模块15.常用API
文章目录
- 模块15.常用API
- 第一章.Math类
- 1.Math类介绍
- 2.Math类方法
- 第二章.BigInteger
- 1.BigInteger介绍
- 2.BigInteger使用
- 第三章.BigDecimal类
- 1.BigDecimal介绍
- 2.BigDecimal使用
- 3.BigDecimal除法过时方法解决
- 第四章.Date日期类
- 1.Date类的介绍
- 2.Date类的使用
- 3.Date类的常用方法
- 第五章.Calendar日历类
- 1.Calendar介绍
- 第六章.SimpleDateFormat日期格式化类
- 1.SimpleDateFormat介绍
- 2.SimpleDateFormat常用方法
- 第七章.JDK8新日期类
- 1. LocalDate 本地日期
- 1.1.获取LocalDate对象
- 1.2.LocalDateTime对象
- 1.3.获取日期字段的方法 : 名字是get开头
- 1.4.设置日期字段的方法 : 名字是with开头
- 1.5.日期字段偏移
- 2.Period和Duration类
- 2.1 Period 计算日期之间的偏差
- 2.2 Duration计算时间之间的偏差
- 3.DateTimeFormatter日期格式化类
- 第八章.System类
- 第九章.Arrays数组工具类
- 第十章.包装类
- 1.基本数据类型对应的引用数据类型(包装类)
- 2.Integer的介绍以及使用
- 2.1.Integer基本使用
- 2.2.自动拆箱装箱
- 3.基本类型和String之间的转换
- 3.1 基本类型往String转
- 3.2 String转成基本数据类型
模块15.常用API
模块14回顾:String:1.构造:String() String(String s) String(char[] chars) String(byte[] bytes)String(char[] chars,int offset,int count) String(byte[] chars,int offset,int count)2.判断方法:equals equalsIgnoreCase3.获取方法:length() concat(String s) charAt(int index) indexOf(String s) subString(开始索引)subString(开始索引,结束索引) -> 含头不含尾4.转换方法:toCharArray() getBytes() getBytes(String charsetName) replace(c1,c2)5.分割方法:split(String regex)6.其他方法:contains(String s) endsWith(String s) statsWith(String s) toLowerCase()toUpperCase() trim()StringBuilder:1.append(任意类型数据)2.reverse()3.toString()模块十五重点:1.会BigInteger和BigDecimal操作2.会Date和SimpleDateFormat的操作3.会System中的常用方法 -> 主要是数组复制4.会Arrays中的常用方法5.会利用包装类定义一个标准的javabean6.会包装类和String之间的转换
第一章.Math类
1.Math类介绍
1.概述:数学工具类
2.作用:主要用于数学运算
3.特点:a.构造方法私有了b.方法都是静态的
4.使用:类名直接调用
2.Math类方法
static int abs(int a) -> 求参数的绝对值
static double ceil(double a) -> 向上取整
static double floor(double a) ->向下取整
static long round(double a) -> 四舍五入
static int max(int a, int b) ->求两个数之间的较大值
static int min(int a, int b) ->求两个数之间的较小值
public class Demo01Math {public static void main(String[] args) {//static int abs(int a) -> 求参数的绝对值System.out.println(Math.abs(-10));//static double ceil(double a) -> 向上取整System.out.println(Math.ceil(3.6));//static double floor(double a) ->向下取整System.out.println(Math.floor(3.6));//static long round(double a) -> 四舍五入System.out.println(Math.round(3.6));System.out.println(Math.round(-2.8));//static int max(int a, int b) ->求两个数之间的较大值System.out.println(Math.max(10,20));//static int min(int a, int b) ->求两个数之间的较小值System.out.println(Math.min(10,20));}
}
第二章.BigInteger
1.BigInteger介绍
1.问题描述:我们操作数据,将来的数据有可能非常大,大到比long还要大,这种数据我们一般称之为"对象"
2.作用:处理超大整数
3.构造:BigInteger(String val) -> 参数的格式必须是数字形式
4.方法:BigInteger add(BigInteger val) 返回其值为 (this + val) 的 BigIntegerBigInteger subtract(BigInteger val) 返回其值为 (this - val) 的 BigIntegerBigInteger multiply(BigInteger val) 返回其值为 (this * val) 的 BigIntegerBigInteger divide(BigInteger val) 返回其值为 (this / val) 的 BigInteger
2.BigInteger使用
public class Demo02BigInteger {public static void main(String[] args) {BigInteger b1 = new BigInteger("121212121212121212121212121212121212121");BigInteger b2 = new BigInteger("121212121212121212121212121212121212121");//BigInteger add(BigInteger val) 返回其值为 (this + val) 的 BigIntegerSystem.out.println(b1.add(b2));//BigInteger subtract(BigInteger val) 返回其值为 (this - val) 的 BigIntegerSystem.out.println(b1.subtract(b2));//BigInteger multiply(BigInteger val) 返回其值为 (this * val) 的 BigIntegerSystem.out.println(b1.multiply(b2));//BigInteger divide(BigInteger val) 返回其值为 (this / val) 的 BigIntegerSystem.out.println(b1.divide(b2));}
}
int intValue() 将BigInteger转成int (调用的时候对象名.方法名调用即可,比如b.intValue() )
long longValue() 将BigInteger 转成 long
BigInteger上限:42亿的21亿次方,内存根本扛不住,所以我们可以认为BigInteger无上限
第三章.BigDecimal类
1.BigDecimal介绍
1.问题描述:我们知道直接用float或者double做运算会出现精度损失的问题,所以将来设计到钱,我们就不能用float或者double直接做运算2.作用:主要是解决float和double直接做运算出现的精度损失问题3.构造方法:BigDecimal(String val) -> val必须要是数字形式(这就是以字符串的形式传入数据,要求字符串里面必须是数字的形式,也就是调他的有参构造方法)4.常用方法:static BigDecimal valueOf(double val) -> 此方法初始化小数时可以传入double型数据(如果传入数据不想用字符串的形式传入,就想直接写小数的形式,那么可以选择上面这种方式。但是实际开发并不推荐这种,更建议使用字符串的形式传入数据)BigDecimal add(BigDecimal val) 返回其值为 (this + val) 的 BigDecimalBigDecimal subtract(BigDecimal val) 返回其值为 (this - val) 的 BigDecimalBigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal val) 返回其值为 (this * val) 的 BigDecimalBigDecimal divide(BigDecimal val) 返回其值为 (this / val) 的 BigDecimal (能整除调用这个)BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal divisor, int scale, int roundingMode) (不能整除调用这个格式)divisor:除号后面的那个数scale:指定保留几位小数roundingMode:取舍方式static int ROUND_UP -> 向上加1static int ROUND_DOWN -> 直接舍去static int ROUND_HALF_UP -> 四舍五入5.注意:如果除不尽,会报错,出现运算异常
2.BigDecimal使用
public class Demo03BigDecimal {public static void main(String[] args) {//big01();//big02();big03();}private static void big03() {BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal("3.55");BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal("2.12");BigDecimal divide = b1.divide(b2, 2, BigDecimal.ROUND_UP);System.out.println("divide = " + divide);//变回基本数据类型:double v = divide.doubleValue();System.out.println("v = " + v);}private static void big02() {BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal("3.55");//BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal("2.12");BigDecimal b2 = BigDecimal.valueOf(2.12);//BigDecimal add(BigDecimal val) 返回其值为 (this + val) 的 BigDecimalBigDecimal add = b1.add(b2);System.out.println("add = " + add);//BigDecimal subtract(BigDecimal val) 返回其值为 (this - val) 的 BigDecimalBigDecimal subtract = b1.subtract(b2);System.out.println("subtract = " + subtract);//BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal val) 返回其值为 (this * val) 的 BigDecimalBigDecimal multiply = b1.multiply(b2);System.out.println("multiply = " + multiply);//BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal val) 返回其值为 (this / val) 的 BigDecimalBigDecimal divide = b1.divide(b2);System.out.println("divide = " + divide);}private static void big01() {//实际开发不要用这种直接使用float的形式float a = 3.55F;float b = 2.12F;float result = a-b;System.out.println("result = " + result);//1.4300001}
}double doubleValue() 将此BigDecimal转成double
3.BigDecimal除法过时方法解决
1.注意:如果调用的成员上面有一个横线,证明此成员过时了,底层会有一个注解@Deprecated修饰,但是过时的成员还能使用,只不过被新的成员代替了,不推荐使用了2.方法:divide(BigDecimal divisor, int scale, RoundingMode roundingMode) divisor:代表除号后面的数据scale:保留几位小数roundingMode:取舍方式-> RoundingMode是一个枚举,里面的成员可以类名直接调用UP:向上加1 DOWN:直接舍去 HALF_UP:四舍五入
private static void big04() {BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal("3.55");BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal("2.12");BigDecimal divide = b1.divide(b2, 2, RoundingMode.HALF_UP);System.out.println("divide = " + divide);}
第四章.Date日期类
1.Date类的介绍
1.概述:表示特定的瞬间,精确到毫秒2.常识:a.1000毫秒 = 1秒b.时间原点:1970年1月1日 0时0分0秒(UNIX系统起始时间),叫做格林威治时间,在0时区上c.时区:北京位于东八区,一个时区经度差15度,时间相差一个小时,所以北京时间比时间原点所在时区时间差8个小时d.北京经纬度:东经116 北纬39.56 -> 温带大陆性季风气候e.赤道 本初子午线(0度经线)
2.Date类的使用
1.构造:Date() -> 获取当前系统时间Date(long time) -> 获取指定时间,传递毫秒值 -> 从时间原点开始算
private static void date01() {//Date() -> 获取当前系统时间Date date1 = new Date();System.out.println("date1 = " + date1);//Date(long time) -> 获取指定时间,传递毫秒值 -> 从时间原点开始算Date date2 = new Date(1000L);System.out.println("date2 = " + date2);}
3.Date类的常用方法
1.void setTime(long time) -> 设置时间,传递毫秒值-> 从时间原点开始算
2.long getTime()->获取时间,返回毫秒值
private static void date02() {Date date = new Date();//1.void setTime(long time) -> 设置时间,传递毫秒值-> 从时间原点开始算date.setTime(1000L);//2.long getTime()->获取时间,返回毫秒值System.out.println(date.getTime());//1000}
第五章.Calendar日历类
1.Calendar介绍
1.概述:日历类,抽象类
2.获取:Calendar中的方法:static Calendar getInstance()
3.月份对比:国外: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11国内: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12

常用方法:int get(int field) ->返回给定日历字段的值void set(int field, int value) :将给定的日历字段设置为指定的值void add(int field, int amount) :根据日历的规则,为给定的日历字段添加或者减去指定的时间量Date getTime():将Calendar转成Date对象field:代表的是日历字段-> 年 月 日 星期等,都是静态的
private static void calendar02() {Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();//多态//int get(int field) ->返回给定日历字段的值int year = calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR);System.out.println("year = " + year);//void set(int field, int value) :将给定的日历字段设置为指定的值//calendar.set(Calendar.YEAR,2028);//System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR));//void add(int field, int amount) :根据日历的规则,为给定的日历字段添加或者减去指定的时间量calendar.add(Calendar.YEAR,-1);System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR));//Date getTime():将Calendar转成Date对象Date date = calendar.getTime();System.out.println("date = " + date);}
扩展方法:
void set(int year, int month, int date) -> 直接设置年月日需求:键盘录入一个年份,判断这一年是闰年,还是平年 步骤: 1.创建Calendar对象 2.创建Scanner对象,键盘录入一个年份 3.调用set方法,传递年,月,日set(年,2,1) -> 国外是0-11,所以设置成2月就是代表3月 4.将day减1天(3月1日减1天,就是2月最后一天,知道2月最后一天了,就知道是平年还是闰年了) 5.获取day判断平年还是闰年,输出结果private static void calendar03() {//1.创建Calendar对象Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();//2.创建Scanner对象,键盘录入一个年份Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);int year = sc.nextInt();//3.调用set方法,传递年,月,日//set(年,2,1) -> 国外是0-11,所以设置成2月就是代表3月calendar.set(year,2,1);//4.将day减1天(3月1日减1天,就是2月最后一天,知道2月最后一天了,就知道是平年还是闰年了)calendar.add(Calendar.DATE,-1);int day = calendar.get(Calendar.DATE);//5.获取day判断平年还是闰年,输出结果if (day==29){System.out.println("闰年");}else{System.out.println("平年");}}
第六章.SimpleDateFormat日期格式化类
1.SimpleDateFormat介绍
1.概述:日期格式化类
2.构造:SimpleDateFormat(String pattern)
3.pattern代表啥:代表的是我们自己指定的日期格式字母不能改变,但是中间的连接符我们可以改变 yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss | 时间字母表示 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| y | 年 |
| M | 月 |
| d | 日 |
| H | 时 |
| m | 分 |
| s | 秒 |
2.SimpleDateFormat常用方法
1.String format(Date date) -> 将Date对象按照指定的格式转成String
2.Date parse(String source)-> 将符合日期格式的字符串转成Date对象
public class Demo03SimpleDateFormat {public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");//1.String format(Date date) -> 将Date对象按照指定的格式转成StringString time1 = sdf.format(new Date());System.out.println("time1 = " + time1);//2.Date parse(String source)-> 将符合日期格式的字符串转成Date对象String time2 = "2000-10-10 10:10:10";Date date = sdf.parse(time2);System.out.println("date = " + date);}
}
第七章.JDK8新日期类
1. LocalDate 本地日期
1.1.获取LocalDate对象
1.概述:LocalDate是一个不可变的日期时间对象,表示日期,通常被视为年月日
2.获取:static LocalDate now() -> 创建LocalDate对象static LocalDate of(int year, int month, int dayOfMonth) -> 创建LocalDate对象,设置年月日
public class Demo04LocalDate {public static void main(String[] args) {//static LocalDate now() -> 创建LocalDate对象LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();System.out.println("localDate = " + localDate);//static LocalDate of(int year, int month, int dayOfMonth) -> 创建LocalDate对象,设置年月日LocalDate localDate1 = LocalDate.of(2000, 10, 10);System.out.println("localDate1 = " + localDate1);}
}
1.2.LocalDateTime对象
1.LocalDateTime概述:LocalDateTime是一个不可变的日期时间对象,代表日期时间,通常被视为年 - 月 - 日 - 时 - 分 - 秒。2.获取:
static LocalDateTime now() 创建LocalDateTime对象
static LocalDateTime of(int year, Month month, int dayOfMonth, int hour, int minute, int second) 创建LocalDateTime对象,设置年月日时分秒
public class Demo05LocalDateTime {public static void main(String[] args) {//static LocalDateTime now() 创建LocalDateTime对象LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();System.out.println("localDateTime = " + localDateTime);//static LocalDateTime of(int year, Month month, int dayOfMonth, int hour, int minute, int second) 创建LocalDateTime对象,设置年月日时分秒LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = LocalDateTime.of(2000, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10);System.out.println("localDateTime1 = " + localDateTime1);}
}
1.3.获取日期字段的方法 : 名字是get开头
int getYear()->获取年份
int getMonthValue()->获取月份
int getDayOfMonth()->获取月中的第几天
private static void get() {LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();//int getYear()->获取年份System.out.println(localDate.getYear());//int getMonthValue()->获取月份System.out.println(localDate.getMonthValue());//int getDayOfMonth()->获取月中的第几天System.out.println(localDate.getDayOfMonth());}
1.4.设置日期字段的方法 : 名字是with开头
LocalDate withYear(int year):设置年份
LocalDate withMonth(int month):设置月份
LocalDate withDayOfMonth(int day):设置月中的天数
private static void with() {LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();//LocalDate withYear(int year):设置年份//LocalDate localDate1 = localDate.withYear(2000);//System.out.println(localDate1);//LocalDate withMonth(int month):设置月份//LocalDate localDate2 = localDate1.withMonth(10);//System.out.println("localDate2 = " + localDate2);//LocalDate withDayOfMonth(int day):设置月中的天数//LocalDate localDate3 = localDate2.withDayOfMonth(10);//System.out.println("localDate3 = " + localDate3);LocalDate localDate1 = localDate.withYear(2000).withMonth(10).withDayOfMonth(10);System.out.println("localDate1 = " + localDate1);}
1.5.日期字段偏移
设置日期字段的偏移量,方法名plus开头,向后偏移
设置日期字段的偏移量,方法名minus开头,向前偏移
/*向后偏移 -> plus开头方法向前偏移 -> minus开头方法*/private static void plusAndMinus() {LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();// LocalDate localDate1 = localDate.plusYears(1L);// System.out.println("localDate1 = " + localDate1);LocalDate localDate1 = localDate.minusYears(1L);System.out.println("localDate1 = " + localDate1);}
2.Period和Duration类
2.1 Period 计算日期之间的偏差
方法:static Period between(LocalDate d1,LocalDate d2):计算两个日期之间的差值getYears()->获取相差的年getMonths()->获取相差的月getDays()->获取相差的天
private static void period() {LocalDate local1 = LocalDate.of(2022, 12, 12);LocalDate local2 = LocalDate.of(2021, 11, 11);Period period = Period.between(local2, local1);System.out.println(period.getYears());System.out.println(period.getMonths());System.out.println(period.getDays());}
2.2 Duration计算时间之间的偏差
1.static Duration between(Temporal startInclusive, Temporal endExclusive) -> 计算时间差
2.Temporal : 是一个接口实现类:LocalDate LocalDateTime3.参数需要传递 Temporal 的实现类对象, 注意要传递LocalDateTime因为Duration计算精确时间偏差,所以需要传递能操作精确时间的 LocalDateTime4.利用Dutation获取相差的时分秒 -> to开头toDays() :获取相差天数toHours(): 获取相差小时toMinutes():获取相差分钟toMillis():获取相差秒(毫秒)
private static void duration() {LocalDateTime local1 = LocalDateTime.of(2022, 12, 12,12,12,12);LocalDateTime local2 = LocalDateTime.of(2021, 11, 11,11,11,11);Duration duration = Duration.between(local2, local1);System.out.println(duration.toDays());System.out.println(duration.toHours());System.out.println(duration.toMinutes());System.out.println(duration.toMillis());}如果计算年月日 ,就用Period
如果计算时分秒,就用Duration
3.DateTimeFormatter日期格式化类
1.获取:static DateTimeFormatter ofPattern(String pattern) -> 获取对象,指定格式
2.方法:String format(TemporalAccessor temporal)-> 将日期对象按照指定的规则转成String TemporalAccessor:接口,子接口有TemporalTemporal的实现类:LocalDate LocalDateTime TemporalAccessor parse(CharSequence text)-> 将符合规则的字符串转成日期对象 如果想将TemporalAccessor转成我们常见的LocalDateTime日期对象,就需要用到LocalDateTime中的静态方法:static LocalDateTime from(TemporalAccessor temporal)
private static void parse() {DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");String time = "2000-10-10 10:10:10";TemporalAccessor temporalAccessor = dtf.parse(time);//System.out.println(temporalAccessor);LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.from(temporalAccessor);System.out.println("localDateTime = " + localDateTime);}
第八章.System类
1.概述:系统相关类,是一个工具类
2.特点:a.构造私有,不能利用构造方法new对象b.方法都是静态的
3.使用:类名直接调用
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| static long currentTimeMillis() | 返回以毫秒为单位的当前时间,可以测效率 |
| static void exit(int status) | 终止当前正在运行的 Java 虚拟机 |
| static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length | 数组复制 src:源数组 srcPos:从源数组的哪个索引开始复制 dest:目标数组 ldestPos:从目标数组哪个索引开始粘贴 length:复制多少个元素 |
public class Demo01System {public static void main(String[] args) {//currentTimeMillis();//exit();arraycopy();}/*static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length)src:源数组srcPos:从源数组的哪个索引开始复制dest:目标数组destPos:从目标数组的哪个索引开始粘贴length:复制多少个元素*/private static void arraycopy() {int[] arr1 = {1,2,3,4,5};int[] arr2 = new int[10];System.arraycopy(arr1,0,arr2,0,5);for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {System.out.print(arr2[i]+" ");}}private static void exit() {for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {if (i==5){System.exit(0);}System.out.println("helloworld"+i);}}private static void currentTimeMillis() {long time = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("time = " + time);}
}
第九章.Arrays数组工具类
1.概述:数组工具类
2.特点:a.构造私有b.方法静态
3.使用:类名直接调用
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| static String toString(int[] a) | 按照格式打印数组元素 [元素1, 元素2, …] |
| static void sort(int[] a) | 升序排序 |
| static int binarySearch(int[] a, int key) | 二分查找(前提是升序) |
| static int[] copyOf(int[] original, int newLength) | 数组扩容 |
public class Demo02Arrays {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {5,3,4,6,5,4,7};System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));System.out.println("==============");Arrays.sort(arr);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));System.out.println("==============");int[] arr1 = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7};int index = Arrays.binarySearch(arr1, 3);System.out.println("index = " + index);System.out.println("==============");int[] arr2 = {1,2,3,4,5};int[] newArr = Arrays.copyOf(arr2, 10);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(newArr));arr2 = newArr;System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));}
}

第十章.包装类
1.基本数据类型对应的引用数据类型(包装类)
1.概述:就是基本类型对应的类(包装类),我们需要将基本类型转成包装类,从而让基本类型拥有类的特性(说白了,将基本类型转成包装类之后,就可以使用包装类中的方法操作数据)2.为啥要学包装类:a.将来有一些特定场景,特定操作,比如调用方法传递包装类比如:ArrayList集合,里面有一个方法add(Integer i),此时我们不能调用add方法之后直接传递基本类型,因为引用类型不能直接接收基本类型的值,就需要先将基本类型转成包装类,传递到add方法中b.将来我们还可以将包装类转成基本类型:包装类不能直接使用+ - * /,所以需要将包装类转成基本类型,才能使用+ - * /
| 基本类型 | 包装类 |
|---|---|
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| char | Charactor |
| boolean | Boolean |
2.Integer的介绍以及使用
2.1.Integer基本使用
1.概述:Integer是int的包装类
2.构造: 不推荐使用了,但是还能用Integer(int value)Integer(String s) s必须是数字形式
public class Demo01Integer {public static void main(String[] args) {Integer i1 = new Integer(10);System.out.println("i1 = " + i1);Integer i2 = new Integer("10");System.out.println("i2 = " + i2);System.out.println("================");Boolean b1 = new Boolean("true");System.out.println("b1 = " + b1);Boolean b2 = new Boolean("false");System.out.println("b2 = " + b2);Boolean b3 = new Boolean("True");System.out.println("b3 = " + b3);}
}

1.装箱:将基本类型转成对应的包装类
2.方法:static Integer valueOf(int i) static Integer valueOf(String s)
public class Demo02Integer {public static void main(String[] args) {Integer i1 = Integer.valueOf(10);System.out.println("i1 = " + i1);Integer i2 = Integer.valueOf("100");System.out.println("i2 = " + i2);}
}
1.拆箱:将包装类转成基本类型
2.方法:int intValue();
public class Demo03Integer {public static void main(String[] args) {Integer i1 = Integer.valueOf(10);System.out.println("i1 = " + i1);int i = i1.intValue();System.out.println("(i+10) = " + (i + 10));}
}
2.2.自动拆箱装箱
1.拆箱和装箱很多时候都是自动完成的
public class Demo04Integer {public static void main(String[] args) {Integer i = 10;//发生了自动装箱了Integer sum = i+10;//发生了自动拆箱装箱System.out.println("sum = " + sum);}
}

public class Demo05Integer { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer i1 = 100; Integer i2 = 100; System.out.println(i1==i2);Integer i3 = 128; Integer i4 = 128; System.out.println(i3==i4); } }
3.基本类型和String之间的转换
3.1 基本类型往String转
1.方式1:+ 拼接
2.方式2:String中的静态方法static String valueOf(int i)
private static void method01() {int i = 10;String s1 = i+"";System.out.println(s1+1);System.out.println("============");String s = String.valueOf(10);System.out.println(s+1);}
3.2 String转成基本数据类型
每个包装类中都有一个类似的方法: parseXXX
| 位置 | 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Byte | static byte parseByte(String s) | 将String转byte类型 |
| Short | static short parseShort(String s) | 将String转成short类型 |
| Integer | static int parseInt(String s) | 将String转成int类型 |
| Long | static long parseLong(String s) | 将String转成long类型 |
| Float | static float parseFloat(String s) | 将String转成float类型 |
| Double | static double parseDouble(String s) | 将String转成double类型 |
| Boolean | static boolean parseBoolean(String s) | 将String转成boolean类型 |
private static void method02() {int number = Integer.parseInt("1111");System.out.println(number+1);}
1.在实际开发过程中如何定义一个标准javabean 定义javabean的时候一般会将基本类型的属性定义成包装类型的属性public class User {//private int uid;//用户idprivate Integer uid;//用户idprivate String username;//用户名private String password;//密码public User() {}public User(Integer uid, String username, String password) {this.uid = uid;this.username = username;this.password = password;}public Integer getUid() {return uid;}public void setUid(Integer uid) {this.uid = uid;}public String getUsername() {return username;}public void setUsername(String username) {this.username = username;}public String getPassword() {return password;}public void setPassword(String password) {this.password = password;} }1.举例:如果uid为Integer型,默认值是null 2.将来javabean中的数据都是和数据库表联系起来的,我们可以将javabean中的数据添加到表中 如果表中的uid为主键自增的,此时添加语句时uid中的数据不用我们单独维护赋值了,添加语句的sql语句就可以这样写: insert into user(uid,username,password) values (NULL,'金莲','36666');3.到时候,我们需要将javabean中封装的数据获取出来放到sql语句中,如果uid为主键自增,而且javabean中的uid为包装类型,默认值为NULL,这样就不用单独维护uid的值了,也不用先给javabean中的uid赋值,然后在保存到数据库中了,咱们就可以直接使用uid的默认值,将默认值放到sql语句的uid列中4.而且将javabean中的属性变成包装类,还可以使用包装类中的方法去操作此属性值
相关文章:

模块15.常用API
文章目录 模块15.常用API第一章.Math类1.Math类介绍2.Math类方法 第二章.BigInteger1.BigInteger介绍2.BigInteger使用 第三章.BigDecimal类1.BigDecimal介绍2.BigDecimal使用3.BigDecimal除法过时方法解决 第四章.Date日期类1.Date类的介绍2.Date类的使用3.Date类的常用方法 第…...

5c/c++内存管理
1. C/C内存分布 int globalVar 1; static int staticGlobalVar 1; void Test() {static int staticVar 1;int localVar 1;int num1[10] { 1, 2, 3, 4 };char char2[] "abcd";const char* pChar3 "abcd";int* ptr1 (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 4);i…...
python实现的可爱卸载动画
在逛掘金时,掘金用户在B站看到的灵感进行的一个卸载窗口的动画效果的实用案例。人类是一种不断在学习的动物,并且是一种模仿能力学习能里比较强的动物。我这里是第三波的学习实践者咯! 相对VUE构建动画效果窗口,我更加喜欢用pytho…...

微服务的春天:基于Spring Boot的架构设计与实践
微服务的春天:基于Spring Boot的架构设计与实践 在如今的技术领域,微服务架构俨然成为了解决复杂系统开发与运维挑战的关键利器。作为一名资深运维和自媒体创作者,笔名Echo_Wish,我将深入探讨基于Spring Boot的微服务架构设计,结合实例代码说明观点,希望能为大家带来启发…...

*VulnHub-FristiLeaks:1.3暴力解法、细节解法,主打软硬都吃,隧道搭建、寻找exp、提权、只要你想没有做不到的姿势
*VulnHub-FristiLeaks:1.3暴力解法、细节解法,主打软硬都吃,隧道搭建、寻找exp、提权、只要你想没有做不到的姿势 一、信息收集 1、扫靶机ip 经典第一步,扫一下靶机ip arp-scan -l 扫描同网段 nmap -sP 192.168.122.0/242、指纹扫描、端口…...

OpenCV 颜色空间:原理与操作指南
颜色空间原理 RGB 颜色空间 RGB(Red, Green, Blue)是最常见的颜色空间,它通过红、绿、蓝三种颜色通道的不同强度组合来表示颜色。在 OpenCV 中,RGB 图像的每个像素由三个 8 位无符号整数(0 - 255)分别表示…...

国产编辑器EverEdit - 超多样式设置
1 设置-编辑-样式 1.1 设置说明 1.1.1 折叠样式 默认为箭头,折叠样式选项如下: 箭头: 矩形和线条 五边形 圆形图标 1.1.2 光标样式 光标用于指示当前用户输入位置,光标样式选项如下: 默认 纤细 字宽 …...

rabbitmq版本升级并部署高可用
RabbitMQ版本升级 先检查是否已经安装rabbitmq rpm -qa|grep rabbitmq|wc -l //如果结果是0,表示没有安装 rpm -e --nodeps $(rpm -qa|grep rabbitmq) //如安装了,则进行卸载 先检查是否已经安装erlang rpm -qa|grep erlang|wc -l //如果结果…...

Visual Studio 2022新建c语言项目的详细步骤
步骤1:点击创建新项目 步骤2:到了项目模板 --> 选择“控制台应用” (在window终端运行代码。默认打印"Hello World") --> 点击 “下一步” 步骤3:到了配置新项目模块 --> 输入“项目名称” --> 更改“位置”路径&…...

Spring Boot使用JDBC /JPA访问达梦数据库
Spring Boot 是一个广泛使用的 Java 框架,用于快速构建基于 Spring 的应用程序。对于达梦数据库(DMDB)的支持,Spring Boot 本身并没有直接内置对达梦数据库的集成,但你可以通过一些配置和依赖来支持达梦数据库。 以下…...
)
Spring Boot 消息队列(以RabbitMQ为例)
文章目录 RabbitMQ 简介与安装1. RabbitMQ 简介2. RabbitMQ 安装 Spring Boot 集成 RabbitMQ1. 创建 Spring Boot 项目2. 配置 RabbitMQ3. 定义消息队列和交换机4. 发送消息5. 接收消息6. 测试消息发送和接收 RabbitMQ 简介与安装 1. RabbitMQ 简介 RabbitMQ 是一个开源的消息…...

单元测试与仿真程序之间的选择
为什么写这篇文章 现在的工作需求,让我有必要总结和整理一下。 凡事都有适用的场景。首先这里我需要提示一下,这里的信息,可能并不普适。 但是可以肯定一点的是,有些人,不论做事还是写书,上下文还没有交待…...

确认机制面临的挑战
在传输控制协议中,确认机制(ACK 机制)是确保数据可靠交付、实现拥塞控制和丢包恢复的重要组成部分。然而,随着网络环境和业务需求的不断演进,确认机制在实际应用中面临着诸多挑战。今天我们探讨确认机制主要面临的几项…...
的测试)
在MATLAB环境中,对矩阵拼接(Matrix Concatenation)的测试
在MATLAB环境中,对矩阵拼接(Matrix Concatenation)的正确性与鲁棒性开展测试时,需要依据不同的拼接场景精心设计测试用例,全面验证矩阵维度、数据顺序、边界条件以及异常处理等关键方面。以下是详尽的测试方法与具体示…...

[MySQL初阶]MySQL(4)基本查询
标题:[MySQL初阶]MySQL(4)基本查询 水墨不写bug 文章目录 一. 数据表设计二、对数据表的操作1. Create 操作(插入数据)查看最近受影响的行数: 2. Retrieve 操作(读取数据)࿰…...

基于STM32的智能家居蓝牙系统(论文+源码)
1总体方案设计 本次基于STM32的智能家居蓝牙系统,其系统总体架构如图2.1所示,采用STM32f103单片机作为控制器,通过DHT11传感器实现温湿度检测,MQ-2烟雾传感器实现烟雾检测,光敏电阻实现光照检测,同时将数据…...

QTS单元测试框架
1.QTS单元测试框架介绍 目前QTS项目采用C/C语言,而CppUnit就是xUnit家族中的一员,它是一个专门面向C的单元测试框架。因此,QTS采用CppUnit测试框架是比较理想的选择。 CppUnit按照层次来管理测试,最底层的就是TestCase,当有了几个TestCase以后,可以将它们组织成Te…...

《水利水电安全员考试各题型对比分析及应对攻略》
《水利水电安全员考试各题型对比分析及应对攻略》 单选题: 特点:四个选项中只有一个正确答案,相对难度较小。主要考查对基础知识的掌握程度。 应对攻略:认真审题,看清题目要求。对于熟悉的知识点,直接选择…...

sqlite3 c++ client选择; c++环境搭建 : abseil-cpp | fnc12/sqlite_orm
sqlite3 c client选择 今日20250305 2.4K星: 7月前最后提交核心: SRombauts/SQLiteCpp.git : 薄封装、命令式sql、非orm、支持事务2.4K星: 1月前最后提交核心: fnc12/sqlite_orm.git : 厚封装、非侵入、真orm、真泛型、类型复杂、支持事务、报错信息不完整(启动事…...
IMX6ULL驱动开发uboot篇02
目录 网络操作 第零步:先将网线跟电脑接好,打开串口连接到开发板上,然后上电,让UBoot停下来 第一步:查看我们的网线构成的虚拟子网是哪一个 第二步:我们必须把虚拟机的网卡模式从NAT改成桥接,…...

手游刚开服就被攻击怎么办?如何防御DDoS?
开服初期是手游最脆弱的阶段,极易成为DDoS攻击的目标。一旦遭遇攻击,可能导致服务器瘫痪、玩家流失,甚至造成巨大经济损失。本文为开发者提供一套简洁有效的应急与防御方案,帮助快速应对并构建长期防护体系。 一、遭遇攻击的紧急应…...
51c自动驾驶~合集58
我自己的原文哦~ https://blog.51cto.com/whaosoft/13967107 #CCA-Attention 全局池化局部保留,CCA-Attention为LLM长文本建模带来突破性进展 琶洲实验室、华南理工大学联合推出关键上下文感知注意力机制(CCA-Attention),…...
《从零掌握MIPI CSI-2: 协议精解与FPGA摄像头开发实战》-- CSI-2 协议详细解析 (一)
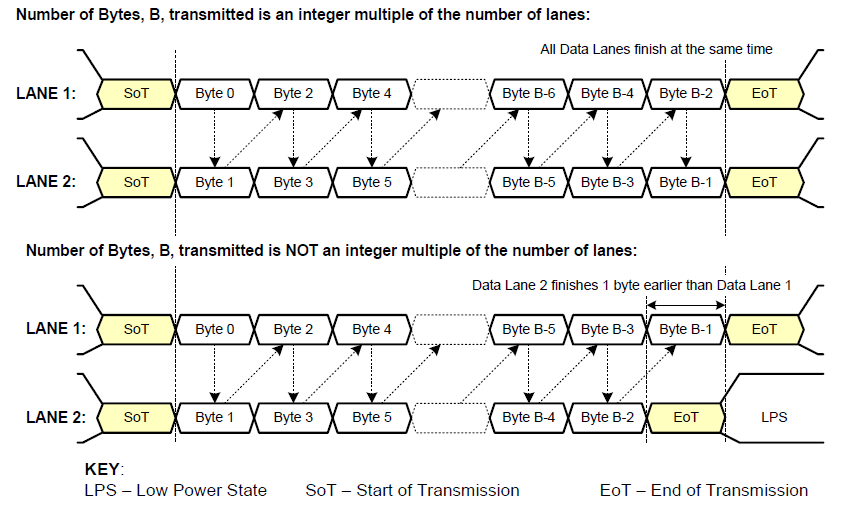
CSI-2 协议详细解析 (一) 1. CSI-2层定义(CSI-2 Layer Definitions) 分层结构 :CSI-2协议分为6层: 物理层(PHY Layer) : 定义电气特性、时钟机制和传输介质(导线&#…...

线程与协程
1. 线程与协程 1.1. “函数调用级别”的切换、上下文切换 1. 函数调用级别的切换 “函数调用级别的切换”是指:像函数调用/返回一样轻量地完成任务切换。 举例说明: 当你在程序中写一个函数调用: funcA() 然后 funcA 执行完后返回&…...
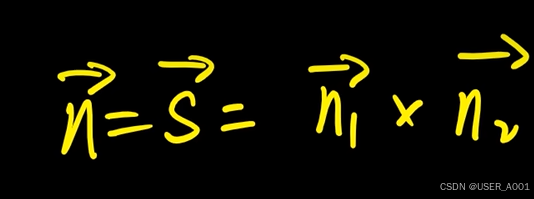
高等数学(下)题型笔记(八)空间解析几何与向量代数
目录 0 前言 1 向量的点乘 1.1 基本公式 1.2 例题 2 向量的叉乘 2.1 基础知识 2.2 例题 3 空间平面方程 3.1 基础知识 3.2 例题 4 空间直线方程 4.1 基础知识 4.2 例题 5 旋转曲面及其方程 5.1 基础知识 5.2 例题 6 空间曲面的法线与切平面 6.1 基础知识 6.2…...
基础光照(Basic Lighting))
C++.OpenGL (10/64)基础光照(Basic Lighting)
基础光照(Basic Lighting) 冯氏光照模型(Phong Lighting Model) #mermaid-svg-GLdskXwWINxNGHso {font-family:"trebuchet ms",verdana,arial,sans-serif;font-size:16px;fill:#333;}#mermaid-svg-GLdskXwWINxNGHso .error-icon{fill:#552222;}#mermaid-svg-GLd…...
MySQL 8.0 OCP 英文题库解析(十三)
Oracle 为庆祝 MySQL 30 周年,截止到 2025.07.31 之前。所有人均可以免费考取原价245美元的MySQL OCP 认证。 从今天开始,将英文题库免费公布出来,并进行解析,帮助大家在一个月之内轻松通过OCP认证。 本期公布试题111~120 试题1…...
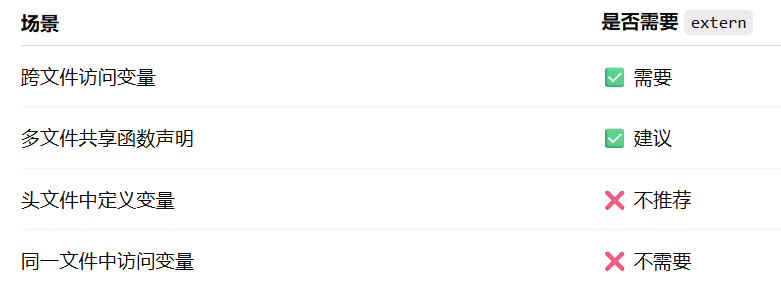
深入解析C++中的extern关键字:跨文件共享变量与函数的终极指南
🚀 C extern 关键字深度解析:跨文件编程的终极指南 📅 更新时间:2025年6月5日 🏷️ 标签:C | extern关键字 | 多文件编程 | 链接与声明 | 现代C 文章目录 前言🔥一、extern 是什么?&…...
:邮件营销与用户参与度的关键指标优化指南)
精益数据分析(97/126):邮件营销与用户参与度的关键指标优化指南
精益数据分析(97/126):邮件营销与用户参与度的关键指标优化指南 在数字化营销时代,邮件列表效度、用户参与度和网站性能等指标往往决定着创业公司的增长成败。今天,我们将深入解析邮件打开率、网站可用性、页面参与时…...
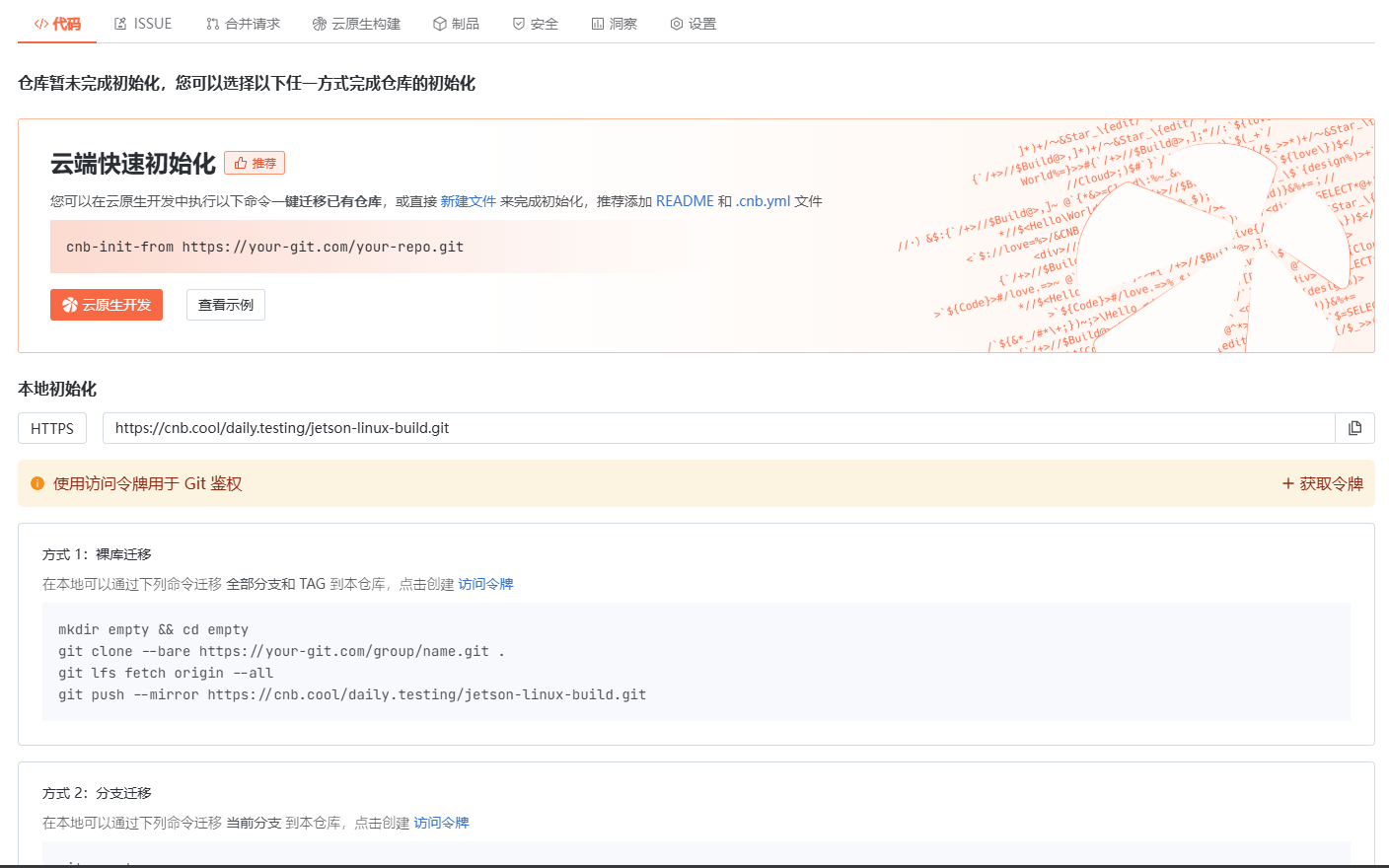
云原生玩法三问:构建自定义开发环境
云原生玩法三问:构建自定义开发环境 引言 临时运维一个古董项目,无文档,无环境,无交接人,俗称三无。 运行设备的环境老,本地环境版本高,ssh不过去。正好最近对 腾讯出品的云原生 cnb 感兴趣&…...
