类和对象( 中 【补充】)
目录
一 . 赋值运算符重载
1.1 运算符重载
1.2 赋值运算符重载
1.3 日期类实现
1.3.1 比较日期的大小 :
1.3.2 日期+=天数 :
1.3.3 日期 -= 天数 :
1.3.4 前置++/后置++
1.3.5 日期 - 日期
1.3.6 流插入 << 和 流提取 >>
二 . 取地址运算符重载
2.1 const 成员函数
2.2 取地址运算符重载
回顾:借助 三道选择题,深刻回顾以下 上一章节的内容!类和对象(中)-CSDN博客
一 . 下列关于构造函数的描述 正确 的是( )
A.构造函数可以声明返回类型
B.构造函数不可以用private修饰
C.构造函数必须与类名相同
D.构造函数不能带参数
C
A . 构造函数不能声明返回类型,void 也不可以!
B . 可以的 , 只不过不能直接实例化对象了
D . 构造函数不光可以带参数,还可以有多个构造函数构成重载
二 . 在函数F中,本地变量a和b的构造函数(constructor)和析构函数(destructor)的调用顺序是: ( )
Class A;
Class B;
void F() {
A a;
B b;
}
A.b构造 a构造 a析构 b析构
B.a构造 a析构 b构造 b析构
C.b构造 a构造 b析构 a析构
D.a构造 b构造 b析构 a析构
构造顺序是按照语句的顺序进行构造,析构是按照构造的相反顺序进行析构 , 对象析构要在生存作用域结束的时候才进行析构
D
三 . 设已经有A,B,C,D4个类的定义,程序中A,B,C,D析构函数调用顺序为?( )
C c;
int main()
{
A a;
B b;
static D d;
return 0;
}
A.D B A C
B.B A D C
C.C D B A
D.A B D C
1、类的析构函数调用一般按照构造函数调用的相反顺序进行调用,但是要注意static对象的存在, 因为static改变了对象的生存作用域,需要等待程序结束时才会析构释放对象
2、全局对象先于局部对象进行构造
3、局部对象按照出现的顺序进行构造,无论是否为static
4、所以构造的顺序为 c a b d
5、析构的顺序按照构造的相反顺序析构,只需注意static改变对象的生存作用域之后,会放在局部 对象之后进行析构
6、因此析构顺序为B A D C
一 . 赋值运算符重载
1.1 运算符重载
- 当运算符被用于类 类型的对象时 , C++语言允许我们通过运算符重载的形式指定新的含义 。 C++规定 类类型对象使用运算符时 , 必须转化成调用对应运算符重载 , 若没有运算符重载 , 则会编译报错 。
- 运算符重载时具有特定名字的函数 , 它的名字是由 operator 和 后面要定义的运算符共同构成 。 和其他函数一样 , 它也 具有其 返回类型 和 参数列表 以及 函数体 。
- 重载运算符函数和参数个数和该运算符作用的运算对象数量一样多 。 一元运算符有一个参数 , 二元运算符有两个参数 , 二元运算符的 左侧运算对象 传给 第一个参数 , 右侧运算对象 传给 第二个参数。
- 如果一个重载运算符函数是成员函数,则它的第一个运算对象默认传给隐式的 this指针,因此运算符重载作为成员函数时,参数比运算对象少一个。
内置类型运算时 , 会比较简单 , 能够直接转化成相应的指令 , 下面举个例子 :
int main()
{int i = 1, j = 3;int ret1 = i + j;bool ret2 = i == j;int ret3 = i ^ j;return 0;
}
我们调试以下 , 转到汇编语言 , 可以看到编译器可以直接转为 add , cmp , xor 指令 , 但是对于自定义类型 , 是由程序员自己定义的 , 需要实现的功能也是由程序员定义的 , 下面我们举一个日期类的例子 :

我们的编译器充当的是翻译功能 , 当需要实现太复杂的对象与对象之间的运算 ,编译器编不出来

所以我们需要写一个运算符重载函数 , 实现相应的运算功能 :


如果这样设为公有 ,成员变量很容易被访问到 ,很不安全 ,以下提供三种方法:


#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(int year, int month, int day){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void Print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day<<endl;}bool operator==(const Date& x){return _year == x._year&& _month == x._month&& _day == x._day;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
int main()
{Date d1(2024, 11, 15);Date d2(2024, 11, 30);bool ret1 = d1 == d2;cout << ret1 << endl;return 0;
}
- 运算符重载以后 , 其优先级和结合性与对应的内置类型运算符保持一致。
- 不能通过连接语法中没有的符号来创建新的操作符 : 比如operator@
- .* :: sizeof ?: . 注意以上5个运算符不能重载 。 !!!!
- 重载操作符至少有一个类 类型参数 , 不能通过运算符重载改变内置类型对象的含义 , 如 int operator+(int x,int y )
- 一个类需要重载那些运算符 , 是看那些运算符重载后有意义 , 比如Date 类 重载 operator- 就有意义 , 但是重载 opearator+ 就没有意义 。
- 重载++运算符时 , 有前置++ 和后置++ , 运算符重载函数名都是operator++ , 无法很好的区分 。 C++规定 , 后置++重载时候 , 增加一个 int 形参 ,跟前置++ 构成函数重载 , 方便区分 。
- 重载<< 和 >> 时 , 需要重载函数为全局函数 , 因为重载为成员函数 , this 指针 默认抢占了第一个形参位置 , 第一个形参位置是左侧运算符对象 ,调用时就变成了 对象<<cout , 不符合使用习惯和可读性 。 重载为全局函数把 ostream/istream 放在第一个形参位置就可以了 , 第二个形参位置当类型对象 。
.* 应用举例 :
//.* 举例#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// 编译报错:“operator +”必须⾄少有⼀个类类型的形参
int operator+(int x, int y)
{return x - y;
}
class A
{
public:void func(){cout << "A::func()" << endl;}
};
typedef void(A::* PF)(); //成员函数指针类型
int main()
{// C++规定成员函数要加&才能取到函数指针PF pf = &A::func;A obj;//定义ob类对象temp// 对象调⽤成员函数指针时,使⽤.*运算符(obj.*pf)();return 0;
}
1.2 赋值运算符重载
赋值运算符重载是一个默认成员函数 , 用于完成两个 已经存在 的对象直接拷贝赋值 , 这里要注意跟拷贝构造区分 , 拷贝构造用于一个对象拷贝初始化给另一个对象 。

赋值运算符重载的特点 :
- 赋值运算符重载是一个运算符重载 , 规定必须重载为成员函数 。 赋值运算重载的参数建议写成 const 当前类 类型引用 , 否则 会 传值传参会有拷贝 。
- 有返回值 , 且建议写成当前类 类型引用 , 引用返回可以提高效率 , 有返回值目的是为了支持连续赋值场景 。
- 没有显式实现时 , 编译器会自动生成一个默认赋值运算符重载 , 默认运算符重载行为跟默认构造函数类似 , 对内置类型成员变量会完成值拷贝 / 浅拷贝(一个字节一个字节的拷贝),对自定义类型成员变量会调用他的拷贝构造 。


什么时候需要实现赋值重载 ?

如果栈 , 进行赋值重载时 , 但是没有进行写赋值重载函数会发生什么情况 :

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(int year, int month, int day){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}//赋值重载 -- 两个都是存在的对象//d2 = d1Date& operator=(const Date& d){if (this != &d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;}void Print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};typedef int STDataType;
class Stack
{
public:Stack(int n = 4){_a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * n);if (nullptr == _a){perror("malloc申请空间失败");return;}_capacity = n;_top = 0;}// st2(st1)Stack(const Stack& st){// 需要对_a指向资源创建同样大的资源再拷贝值_a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * st._capacity);if (nullptr == _a){perror("malloc申请空间失败!!!");return;}memcpy(_a, st._a, sizeof(STDataType) * st._top);_top = st._top;_capacity = st._capacity;}// st1 = st3// st1 = st1;Stack& operator=(const Stack& st){if (this != &st){free(_a);_a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * st._capacity);if (nullptr == _a){perror("malloc申请空间失败!!!");return *this;}memcpy(_a, st._a, sizeof(STDataType) * st._top);_top = st._top;_capacity = st._capacity;}return *this;}void Push(STDataType x){if (_top == _capacity){int newcapacity = _capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(_a, newcapacity *sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}_a = tmp;_capacity = newcapacity;}_a[_top++] = x;}void Pop(){_a[_top - 1] = -1;--_top;}int Top(){return _a[_top - 1];}~Stack(){cout << "~Stack()" << endl;free(_a);_a = nullptr;_top = _capacity = 0;}
private:STDataType* _a;size_t _capacity;size_t _top;
};class MyQueue
{
private:Stack _pushst;Stack _popst;
};int main()
{Date d1(2024, 11, 20);d1.Print();Date d2(2024, 11, 30);d2.Print();Date d3 = d2;d3.Print();Stack st1;st1.Push(1);st1.Push(2);st1.Push(3);st1.Push(4);Stack st2(10);for (size_t i = 0; i < 10; i++){st2.Push(i * 10);}st1 = st2;MyQueue q1;MyQueue q2(q1);MyQueue q3;q1 = q3;return 0;
}1.3 日期类实现
为了更好的进行文件管理 , 我们创建三个文件 : Date.cpp , Date.h , test,cpp
日期类的实现 需要结合实际生活中的客观现象 : 比如闰年2月为29天等;
1.3.1 比较日期的大小 :

bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{if (_year > d._year){return true;}else if(_year == d._year&&_month >d._month){return true;}else if(_year == d._year && _month == d._month){return _day > d._day;}return false;
}bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d)
{return *this > d || *this == d;
}bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)
{return !(*this >= d);
}bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d)
{return !(*this > d);
}bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;
}bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d)
{return !(*this == d);
}
1.3.2 日期+=天数 :


// GetMonthDayint GetMonthDay(int year, int month){static int monthDayArry[13] = { -1,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0){return 29;}return monthDayArry[month];}// +=
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);//天满进月++_month;//月满进年if (_month == 13){_month = 1;++_year;}}return *this;
}// +
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp._day += day;while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month)){tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);//天满进月++tmp._month;//月满进年if (tmp._month == 13){tmp._month = 1;++tmp._year;}}return tmp;
}+ 与 += 比较 :
Date d1 ;
Date d2 = d1 + 50;
+ : d1 不变(*this)
Date d1;
Date d2 = d1 += 50;
+= : d1 改变(*this)

可以使用 + 复用实现 += :
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp._day += day;while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month)){tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);//天满进月++tmp._month;//月满进年if (tmp._month == 13){tmp._month = 1;++tmp._year;}}return tmp;
}// + 复用实现 +=
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{*this = *this + _day;return *this;
}可以使用 += 复用实现 + :
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);//天满进月++_month;//月满进年if (_month == 13){_month = 1;++_year;}}return *this;
}//+= 复用实现 +
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp += day;return tmp;
}+ 复用实现 += 的情况好 还是 += 复用实现 + 的情况好 ?
对比调用拷贝构造的次数 :
使用 += 复用 + 更好 !

1.3.3 日期 -= 天数 :

Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{_day -= day;while (_day<=0){//借位--_month;if (_month == 0){--_year;_month = 12;}_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}Date Date::operator-(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp._day -= day;while (tmp._day <= 0){//借位--tmp._month;if (tmp._month == 0){--tmp._year;tmp._month = 12;}tmp._day += GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);}return tmp;
}如果 d1 += -100
d2 -= -100
在程序中可以得到合理结果吗?
运行 --- -28 日不存在 -- 不合理 !


1 ) d1 += -100 -----> 实际就是 -=100
2 ) d2 -= -100 -----> 实际就是 +=100
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{if (day < 0)return *this -= (-day);_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);//天满进月++_month;//月满进年if (_month == 13){_month = 1;++_year;}}return *this;
}Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{if (day < 0)return *this += (-day);_day -= day;while (_day<=0){//借位--_month;if (_month == 0){--_year;_month = 12;}_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}1.3.4 前置++/后置++
重载++运算符时 , 有前置++ 和 后置 ++ , 运算符重载函数名都是 operator++ , 无法很好的区分 , C++规定 , 后置++ 重载时 , 增加一个 int 形参 , 跟前置 ++ 构成函数重载 , 方便区分!
多了一个参数仅仅是为了区分前置和后置
//前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{*this = *this + 1;return *this;
}
//后置++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{Date tmp = *this;*this = *this + 1;return tmp;
}//前置--
Date& Date::operator--()
{*this = *this - 1;return *this;
}
//后置--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{Date tmp = *this;*this = *this - 1;return tmp;
}
1.3.5 日期 - 日期

//d1 - d2
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{int flag = 1;Date max = *this;Date min = d;if (*this < d){max = d;min = *this;flag = -1;}//对于++,前置++的效率更大int n = 0;while (min != max){++min;++n;}return flag * n;
}1.3.6 流插入 << 和 流提取 >>
注意 : 如果<< 的运算符重载写在成员函数里 , 第一个参数一定是this ,那么插入操作就必须写成 d1<<cout , 代码可读性大大降低 ;
所以我们需要把 <<的运算符重载 , 写在类外 , 但是这样会导致私有的成员变量访问异常,所以我们在类内 把运算符重载函数设为友元函数

// 流插入<< 读
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;return out;
}// 流提取 >> 写
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{cout << "请依次输入年月日:>";//默认用空格 或者 换行 分割in>> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;return in;
}但是 如果我输入2023年2月29日 ( 不合法的日期) 是否可以正常打印呢 ?

那就意味着我们还需要写一个 合法检查函数 , 控制在输入 和 构造函数 必须是合法的日期;

bool Date::CheckDate()
{if (_month < 1 || _month > 12|| _day < 1 || _day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){return false;}else{return true;}
}Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;if (!CheckDate()){cout << "日期非法:" << *this << endl;}
}// 流提取 >> 写
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{while (1){cout << "请依次输入年月日:>";//默认用空格 或者 换行 分割in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;if (d.CheckDate()){break;}else{cout << "输入的日期非法,请重新输入:"<<endl;}}return in;
}二 . 取地址运算符重载
2.1 const 成员函数
- 将const 修饰的成员函数称之为 const 成员函数 , const 修饰成员函数放在成员函数参数后面 。
- const 实际修饰 该成员函数隐含的 this 指针 ,表明在该成员函数中不能对类的任何成员进行修改 。 const 修饰Date 类的 Print成员函数 , Print 隐含的 this指针由 Date* const this 变为 Date* const this
2.2 取地址运算符重载
取地址运算符重载分为普通取地址运算符重载 和 const取地址运算符重载 , 一般这两个函数编译器自动生成的就可以够我们用了 , 不需要去显示实现 。 除非一些很特殊的场景 , 比如我们不想取到当前类对象的地址 , 就可以自己实现一份 , 胡乱返回一个地址 。
class Date
{
public:Date* operator&(){return this;// return nullptr;}const Date * operator&()const{return this;// return nullptr;}
private:int _year; // 年int _month; // ⽉int _day; // ⽇
};另 : 不要过分相信编译器的红色波浪线的报错 , 一切以编译的结果为准 , 因为编译器在这里进行的只是预检查 , 可能具有滞后性 , 或者一些BUG
总代码:
Date.cpp
#include "Date.h"bool Date::CheckDate()
{if (_month < 1 || _month > 12|| _day < 1 || _day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){return false;}else{return true;}
}Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;if (!CheckDate()){cout << "日期非法:" << *this << endl;}
}Date* Date::operator&()
{return this;// return nullptr;
}
const Date* Date::operator&()const
{return this;// return nullptr;
}void Date::Print()const
{cout << _year << "/" << _month <<"/" << _day<<endl;
}bool Date::operator>(const Date& d) const
{if (_year > d._year){return true;}else if(_year == d._year&&_month >d._month){return true;}else if(_year == d._year && _month == d._month){return _day > d._day;}return false;
}bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d) const
{return *this > d || *this == d;
}bool Date::operator<(const Date& d) const
{return !(*this >= d);
}bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d) const
{return !(*this > d);
}bool Date::operator==(const Date& d) const
{return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;
}bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d) const
{return !(*this == d);
}Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{if (day < 0)return *this -= (-day);_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);//天满进月++_month;//月满进年if (_month == 13){_month = 1;++_year;}}return *this;
}//Date Date::operator+(int day)
//{
// Date tmp(*this);
// tmp._day += day;
// while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))
// {
// tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
// 天满进月
// ++tmp._month;
// 月满进年
// if (tmp._month == 13)
// {
// tmp._month = 1;
// ++tmp._year;
// }
// }
// return tmp;
//}// + 复用实现 +=
//Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
//{
// *this = *this + _day;
// return *this;
//}//+= 复用实现 +
Date Date::operator+(int day) const
{Date tmp(*this);tmp += day;return tmp;
}Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{if (day < 0)return *this += (-day);_day -= day;while (_day<=0){//借位--_month;if (_month == 0){--_year;_month = 12;}_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}Date Date::operator-(int day) const
{Date tmp(*this);tmp._day -= day;return tmp;
}//前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{*this = *this + 1;return *this;
}
//后置++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{Date tmp = *this;*this = *this + 1;return tmp;
}//前置--
Date& Date::operator--()
{*this = *this - 1;return *this;
}
//后置--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{Date tmp = *this;*this = *this - 1;return tmp;
}//d1 - d2
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const
{int flag = 1;Date max = *this;Date min = d;if (*this < d){max = d;min = *this;flag = -1;}//对于++,前置++的效率更大int n = 0;while (min != max){++min;++n;}return flag * n;
}// 流插入<< 读
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;return out;
}// 流提取 >> 写
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{while (1){cout << "请依次输入年月日:>";//默认用空格 或者 换行 分割in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;if (d.CheckDate()){break;}else{cout << "输入的日期非法,请重新输入:"<<endl;}}return in;
}Date.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;class Date
{//友元函数friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1);void Print()const;//Date* operator&();const Date* operator&()const;bool CheckDate();int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){static int monthDayArry[13] = { -1,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0){return 29;}return monthDayArry[month];}//运算符重载bool operator>(const Date& d) const;bool operator>=(const Date& d) const;bool operator<(const Date& d) const;bool operator<=(const Date& d) const;bool operator==(const Date& d) const;bool operator!=(const Date& d) const;//d1 += 天数Date operator+(int day)const;Date& operator+=(int day);//d1 -= 天数Date operator-(int day)const;Date& operator-=(int day);//前置 / 后置 ++//前置++Date& operator++();//后置++Date operator++(int);//前置 / 后置 --//前置--Date& operator--();//后置--Date operator--(int);//d1 - d2int operator-(const Date& d) const;private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};// 流插入 <<
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);// 流提取 >>
istream& operator>>(istream& in,Date& d);Test.cpp
#include "Date.h"void Test1()
{// >Date d1(2024, 11, 22);Date d2(2024, 11, 1);Date d3(d1);d1.Print();d2.Print();d3.Print();cout << (d2 > d1) << endl;cout << (d2 >= d3) << endl;cout << (d2 < d1) << endl;cout << (d2 <= d1) << endl;cout << (d1 == d3) << endl;cout << (d1 != d3) << endl;}void Test2()
{//+ / += //Date d1(2024, 11, 1);//Date d2 = d1 += 50;//Date d3 = d1 + 50;//d1.Print();//d2.Print();//d3.Print();//d1.Print();//Date d1(2024, 11, 22);//Date d2 = d1 += -50;//d1.Print();//d2.Print();Date d3(2024, 11, 22);//Date d4 = d3--;//Date d5 = --d3;//d4.Print();//d5.Print();//d3.Print();cout << d3;}void Test3()
{Date d1(2024, 11, 22);Date d2(2024, 11, 1);cout << d1 << d2 <<" "<<d1;cin >> d1 >> d2;
}void Test4()
{Date d1(2024, 2, 29);Date d2(2023, 2, 29);cin >> d1 >> d2;cout << d1 << d2;
}void Test5()
{const Date d1(2024, 2, 29);Date d2(2023, 2, 29);
}
int main()
{//Test1();//Test2();//Test3();Test4();return 0;
}相关文章:

类和对象( 中 【补充】)
目录 一 . 赋值运算符重载 1.1 运算符重载 1.2 赋值运算符重载 1.3 日期类实现 1.3.1 比较日期的大小 : 1.3.2 日期天数 : 1.3.3 日期 - 天数 : 1.3.4 前置/后置 1.3.5 日期 - 日期 1.3.6 流插入 << 和 流提取 >> 二 . 取地址运算符重载 2.1 const…...
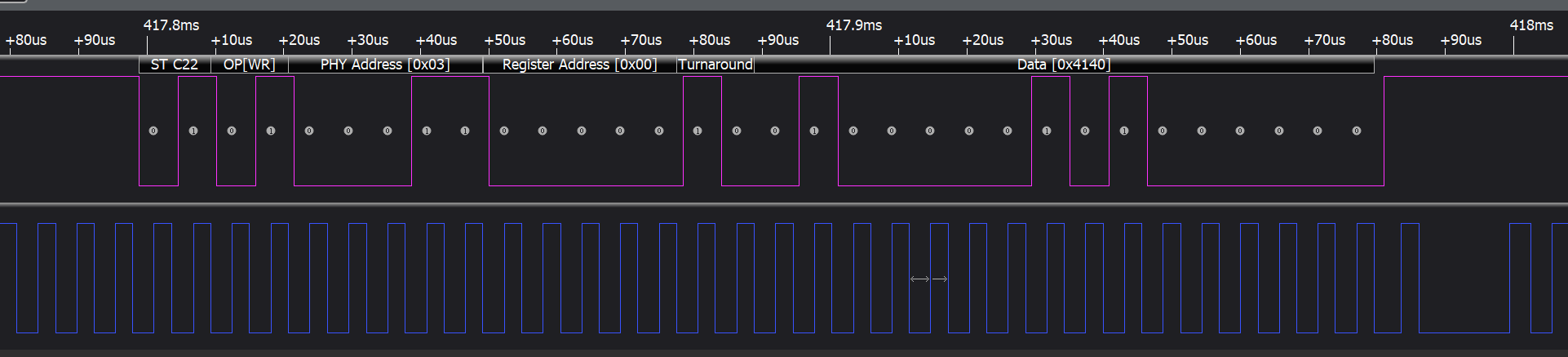
如何使用gpio模拟mdio通信?
一、前言 实际项目开发中,由于设计原因,会将phy的mdio引脚连接到SoC的2个空闲gpio上, 这样就无法通过Gmac自有的架构实现修改phy, 因此只能通过GPIO模拟的方式实现MDIO, 好在Linux支持MDIO via GPIO功能。 该功能…...

C# 中的事件和委托:构建响应式应用程序
C#中的事件和委托。事件和委托是C#中用于实现观察者模式和异步回调的重要机制,它们在构建响应式和交互式应用程序中发挥着重要作用。以下是一篇关于C#中事件和委托的文章。 引言 事件和委托是C#语言中非常重要的特性,它们允许你实现观察者模式和异步回…...

科技赋能健康:多商户Java版商城系统引领亚健康服务数字化变革
在当今社会,随着生活节奏的加快和工作压力的增大,越来越多的人处于亚健康状态。据《The Lancet》期刊2023年的统计数据显示,全球亚健康状态的人群比例已高达82.8%,这一数字背后,隐藏着巨大的健康风险和社会成本。亚健康…...
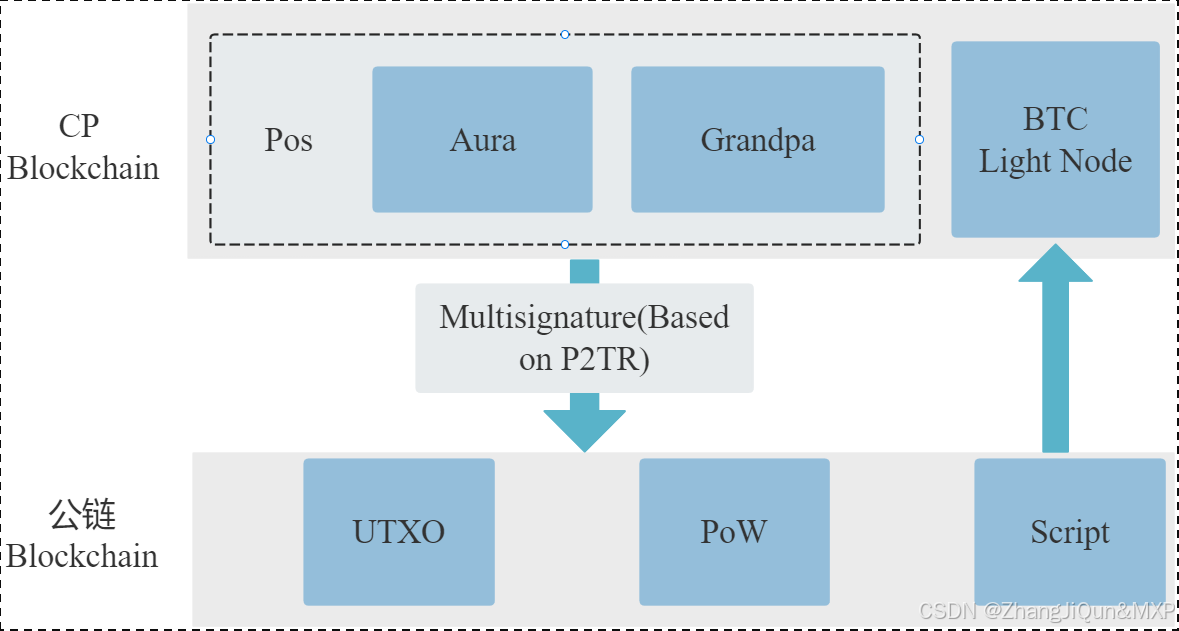
区块链网络示意图;Aura共识和Grandpa共识(BFT共识)
目录 区块链网络示意图 Aura共识和Grandpa共识(BFT共识) Aura共识 Grandpa共识(BFT共识) Aura与Grandpa的结合 区块链网络示意图 CP Blockchain:这是中央处理区块链(或可能指某种特定的处理单元区块链)的缩写。它可能代表了该区块链网络的主要处理或存储单元。在这…...
Javaweb梳理18——JavaScript
今日目标 掌握 JavaScript 的基础语法掌握 JavaScript 的常用对象(Array、String)能根据需求灵活运用定时器及通过 js 代码进行页面跳转能通过DOM 对象对标签进行常规操作掌握常用的事件能独立完成表单校验案例 18.1 JavaScript简介 JavaScript 是一门跨…...

面向对象-接口的使用
1. 接口的概述 为什么有接口? 借口是一种规则,对于继承而言,部分子类之间有共同的方法,为了约束方法的使用,使用接口。 接口的应用: 接口不是一类事物,它是对行为的抽象。 2. 接口的定义和使…...
)
失落的Apache JDBM(Java Database Management)
简介 Apache JDBM(Java Database Management)是一个轻量级的、基于 Java 的嵌入式数据库管理系统。它主要用于在 Java 应用程序中存储和管理数据。这个项目已经过时了,只是发表一下以示纪念,现在已经大多数被SQLite和Derby代替。…...
Vue3+SpringBoot3+Sa-Token+Redis+mysql8通用权限系统
sa-token支持分布式token 前后端代码,地球号: bright12389...

MySQL 三大日志详解
在 MySQL 数据库中,binlog(二进制日志)、redo log(重做日志)和 undo log(回滚日志)起着至关重要的作用。它们共同保障了数据库的高可用性、数据一致性和事务的可靠性。下面将对这三大日志进行详…...
Java 岗面试八股文及答案整理(2024最新版)
春招,秋招,社招,我们 Java 程序员的面试之路,是挺难的,过了 HR,还得被技术面,小刀在去各个厂面试的时候,经常是通宵睡不着觉,头发都脱了一大把,还好最终侥幸能…...
Web3.0安全开发实践:Clarity最佳实践总结
在过去的一段时间里,CertiK团队对比特币生态系统及其发展进行了深入研究。同时,团队还审计了多个比特币项目以及基于不同编程语言的智能合约,包括OKX的BRC-20钱包和MVC DAO的sCrypt智能合约实现。 现在,我们的研究重点转向了Clar…...
基于Springboot+Vue动漫推荐平台管理系统(源码+lw+讲解部署+PPT)
前言 详细视频演示 论文参考 系统介绍 系统概述 核心功能 用户角色与功能 具体实现截图 1. 热门动漫功能 2. 文章专栏功能 3. 会员分享功能 4. 热门动漫管理功能(管理员端) 5. 动漫分类管理功能 技术栈 后端框架SpringBoot 前端框架Vue …...

秋意浓,森林披金装
秋意浓,森林披金装, 枫叶如火,漫山遍野狂。 松间轻风送寒意, 鸟鸣悠扬入云翔。 林间小径蜿蜒行, 落叶铺成金色毯。 溪水潺潺绕石转, 映出天边一抹霞。 野菊点缀在草间, 白云悠悠随意闲。…...
Chrome离线安装包下载
1、问Chrome的官网:https://www.google.cn/chrome/ 直接下载的是在线安装包,安装需要联网。 2、如果需要在无法联网的设备上安装Chrome,需要在上面的地址后面加上?standalone1。 Chrome离线安装包下载地址:https://www.google.c…...
安卓手机5G网络频繁掉4G 问题解决 手机5G网络优化方案
问题环境 在某个长期停留的位置(例如:躺平)使用手机时网络突然从5G跳到4G,偶尔跳来跳去导致网络体验很差,经过调整5G网络情况下网速及其他体验都要更好,基于这样的情况使用一种简单的操作,锁定5…...

使用LLaMA-Factory微调时的问题与解决方案记录
文章目录 如何指定微调使用的显卡如何解决显卡通信导致的报错模型微调的实际epoch和step如何计算如何实现多卡全量微调模型微调后的结果如何查看模型测试后的指标如何理解如何指定微调使用的显卡 启动网页时使用这种执行命令 CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=5,6,7 llamafactory-cli we…...

Go语言switch语句
在Go语言中,switch,是一个高度灵活,其功能强大的控制结构,相比较Java中的switch,更受到语言重视。 目录 1.基础用法2.多值匹配3.不指定表达式的 switch4.使用 fallthrough 强制进入下一个分支5.使用类型断言的 switch…...

JavaScript DOM使用
DOM Document Object Model 简单而言,就是JavaScript将HTML文档的各个组成部分封装为对象。 封装的对象分别为: Document:整个HTML的文档对象 Element:元素对象(也就是HTML中的标签) Attribute:…...
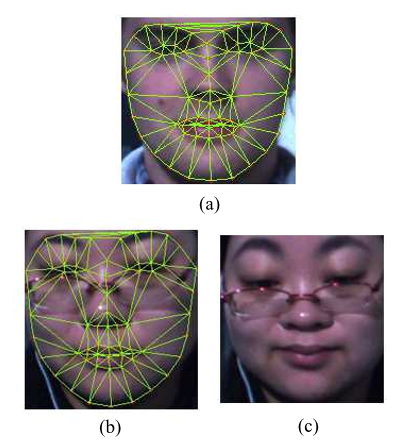
人工智能|计算机视觉——微表情识别(Micro expression recognition)的研究现状
一、简述 微表情是一种特殊的面部表情,与普通的表情相比,微表情主要有以下特点: 持续时间短,通常只有1/25s~1/3s;动作强度低,难以察觉;在无意识状态下产生,通常难以掩饰或伪装;对微表情的分析通常需要在视频中,而普通表情在图像中就可以分析。由于微表情在无意识状态…...

基于大模型的 UI 自动化系统
基于大模型的 UI 自动化系统 下面是一个完整的 Python 系统,利用大模型实现智能 UI 自动化,结合计算机视觉和自然语言处理技术,实现"看屏操作"的能力。 系统架构设计 #mermaid-svg-2gn2GRvh5WCP2ktF {font-family:"trebuchet ms",verdana,arial,sans-…...
srs linux
下载编译运行 git clone https:///ossrs/srs.git ./configure --h265on make 编译完成后即可启动SRS # 启动 ./objs/srs -c conf/srs.conf # 查看日志 tail -n 30 -f ./objs/srs.log 开放端口 默认RTMP接收推流端口是1935,SRS管理页面端口是8080,可…...
dify打造数据可视化图表
一、概述 在日常工作和学习中,我们经常需要和数据打交道。无论是分析报告、项目展示,还是简单的数据洞察,一个清晰直观的图表,往往能胜过千言万语。 一款能让数据可视化变得超级简单的 MCP Server,由蚂蚁集团 AntV 团队…...

IP如何挑?2025年海外专线IP如何购买?
你花了时间和预算买了IP,结果IP质量不佳,项目效率低下不说,还可能带来莫名的网络问题,是不是太闹心了?尤其是在面对海外专线IP时,到底怎么才能买到适合自己的呢?所以,挑IP绝对是个技…...

【SSH疑难排查】轻松解决新版OpenSSH连接旧服务器的“no matching...“系列算法协商失败问题
【SSH疑难排查】轻松解决新版OpenSSH连接旧服务器的"no matching..."系列算法协商失败问题 摘要: 近期,在使用较新版本的OpenSSH客户端连接老旧SSH服务器时,会遇到 "no matching key exchange method found", "n…...
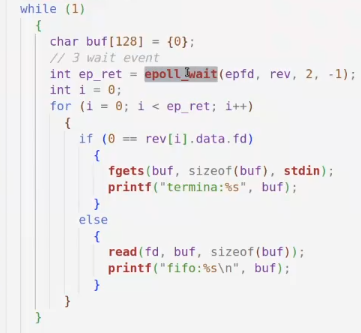
day36-多路IO复用
一、基本概念 (服务器多客户端模型) 定义:单线程或单进程同时监测若干个文件描述符是否可以执行IO操作的能力 作用:应用程序通常需要处理来自多条事件流中的事件,比如我现在用的电脑,需要同时处理键盘鼠标…...

Vue 模板语句的数据来源
🧩 Vue 模板语句的数据来源:全方位解析 Vue 模板(<template> 部分)中的表达式、指令绑定(如 v-bind, v-on)和插值({{ }})都在一个特定的作用域内求值。这个作用域由当前 组件…...

全面解析数据库:从基础概念到前沿应用
在数字化时代,数据已成为企业和社会发展的核心资产,而数据库作为存储、管理和处理数据的关键工具,在各个领域发挥着举足轻重的作用。从电商平台的商品信息管理,到社交网络的用户数据存储,再到金融行业的交易记录处理&a…...
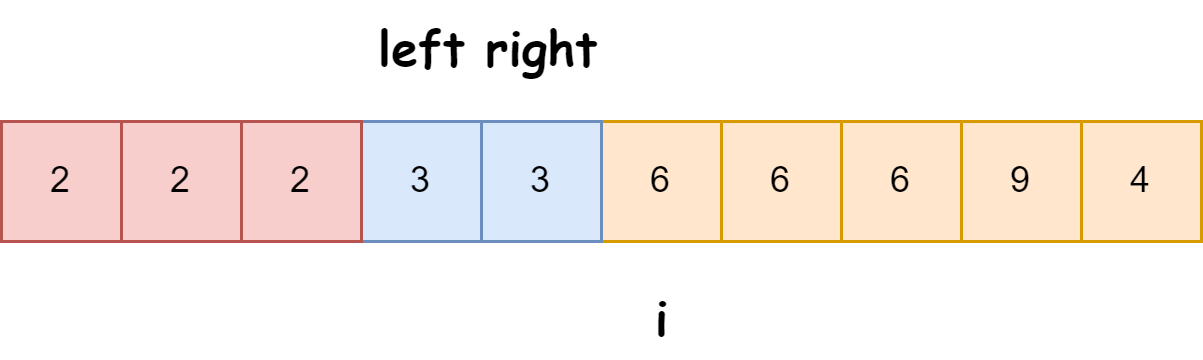
快速排序算法改进:随机快排-荷兰国旗划分详解
随机快速排序-荷兰国旗划分算法详解 一、基础知识回顾1.1 快速排序简介1.2 荷兰国旗问题 二、随机快排 - 荷兰国旗划分原理2.1 随机化枢轴选择2.2 荷兰国旗划分过程2.3 结合随机快排与荷兰国旗划分 三、代码实现3.1 Python实现3.2 Java实现3.3 C实现 四、性能分析4.1 时间复杂度…...

Vue 实例的数据对象详解
Vue 实例的数据对象详解 在 Vue 中,数据对象是响应式系统的核心,也是组件状态的载体。理解数据对象的原理和使用方式是成为 Vue 专家的关键一步。我将从多个维度深入剖析 Vue 实例的数据对象。 一、数据对象的定义方式 1. Options API 中的定义 在 Options API 中,使用 …...

