如何在24GB的GPU上运行DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B
如何在24GB的GPU上运行DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B
- 一、背景
- 二、解决方案
- 三、操作步骤
- 1.下载模型
- 2.安装依赖
- 3.量化
- 4.生成推理代码
- 5.运行
- A.缓存上限为128条
- B.不限制缓存上限
- C.输出内容
一、背景
随着深度学习的不断发展,大型语言模型(LLM,Large Language Model)在自然语言处理领域展现出了强大的能力。然而,伴随着模型参数规模的指数级增长,运行这些模型所需的计算资源也变得异常庞大,尤其是对显存(GPU内存)的需求。因此,如何在有限的GPU显存下有效地运行超大规模的LLM,成为了一个亟待解决的挑战。
本文验证在GPU显存受限的情况下,如何高效地运行超出GPU内存容量的LLM模型。通过对模型权重的量化和内存管理策略的优化,期望能够突破硬件瓶颈,为大型模型的部署和应用提供新的思路。
二、解决方案
下面的方案,主要包括权重量化、内存缓存机制以及自定义Linear的设计。具体方案如下:
-
权重的INT4块量化
- 量化策略:将模型的权重参数进行INT4(4位整数)块量化处理,量化的块大小设定为128。这种量化方式能够大幅度减少模型权重所占用的存储空间。
- 内存优势:经过INT4量化后的权重占用空间显著降低,使得所有权重可以加载到主机(HOST)内存中。这不仅缓解了GPU显存的压力,还为后续的高效读取奠定了基础。
-
减少磁盘I/O操作
- 全量加载:将所有量化后的INT4权重一次性加载到HOST内存中,避免了在模型运行过程中频繁进行磁盘读写操作。这种方式有效减少了磁盘I/O带来的时间开销和性能瓶颈。
-
设备内存缓存机制
- 缓存设计:在GPU设备内存中建立一个缓存机制,设定最大缓存条目数为N。N的取值与具体的GPU配置相关,目的是充分利用可用的设备内存,最大化其占用率,提升数据读取效率。
- 动态管理:缓存机制需要智能地管理内存的分配和释放,确保在不超过设备内存上限的情况下,高效地存取所需的数据。
-
权重预加载线程
- 职责分离:引入一个专门的权重预加载线程,负责将HOST内存中的INT4权重进行反量化处理(即将INT4还原为计算所需的格式),并将处理后的权重加载到GPU设备内存的缓存中。
- 效率优化:通过预加载线程的异步处理,提升了数据准备的效率,确保模型在需要数据时可以及时获取,最大程度减少等待时间。
-
自定义Linear模块
- 模块替换:将原有的
nn.Linear层替换为自定义的Module。在模型构建和加载过程中,使用该自定义模块来承载线性计算任务。 - 运行机制:自定义的Module在前向传播(forward)过程中,从设备内存的缓存中获取所需的权重进行计算。计算完成后,立即释放权重占用的设备内存,以供后续的计算任务使用。
- 优势:这种动态加载和释放的机制,避免了在整个计算过程中权重长时间占用设备内存,极大地提高了内存的利用效率。
- 模块替换:将原有的
三、操作步骤
1.下载模型
# 模型介绍: https://www.modelscope.cn/models/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B# 下载模型
apt install git-lfs -y
git clone https://www.modelscope.cn/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B.git
2.安装依赖
MAX_JOBS=4 pip install flash-attn==2.3.6
pip install torch-tb-profiler
3.量化
cat > extract_weights.py << EOF
import torch
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
from glob import glob
import torch
import sys
from safetensors.torch import safe_open, save_filedef quantize_tensor_int4(tensor):"""将bfloat16的Tensor按照块大小128进行量化为int4,并返回每个块的scale。参数:tensor (torch.Tensor): bfloat16类型的输入Tensor。返回:int4_tensor (torch.Tensor): 量化后的uint8类型的Tensor,存储int4值,每个元素包含两个int4值。scales (torch.Tensor): 每个块对应的bfloat16类型的scale值。"""# 确保输入Tensor为bfloat16类型tensor = tensor.to(torch.bfloat16)# 将Tensor展平为一维flat_tensor = tensor.flatten()N = flat_tensor.numel()block_size = 128num_blocks = (N + block_size - 1) // block_size # 计算块的数量# 计算每个元素的块索引indices = torch.arange(N, device=flat_tensor.device)block_indices = indices // block_size # shape: [N]# 计算每个块的x_maxabs_tensor = flat_tensor.abs()zeros_needed = num_blocks * block_size - N# 对张量进行填充,使其长度为num_blocks * block_sizeif zeros_needed > 0:padded_abs_tensor = torch.cat([abs_tensor, torch.zeros(zeros_needed, device=abs_tensor.device, dtype=abs_tensor.dtype)])else:padded_abs_tensor = abs_tensorreshaped_abs_tensor = padded_abs_tensor.view(num_blocks, block_size)x_max = reshaped_abs_tensor.max(dim=1).values # shape: [num_blocks]# 处理x_max为0的情况,避免除以0x_max_nonzero = x_max.clone()x_max_nonzero[x_max_nonzero == 0] = 1.0 # 防止除以0# 计算scalescales = x_max_nonzero / 7.0 # shape: [num_blocks]scales = scales.to(torch.bfloat16)# 量化scales_expanded = scales[block_indices] # shape: [N]q = torch.round(flat_tensor / scales_expanded).clamp(-8, 7).to(torch.int8)# 将有符号int4转换为无符号表示q_unsigned = q & 0x0F # 将范围[-8,7]映射到[0,15]# 如果元素数量是奇数,补充一个零if N % 2 != 0:q_unsigned = torch.cat([q_unsigned, torch.zeros(1, dtype=torch.int8, device=q.device)])# 打包两个int4到一个uint8q_pairs = q_unsigned.view(-1, 2)int4_tensor = (q_pairs[:, 0].to(torch.uint8) << 4) | q_pairs[:, 1].to(torch.uint8)return int4_tensor, scalestorch.set_default_device("cuda")
if len(sys.argv)!=3:print(f"{sys.argv[0]} input_model_dir output_dir")
else:input_model_dir=sys.argv[1]output_dir=sys.argv[2]if not os.path.exists(output_dir):os.makedirs(output_dir)state_dicts = {}for file_path in tqdm(glob(os.path.join(input_model_dir, "*.safetensors"))):with safe_open(file_path, framework="pt", device="cuda") as f:for name in f.keys():param: torch.Tensor = f.get_tensor(name)#print(name,param.shape,param.dtype)if "norm" in name or "embed" in name:state_dicts[name] = paramelse:if "weight" in name:int4_tensor, scales=quantize_tensor_int4(param)state_dict={}state_dict["w"]=int4_tensor.datastate_dict["scales"]=scales.datastate_dict["shape"]=param.shapetorch.save(state_dict, os.path.join(output_dir, f"{name}.pt"))else:torch.save(param.data, os.path.join(output_dir, f"{name}.pt"))torch.save(state_dicts, os.path.join(output_dir, "others.pt"))
EOF
python extract_weights.py DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B ./data
4.生成推理代码
cat > infer.py << EOF
import sys
import os
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer,BitsAndBytesConfig
import torch
import time
import numpy as np
import json
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
import threading
from torch import Tensor
from tqdm import tqdm
import triton
import triton.language as tl
import time
import queue
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")@triton.jit
def dequantize_kernel(int4_ptr, # 量化后的 int4 张量指针scales_ptr, # 每个块的 scale 值指针output_ptr, # 输出张量指针N, # 总元素数量num_blocks, # 总块数BLOCK_SIZE: tl.constexpr # 每个线程块处理的元素数量
):# 计算全局元素索引pid = tl.program_id(axis=0)offs = pid * BLOCK_SIZE + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE)mask = offs < N# 计算 int4 张量中的索引int4_idxs = offs // 2 # 每个 uint8 包含两个 int4 值int4_vals = tl.load(int4_ptr + int4_idxs, mask=int4_idxs < (N + 1) // 2)# 提取高 4 位和低 4 位的 int4 值shift = 4 * (1 - (offs % 2))q = (int4_vals >> shift) & 0x0Fq = q.to(tl.int8)# 将无符号 int4 转换为有符号表示q = (q + 8) % 16 - 8 # 将范围 [0, 15] 映射回 [-8, 7]# 计算每个元素所属的块索引block_size = 128block_idxs = offs // block_sizescales = tl.load(scales_ptr + block_idxs, mask=block_idxs < num_blocks)# 反量化dequantized = q.to(tl.float32) * scales# 存储结果tl.store(output_ptr + offs, dequantized, mask=mask)def dequantize_tensor_int4_triton(int4_tensor, scales, original_shape):N = original_shape.numel()num_blocks = scales.numel()output = torch.empty(N, dtype=torch.bfloat16, device=int4_tensor.device)# 动态调整块大小(A100建议512-1024)BLOCK_SIZE = min(1024, triton.next_power_of_2(N))grid = (triton.cdiv(N, BLOCK_SIZE),)dequantize_kernel[grid](int4_tensor, scales, output,N, scales.numel(), BLOCK_SIZE=BLOCK_SIZE)output = output.view(original_shape)return outputdef load_pinned_tensor(path):data = torch.load(path, map_location='cpu',weights_only=True) # 先加载到CPU# 递归遍历所有对象,对Tensor设置pin_memorydef _pin(tensor):if isinstance(tensor, torch.Tensor):return tensor.pin_memory()elif isinstance(tensor, dict):return {k: _pin(v) for k, v in tensor.items()}elif isinstance(tensor, (list, tuple)):return type(tensor)(_pin(x) for x in tensor)else:return tensorreturn _pin(data)class WeightCache:def __init__(self, weight_names, weight_dir, max_cache_size):self.weight_names = weight_namesself.weight_dir = weight_dirif max_cache_size==-1:self.max_cache_size = len(weight_names)else:self.max_cache_size = max_cache_sizeself.cache = {}self.cache_lock = threading.Lock()self.condition = threading.Condition(self.cache_lock)self.index = 0self.weight_cpu = []self.dequantized = {}self.accessed_weights = set() # 用于记录被 get 过的权值for name in tqdm(self.weight_names):weight_path = os.path.join(self.weight_dir, name + ".pt")self.weight_cpu.append(load_pinned_tensor(weight_path))self.loader_thread = threading.Thread(target=self._loader)self.loader_thread.daemon = Trueself.loader_thread.start()self.last_ts = time.time()def _loader(self):stream = torch.cuda.Stream()while True:with self.condition:while len(self.cache) > self.max_cache_size:# 尝试删除已被 get 过的权值removed = Falsefor weight_name in list(self.cache.keys()):if weight_name in self.accessed_weights:del self.cache[weight_name]self.accessed_weights.remove(weight_name)removed = Truebreak # 每次删除一个if not removed:self.condition.wait()# 加载新的权值到缓存if self.index >= len(self.weight_names):self.index = 0weight_name = self.weight_names[self.index]if weight_name in self.cache:time.sleep(0.01)continuew = self.weight_cpu[self.index]with torch.cuda.stream(stream):if "weight" in weight_name:new_weight = {"w": w['w'].to(device, non_blocking=False),"scales": w['scales'].to(device, non_blocking=False),"shape": w['shape']}else:new_weight = w.to(device, non_blocking=False)with self.condition:self.cache[weight_name] = new_weightself.index += 1self.condition.notify_all()def wait_full(self):with self.condition:while len(self.cache) < self.max_cache_size:self.condition.wait()print(len(self.cache), self.max_cache_size)def get(self, weight_name):with self.condition:while weight_name not in self.cache:self.condition.wait()weight = self.cache[weight_name] # 不再从缓存中删除self.accessed_weights.add(weight_name) # 记录被 get 过的权值self.condition.notify_all()return weightclass TextGenerationDataset(Dataset):def __init__(self, json_data):self.data = json.loads(json_data)def __len__(self):return len(self.data)def __getitem__(self, idx):item = self.data[idx]input_text = item['input']expected_output = item['expected_output']return input_text, expected_outputclass Streamer:def __init__(self, tokenizer):self.cache = []self.tokenizer = tokenizerself.start_time = None # 用于记录开始时间self.token_count = 0 # 用于记录生成的令牌数量def put(self, token):if self.start_time is None:self.start_time = time.time() # 初始化开始时间decoded = self.tokenizer.decode(token[0], skip_special_tokens=True)self.cache.append(decoded)self.token_count += token.numel() # 增加令牌计数elapsed_time = time.time() - self.start_timetokens_per_sec = self.token_count / elapsed_time if elapsed_time > 0 else 0print(f"{tokens_per_sec:.2f} tokens/sec| {''.join(self.cache)}", end="\r", flush=True)def end(self):total_time = time.time() - self.start_time if self.start_time else 0print("\nGeneration complete.")if total_time > 0:avg_tokens_per_sec = self.token_count / total_timeprint(f"总令牌数: {self.token_count}, 总耗时: {total_time:.2f}s, 平均速度: {avg_tokens_per_sec:.2f} tokens/sec.")else:print("总耗时过短,无法计算每秒生成的令牌数。")class MyLinear(torch.nn.Module):__constants__ = ['in_features', 'out_features']in_features: intout_features: intweight: Tensordef __init__(self, in_features: int,out_features: int,bias: bool = True,device=None,dtype=None) -> None:factory_kwargs = {'device': device, 'dtype': dtype}super().__init__()self.in_features = in_featuresself.out_features = out_featuresself.weight = Trueif bias:self.bias = Trueelse:self.bias = Falsedef forward(self, x):w = self.weight_cache.get(f"{self.w_name}.weight")weight=dequantize_tensor_int4_triton(w['w'], w['scales'],w['shape'])if self.bias:bias = self.weight_cache.get(f"{self.w_name}.bias")else:bias = Nonereturn torch.nn.functional.linear(x,weight,bias)def set_linear_name(model,weight_cache):for name, module in model.named_modules():if isinstance(module, torch.nn.Linear):module.w_name=namemodule.weight_cache=weight_cachetorch.nn.Linear=MyLinearinput_model_dir=sys.argv[1]
input_weights_dir=sys.argv[2]
cache_queue_size=int(sys.argv[3])torch.set_default_device('cuda')
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(input_model_dir)
from transformers.models.qwen2 import Qwen2ForCausalLM,Qwen2Config
config=Qwen2Config.from_pretrained(f"{input_model_dir}/config.json")
config.use_cache=True
config.torch_dtype=torch.float16
config._attn_implementation="flash_attention_2"
model =Qwen2ForCausalLM(config).bfloat16().bfloat16().to(device)
checkpoint=torch.load(f"{input_weights_dir}/others.pt",weights_only=True)
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint)weight_map=[]
with open(os.path.join(input_model_dir,"model.safetensors.index.json")) as f:for name in json.load(f)["weight_map"].keys():if "norm" in name or "embed" in name:passelse:weight_map.append(name)json_data =r'''
[{"input": "1.1+2.3=?", "expected_output": "TODO"}
]
'''weight_cache = WeightCache(weight_map,input_weights_dir,cache_queue_size)
print("wait done")
set_linear_name(model,weight_cache)
model.eval()test_dataset = TextGenerationDataset(json_data)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=1, shuffle=False)dataloader_iter = iter(test_dataloader)
input_text, expected_output=next(dataloader_iter)
inputs = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
streamer = Streamer(tokenizer)if True:stream = torch.cuda.Stream()with torch.cuda.stream(stream):with torch.inference_mode():#outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_length=4096,streamer=streamer,do_sample=True,pad_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,num_beams=1,repetition_penalty=1.1)outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_length=4096,streamer=streamer,use_cache=config.use_cache)
else:def trace_handler(prof):print(prof.key_averages().table(sort_by="self_cuda_time_total", row_limit=-1))prof.export_chrome_trace("output.json")import torch.autograd.profiler as profilerfrom torch.profiler import profile, record_function, ProfilerActivitywith torch.profiler.profile(activities=[torch.profiler.ProfilerActivity.CPU,torch.profiler.ProfilerActivity.CUDA],on_trace_ready=trace_handler) as p:stream = torch.cuda.Stream()with torch.cuda.stream(stream):with torch.inference_mode():outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_length=4096,streamer=streamer,use_cache=True,do_sample=True,pad_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,num_beams=1,repetition_penalty=1.1)#outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_length=4096,streamer=streamer)#outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_length=8)p.step()
EOF
5.运行
A.缓存上限为128条
export TRITON_CACHE_DIR=$PWD/cache
python infer.py DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B data 128
性能
总令牌数: 403, 总耗时: 572.34s, 平均速度: 0.70 tokens/sec.
GPU利用率
|=========================================+========================+======================|
| 0 NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 Off | 00000000:03:00.0 Off | N/A |
| 71% 62C P0 186W / 350W | 10354MiB / 24576MiB | 95% Default |
| | | N/A |
+-----------------------------------------+------------------------+----------------------+
| 0 N/A N/A 47129 C python 10258MiB |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
B.不限制缓存上限
export TRITON_CACHE_DIR=$PWD/cache
python infer.py DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B data -1
性能
总令牌数: 403, 总耗时: 72.84s, 平均速度: 5.53 tokens/sec.
GPU利用率
|=========================================+========================+======================|
| 0 NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 Off | 00000000:03:00.0 Off | N/A |
| 73% 65C P0 330W / 350W | 22678MiB / 24576MiB | 97% Default |
| | | N/A |
+-----------------------------------------+------------------------+----------------------+
| 0 N/A N/A 47903 C python 22582MiB |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
C.输出内容
1.1+2.3=? Let me think.
Okay, so I need to add 1.1 and 2.3 together. Hmm, let me visualize this. I remember that when adding decimals, it’s important to line up the decimal points to make sure each place value is correctly added. So, I can write them one under the other like this:
1.1
+2.3
------
Starting from the rightmost digit, which is the tenths place. 1 (from 1.1) plus 3 (from 2.3) equals 4. So, I write down 4 in the tenths place.
Next, moving to the units place. 1 (from 1.1) plus 2 (from 2.3) equals 3. So, I write down 3 in the units place.
Putting it all together, the sum is 3.4. Let me double-check to make sure I didn’t make a mistake. 1.1 plus 2 is 3.1, and then adding the 0.3 more gives me 3.4. Yep, that seems right.
I think I got it! The answer should be 3.4.
To add 1.1 and 2.3, follow these steps:
- Align the decimal points:
1.1
+2.3
------
- Add the tenths place:
1 (from 1.1) + 3 (from 2.3) = 4
- Add the units place:
1 (from 1.1) + 2 (from 2.3) = 3
- Combine the results:
3.4
Final Answer: \boxed{3.4}
Generation complete.
相关文章:

如何在24GB的GPU上运行DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B
如何在24GB的GPU上运行DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B 一、背景二、解决方案三、操作步骤1.下载模型2.安装依赖3.量化4.生成推理代码5.运行A.缓存上限为128条B.不限制缓存上限C.输出内容 一、背景 随着深度学习的不断发展,大型语言模型(LLM,L…...

2025年二级建造师报名流程图解
2025年二级建造师报名时间!附报名流程! ⏰️已公布25年二建考试时间的省份如下: ️4月19日、20日考试的城市有:贵州 ️5月10日、11日考试的城市有:湖北、陕西、宁夏、甘肃、福建、浙江、江西、黑龙江、河南、湖南、…...

深入浅出:Python 中的异步编程与协程
引言 大家好,今天我们来聊聊 异步编程 和 协程,这是近年来编程语言领域中的热点话题之一,尤其在 Python 中,它作为一种全新的编程模型,已经成为处理 IO密集型 任务的强力工具。尽管很多人对异步编程望而却步࿰…...

八大排序——简单选择排序
目录 1.1基本操作: 1.2动态图: 1.3代码: 代码解释 1. main 方法 2. selectSort 方法 示例运行过程 初始数组 每轮排序后的数组 最终排序结果 代码总结 1.1基本操作: 选择排序(select sorting)也…...

vue使用CSS布局技术,实现div定位到页面底部或顶部并居中功能
<template> <div > <div class"bottom-element"> 我在底部,并居中了 </div> </div> </template> 使用CSS布局技术,通过设置CSS属性来实现页面底部定位。 <style lang"scs…...

Jenkins 部署 之 Mac 一
Jenkins 部署 之 Mac 一 一.Jenkins 部署依赖 JDK 环境 查看 Mac JDK 环境,如果没有安装,先安装 打开终端输入命令:java -version Mac安装配置 JDK 二. 检查 HomeBrew 安装 检查 HomeBrew 是否安装,终端输入命令:brew -v Mac安装HomeB…...

【FastAPI 使用FastAPI和uvicorn来同时运行HTTP和HTTPS的Python应用程序】
在本文中,我们将介绍如何使用 FastAPI和uvicorn来同时运行HTTP和HTTPS的 Python应用程序。 简介 FastAPI是一个高性能的Web框架,可以用于构建快速、可靠的API。它基于Python的类型提示和异步支持,使得开发者可以轻松地编写出安全且高效的代…...

HCIA-路由器相关知识和面试问题
二、 路由器 2.1 关于路由器的知识 2.1.1 什么是路由器 路由器是一种网络层互联设备,主要用于连接多个逻辑上分开的网络,实现不同网络之间的数据路由和通信。它能根据网络层地址(如 IP 地址)来转发数据包,在网络中起…...

Docker+Jenkins自动化部署SpringBoot项目【详解git,jdk,maven,ssh配置等各种配置,附有示例+代码】
文章目录 DockerJenkins部署SpringBoot项目一.准备工作1.1安装jdk111.2安装Maven 二.Docker安装Jenkins2.1安装Docker2.2 安装Jenkins2.3进入jenkins 三.Jenkins设置3.1安装jenkins插件3.2全局工具配置全局配置jdk全局配置maven全局配置git 3.3 系统配置安装 Publish Over SSH …...
)
PCL 点云数学形态学操作(腐蚀)
文章目录 一、简介二、实现代码三、实现效果参考资料一、简介 基本原理:使用结构元素(通常为滤波的窗口)的窗口模板作为处理单元,利用形态学中的膨胀与腐蚀相组合即可达到滤波的效果。 点云数据中的数学形态学运算其实和二维图像上的运算非常相似,图像上像素有x,y和亮度值…...

【设计模式】【行为型模式】观察者模式(Observer)
👋hi,我不是一名外包公司的员工,也不会偷吃茶水间的零食,我的梦想是能写高端CRUD 🔥 2025本人正在沉淀中… 博客更新速度 👍 欢迎点赞、收藏、关注,跟上我的更新节奏 🎵 当你的天空突…...

RAGFlow和Dify对比
RAGFlow和Dify都是基于大语言模型(LLM)的应用开发平台,具有相似的功能和应用场景,但它们在技术架构、部署要求和用户体验上存在一些差异。 RAGFlow和Dify对比 2025-02-13 22.08 RAGFlow 技术栈:RAGFlow…...

AI前端开发:蓬勃发展的机遇与挑战
人工智能(AI)领域的飞速发展,正深刻地改变着我们的生活方式,也为技术人才,特别是AI代码生成领域的专业人士,带来了前所未有的机遇。而作为AI应用与用户之间桥梁的前端开发,其重要性更是日益凸显…...

结构型模式---代理模式
概念 代理模式是一种结构型模式,主要用于在客户端和接口之间添加一个中间层,用于在客户端和接口之间进行权限控制或者其他的中间层操作。 使用场景 1、延缓初始化,当我们偶尔需要使用一个重量级的服务对象,如果一直保持该对象的…...

Java面向对象一:相关概念
面向过程&面向对象 面向过程思想 步骤清晰简单,第一步做什么,第二步做什么… 面对过程适合处理一些较为简单的问题面向对象思想 物以类聚,分类的思维模式,思考问题首先会解决问题需要哪些分类,然后对这些分类进行…...

CEF132 编译指南 MacOS 篇 - depot_tools 安装与配置 (四)
1. 引言 在 CEF132(Chromium Embedded Framework)的编译过程中,depot_tools 扮演着举足轻重的角色。这套由 Chromium 项目精心打造的脚本和工具集,专门用于获取、管理和更新 Chromium 及其相关项目(包括 CEFÿ…...

React VS Vue
React 和 Vue 是目前最流行的两个前端框架,它们在设计理念、生态系统和开发体验上各有特点。以下是对 React 和 Vue 的全方位对比: 1. 核心设计理念 React 库而非框架:React 是一个用于构建 UI 的库,专注于视图层,其…...

伺服报警的含义
前言: 大家好,我是上位机马工,硕士毕业4年年入40万,目前在一家自动化公司担任软件经理,从事C#上位机软件开发8年以上!我们在开发C#的运动控制程序的时候,一个必要的步骤就是设置伺服报警信号的…...

CSS 属性选择器详解与实战示例
CSS 属性选择器是 CSS 中非常强大且灵活的一类选择器,它能够根据 HTML 元素的属性和值来进行精准选中。在实际开发过程中,属性选择器不仅可以提高代码的可维护性,而且能够大大优化页面的样式控制。本文将结合菜鸟教程的示例,从基础…...
C语言程序设计)
基于STM32、HAL库、HS12864(ST7920,并行接口)C语言程序设计
1、hs12864.h头文件: #ifndef __HS12864_H #define __HS12864_H #ifdef __cplusplus extern "C" {#endif #include "stm32l4xx_hal.h" // 控制线定义 - 根据实际硬件修改 #define HS12864_RS_GPIO_PORT GPIOC #define HS12864_RS_PIN GPIO_PI…...
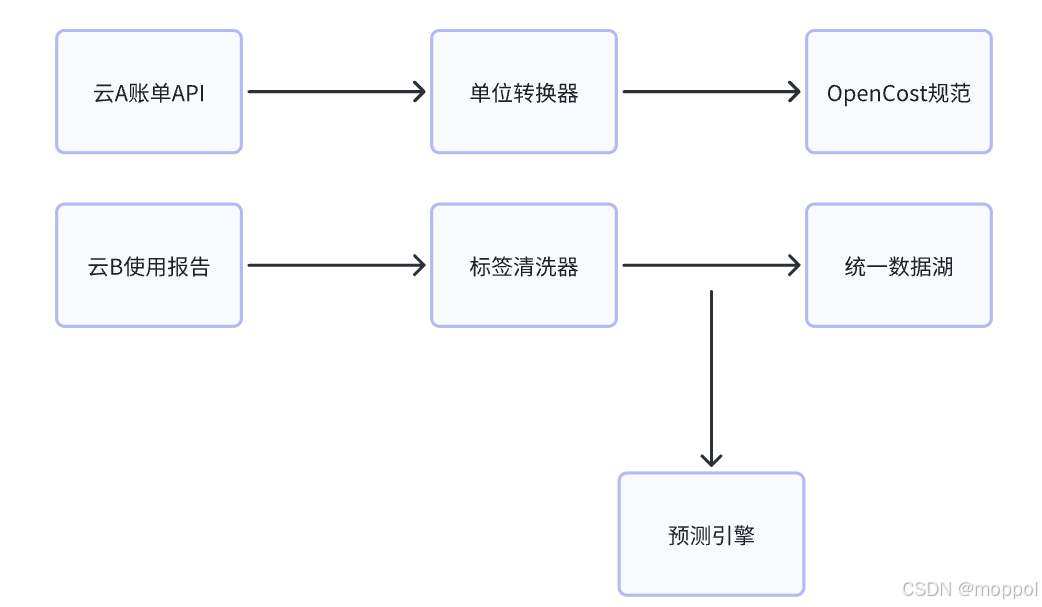
多云管理“拦路虎”:深入解析网络互联、身份同步与成本可视化的技术复杂度
一、引言:多云环境的技术复杂性本质 企业采用多云策略已从技术选型升维至生存刚需。当业务系统分散部署在多个云平台时,基础设施的技术债呈现指数级积累。网络连接、身份认证、成本管理这三大核心挑战相互嵌套:跨云网络构建数据…...
(十)学生端搭建
本次旨在将之前的已完成的部分功能进行拼装到学生端,同时完善学生端的构建。本次工作主要包括: 1.学生端整体界面布局 2.模拟考场与部分个人画像流程的串联 3.整体学生端逻辑 一、学生端 在主界面可以选择自己的用户角色 选择学生则进入学生登录界面…...

数据链路层的主要功能是什么
数据链路层(OSI模型第2层)的核心功能是在相邻网络节点(如交换机、主机)间提供可靠的数据帧传输服务,主要职责包括: 🔑 核心功能详解: 帧封装与解封装 封装: 将网络层下发…...
【单片机期末】单片机系统设计
主要内容:系统状态机,系统时基,系统需求分析,系统构建,系统状态流图 一、题目要求 二、绘制系统状态流图 题目:根据上述描述绘制系统状态流图,注明状态转移条件及方向。 三、利用定时器产生时…...
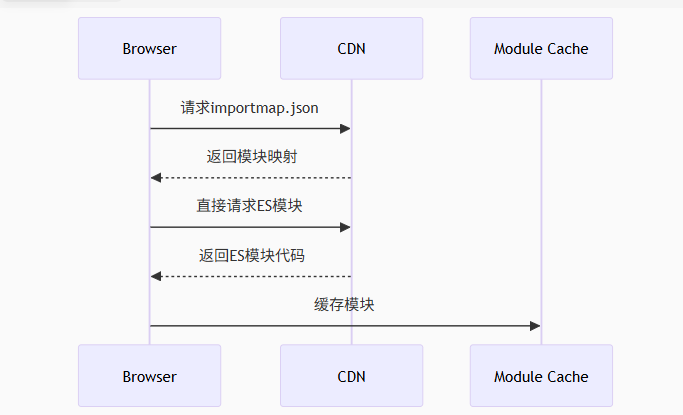
Module Federation 和 Native Federation 的比较
前言 Module Federation 是 Webpack 5 引入的微前端架构方案,允许不同独立构建的应用在运行时动态共享模块。 Native Federation 是 Angular 官方基于 Module Federation 理念实现的专为 Angular 优化的微前端方案。 概念解析 Module Federation (模块联邦) Modul…...

Python如何给视频添加音频和字幕
在Python中,给视频添加音频和字幕可以使用电影文件处理库MoviePy和字幕处理库Subtitles。下面将详细介绍如何使用这些库来实现视频的音频和字幕添加,包括必要的代码示例和详细解释。 环境准备 在开始之前,需要安装以下Python库:…...

爬虫基础学习day2
# 爬虫设计领域 工商:企查查、天眼查短视频:抖音、快手、西瓜 ---> 飞瓜电商:京东、淘宝、聚美优品、亚马逊 ---> 分析店铺经营决策标题、排名航空:抓取所有航空公司价格 ---> 去哪儿自媒体:采集自媒体数据进…...
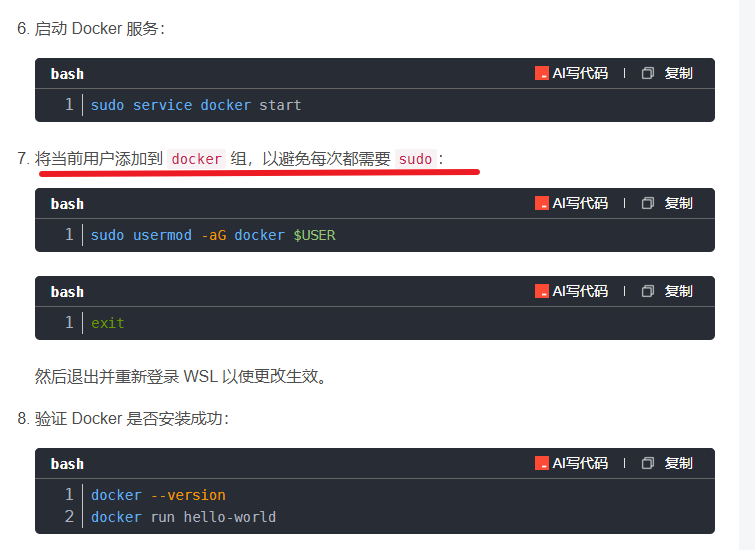
在WSL2的Ubuntu镜像中安装Docker
Docker官网链接: https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ubuntu/ 1、运行以下命令卸载所有冲突的软件包: for pkg in docker.io docker-doc docker-compose docker-compose-v2 podman-docker containerd runc; do sudo apt-get remove $pkg; done2、设置Docker…...
第 86 场周赛:矩阵中的幻方、钥匙和房间、将数组拆分成斐波那契序列、猜猜这个单词
Q1、[中等] 矩阵中的幻方 1、题目描述 3 x 3 的幻方是一个填充有 从 1 到 9 的不同数字的 3 x 3 矩阵,其中每行,每列以及两条对角线上的各数之和都相等。 给定一个由整数组成的row x col 的 grid,其中有多少个 3 3 的 “幻方” 子矩阵&am…...
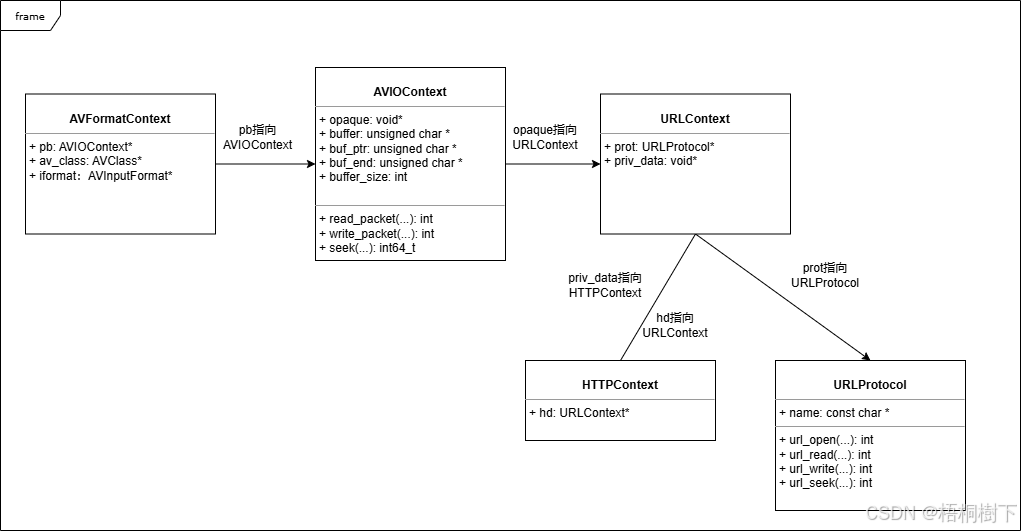
FFmpeg avformat_open_input函数分析
函数内部的总体流程如下: avformat_open_input 精简后的代码如下: int avformat_open_input(AVFormatContext **ps, const char *filename,ff_const59 AVInputFormat *fmt, AVDictionary **options) {AVFormatContext *s *ps;int i, ret 0;AVDictio…...
