Rust常用数据结构教程 序列
文章目录
- 一、Vec
- 1.Vec与堆栈
- 2.什么时候需要Vec
- 3.get()方法
- 4.与枚举的结合
- 二、VecDeque
- 1.什么情况适合VecDeque
- 2.VecDeque的方法
- 三、LinkedList
- 1.什么时候用LinkedList
- 参考
一、Vec
可变数组(vector)数组存储在heap上,在运行时(runtime)可以增加或减少数组
长度
- 有人把Vector翻译为矢量
- 注意默认还是不可变
1.Vec与堆栈
Vec的buf是存储在heap上的,其他存储在栈上
pub struct Vec<T, #[unstable(feature = "allocator_api'", issue = "32838")] A:Alocator=Global>
{
buf: RawVec<T, A>,
len: usize, //长度
}pub(crate) struct RawVec<T, A: Allocator = Global> {
ptr: Unique<T>, // 指向
cap: usize, // capacity
alloc: A,
}
2.什么时候需要Vec
·首选Vec:当你不知道用什么的时候,试试Vec,性能强悍有保证
·当你想要一个长度实时变化的数据存储单元时
·当你希望自己的存储单元有序时
·当你希望内存中各个元素的存储地址是连续时
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]
struct Car {id: i32,name: String,
}fn main() {// 初始化方法let my_vec = vec![2, 3, 4];println!("{:#?}: {}", my_vec, my_vec.capacity());// /这里的语法表示创建一个长度为 3 的向量,并用 2 填充每个元素let my_vec = vec![2; 3];println!("{:#?}: {}", my_vec, my_vec.capacity());// 可以显示声明类型,也可以不显示声明类型let my_vec: Vec<i32> = Vec::new();println!("{:#?}: {}", my_vec, my_vec.capacity());let my_vec: Vec<i32> = Vec::with_capacity(5);println!("{:#?}: {}", my_vec, my_vec.capacity());// pushlet mut cars = Vec::new();for i in 1..11 {let car_type = if i % 2 == 0 { "car" } else { "bus" };cars.push(Car {id: i,name: format!("{}-{}", car_type, i),});}println!("{:?}", cars);//删除poplet car = cars.pop().unwrap();println!("{:?}", cars);println!("{:?}", car);//删除:固定index删除let car = cars.remove(0);println!("{:?}", cars);println!("{:?}", car);//队尾插入:pushcars.push(car.clone());println!("{:?}", cars);// 队首插入:insertcars.insert(0, car.clone());println!("{:?}", cars);// get set// 不推荐cars[9] = Car {id: 11,name: "car-11".to_string(),};println!("{:?}", cars);// 推荐let item = cars.get(0);println!("{:?}", item);let item = cars.get_mut(9).unwrap();*item = Car {id: 10,name: "car-10".to_owned(),};println!("{:?}", cars);let mut cars2 = vec![car.clone(), car.clone()];cars.append(&mut cars2);println!("{:?}", cars);println!("{:?}", cars2);let car_slice = cars.as_slice();println!("{:?}", car_slice);// 清理cars.clear();println!("{:?}", cars);println!("{:?}", cars.is_empty());
}编译及运行
cargo runCompiling data_struct v0.1.0 (/home/wangji/installer/rust/data_struct/data_struct)
warning: fields `id` and `name` are never read--> src/main.rs:3:5|
2 | struct Car {| --- fields in this struct
3 | id: i32,| ^^
4 | name: String,| ^^^^|= note: `Car` has derived impls for the traits `Clone` and `Debug`, but these are intentionally ignored during dead code analysis= note: `#[warn(dead_code)]` on by defaultwarning: `data_struct` (bin "data_struct") generated 1 warningFinished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 5.81sRunning `target/debug/data_struct`
[2,3,4,
]: 3
[2,2,2,
]: 3
[]: 0
[]: 5
[Car { id: 1, name: "bus-1" }, Car { id: 2, name: "car-2" }, Car { id: 3, name: "bus-3" }, Car { id: 4, name: "car-4" }, Car { id: 5, name: "bus-5" }, Car { id: 6, name: "car-6" }, Car { id: 7, name: "bus-7" }, Car { id: 8, name: "car-8" }, Car { id: 9, name: "bus-9" }, Car { id: 10, name: "car-10" }]
[Car { id: 1, name: "bus-1" }, Car { id: 2, name: "car-2" }, Car { id: 3, name: "bus-3" }, Car { id: 4, name: "car-4" }, Car { id: 5, name: "bus-5" }, Car { id: 6, name: "car-6" }, Car { id: 7, name: "bus-7" }, Car { id: 8, name: "car-8" }, Car { id: 9, name: "bus-9" }]
Car { id: 10, name: "car-10" }
[Car { id: 2, name: "car-2" }, Car { id: 3, name: "bus-3" }, Car { id: 4, name: "car-4" }, Car { id: 5, name: "bus-5" }, Car { id: 6, name: "car-6" }, Car { id: 7, name: "bus-7" }, Car { id: 8, name: "car-8" }, Car { id: 9, name: "bus-9" }]
Car { id: 1, name: "bus-1" }
[Car { id: 2, name: "car-2" }, Car { id: 3, name: "bus-3" }, Car { id: 4, name: "car-4" }, Car { id: 5, name: "bus-5" }, Car { id: 6, name: "car-6" }, Car { id: 7, name: "bus-7" }, Car { id: 8, name: "car-8" }, Car { id: 9, name: "bus-9" }, Car { id: 1, name: "bus-1" }]
[Car { id: 1, name: "bus-1" }, Car { id: 2, name: "car-2" }, Car { id: 3, name: "bus-3" }, Car { id: 4, name: "car-4" }, Car { id: 5, name: "bus-5" }, Car { id: 6, name: "car-6" }, Car { id: 7, name: "bus-7" }, Car { id: 8, name: "car-8" }, Car { id: 9, name: "bus-9" }, Car { id: 1, name: "bus-1" }]
[Car { id: 1, name: "bus-1" }, Car { id: 2, name: "car-2" }, Car { id: 3, name: "bus-3" }, Car { id: 4, name: "car-4" }, Car { id: 5, name: "bus-5" }, Car { id: 6, name: "car-6" }, Car { id: 7, name: "bus-7" }, Car { id: 8, name: "car-8" }, Car { id: 9, name: "bus-9" }, Car { id: 11, name: "car-11" }]
Some(Car { id: 1, name: "bus-1" })
[Car { id: 1, name: "bus-1" }, Car { id: 2, name: "car-2" }, Car { id: 3, name: "bus-3" }, Car { id: 4, name: "car-4" }, Car { id: 5, name: "bus-5" }, Car { id: 6, name: "car-6" }, Car { id: 7, name: "bus-7" }, Car { id: 8, name: "car-8" }, Car { id: 9, name: "bus-9" }, Car { id: 10, name: "car-10" }]
[Car { id: 1, name: "bus-1" }, Car { id: 2, name: "car-2" }, Car { id: 3, name: "bus-3" }, Car { id: 4, name: "car-4" }, Car { id: 5, name: "bus-5" }, Car { id: 6, name: "car-6" }, Car { id: 7, name: "bus-7" }, Car { id: 8, name: "car-8" }, Car { id: 9, name: "bus-9" }, Car { id: 10, name: "car-10" }, Car { id: 1, name: "bus-1" }, Car { id: 1, name: "bus-1" }]
[]
[Car { id: 1, name: "bus-1" }, Car { id: 2, name: "car-2" }, Car { id: 3, name: "bus-3" }, Car { id: 4, name: "car-4" }, Car { id: 5, name: "bus-5" }, Car { id: 6, name: "car-6" }, Car { id: 7, name: "bus-7" }, Car { id: 8, name: "car-8" }, Car { id: 9, name: "bus-9" }, Car { id: 10, name: "car-10" }, Car { id: 1, name: "bus-1" }, Car { id: 1, name: "bus-1" }]
[]
true
3.get()方法
#![allow(unused)]
fn main() {
let v = vec![1, 2, 3, 4, 5];let third: &i32 = &v[2];
println!("The third element is {}", third);match v.get(2) {Some(third) => println!("The third element is {}", third),None => println!("There is no third element."),
}
}~/installer/rust/bobo/abc master
cargo runCompiling abc v0.1.0 (/home/wangji/installer/rust/bobo/abc)Finished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 7.48sRunning `target/debug/abc`
The third element is 3
The third element is 3
~/installer/rust/bobo/abc master
4.与枚举的结合
#![allow(unused)]
fn main() {enum SpreadsheetCell {Int(i32),Float(f64),Text(String),}let row = vec![SpreadsheetCell::Int(3),SpreadsheetCell::Text(String::from("blue")),SpreadsheetCell::Float(10.12),];match &row[1] {SpreadsheetCell::Int(i) => println!("Found an int: {}", i),_ => println!("No int found"),}
}编译及运行
cargo runCompiling abc v0.1.0 (/home/wangji/installer/rust/bobo/abc)Finished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.29sRunning `target/debug/abc`
No int found
二、VecDeque
一个双向的动态数组
与Vec 类似,与Vec 不同的是,它对容器的两端进行 移除和插入
VecDeque的两端插入、删除都是O(1)级别的
VecDeque并一定是连续的
1.什么情况适合VecDeque
有双端插入和删除需求的
双向需求queue
2.VecDeque的方法
继承了Vec的所有方法
自身的方法
push_back\push_front (取代了push)
pop_frontlpop_back(取代了pop)
contains
frontifront_mut
back\back_mut
Example:
use std::collections::VecDeque;
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]
struct Car {id: i32,name: String,
}fn main() {let mut int_queue: VecDeque<i32> = VecDeque::new();println!("{:?} cap {}", int_queue, int_queue.capacity());int_queue.push_back(3);println!("{:?} cap {}", int_queue, int_queue.capacity());let mut int_queue: VecDeque<i32> = VecDeque::with_capacity(20);println!("{:?} cap {}", int_queue, int_queue.capacity());let mut cars = VecDeque::from([Car {id: 1,name: String::from("Car-1"),},Car {id: 2,name: String::from("Car-2"),},Car {id: 3,name: String::from("Car-3"),},]);println!("{:?} cap {}", cars, cars.capacity());// VecDeque// pushcars.push_back(Car {id: 4,name: "Car-4".to_string(),});println!("{:?} cap {}", cars, cars.capacity());cars.push_front(Car {id: 0,name: "Car-0".to_string(),});println!("{:?} cap {}", cars, cars.capacity());// poplet back_car = cars.pop_back();println!("{:?}", back_car);println!("{:?} cap {}", cars, cars.capacity());let front_car = cars.pop_front();println!("{:?} ", front_car);println!("{:?} cap {}", cars, cars.capacity());// front// backprintln!("{:?}", cars.front());println!("{:?}", cars.back());// getprintln!("car{:?}", cars[1]); //不安全操作let car = cars.get(1).unwrap(); //安全操作println!("car{:?}", car);let car = cars.get_mut(1).unwrap();*car = Car {id: 10,name: "Car-n".to_owned(),};println!("car{:?}", cars);cars.clear();println!("{:?}", cars.is_empty());
}编译及运行
cargo runBlocking waiting for file lock on build directoryCompiling data_struct v0.1.0 (/home/wangji/installer/rust/data_struct/data_struct)
warning: variable does not need to be mutable--> src/main.rs:13:9|
13 | let mut int_queue: VecDeque<i32> = VecDeque::with_capacity(20);| ----^^^^^^^^^| || help: remove this `mut`|= note: `#[warn(unused_mut)]` on by defaultwarning: fields `id` and `name` are never read--> src/main.rs:4:5|
3 | struct Car {| --- fields in this struct
4 | id: i32,| ^^
5 | name: String,| ^^^^|= note: `Car` has derived impls for the traits `Clone` and `Debug`, but these are intentionally ignored during dead code analysis= note: `#[warn(dead_code)]` on by defaultwarning: `data_struct` (bin "data_struct") generated 2 warnings (run `cargo fix --bin "data_struct"` to apply 1 suggestion)Finished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 8.30sRunning `target/debug/data_struct`
[] cap 0
[3] cap 4
[] cap 20
[Car { id: 1, name: "Car-1" }, Car { id: 2, name: "Car-2" }, Car { id: 3, name: "Car-3" }] cap 3
[Car { id: 1, name: "Car-1" }, Car { id: 2, name: "Car-2" }, Car { id: 3, name: "Car-3" }, Car { id: 4, name: "Car-4" }] cap 6
[Car { id: 0, name: "Car-0" }, Car { id: 1, name: "Car-1" }, Car { id: 2, name: "Car-2" }, Car { id: 3, name: "Car-3" }, Car { id: 4, name: "Car-4" }] cap 6
Some(Car { id: 4, name: "Car-4" })
[Car { id: 0, name: "Car-0" }, Car { id: 1, name: "Car-1" }, Car { id: 2, name: "Car-2" }, Car { id: 3, name: "Car-3" }] cap 6
Some(Car { id: 0, name: "Car-0" })
[Car { id: 1, name: "Car-1" }, Car { id: 2, name: "Car-2" }, Car { id: 3, name: "Car-3" }] cap 6
Some(Car { id: 1, name: "Car-1" })
Some(Car { id: 3, name: "Car-3" })
carCar { id: 2, name: "Car-2" }
carCar { id: 2, name: "Car-2" }
car[Car { id: 1, name: "Car-1" }, Car { id: 10, name: "Car-n" }, Car { id: 3, name: "Car-3" }]
true
三、LinkedList
通过链式存储数据的一种序列数据结构
A double-linked with owned nodes
1.什么时候用LinkedList
·根据Rust文档,LinkedList数据结构在分割/追加方面是高效的
如果您希望对分配多少内存以及何时分配内存有非常细粒度的控制,那么链表是一个不错的选择。但是绝大多数你用不到,而且你要考虑成本
use std::collections::LinkedList;#[derive(Debug, Clone)]
struct Car {id: i32,name: String,
}
// vecque 方法都有
// vec 无
fn main() {let mut int_link: LinkedList<i32> = LinkedList::new();let mut cars = LinkedList::from([Car {id: 1,name: "Car-1".to_string(),},Car {id: 2,name: "Car-2".to_string(),},Car {id: 3,name: "Car-3".to_string(),},]);cars.push_back(Car {id: 4,name: "Car-4".to_string(),});println!("back: {:?}", cars.back());cars.push_front(Car {id: 0,name: "Car-0".to_string(),});println!("front: {:?}", cars.front());println!("{:?}", cars);let car = cars.pop_back().unwrap();println!("{:?}", car);let car = cars.pop_front().unwrap();println!("{:?}", car);/*** split_off 是一个方法,用于将 Vec 切成两部分。它会将 cars 向量从指定的索引位置分成两部分,并返回从该位置开始的所有元素,同时将这些元素从原向量中移除。*/let mut car_list = cars.split_off(cars.len() - 2);println!("---{:?}", car_list);println!("{:?}", cars);cars.append(&mut car_list);println!("{:?}", cars);println!("{:?}", car_list);cars.clear();println!("{}", cars.is_empty());
}编译及运行:
cargo runCompiling data_struct v0.1.0 (/home/wangji/installer/rust/data_struct/data_struct)
warning: unused doc comment--> src/main.rs:44:5|
44 | / /**
45 | | * split_off 是一个方法,用于将 Vec 切成两部分。它会将 cars 向量从指定的索引位置分成两部分,并返回从该位置开始的所有元素,同时将这些元素从原向量中移除。
46 | | */| |_______^
47 | let mut car_list = cars.split_off(cars.len() - 2);| -------------------------------------------------- rustdoc does not generate documentation for statements|= help: use `/* */` for a plain comment= note: `#[warn(unused_doc_comments)]` on by defaultwarning: unused variable: `int_link`--> src/main.rs:11:13|
11 | let mut int_link: LinkedList<i32> = LinkedList::new();| ^^^^^^^^ help: if this is intentional, prefix it with an underscore: `_int_link`|= note: `#[warn(unused_variables)]` on by defaultwarning: variable does not need to be mutable--> src/main.rs:11:9|
11 | let mut int_link: LinkedList<i32> = LinkedList::new();| ----^^^^^^^^| || help: remove this `mut`|= note: `#[warn(unused_mut)]` on by defaultwarning: fields `id` and `name` are never read--> src/main.rs:5:5|
4 | struct Car {| --- fields in this struct
5 | id: i32,| ^^
6 | name: String,| ^^^^|= note: `Car` has derived impls for the traits `Clone` and `Debug`, but these are intentionally ignored during dead code analysis= note: `#[warn(dead_code)]` on by defaultwarning: `data_struct` (bin "data_struct") generated 4 warnings (run `cargo fix --bin "data_struct"` to apply 1 suggestion)Finished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 6.13sRunning `target/debug/data_struct`
back: Some(Car { id: 4, name: "Car-4" })
front: Some(Car { id: 0, name: "Car-0" })
[Car { id: 0, name: "Car-0" }, Car { id: 1, name: "Car-1" }, Car { id: 2, name: "Car-2" }, Car { id: 3, name: "Car-3" }, Car { id: 4, name: "Car-4" }]
Car { id: 4, name: "Car-4" }
Car { id: 0, name: "Car-0" }
---[Car { id: 2, name: "Car-2" }, Car { id: 3, name: "Car-3" }]
[Car { id: 1, name: "Car-1" }]
[Car { id: 1, name: "Car-1" }, Car { id: 2, name: "Car-2" }, Car { id: 3, name: "Car-3" }]
[]
true
参考
- Rust常用数据结构教程
相关文章:

Rust常用数据结构教程 序列
文章目录 一、Vec1.Vec与堆栈2.什么时候需要Vec3.get()方法4.与枚举的结合 二、VecDeque1.什么情况适合VecDeque2.VecDeque的方法 三、LinkedList1.什么时候用LinkedList 参考 一、Vec 可变数组(vector)数组存储在heap上,在运行时(runtime)可以增加或减少数组 长度 有人把Ve…...
智慧城市路面垃圾识别系统产品介绍方案
方案介绍 智慧城市中的路面垃圾识别算法通常基于深度学习框架,这些算法因其在速度和精度上的优势而被广泛采用。这些模型能够通过训练识别多种类型的垃圾,包括塑料袋、纸屑、玻璃瓶等。系统通过训练深度学习模型,使其能够识别并定位多种类型…...

网络安全:构建坚固的数字堡垒
网络安全:构建坚固的数字堡垒 在当今数字化时代,网络安全已经成为企业和个人不可忽视的重要议题。随着互联网的普及和信息技术的快速发展,网络攻击、数据泄露和隐私侵犯等问题日益严重,给企业和个人带来了巨大的风险和损失。本文…...

LeetCode题练习与总结:打乱数组--384
一、题目描述 给你一个整数数组 nums ,设计算法来打乱一个没有重复元素的数组。打乱后,数组的所有排列应该是 等可能 的。 实现 Solution class: Solution(int[] nums) 使用整数数组 nums 初始化对象int[] reset() 重设数组到它的初始状态并返回int[]…...

科技改变生活:最新智能开关、调光器及插座产品亮相
根据QYResearch调研团队的最新力作《欧洲开关、调光器和插座市场报告2023-2029》显示,预计到2029年,欧洲开关、调光器和插座市场的规模将攀升至57.8亿美元,并且在接下来的几年里,将以4.2%的复合年增长率(CAGRÿ…...

传统RAG流程;密集检索器,稀疏检索器:中文的M3E
目录 传统RAG流程 相似性搜索中:神经网络的密集检索器,稀疏检索器 密集检索器 BGE系列模型 text-embedding-ada-002模型 M3E模型 稀疏检索器 示例一:基于TF-IDF的稀疏检索器 示例二:基于BM25的稀疏检索器 稀疏检索器的特点与优势 传统RAG流程 相似性搜索中:神经…...

基于统计方法的语言模型
基于统计方法的语言模型 基于统计方法的语言模型主要是指利用统计学原理和方法来构建的语言模型,这类模型通过分析和学习大量语料库中的语言数据,来预测词、短语或句子出现的概率。 N-gram模型:这是最基础的统计语言模型之一,它基…...

Flux comfyui 部署笔记,整合包下载
目录 comfyui启动: 1、下载 Flux 模型 2、Flux 库位置 工作流示例: Flux学习资料免费分享 comfyui启动: # 配置下载模型走镜像站 export HF_ENDPOINT="https://hf-mirror.com" python3 main.py --listen 0.0.0.0 --port 8188 vscode 点击 port 映射到本地,…...

高性能分布式缓存Redis-数据管理与性能提升之道
一、持久化原理 Redis是内存数据库,数据都是存储在内存中,为了避免进程退出导致数据的永久丢失,需要定期将Redis中的数据以某种形式(数据或命令)从内存保存到硬盘;当下次Redis重启时,利用持久化文件实现数据恢复。除此…...

BO-CNN-LSTM回归预测 | MATLAB实现BO-CNN-LSTM贝叶斯优化卷积神经网络-长短期记忆网络多输入单输出回归预测
BO-CNN-LSTM回归预测 | MATLAB实现BO-CNN-LSTM贝叶斯优化卷积神经网络-长短期记忆网络多输入单输出回归预测 目录 BO-CNN-LSTM回归预测 | MATLAB实现BO-CNN-LSTM贝叶斯优化卷积神经网络-长短期记忆网络多输入单输出回归预测效果一览基本介绍模型搭建程序设计参考资料 效果一览 …...

DataWind将字符串数组拆出多行的方法
摘要: 可视化建模中先将字符串split为array再用explode(array)即可 可视化建模 进入“可视化建模”页面 1.1 新建任务 如果团队内没有可视化建模任务。请点击“新建任务”,输入名称并确定。 1.2 建立数据连接 在左边栏中选择“数据连接”,…...

try...catch 和then...catch的异同点分析
try…catch 和 then…catch 的异同点分析 在现代 JavaScript 编程中,异常处理和 Promise 的处理是非常常见的两种方式。try...catch 语句主要用于同步代码的异常处理,而 .then().catch() 是 Promise 中的异步处理方法。 1. 基础概念 1.1 try…catch …...
Mit6.S081-实验环境搭建
Mit6.S081-实验环境搭建 注:大家每次做一些操作的时候觉得不太保险就先把虚拟机克隆一份 前言 qemu(quick emulator):这是一个模拟硬件环境的软件,利用它可以运行我们编译好的操作系统。 准备一个Linux系统…...

以太网交换安全:MAC地址漂移
一、什么是MAC地址漂移? MAC地址漂移是指设备上一个VLAN内有两个端口学习到同一个MAC地址,后学习到的MAC地址表项覆盖原MAC地址表项的现象。 MAC地址漂移的定义与现象 基本定义:MAC地址漂移发生在一个VLAN内的两个不同端口学习到相同的MAC地…...

STM32实现串口接收不定长数据
原理 STM32实现串口接收不定长数据,主要靠的就是串口空闲(idle)中断,此中断的触发条件与接收的字节数无关,只有当Rx引脚无后续数据进入时(串口空闲时),认为这时候代表一个数据包接收完成了&…...

AAA 数据库事务隔离级别及死锁
目录 一、事务的四大特性(ACID) 1. 原子性(atomicity): 2. 一致性(consistency): 3. 隔离性(isolation): 4. 持久性(durability): 二、死锁的产生及解决方法 三、事务的四种隔离级别 0 .封锁协议 …...

外接数据库给streamlit等web APP带来的变化
之前我采用sreamlit制作了一个调查问卷的APP, 又使用MongoDB作为外部数据存储,隐约觉得外部数据库对于web APP具有多方面的意义,代表了web APP发展的趋势之一,似乎是作为对这种趋势的响应,streamlit官方近期开发了st.c…...

Gitpod: 我们正在离开 Kubernetes
原文:Christian Weichel - 2024.10.31 Kubernetes 似乎是构建远程、标准化和自动化开发环境的显而易见选择。我们也曾这样认为,并且花费了六年时间,致力于打造最受欢迎的云开发环境平台,并达到了互联网级的规模。我们的用户数量达…...

1.每日SQL----2024/11/7
题目: 计算用户次日留存率,即用户第二天继续登录的概率 表: iddevice_iddate121382024-05-03232142024-05-09332142024-06-15465432024-08-13523152024-08-13623152024-08-14723152024-08-15832142024-05-09932142024-08-151065432024-08-131123152024-…...
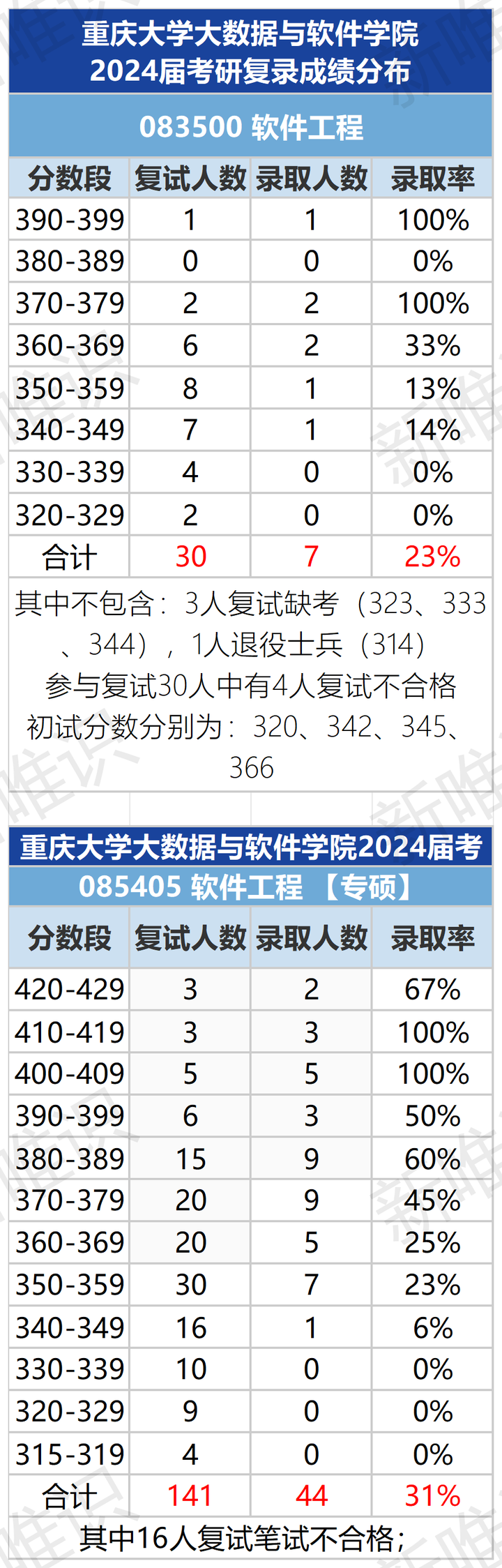
普通一本大二学生,软件工程,想考研985,想知道哪个大学的软件工程好,又不至于完全考不起的?
竞争难度适中:相较于顶尖985院校,重庆大学作为实力派985高校,其竞争烈度较为温和,考研难度适中偏易,为追求高性价比深造路径的考生提供了理想之选。 考试难度友好:重庆地区考研评分标准相对宽松࿰…...
使用分级同态加密防御梯度泄漏
抽象 联邦学习 (FL) 支持跨分布式客户端进行协作模型训练,而无需共享原始数据,这使其成为在互联和自动驾驶汽车 (CAV) 等领域保护隐私的机器学习的一种很有前途的方法。然而,最近的研究表明&…...
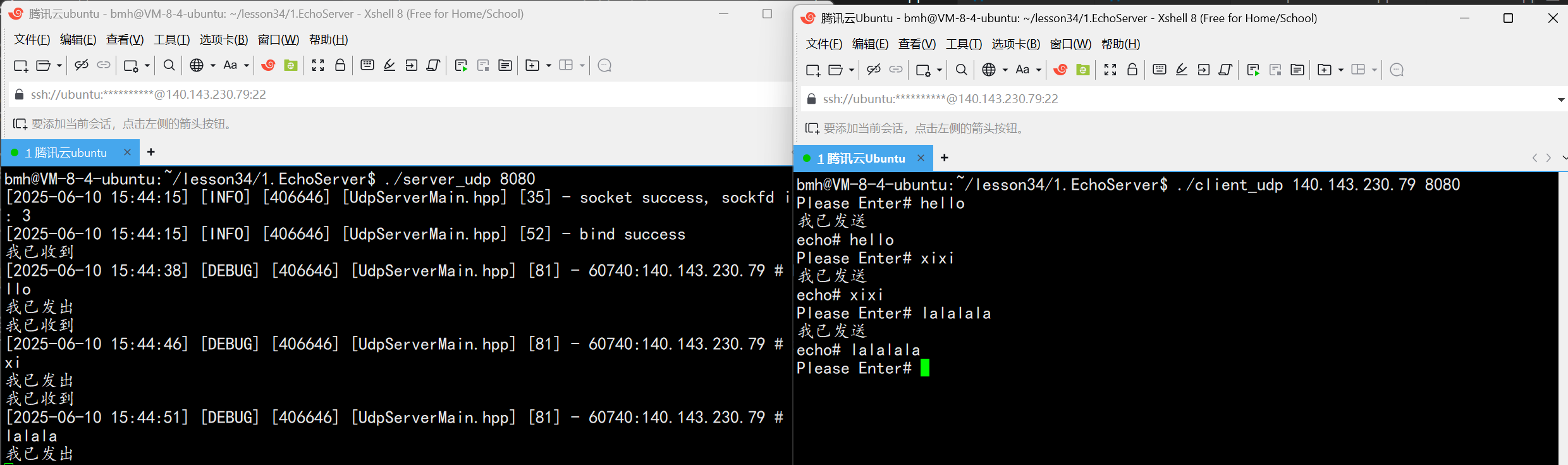
UDP(Echoserver)
网络命令 Ping 命令 检测网络是否连通 使用方法: ping -c 次数 网址ping -c 3 www.baidu.comnetstat 命令 netstat 是一个用来查看网络状态的重要工具. 语法:netstat [选项] 功能:查看网络状态 常用选项: n 拒绝显示别名&#…...

MODBUS TCP转CANopen 技术赋能高效协同作业
在现代工业自动化领域,MODBUS TCP和CANopen两种通讯协议因其稳定性和高效性被广泛应用于各种设备和系统中。而随着科技的不断进步,这两种通讯协议也正在被逐步融合,形成了一种新型的通讯方式——开疆智能MODBUS TCP转CANopen网关KJ-TCPC-CANP…...
)
GitHub 趋势日报 (2025年06月08日)
📊 由 TrendForge 系统生成 | 🌐 https://trendforge.devlive.org/ 🌐 本日报中的项目描述已自动翻译为中文 📈 今日获星趋势图 今日获星趋势图 884 cognee 566 dify 414 HumanSystemOptimization 414 omni-tools 321 note-gen …...
【笔记】WSL 中 Rust 安装与测试完整记录
#工作记录 WSL 中 Rust 安装与测试完整记录 1. 运行环境 系统:Ubuntu 24.04 LTS (WSL2)架构:x86_64 (GNU/Linux)Rust 版本:rustc 1.87.0 (2025-05-09)Cargo 版本:cargo 1.87.0 (2025-05-06) 2. 安装 Rust 2.1 使用 Rust 官方安…...

【无标题】路径问题的革命性重构:基于二维拓扑收缩色动力学模型的零点隧穿理论
路径问题的革命性重构:基于二维拓扑收缩色动力学模型的零点隧穿理论 一、传统路径模型的根本缺陷 在经典正方形路径问题中(图1): mermaid graph LR A((A)) --- B((B)) B --- C((C)) C --- D((D)) D --- A A -.- C[无直接路径] B -…...

解读《网络安全法》最新修订,把握网络安全新趋势
《网络安全法》自2017年施行以来,在维护网络空间安全方面发挥了重要作用。但随着网络环境的日益复杂,网络攻击、数据泄露等事件频发,现行法律已难以完全适应新的风险挑战。 2025年3月28日,国家网信办会同相关部门起草了《网络安全…...

计算机基础知识解析:从应用到架构的全面拆解
目录 前言 1、 计算机的应用领域:无处不在的数字助手 2、 计算机的进化史:从算盘到量子计算 3、计算机的分类:不止 “台式机和笔记本” 4、计算机的组件:硬件与软件的协同 4.1 硬件:五大核心部件 4.2 软件&#…...

区块链技术概述
区块链技术是一种去中心化、分布式账本技术,通过密码学、共识机制和智能合约等核心组件,实现数据不可篡改、透明可追溯的系统。 一、核心技术 1. 去中心化 特点:数据存储在网络中的多个节点(计算机),而非…...
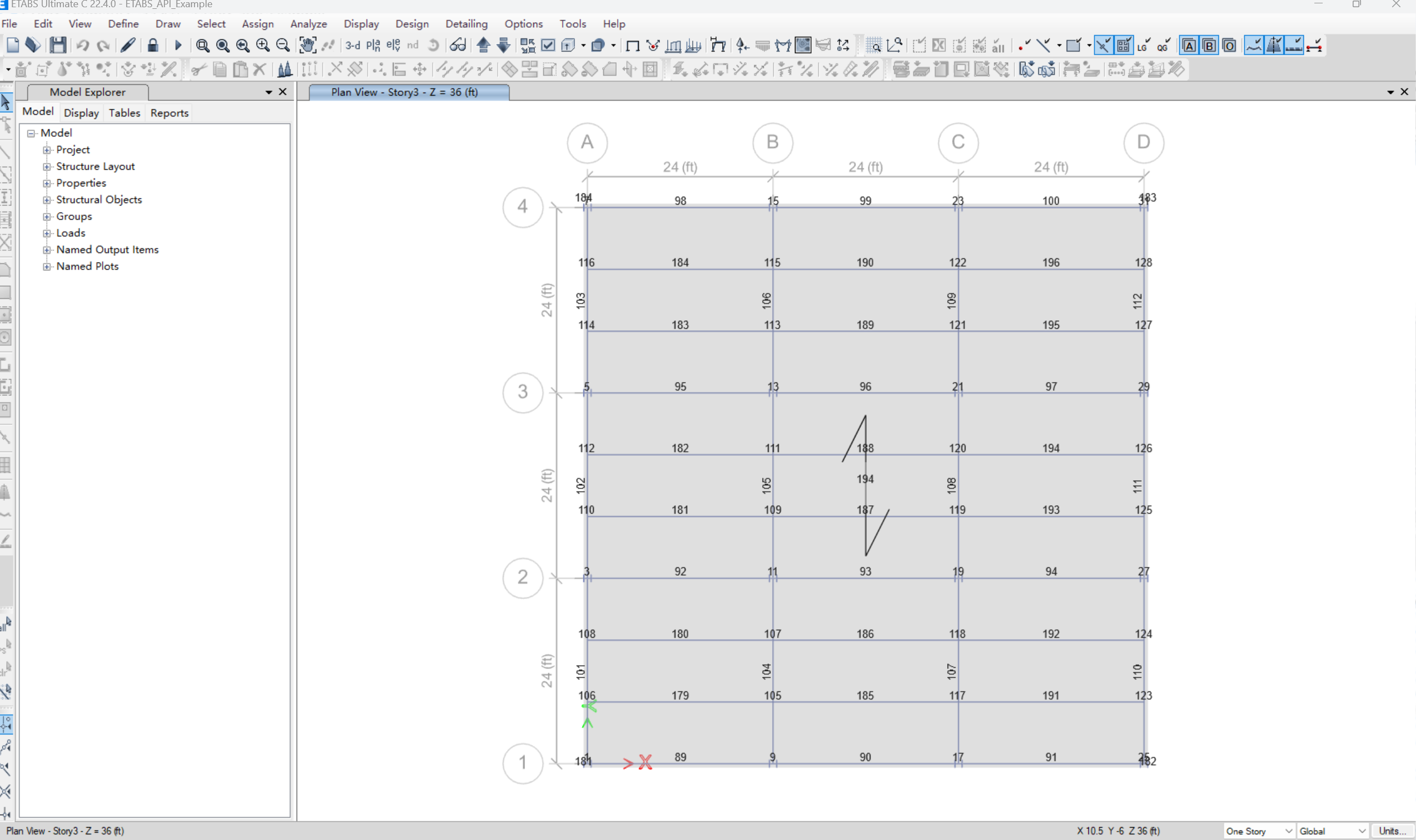
【Post-process】【VBA】ETABS VBA FrameObj.GetNameList and write to EXCEL
ETABS API实战:导出框架元素数据到Excel 在结构工程师的日常工作中,经常需要从ETABS模型中提取框架元素信息进行后续分析。手动复制粘贴不仅耗时,还容易出错。今天我们来用简单的VBA代码实现自动化导出。 🎯 我们要实现什么? 一键点击,就能将ETABS中所有框架元素的基…...
