14 2D矩形模块( rect.rs)
一、 rect.rs源码
// Copyright 2013 The Servo Project Developers. See the COPYRIGHT
// file at the top-level directory of this distribution.
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 <LICENSE-APACHE or
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0> or the MIT license
// <LICENSE-MIT or http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT>, at your
// option. This file may not be copied, modified, or distributed
// except according to those terms.use super::UnknownUnit;
use crate::box2d::Box2D;
use crate::num::*;
use crate::point::Point2D;
use crate::scale::Scale;
use crate::side_offsets::SideOffsets2D;
use crate::size::Size2D;
use crate::vector::Vector2D;#[cfg(feature = "bytemuck")]
use bytemuck::{Pod, Zeroable};
use num_traits::{Float, NumCast};
#[cfg(feature = "serde")]
use serde::{Deserialize, Serialize};use core::borrow::Borrow;
use core::cmp::PartialOrd;
use core::fmt;
use core::hash::{Hash, Hasher};
use core::ops::{Add, Div, DivAssign, Mul, MulAssign, Range, Sub};/// A 2d Rectangle optionally tagged with a unit.
///
/// # Representation
///
/// `Rect` is represented by an origin point and a size.
///
/// See [`Box2D`] for a rectangle represented by two endpoints.
///
/// # Empty rectangle
///
/// A rectangle is considered empty (see [`is_empty`]) if any of the following is true:
/// - it's area is empty,
/// - it's area is negative (`size.x < 0` or `size.y < 0`),
/// - it contains NaNs.
///
/// [`is_empty`]: Self::is_empty
#[repr(C)]
#[cfg_attr(feature = "serde", derive(Serialize, Deserialize))]
#[cfg_attr(feature = "serde",serde(bound(serialize = "T: Serialize", deserialize = "T: Deserialize<'de>"))
)]
pub struct Rect<T, U> {pub origin: Point2D<T, U>,pub size: Size2D<T, U>,
}#[cfg(feature = "arbitrary")]
impl<'a, T, U> arbitrary::Arbitrary<'a> for Rect<T, U>
whereT: arbitrary::Arbitrary<'a>,
{fn arbitrary(u: &mut arbitrary::Unstructured<'a>) -> arbitrary::Result<Self> {let (origin, size) = arbitrary::Arbitrary::arbitrary(u)?;Ok(Rect { origin, size })}
}#[cfg(feature = "bytemuck")]
unsafe impl<T: Zeroable, U> Zeroable for Rect<T, U> {}#[cfg(feature = "bytemuck")]
unsafe impl<T: Pod, U: 'static> Pod for Rect<T, U> {}impl<T: Hash, U> Hash for Rect<T, U> {fn hash<H: Hasher>(&self, h: &mut H) {self.origin.hash(h);self.size.hash(h);}
}impl<T: Copy, U> Copy for Rect<T, U> {}impl<T: Clone, U> Clone for Rect<T, U> {fn clone(&self) -> Self {Self::new(self.origin.clone(), self.size.clone())}
}impl<T: PartialEq, U> PartialEq for Rect<T, U> {fn eq(&self, other: &Self) -> bool {self.origin.eq(&other.origin) && self.size.eq(&other.size)}
}impl<T: Eq, U> Eq for Rect<T, U> {}impl<T: fmt::Debug, U> fmt::Debug for Rect<T, U> {fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result {write!(f, "Rect(")?;fmt::Debug::fmt(&self.size, f)?;write!(f, " at ")?;fmt::Debug::fmt(&self.origin, f)?;write!(f, ")")}
}impl<T: Default, U> Default for Rect<T, U> {fn default() -> Self {Rect::new(Default::default(), Default::default())}
}impl<T, U> Rect<T, U> {/// Constructor.#[inline]pub const fn new(origin: Point2D<T, U>, size: Size2D<T, U>) -> Self {Rect { origin, size }}
}impl<T, U> Rect<T, U>
whereT: Zero,
{/// Constructor, setting all sides to zero.#[inline]pub fn zero() -> Self {Rect::new(Point2D::origin(), Size2D::zero())}/// Creates a rect of the given size, at offset zero.#[inline]pub fn from_size(size: Size2D<T, U>) -> Self {Rect {origin: Point2D::zero(),size,}}
}impl<T, U> Rect<T, U>
whereT: Copy + Add<T, Output = T>,
{#[inline]pub fn min(&self) -> Point2D<T, U> {self.origin}#[inline]pub fn max(&self) -> Point2D<T, U> {self.origin + self.size}#[inline]pub fn max_x(&self) -> T {self.origin.x + self.size.width}#[inline]pub fn min_x(&self) -> T {self.origin.x}#[inline]pub fn max_y(&self) -> T {self.origin.y + self.size.height}#[inline]pub fn min_y(&self) -> T {self.origin.y}#[inline]pub fn width(&self) -> T {self.size.width}#[inline]pub fn height(&self) -> T {self.size.height}#[inline]pub fn x_range(&self) -> Range<T> {self.min_x()..self.max_x()}#[inline]pub fn y_range(&self) -> Range<T> {self.min_y()..self.max_y()}/// Returns the same rectangle, translated by a vector.#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn translate(&self, by: Vector2D<T, U>) -> Self {Self::new(self.origin + by, self.size)}#[inline]pub fn to_box2d(&self) -> Box2D<T, U> {Box2D {min: self.min(),max: self.max(),}}
}impl<T, U> Rect<T, U>
whereT: Copy + PartialOrd + Add<T, Output = T>,
{/// Returns `true` if this rectangle contains the point. Points are considered/// in the rectangle if they are on the left or top edge, but outside if they/// are on the right or bottom edge.#[inline]pub fn contains(&self, p: Point2D<T, U>) -> bool {self.to_box2d().contains(p)}#[inline]pub fn intersects(&self, other: &Self) -> bool {self.to_box2d().intersects(&other.to_box2d())}
}impl<T, U> Rect<T, U>
whereT: Copy + PartialOrd + Add<T, Output = T> + Sub<T, Output = T>,
{#[inline]pub fn intersection(&self, other: &Self) -> Option<Self> {let box2d = self.to_box2d().intersection_unchecked(&other.to_box2d());if box2d.is_empty() {return None;}Some(box2d.to_rect())}
}impl<T, U> Rect<T, U>
whereT: Copy + Add<T, Output = T> + Sub<T, Output = T>,
{#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn inflate(&self, width: T, height: T) -> Self {Rect::new(Point2D::new(self.origin.x - width, self.origin.y - height),Size2D::new(self.size.width + width + width,self.size.height + height + height,),)}
}impl<T, U> Rect<T, U>
whereT: Copy + Zero + PartialOrd + Add<T, Output = T>,
{/// Returns `true` if this rectangle contains the interior of `rect`. Always/// returns `true` if `rect` is empty, and always returns `false` if `rect` is/// nonempty but this rectangle is empty.#[inline]pub fn contains_rect(&self, rect: &Self) -> bool {rect.is_empty()|| (self.min_x() <= rect.min_x()&& rect.max_x() <= self.max_x()&& self.min_y() <= rect.min_y()&& rect.max_y() <= self.max_y())}
}impl<T, U> Rect<T, U>
whereT: Copy + Zero + PartialOrd + Add<T, Output = T> + Sub<T, Output = T>,
{/// Calculate the size and position of an inner rectangle.////// Subtracts the side offsets from all sides. The horizontal and vertical/// offsets must not be larger than the original side length./// This method assumes y oriented downward.pub fn inner_rect(&self, offsets: SideOffsets2D<T, U>) -> Self {let rect = Rect::new(Point2D::new(self.origin.x + offsets.left, self.origin.y + offsets.top),Size2D::new(self.size.width - offsets.horizontal(),self.size.height - offsets.vertical(),),);debug_assert!(rect.size.width >= Zero::zero());debug_assert!(rect.size.height >= Zero::zero());rect}
}impl<T, U> Rect<T, U>
whereT: Copy + Add<T, Output = T> + Sub<T, Output = T>,
{/// Calculate the size and position of an outer rectangle.////// Add the offsets to all sides. The expanded rectangle is returned./// This method assumes y oriented downward.pub fn outer_rect(&self, offsets: SideOffsets2D<T, U>) -> Self {Rect::new(Point2D::new(self.origin.x - offsets.left, self.origin.y - offsets.top),Size2D::new(self.size.width + offsets.horizontal(),self.size.height + offsets.vertical(),),)}
}impl<T, U> Rect<T, U>
whereT: Copy + Zero + PartialOrd + Sub<T, Output = T>,
{/// Returns the smallest rectangle defined by the top/bottom/left/right-most/// points provided as parameter.////// Note: This function has a behavior that can be surprising because/// the right-most and bottom-most points are exactly on the edge/// of the rectangle while the [`Rect::contains`] function is has exclusive/// semantic on these edges. This means that the right-most and bottom-most/// points provided to [`Rect::from_points`] will count as not contained by the rect./// This behavior may change in the future.////// See [`Box2D::from_points`] for more details.pub fn from_points<I>(points: I) -> SelfwhereI: IntoIterator,I::Item: Borrow<Point2D<T, U>>,{Box2D::from_points(points).to_rect()}
}impl<T, U> Rect<T, U>
whereT: Copy + One + Add<Output = T> + Sub<Output = T> + Mul<Output = T>,
{/// Linearly interpolate between this rectangle and another rectangle.#[inline]pub fn lerp(&self, other: Self, t: T) -> Self {Self::new(self.origin.lerp(other.origin, t),self.size.lerp(other.size, t),)}
}impl<T, U> Rect<T, U>
whereT: Copy + One + Add<Output = T> + Div<Output = T>,
{pub fn center(&self) -> Point2D<T, U> {let two = T::one() + T::one();self.origin + self.size.to_vector() / two}
}impl<T, U> Rect<T, U>
whereT: Copy + PartialOrd + Add<T, Output = T> + Sub<T, Output = T> + Zero,
{#[inline]pub fn union(&self, other: &Self) -> Self {self.to_box2d().union(&other.to_box2d()).to_rect()}
}impl<T, U> Rect<T, U> {#[inline]pub fn scale<S: Copy>(&self, x: S, y: S) -> SelfwhereT: Copy + Mul<S, Output = T>,{Rect::new(Point2D::new(self.origin.x * x, self.origin.y * y),Size2D::new(self.size.width * x, self.size.height * y),)}
}impl<T: Copy + Mul<T, Output = T>, U> Rect<T, U> {#[inline]pub fn area(&self) -> T {self.size.area()}
}impl<T: Copy + Zero + PartialOrd, U> Rect<T, U> {#[inline]pub fn is_empty(&self) -> bool {self.size.is_empty()}
}impl<T: Copy + Zero + PartialOrd, U> Rect<T, U> {#[inline]pub fn to_non_empty(&self) -> Option<Self> {if self.is_empty() {return None;}Some(*self)}
}impl<T: Copy + Mul, U> Mul<T> for Rect<T, U> {type Output = Rect<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn mul(self, scale: T) -> Self::Output {Rect::new(self.origin * scale, self.size * scale)}
}impl<T: Copy + MulAssign, U> MulAssign<T> for Rect<T, U> {#[inline]fn mul_assign(&mut self, scale: T) {*self *= Scale::new(scale);}
}impl<T: Copy + Div, U> Div<T> for Rect<T, U> {type Output = Rect<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn div(self, scale: T) -> Self::Output {Rect::new(self.origin / scale.clone(), self.size / scale)}
}impl<T: Copy + DivAssign, U> DivAssign<T> for Rect<T, U> {#[inline]fn div_assign(&mut self, scale: T) {*self /= Scale::new(scale);}
}impl<T: Copy + Mul, U1, U2> Mul<Scale<T, U1, U2>> for Rect<T, U1> {type Output = Rect<T::Output, U2>;#[inline]fn mul(self, scale: Scale<T, U1, U2>) -> Self::Output {Rect::new(self.origin * scale.clone(), self.size * scale)}
}impl<T: Copy + MulAssign, U> MulAssign<Scale<T, U, U>> for Rect<T, U> {#[inline]fn mul_assign(&mut self, scale: Scale<T, U, U>) {self.origin *= scale.clone();self.size *= scale;}
}impl<T: Copy + Div, U1, U2> Div<Scale<T, U1, U2>> for Rect<T, U2> {type Output = Rect<T::Output, U1>;#[inline]fn div(self, scale: Scale<T, U1, U2>) -> Self::Output {Rect::new(self.origin / scale.clone(), self.size / scale)}
}impl<T: Copy + DivAssign, U> DivAssign<Scale<T, U, U>> for Rect<T, U> {#[inline]fn div_assign(&mut self, scale: Scale<T, U, U>) {self.origin /= scale.clone();self.size /= scale;}
}impl<T: Copy, U> Rect<T, U> {/// Drop the units, preserving only the numeric value.#[inline]pub fn to_untyped(&self) -> Rect<T, UnknownUnit> {Rect::new(self.origin.to_untyped(), self.size.to_untyped())}/// Tag a unitless value with units.#[inline]pub fn from_untyped(r: &Rect<T, UnknownUnit>) -> Rect<T, U> {Rect::new(Point2D::from_untyped(r.origin),Size2D::from_untyped(r.size),)}/// Cast the unit#[inline]pub fn cast_unit<V>(&self) -> Rect<T, V> {Rect::new(self.origin.cast_unit(), self.size.cast_unit())}
}impl<T: NumCast + Copy, U> Rect<T, U> {/// Cast from one numeric representation to another, preserving the units.////// When casting from floating point to integer coordinates, the decimals are truncated/// as one would expect from a simple cast, but this behavior does not always make sense/// geometrically. Consider using [`round`], [`round_in`] or [`round_out`] before casting.////// [`round`]: Self::round/// [`round_in`]: Self::round_in/// [`round_out`]: Self::round_out#[inline]pub fn cast<NewT: NumCast>(&self) -> Rect<NewT, U> {Rect::new(self.origin.cast(), self.size.cast())}/// Fallible cast from one numeric representation to another, preserving the units.////// When casting from floating point to integer coordinates, the decimals are truncated/// as one would expect from a simple cast, but this behavior does not always make sense/// geometrically. Consider using [`round`], [`round_in`] or [`round_out` before casting.////// [`round`]: Self::round/// [`round_in`]: Self::round_in/// [`round_out`]: Self::round_outpub fn try_cast<NewT: NumCast>(&self) -> Option<Rect<NewT, U>> {match (self.origin.try_cast(), self.size.try_cast()) {(Some(origin), Some(size)) => Some(Rect::new(origin, size)),_ => None,}}// Convenience functions for common casts/// Cast into an `f32` rectangle.#[inline]pub fn to_f32(&self) -> Rect<f32, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `f64` rectangle.#[inline]pub fn to_f64(&self) -> Rect<f64, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `usize` rectangle, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating point rectangles, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `round_in()` or `round_out()` before the cast in order to/// obtain the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_usize(&self) -> Rect<usize, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `u32` rectangle, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating point rectangles, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `round_in()` or `round_out()` before the cast in order to/// obtain the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_u32(&self) -> Rect<u32, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `u64` rectangle, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating point rectangles, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `round_in()` or `round_out()` before the cast in order to/// obtain the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_u64(&self) -> Rect<u64, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `i32` rectangle, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating point rectangles, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `round_in()` or `round_out()` before the cast in order to/// obtain the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_i32(&self) -> Rect<i32, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `i64` rectangle, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating point rectangles, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `round_in()` or `round_out()` before the cast in order to/// obtain the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_i64(&self) -> Rect<i64, U> {self.cast()}
}impl<T: Float, U> Rect<T, U> {/// Returns `true` if all members are finite.#[inline]pub fn is_finite(self) -> bool {self.origin.is_finite() && self.size.is_finite()}
}impl<T: Floor + Ceil + Round + Add<T, Output = T> + Sub<T, Output = T>, U> Rect<T, U> {/// Return a rectangle with edges rounded to integer coordinates, such that/// the returned rectangle has the same set of pixel centers as the original/// one./// Edges at offset 0.5 round up./// Suitable for most places where integral device coordinates/// are needed, but note that any translation should be applied first to/// avoid pixel rounding errors./// Note that this is *not* rounding to nearest integer if the values are negative./// They are always rounding as floor(n + 0.5).////// # Usage notes/// Note, that when using with floating-point `T` types that method can significantly/// lose precision for large values, so if you need to call this method very often it/// is better to use [`Box2D`].#[must_use]pub fn round(&self) -> Self {self.to_box2d().round().to_rect()}/// Return a rectangle with edges rounded to integer coordinates, such that/// the original rectangle contains the resulting rectangle.////// # Usage notes/// Note, that when using with floating-point `T` types that method can significantly/// lose precision for large values, so if you need to call this method very often it/// is better to use [`Box2D`].#[must_use]pub fn round_in(&self) -> Self {self.to_box2d().round_in().to_rect()}/// Return a rectangle with edges rounded to integer coordinates, such that/// the original rectangle is contained in the resulting rectangle.////// # Usage notes/// Note, that when using with floating-point `T` types that method can significantly/// lose precision for large values, so if you need to call this method very often it/// is better to use [`Box2D`].#[must_use]pub fn round_out(&self) -> Self {self.to_box2d().round_out().to_rect()}
}impl<T, U> From<Size2D<T, U>> for Rect<T, U>
whereT: Zero,
{fn from(size: Size2D<T, U>) -> Self {Self::from_size(size)}
}/// Shorthand for `Rect::new(Point2D::new(x, y), Size2D::new(w, h))`.
pub const fn rect<T, U>(x: T, y: T, w: T, h: T) -> Rect<T, U> {Rect::new(Point2D::new(x, y), Size2D::new(w, h))
}#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {use crate::default::{Point2D, Rect, Size2D};use crate::side_offsets::SideOffsets2D;use crate::{point2, rect, size2, vec2};#[test]fn test_translate() {let p = Rect::new(Point2D::new(0u32, 0u32), Size2D::new(50u32, 40u32));let pp = p.translate(vec2(10, 15));assert!(pp.size.width == 50);assert!(pp.size.height == 40);assert!(pp.origin.x == 10);assert!(pp.origin.y == 15);let r = Rect::new(Point2D::new(-10, -5), Size2D::new(50, 40));let rr = r.translate(vec2(0, -10));assert!(rr.size.width == 50);assert!(rr.size.height == 40);assert!(rr.origin.x == -10);assert!(rr.origin.y == -15);}#[test]fn test_union() {let p = Rect::new(Point2D::new(0, 0), Size2D::new(50, 40));let q = Rect::new(Point2D::new(20, 20), Size2D::new(5, 5));let r = Rect::new(Point2D::new(-15, -30), Size2D::new(200, 15));let s = Rect::new(Point2D::new(20, -15), Size2D::new(250, 200));let pq = p.union(&q);assert!(pq.origin == Point2D::new(0, 0));assert!(pq.size == Size2D::new(50, 40));let pr = p.union(&r);assert!(pr.origin == Point2D::new(-15, -30));assert!(pr.size == Size2D::new(200, 70));let ps = p.union(&s);assert!(ps.origin == Point2D::new(0, -15));assert!(ps.size == Size2D::new(270, 200));}#[test]fn test_intersection() {let p = Rect::new(Point2D::new(0, 0), Size2D::new(10, 20));let q = Rect::new(Point2D::new(5, 15), Size2D::new(10, 10));let r = Rect::new(Point2D::new(-5, -5), Size2D::new(8, 8));let pq = p.intersection(&q);assert!(pq.is_some());let pq = pq.unwrap();assert!(pq.origin == Point2D::new(5, 15));assert!(pq.size == Size2D::new(5, 5));let pr = p.intersection(&r);assert!(pr.is_some());let pr = pr.unwrap();assert!(pr.origin == Point2D::new(0, 0));assert!(pr.size == Size2D::new(3, 3));let qr = q.intersection(&r);assert!(qr.is_none());}#[test]fn test_intersection_overflow() {// test some scenarios where the intersection can overflow but// the min_x() and max_x() don't. Gecko currently fails these caseslet p = Rect::new(Point2D::new(-2147483648, -2147483648), Size2D::new(0, 0));let q = Rect::new(Point2D::new(2136893440, 2136893440),Size2D::new(279552, 279552),);let r = Rect::new(Point2D::new(-2147483648, -2147483648), Size2D::new(1, 1));assert!(p.is_empty());let pq = p.intersection(&q);assert!(pq.is_none());let qr = q.intersection(&r);assert!(qr.is_none());}#[test]fn test_contains() {let r = Rect::new(Point2D::new(-20, 15), Size2D::new(100, 200));assert!(r.contains(Point2D::new(0, 50)));assert!(r.contains(Point2D::new(-10, 200)));// The `contains` method is inclusive of the top/left edges, but not the// bottom/right edges.assert!(r.contains(Point2D::new(-20, 15)));assert!(!r.contains(Point2D::new(80, 15)));assert!(!r.contains(Point2D::new(80, 215)));assert!(!r.contains(Point2D::new(-20, 215)));// Points beyond the top-left corner.assert!(!r.contains(Point2D::new(-25, 15)));assert!(!r.contains(Point2D::new(-15, 10)));// Points beyond the top-right corner.assert!(!r.contains(Point2D::new(85, 20)));assert!(!r.contains(Point2D::new(75, 10)));// Points beyond the bottom-right corner.assert!(!r.contains(Point2D::new(85, 210)));assert!(!r.contains(Point2D::new(75, 220)));// Points beyond the bottom-left corner.assert!(!r.contains(Point2D::new(-25, 210)));assert!(!r.contains(Point2D::new(-15, 220)));let r = Rect::new(Point2D::new(-20.0, 15.0), Size2D::new(100.0, 200.0));assert!(r.contains_rect(&r));assert!(!r.contains_rect(&r.translate(vec2(0.1, 0.0))));assert!(!r.contains_rect(&r.translate(vec2(-0.1, 0.0))));assert!(!r.contains_rect(&r.translate(vec2(0.0, 0.1))));assert!(!r.contains_rect(&r.translate(vec2(0.0, -0.1))));// Empty rectangles are always considered as contained in other rectangles,// even if their origin is not.let p = Point2D::new(1.0, 1.0);assert!(!r.contains(p));assert!(r.contains_rect(&Rect::new(p, Size2D::zero())));}#[test]fn test_scale() {let p = Rect::new(Point2D::new(0u32, 0u32), Size2D::new(50u32, 40u32));let pp = p.scale(10, 15);assert!(pp.size.width == 500);assert!(pp.size.height == 600);assert!(pp.origin.x == 0);assert!(pp.origin.y == 0);let r = Rect::new(Point2D::new(-10, -5), Size2D::new(50, 40));let rr = r.scale(1, 20);assert!(rr.size.width == 50);assert!(rr.size.height == 800);assert!(rr.origin.x == -10);assert!(rr.origin.y == -100);}#[test]fn test_inflate() {let p = Rect::new(Point2D::new(0, 0), Size2D::new(10, 10));let pp = p.inflate(10, 20);assert!(pp.size.width == 30);assert!(pp.size.height == 50);assert!(pp.origin.x == -10);assert!(pp.origin.y == -20);let r = Rect::new(Point2D::new(0, 0), Size2D::new(10, 20));let rr = r.inflate(-2, -5);assert!(rr.size.width == 6);assert!(rr.size.height == 10);assert!(rr.origin.x == 2);assert!(rr.origin.y == 5);}#[test]fn test_inner_outer_rect() {let inner_rect = Rect::new(point2(20, 40), size2(80, 100));let offsets = SideOffsets2D::new(20, 10, 10, 10);let outer_rect = inner_rect.outer_rect(offsets);assert_eq!(outer_rect.origin.x, 10);assert_eq!(outer_rect.origin.y, 20);assert_eq!(outer_rect.size.width, 100);assert_eq!(outer_rect.size.height, 130);assert_eq!(outer_rect.inner_rect(offsets), inner_rect);}#[test]fn test_min_max_x_y() {let p = Rect::new(Point2D::new(0u32, 0u32), Size2D::new(50u32, 40u32));assert!(p.max_y() == 40);assert!(p.min_y() == 0);assert!(p.max_x() == 50);assert!(p.min_x() == 0);let r = Rect::new(Point2D::new(-10, -5), Size2D::new(50, 40));assert!(r.max_y() == 35);assert!(r.min_y() == -5);assert!(r.max_x() == 40);assert!(r.min_x() == -10);}#[test]fn test_width_height() {let r = Rect::new(Point2D::new(-10, -5), Size2D::new(50, 40));assert!(r.width() == 50);assert!(r.height() == 40);}#[test]fn test_is_empty() {assert!(Rect::new(Point2D::new(0u32, 0u32), Size2D::new(0u32, 0u32)).is_empty());assert!(Rect::new(Point2D::new(0u32, 0u32), Size2D::new(10u32, 0u32)).is_empty());assert!(Rect::new(Point2D::new(0u32, 0u32), Size2D::new(0u32, 10u32)).is_empty());assert!(!Rect::new(Point2D::new(0u32, 0u32), Size2D::new(1u32, 1u32)).is_empty());assert!(Rect::new(Point2D::new(10u32, 10u32), Size2D::new(0u32, 0u32)).is_empty());assert!(Rect::new(Point2D::new(10u32, 10u32), Size2D::new(10u32, 0u32)).is_empty());assert!(Rect::new(Point2D::new(10u32, 10u32), Size2D::new(0u32, 10u32)).is_empty());assert!(!Rect::new(Point2D::new(10u32, 10u32), Size2D::new(1u32, 1u32)).is_empty());}#[test]fn test_round() {let mut x = -2.0;let mut y = -2.0;let mut w = -2.0;let mut h = -2.0;while x < 2.0 {while y < 2.0 {while w < 2.0 {while h < 2.0 {let rect = Rect::new(Point2D::new(x, y), Size2D::new(w, h));assert!(rect.contains_rect(&rect.round_in()));assert!(rect.round_in().inflate(1.0, 1.0).contains_rect(&rect));assert!(rect.round_out().contains_rect(&rect));assert!(rect.inflate(1.0, 1.0).contains_rect(&rect.round_out()));assert!(rect.inflate(1.0, 1.0).contains_rect(&rect.round()));assert!(rect.round().inflate(1.0, 1.0).contains_rect(&rect));h += 0.1;}w += 0.1;}y += 0.1;}x += 0.1;}}#[test]fn test_center() {let r: Rect<i32> = rect(-2, 5, 4, 10);assert_eq!(r.center(), point2(0, 10));let r: Rect<f32> = rect(1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0);assert_eq!(r.center(), point2(2.5, 4.0));}#[test]fn test_nan() {let r1: Rect<f32> = rect(-2.0, 5.0, 4.0, std::f32::NAN);let r2: Rect<f32> = rect(std::f32::NAN, -1.0, 3.0, 10.0);assert_eq!(r1.intersection(&r2), None);}
}相关文章:
)
14 2D矩形模块( rect.rs)
一、 rect.rs源码 // Copyright 2013 The Servo Project Developers. See the COPYRIGHT // file at the top-level directory of this distribution. // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 <LICENSE-APACHE or // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENS…...
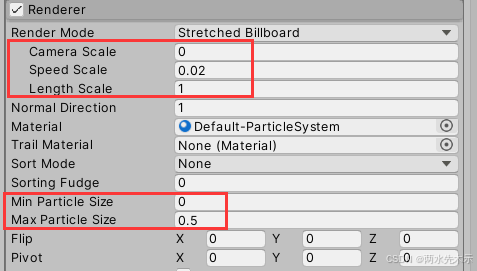
【Unity3D】实现2D角色/怪物死亡消散粒子效果
核心:这是一个Unity粒子系统自带的一种功能,可将粒子生成控制在一个Texture图片网格范围内,并且粒子颜色会自动采样图片的像素点颜色,之后则是粒子编辑出消散效果。 Particle System1物体(爆发式随机速度扩散10000个粒…...
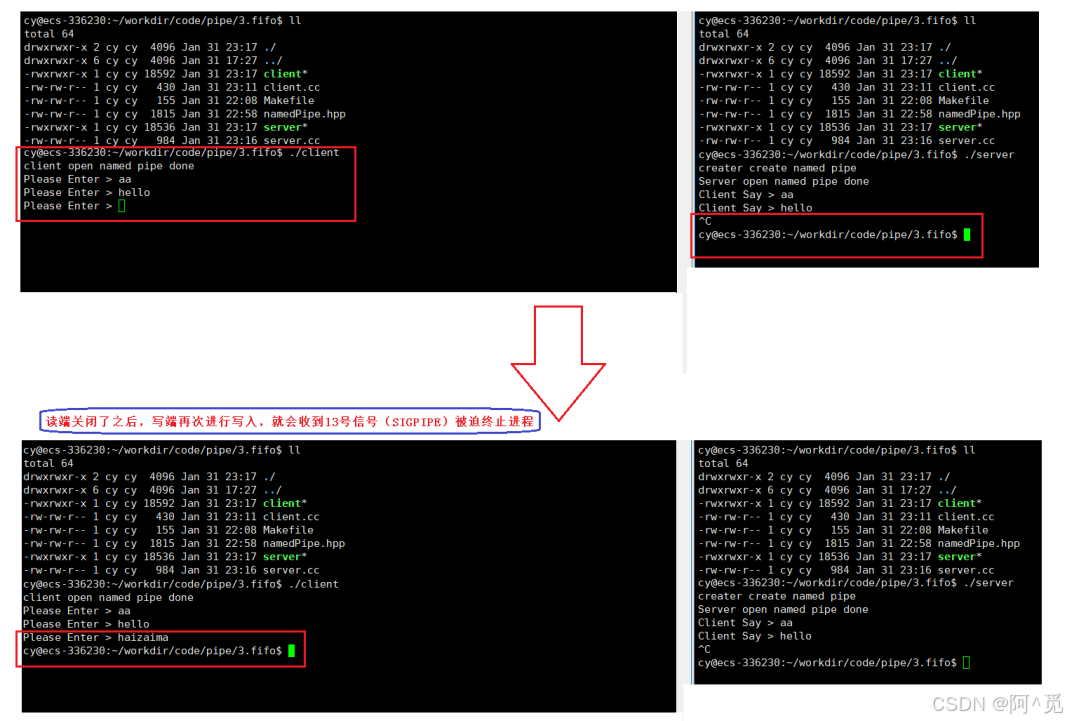
Linux - 进程间通信(3)
目录 3、解决遗留BUG -- 边关闭信道边回收进程 1)解决方案 2)两种方法相比较 4、命名管道 1)理解命名管道 2)创建命名管道 a. 命令行指令 b. 系统调用方法 3)代码实现命名管道 构建类进行封装命名管道&#…...
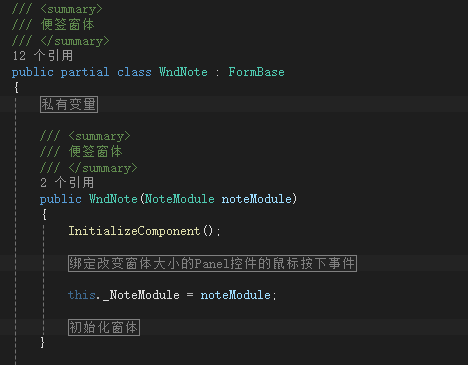
3、C#基于.net framework的应用开发实战编程 - 实现(三、三) - 编程手把手系列文章...
三、 实现; 三.三、编写应用程序; 此文主要是实现应用的主要编码工作。 1、 分层; 此例子主要分为UI、Helper、DAL等层。UI负责便签的界面显示;Helper主要是链接UI和数据库操作的中间层;DAL为对数据库的操…...
)
C++编程语言:抽象机制:泛型编程(Bjarne Stroustrup)
泛型编程(Generic Programming) 目录 24.1 引言(Introduction) 24.2 算法和(通用性的)提升(Algorithms and Lifting) 24.3 概念(此指模板参数的插件)(Concepts) 24.3.1 发现插件集(Discovering a Concept) 24.3.2 概念与约束(Concepts and Constraints) 24.4 具体化…...

Python面试宝典13 | Python 变量作用域,从入门到精通
今天,我们来深入探讨一下 Python 中一个非常重要的概念——变量作用域。理解变量作用域对于编写清晰、可维护、无 bug 的代码至关重要。 什么是变量作用域? 简单来说,变量作用域就是指一个变量在程序中可以被访问的范围。Python 中有四种作…...

基于最近邻数据进行分类
人工智能例子汇总:AI常见的算法和例子-CSDN博客 完整代码: import torch import numpy as np from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 生成一个简单的数据…...

DeepSeek V3 vs R1:大模型技术路径的“瑞士军刀“与“手术刀“进化
DeepSeek V3 vs R1:——大模型技术路径的"瑞士军刀"与"手术刀"进化 大模型分水岭:从通用智能到垂直突破 2023年,GPT-4 Turbo的发布标志着通用大模型进入性能瓶颈期。当模型参数量突破万亿级门槛后,研究者们开…...
一、TensorFlow的建模流程
1. 数据准备与预处理: 加载数据:使用内置数据集或自定义数据。 预处理:归一化、调整维度、数据增强。 划分数据集:训练集、验证集、测试集。 转换为Dataset对象:利用tf.data优化数据流水线。 import tensorflow a…...

指导初学者使用Anaconda运行GitHub上One - DM项目的步骤
以下是指导初学者使用Anaconda运行GitHub上One - DM项目的步骤: 1. 安装Anaconda 下载Anaconda: 让初学者访问Anaconda官网(https://www.anaconda.com/products/distribution),根据其操作系统(Windows、M…...

7层还是4层?网络模型又为什么要分层?
~犬📰余~ “我欲贱而贵,愚而智,贫而富,可乎? 曰:其唯学乎” 一、为什么要分层 \quad 网络通信的复杂性促使我们需要一种分层的方法来理解和管理网络。就像建筑一样,我们不会把所有功能都混在一起…...

C++:抽象类习题
题目内容: 求正方体、球、圆柱的表面积,抽象出一个公共的基类Container为抽象类,在其中定义一个公共的数据成员radius(此数据可以作为正方形的边长、球的半径、圆柱体底面圆半径),以及求表面积的纯虚函数area()。由此抽象类派生出…...
)
C++ 泛型编程指南02 (模板参数的类型推导)
文章目录 一 深入了解C中的函数模板类型推断什么是类型推断?使用Boost TypeIndex库进行类型推断分析示例代码关键点解析 2. 理解函数模板类型推断2.1 指针或引用类型2.1.1 忽略引用2.1.2 保持const属性2.1.3 处理指针类型 2.2 万能引用类型2.3 传值方式2.4 传值方式…...
——FFmpeg源码中,解析SDP的实现)
音视频入门基础:RTP专题(5)——FFmpeg源码中,解析SDP的实现
一、引言 FFmpeg源码中通过ff_sdp_parse函数解析SDP。该函数定义在libavformat/rtsp.c中: int ff_sdp_parse(AVFormatContext *s, const char *content) {const char *p;int letter, i;char buf[SDP_MAX_SIZE], *q;SDPParseState sdp_parse_state { { 0 } }, *s1…...

计算机网络 应用层 笔记 (电子邮件系统,SMTP,POP3,MIME,IMAP,万维网,HTTP,html)
电子邮件系统: SMTP协议 基本概念 工作原理 连接建立: 命令交互 客户端发送命令: 服务器响应: 邮件传输: 连接关闭: 主要命令 邮件发送流程 SMTP的缺点: MIME: POP3协议 基本概念…...

【视频+图文详解】HTML基础3-html常用标签
图文教程 html常用标签 常用标签 1. 文档结构 <!DOCTYPE html>:声明HTML文档类型。<html>:定义HTML文档的根元素。<head>:定义文档头部,包含元数据。<title>:设置网页标题,浏览…...
FreeRTOS学习 --- 消息队列
队列简介 队列是任务到任务、任务到中断、中断到任务数据交流的一种机制(消息传递) 全局变量的弊端:数据无保护,导致数据不安全,当多个任务同时对该变量操作时,数据易受损 使用队列的情况如下:…...

PHP If...Else 语句详解
PHP If...Else 语句详解 引言 在PHP编程中,if...else语句是流程控制的重要组成部分,它允许程序根据条件判断执行不同的代码块。本文将详细解析PHP中的if...else语句,包括其基本用法、高级技巧以及注意事项。 一、基本用法 if...else语句的…...

pytorch使用SVM实现文本分类
人工智能例子汇总:AI常见的算法和例子-CSDN博客 完整代码: import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim import jieba import numpy as np from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.feature_extract…...
读取手机通讯录【Android移动开发基础案例教程(第2版)黑马程序员】)
安卓(android)读取手机通讯录【Android移动开发基础案例教程(第2版)黑马程序员】
一、实验目的(如果代码有错漏,可在代码地址查看) 1.熟悉内容提供者(Content Provider)的概念和作用。 2.掌握内容提供者的创建和使用方法。 4.掌握内容URI的结构和用途。 二、实验条件 1.熟悉内容提供者的工作原理。 2.掌握内容提供者访问其…...
深入浅出Asp.Net Core MVC应用开发系列-AspNetCore中的日志记录
ASP.NET Core 是一个跨平台的开源框架,用于在 Windows、macOS 或 Linux 上生成基于云的新式 Web 应用。 ASP.NET Core 中的日志记录 .NET 通过 ILogger API 支持高性能结构化日志记录,以帮助监视应用程序行为和诊断问题。 可以通过配置不同的记录提供程…...

智慧医疗能源事业线深度画像分析(上)
引言 医疗行业作为现代社会的关键基础设施,其能源消耗与环境影响正日益受到关注。随着全球"双碳"目标的推进和可持续发展理念的深入,智慧医疗能源事业线应运而生,致力于通过创新技术与管理方案,重构医疗领域的能源使用模式。这一事业线融合了能源管理、可持续发…...
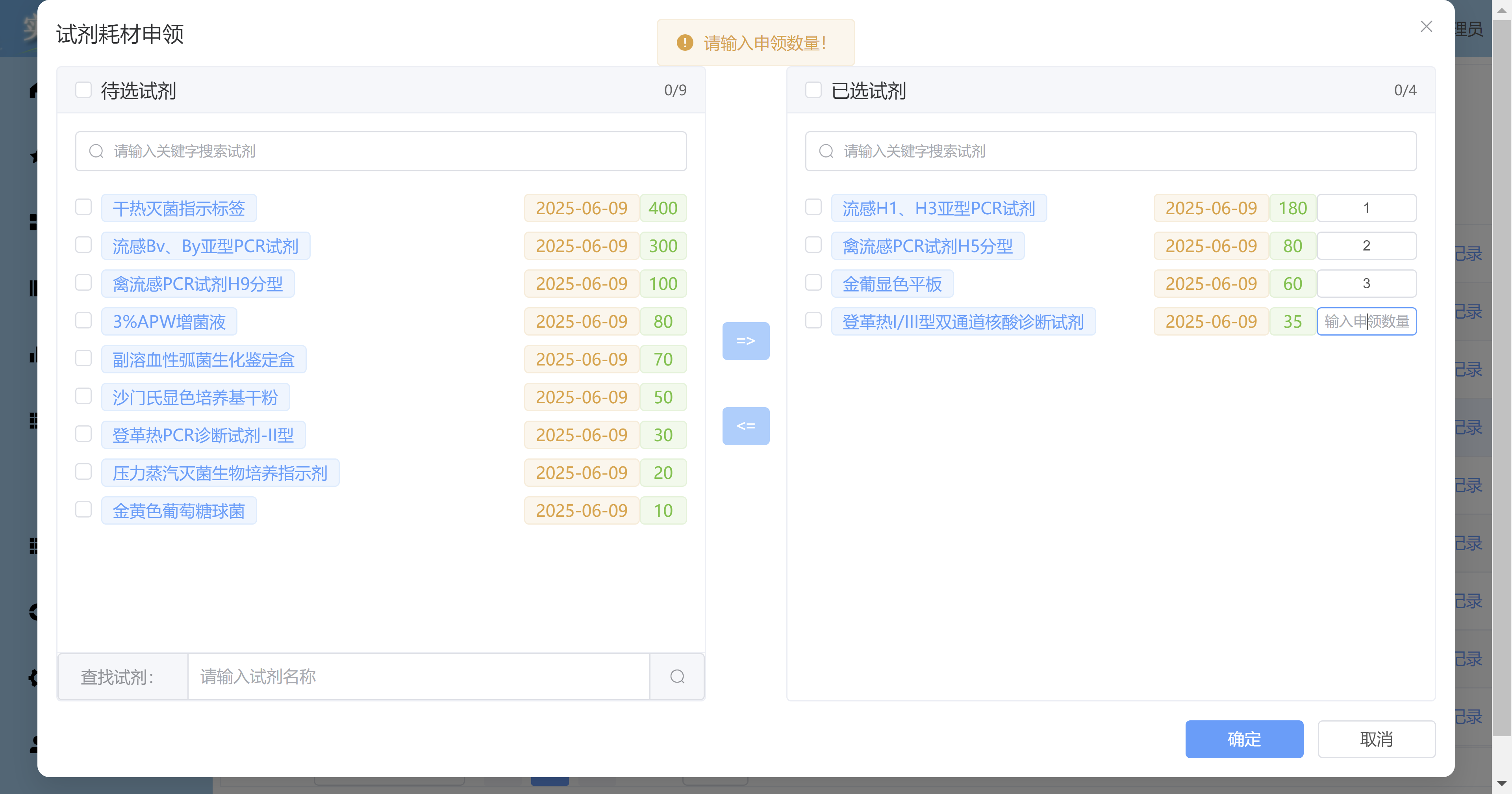
Vue3 + Element Plus + TypeScript中el-transfer穿梭框组件使用详解及示例
使用详解 Element Plus 的 el-transfer 组件是一个强大的穿梭框组件,常用于在两个集合之间进行数据转移,如权限分配、数据选择等场景。下面我将详细介绍其用法并提供一个完整示例。 核心特性与用法 基本属性 v-model:绑定右侧列表的值&…...
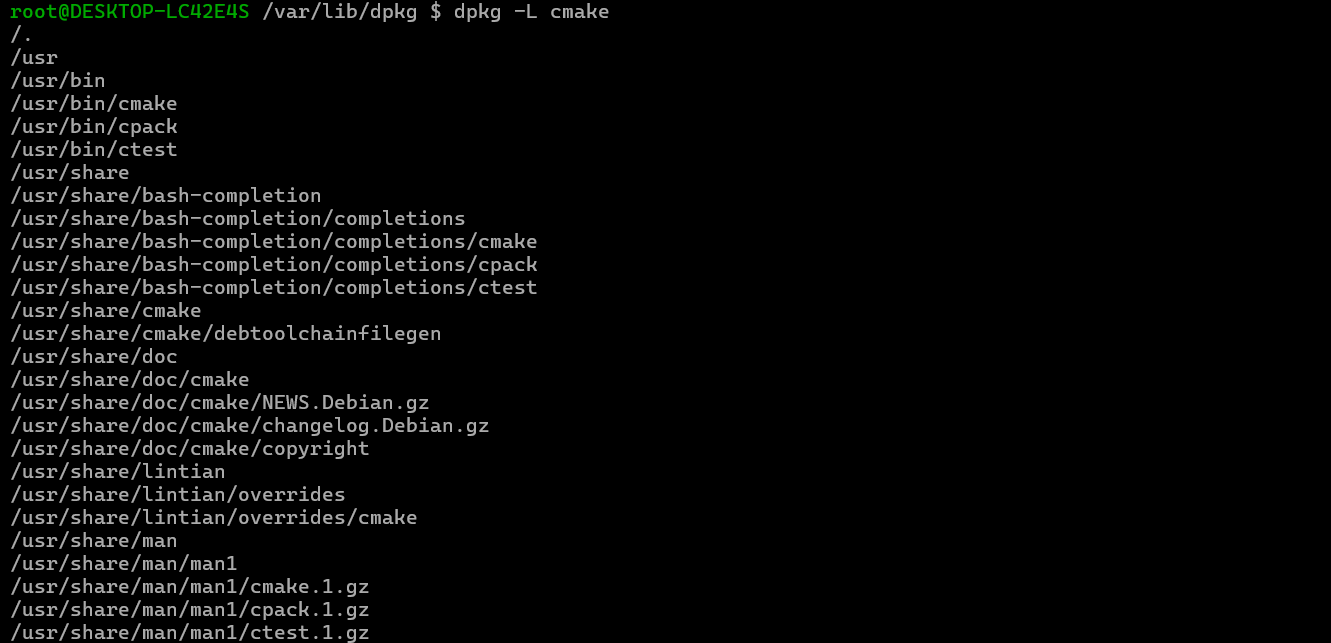
Debian系统简介
目录 Debian系统介绍 Debian版本介绍 Debian软件源介绍 软件包管理工具dpkg dpkg核心指令详解 安装软件包 卸载软件包 查询软件包状态 验证软件包完整性 手动处理依赖关系 dpkg vs apt Debian系统介绍 Debian 和 Ubuntu 都是基于 Debian内核 的 Linux 发行版ÿ…...
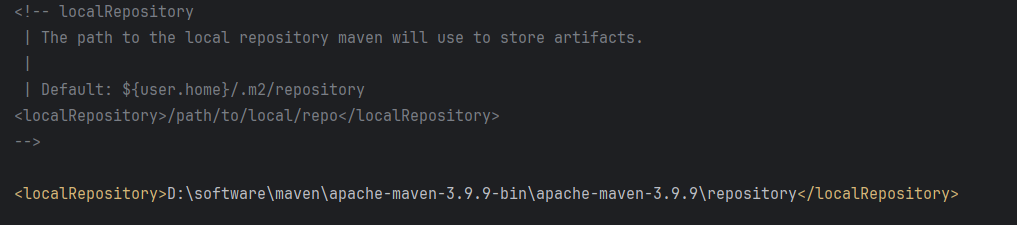
Maven 概述、安装、配置、仓库、私服详解
目录 1、Maven 概述 1.1 Maven 的定义 1.2 Maven 解决的问题 1.3 Maven 的核心特性与优势 2、Maven 安装 2.1 下载 Maven 2.2 安装配置 Maven 2.3 测试安装 2.4 修改 Maven 本地仓库的默认路径 3、Maven 配置 3.1 配置本地仓库 3.2 配置 JDK 3.3 IDEA 配置本地 Ma…...
基于 TAPD 进行项目管理
起因 自己写了个小工具,仓库用的Github。之前在用markdown进行需求管理,现在随着功能的增加,感觉有点难以管理了,所以用TAPD这个工具进行需求、Bug管理。 操作流程 注册 TAPD,需要提供一个企业名新建一个项目&#…...

招商蛇口 | 执笔CID,启幕低密生活新境
作为中国城市生长的力量,招商蛇口以“美好生活承载者”为使命,深耕全球111座城市,以央企担当匠造时代理想人居。从深圳湾的开拓基因到西安高新CID的战略落子,招商蛇口始终与城市发展同频共振,以建筑诠释对土地与生活的…...
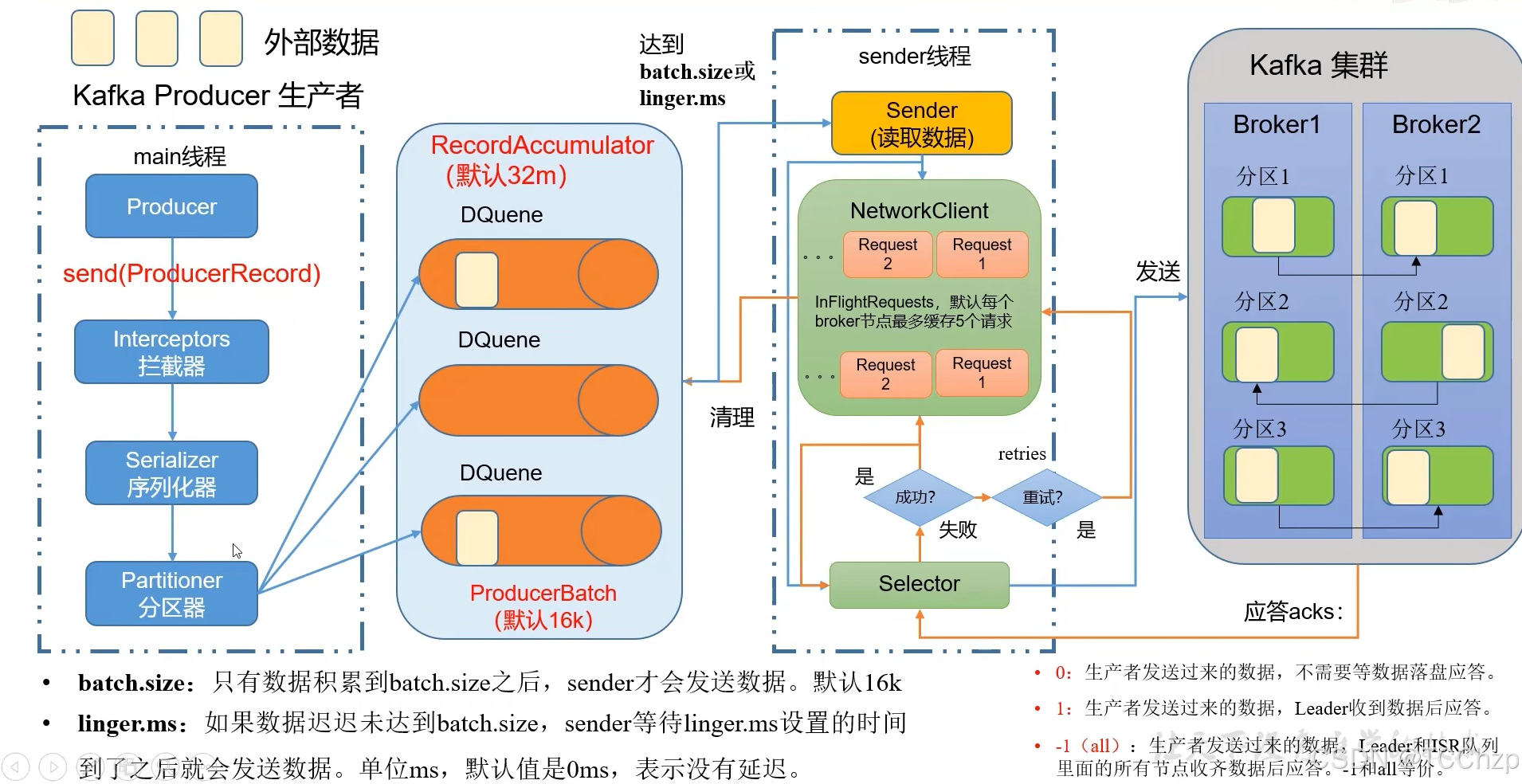
Kafka入门-生产者
生产者 生产者发送流程: 延迟时间为0ms时,也就意味着每当有数据就会直接发送 异步发送API 异步发送和同步发送的不同在于:异步发送不需要等待结果,同步发送必须等待结果才能进行下一步发送。 普通异步发送 首先导入所需的k…...

第7篇:中间件全链路监控与 SQL 性能分析实践
7.1 章节导读 在构建数据库中间件的过程中,可观测性 和 性能分析 是保障系统稳定性与可维护性的核心能力。 特别是在复杂分布式场景中,必须做到: 🔍 追踪每一条 SQL 的生命周期(从入口到数据库执行)&#…...

TSN交换机正在重构工业网络,PROFINET和EtherCAT会被取代吗?
在工业自动化持续演进的今天,通信网络的角色正变得愈发关键。 2025年6月6日,为期三天的华南国际工业博览会在深圳国际会展中心(宝安)圆满落幕。作为国内工业通信领域的技术型企业,光路科技(Fiberroad&…...
