E7%A8%8B/goroutine.html 1. main()函数默认的Goroutine 场景再现: 今天在看到这个教程的时候,在自己的电…...

Git常用命令完全指南:从入门到精通
Git常用命令完全指南:从入门到精通 一、基础配置命令 1. 用户信息配置 # 设置全局用户名 git config --global user.name "你的名字"# 设置全局邮箱 git config --global user.email "你的邮箱example.com"# 查看所有配置 git config --list…...
)
【LeetCode】3309. 连接二进制表示可形成的最大数值(递归|回溯|位运算)
LeetCode 3309. 连接二进制表示可形成的最大数值(中等) 题目描述解题思路Java代码 题目描述 题目链接:LeetCode 3309. 连接二进制表示可形成的最大数值(中等) 给你一个长度为 3 的整数数组 nums。 现以某种顺序 连接…...
)
uniapp 集成腾讯云 IM 富媒体消息(地理位置/文件)
UniApp 集成腾讯云 IM 富媒体消息全攻略(地理位置/文件) 一、功能实现原理 腾讯云 IM 通过 消息扩展机制 支持富媒体类型,核心实现方式: 标准消息类型:直接使用 SDK 内置类型(文件、图片等)自…...
