12 向量结构模块(vector.rs)
一vector.rs源码
// Copyright 2013 The Servo Project Developers. See the COPYRIGHT
// file at the top-level directory of this distribution.
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 <LICENSE-APACHE or
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0> or the MIT license
// <LICENSE-MIT or http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT>, at your
// option. This file may not be copied, modified, or distributed
// except according to those terms.use super::UnknownUnit;
use crate::approxeq::ApproxEq;
use crate::approxord::{max, min};
use crate::length::Length;
use crate::num::*;
use crate::point::{point2, point3, Point2D, Point3D};
use crate::scale::Scale;
use crate::size::{size2, size3, Size2D, Size3D};
use crate::transform2d::Transform2D;
use crate::transform3d::Transform3D;
use crate::trig::Trig;
use crate::Angle;
use core::cmp::{Eq, PartialEq};
use core::fmt;
use core::hash::Hash;
use core::iter::Sum;
use core::marker::PhantomData;
use core::ops::{Add, AddAssign, Div, DivAssign, Mul, MulAssign, Neg, Sub, SubAssign};
#[cfg(feature = "mint")]
use mint;
use num_traits::real::Real;
use num_traits::{Float, NumCast, Signed};
#[cfg(feature = "serde")]
use serde;#[cfg(feature = "bytemuck")]
use bytemuck::{Pod, Zeroable};/// A 2d Vector tagged with a unit.
#[repr(C)]
pub struct Vector2D<T, U> {/// The `x` (traditionally, horizontal) coordinate.pub x: T,/// The `y` (traditionally, vertical) coordinate.pub y: T,#[doc(hidden)]pub _unit: PhantomData<U>,
}mint_vec!(Vector2D[x, y] = Vector2);impl<T: Copy, U> Copy for Vector2D<T, U> {}impl<T: Clone, U> Clone for Vector2D<T, U> {fn clone(&self) -> Self {Vector2D {x: self.x.clone(),y: self.y.clone(),_unit: PhantomData,}}
}#[cfg(feature = "serde")]
impl<'de, T, U> serde::Deserialize<'de> for Vector2D<T, U>
whereT: serde::Deserialize<'de>,
{fn deserialize<D>(deserializer: D) -> Result<Self, D::Error>whereD: serde::Deserializer<'de>,{let (x, y) = serde::Deserialize::deserialize(deserializer)?;Ok(Vector2D {x,y,_unit: PhantomData,})}
}#[cfg(feature = "serde")]
impl<T, U> serde::Serialize for Vector2D<T, U>
whereT: serde::Serialize,
{fn serialize<S>(&self, serializer: S) -> Result<S::Ok, S::Error>whereS: serde::Serializer,{(&self.x, &self.y).serialize(serializer)}
}#[cfg(feature = "arbitrary")]
impl<'a, T, U> arbitrary::Arbitrary<'a> for Vector2D<T, U>
whereT: arbitrary::Arbitrary<'a>,
{fn arbitrary(u: &mut arbitrary::Unstructured<'a>) -> arbitrary::Result<Self> {let (x, y) = arbitrary::Arbitrary::arbitrary(u)?;Ok(Vector2D {x,y,_unit: PhantomData,})}
}#[cfg(feature = "bytemuck")]
unsafe impl<T: Zeroable, U> Zeroable for Vector2D<T, U> {}#[cfg(feature = "bytemuck")]
unsafe impl<T: Pod, U: 'static> Pod for Vector2D<T, U> {}impl<T: Eq, U> Eq for Vector2D<T, U> {}impl<T: PartialEq, U> PartialEq for Vector2D<T, U> {fn eq(&self, other: &Self) -> bool {self.x == other.x && self.y == other.y}
}impl<T: Hash, U> Hash for Vector2D<T, U> {fn hash<H: core::hash::Hasher>(&self, h: &mut H) {self.x.hash(h);self.y.hash(h);}
}impl<T: Zero, U> Zero for Vector2D<T, U> {/// Constructor, setting all components to zero.#[inline]fn zero() -> Self {Vector2D::new(Zero::zero(), Zero::zero())}
}impl<T: fmt::Debug, U> fmt::Debug for Vector2D<T, U> {fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result {f.debug_tuple("").field(&self.x).field(&self.y).finish()}
}impl<T: Default, U> Default for Vector2D<T, U> {fn default() -> Self {Vector2D::new(Default::default(), Default::default())}
}impl<T, U> Vector2D<T, U> {/// Constructor, setting all components to zero.#[inline]pub fn zero() -> SelfwhereT: Zero,{Vector2D::new(Zero::zero(), Zero::zero())}/// Constructor, setting all components to one.#[inline]pub fn one() -> SelfwhereT: One,{Vector2D::new(One::one(), One::one())}/// Constructor taking scalar values directly.#[inline]pub const fn new(x: T, y: T) -> Self {Vector2D {x,y,_unit: PhantomData,}}/// Constructor setting all components to the same value.#[inline]pub fn splat(v: T) -> SelfwhereT: Clone,{Vector2D {x: v.clone(),y: v,_unit: PhantomData,}}/// Constructor taking angle and lengthpub fn from_angle_and_length(angle: Angle<T>, length: T) -> SelfwhereT: Trig + Mul<Output = T> + Copy,{vec2(length * angle.radians.cos(), length * angle.radians.sin())}/// Constructor taking properly Lengths instead of scalar values.#[inline]pub fn from_lengths(x: Length<T, U>, y: Length<T, U>) -> Self {vec2(x.0, y.0)}/// Tag a unit-less value with units.#[inline]pub fn from_untyped(p: Vector2D<T, UnknownUnit>) -> Self {vec2(p.x, p.y)}/// Apply the function `f` to each component of this vector.////// # Example////// This may be used to perform unusual arithmetic which is not already offered as methods.////// ```/// use euclid::default::Vector2D;////// let p = Vector2D::<u32>::new(5, 11);/// assert_eq!(p.map(|coord| coord.saturating_sub(10)), Vector2D::new(0, 1));/// ```#[inline]pub fn map<V, F: FnMut(T) -> V>(self, mut f: F) -> Vector2D<V, U> {vec2(f(self.x), f(self.y))}/// Apply the function `f` to each pair of components of this point and `rhs`.////// # Example////// This may be used to perform unusual arithmetic which is not already offered as methods.////// ```/// use euclid::default::Vector2D;////// let a: Vector2D<u8> = Vector2D::new(50, 200);/// let b: Vector2D<u8> = Vector2D::new(100, 100);/// assert_eq!(a.zip(b, u8::saturating_add), Vector2D::new(150, 255));/// ```#[inline]pub fn zip<V, F: FnMut(T, T) -> V>(self, rhs: Self, mut f: F) -> Vector2D<V, U> {vec2(f(self.x, rhs.x), f(self.y, rhs.y))}/// Computes the vector with absolute values of each component.////// # Example////// ```rust/// # use std::{i32, f32};/// # use euclid::vec2;/// enum U {}////// assert_eq!(vec2::<_, U>(-1, 2).abs(), vec2(1, 2));////// let vec = vec2::<_, U>(f32::NAN, -f32::MAX).abs();/// assert!(vec.x.is_nan());/// assert_eq!(vec.y, f32::MAX);/// ```////// # Panics////// The behavior for each component follows the scalar type's implementation of/// `num_traits::Signed::abs`.pub fn abs(self) -> SelfwhereT: Signed,{vec2(self.x.abs(), self.y.abs())}/// Dot product.#[inline]pub fn dot(self, other: Self) -> TwhereT: Add<Output = T> + Mul<Output = T>,{self.x * other.x + self.y * other.y}/// Returns the norm of the cross product [self.x, self.y, 0] x [other.x, other.y, 0].#[inline]pub fn cross(self, other: Self) -> TwhereT: Sub<Output = T> + Mul<Output = T>,{self.x * other.y - self.y * other.x}/// Returns the component-wise multiplication of the two vectors.#[inline]pub fn component_mul(self, other: Self) -> SelfwhereT: Mul<Output = T>,{vec2(self.x * other.x, self.y * other.y)}/// Returns the component-wise division of the two vectors.#[inline]pub fn component_div(self, other: Self) -> SelfwhereT: Div<Output = T>,{vec2(self.x / other.x, self.y / other.y)}
}impl<T: Copy, U> Vector2D<T, U> {/// Create a 3d vector from this one, using the specified z value.#[inline]pub fn extend(self, z: T) -> Vector3D<T, U> {vec3(self.x, self.y, z)}/// Cast this vector into a point.////// Equivalent to adding this vector to the origin.#[inline]pub fn to_point(self) -> Point2D<T, U> {Point2D {x: self.x,y: self.y,_unit: PhantomData,}}/// Swap x and y.#[inline]pub fn yx(self) -> Self {vec2(self.y, self.x)}/// Cast this vector into a size.#[inline]pub fn to_size(self) -> Size2D<T, U> {size2(self.x, self.y)}/// Drop the units, preserving only the numeric value.#[inline]pub fn to_untyped(self) -> Vector2D<T, UnknownUnit> {vec2(self.x, self.y)}/// Cast the unit.#[inline]pub fn cast_unit<V>(self) -> Vector2D<T, V> {vec2(self.x, self.y)}/// Cast into an array with x and y.#[inline]pub fn to_array(self) -> [T; 2] {[self.x, self.y]}/// Cast into a tuple with x and y.#[inline]pub fn to_tuple(self) -> (T, T) {(self.x, self.y)}/// Convert into a 3d vector with `z` coordinate equals to `T::zero()`.#[inline]pub fn to_3d(self) -> Vector3D<T, U>whereT: Zero,{vec3(self.x, self.y, Zero::zero())}/// Rounds each component to the nearest integer value.////// This behavior is preserved for negative values (unlike the basic cast).////// ```rust/// # use euclid::vec2;/// enum Mm {}////// assert_eq!(vec2::<_, Mm>(-0.1, -0.8).round(), vec2::<_, Mm>(0.0, -1.0))/// ```#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn round(self) -> SelfwhereT: Round,{vec2(self.x.round(), self.y.round())}/// Rounds each component to the smallest integer equal or greater than the original value.////// This behavior is preserved for negative values (unlike the basic cast).////// ```rust/// # use euclid::vec2;/// enum Mm {}////// assert_eq!(vec2::<_, Mm>(-0.1, -0.8).ceil(), vec2::<_, Mm>(0.0, 0.0))/// ```#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn ceil(self) -> SelfwhereT: Ceil,{vec2(self.x.ceil(), self.y.ceil())}/// Rounds each component to the biggest integer equal or lower than the original value.////// This behavior is preserved for negative values (unlike the basic cast).////// ```rust/// # use euclid::vec2;/// enum Mm {}////// assert_eq!(vec2::<_, Mm>(-0.1, -0.8).floor(), vec2::<_, Mm>(-1.0, -1.0))/// ```#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn floor(self) -> SelfwhereT: Floor,{vec2(self.x.floor(), self.y.floor())}/// Returns the signed angle between this vector and the x axis./// Positive values counted counterclockwise, where 0 is `+x` axis, `PI/2`/// is `+y` axis.////// The returned angle is between -PI and PI.pub fn angle_from_x_axis(self) -> Angle<T>whereT: Trig,{Angle::radians(Trig::fast_atan2(self.y, self.x))}/// Creates translation by this vector in vector units.#[inline]pub fn to_transform(self) -> Transform2D<T, U, U>whereT: Zero + One,{Transform2D::translation(self.x, self.y)}
}impl<T, U> Vector2D<T, U>
whereT: Copy + Mul<T, Output = T> + Add<T, Output = T>,
{/// Returns the vector's length squared.#[inline]pub fn square_length(self) -> T {self.x * self.x + self.y * self.y}/// Returns this vector projected onto another one.////// Projecting onto a nil vector will cause a division by zero.#[inline]pub fn project_onto_vector(self, onto: Self) -> SelfwhereT: Sub<T, Output = T> + Div<T, Output = T>,{onto * (self.dot(onto) / onto.square_length())}/// Returns the signed angle between this vector and another vector.////// The returned angle is between -PI and PI.pub fn angle_to(self, other: Self) -> Angle<T>whereT: Sub<Output = T> + Trig,{Angle::radians(Trig::fast_atan2(self.cross(other), self.dot(other)))}
}impl<T: Float, U> Vector2D<T, U> {/// Return the normalized vector even if the length is larger than the max value of Float.#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn robust_normalize(self) -> Self {let length = self.length();if length.is_infinite() {let scaled = self / T::max_value();scaled / scaled.length()} else {self / length}}/// Returns `true` if all members are finite.#[inline]pub fn is_finite(self) -> bool {self.x.is_finite() && self.y.is_finite()}
}impl<T: Real, U> Vector2D<T, U> {/// Returns the vector length.#[inline]pub fn length(self) -> T {self.square_length().sqrt()}/// Returns the vector with length of one unit.#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn normalize(self) -> Self {self / self.length()}/// Returns the vector with length of one unit.////// Unlike [`Vector2D::normalize`], this returns `None` in the case that the/// length of the vector is zero.#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn try_normalize(self) -> Option<Self> {let len = self.length();if len == T::zero() {None} else {Some(self / len)}}/// Return this vector scaled to fit the provided length.#[inline]pub fn with_length(self, length: T) -> Self {self.normalize() * length}/// Return this vector capped to a maximum length.#[inline]pub fn with_max_length(self, max_length: T) -> Self {let square_length = self.square_length();if square_length > max_length * max_length {return self * (max_length / square_length.sqrt());}self}/// Return this vector with a minimum length applied.#[inline]pub fn with_min_length(self, min_length: T) -> Self {let square_length = self.square_length();if square_length < min_length * min_length {return self * (min_length / square_length.sqrt());}self}/// Return this vector with minimum and maximum lengths applied.#[inline]pub fn clamp_length(self, min: T, max: T) -> Self {debug_assert!(min <= max);self.with_min_length(min).with_max_length(max)}
}impl<T, U> Vector2D<T, U>
whereT: Copy + One + Add<Output = T> + Sub<Output = T> + Mul<Output = T>,
{/// Linearly interpolate each component between this vector and another vector.////// # Example////// ```rust/// use euclid::vec2;/// use euclid::default::Vector2D;////// let from: Vector2D<_> = vec2(0.0, 10.0);/// let to: Vector2D<_> = vec2(8.0, -4.0);////// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, -1.0), vec2(-8.0, 24.0));/// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, 0.0), vec2( 0.0, 10.0));/// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, 0.5), vec2( 4.0, 3.0));/// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, 1.0), vec2( 8.0, -4.0));/// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, 2.0), vec2(16.0, -18.0));/// ```#[inline]pub fn lerp(self, other: Self, t: T) -> Self {let one_t = T::one() - t;self * one_t + other * t}/// Returns a reflection vector using an incident ray and a surface normal.#[inline]pub fn reflect(self, normal: Self) -> Self {let two = T::one() + T::one();self - normal * two * self.dot(normal)}
}impl<T: PartialOrd, U> Vector2D<T, U> {/// Returns the vector each component of which are minimum of this vector and another.#[inline]pub fn min(self, other: Self) -> Self {vec2(min(self.x, other.x), min(self.y, other.y))}/// Returns the vector each component of which are maximum of this vector and another.#[inline]pub fn max(self, other: Self) -> Self {vec2(max(self.x, other.x), max(self.y, other.y))}/// Returns the vector each component of which is clamped by corresponding/// components of `start` and `end`.////// Shortcut for `self.max(start).min(end)`.#[inline]pub fn clamp(self, start: Self, end: Self) -> SelfwhereT: Copy,{self.max(start).min(end)}/// Returns vector with results of "greater than" operation on each component.#[inline]pub fn greater_than(self, other: Self) -> BoolVector2D {BoolVector2D {x: self.x > other.x,y: self.y > other.y,}}/// Returns vector with results of "lower than" operation on each component.#[inline]pub fn lower_than(self, other: Self) -> BoolVector2D {BoolVector2D {x: self.x < other.x,y: self.y < other.y,}}
}impl<T: PartialEq, U> Vector2D<T, U> {/// Returns vector with results of "equal" operation on each component.#[inline]pub fn equal(self, other: Self) -> BoolVector2D {BoolVector2D {x: self.x == other.x,y: self.y == other.y,}}/// Returns vector with results of "not equal" operation on each component.#[inline]pub fn not_equal(self, other: Self) -> BoolVector2D {BoolVector2D {x: self.x != other.x,y: self.y != other.y,}}
}impl<T: NumCast + Copy, U> Vector2D<T, U> {/// Cast from one numeric representation to another, preserving the units.////// When casting from floating vector to integer coordinates, the decimals are truncated/// as one would expect from a simple cast, but this behavior does not always make sense/// geometrically. Consider using `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before casting.#[inline]pub fn cast<NewT: NumCast>(self) -> Vector2D<NewT, U> {self.try_cast().unwrap()}/// Fallible cast from one numeric representation to another, preserving the units.////// When casting from floating vector to integer coordinates, the decimals are truncated/// as one would expect from a simple cast, but this behavior does not always make sense/// geometrically. Consider using `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before casting.pub fn try_cast<NewT: NumCast>(self) -> Option<Vector2D<NewT, U>> {match (NumCast::from(self.x), NumCast::from(self.y)) {(Some(x), Some(y)) => Some(Vector2D::new(x, y)),_ => None,}}// Convenience functions for common casts./// Cast into an `f32` vector.#[inline]pub fn to_f32(self) -> Vector2D<f32, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `f64` vector.#[inline]pub fn to_f64(self) -> Vector2D<f64, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `usize` vector, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating vector vectors, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_usize(self) -> Vector2D<usize, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `isize` vector, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating vector vectors, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_isize(self) -> Vector2D<isize, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `u32` vector, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating vector vectors, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_u32(self) -> Vector2D<u32, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an i32 vector, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating vector vectors, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_i32(self) -> Vector2D<i32, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an i64 vector, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating vector vectors, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_i64(self) -> Vector2D<i64, U> {self.cast()}
}impl<T: Neg, U> Neg for Vector2D<T, U> {type Output = Vector2D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn neg(self) -> Self::Output {vec2(-self.x, -self.y)}
}impl<T: Add, U> Add for Vector2D<T, U> {type Output = Vector2D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn add(self, other: Self) -> Self::Output {Vector2D::new(self.x + other.x, self.y + other.y)}
}impl<T: Add + Copy, U> Add<&Self> for Vector2D<T, U> {type Output = Vector2D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn add(self, other: &Self) -> Self::Output {Vector2D::new(self.x + other.x, self.y + other.y)}
}impl<T: Add<Output = T> + Zero, U> Sum for Vector2D<T, U> {fn sum<I: Iterator<Item = Self>>(iter: I) -> Self {iter.fold(Self::zero(), Add::add)}
}impl<'a, T: 'a + Add<Output = T> + Copy + Zero, U: 'a> Sum<&'a Self> for Vector2D<T, U> {fn sum<I: Iterator<Item = &'a Self>>(iter: I) -> Self {iter.fold(Self::zero(), Add::add)}
}impl<T: Copy + Add<T, Output = T>, U> AddAssign for Vector2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn add_assign(&mut self, other: Self) {*self = *self + other;}
}impl<T: Sub, U> Sub for Vector2D<T, U> {type Output = Vector2D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn sub(self, other: Self) -> Self::Output {vec2(self.x - other.x, self.y - other.y)}
}impl<T: Copy + Sub<T, Output = T>, U> SubAssign<Vector2D<T, U>> for Vector2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn sub_assign(&mut self, other: Self) {*self = *self - other;}
}impl<T: Copy + Mul, U> Mul<T> for Vector2D<T, U> {type Output = Vector2D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn mul(self, scale: T) -> Self::Output {vec2(self.x * scale, self.y * scale)}
}impl<T: Copy + Mul<T, Output = T>, U> MulAssign<T> for Vector2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn mul_assign(&mut self, scale: T) {*self = *self * scale;}
}impl<T: Copy + Mul, U1, U2> Mul<Scale<T, U1, U2>> for Vector2D<T, U1> {type Output = Vector2D<T::Output, U2>;#[inline]fn mul(self, scale: Scale<T, U1, U2>) -> Self::Output {vec2(self.x * scale.0, self.y * scale.0)}
}impl<T: Copy + MulAssign, U> MulAssign<Scale<T, U, U>> for Vector2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn mul_assign(&mut self, scale: Scale<T, U, U>) {self.x *= scale.0;self.y *= scale.0;}
}impl<T: Copy + Div, U> Div<T> for Vector2D<T, U> {type Output = Vector2D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn div(self, scale: T) -> Self::Output {vec2(self.x / scale, self.y / scale)}
}impl<T: Copy + Div<T, Output = T>, U> DivAssign<T> for Vector2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn div_assign(&mut self, scale: T) {*self = *self / scale;}
}impl<T: Copy + Div, U1, U2> Div<Scale<T, U1, U2>> for Vector2D<T, U2> {type Output = Vector2D<T::Output, U1>;#[inline]fn div(self, scale: Scale<T, U1, U2>) -> Self::Output {vec2(self.x / scale.0, self.y / scale.0)}
}impl<T: Copy + DivAssign, U> DivAssign<Scale<T, U, U>> for Vector2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn div_assign(&mut self, scale: Scale<T, U, U>) {self.x /= scale.0;self.y /= scale.0;}
}impl<T: Round, U> Round for Vector2D<T, U> {/// See [`Vector2D::round`].#[inline]fn round(self) -> Self {self.round()}
}impl<T: Ceil, U> Ceil for Vector2D<T, U> {/// See [`Vector2D::ceil`].#[inline]fn ceil(self) -> Self {self.ceil()}
}impl<T: Floor, U> Floor for Vector2D<T, U> {/// See [`Vector2D::floor`].#[inline]fn floor(self) -> Self {self.floor()}
}impl<T: ApproxEq<T>, U> ApproxEq<Vector2D<T, U>> for Vector2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn approx_epsilon() -> Self {vec2(T::approx_epsilon(), T::approx_epsilon())}#[inline]fn approx_eq_eps(&self, other: &Self, eps: &Self) -> bool {self.x.approx_eq_eps(&other.x, &eps.x) && self.y.approx_eq_eps(&other.y, &eps.y)}
}impl<T, U> From<Vector2D<T, U>> for [T; 2] {fn from(v: Vector2D<T, U>) -> Self {[v.x, v.y]}
}impl<T, U> From<[T; 2]> for Vector2D<T, U> {fn from([x, y]: [T; 2]) -> Self {vec2(x, y)}
}impl<T, U> From<Vector2D<T, U>> for (T, T) {fn from(v: Vector2D<T, U>) -> Self {(v.x, v.y)}
}impl<T, U> From<(T, T)> for Vector2D<T, U> {fn from(tuple: (T, T)) -> Self {vec2(tuple.0, tuple.1)}
}impl<T, U> From<Size2D<T, U>> for Vector2D<T, U> {fn from(s: Size2D<T, U>) -> Self {vec2(s.width, s.height)}
}/// A 3d Vector tagged with a unit.
#[repr(C)]
pub struct Vector3D<T, U> {/// The `x` (traditionally, horizontal) coordinate.pub x: T,/// The `y` (traditionally, vertical) coordinate.pub y: T,/// The `z` (traditionally, depth) coordinate.pub z: T,#[doc(hidden)]pub _unit: PhantomData<U>,
}mint_vec!(Vector3D[x, y, z] = Vector3);impl<T: Copy, U> Copy for Vector3D<T, U> {}impl<T: Clone, U> Clone for Vector3D<T, U> {fn clone(&self) -> Self {Vector3D {x: self.x.clone(),y: self.y.clone(),z: self.z.clone(),_unit: PhantomData,}}
}#[cfg(feature = "serde")]
impl<'de, T, U> serde::Deserialize<'de> for Vector3D<T, U>
whereT: serde::Deserialize<'de>,
{fn deserialize<D>(deserializer: D) -> Result<Self, D::Error>whereD: serde::Deserializer<'de>,{let (x, y, z) = serde::Deserialize::deserialize(deserializer)?;Ok(Vector3D {x,y,z,_unit: PhantomData,})}
}#[cfg(feature = "serde")]
impl<T, U> serde::Serialize for Vector3D<T, U>
whereT: serde::Serialize,
{fn serialize<S>(&self, serializer: S) -> Result<S::Ok, S::Error>whereS: serde::Serializer,{(&self.x, &self.y, &self.z).serialize(serializer)}
}#[cfg(feature = "arbitrary")]
impl<'a, T, U> arbitrary::Arbitrary<'a> for Vector3D<T, U>
whereT: arbitrary::Arbitrary<'a>,
{fn arbitrary(u: &mut arbitrary::Unstructured<'a>) -> arbitrary::Result<Self> {let (x, y, z) = arbitrary::Arbitrary::arbitrary(u)?;Ok(Vector3D {x,y,z,_unit: PhantomData,})}
}#[cfg(feature = "bytemuck")]
unsafe impl<T: Zeroable, U> Zeroable for Vector3D<T, U> {}#[cfg(feature = "bytemuck")]
unsafe impl<T: Pod, U: 'static> Pod for Vector3D<T, U> {}impl<T: Eq, U> Eq for Vector3D<T, U> {}impl<T: PartialEq, U> PartialEq for Vector3D<T, U> {fn eq(&self, other: &Self) -> bool {self.x == other.x && self.y == other.y && self.z == other.z}
}impl<T: Hash, U> Hash for Vector3D<T, U> {fn hash<H: core::hash::Hasher>(&self, h: &mut H) {self.x.hash(h);self.y.hash(h);self.z.hash(h);}
}impl<T: Zero, U> Zero for Vector3D<T, U> {/// Constructor, setting all components to zero.#[inline]fn zero() -> Self {vec3(Zero::zero(), Zero::zero(), Zero::zero())}
}impl<T: fmt::Debug, U> fmt::Debug for Vector3D<T, U> {fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result {f.debug_tuple("").field(&self.x).field(&self.y).field(&self.z).finish()}
}impl<T: Default, U> Default for Vector3D<T, U> {fn default() -> Self {Vector3D::new(Default::default(), Default::default(), Default::default())}
}impl<T, U> Vector3D<T, U> {/// Constructor, setting all components to zero.#[inline]pub fn zero() -> SelfwhereT: Zero,{vec3(Zero::zero(), Zero::zero(), Zero::zero())}/// Constructor, setting all components to one.#[inline]pub fn one() -> SelfwhereT: One,{vec3(One::one(), One::one(), One::one())}/// Constructor taking scalar values directly.#[inline]pub const fn new(x: T, y: T, z: T) -> Self {Vector3D {x,y,z,_unit: PhantomData,}}/// Constructor setting all components to the same value.#[inline]pub fn splat(v: T) -> SelfwhereT: Clone,{Vector3D {x: v.clone(),y: v.clone(),z: v,_unit: PhantomData,}}/// Constructor taking properly Lengths instead of scalar values.#[inline]pub fn from_lengths(x: Length<T, U>, y: Length<T, U>, z: Length<T, U>) -> Vector3D<T, U> {vec3(x.0, y.0, z.0)}/// Tag a unitless value with units.#[inline]pub fn from_untyped(p: Vector3D<T, UnknownUnit>) -> Self {vec3(p.x, p.y, p.z)}/// Apply the function `f` to each component of this vector.////// # Example////// This may be used to perform unusual arithmetic which is not already offered as methods.////// ```/// use euclid::default::Vector3D;////// let p = Vector3D::<u32>::new(5, 11, 15);/// assert_eq!(p.map(|coord| coord.saturating_sub(10)), Vector3D::new(0, 1, 5));/// ```#[inline]pub fn map<V, F: FnMut(T) -> V>(self, mut f: F) -> Vector3D<V, U> {vec3(f(self.x), f(self.y), f(self.z))}/// Apply the function `f` to each pair of components of this point and `rhs`.////// # Example////// This may be used to perform unusual arithmetic which is not already offered as methods.////// ```/// use euclid::default::Vector3D;////// let a: Vector3D<u8> = Vector3D::new(50, 200, 10);/// let b: Vector3D<u8> = Vector3D::new(100, 100, 0);/// assert_eq!(a.zip(b, u8::saturating_add), Vector3D::new(150, 255, 10));/// ```#[inline]pub fn zip<V, F: FnMut(T, T) -> V>(self, rhs: Self, mut f: F) -> Vector3D<V, U> {vec3(f(self.x, rhs.x), f(self.y, rhs.y), f(self.z, rhs.z))}/// Computes the vector with absolute values of each component.////// # Example////// ```rust/// # use std::{i32, f32};/// # use euclid::vec3;/// enum U {}////// assert_eq!(vec3::<_, U>(-1, 0, 2).abs(), vec3(1, 0, 2));////// let vec = vec3::<_, U>(f32::NAN, 0.0, -f32::MAX).abs();/// assert!(vec.x.is_nan());/// assert_eq!(vec.y, 0.0);/// assert_eq!(vec.z, f32::MAX);/// ```////// # Panics////// The behavior for each component follows the scalar type's implementation of/// `num_traits::Signed::abs`.pub fn abs(self) -> SelfwhereT: Signed,{vec3(self.x.abs(), self.y.abs(), self.z.abs())}/// Dot product.#[inline]pub fn dot(self, other: Self) -> TwhereT: Add<Output = T> + Mul<Output = T>,{self.x * other.x + self.y * other.y + self.z * other.z}
}impl<T: Copy, U> Vector3D<T, U> {/// Cross product.#[inline]pub fn cross(self, other: Self) -> SelfwhereT: Sub<Output = T> + Mul<Output = T>,{vec3(self.y * other.z - self.z * other.y,self.z * other.x - self.x * other.z,self.x * other.y - self.y * other.x,)}/// Returns the component-wise multiplication of the two vectors.#[inline]pub fn component_mul(self, other: Self) -> SelfwhereT: Mul<Output = T>,{vec3(self.x * other.x, self.y * other.y, self.z * other.z)}/// Returns the component-wise division of the two vectors.#[inline]pub fn component_div(self, other: Self) -> SelfwhereT: Div<Output = T>,{vec3(self.x / other.x, self.y / other.y, self.z / other.z)}/// Cast this vector into a point.////// Equivalent to adding this vector to the origin.#[inline]pub fn to_point(self) -> Point3D<T, U> {point3(self.x, self.y, self.z)}/// Returns a 2d vector using this vector's x and y coordinates#[inline]pub fn xy(self) -> Vector2D<T, U> {vec2(self.x, self.y)}/// Returns a 2d vector using this vector's x and z coordinates#[inline]pub fn xz(self) -> Vector2D<T, U> {vec2(self.x, self.z)}/// Returns a 2d vector using this vector's x and z coordinates#[inline]pub fn yz(self) -> Vector2D<T, U> {vec2(self.y, self.z)}/// Cast into an array with x, y and z.#[inline]pub fn to_array(self) -> [T; 3] {[self.x, self.y, self.z]}/// Cast into an array with x, y, z and 0.#[inline]pub fn to_array_4d(self) -> [T; 4]whereT: Zero,{[self.x, self.y, self.z, Zero::zero()]}/// Cast into a tuple with x, y and z.#[inline]pub fn to_tuple(self) -> (T, T, T) {(self.x, self.y, self.z)}/// Cast into a tuple with x, y, z and 0.#[inline]pub fn to_tuple_4d(self) -> (T, T, T, T)whereT: Zero,{(self.x, self.y, self.z, Zero::zero())}/// Drop the units, preserving only the numeric value.#[inline]pub fn to_untyped(self) -> Vector3D<T, UnknownUnit> {vec3(self.x, self.y, self.z)}/// Cast the unit.#[inline]pub fn cast_unit<V>(self) -> Vector3D<T, V> {vec3(self.x, self.y, self.z)}/// Convert into a 2d vector.#[inline]pub fn to_2d(self) -> Vector2D<T, U> {self.xy()}/// Rounds each component to the nearest integer value.////// This behavior is preserved for negative values (unlike the basic cast).////// ```rust/// # use euclid::vec3;/// enum Mm {}////// assert_eq!(vec3::<_, Mm>(-0.1, -0.8, 0.4).round(), vec3::<_, Mm>(0.0, -1.0, 0.0))/// ```#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn round(self) -> SelfwhereT: Round,{vec3(self.x.round(), self.y.round(), self.z.round())}/// Rounds each component to the smallest integer equal or greater than the original value.////// This behavior is preserved for negative values (unlike the basic cast).////// ```rust/// # use euclid::vec3;/// enum Mm {}////// assert_eq!(vec3::<_, Mm>(-0.1, -0.8, 0.4).ceil(), vec3::<_, Mm>(0.0, 0.0, 1.0))/// ```#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn ceil(self) -> SelfwhereT: Ceil,{vec3(self.x.ceil(), self.y.ceil(), self.z.ceil())}/// Rounds each component to the biggest integer equal or lower than the original value.////// This behavior is preserved for negative values (unlike the basic cast).////// ```rust/// # use euclid::vec3;/// enum Mm {}////// assert_eq!(vec3::<_, Mm>(-0.1, -0.8, 0.4).floor(), vec3::<_, Mm>(-1.0, -1.0, 0.0))/// ```#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn floor(self) -> SelfwhereT: Floor,{vec3(self.x.floor(), self.y.floor(), self.z.floor())}/// Creates translation by this vector in vector units#[inline]pub fn to_transform(self) -> Transform3D<T, U, U>whereT: Zero + One,{Transform3D::translation(self.x, self.y, self.z)}
}impl<T, U> Vector3D<T, U>
whereT: Copy + Mul<T, Output = T> + Add<T, Output = T>,
{/// Returns the vector's length squared.#[inline]pub fn square_length(self) -> T {self.x * self.x + self.y * self.y + self.z * self.z}/// Returns this vector projected onto another one.////// Projecting onto a nil vector will cause a division by zero.#[inline]pub fn project_onto_vector(self, onto: Self) -> SelfwhereT: Sub<T, Output = T> + Div<T, Output = T>,{onto * (self.dot(onto) / onto.square_length())}
}impl<T: Float, U> Vector3D<T, U> {/// Return the normalized vector even if the length is larger than the max value of Float.#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn robust_normalize(self) -> Self {let length = self.length();if length.is_infinite() {let scaled = self / T::max_value();scaled / scaled.length()} else {self / length}}/// Returns `true` if all members are finite.#[inline]pub fn is_finite(self) -> bool {self.x.is_finite() && self.y.is_finite() && self.z.is_finite()}
}impl<T: Real, U> Vector3D<T, U> {/// Returns the positive angle between this vector and another vector.////// The returned angle is between 0 and PI.pub fn angle_to(self, other: Self) -> Angle<T>whereT: Trig,{Angle::radians(Trig::fast_atan2(self.cross(other).length(),self.dot(other),))}/// Returns the vector length.#[inline]pub fn length(self) -> T {self.square_length().sqrt()}/// Returns the vector with length of one unit#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn normalize(self) -> Self {self / self.length()}/// Returns the vector with length of one unit.////// Unlike [`Vector2D::normalize`], this returns `None` in the case that the/// length of the vector is zero.#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn try_normalize(self) -> Option<Self> {let len = self.length();if len == T::zero() {None} else {Some(self / len)}}/// Return this vector capped to a maximum length.#[inline]pub fn with_max_length(self, max_length: T) -> Self {let square_length = self.square_length();if square_length > max_length * max_length {return self * (max_length / square_length.sqrt());}self}/// Return this vector with a minimum length applied.#[inline]pub fn with_min_length(self, min_length: T) -> Self {let square_length = self.square_length();if square_length < min_length * min_length {return self * (min_length / square_length.sqrt());}self}/// Return this vector with minimum and maximum lengths applied.#[inline]pub fn clamp_length(self, min: T, max: T) -> Self {debug_assert!(min <= max);self.with_min_length(min).with_max_length(max)}
}impl<T, U> Vector3D<T, U>
whereT: Copy + One + Add<Output = T> + Sub<Output = T> + Mul<Output = T>,
{/// Linearly interpolate each component between this vector and another vector.////// # Example////// ```rust/// use euclid::vec3;/// use euclid::default::Vector3D;////// let from: Vector3D<_> = vec3(0.0, 10.0, -1.0);/// let to: Vector3D<_> = vec3(8.0, -4.0, 0.0);////// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, -1.0), vec3(-8.0, 24.0, -2.0));/// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, 0.0), vec3( 0.0, 10.0, -1.0));/// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, 0.5), vec3( 4.0, 3.0, -0.5));/// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, 1.0), vec3( 8.0, -4.0, 0.0));/// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, 2.0), vec3(16.0, -18.0, 1.0));/// ```#[inline]pub fn lerp(self, other: Self, t: T) -> Self {let one_t = T::one() - t;self * one_t + other * t}/// Returns a reflection vector using an incident ray and a surface normal.#[inline]pub fn reflect(self, normal: Self) -> Self {let two = T::one() + T::one();self - normal * two * self.dot(normal)}
}impl<T: PartialOrd, U> Vector3D<T, U> {/// Returns the vector each component of which are minimum of this vector and another.#[inline]pub fn min(self, other: Self) -> Self {vec3(min(self.x, other.x),min(self.y, other.y),min(self.z, other.z),)}/// Returns the vector each component of which are maximum of this vector and another.#[inline]pub fn max(self, other: Self) -> Self {vec3(max(self.x, other.x),max(self.y, other.y),max(self.z, other.z),)}/// Returns the vector each component of which is clamped by corresponding/// components of `start` and `end`.////// Shortcut for `self.max(start).min(end)`.#[inline]pub fn clamp(self, start: Self, end: Self) -> SelfwhereT: Copy,{self.max(start).min(end)}/// Returns vector with results of "greater than" operation on each component.#[inline]pub fn greater_than(self, other: Self) -> BoolVector3D {BoolVector3D {x: self.x > other.x,y: self.y > other.y,z: self.z > other.z,}}/// Returns vector with results of "lower than" operation on each component.#[inline]pub fn lower_than(self, other: Self) -> BoolVector3D {BoolVector3D {x: self.x < other.x,y: self.y < other.y,z: self.z < other.z,}}
}impl<T: PartialEq, U> Vector3D<T, U> {/// Returns vector with results of "equal" operation on each component.#[inline]pub fn equal(self, other: Self) -> BoolVector3D {BoolVector3D {x: self.x == other.x,y: self.y == other.y,z: self.z == other.z,}}/// Returns vector with results of "not equal" operation on each component.#[inline]pub fn not_equal(self, other: Self) -> BoolVector3D {BoolVector3D {x: self.x != other.x,y: self.y != other.y,z: self.z != other.z,}}
}impl<T: NumCast + Copy, U> Vector3D<T, U> {/// Cast from one numeric representation to another, preserving the units.////// When casting from floating vector to integer coordinates, the decimals are truncated/// as one would expect from a simple cast, but this behavior does not always make sense/// geometrically. Consider using `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before casting.#[inline]pub fn cast<NewT: NumCast>(self) -> Vector3D<NewT, U> {self.try_cast().unwrap()}/// Fallible cast from one numeric representation to another, preserving the units.////// When casting from floating vector to integer coordinates, the decimals are truncated/// as one would expect from a simple cast, but this behavior does not always make sense/// geometrically. Consider using `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before casting.pub fn try_cast<NewT: NumCast>(self) -> Option<Vector3D<NewT, U>> {match (NumCast::from(self.x),NumCast::from(self.y),NumCast::from(self.z),) {(Some(x), Some(y), Some(z)) => Some(vec3(x, y, z)),_ => None,}}// Convenience functions for common casts./// Cast into an `f32` vector.#[inline]pub fn to_f32(self) -> Vector3D<f32, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `f64` vector.#[inline]pub fn to_f64(self) -> Vector3D<f64, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `usize` vector, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating vector vectors, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_usize(self) -> Vector3D<usize, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `isize` vector, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating vector vectors, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_isize(self) -> Vector3D<isize, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `u32` vector, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating vector vectors, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_u32(self) -> Vector3D<u32, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `i32` vector, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating vector vectors, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_i32(self) -> Vector3D<i32, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `i64` vector, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating vector vectors, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_i64(self) -> Vector3D<i64, U> {self.cast()}
}impl<T: Neg, U> Neg for Vector3D<T, U> {type Output = Vector3D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn neg(self) -> Self::Output {vec3(-self.x, -self.y, -self.z)}
}impl<T: Add, U> Add for Vector3D<T, U> {type Output = Vector3D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn add(self, other: Self) -> Self::Output {vec3(self.x + other.x, self.y + other.y, self.z + other.z)}
}impl<'a, T: 'a + Add + Copy, U: 'a> Add<&Self> for Vector3D<T, U> {type Output = Vector3D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn add(self, other: &Self) -> Self::Output {vec3(self.x + other.x, self.y + other.y, self.z + other.z)}
}impl<T: Add<Output = T> + Zero, U> Sum for Vector3D<T, U> {fn sum<I: Iterator<Item = Self>>(iter: I) -> Self {iter.fold(Self::zero(), Add::add)}
}impl<'a, T: 'a + Add<Output = T> + Copy + Zero, U: 'a> Sum<&'a Self> for Vector3D<T, U> {fn sum<I: Iterator<Item = &'a Self>>(iter: I) -> Self {iter.fold(Self::zero(), Add::add)}
}impl<T: Copy + Add<T, Output = T>, U> AddAssign for Vector3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn add_assign(&mut self, other: Self) {*self = *self + other;}
}impl<T: Sub, U> Sub for Vector3D<T, U> {type Output = Vector3D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn sub(self, other: Self) -> Self::Output {vec3(self.x - other.x, self.y - other.y, self.z - other.z)}
}impl<T: Copy + Sub<T, Output = T>, U> SubAssign<Vector3D<T, U>> for Vector3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn sub_assign(&mut self, other: Self) {*self = *self - other;}
}impl<T: Copy + Mul, U> Mul<T> for Vector3D<T, U> {type Output = Vector3D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn mul(self, scale: T) -> Self::Output {vec3(self.x * scale, self.y * scale, self.z * scale)}
}impl<T: Copy + Mul<T, Output = T>, U> MulAssign<T> for Vector3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn mul_assign(&mut self, scale: T) {*self = *self * scale;}
}impl<T: Copy + Mul, U1, U2> Mul<Scale<T, U1, U2>> for Vector3D<T, U1> {type Output = Vector3D<T::Output, U2>;#[inline]fn mul(self, scale: Scale<T, U1, U2>) -> Self::Output {vec3(self.x * scale.0, self.y * scale.0, self.z * scale.0)}
}impl<T: Copy + MulAssign, U> MulAssign<Scale<T, U, U>> for Vector3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn mul_assign(&mut self, scale: Scale<T, U, U>) {self.x *= scale.0;self.y *= scale.0;self.z *= scale.0;}
}impl<T: Copy + Div, U> Div<T> for Vector3D<T, U> {type Output = Vector3D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn div(self, scale: T) -> Self::Output {vec3(self.x / scale, self.y / scale, self.z / scale)}
}impl<T: Copy + Div<T, Output = T>, U> DivAssign<T> for Vector3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn div_assign(&mut self, scale: T) {*self = *self / scale;}
}impl<T: Copy + Div, U1, U2> Div<Scale<T, U1, U2>> for Vector3D<T, U2> {type Output = Vector3D<T::Output, U1>;#[inline]fn div(self, scale: Scale<T, U1, U2>) -> Self::Output {vec3(self.x / scale.0, self.y / scale.0, self.z / scale.0)}
}impl<T: Copy + DivAssign, U> DivAssign<Scale<T, U, U>> for Vector3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn div_assign(&mut self, scale: Scale<T, U, U>) {self.x /= scale.0;self.y /= scale.0;self.z /= scale.0;}
}impl<T: Round, U> Round for Vector3D<T, U> {/// See [`Vector3D::round`].#[inline]fn round(self) -> Self {self.round()}
}impl<T: Ceil, U> Ceil for Vector3D<T, U> {/// See [`Vector3D::ceil`].#[inline]fn ceil(self) -> Self {self.ceil()}
}impl<T: Floor, U> Floor for Vector3D<T, U> {/// See [`Vector3D::floor`].#[inline]fn floor(self) -> Self {self.floor()}
}impl<T: ApproxEq<T>, U> ApproxEq<Vector3D<T, U>> for Vector3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn approx_epsilon() -> Self {vec3(T::approx_epsilon(),T::approx_epsilon(),T::approx_epsilon(),)}#[inline]fn approx_eq_eps(&self, other: &Self, eps: &Self) -> bool {self.x.approx_eq_eps(&other.x, &eps.x)&& self.y.approx_eq_eps(&other.y, &eps.y)&& self.z.approx_eq_eps(&other.z, &eps.z)}
}impl<T, U> From<Vector3D<T, U>> for [T; 3] {fn from(v: Vector3D<T, U>) -> Self {[v.x, v.y, v.z]}
}impl<T, U> From<[T; 3]> for Vector3D<T, U> {fn from([x, y, z]: [T; 3]) -> Self {vec3(x, y, z)}
}impl<T, U> From<Vector3D<T, U>> for (T, T, T) {fn from(v: Vector3D<T, U>) -> Self {(v.x, v.y, v.z)}
}impl<T, U> From<(T, T, T)> for Vector3D<T, U> {fn from(tuple: (T, T, T)) -> Self {vec3(tuple.0, tuple.1, tuple.2)}
}/// A 2d vector of booleans, useful for component-wise logic operations.
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq, Hash)]
pub struct BoolVector2D {pub x: bool,pub y: bool,
}/// A 3d vector of booleans, useful for component-wise logic operations.
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq, Hash)]
pub struct BoolVector3D {pub x: bool,pub y: bool,pub z: bool,
}impl BoolVector2D {/// Returns `true` if all components are `true` and `false` otherwise.#[inline]pub fn all(self) -> bool {self.x && self.y}/// Returns `true` if any component are `true` and `false` otherwise.#[inline]pub fn any(self) -> bool {self.x || self.y}/// Returns `true` if all components are `false` and `false` otherwise. Negation of `any()`.#[inline]pub fn none(self) -> bool {!self.any()}/// Returns new vector with by-component AND operation applied.#[inline]pub fn and(self, other: Self) -> Self {BoolVector2D {x: self.x && other.x,y: self.y && other.y,}}/// Returns new vector with by-component OR operation applied.#[inline]pub fn or(self, other: Self) -> Self {BoolVector2D {x: self.x || other.x,y: self.y || other.y,}}/// Returns new vector with results of negation operation on each component.#[inline]pub fn not(self) -> Self {BoolVector2D {x: !self.x,y: !self.y,}}/// Returns point, each component of which or from `a`, or from `b` depending on truly value/// of corresponding vector component. `true` selects value from `a` and `false` from `b`.#[inline]pub fn select_point<T, U>(self, a: Point2D<T, U>, b: Point2D<T, U>) -> Point2D<T, U> {point2(if self.x { a.x } else { b.x },if self.y { a.y } else { b.y },)}/// Returns vector, each component of which or from `a`, or from `b` depending on truly value/// of corresponding vector component. `true` selects value from `a` and `false` from `b`.#[inline]pub fn select_vector<T, U>(self, a: Vector2D<T, U>, b: Vector2D<T, U>) -> Vector2D<T, U> {vec2(if self.x { a.x } else { b.x },if self.y { a.y } else { b.y },)}/// Returns size, each component of which or from `a`, or from `b` depending on truly value/// of corresponding vector component. `true` selects value from `a` and `false` from `b`.#[inline]pub fn select_size<T, U>(self, a: Size2D<T, U>, b: Size2D<T, U>) -> Size2D<T, U> {size2(if self.x { a.width } else { b.width },if self.y { a.height } else { b.height },)}
}impl BoolVector3D {/// Returns `true` if all components are `true` and `false` otherwise.#[inline]pub fn all(self) -> bool {self.x && self.y && self.z}/// Returns `true` if any component are `true` and `false` otherwise.#[inline]pub fn any(self) -> bool {self.x || self.y || self.z}/// Returns `true` if all components are `false` and `false` otherwise. Negation of `any()`.#[inline]pub fn none(self) -> bool {!self.any()}/// Returns new vector with by-component AND operation applied.#[inline]pub fn and(self, other: Self) -> Self {BoolVector3D {x: self.x && other.x,y: self.y && other.y,z: self.z && other.z,}}/// Returns new vector with by-component OR operation applied.#[inline]pub fn or(self, other: Self) -> Self {BoolVector3D {x: self.x || other.x,y: self.y || other.y,z: self.z || other.z,}}/// Returns new vector with results of negation operation on each component.#[inline]pub fn not(self) -> Self {BoolVector3D {x: !self.x,y: !self.y,z: !self.z,}}/// Returns point, each component of which or from `a`, or from `b` depending on truly value/// of corresponding vector component. `true` selects value from `a` and `false` from `b`.#[inline]pub fn select_point<T, U>(self, a: Point3D<T, U>, b: Point3D<T, U>) -> Point3D<T, U> {point3(if self.x { a.x } else { b.x },if self.y { a.y } else { b.y },if self.z { a.z } else { b.z },)}/// Returns vector, each component of which or from `a`, or from `b` depending on truly value/// of corresponding vector component. `true` selects value from `a` and `false` from `b`.#[inline]pub fn select_vector<T, U>(self, a: Vector3D<T, U>, b: Vector3D<T, U>) -> Vector3D<T, U> {vec3(if self.x { a.x } else { b.x },if self.y { a.y } else { b.y },if self.z { a.z } else { b.z },)}/// Returns size, each component of which or from `a`, or from `b` depending on truly value/// of corresponding vector component. `true` selects value from `a` and `false` from `b`.#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn select_size<T, U>(self, a: Size3D<T, U>, b: Size3D<T, U>) -> Size3D<T, U> {size3(if self.x { a.width } else { b.width },if self.y { a.height } else { b.height },if self.z { a.depth } else { b.depth },)}/// Returns a 2d vector using this vector's x and y coordinates.#[inline]pub fn xy(self) -> BoolVector2D {BoolVector2D {x: self.x,y: self.y,}}/// Returns a 2d vector using this vector's x and z coordinates.#[inline]pub fn xz(self) -> BoolVector2D {BoolVector2D {x: self.x,y: self.z,}}/// Returns a 2d vector using this vector's y and z coordinates.#[inline]pub fn yz(self) -> BoolVector2D {BoolVector2D {x: self.y,y: self.z,}}
}#[cfg(feature = "arbitrary")]
impl<'a> arbitrary::Arbitrary<'a> for BoolVector2D {fn arbitrary(u: &mut arbitrary::Unstructured<'a>) -> arbitrary::Result<Self> {Ok(BoolVector2D {x: arbitrary::Arbitrary::arbitrary(u)?,y: arbitrary::Arbitrary::arbitrary(u)?,})}
}#[cfg(feature = "arbitrary")]
impl<'a> arbitrary::Arbitrary<'a> for BoolVector3D {fn arbitrary(u: &mut arbitrary::Unstructured<'a>) -> arbitrary::Result<Self> {Ok(BoolVector3D {x: arbitrary::Arbitrary::arbitrary(u)?,y: arbitrary::Arbitrary::arbitrary(u)?,z: arbitrary::Arbitrary::arbitrary(u)?,})}
}/// Convenience constructor.
#[inline]
pub const fn vec2<T, U>(x: T, y: T) -> Vector2D<T, U> {Vector2D {x,y,_unit: PhantomData,}
}/// Convenience constructor.
#[inline]
pub const fn vec3<T, U>(x: T, y: T, z: T) -> Vector3D<T, U> {Vector3D {x,y,z,_unit: PhantomData,}
}/// Shorthand for `BoolVector2D { x, y }`.
#[inline]
pub const fn bvec2(x: bool, y: bool) -> BoolVector2D {BoolVector2D { x, y }
}/// Shorthand for `BoolVector3D { x, y, z }`.
#[inline]
pub const fn bvec3(x: bool, y: bool, z: bool) -> BoolVector3D {BoolVector3D { x, y, z }
}#[cfg(test)]
mod vector2d {use crate::scale::Scale;use crate::{default, vec2};#[cfg(feature = "mint")]use mint;type Vec2 = default::Vector2D<f32>;#[test]pub fn test_scalar_mul() {let p1: Vec2 = vec2(3.0, 5.0);let result = p1 * 5.0;assert_eq!(result, Vec2::new(15.0, 25.0));}#[test]pub fn test_dot() {let p1: Vec2 = vec2(2.0, 7.0);let p2: Vec2 = vec2(13.0, 11.0);assert_eq!(p1.dot(p2), 103.0);}#[test]pub fn test_cross() {let p1: Vec2 = vec2(4.0, 7.0);let p2: Vec2 = vec2(13.0, 8.0);let r = p1.cross(p2);assert_eq!(r, -59.0);}#[test]pub fn test_normalize() {use std::f32;let p0: Vec2 = Vec2::zero();let p1: Vec2 = vec2(4.0, 0.0);let p2: Vec2 = vec2(3.0, -4.0);assert!(p0.normalize().x.is_nan() && p0.normalize().y.is_nan());assert_eq!(p1.normalize(), vec2(1.0, 0.0));assert_eq!(p2.normalize(), vec2(0.6, -0.8));let p3: Vec2 = vec2(::std::f32::MAX, ::std::f32::MAX);assert_ne!(p3.normalize(),vec2(1.0 / 2.0f32.sqrt(), 1.0 / 2.0f32.sqrt()));assert_eq!(p3.robust_normalize(),vec2(1.0 / 2.0f32.sqrt(), 1.0 / 2.0f32.sqrt()));let p4: Vec2 = Vec2::zero();assert!(p4.try_normalize().is_none());let p5: Vec2 = Vec2::new(f32::MIN_POSITIVE, f32::MIN_POSITIVE);assert!(p5.try_normalize().is_none());let p6: Vec2 = vec2(4.0, 0.0);let p7: Vec2 = vec2(3.0, -4.0);assert_eq!(p6.try_normalize().unwrap(), vec2(1.0, 0.0));assert_eq!(p7.try_normalize().unwrap(), vec2(0.6, -0.8));}#[test]pub fn test_min() {let p1: Vec2 = vec2(1.0, 3.0);let p2: Vec2 = vec2(2.0, 2.0);let result = p1.min(p2);assert_eq!(result, vec2(1.0, 2.0));}#[test]pub fn test_max() {let p1: Vec2 = vec2(1.0, 3.0);let p2: Vec2 = vec2(2.0, 2.0);let result = p1.max(p2);assert_eq!(result, vec2(2.0, 3.0));}#[test]pub fn test_angle_from_x_axis() {use crate::approxeq::ApproxEq;use core::f32::consts::FRAC_PI_2;let right: Vec2 = vec2(10.0, 0.0);let down: Vec2 = vec2(0.0, 4.0);let up: Vec2 = vec2(0.0, -1.0);assert!(right.angle_from_x_axis().get().approx_eq(&0.0));assert!(down.angle_from_x_axis().get().approx_eq(&FRAC_PI_2));assert!(up.angle_from_x_axis().get().approx_eq(&-FRAC_PI_2));}#[test]pub fn test_angle_to() {use crate::approxeq::ApproxEq;use core::f32::consts::FRAC_PI_2;let right: Vec2 = vec2(10.0, 0.0);let right2: Vec2 = vec2(1.0, 0.0);let up: Vec2 = vec2(0.0, -1.0);let up_left: Vec2 = vec2(-1.0, -1.0);assert!(right.angle_to(right2).get().approx_eq(&0.0));assert!(right.angle_to(up).get().approx_eq(&-FRAC_PI_2));assert!(up.angle_to(right).get().approx_eq(&FRAC_PI_2));assert!(up_left.angle_to(up).get().approx_eq_eps(&(0.5 * FRAC_PI_2), &0.0005));}#[test]pub fn test_with_max_length() {use crate::approxeq::ApproxEq;let v1: Vec2 = vec2(0.5, 0.5);let v2: Vec2 = vec2(1.0, 0.0);let v3: Vec2 = vec2(0.1, 0.2);let v4: Vec2 = vec2(2.0, -2.0);let v5: Vec2 = vec2(1.0, 2.0);let v6: Vec2 = vec2(-1.0, 3.0);assert_eq!(v1.with_max_length(1.0), v1);assert_eq!(v2.with_max_length(1.0), v2);assert_eq!(v3.with_max_length(1.0), v3);assert_eq!(v4.with_max_length(10.0), v4);assert_eq!(v5.with_max_length(10.0), v5);assert_eq!(v6.with_max_length(10.0), v6);let v4_clamped = v4.with_max_length(1.0);assert!(v4_clamped.length().approx_eq(&1.0));assert!(v4_clamped.normalize().approx_eq(&v4.normalize()));let v5_clamped = v5.with_max_length(1.5);assert!(v5_clamped.length().approx_eq(&1.5));assert!(v5_clamped.normalize().approx_eq(&v5.normalize()));let v6_clamped = v6.with_max_length(2.5);assert!(v6_clamped.length().approx_eq(&2.5));assert!(v6_clamped.normalize().approx_eq(&v6.normalize()));}#[test]pub fn test_project_onto_vector() {use crate::approxeq::ApproxEq;let v1: Vec2 = vec2(1.0, 2.0);let x: Vec2 = vec2(1.0, 0.0);let y: Vec2 = vec2(0.0, 1.0);assert!(v1.project_onto_vector(x).approx_eq(&vec2(1.0, 0.0)));assert!(v1.project_onto_vector(y).approx_eq(&vec2(0.0, 2.0)));assert!(v1.project_onto_vector(-x).approx_eq(&vec2(1.0, 0.0)));assert!(v1.project_onto_vector(x * 10.0).approx_eq(&vec2(1.0, 0.0)));assert!(v1.project_onto_vector(v1 * 2.0).approx_eq(&v1));assert!(v1.project_onto_vector(-v1).approx_eq(&v1));}#[cfg(feature = "mint")]#[test]pub fn test_mint() {let v1 = Vec2::new(1.0, 3.0);let vm: mint::Vector2<_> = v1.into();let v2 = Vec2::from(vm);assert_eq!(v1, v2);}pub enum Mm {}pub enum Cm {}pub type Vector2DMm<T> = super::Vector2D<T, Mm>;pub type Vector2DCm<T> = super::Vector2D<T, Cm>;#[test]pub fn test_add() {let p1 = Vector2DMm::new(1.0, 2.0);let p2 = Vector2DMm::new(3.0, 4.0);assert_eq!(p1 + p2, vec2(4.0, 6.0));assert_eq!(p1 + &p2, vec2(4.0, 6.0));}#[test]pub fn test_sum() {let vecs = [Vector2DMm::new(1.0, 2.0),Vector2DMm::new(3.0, 4.0),Vector2DMm::new(5.0, 6.0),];let sum = Vector2DMm::new(9.0, 12.0);assert_eq!(vecs.iter().sum::<Vector2DMm<_>>(), sum);}#[test]pub fn test_add_assign() {let mut p1 = Vector2DMm::new(1.0, 2.0);p1 += vec2(3.0, 4.0);assert_eq!(p1, vec2(4.0, 6.0));}#[test]pub fn test_typed_scalar_mul() {let p1 = Vector2DMm::new(1.0, 2.0);let cm_per_mm = Scale::<f32, Mm, Cm>::new(0.1);let result: Vector2DCm<f32> = p1 * cm_per_mm;assert_eq!(result, vec2(0.1, 0.2));}#[test]pub fn test_swizzling() {let p: default::Vector2D<i32> = vec2(1, 2);assert_eq!(p.yx(), vec2(2, 1));}#[test]pub fn test_reflect() {use crate::approxeq::ApproxEq;let a: Vec2 = vec2(1.0, 3.0);let n1: Vec2 = vec2(0.0, -1.0);let n2: Vec2 = vec2(1.0, -1.0).normalize();assert!(a.reflect(n1).approx_eq(&vec2(1.0, -3.0)));assert!(a.reflect(n2).approx_eq(&vec2(3.0, 1.0)));}
}#[cfg(test)]
mod vector3d {use crate::scale::Scale;use crate::{default, vec2, vec3};#[cfg(feature = "mint")]use mint;type Vec3 = default::Vector3D<f32>;#[test]pub fn test_add() {let p1 = Vec3::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);let p2 = Vec3::new(4.0, 5.0, 6.0);assert_eq!(p1 + p2, vec3(5.0, 7.0, 9.0));assert_eq!(p1 + &p2, vec3(5.0, 7.0, 9.0));}#[test]pub fn test_sum() {let vecs = [Vec3::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0),Vec3::new(4.0, 5.0, 6.0),Vec3::new(7.0, 8.0, 9.0),];let sum = Vec3::new(12.0, 15.0, 18.0);assert_eq!(vecs.iter().sum::<Vec3>(), sum);}#[test]pub fn test_dot() {let p1: Vec3 = vec3(7.0, 21.0, 32.0);let p2: Vec3 = vec3(43.0, 5.0, 16.0);assert_eq!(p1.dot(p2), 918.0);}#[test]pub fn test_cross() {let p1: Vec3 = vec3(4.0, 7.0, 9.0);let p2: Vec3 = vec3(13.0, 8.0, 3.0);let p3 = p1.cross(p2);assert_eq!(p3, vec3(-51.0, 105.0, -59.0));}#[test]pub fn test_normalize() {use std::f32;let p0: Vec3 = Vec3::zero();let p1: Vec3 = vec3(0.0, -6.0, 0.0);let p2: Vec3 = vec3(1.0, 2.0, -2.0);assert!(p0.normalize().x.is_nan() && p0.normalize().y.is_nan() && p0.normalize().z.is_nan());assert_eq!(p1.normalize(), vec3(0.0, -1.0, 0.0));assert_eq!(p2.normalize(), vec3(1.0 / 3.0, 2.0 / 3.0, -2.0 / 3.0));let p3: Vec3 = vec3(::std::f32::MAX, ::std::f32::MAX, 0.0);assert_ne!(p3.normalize(),vec3(1.0 / 2.0f32.sqrt(), 1.0 / 2.0f32.sqrt(), 0.0));assert_eq!(p3.robust_normalize(),vec3(1.0 / 2.0f32.sqrt(), 1.0 / 2.0f32.sqrt(), 0.0));let p4: Vec3 = Vec3::zero();assert!(p4.try_normalize().is_none());let p5: Vec3 = Vec3::new(f32::MIN_POSITIVE, f32::MIN_POSITIVE, f32::MIN_POSITIVE);assert!(p5.try_normalize().is_none());let p6: Vec3 = vec3(4.0, 0.0, 3.0);let p7: Vec3 = vec3(3.0, -4.0, 0.0);assert_eq!(p6.try_normalize().unwrap(), vec3(0.8, 0.0, 0.6));assert_eq!(p7.try_normalize().unwrap(), vec3(0.6, -0.8, 0.0));}#[test]pub fn test_min() {let p1: Vec3 = vec3(1.0, 3.0, 5.0);let p2: Vec3 = vec3(2.0, 2.0, -1.0);let result = p1.min(p2);assert_eq!(result, vec3(1.0, 2.0, -1.0));}#[test]pub fn test_max() {let p1: Vec3 = vec3(1.0, 3.0, 5.0);let p2: Vec3 = vec3(2.0, 2.0, -1.0);let result = p1.max(p2);assert_eq!(result, vec3(2.0, 3.0, 5.0));}#[test]pub fn test_clamp() {let p1: Vec3 = vec3(1.0, -1.0, 5.0);let p2: Vec3 = vec3(2.0, 5.0, 10.0);let p3: Vec3 = vec3(-1.0, 2.0, 20.0);let result = p3.clamp(p1, p2);assert_eq!(result, vec3(1.0, 2.0, 10.0));}#[test]pub fn test_typed_scalar_mul() {enum Mm {}enum Cm {}let p1 = super::Vector3D::<f32, Mm>::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);let cm_per_mm = Scale::<f32, Mm, Cm>::new(0.1);let result: super::Vector3D<f32, Cm> = p1 * cm_per_mm;assert_eq!(result, vec3(0.1, 0.2, 0.3));}#[test]pub fn test_swizzling() {let p: Vec3 = vec3(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);assert_eq!(p.xy(), vec2(1.0, 2.0));assert_eq!(p.xz(), vec2(1.0, 3.0));assert_eq!(p.yz(), vec2(2.0, 3.0));}#[cfg(feature = "mint")]#[test]pub fn test_mint() {let v1 = Vec3::new(1.0, 3.0, 5.0);let vm: mint::Vector3<_> = v1.into();let v2 = Vec3::from(vm);assert_eq!(v1, v2);}#[test]pub fn test_reflect() {use crate::approxeq::ApproxEq;let a: Vec3 = vec3(1.0, 3.0, 2.0);let n1: Vec3 = vec3(0.0, -1.0, 0.0);let n2: Vec3 = vec3(0.0, 1.0, 1.0).normalize();assert!(a.reflect(n1).approx_eq(&vec3(1.0, -3.0, 2.0)));assert!(a.reflect(n2).approx_eq(&vec3(1.0, -2.0, -3.0)));}#[test]pub fn test_angle_to() {use crate::approxeq::ApproxEq;use core::f32::consts::FRAC_PI_2;let right: Vec3 = vec3(10.0, 0.0, 0.0);let right2: Vec3 = vec3(1.0, 0.0, 0.0);let up: Vec3 = vec3(0.0, -1.0, 0.0);let up_left: Vec3 = vec3(-1.0, -1.0, 0.0);assert!(right.angle_to(right2).get().approx_eq(&0.0));assert!(right.angle_to(up).get().approx_eq(&FRAC_PI_2));assert!(up.angle_to(right).get().approx_eq(&FRAC_PI_2));assert!(up_left.angle_to(up).get().approx_eq_eps(&(0.5 * FRAC_PI_2), &0.0005));}#[test]pub fn test_with_max_length() {use crate::approxeq::ApproxEq;let v1: Vec3 = vec3(0.5, 0.5, 0.0);let v2: Vec3 = vec3(1.0, 0.0, 0.0);let v3: Vec3 = vec3(0.1, 0.2, 0.3);let v4: Vec3 = vec3(2.0, -2.0, 2.0);let v5: Vec3 = vec3(1.0, 2.0, -3.0);let v6: Vec3 = vec3(-1.0, 3.0, 2.0);assert_eq!(v1.with_max_length(1.0), v1);assert_eq!(v2.with_max_length(1.0), v2);assert_eq!(v3.with_max_length(1.0), v3);assert_eq!(v4.with_max_length(10.0), v4);assert_eq!(v5.with_max_length(10.0), v5);assert_eq!(v6.with_max_length(10.0), v6);let v4_clamped = v4.with_max_length(1.0);assert!(v4_clamped.length().approx_eq(&1.0));assert!(v4_clamped.normalize().approx_eq(&v4.normalize()));let v5_clamped = v5.with_max_length(1.5);assert!(v5_clamped.length().approx_eq(&1.5));assert!(v5_clamped.normalize().approx_eq(&v5.normalize()));let v6_clamped = v6.with_max_length(2.5);assert!(v6_clamped.length().approx_eq(&2.5));assert!(v6_clamped.normalize().approx_eq(&v6.normalize()));}#[test]pub fn test_project_onto_vector() {use crate::approxeq::ApproxEq;let v1: Vec3 = vec3(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);let x: Vec3 = vec3(1.0, 0.0, 0.0);let y: Vec3 = vec3(0.0, 1.0, 0.0);let z: Vec3 = vec3(0.0, 0.0, 1.0);assert!(v1.project_onto_vector(x).approx_eq(&vec3(1.0, 0.0, 0.0)));assert!(v1.project_onto_vector(y).approx_eq(&vec3(0.0, 2.0, 0.0)));assert!(v1.project_onto_vector(z).approx_eq(&vec3(0.0, 0.0, 3.0)));assert!(v1.project_onto_vector(-x).approx_eq(&vec3(1.0, 0.0, 0.0)));assert!(v1.project_onto_vector(x * 10.0).approx_eq(&vec3(1.0, 0.0, 0.0)));assert!(v1.project_onto_vector(v1 * 2.0).approx_eq(&v1));assert!(v1.project_onto_vector(-v1).approx_eq(&v1));}
}#[cfg(test)]
mod bool_vector {use super::*;use crate::default;type Vec2 = default::Vector2D<f32>;type Vec3 = default::Vector3D<f32>;#[test]fn test_bvec2() {assert_eq!(Vec2::new(1.0, 2.0).greater_than(Vec2::new(2.0, 1.0)),bvec2(false, true),);assert_eq!(Vec2::new(1.0, 2.0).lower_than(Vec2::new(2.0, 1.0)),bvec2(true, false),);assert_eq!(Vec2::new(1.0, 2.0).equal(Vec2::new(1.0, 3.0)),bvec2(true, false),);assert_eq!(Vec2::new(1.0, 2.0).not_equal(Vec2::new(1.0, 3.0)),bvec2(false, true),);assert!(bvec2(true, true).any());assert!(bvec2(false, true).any());assert!(bvec2(true, false).any());assert!(!bvec2(false, false).any());assert!(bvec2(false, false).none());assert!(bvec2(true, true).all());assert!(!bvec2(false, true).all());assert!(!bvec2(true, false).all());assert!(!bvec2(false, false).all());assert_eq!(bvec2(true, false).not(), bvec2(false, true));assert_eq!(bvec2(true, false).and(bvec2(true, true)),bvec2(true, false));assert_eq!(bvec2(true, false).or(bvec2(true, true)), bvec2(true, true));assert_eq!(bvec2(true, false).select_vector(Vec2::new(1.0, 2.0), Vec2::new(3.0, 4.0)),Vec2::new(1.0, 4.0),);}#[test]fn test_bvec3() {assert_eq!(Vec3::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0).greater_than(Vec3::new(3.0, 2.0, 1.0)),bvec3(false, false, true),);assert_eq!(Vec3::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0).lower_than(Vec3::new(3.0, 2.0, 1.0)),bvec3(true, false, false),);assert_eq!(Vec3::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0).equal(Vec3::new(3.0, 2.0, 1.0)),bvec3(false, true, false),);assert_eq!(Vec3::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0).not_equal(Vec3::new(3.0, 2.0, 1.0)),bvec3(true, false, true),);assert!(bvec3(true, true, false).any());assert!(bvec3(false, true, false).any());assert!(bvec3(true, false, false).any());assert!(!bvec3(false, false, false).any());assert!(bvec3(false, false, false).none());assert!(bvec3(true, true, true).all());assert!(!bvec3(false, true, false).all());assert!(!bvec3(true, false, false).all());assert!(!bvec3(false, false, false).all());assert_eq!(bvec3(true, false, true).not(), bvec3(false, true, false));assert_eq!(bvec3(true, false, true).and(bvec3(true, true, false)),bvec3(true, false, false));assert_eq!(bvec3(true, false, false).or(bvec3(true, true, false)),bvec3(true, true, false));assert_eq!(bvec3(true, false, true).select_vector(Vec3::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0), Vec3::new(4.0, 5.0, 6.0)),Vec3::new(1.0, 5.0, 3.0),);}
}
二、说明
Vector2D、Vector3D比Point2D、Point3D有更多方法,建议修改为Point2D、Point3D别名,效果更佳。
相关文章:
)
12 向量结构模块(vector.rs)
一vector.rs源码 // Copyright 2013 The Servo Project Developers. See the COPYRIGHT // file at the top-level directory of this distribution. // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 <LICENSE-APACHE or // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE…...
编译讯为3568开发板安卓)
Android车机DIY开发之学习篇(六)编译讯为3568开发板安卓
Android车机DIY开发之学习篇(六)编译讯为3568开发板安卓 1.SDK解压到家目录下的 rk3588_android_sdk 目录 一. 全部编译 ###安装所需环境 sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install git-core gnupg flex bison gperf build-essential zip curl zlib1g-dev gcc-multilib g…...
 E. Living Sequence)
Codeforces Round 863 (Div. 3) E. Living Sequence
题目链接 头一回用不是正解的方法做出来,也是比较极限,直接说做法就是二分数位dp 数位 d p dp dp 求 1 − n 1-n 1−n出现多少含 4 4 4的数字个数 这纯纯板子了 \sout{这纯纯板子了} 这纯纯板子了 设 f ( x ) f(x) f(x) 为 1 − x 1-x 1−x 中含有4的…...

一文讲解HashMap线程安全相关问题(上)
HashMap不是线程安全的,主要有以下几个问题: ①、多线程下扩容会死循环。JDK1.7 中的 HashMap 使用的是头插法插入元素,在多线程的环境下,扩容的时候就有可能导致出现环形链表,造成死循环。 JDK 8 时已经修复了这个问…...

MFC 创建Ribbon样式窗口
然后点击下一步直到完成即可...

uv 安装包
是的,你可以使用 uv 来安装 Python 包。uv 是一个高性能的 Python 包安装器和解析器,由 astral.sh 团队开发,旨在替代 pip 和 pip-tools,提供更快的包安装体验。 ### 如何使用 uv 安装包 1. **安装 uv**: 如果你还…...

IELTS口语练习题库
IELTS口语1-4月题库 Part 1 Gifts Have you ever sent handmade gifts to others? Yes, I have. I once made a scrapbook for my best friend’s birthday. It included photos of our memories together and some handwritten notes. She loved it because it was personal…...

图书管理系统 Axios 源码__获取图书列表
目录 核心功能 源码介绍 1. 获取图书列表 技术要点 适用人群 本项目是一个基于 HTML Bootstrap JavaScript Axios 开发的图书管理系统,可用于 添加、编辑、删除和管理图书信息,适合前端开发者学习 前端交互设计、Axios 数据请求 以及 Bootstrap 样…...

基于OSAL的嵌入式裸机事件驱动框架——整体架构调度机制
参考B站up主【架构分析】嵌入式祼机事件驱动框架 感谢大佬分享 任务ID : TASK_XXX TASK_XXX 在系统中每个任务的ID是唯一的,范围是 0 to 0xFFFE,0xFFFF保留为SYS_TSK_INIT。 同时任务ID的大小也充当任务调度的优先级,ID越大&#…...

c++ string类 +底层模拟实现
提醒: 本片博客只是小编的听课笔记,介意勿看。 基础 包含在头文件<string>,才能使用string类似函数接口。 string常见构造类 string s1; cin>>s1;//无参构造 string s2(s1);//拷贝构造 string s1("jfksa");//传参构造 三种…...

六十分之三十七——一转眼、时光飞逝
一、目标 明确可落地,对于自身执行完成需要一定的努力才可以完成的 1.第三版分组、激励、立体化权限、智能设备、AIPPT做课 2.8本书 3.得到:头条、吴军来信2、卓克科技参考3 4.总结思考 二、计划 科学规律的,要结合番茄工作法、快速阅读、…...

Shell基础:中括号的使用
在Shell脚本中,中括号([ ... ] 和 [[ ... ]])是一种常见的条件测试结构。它们用于进行文件类型检查、值比较以及逻辑判断。通过了解它们的不同特点和用法,能够帮助你编写更加高效、安全且易读的脚本。本文将详细介绍Shell中单中括…...

《基于Scapy的综合性网络扫描与通信工具集解析》
在网络管理和安全评估中,网络扫描和通信是两个至关重要的环节。Python 的 Scapy 库因其强大的网络数据包处理能力,成为开发和实现这些功能的理想工具。本文将介绍一个基于 Scapy 编写的 Python 脚本,该脚本集成了 ARP 扫描、端口扫描以及 TCP…...

面经--C语言——sizeof和strlen,数组和链表,#include <>和 #include ““ #define 和typedef 内存对齐概述
文章目录 sizeof 和 strlen数组和链表总结 #include <>和 #include ""#define 和typedef内存对齐概述对齐规则示例:结构体的内存对齐分析: 内存对齐的常见规则:填充字节的计算对齐影响的实际例子 sizeof 和 strlen 特性size…...

使用 Kotlin 将 Vertx 和 Springboot 整合
本篇文章目的是将 Springboot 和 Vertx 进行简单整合。整合目的仅仅是为了整活,因为两个不同的东西整合在一起提升的性能并没有只使用 Vertx 性能高,因此追求高性能的话这是在我来说不推荐。而且他们不仅没有提高很多性能甚至增加了学习成本 一、整合流…...

线性回归算法-01
线性回归简介 学习目标 了解线性回归的应用场景知道线性回归的定义 1 线性回归应用场景 房价预测销售额度预测贷款额度预测 2 什么是线性回归 2.1 定义与公式 线性回归(Linear regression)是利用 回归方程(函数)对 一个或多个自变量(特征值)和因变量(目标值)之间关系进行建模…...

洛谷 P1130 红牌 C语言
题目描述 某地临时居民想获得长期居住权就必须申请拿到红牌。获得红牌的过程是相当复杂,一共包括 N 个步骤。每一步骤都由政府的某个工作人员负责检查你所提交的材料是否符合条件。为了加快进程,每一步政府都派了 M 个工作人员来检查材料。不幸的是&…...

虚幻UE5手机安卓Android Studio开发设置2025
一、下载Android Studio历史版本 步骤1:虚幻4.27、5.0、5.1、5.2官方要求Andrd Studio 4.0版本; 5.3、5.4、5.5官方要求的版本为Android Studio Flamingo | 2022.2.1 Patch 2 May 24, 2023 虚幻官网查看对应Andrd Studiob下载版本: https:/…...

线性代数复习笔记
1. 课程学习 1.1 3Blue1Brown 线性代数 2. 基本术语 eigenvector(特征向量):线性变换中方向保持不变的向量 可以视作3D旋转矩阵形成的旋转的轴...

你需要更深层次的解放
先谈一谈理性认知中的属性替换原则。简单来说,属性替换就是用简单的问题取代难题。 当人们需要评估属性A时,却发现评估属性B更容易一些(A与B之间存在一定的关系),于是就改为评估属性B。这叫做属性替换。 作为一种认知…...
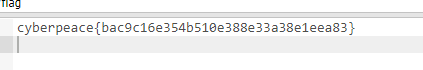
XCTF-web-easyupload
试了试php,php7,pht,phtml等,都没有用 尝试.user.ini 抓包修改将.user.ini修改为jpg图片 在上传一个123.jpg 用蚁剑连接,得到flag...

Python爬虫实战:研究feedparser库相关技术
1. 引言 1.1 研究背景与意义 在当今信息爆炸的时代,互联网上存在着海量的信息资源。RSS(Really Simple Syndication)作为一种标准化的信息聚合技术,被广泛用于网站内容的发布和订阅。通过 RSS,用户可以方便地获取网站更新的内容,而无需频繁访问各个网站。 然而,互联网…...

蓝桥杯 2024 15届国赛 A组 儿童节快乐
P10576 [蓝桥杯 2024 国 A] 儿童节快乐 题目描述 五彩斑斓的气球在蓝天下悠然飘荡,轻快的音乐在耳边持续回荡,小朋友们手牵着手一同畅快欢笑。在这样一片安乐祥和的氛围下,六一来了。 今天是六一儿童节,小蓝老师为了让大家在节…...

Leetcode 3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations
Leetcode 3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations 1. 解题思路2. 代码实现 题目链接:3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations 1. 解题思路 这一题其实就是一个脑筋急转弯,要想要能够将所有的电脑解锁&#x…...
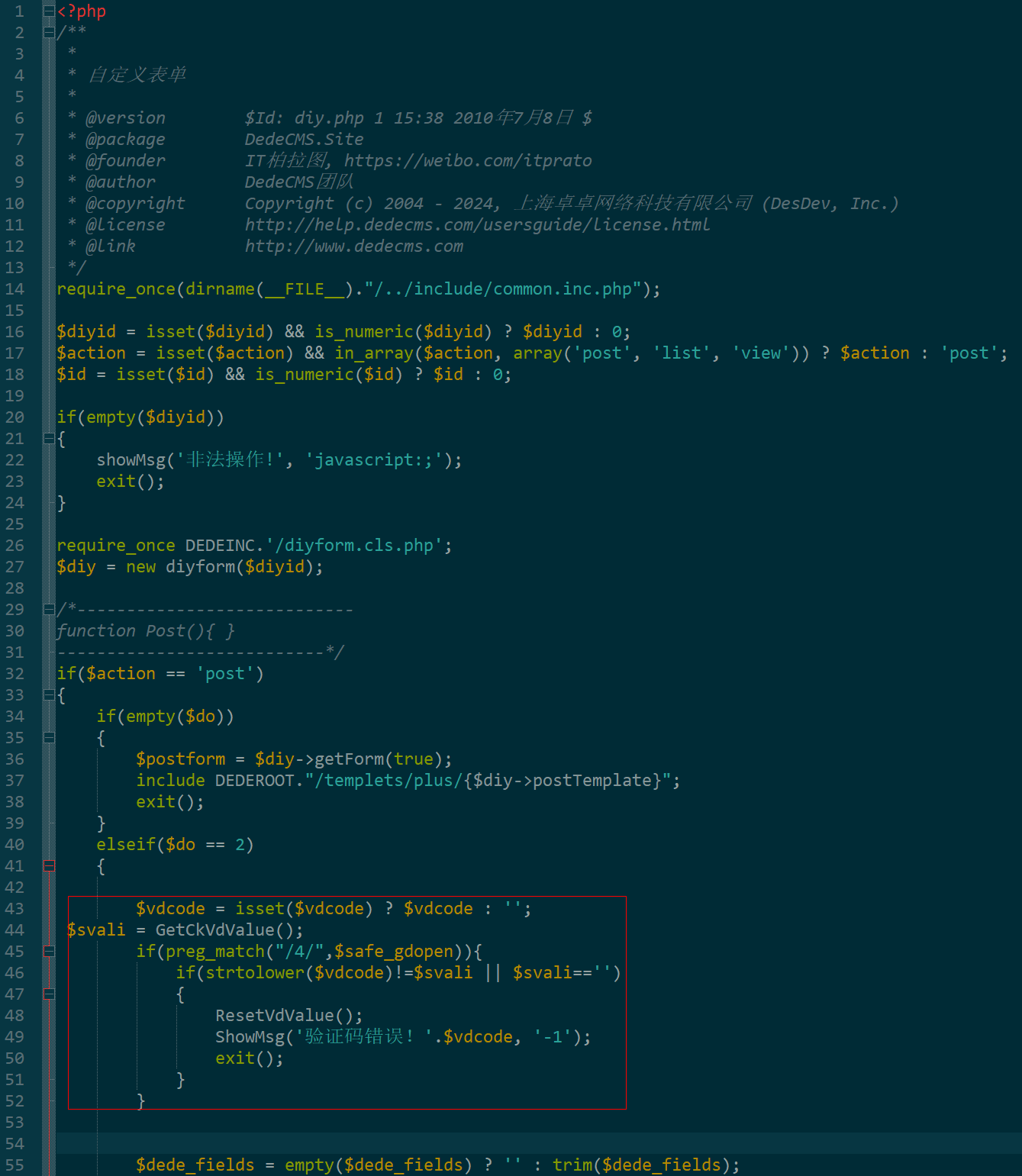
dedecms 织梦自定义表单留言增加ajax验证码功能
增加ajax功能模块,用户不点击提交按钮,只要输入框失去焦点,就会提前提示验证码是否正确。 一,模板上增加验证码 <input name"vdcode"id"vdcode" placeholder"请输入验证码" type"text&quo…...

Nginx server_name 配置说明
Nginx 是一个高性能的反向代理和负载均衡服务器,其核心配置之一是 server 块中的 server_name 指令。server_name 决定了 Nginx 如何根据客户端请求的 Host 头匹配对应的虚拟主机(Virtual Host)。 1. 简介 Nginx 使用 server_name 指令来确定…...
selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】
selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】 文章目录 selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】一、声明二、学习目标三、安装依赖3.1 安装selenium库3.2 安装浏览器驱动3.2.1 查看Edge版本3.2.2 驱动安装 四、代码讲解4.1 配置浏览器4.2 加载更多4.3 寻找内容4.4 完整代码 五、报告文件爬取5.1 提…...
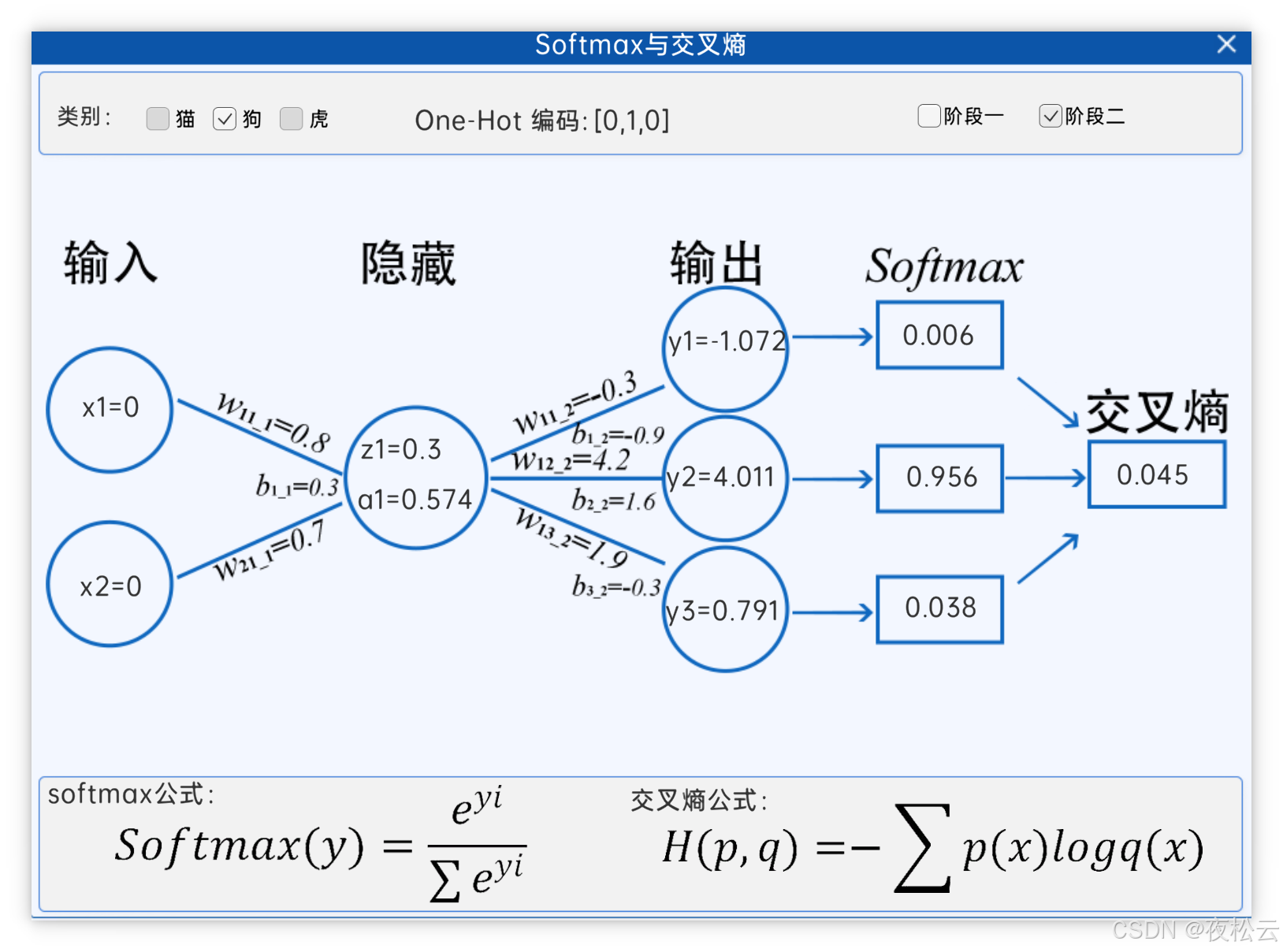
深入浅出深度学习基础:从感知机到全连接神经网络的核心原理与应用
文章目录 前言一、感知机 (Perceptron)1.1 基础介绍1.1.1 感知机是什么?1.1.2 感知机的工作原理 1.2 感知机的简单应用:基本逻辑门1.2.1 逻辑与 (Logic AND)1.2.2 逻辑或 (Logic OR)1.2.3 逻辑与非 (Logic NAND) 1.3 感知机的实现1.3.1 简单实现 (基于阈…...

【Android】Android 开发 ADB 常用指令
查看当前连接的设备 adb devices 连接设备 adb connect 设备IP 断开已连接的设备 adb disconnect 设备IP 安装应用 adb install 安装包的路径 卸载应用 adb uninstall 应用包名 查看已安装的应用包名 adb shell pm list packages 查看已安装的第三方应用包名 adb shell pm list…...
 error)
【前端异常】JavaScript错误处理:分析 Uncaught (in promise) error
在前端开发中,JavaScript 异常是不可避免的。随着现代前端应用越来越多地使用异步操作(如 Promise、async/await 等),开发者常常会遇到 Uncaught (in promise) error 错误。这个错误是由于未正确处理 Promise 的拒绝(r…...
