线程局部存储tls的原理和使用
一、背景
tls即Thread Local Storage,也就是线程局部存储,可在进程内,多线程按照各个线程分开进行存储。对于一些与线程上下文相关的变量,可放到tls中,减少多线程之间的数据同步的开销。
有人可能会问,我在进程内维护一个按照线程tid为key的map,是不是也可以做出一样的效果?对于线程数量较少,map的索引也比较快,效果应该是差不多的,但是对于线程数量较多,map管理上的开销增大以后,就不如tls机制来得快了,tls机制的按线程进行索引的速度达到了O1级别,且tls机制是glibc带的默认的功能,用起来也相当方便。
但是tls机制美中不足的是并没有提供tls数据的遍历动作,但是tls数据跟随线程的创建和释放的机制是有的,我们要进行tls数据的遍历就需要自行添加相关的链表或者其他数据结构来实现遍历。
我们在第二章里会进行使用上的介绍并给出使用上的提示,然后在第三章里展开tls的底层实现原理的介绍并做一些实验来验证。
二、使用介绍
tls机制是glibc库默认带上的功能,相关原理介绍我们会在第三章里展开,这一章我们只讲如何使用和使用上的注意事项。
我们可以用C方式的来进行tls变量的声明,一旦声明成tls变量,那么所有的线程包括主线程,都会有该变量的
2.1 可使用C方式的__thread来声明POD数据结构的变量
先说一下POD的概念,POD即Plain old data structure,简单来说就是可用于兼容C的数据结构,如下class testb就是一个POD数据结构:
testb 图一

![]()
但是,如果我们给testb增加一个构造函数,那么这时候class testb就不是一个POD数据结构。如下:

![]()
当然,POD的概念,还有不少细节,这里就不展开了。
如下图,如果我们使用__thread来修饰图一的testb,是可以编过的:

但是如果我们使用__thread来修饰图二的testb,是不可以编过的,提示:

2.1.1 如果需要做线程退出后的释放逻辑,我们需要使用pthread_key_create和pthread_setspecific进行__thread变量的释放逻辑的关联和绑定
关键逻辑代码:
创建一个key(这个动作同一个线程里可以执行多次,每次都能成功,主线程执行过后,进程里的其他线程也可以重复执行,并可以重复执行多次):
需要先定义一个key:
![]()
再用这个key来创建,关联上线程退出时的清理函数:

各个线程上下文里,如果需要触发清理函数的线程,都需要执行pthread_setspecifc函数来关联key对应的变量:

再次强调,要触发清理函数的线程,都需要执行pthread_setspecifc!
完整源码:
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <csignal>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
#include <ctime>
#include <atomic>
#include <cmath>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
#include <map>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>const int NUM_THREADS = 16;
const int NUM_TLS_VARS = 32;thread_local int b;// [NUM_TLS_VARS] ; // 线程局部变量数组class testb {
public:int b;int c;void run(){printf("run\n");}
};int aaa;__thread testb _tls_b;//__thread int __tls_a = 0;class testa {
public:testa() {a = -2;pid = getpid();tid = gettid();a = -3;printf("testa,pid[%d]tid[%d]\n", pid, tid);}~testa() {printf("~testa,pid[%d]tid[%d]\n", pid, tid);}int a = -1;int pid = 0;int tid = 0;
};
thread_local testa ta;#include <assert.h>pthread_key_t tsd_testb;static int test = 0;void testb_cleanup(void* arg) {//test++;printf("testb_cleanup\n");
}void threadFunction(int threadId) {int ret = 0;if ((ret = pthread_setspecific(tsd_testb, (void*)(&_tls_b))) != 0) {printf("error:%s\n", strerror(ret));return;}printf("_tls_b.b=%d,_tls_b.c=%d\n", _tls_b.b, _tls_b.c);_tls_b.b++;_tls_b.c++;printf("_tls_b.b=%d,_tls_b.c=%d\n", _tls_b.b, _tls_b.c);pthread_setname_np(pthread_self(), "tlstesttls");for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {ta.a++;//printf("errno=%d[0x%llx]\n", errno, &errno);std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));}
}//void run();int main() {int ret = 0;_tls_b.b++;printf("%llx,%llx\n", testb_cleanup, &testb_cleanup);if ((ret = pthread_key_create(&tsd_testb, &testb_cleanup)) != 0) {printf("error:%s\n", strerror(ret));return -1;}if ((ret = pthread_setspecific(tsd_testb, (void*)(&_tls_b))) != 0) {printf("error:%s\n", strerror(ret));return -1;}//assert(0);std::vector<std::thread> threads;ta.a++;std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(2));//_tls_a.b++;for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {threads.emplace_back(threadFunction, i);}//exit(0);// 等待所有线程完成for (auto& t : threads) {t.join();}printf("test=%d\n", test);return 0;
}
运行以后从下图截图里可以看到,注册清理的函数testb_cleanup被执行了5次:

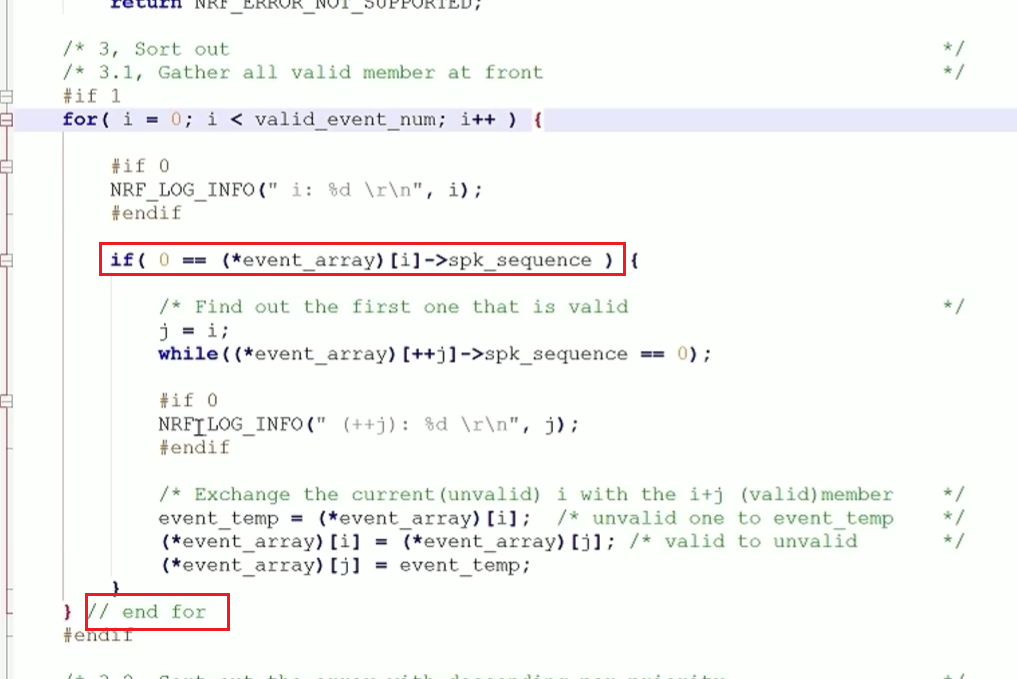
2.1.2 调用pthread_setspecific的线程,无论是否真正使用它,都是会触发注册的清理函数回调的
我们如下图,去掉__thread testb _tls_b在线程里的所有使用:

可以如下图看到,注册的清理函数还是会被执行到的:

2.1.3 线程未“正常”退出的话,注册的清理函数是极有可能未执行到的
如 2.1.1 里的程序,我们如下改动,不去join直接exit:

可以如下图看到testb_cleanup是一次都没有执行的:

2.2 可使用C++方式的thread_local来声明数据结构的变量
不同于C的__thread的方式,使用thread_local方式来声明的变量的数据结构不要求是POD的。如下例子:

2.2.1 在线程第一次使用thread_local变量时触发thread_local变量的构造函数
我们使用的是vs2019进行ssh登录来进行gdb的调试,相关细节参考之前的博客 vs2019进行远程linux用户态调试_vs2019 root 调试-CSDN博客。
如下图,我们在testa的构造函数里进行printf打印:

在主线程里在使用thread_local声明的testa的变量ta前设置了断点:
![]()

在执行上图中的ta.a++的动作之前,是没有执行到testa构造函数里的断点,也没有printf打印出来的:

而在执行了ta.a++之后,就能看到printf打印出来了:

2.2.2 在线程退出但进程还未退出时会触发线程退出时的thread_local变量的析构函数
为了做测试实验,我们并不join线程结束,而是直接用exit(0)来退出,如下图:

这样,进程在退出时,线程的用户态释放逻辑并不会全部执行干净,包括thread_local变量的析构函数里的逻辑(打印逻辑):

可以从下图中看到,在程序退出时只执行到了一个线程的thread_local testa变量的析构函数:

完整的程序代码:
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <csignal>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
#include <ctime>
#include <atomic>
#include <cmath>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
#include <map>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>const int NUM_THREADS = 16;
const int NUM_TLS_VARS = 32;thread_local int b;// [NUM_TLS_VARS] ; // 线程局部变量数组class testb {
public:int b;int c;
public:void run(){b = c;}
};int aaa;__thread testb _tls_a;//__thread int __tls_a = 0;class testa {
public:testa() {a = -2;pid = getpid();tid = gettid();a = -3;printf("testa,pid[%d]tid[%d]\n", pid, tid);}~testa() {printf("~testa,pid[%d]tid[%d]\n", pid, tid);}int a = -1;int pid = 0;int tid = 0;
};
thread_local testa ta;void threadFunction(int threadId) {pthread_setname_np(pthread_self(), "tlstesttls");for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {ta.a++;printf("errno=%d[0x%llx]\n", errno, &errno);std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));}
}//void run();#include <assert.h>int main() {//assert(0);std::vector<std::thread> threads;ta.a++;std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(2));//_tls_a.b++;for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {threads.emplace_back(threadFunction, i);}exit(0);// 等待所有线程完成for (auto& t : threads) {t.join();}return 0;
}
2.3 库里也是可以使用tls机制的
这一节的实验是基于C的方式的tls机制来做的。另外,这一节的实验,我们只做了程序使用so库的场景,对于so库A和so库B的实验就省略了,是差不多的。
这其实是很显然的,因为像jemalloc的库或者glibc的库里的errno,都是用了tls机制的。
但是有几个注意事项:
1)程序和库里可以用一样的pthread_key_t的变量来定义,对应的__thread的变量也是可以设置成同名的,这里面的原因其实很好理解,因为无论是key还是__thread修饰的变量,tls机制里看到的都是编译器管理的地址,库和程序在不同的地址段里,这些变量自然就不会冲突。
2)pthread_key_create所注册的清理函数,程序和库里的清理函数需要名字不重名,否则会导致清理函数调用的函数不符合预期,或者重名也行,得用static来修饰函数(使用static来修饰私有的函数事实证明是一个好习惯!)
对于上面说到的2)的实验结果截图如下:
程序里的清理函数叫testb_cleanup:

so库里如果也叫testb_cleanup且并不定义成static,如下图:

就会出现如下图的运行后的情况,运行了两次程序里定义的清理函数:

增加了static后的so库的源码:
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <csignal>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
#include <ctime>
#include <atomic>
#include <cmath>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
#include <map>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>thread_local int b = 1;pthread_key_t tsd_testb;
__thread int _tls_b = 0;int cc;static void testb_cleanup(void* arg) {//test++;printf("testtlsso_cleanup\n");
}void run()
{int ret = 0;if ((ret = pthread_key_create(&tsd_testb, &testb_cleanup)) != 0) {printf("error:%s\n", strerror(ret));return;}if ((ret = pthread_setspecific(tsd_testb, (void*)(&_tls_b))) != 0) {printf("error:%s\n", strerror(ret));return;}_tls_b++;b++;printf("run\n");
}//int main()
//{
// run();
// return 1;
//}程序源码:
程序里主要是在线程函数里增加了:

完整源码:
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <csignal>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
#include <ctime>
#include <atomic>
#include <cmath>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
#include <map>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>const int NUM_THREADS = 16;
const int NUM_TLS_VARS = 32;thread_local int b;// [NUM_TLS_VARS] ; // 线程局部变量数组class testb {
public:int b;int c;void run(){printf("run\n");}
};int aaa;__thread testb _tls_b;//__thread int __tls_a = 0;class testa {
public:testa() {a = -2;pid = getpid();tid = gettid();a = -3;printf("testa,pid[%d]tid[%d]\n", pid, tid);}~testa() {printf("~testa,pid[%d]tid[%d]\n", pid, tid);}int a = -1;int pid = 0;int tid = 0;
};
thread_local testa ta;#include <assert.h>pthread_key_t tsd_testb;static int test = 0;void testb_cleanup(void* arg) {//test++;printf("testb_cleanup\n");
}extern void run();void threadFunction(int threadId) {int ret = 0;if ((ret = pthread_setspecific(tsd_testb, (void*)(&_tls_b))) != 0) {printf("error:%s\n", strerror(ret));return;}//printf("_tls_b.b=%d,_tls_b.c=%d\n", _tls_b.b, _tls_b.c);//_tls_b.b++;//_tls_b.c++;//printf("_tls_b.b=%d,_tls_b.c=%d\n", _tls_b.b, _tls_b.c);pthread_setname_np(pthread_self(), "tlstesttls");for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {ta.a++;//printf("errno=%d[0x%llx]\n", errno, &errno);std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));}run();
}//void run();int main() {int ret = 0;_tls_b.b++;printf("%llx,%llx\n", testb_cleanup, &testb_cleanup);if ((ret = pthread_key_create(&tsd_testb, &testb_cleanup)) != 0) {printf("error:%s\n", strerror(ret));return -1;}if ((ret = pthread_setspecific(tsd_testb, (void*)(&_tls_b))) != 0) {printf("error:%s\n", strerror(ret));return -1;}//assert(0);std::vector<std::thread> threads;ta.a++;std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(2));//_tls_a.b++;for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {threads.emplace_back(threadFunction, i);}//exit(0);// 等待所有线程完成for (auto& t : threads) {t.join();}printf("test=%d\n", test);return 0;
}
运行后的截图:

2.4 总结一下tls使用上的注意事项
2.3.1 errno变量其实就是tls变量
我们在线程的函数里打印了errno的地址,可以如下图看到不同的线程,其errno的地址是不同的:


我们来看一下glibc-2.35版本的源码。在errno.c里,我们就可以看到使用了__thread修饰了int errno变量:

errno用tls机制来存储是为了多线程的错误码可以相互间不干扰。
2.3.2 tls的C机制是线程调用过pthread_setspecific则触发释放的回调,thread_local机制是按需触发析构
从 2.1.1 可以看到,C机制得每个需要触发释放回调的线程各自子线程上下文里执行一下pthread_setspecific来触发回调(无论使用过与否)
从 2.2.1 可以看到,thread_local机制,是按需触发,即在第一次使用定义的变量时才会触发thread_local的构造函数,触发过构造函数自然对应的在线程“正常”退出时触发析构。
2.3.3 进程退出时线程未“正常”退出的话,对应清理函数或者析构函数可能不会被执行到
从 2.1.3 和 2.2.2 就可以看到,无论是__thread机制还是thread_local机制,对应的已经注册的清理函数或者使用过变量对应的析构函数都可能不会被执行到
这其实就提示了我们,如果需要确定性的线程退出要去保证去做的逻辑,依赖tls机制是不行的,还是得配合通过内核的节点的.release行为去保障。
2.3.4 如果用C方式的tls机制,要注意库里注册的清理函数的名字要和程序里或其他库里注册的清理函数名字不重名,担心重名的话,需要用static来修饰
细节见 2.3 一节
三、原理介绍及实验验证
这一章我们基于x86_64平台来分析原理并做一些实验验证。在 3.1 里我们先用一个简单的场景的例子,即在bin里直接使用tls变量的场景,看其汇编实现,然后引申到fs/gs段寄存器,在 3.2 里我们介绍fsindex和fsbase的概念,目前tls机制就是用的fsindex是0的fsbase来作为线程局部存储的基址。然后在 3.3 里,我们介绍tls机制,glibc和内核是如何配合的,并做一些相关细节上的实验验证,最后,我们在 3.4 里展示在so库里使用tls变量的场景,看其汇编实现,是否和bin里直接使用tls变量有何不同。
3.1 bin里直接使用tls变量的汇编实现及fs/gs段寄存器
这里说的是直接在bin里使用tls变量,而不是在库里使用。
如下代码,在线程的function里使用__thread int _a这个tls变量:

对应的汇编如下:

注意,linux下默认使用的是AT&T格式的汇编,不同于intel汇编,AT&T格式的汇编src在前,dst在后。上面红色框出的三行汇编意思就是把%fs:0xfffffffffffffffc位置的数赋值给eax寄存器里,然后eax寄存里的值+1后,再赋值回%fs:0xfffffffffffffffc位置。
那么什么是%fs:0xfffffffffffffffc位置呢?
fs是x86_64下的段寄存器,在之前的博客 监测各个核上cpu上的线程是内核线程还是用户线程,处于内核态还是用户态的方法_取当前线程 是否内核模式-CSDN博客 里的 3.2.1 一节我们讲到cs和ss这两个段寄存器的使用,不同于cs和ss,fs以及gs都是后来拓展的段寄存器,用于性能优化用途。为什么这么说呢?fs是用来服务于glibc的tls机制,用于用户态的线程局部存储,其本质就是一种性能优化的手段(让线程私有的数据更高效地访问和修改,也避免多线程间的同步开销),目前内核态并没有使用fs寄存器。而gs段寄存器,用于内核的per-cpu变量的获取,如下图(x86下的preempt_count是per-cpu变量,对应汇编就用了%gs这个gs段寄存器,关于preempt_count在之前的中断上下文及抢占标志位的检查——基于调度及锁举例_中断上下文 锁-CSDN博客 博客有详细的介绍):

3.2 tls机制用fsindex是0的fsbase来作为线程局部存储的基址
fs和gs这两个段寄存器是386时新增的段寄存器,段寄存器在演进过程中,为了解决地址保护的问题,不把详细的基址暴露给用户,引入了中间结构体,即段描述符,要找到段描述符就需要有索引,而fs寄存器就是存储的这个索引。如下图,获取到的%fs的值即fsindex是0,内核里也就是用fsindex这个变量名字。
![]()
tls机制从实现上经过了多次迭代,早期glibc用了ldt的方式,但是受制于段描述符的条目限制,index是15:3(如下图),总共13位,即最多8192条,导致了当时进程内最多8192个线程的限制。

而现在glibc x86-64用的是借助arch_prctl系统调用来做线程的fsbase的设置。
对于支持X86_FEATURE_FSGSBASE特性的cpu而言,理论上并不需要一定要陷入内核才能进行fs/gs的base寄存器的读写,但是目前glibc并没有打通这一方式。
相关的glibc和内核配合的tls相关的逻辑细节见 3.3 一节。
tls机制用的是fsindex是0,这相当于是一个与glibc配合的一个约定。内核里关于它有一些注释:


3.3 glibc和内核的配合的tls逻辑细节及实验验证
3.3.1 glibc和内核的配合的tls逻辑细节
对于bin里直接使用tls变量这种情况,一旦程序运行起来以后,主线程运行前,tls变量这部分的内存就应该被预留出来,这种tls可以认为是静态tls,静态tls变量的引用和修改的汇编代码相对比较简单,如下图,直接用fs的base来偏移一个固定值就可以访问和修改:

具体如何计算,涉及到glibc的实现里,TCB(Thread Control Block)及DTV(dynamic thread vector)相关的细节,这里不展开。这里我们主要关注与内核配合的那一部分的逻辑,也就是fs寄存器相关的逻辑。
虽然bin里使用tls变量可以直接用fs寄存器配合offset来引用和修改,但是fs寄存器实际用的fsbase还是得有人设下去,谁去设的呢?
glibc里在dl_main里会根据case由init_tls间接调用TLS_INIT_TP或dl_main里直接调用TLS_INIT_TP,TLS_INIT_TP的宏如下:

如上图,里面核心逻辑就是调用arch_prctl的系统调用,执行ARCH_SET_FS的操作。
内核里对应于响应ARCH_SET_FS的逻辑如下,x86_64平台下是process_64.c文件里的do_arch_prctl_64函数:

可以从上图中看到可以设置本进程,也可以设置非本进程。
对于设置本进程,需要分为两步,先设置fsindex,再设置fsbase。
设置fsindex的loadseg函数:

loadseg最终调用了loadsegment函数进行的fsindex的设置:

设置fsbase用的是x86_fsbase_write_cpu函数:

在我实验的x86_64平台上,boot_cpu_has(X86_FEATURE_FSGSBASE)是true的:

![]()
所以,用的是wrfsbase来进行的设置:

另外,我们也可以通过如下方式进行fsbase的读取:
rdmsrl(MSR_FS_BASE, fsval);而对于非本进程而言,仅仅是保存一下数值到task_struct.thread.fsindex和task_struct.thread.fsbase里:
![]()

3.3.2 相关实验的内核模块代码及pthread_self
我们写了一个内核模块,来针对我们的实验的线程进行fsindex和fsbase的抓取,与此同时,通过gdb断点下来,打印出tls变量的地址,与gdb看到的用户态汇编及内核模块打印的fsbase做比对,来验证这个fs+offset的访问的逻辑。
下面的内核模块是通过sched_switch的tracepoint来捕获tlstesttls名字的线程,打印fsindex和fsbase的数值(关于tracepoint的使用见之前的博客):
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/capability.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/ctype.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/stddef.h>
#include <linux/lockdep.h>
#include <linux/kthread.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <asm/atomic.h>
#include <trace/events/workqueue.h>
#include <linux/sched/clock.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/mm.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/tracepoint.h>
#include <trace/events/osmonitor.h>
#include <trace/events/sched.h>
#include <trace/events/irq.h>
#include <trace/events/kmem.h>
#include <linux/ptrace.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/processor.h>
#include <linux/sched/task_stack.h>
#include <linux/nmi.h>
#include <asm/apic.h>
#include <linux/version.h>
#include <asm/irq_regs.h>
#include <asm/segment.h>
#include <linux/kdebug.h>static void cb_sched_switch(void *i_data, bool i_preempt,struct task_struct *i_prev,struct task_struct *i_next,unsigned int i_prev_state)
{if (strcmp(i_prev->comm, "tlstesttls") == 0) {struct pt_regs *regs = NULL;unsigned int fsindex;unsigned long fsbase;//loadsegment(fs, fsbase);//savesegment(fs, fsbase);asm("movl %%fs,%0" : "=r" (fsindex));rdmsrl(MSR_FS_BASE, fsbase);printk("tlstesttls fs:%u, 0x%llx\n", fsindex, fsbase);printk("tlstesttls fs:%016lx, 0x%llx\n", fsindex, fsbase);printk("task->thread.fsindex=%hu\n", i_prev->thread.fsindex);}
}struct kern_tracepoint {void *callback;struct tracepoint *ptr;bool bregister;
};static void clear_kern_tracepoint(struct kern_tracepoint *tp)
{if (tp->bregister) {tracepoint_probe_unregister(tp->ptr, tp->callback, NULL);}
}#define INIT_KERN_TRACEPOINT(tracepoint_name) \static struct kern_tracepoint mykern_##tracepoint_name = {.callback = NULL, .ptr = NULL, .bregister = false};#define TRACEPOINT_CHECK_AND_SET(tracepoint_name) \static void tracepoint_name##_tracepoint_check_and_set(struct tracepoint *tp, void *priv) \{ \if (!strcmp(#tracepoint_name, tp->name)) \{ \((struct kern_tracepoint *)priv)->ptr = tp; \return; \} \}INIT_KERN_TRACEPOINT(sched_switch)
TRACEPOINT_CHECK_AND_SET(sched_switch)// 模块初始化
static int __init my_module_init(void) {if (static_cpu_has(X86_FEATURE_FSGSBASE)) {printk("has X86_FEATURE_FSGSBASE\n");}mykern_sched_switch.callback = cb_sched_switch;for_each_kernel_tracepoint(sched_switch_tracepoint_check_and_set, &mykern_sched_switch);if (!mykern_sched_switch.ptr) {printk("mykern_sched_switch register failed!\n");return 0;}else {printk("mykern_sched_switch register succeeded!\n");}tracepoint_probe_register(mykern_sched_switch.ptr, mykern_sched_switch.callback, NULL);mykern_sched_switch.bregister = 1;return 0;
}// 模块清理
static void __exit my_module_exit(void) {clear_kern_tracepoint(&mykern_sched_switch);tracepoint_synchronize_unregister();printk(KERN_INFO "Unloading my module...\n");
}module_init(my_module_init);
module_exit(my_module_exit);MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("Your Name");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("A simple example of tls in a kernel module");另外一边,用户态的程序代码如下(通过pthread_setname_np(pthread_self(), "tlstesttls");来设置线程的comm名字是“tlstesttls”):
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <csignal>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
#include <ctime>
#include <atomic>
#include <cmath>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
#include <map>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>const int NUM_THREADS = 16;
const int NUM_TLS_VARS = 32;//thread_local int b;// [NUM_TLS_VARS] ; // 线程局部变量数组class testb {
public:int b;int c;void run(){printf("run\n");}
};int aaa;//__thread testb _tls_b;//__thread int __tls_a = 0;class testa {
public:testa() {a = -2;pid = getpid();tid = gettid();a = -3;printf("testa,pid[%d]tid[%d]\n", pid, tid);}~testa() {printf("~testa,pid[%d]tid[%d]\n", pid, tid);}int a = -1;int pid = 0;int tid = 0;
};
//thread_local testa ta;#include <assert.h>pthread_key_t tsd_testb;static int test = 0;void testb_cleanup(void* arg) {//test++;printf("testb_cleanup\n");
}extern void run();__thread int _a;void threadFunction(int threadId) {pthread_setname_np(pthread_self(), "tlstesttls");_a++;printf("pthread_self[%d][0x%llx]\n", threadId, pthread_self());
}//int ret = 0;//if ((ret = pthread_setspecific(tsd_testb, (void*)(&_tls_b))) != 0) {// printf("error:%s\n", strerror(ret));// return;//}//printf("_tls_b.b=%d,_tls_b.c=%d\n", _tls_b.b, _tls_b.c);//_tls_b.b++;//_tls_b.c++;//printf("_tls_b.b=%d,_tls_b.c=%d\n", _tls_b.b, _tls_b.c);//pthread_setname_np(pthread_self(), "tlstesttls");//printf("pthread_self[%d][0x%llx]\n", threadId, pthread_self());//for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {//ta.a++;//printf("errno=%d[0x%llx]\n", errno, &errno);// std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));//}//run();
//}//void run();int main() {int ret = 0;//_tls_b.b++;printf("%llx,%llx\n", testb_cleanup, &testb_cleanup);//if ((ret = pthread_key_create(&tsd_testb, &testb_cleanup)) != 0) {// printf("error:%s\n", strerror(ret));// return -1;//}//if ((ret = pthread_setspecific(tsd_testb, (void*)(&_tls_b))) != 0) {// printf("error:%s\n", strerror(ret));// return -1;//}//assert(0);std::vector<std::thread> threads;//ta.a++;std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(2));//_tls_a.b++;for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {threads.emplace_back(threadFunction, i);}//exit(0);// 等待所有线程完成for (auto& t : threads) {t.join();}printf("test=%d\n", test);return 0;
}
我们把断点断在下图这里:

运行以后,断点断下来的情况,如下方式添加监视的数据,把tls变量_a的地址打印出来:

可以从上图中看到_a的地址是0x7ffff77ff63c。
另外一边,insmod模块ko后,dmesg看到的相关打印,fsbase的值是0x7ffff77ff640:

然后再反汇编窗口看到下图里的这句,0xfffffffffffffffc是-4,fsbase减去4正好是_a的地址。

接下来我们来看一下pthread_self的返回值:
刚才抓到的fsbase是threadId是0的(如下图),fsbase是0x7ffff77ff640。

继续运行,看打印:
![]()
可以看到pthread_self的返回值和fsbase是一样的。事实上,pthread_self的实现如下图,即__pthread_self,用的是THREAD_SELF宏来返回

而THREAD_SELF宏的意思就是用就是获取fsbase的地址加一个offsetof(struct pthread, header.self)上的数值

而fsbase的地址在 3.3.1 里也讲到是由TLS_INIT_TP来设下去的,而如下图红框可以得知,设下去的值就是tcbhead_t的首地址,也就是pthread的首地址:

因为pthread的第一个成员就是tcbhead_t:

所以,用THREAD_SELF宏得到的就是在TLS_INIT_TP宏里设置的tcbhead_t的self变量,也就是pthread的首地址,且和fsbase的值一样:

3.4 so库里使用tls变量的汇编实现
这一节展示一下调用so库的函数,so库的函数里使用tls变量的情况,汇编是如何实现的:
程序里调用了一个so库里的函数run,如下图(断点断在调用处):

然后,gdb单步陷入执行,打开so库的run函数实现的源文件,再断点断到对应的引用tls变量的地方(关于图示里用的vs2019的gdb远程ssh调试so库的操作细节见之前的博客 linux上对于so库的调试——包含通过vs2019远程ssh调试so库_clion远程调试so动态库-CSDN博客):

可以从上图中看到,so库访问tls变量,并没有像bin里访问tls变量那么简单明了,而是使用了data16汇编语句,还用到了glibc库里的__tls_get_addr函数。这块涉及到了动态tls的分配,在编译bin时,肯定并不知道真正运行时调用的so库里的函数是否真的用到了tls变量,因为编译用的和运行用的有时候并不一样,所以,在生成bin时,肯定不会包含so库里潜在所可能用到的tls变量,tls变量的引用的逻辑包括动态找tls block等逻辑,都不是bin的职责范围,而so库自己连加载在哪段的地址段都不知道,而so要用到tls变量的话,直接用线程的fsbase像bin使用tls变量一样去加一个固定的偏移肯定不是不行的,因为它会和bin里的内容发生冲突,因为so库自己肯定是不知道bin的内存使用情况的,所以,这就需要glibc的底层接口和底层机制来保障,__tls_get_addr就是做tls的block分配到哪里的动态分配的逻辑。它覆盖了直接链接so的方式和dlopen的方式。
相关文章:

线程局部存储tls的原理和使用
一、背景 tls即Thread Local Storage,也就是线程局部存储,可在进程内,多线程按照各个线程分开进行存储。对于一些与线程上下文相关的变量,可放到tls中,减少多线程之间的数据同步的开销。 有人可能会问,我…...

RK3588平台开发系列讲解(ARM篇)ARM64底层中断处理
文章目录 一、异常级别二、异常分类2.1、同步异常2.2、异步异常三、中断向量表沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!😄 一、异常级别 ARM64处理器确实定义了4个异常级别(Exception Levels, EL),分别是EL0到EL3。这些级别用于管理处理器的特权级别和权限,级别越高…...

CAN总线
1. 数据帧(Data Frame) 数据帧是 CAN 总线中最常用的帧类型,用于传输实际的数据。其结构如下: 起始位(Start of Frame, SOF):标志帧的开始。标识符(Identifier)&#x…...

qwen2.5-vl:阿里开源超强多模态大模型(包含使用方法、微调方法介绍)
1.简介 在 Qwen2-VL 发布后的五个月里,众多开发者基于该视觉语言模型开发了新的模型,并向 Qwen 团队提供了极具价值的反馈。在此期间,Qwen 团队始终致力于打造更具实用性的视觉语言模型。今天,Qwen 家族的最新成员——Qwen2.5-VL…...

python实现dbscan
python实现dbscan 原理 DBSCAN(Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise)是一个比较有代表性的基于密度的聚类算法。它将簇定义为密度相连的点的最大集合,能够把具有足够高密度的区域划分为簇,并可在噪声的空间数据库中发现任意形…...

学习数据结构(3)顺序表
1.动态顺序表的实现 (1)初始化 (2)扩容 (3)头部插入 (4)尾部插入 (5)头部删除 (这里注意要保证有效数据个数不为0) (6&a…...
)
正在更新丨豆瓣电影详细数据的采集与可视化分析(scrapy+mysql+matplotlib+flask)
文章目录 豆瓣电影详细数据的采集与可视化分析(scrapy+mysql+matplotlib+flask)写在前面数据采集0.注意事项1.创建Scrapy项目`douban2025`2.用`PyCharm`打开项目3.创建爬虫脚本`douban.py`4.修改`items.py`的代码5.修改`pipelines.py`代码6.修改`settings.py`代码7.启动`doub…...

wx043基于springboot+vue+uniapp的智慧物流小程序
开发语言:Java框架:springbootuniappJDK版本:JDK1.8服务器:tomcat7数据库:mysql 5.7(一定要5.7版本)数据库工具:Navicat11开发软件:eclipse/myeclipse/ideaMaven包&#…...

每日一题 430. 扁平化多级双向链表
430. 扁平化多级双向链表 简单 /*class Solution { public:Node* flatten(Node* head) {Node* tail nullptr;return dfs(head);}Node* dfs(Node* head){Node* cur head;while(cur ! nullptr){if(cur->child ! nullptr){Node* curChild getTail(cur->child);Node* te…...

UE学习日志#14 GAS--ASC源码简要分析10 GC相关
注:1.这个分类是按照源码里的注释分类的 2.本篇是通读并给出一些注释形式的,并不涉及结构性的分析 3.看之前要对UE的GAS系统的定义有初步了解 4.因为都是接口函数,有些没细看的研究那一部分的时候会细看 1 一些接口函数,但是…...

使用Python和Qt6创建GUI应用程序--关于Qt的一点介绍
关于Qt的一点介绍 Qt是一个免费的开源部件工具包,用于创建跨平台GUI应用程序,允许应用程序从Windows瞄准多个平台,macOS, Linux和Android的单一代码库。但是Qt不仅仅是一个Widget工具箱和功能内置支持多媒体,数据库&am…...

C#@符号在string.Format方法中作用
本文详解@符号在string.Format方法中作用。...

Next.js 14 TS 中使用jwt 和 App Router 进行管理
jwt是一个很基础的工作。但是因为架构不一样,就算是相同的架构,版本不一样,加jwt都会有一定的差别。现在我们的项目是Next.js 14 TS 的 App Router项目(就是没有pages那种),添加jwt的步骤: 1、…...

【贪心算法】洛谷P1090 合并果子 / [USACO06NOV] Fence Repair G
2025 - 01 - 21 - 第 45 篇 【洛谷】贪心算法题单 -【 贪心算法】 - 【学习笔记】 作者(Author): 郑龙浩 / 仟濹(CSND账号名) 洛谷 P1090[NOIP2004 提高组] 合并果子 / [USACO06NOV] Fence Repair G 【贪心算法】 文章目录 洛谷 P1090[NOIP2004 提高组] 合并果子 / [USACO06…...

Windows11无法打开Windows安全中心主界面
# 问题描述 安全中心无法打卡主界面,并弹出“需要使用新应用以打开此windowsdefender连接”. 解决方法 以管理员权限打开PowerShell,推荐使用快捷键win x打开快捷界面,选择Windows终端(管理员),并在终…...

下载arm架构的deb包的方法
在ARM板上操作 如果你是在arm板上使用apt安装和下载包,那么安装过的包会在以下路径里: /var/cache/apt/archives只需要复制出来就可以 如果只下载不安装,可以使用命令 sudo apt-get -d install package_name:arm64 # 如果是32位࿰…...

【Day29 LeetCode】动态规划DP
一、动态规划DP 1、不同路径 62 首先是dp数组,dp[i][j]表示从起点(0, 0)到达当前位置(i, j)的路径数,转移方程从只能向下和向右移动可知,初始化边界可直观推出第一行和第一列上的位置只有一条路径。 class Solution { public:int uniquePa…...

5分钟带你获取deepseek api并搭建简易问答应用
目录 1、获取api 2、获取base_url和chat_model 3、配置模型参数 方法一:终端中临时将加入 方法二:创建.env文件 4、 配置client 5、利用deepseek大模型实现简易问答 deepseek-v3是截止博文撰写之日,无论是国内还是国际上发布的大模型中…...

LeetCode题练习与总结:最短无序连续子数组--581
一、题目描述 给你一个整数数组 nums ,你需要找出一个 连续子数组 ,如果对这个子数组进行升序排序,那么整个数组都会变为升序排序。 请你找出符合题意的 最短 子数组,并输出它的长度。 示例 1: 输入:num…...

探秘 TCP TLP:从背景到实现
回家的路上还讨论了个关于 TCP TLP 的问题,闲着无事缕一缕。本文内容参考自 Tail Loss Probe (TLP): An Algorithm for Fast Recovery of Tail Losses 以及 Linux 内核源码。 TLP,先说缘由。自 TCP 引入 Fast retrans 机制就是为了尽力避免 RTO…...

对WWDC 2025 Keynote 内容的预测
借助我们以往对苹果公司发展路径的深入研究经验,以及大语言模型的分析能力,我们系统梳理了多年来苹果 WWDC 主题演讲的规律。在 WWDC 2025 即将揭幕之际,我们让 ChatGPT 对今年的 Keynote 内容进行了一个初步预测,聊作存档。等到明…...
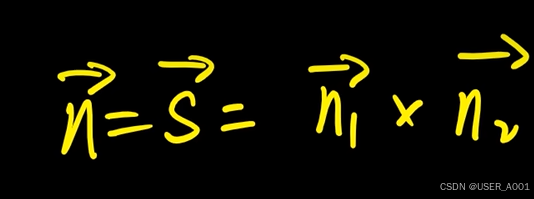
高等数学(下)题型笔记(八)空间解析几何与向量代数
目录 0 前言 1 向量的点乘 1.1 基本公式 1.2 例题 2 向量的叉乘 2.1 基础知识 2.2 例题 3 空间平面方程 3.1 基础知识 3.2 例题 4 空间直线方程 4.1 基础知识 4.2 例题 5 旋转曲面及其方程 5.1 基础知识 5.2 例题 6 空间曲面的法线与切平面 6.1 基础知识 6.2…...

屋顶变身“发电站” ,中天合创屋面分布式光伏发电项目顺利并网!
5月28日,中天合创屋面分布式光伏发电项目顺利并网发电,该项目位于内蒙古自治区鄂尔多斯市乌审旗,项目利用中天合创聚乙烯、聚丙烯仓库屋面作为场地建设光伏电站,总装机容量为9.96MWp。 项目投运后,每年可节约标煤3670…...
SpringBoot+uniapp 的 Champion 俱乐部微信小程序设计与实现,论文初版实现
摘要 本论文旨在设计并实现基于 SpringBoot 和 uniapp 的 Champion 俱乐部微信小程序,以满足俱乐部线上活动推广、会员管理、社交互动等需求。通过 SpringBoot 搭建后端服务,提供稳定高效的数据处理与业务逻辑支持;利用 uniapp 实现跨平台前…...

Neo4j 集群管理:原理、技术与最佳实践深度解析
Neo4j 的集群技术是其企业级高可用性、可扩展性和容错能力的核心。通过深入分析官方文档,本文将系统阐述其集群管理的核心原理、关键技术、实用技巧和行业最佳实践。 Neo4j 的 Causal Clustering 架构提供了一个强大而灵活的基石,用于构建高可用、可扩展且一致的图数据库服务…...

拉力测试cuda pytorch 把 4070显卡拉满
import torch import timedef stress_test_gpu(matrix_size16384, duration300):"""对GPU进行压力测试,通过持续的矩阵乘法来最大化GPU利用率参数:matrix_size: 矩阵维度大小,增大可提高计算复杂度duration: 测试持续时间(秒&…...

【Oracle】分区表
个人主页:Guiat 归属专栏:Oracle 文章目录 1. 分区表基础概述1.1 分区表的概念与优势1.2 分区类型概览1.3 分区表的工作原理 2. 范围分区 (RANGE Partitioning)2.1 基础范围分区2.1.1 按日期范围分区2.1.2 按数值范围分区 2.2 间隔分区 (INTERVAL Partit…...
云原生玩法三问:构建自定义开发环境
云原生玩法三问:构建自定义开发环境 引言 临时运维一个古董项目,无文档,无环境,无交接人,俗称三无。 运行设备的环境老,本地环境版本高,ssh不过去。正好最近对 腾讯出品的云原生 cnb 感兴趣&…...

无人机侦测与反制技术的进展与应用
国家电网无人机侦测与反制技术的进展与应用 引言 随着无人机(无人驾驶飞行器,UAV)技术的快速发展,其在商业、娱乐和军事领域的广泛应用带来了新的安全挑战。特别是对于关键基础设施如电力系统,无人机的“黑飞”&…...
代码规范和架构【立芯理论一】(2025.06.08)
1、代码规范的目标 代码简洁精炼、美观,可持续性好高效率高复用,可移植性好高内聚,低耦合没有冗余规范性,代码有规可循,可以看出自己当时的思考过程特殊排版,特殊语法,特殊指令,必须…...
