Open3D解决SceneWidget加入布局中消失的问题
Open3D解决SceneWidget加入布局中消失的问题
- Open3D解决SceneWidget加入布局中消失的问题
- 1. 问题
- 2. 问题代码
- 3. 解决
Open3D解决SceneWidget加入布局中消失的问题
1. 问题
把SceneWidget加到布局管理其中图形可以展示出来,但是鼠标点击就消失了。
stackoverflow上已经有人提出这个问题了,还是2022年的时候,可是现在好像也没有解决。
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/71706506/why-does-open3d-visualization-disappear-when-i-left-click-the-window
2. 问题代码

# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# - Open3D: www.open3d.org -
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Copyright (c) 2018-2024 www.open3d.org
# SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------import open3d as o3d
import open3d.visualization.gui as gui
import open3d.visualization.rendering as rendering
import platform
import random
import threading
import timeisMacOS = (platform.system() == "Darwin")# This example shows two methods of adding geometry to an existing scene.
# 1) add via a UI callback (in this case a menu, but a button would be similar,
# you would call `button.set_on_clicked(self.on_menu_sphere_)` when
# configuring the button. See `on_menu_sphere()`.
# 2) add asynchronously by polling from another thread. GUI functions must be
# called from the UI thread, so use Application.post_to_main_thread().
# See `on_menu_random()`.
# Running the example will show a simple window with a Debug menu item with the
# two different options. The second method will add random spheres for
# 20 seconds, during which time you can be interacting with the scene, rotating,
# etc.
class SpheresApp:MENU_SPHERE = 1MENU_RANDOM = 2MENU_QUIT = 3def __init__(self):self._id = 0self.window = gui.Application.instance.create_window("Add Spheres Example", 800, 600)# The menu is global (because the macOS menu is global), so only create# it once, no matter how many windows are createdif gui.Application.instance.menubar is None:if isMacOS:app_menu = gui.Menu()app_menu.add_item("Quit", SpheresApp.MENU_QUIT)debug_menu = gui.Menu()debug_menu.add_item("Add Sphere", SpheresApp.MENU_SPHERE)debug_menu.add_item("Add Random Spheres", SpheresApp.MENU_RANDOM)if not isMacOS:debug_menu.add_separator()debug_menu.add_item("Quit", SpheresApp.MENU_QUIT)menu = gui.Menu()if isMacOS:# macOS will name the first menu item for the running application# (in our case, probably "Python"), regardless of what we call# it. This is the application menu, and it is where the# About..., Preferences..., and Quit menu items typically go.menu.add_menu("Example", app_menu)menu.add_menu("Debug", debug_menu)else:menu.add_menu("Debug", debug_menu)gui.Application.instance.menubar = menu# The menubar is global, but we need to connect the menu items to the# window, so that the window can call the appropriate function when the# menu item is activated.self.window.set_on_menu_item_activated(SpheresApp.MENU_SPHERE,self._on_menu_sphere)self.window.set_on_menu_item_activated(SpheresApp.MENU_RANDOM,self._on_menu_random)self.window.set_on_menu_item_activated(SpheresApp.MENU_QUIT,self._on_menu_quit)self.scene = gui.SceneWidget()self.scene.scene = rendering.Open3DScene(self.window.renderer)self.scene.scene.show_axes(True)mesh = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_sphere()mesh.compute_vertex_normals()material = rendering.MaterialRecord()material.shader = "defaultLit"self.scene.scene.add_geometry("sphere" + str(self._id), mesh, material)em = self.window.theme.font_sizeself.layout = gui.Horiz(0, gui.Margins(0.25*em,0.25*em,0.25*em,0.254*em))self.layout.add_child(gui.Label("Model file"))self.layout.add_fixed(0.25 * em)self.window.set_on_layout(self.on_window_layout)self.vlayout = gui.Vert(0, gui.Margins(0.25 * em, 0.25 * em, 0.25 * em, 0.254 * em))self.vlayout.add_child(self.scene)self.vlayout.add_fixed(0.25 * em)self.window.add_child(self.vlayout)self.window.add_child(self.layout)def on_window_layout(self, layout: gui.LayoutContext) -> None:"""This is called when layout is required for this widgets *immediate children*, like on resize. Only the immediatechildren are *manually* positioned here, by setting the x, y, width, and height of their frames. Thegrandchildren are *not* touched here; they're automatically handled after this."""# This is the area in this widget available to place child widgets in. The *units* here aren't window screen# pixels, like from the width/height here when setting up the window: gui.Application.instance.create_window("Test", width=500, height=600).rect = self.window.content_rectr = self.window.content_rectprint(r)print(layout.theme.default_layout_spacing)print(layout.theme.default_margin)print(layout.theme.font_size)# Put the layout (containing the controls) on the left 1/3 and the and scene on the right 2/3.x_division = rect.width // 3# Set the layout (gui.Vert) on left to 1/3 available width, full height.# gui.Rect(x, y, width, height)# Set the SceneWidget on on right, 2/3 available width, full heightself.vlayout.frame = gui.Rect(0, 0, r.width - x_division, r.height)self.layout.frame = gui.Rect(r.width - x_division, 0, x_division, r.height)def add_sphere(self):self._id += 1mat = rendering.MaterialRecord()mat.base_color = [random.random(),random.random(),random.random(), 1.0]mat.shader = "defaultLit"sphere = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_sphere(0.5)sphere.compute_vertex_normals()sphere.translate([10.0 * random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0), 10.0 * random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0),10.0 * random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0)])self.scene.scene.add_geometry("sphere" + str(self._id), sphere, mat)def _on_menu_sphere(self):# GUI callbacks happen on the main thread, so we can do everything# normally here.self.scene.scene.clear_geometry()self.add_sphere()def _on_menu_random(self):# This adds spheres asynchronously. This pattern is useful if you have# data coming in from another source than user interaction.def thread_main():for _ in range(0, 20):# We can only modify GUI objects on the main thread, so we# need to post the function to call to the main thread.gui.Application.instance.post_to_main_thread(self.window, self.add_sphere)time.sleep(0.5)threading.Thread(target=thread_main).start()def _on_menu_quit(self):gui.Application.instance.quit()def main():gui.Application.instance.initialize()SpheresApp()gui.Application.instance.run()if __name__ == "__main__":main()3. 解决
不能放在布局中就直接手动布局吧,
不加到布局中去。。。

# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# - Open3D: www.open3d.org -
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Copyright (c) 2018-2024 www.open3d.org
# SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------import open3d as o3d
import open3d.visualization.gui as gui
import open3d.visualization.rendering as rendering
import platform
import random
import threading
import timeisMacOS = (platform.system() == "Darwin")# This example shows two methods of adding geometry to an existing scene.
# 1) add via a UI callback (in this case a menu, but a button would be similar,
# you would call `button.set_on_clicked(self.on_menu_sphere_)` when
# configuring the button. See `on_menu_sphere()`.
# 2) add asynchronously by polling from another thread. GUI functions must be
# called from the UI thread, so use Application.post_to_main_thread().
# See `on_menu_random()`.
# Running the example will show a simple window with a Debug menu item with the
# two different options. The second method will add random spheres for
# 20 seconds, during which time you can be interacting with the scene, rotating,
# etc.
class SpheresApp:MENU_SPHERE = 1MENU_RANDOM = 2MENU_QUIT = 3def __init__(self):self._id = 0self.window = gui.Application.instance.create_window("Add Spheres Example", 800, 600)# The menu is global (because the macOS menu is global), so only create# it once, no matter how many windows are createdif gui.Application.instance.menubar is None:if isMacOS:app_menu = gui.Menu()app_menu.add_item("Quit", SpheresApp.MENU_QUIT)debug_menu = gui.Menu()debug_menu.add_item("Add Sphere", SpheresApp.MENU_SPHERE)debug_menu.add_item("Add Random Spheres", SpheresApp.MENU_RANDOM)if not isMacOS:debug_menu.add_separator()debug_menu.add_item("Quit", SpheresApp.MENU_QUIT)menu = gui.Menu()if isMacOS:# macOS will name the first menu item for the running application# (in our case, probably "Python"), regardless of what we call# it. This is the application menu, and it is where the# About..., Preferences..., and Quit menu items typically go.menu.add_menu("Example", app_menu)menu.add_menu("Debug", debug_menu)else:menu.add_menu("Debug", debug_menu)gui.Application.instance.menubar = menu# The menubar is global, but we need to connect the menu items to the# window, so that the window can call the appropriate function when the# menu item is activated.self.window.set_on_menu_item_activated(SpheresApp.MENU_SPHERE,self._on_menu_sphere)self.window.set_on_menu_item_activated(SpheresApp.MENU_RANDOM,self._on_menu_random)self.window.set_on_menu_item_activated(SpheresApp.MENU_QUIT,self._on_menu_quit)self.scene = gui.SceneWidget()self.scene.scene = rendering.Open3DScene(self.window.renderer)self.scene.scene.show_axes(True)mesh = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_sphere()mesh.compute_vertex_normals()material = rendering.MaterialRecord()material.shader = "defaultLit"self.scene.scene.add_geometry("sphere" + str(self._id), mesh, material)em = self.window.theme.font_sizeself.layout = gui.Horiz(0, gui.Margins(0.25*em,0.25*em,0.25*em,0.254*em))self.layout.add_child(gui.Label("Model file"))self.layout.add_fixed(0.25 * em)self.window.set_on_layout(self.on_window_layout)self.window.add_child(self.scene)self.window.add_child(self.layout)def on_window_layout(self, layout: gui.LayoutContext) -> None:"""This is called when layout is required for this widgets *immediate children*, like on resize. Only the immediatechildren are *manually* positioned here, by setting the x, y, width, and height of their frames. Thegrandchildren are *not* touched here; they're automatically handled after this."""# This is the area in this widget available to place child widgets in. The *units* here aren't window screen# pixels, like from the width/height here when setting up the window: gui.Application.instance.create_window("Test", width=500, height=600).rect = self.window.content_rectr = self.window.content_rectprint(r)print(layout.theme.default_layout_spacing)print(layout.theme.default_margin)print(layout.theme.font_size)# Put the layout (containing the controls) on the left 1/3 and the and scene on the right 2/3.x_division = rect.width // 3# Set the layout (gui.Vert) on left to 1/3 available width, full height.# gui.Rect(x, y, width, height)# Set the SceneWidget on on right, 2/3 available width, full heightself.scene.frame = gui.Rect(0, 0, r.width - x_division, r.height)self.layout.frame = gui.Rect(r.width - x_division, 0, x_division, r.height)def add_sphere(self):self._id += 1mat = rendering.MaterialRecord()mat.base_color = [random.random(),random.random(),random.random(), 1.0]mat.shader = "defaultLit"sphere = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_sphere(0.5)sphere.compute_vertex_normals()sphere.translate([10.0 * random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0), 10.0 * random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0),10.0 * random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0)])self.scene.scene.add_geometry("sphere" + str(self._id), sphere, mat)def _on_menu_sphere(self):# GUI callbacks happen on the main thread, so we can do everything# normally here.self.scene.scene.clear_geometry()self.add_sphere()def _on_menu_random(self):# This adds spheres asynchronously. This pattern is useful if you have# data coming in from another source than user interaction.def thread_main():for _ in range(0, 20):# We can only modify GUI objects on the main thread, so we# need to post the function to call to the main thread.gui.Application.instance.post_to_main_thread(self.window, self.add_sphere)time.sleep(0.5)threading.Thread(target=thread_main).start()def _on_menu_quit(self):gui.Application.instance.quit()def main():gui.Application.instance.initialize()SpheresApp()gui.Application.instance.run()if __name__ == "__main__":main()相关文章:

Open3D解决SceneWidget加入布局中消失的问题
Open3D解决SceneWidget加入布局中消失的问题 Open3D解决SceneWidget加入布局中消失的问题1. 问题2. 问题代码3. 解决 Open3D解决SceneWidget加入布局中消失的问题 1. 问题 把SceneWidget加到布局管理其中图形可以展示出来,但是鼠标点击就消失了。 stackoverflow上已…...

计算机毕业设计Python+DeepSeek-R1大模型游戏推荐系统 Steam游戏推荐系统 游戏可视化 游戏数据分析(源码+文档+PPT+讲解)
温馨提示:文末有 CSDN 平台官方提供的学长联系方式的名片! 温馨提示:文末有 CSDN 平台官方提供的学长联系方式的名片! 温馨提示:文末有 CSDN 平台官方提供的学长联系方式的名片! 作者简介:Java领…...

Linux笔记---缓冲区
1. 什么是缓冲区 在计算机系统中,缓冲区(Buffer) 是一种临时存储数据的区域,主要用于协调不同速度或不同时序的组件之间的数据传输,以提高效率并减少资源冲突。它是系统设计中的重要概念,尤其在I/O操作、网…...

如何流畅访问github
1.传输数据原理 本地计算机通过本地网接入运营骨干网,经过DNS域名解析,将输入的字符解析为要连接的真实IP地址,服务器返还一个数据包(github)给计算机 2.原因 DNS域名污染-DNS解析出现问题,导致访问一个不存在的服务器 3.解决…...

java基础+面向对象
Java基础语法 CMD命令 cls 清屏 cd 目录进入文件 cd… 退回 dir 查看当前目录所有文件 E:进入E盘 exit 退出 环境变量就是不用去专门的盘符去找,直接去环境变量里找到文件 语言优势 编译型语言c: 整体翻译 解释型语言python&#x…...

Linux 检测内存泄漏方法总结
文章目录 strace检测asan内存检测linux下gperf工具(tcmalloc)检查C/C代码内存泄露问题参考 strace检测 (1)启动程序 (2) strace -f -p <PID> -tt -e brk,mmap,mmap2,munmapbrk 变大 → 说明堆增长…...

本地部署deepseek大模型后使用c# winform调用(可离线)
介于最近deepseek的大火,我就在想能不能用winform也玩一玩本地部署,于是经过查阅资料,然后了解到ollama部署deepseek,最后用ollama sharp NUGet包来实现winform调用ollama 部署的deepseek。 本项目使用Vs2022和.net 8.0开发,ollam…...

Python----数据分析(Numpy:安装,数组创建,切片和索引,数组的属性,数据类型,数组形状,数组的运算,基本函数)
一、 Numpy库简介 1.1、概念 NumPy(Numerical Python)是一个开源的Python科学计算库,旨在为Python提供 高性能的多维数组对象和一系列工具。NumPy数组是Python数据分析的基础,许多 其他的数据处理库(如Pandas、SciPy)都依赖于Num…...

Leetcode-最大矩形(单调栈)
一、题目描述 给定一个仅包含 0 和 1 、大小为 rows x cols 的二维二进制矩阵,找出只包含 1 的最大矩形,并返回其面积。 输入:matrix [["1","0","1","0","0"],["1","0&…...

域内委派维权
为某个服务账户配置 krbtgt 用户的非约束性委派或基于资源的约束性委派。这里我的 krbtgt 的基于资源约束性委派我利用不了,所以使用的是域控的机器账户 dc01$ 进行维权。 抓取所有 hash。 mimikatz.exe "privilege::debug" "lsadump::dcsync /doma…...

leetcode---LCR 140.训练计划
给定一个头节点为 head 的链表用于记录一系列核心肌群训练项目编号,请查找并返回倒数第 cnt 个训练项目编号。 示例 1: 输入:head [2,4,7,8], cnt 1 输出:8 提示: 1 < head.length < 1000 < head[i] <…...
整理)
Linux基础 -- ARM 32位常用机器码(指令)整理
ARM 32位常用机器码(指令)整理 1. 数据处理指令(运算、逻辑、比较) 指令含义示例备注MOV赋值(寄存器传输)MOV R0, R1直接将 R1 复制到 R0MVN取反MVN R0, R1R0 ~R1ADD加法ADD R0, R1, R2R0 R1 R2ADC带进…...

内存中的缓存区
在 Java 的 I/O 流设计中,BufferedInputStream 和 BufferedOutputStream 的“缓冲区”是 内存中的缓存区(具体是 JVM 堆内存的一部分),但它们的作用是优化数据的传输效率,并不是直接操作硬盘和内存之间的缓存。以下是详…...

基于 Spring Boot 的 +Vue“宠物咖啡馆平台” 系统的设计与实现
大家好,今天要和大家聊的是一款基于 Spring Boot 的 “宠物咖啡馆平台” 系统的设计与实现。项目源码以及部署相关事宜请联系我,文末附上联系方式。 项目简介 基于 Spring Boot 的 “宠物咖啡馆平台” 系统设计与实现的主要使用者分为 管理员、用户 和…...

LeetCode 解题思路 7(Hot 100)
解题思路: 初始化窗口元素: 遍历前 k 个元素,构建初始单调队列。若当前索引对应值大于等于队尾索引对应值,移除队尾索引,将当前索引加入队尾。遍历结束时当前队头索引即为当前窗口最大值,将其存入结果数组…...

linux-Dockerfile及docker-compose.yml相关字段用途
文章目录 计算机系统5G云计算LINUX Dockerfile及docker-conpose.yml相关字段用途一、Dockerfile1、基础指令2、.高级指令3、多阶段构建指令 二、Docker-Compose.yml1、服务定义(services)2、高级服务配置3、网络配置 (networks)4、卷配置 (volumes)5、扩…...

deepseek部署:ELK + Filebeat + Zookeeper + Kafka
## 1. 概述 本文档旨在指导如何在7台机器上部署ELK(Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana)堆栈、Filebeat、Zookeeper和Kafka。该部署方案适用于日志收集、处理和可视化场景。 ## 2. 环境准备 ### 2.1 机器分配 | 机器编号 | 主机名 | IP地址 | 部署组件 |-…...
微软Office 2016-2024 x86直装版 v16.0.18324 32位
微软 Office 是一款由微软公司开发的办公软件套装,能满足各种办公需求。包含 Word、Excel、PowerPoint、Outlook 和 OneNote 等软件。Word 有强大文档编辑功能和多人协作;Excel 可处理分析大量数据及支持宏编程;PowerPoint 用于制作演示文稿且…...

CMake宏定义管理:如何优雅处理第三方库的宏冲突
在C/C项目开发中,我们常常会遇到这样的困境: 当引入一个功能强大的第三方库时,却发现它定义的某个宏与我们的项目产生冲突。比如: 库定义了 BUFFER_SIZE 1024,而我们需要 BUFFER_SIZE 2048库内部使用 DEBUG 宏控制日志…...

【SpringCloud】Gateway
目录 一、网关路由 1.1.认识网关 1.2.快速入门? 1.2.1.引入依赖 1.2.2.配置路由 二、网关登录校验 2.1.Gateway工作原理 ?2.2.自定义过滤器 2.3.登录校验 2.4.微服务获取用户 2.4.1.保存用户信息到请求头 2.4.2.拦截器获取用户? ?2.5.OpenFeign传递用户 三、…...

SkyWalking 10.2.0 SWCK 配置过程
SkyWalking 10.2.0 & SWCK 配置过程 skywalking oap-server & ui 使用Docker安装在K8S集群以外,K8S集群中的微服务使用initContainer按命名空间将skywalking-java-agent注入到业务容器中。 SWCK有整套的解决方案,全安装在K8S群集中。 具体可参…...

Leetcode 3576. Transform Array to All Equal Elements
Leetcode 3576. Transform Array to All Equal Elements 1. 解题思路2. 代码实现 题目链接:3576. Transform Array to All Equal Elements 1. 解题思路 这一题思路上就是分别考察一下是否能将其转化为全1或者全-1数组即可。 至于每一种情况是否可以达到…...

Java如何权衡是使用无序的数组还是有序的数组
在 Java 中,选择有序数组还是无序数组取决于具体场景的性能需求与操作特点。以下是关键权衡因素及决策指南: ⚖️ 核心权衡维度 维度有序数组无序数组查询性能二分查找 O(log n) ✅线性扫描 O(n) ❌插入/删除需移位维护顺序 O(n) ❌直接操作尾部 O(1) ✅内存开销与无序数组相…...
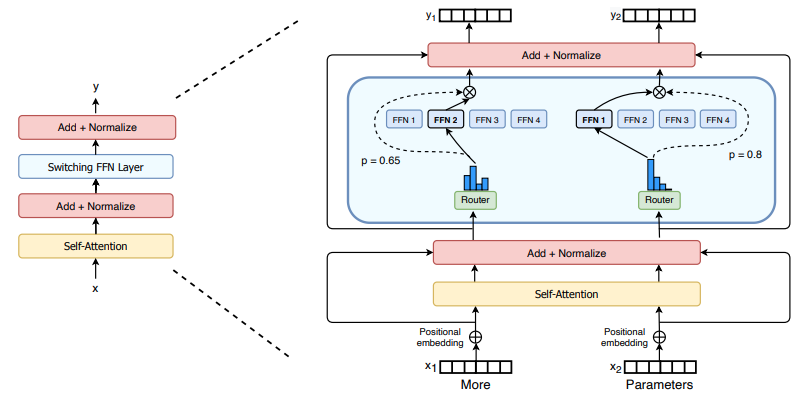
(二)TensorRT-LLM | 模型导出(v0.20.0rc3)
0. 概述 上一节 对安装和使用有个基本介绍。根据这个 issue 的描述,后续 TensorRT-LLM 团队可能更专注于更新和维护 pytorch backend。但 tensorrt backend 作为先前一直开发的工作,其中包含了大量可以学习的地方。本文主要看看它导出模型的部分&#x…...
)
OpenLayers 分屏对比(地图联动)
注:当前使用的是 ol 5.3.0 版本,天地图使用的key请到天地图官网申请,并替换为自己的key 地图分屏对比在WebGIS开发中是很常见的功能,和卷帘图层不一样的是,分屏对比是在各个地图中添加相同或者不同的图层进行对比查看。…...

2025季度云服务器排行榜
在全球云服务器市场,各厂商的排名和地位并非一成不变,而是由其独特的优势、战略布局和市场适应性共同决定的。以下是根据2025年市场趋势,对主要云服务器厂商在排行榜中占据重要位置的原因和优势进行深度分析: 一、全球“三巨头”…...

Aspose.PDF 限制绕过方案:Java 字节码技术实战分享(仅供学习)
Aspose.PDF 限制绕过方案:Java 字节码技术实战分享(仅供学习) 一、Aspose.PDF 简介二、说明(⚠️仅供学习与研究使用)三、技术流程总览四、准备工作1. 下载 Jar 包2. Maven 项目依赖配置 五、字节码修改实现代码&#…...
安装docker)
Linux离线(zip方式)安装docker
目录 基础信息操作系统信息docker信息 安装实例安装步骤示例 遇到的问题问题1:修改默认工作路径启动失败问题2 找不到对应组 基础信息 操作系统信息 OS版本:CentOS 7 64位 内核版本:3.10.0 相关命令: uname -rcat /etc/os-rele…...

MySQL JOIN 表过多的优化思路
当 MySQL 查询涉及大量表 JOIN 时,性能会显著下降。以下是优化思路和简易实现方法: 一、核心优化思路 减少 JOIN 数量 数据冗余:添加必要的冗余字段(如订单表直接存储用户名)合并表:将频繁关联的小表合并成…...
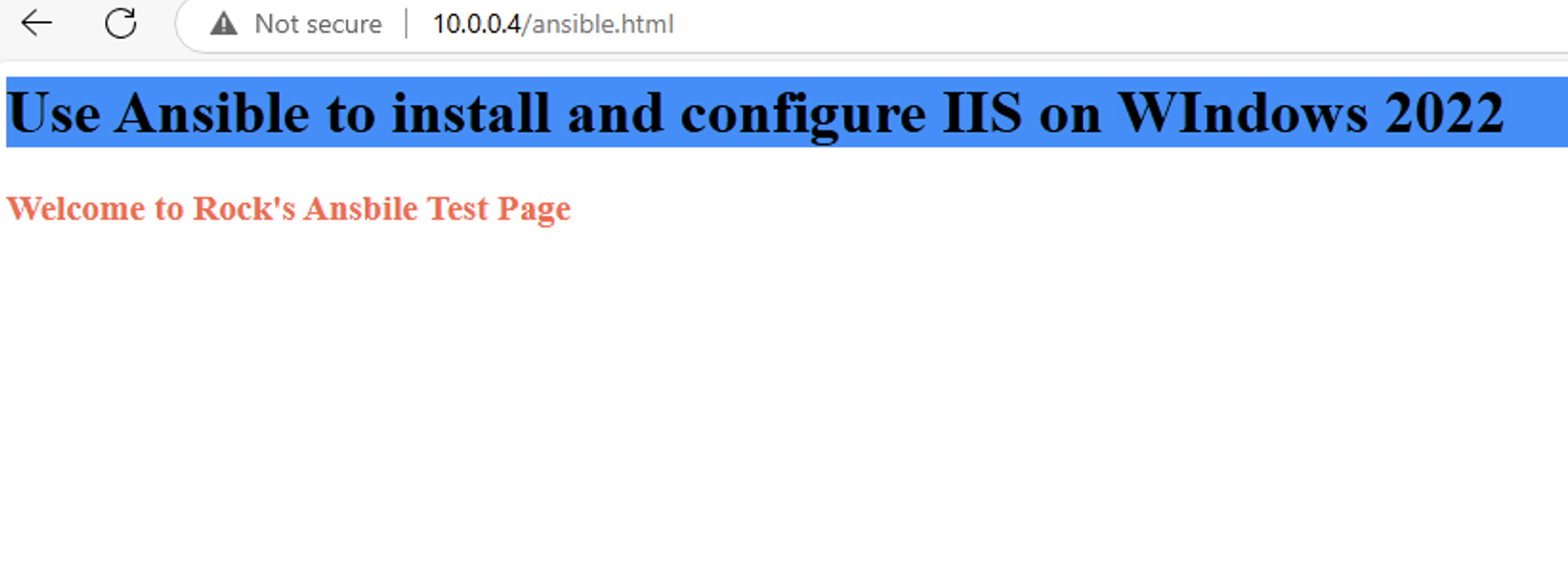
通过 Ansible 在 Windows 2022 上安装 IIS Web 服务器
拓扑结构 这是一个用于通过 Ansible 部署 IIS Web 服务器的实验室拓扑。 前提条件: 在被管理的节点上安装WinRm 准备一张自签名的证书 开放防火墙入站tcp 5985 5986端口 准备自签名证书 PS C:\Users\azureuser> $cert New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName &…...
