使用 Kotlin 将 Vertx 和 Springboot 整合
本篇文章目的是将 Springboot 和 Vertx 进行简单整合。整合目的仅仅是为了整活,因为两个不同的东西整合在一起提升的性能并没有只使用 Vertx 性能高,因此追求高性能的话这是在我来说不推荐。而且他们不仅没有提高很多性能甚至增加了学习成本
一、整合流程
首先呢目标是将Vertx 最终整合成和使用Springboot web 一样简单的 httpserver。
步骤:
- 获取Springboot 所有的Bean
- 注册路由: 检查Bean 中是否是存在实现了 Router 的方法,并交给 router
- 开启服务器,等待请求
二、扫描 Bean
最终目标呢,是实现和使用Springboot 一样简便,所以就需要注解来对需要的方法进行标注
最终效果预览
@RouterController
class HelloRouter(val test :PlayerUnlockTechService
) {/*** 注册路由* 正则路由以 ^ 开始** 方法参数可以是 routingContext 或者 router 或者 routingContext 内的任何东西。以及其他的任何东西,或者 bean**/@Rout("/hello")fun hello(response: HttpServerResponse, request: HttpServerRequest) {request.bodyHandler {response.end(test.getPlayerUnlockTechsByBuilding("BD12DC34624208045CCA1ECE32071F20").toString())}}
- 创建注解
主要注解有:
- RouterController 标注类中有 Router 需要的路由实现
- Rout 标注方法是个路由实现
- AutoClose 标注方法执行完成后自动关闭连接
/**** @author : zimo* @date : 2025/01/03*/
@Target(AnnotationTarget.CLASS, AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION)
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME)
@MustBeDocumented
@Component
annotation class RouterController/**** @author : zimo* @date : 2025/01/03*/
@Target(AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION)
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME)
@MustBeDocumented
annotation class Router(val path: String,val method: String = ""
)@Target(AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION)
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME)
@MustBeDocumented
annotation class Rout(val path: String,val method: String = ""
)@Target(AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION)
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME)
@MustBeDocumented
annotation class RouterGet(val path: String,val method: String = "GET"
)@Target(AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION)
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME)
@MustBeDocumented
annotation class RouterPost(val path: String,val method: String = "POST"
)@Target(AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION)
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME)
@MustBeDocumented
annotation class RouterPut(val path: String,val method: String = "PUT"
)@Target(AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION)
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME)
@MustBeDocumented
annotation class RouterDelete(val path: String,val method: String = "DELETE"
)@Target(AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION)
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME)
@MustBeDocumented
annotation class RouterPatch(val path: String,val method: String = "PATCH"
)@Target(AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION)
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME)
@MustBeDocumented
annotation class RouterHead(val path: String,val method: String = "HEAD"
)@Target(AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION)
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME)
@MustBeDocumented
annotation class RouterOptions(val path: String,val method: String = "OPTIONS"
)@Target(AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION)
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME)
@MustBeDocumented
annotation class AutoClose
- 获取 Beans
在当前类中注入applicationContext并通过applicationContext.beanDefinitionNames获取所有的 Bean
@Component
class RouterProcessor(val applicationContext: ApplicationContext) {/*** 初始化完成后的 bean 列表*/private val initializedBeanInstances by lazy {applicationContext.beanDefinitionNames.filter {it != this.javaClass.simpleName && it != Connection::class.simpleName}.mapNotNull {applicationContext.getBean(it)}}
}
- 检测出所有的Router 方法
检测出是否被标注为了一个 Router 方法,并注册到 router
for (method in clazz.methods) {if (method.isAnnotationPresent(io.github.zimoyin.ra3.annotations.Router::class.java)) {val path = method.getAnnotation(io.github.zimoyin.ra3.annotations.Router::class.java).pathrouter.let {if (path.startsWith("^")) it.routeWithRegex(path.replaceFirst("^", ""))else it.route(path)// order 可以放到注解里,这样可以动态设置了}.order(0).handler {// 执行方法的封装invoke(method, bean, it)}return}// ... 其他注解处理
}三、执行Router方法
这里只有两个重点,一个是自动关闭,一个是执行方法传入的参数实例
- 自动关闭,如果方法上存在
AutoClose注解就在执行方法结束后尝试关闭连接 - 方法参数,从Bean、Context 中获取。如果没有则通过上下文创建 Bean
fun invoke(method: Method, bean: Any, routingContext: RoutingContext) {val args = arrayListOf<Any>()val isHasAutoClose = method.isAnnotationPresent(AutoClose::class.java)// 获取方法需要的参数method.parameters.forEach {val bean0 = kotlin.runCatching { applicationContext.getBean(it.name, it.type) }.getOrNull()?: kotlin.runCatching { applicationContext.getBean(it.type) }.getOrNull()if (bean0 != null) {args.add(bean0)} else {args.add(createParameter(it, routingContext))}}//执行方法try {routingContext.request().paramsCharset = "UTF-8"val result = method.invoke(bean, *args.toTypedArray())kotlin.runCatching {// 自动关闭,如果方法上存在 `AutoClose` 注解就在执行方法结束后尝试关闭连接// 获取方法的返回值,并以方法的返回值作为自动关闭的参数if (isHasAutoClose) {val response = routingContext.response()response.putHeader("content-type", "application/json")if (method.returnType == Unit::class.java) {response.end()}if (result == null) {response.end()}if (result is String) {response.end(result)} else if (result is Number || result is Comparable<*>) {response.end(result.toString())} else {kotlin.runCatching {response.end(result.toJsonObject().toString())}.onFailure {response.end()logger.debug("自动关闭连接失败", it)}}}}} catch (e: InvocationTargetException) {kotlin.runCatching { routingContext.response().end("Server Error!!!!") }logger.error("路由执行失败, $method 方法内部存在错误逻辑导致方法执行失败", e)} catch (e: Exception) {kotlin.runCatching { routingContext.response().end("Server Error!!!!") }logger.error("路由执行失败", e)}}
获取 routingContext 中的参数,或者创建一个参数
private fun createParameter(value: Parameter, routingContext: RoutingContext): Any {val name = value.nameval type = value.typewhen (name) {"res", "response", "resp" -> return routingContext.response()"req", "request", "requ" -> return routingContext.request()"body", "reqBody", "requestBody" -> return routingContext.body()"headers", "header", "reqHeader", "requestHeader", "reqHeaders", "requestHeaders" -> return routingContext.request().headers()"query", "reqQuery", "requestQuery", "reqQueries", "requestQueries" -> return routingContext.queryParams()"data", "reqData", "requestData" -> return routingContext.data()"params", "reqParams", "requestParams" -> return routingContext.pathParams()"cookie", "reqCookie", "requestCookie" -> return routingContext.cookieMap()"session", "reqSession", "requestSession" -> return routingContext.session()"user", "reqUser", "requestUser" -> return routingContext.user()"bodyAsString", "reqBodyAsString", "requestBodyAsString" -> return routingContext.bodyAsString"bodyAsJson", "reqBodyAsJson", "requestBodyAsJson" -> return routingContext.bodyAsJson"bodyAsBuffer", "reqBodyAsBuffer", "requestBodyAsBuffer" -> return routingContext.body().buffer()"routingContext", "context", "routerContext", "routContext" -> return routingContext"rout", "router" -> return routingContext.currentRoute()"vertx", "vertxContext" -> return routingContext.vertx()"responseHeaders", "responseHeader" -> return routingContext.response().headers()"uri" -> return routingContext.request().uri()"absoluteURI" -> return routingContext.request().absoluteURI()"authority" -> return routingContext.request().authority()"isSSL", "ssl", "isSsl", "isSSl", "isssl", "SSL", "Ssl" -> return routingContext.request().isSSL}// 如果都不是以上的参数则创建一个kotlin.runCatching {applicationContext.autowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean(type)}.onSuccess {return it}throw IllegalArgumentException("Unable to parse parameters:$name")}
四、全部代码
通过 @EventListener(ApplicationReadyEvent::class) 注解来确保,该初始化方法可以在Springboot 启动完成后执行
注意: 需要提前将 Router 注册到Springboot
@Component
class RouterProcessor(val applicationContext: ApplicationContext) {private lateinit var router: io.vertx.ext.web.Routerprivate val logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RouterProcessor::class.java)@EventListener(ApplicationReadyEvent::class)fun init(event: ApplicationReadyEvent) {kotlin.runCatching {router = applicationContext.getBeanByName("router")for (bean in initializedBeanInstances) {registerBean(bean)}}.onFailure {logger.error(" Vertx WebRouter 初始化失败: ${it.message}", it)}}/*** 初始化完成后的 bean 列表*/private val initializedBeanInstances by lazy {applicationContext.beanDefinitionNames.filter {it != this.javaClass.simpleName &&it != Connection::class.simpleName}.mapNotNull {applicationContext.getBean(it)}}fun registerBean(bean: Any) {val clazz = bean.javaClassfor (method in clazz.methods) {runCatch {registerMethod(method, bean)}}}fun registerMethod(method: Method, bean: Any) {if (method.isAnnotationPresent(io.github.zimoyin.ra3.annotations.Router::class.java)) {val path = method.getAnnotation(io.github.zimoyin.ra3.annotations.Router::class.java).pathrouter.let {if (path.startsWith("^")) it.routeWithRegex(path.replaceFirst("^", ""))else it.route(path)}.order(0).handler {invoke(method, bean, it)}return}if (method.isAnnotationPresent(Rout::class.java)) {val path = method.getAnnotation(Rout::class.java).pathrouter.let {if (path.startsWith("^")) it.routeWithRegex(path.replaceFirst("^", ""))else it.route(path)}.order(0).handler {invoke(method, bean, it)}return}if (method.isAnnotationPresent(RouterPost::class.java)) {val path = method.getAnnotation(RouterPost::class.java).pathrouter.let {if (path.startsWith("^")) it.postWithRegex(path.replaceFirst("^", ""))else it.post(path)}.order(0).handler {invoke(method, bean, it)}return}if (method.isAnnotationPresent(RouterGet::class.java)) {val path = method.getAnnotation(RouterGet::class.java).pathrouter.let {if (path.startsWith("^")) it.getWithRegex(path.replaceFirst("^", ""))else it.get(path)}.order(0).handler {invoke(method, bean, it)}return}if (method.isAnnotationPresent(RouterPut::class.java)) {val path = method.getAnnotation(RouterPut::class.java).pathrouter.let {if (path.startsWith("^")) it.putWithRegex(path.replaceFirst("^", ""))else it.put(path)}.order(0).handler {invoke(method, bean, it)}return}if (method.isAnnotationPresent(RouterPatch::class.java)) {val path = method.getAnnotation(RouterPatch::class.java).pathrouter.let {if (path.startsWith("^")) it.patchWithRegex(path.replaceFirst("^", ""))else it.patch(path)}.order(0).handler {invoke(method, bean, it)}return}if (method.isAnnotationPresent(RouterPatch::class.java)) {val path = method.getAnnotation(RouterDelete::class.java).pathrouter.let {if (path.startsWith("^")) it.deleteWithRegex(path.replaceFirst("^", ""))else it.delete(path)}.order(0).handler {invoke(method, bean, it)}return}if (method.isAnnotationPresent(RouterHead::class.java)) {val path = method.getAnnotation(RouterHead::class.java).pathrouter.let {if (path.startsWith("^")) it.headWithRegex(path.replaceFirst("^", ""))else it.head(path)}.order(0).handler {invoke(method, bean, it)}return}if (method.isAnnotationPresent(RouterOptions::class.java)) {val path = method.getAnnotation(RouterOptions::class.java).pathrouter.let {if (path.startsWith("^")) it.optionsWithRegex(path.replaceFirst("^", ""))else it.options(path)}.order(0).handler {invoke(method, bean, it)}return}}fun invoke(method: Method, bean: Any, routingContext: RoutingContext) {val args = arrayListOf<Any>()val isHasAutoClose = method.isAnnotationPresent(AutoClose::class.java)method.parameters.forEach {val bean0 = kotlin.runCatching { applicationContext.getBean(it.name, it.type) }.getOrNull()?: kotlin.runCatching { applicationContext.getBean(it.type) }.getOrNull()if (bean0 != null) {args.add(bean0)} else {args.add(createParameter(it, routingContext))}}//执行方法try {routingContext.request().paramsCharset = "UTF-8"val result = method.invoke(bean, *args.toTypedArray())kotlin.runCatching {if (isHasAutoClose) {val response = routingContext.response()response.putHeader("content-type", "application/json")if (method.returnType == Unit::class.java) {response.end()}if (result == null) {response.end()}if (result is String) {response.end(result)} else if (result is Number || result is Comparable<*>) {response.end(result.toString())} else {kotlin.runCatching {response.end(result.toJsonObject().toString())}.onFailure {response.end()logger.debug("自动关闭连接失败", it)}}}}} catch (e: InvocationTargetException) {kotlin.runCatching { routingContext.response().end("Server Error!!!!") }logger.error("路由执行失败, $method 方法内部存在错误逻辑导致方法执行失败", e)} catch (e: Exception) {kotlin.runCatching { routingContext.response().end("Server Error!!!!") }logger.error("路由执行失败", e)}}private fun createParameter(value: Parameter, routingContext: RoutingContext): Any {val name = value.nameval type = value.typewhen (name) {"res", "response", "resp" -> return routingContext.response()"req", "request", "requ" -> return routingContext.request()"body", "reqBody", "requestBody" -> return routingContext.body()"headers", "header", "reqHeader", "requestHeader", "reqHeaders", "requestHeaders" -> return routingContext.request().headers()"query", "reqQuery", "requestQuery", "reqQueries", "requestQueries" -> return routingContext.queryParams()"data", "reqData", "requestData" -> return routingContext.data()"params", "reqParams", "requestParams" -> return routingContext.pathParams()"cookie", "reqCookie", "requestCookie" -> return routingContext.cookieMap()"session", "reqSession", "requestSession" -> return routingContext.session()"user", "reqUser", "requestUser" -> return routingContext.user()"bodyAsString", "reqBodyAsString", "requestBodyAsString" -> return routingContext.bodyAsString"bodyAsJson", "reqBodyAsJson", "requestBodyAsJson" -> return routingContext.bodyAsJson"bodyAsBuffer", "reqBodyAsBuffer", "requestBodyAsBuffer" -> return routingContext.body().buffer()"routingContext", "context", "routerContext", "routContext" -> return routingContext"rout", "router" -> return routingContext.currentRoute()"vertx", "vertxContext" -> return routingContext.vertx()"responseHeaders", "responseHeader" -> return routingContext.response().headers()"uri" -> return routingContext.request().uri()"absoluteURI" -> return routingContext.request().absoluteURI()"authority" -> return routingContext.request().authority()"isSSL", "ssl", "isSsl", "isSSl", "isssl", "SSL", "Ssl" -> return routingContext.request().isSSL}kotlin.runCatching {applicationContext.autowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean(type)}.onSuccess {return it}throw IllegalArgumentException("Unable to parse parameters:$name")}fun <T : Any> runCatch(block: () -> T): T? {try {return block()} catch (e: Exception) {logger.error("路由捕获到异常", e)}return null}
}
使用示例
/**** @author : zimo* @date : 2025/01/04*/
@RouterController
class HelloRouter(val test :PlayerUnlockTechService
) {/*** 注册路由* 正则路由以 ^ 开始* 请求处理方法: 所有* 方法参数可以是 routingContext 或者 router 或者 routingContext 内的任何东西。以及其他的任何东西,或者 bean**/@Rout("/hello")
// @RouterGetfun hello(response: HttpServerResponse, request: HttpServerRequest) {request.bodyHandler {response.end(test.getPlayerUnlockTechsByBuilding("BD12DC34624208045CCA1ECE32071F20").toString())}}/*** 注册路由(并自动关闭,将返回值发送会前端)* 正则路由以 ^ 开始* 请求处理方法: GET* 方法参数可以是 routingContext 或者 router 或者 routingContext 内的任何东西。以及其他的任何东西,或者 bean**/@RouterGet("/test/send_message/:message")@AutoClosefun send(response: HttpServerResponse, request: HttpServerRequest):String {return "你好"}}
}
Main 方法
/**** @author : zimo* @date : 2025/01/03*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
@MapperScan(basePackages = ["io.github.zimoyin.ra3.mapper"])
class ApplicationStart2(val vertx: Vertx,val router: Router
) {companion object {@JvmStaticfun main(args: Array<String>) {runApplication<ApplicationStart2>(*args)}}@PostConstructfun onStartVertxWeb() {vertx.createHttpServer().requestHandler(router).listen(8090).onSuccess {println("启动成功")}}
}@Configuration
class VertxConfig {@Bean("vertx")fun vertx(): Vertx {return Vertx.vertx()}@Bean("router")fun router(vertx: Vertx): Router? {return Router.router(vertx)}
}相关文章:

使用 Kotlin 将 Vertx 和 Springboot 整合
本篇文章目的是将 Springboot 和 Vertx 进行简单整合。整合目的仅仅是为了整活,因为两个不同的东西整合在一起提升的性能并没有只使用 Vertx 性能高,因此追求高性能的话这是在我来说不推荐。而且他们不仅没有提高很多性能甚至增加了学习成本 一、整合流…...

线性回归算法-01
线性回归简介 学习目标 了解线性回归的应用场景知道线性回归的定义 1 线性回归应用场景 房价预测销售额度预测贷款额度预测 2 什么是线性回归 2.1 定义与公式 线性回归(Linear regression)是利用 回归方程(函数)对 一个或多个自变量(特征值)和因变量(目标值)之间关系进行建模…...

洛谷 P1130 红牌 C语言
题目描述 某地临时居民想获得长期居住权就必须申请拿到红牌。获得红牌的过程是相当复杂,一共包括 N 个步骤。每一步骤都由政府的某个工作人员负责检查你所提交的材料是否符合条件。为了加快进程,每一步政府都派了 M 个工作人员来检查材料。不幸的是&…...

虚幻UE5手机安卓Android Studio开发设置2025
一、下载Android Studio历史版本 步骤1:虚幻4.27、5.0、5.1、5.2官方要求Andrd Studio 4.0版本; 5.3、5.4、5.5官方要求的版本为Android Studio Flamingo | 2022.2.1 Patch 2 May 24, 2023 虚幻官网查看对应Andrd Studiob下载版本: https:/…...

线性代数复习笔记
1. 课程学习 1.1 3Blue1Brown 线性代数 2. 基本术语 eigenvector(特征向量):线性变换中方向保持不变的向量 可以视作3D旋转矩阵形成的旋转的轴...

你需要更深层次的解放
先谈一谈理性认知中的属性替换原则。简单来说,属性替换就是用简单的问题取代难题。 当人们需要评估属性A时,却发现评估属性B更容易一些(A与B之间存在一定的关系),于是就改为评估属性B。这叫做属性替换。 作为一种认知…...

机器学习算法在网络安全中的实践
机器学习算法在网络安全中的实践 本文将深入探讨机器学习算法在网络安全领域的应用实践,包括基本概念、常见算法及其应用案例,从而帮助程序员更好地理解和应用这一领域的技术。"> 序言 网络安全一直是信息技术领域的重要议题,随着互联…...

Qt事件处理:理解处理器、过滤器与事件系统
1. 事件 事件 是一个描述应用程序中、发生的某些事情的对象。 在 Qt 中,所有事件都继承自 QEvent ,并且每个事件都有特定的标识符,如:Qt::MouseButtonPress 代表鼠标按下事件。 每个事件对象包含该事件的所有相关信息ÿ…...

DeepSeek相关技术整理
相关介绍 2024年12月26日,DeepSeek V3模型发布(用更低的训练成本,训练出更好的效果)671B参数,激活37B。2025年1月20日,DeepSeek-R1模型发布(仅需少量标注数据(高质量长cotÿ…...

DeepSeek 遭 DDoS 攻击背后:DDoS 攻击的 “千层套路” 与安全防御 “金钟罩”
当算力博弈升级为网络战争:拆解DDoS攻击背后的技术攻防战——从DeepSeek遇袭看全球网络安全新趋势 在数字化浪潮席卷全球的当下,网络已然成为人类社会运转的关键基础设施,深刻融入经济、生活、政务等各个领域。从金融交易的实时清算…...

蓝桥杯之c++入门(二)【输入输出(上)】
目录 前言1.getchar和 putchar1.1 getchar()1.2 putchar() 2.scanf和 printf2.1 printf2.1.1基本用法2.1.2占位符2.1.3格式化输出2.1.3.1 限定宽度2.1.3.2 限定小数位数 2.2 scanf2.2.1基本用法2.2.2 占位符2.2.3 scanf的返回值 2.3练习练习1:…...

消息队列应用示例MessageQueues-STM32CubeMX-FreeRTOS《嵌入式系统设计》P343-P347
消息队列 使用信号量、事件标志组和线标志进行任务同步时,只能提供同步的时刻信息,无法在任务之间进行数据传输。要实现任务间的数据传输,一般使用两种方式: 1. 全局变量 在 RTOS 中使用全局变量时,必须保证每个任务…...

算法题(55):用最少数量的箭引爆气球
审题: 本题需要我们找到最少需要的箭数,并返回 思路: 首先我们需要把本题描述的问题理解准确 (1)arrow从x轴任一点垂直射出 (2)一旦射出,无限前进 也就是说如果气球有公共区域(交集&…...

谭浩强C语言程序设计(4) 8章(下)
1、输入三个字符串按照字母顺序从小到大输出 #include <cstdio> // 包含cstdio头文件,用于输入输出函数 #include <cstring> // 包含cstring头文件,用于字符串处理函数#define N 20 // 定义字符串的最大长度为20// 函数:…...

AlexNet论文代码阅读
论文标题: ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks 论文链接: https://volctracer.com/w/BX18q92F 代码链接: https://github.com/dansuh17/alexnet-pytorch 内容概述 训练了一个大型的深度卷积神经网络…...

62.病毒在封闭空间中的传播时间|Marscode AI刷题
1.题目 问题描述 在一个封闭的房间里摆满了座位,每个座位东西向和南北向都有固定 1 米的间隔。座位上坐满了人,坐着的人可能带了口罩,也可能没有带口罩。我们已经知道房间里的某个人已经感染了病毒,病毒的传播速度是每秒钟感染距…...

Elixir语言的安全开发
Elixir语言的安全开发 引言 在当今这个互联网高度发展的时代,软件的安全性变得越来越重要。随着网络攻击的增多,软件漏洞的频繁暴露,开发者面临着前所未有的安全挑战。Elixir,作为一种现代化的函数式编程语言,以其高…...

Rust 条件语句
Rust 条件语句 在编程语言中,条件语句是进行决策和实现分支逻辑的关键。Rust 语言作为一门系统编程语言,其条件语句的使用同样至关重要。本文将详细介绍 Rust 中的条件语句,包括其基本用法、常见场景以及如何避免常见错误。 基本用法 Rust…...

小红的合数寻找
A-小红的合数寻找_牛客周赛 Round 79 题目描述 小红拿到了一个正整数 x,她希望你在 [x,2x] 区间内找到一个合数,你能帮帮她吗? 一个数为合数,当且仅当这个数是大于1的整数,并且不是质数。 输入描述 在一行上输入一…...

使用等宽等频法进行数据特征离散化
在数据分析与处理的过程中,特征离散化是一种常见的操作。通过将连续的数值型数据转换为离散类别,能够更好地处理数据,尤其是在机器学习模型中进行分类问题的建模时。离散化能够简化数据结构,减少数据噪声,并提高模型的解释性。 本文将详细介绍如何使用 pandas 库中的 cut…...

[特殊字符] 智能合约中的数据是如何在区块链中保持一致的?
🧠 智能合约中的数据是如何在区块链中保持一致的? 为什么所有区块链节点都能得出相同结果?合约调用这么复杂,状态真能保持一致吗?本篇带你从底层视角理解“状态一致性”的真相。 一、智能合约的数据存储在哪里…...
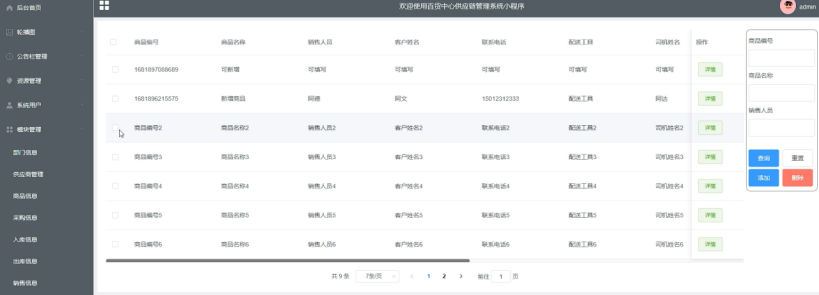
springboot 百货中心供应链管理系统小程序
一、前言 随着我国经济迅速发展,人们对手机的需求越来越大,各种手机软件也都在被广泛应用,但是对于手机进行数据信息管理,对于手机的各种软件也是备受用户的喜爱,百货中心供应链管理系统被用户普遍使用,为方…...
)
【位运算】消失的两个数字(hard)
消失的两个数字(hard) 题⽬描述:解法(位运算):Java 算法代码:更简便代码 题⽬链接:⾯试题 17.19. 消失的两个数字 题⽬描述: 给定⼀个数组,包含从 1 到 N 所有…...
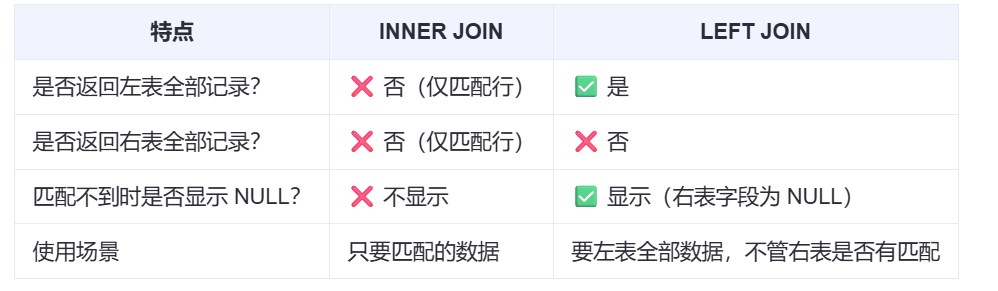
【SQL学习笔记1】增删改查+多表连接全解析(内附SQL免费在线练习工具)
可以使用Sqliteviz这个网站免费编写sql语句,它能够让用户直接在浏览器内练习SQL的语法,不需要安装任何软件。 链接如下: sqliteviz 注意: 在转写SQL语法时,关键字之间有一个特定的顺序,这个顺序会影响到…...
2025盘古石杯决赛【手机取证】
前言 第三届盘古石杯国际电子数据取证大赛决赛 最后一题没有解出来,实在找不到,希望有大佬教一下我。 还有就会议时间,我感觉不是图片时间,因为在电脑看到是其他时间用老会议系统开的会。 手机取证 1、分析鸿蒙手机检材&#x…...

三体问题详解
从物理学角度,三体问题之所以不稳定,是因为三个天体在万有引力作用下相互作用,形成一个非线性耦合系统。我们可以从牛顿经典力学出发,列出具体的运动方程,并说明为何这个系统本质上是混沌的,无法得到一般解…...
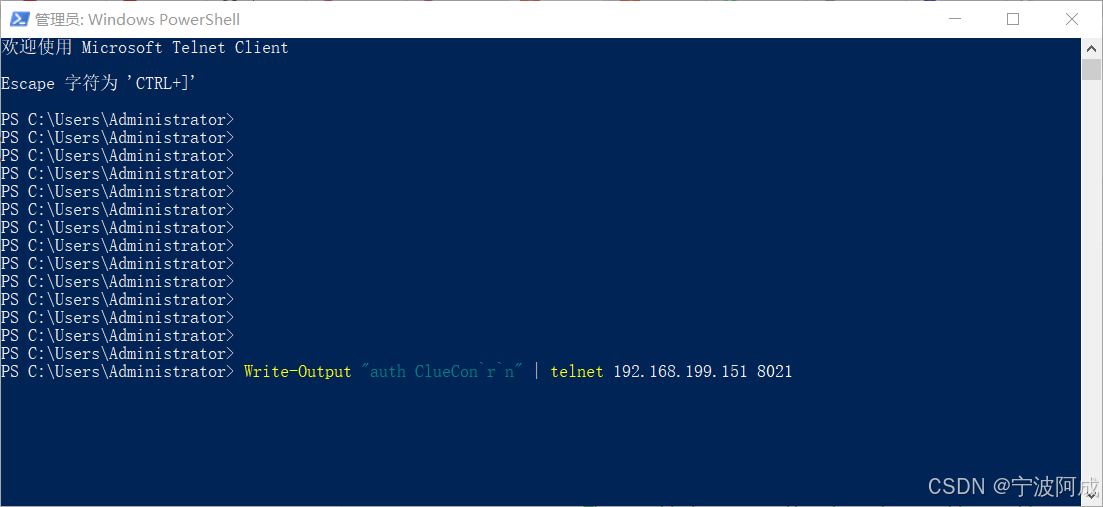
用docker来安装部署freeswitch记录
今天刚才测试一个callcenter的项目,所以尝试安装freeswitch 1、使用轩辕镜像 - 中国开发者首选的专业 Docker 镜像加速服务平台 编辑下面/etc/docker/daemon.json文件为 {"registry-mirrors": ["https://docker.xuanyuan.me"] }同时可以进入轩…...

2025季度云服务器排行榜
在全球云服务器市场,各厂商的排名和地位并非一成不变,而是由其独特的优势、战略布局和市场适应性共同决定的。以下是根据2025年市场趋势,对主要云服务器厂商在排行榜中占据重要位置的原因和优势进行深度分析: 一、全球“三巨头”…...

Java求职者面试指南:计算机基础与源码原理深度解析
Java求职者面试指南:计算机基础与源码原理深度解析 第一轮提问:基础概念问题 1. 请解释什么是进程和线程的区别? 面试官:进程是程序的一次执行过程,是系统进行资源分配和调度的基本单位;而线程是进程中的…...

前端中slice和splic的区别
1. slice slice 用于从数组中提取一部分元素,返回一个新的数组。 特点: 不修改原数组:slice 不会改变原数组,而是返回一个新的数组。提取数组的部分:slice 会根据指定的开始索引和结束索引提取数组的一部分。不包含…...
