ROS 下 激光扫描仪 YDLidar-G4 使用
环境配置:
ubuntu20.04 LTS
ROS noetic
编程工具:vs code,远程通过ssh访问
扫描仪:YDLidar-G4
YDLidar驱动:
YDLidar SDK
YDLidar ROS 功能包
此环境包含树莓派,以下过程在树莓派3B上测试通过,不必任何修改。
1 . YDLidar-SDK通信协议
雷达扫描输出的数据以十六进制格式输出到通信接口。
无强度字节偏移的数据包格式:(12字节)
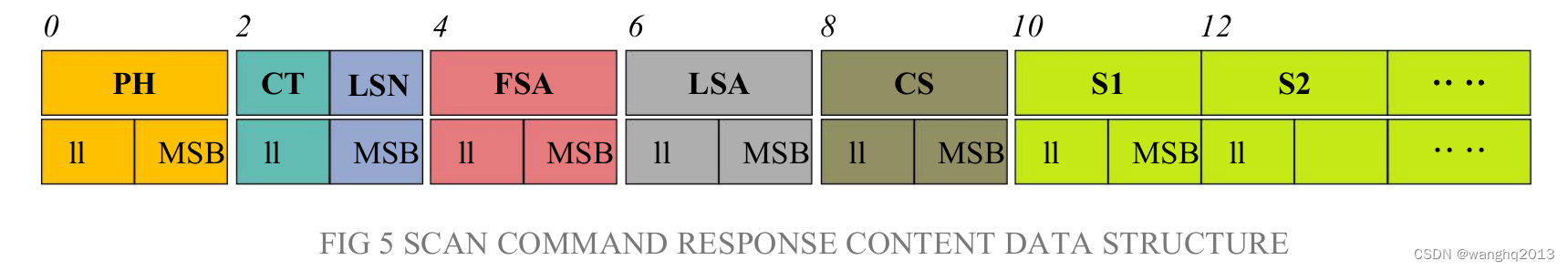
有强度字节偏移的数据包格式:(13字节)
 雷达扫描输出数据格式表:
雷达扫描输出数据格式表:
| 内容 | 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| H(2B) | Packet header | 2 Byte in length, Fixed at 0x55AA, low is front, high in back. |
| CT(1B) | Package type | Indicates the current packet type. (0x00 = CT & 0x01): Normal Point cloud packet. (0x01 = CT & 0x01): Zero packet. |
| LSN(1B) | Sample Data Number | ndicates the number of sampling points contained in the current packet. There is only once zero point of data in thre zero packet. the value is 1. |
| FSA(2B) | Starting angle | The angle data corresponding to the first sample point in the smapled data. |
| LSA(2B) | End angle | The angle data corresponding to the last sample point in the sampled data. |
| CS(2B) | Check code | The check code of the current data packet uses a two-byte exclusive OR to check the current data packet. |
| Si(2B/3B) | Sampling data | The system test sampling data is the distance data of the sampling point. Note: If the LiDAR has intensity, Si is 3 Byte. otherwise is 2 Byte. Si(3B)–>I(1B)(D(2B)): first Byte is Inentsity, The last two bytes are the Distance. |
Zero resolution
Start data packet: (CT & 0x01) = 0x01, LSN = 1, Si = 1.
scan frequency: When it was a zero packet, The Lidar Scan frequency: SF = (CT >> 1) / 10.f; The Calculated frequency is the Lidar real-time frequency of the previous frame. If SF is non-zero, the protocol has real-time frequency.
Distance analysis:
Distance solution formula:
Triangle LiDAR: Distance(i) = Si / 4;
TOF LiDAR: Distance(i) = Si;
Intensity analysis:
Si(3B) split into three bytes : S(0) S(1) S(2)
Inensity solution formula:
Triangle LiDAR:
Intensity(i) = uint16_t((S(1) & 0x03)<< 8 | S(0));
Distance(i) = uint16_t(S(2) << 8 | S(1)) >> 2;
Angle analysis:(4字节)
First level analysis:
Starting angle solution formula: A n g l e F S A = R s h i f t b i t ( F S A , 1 ) 64 Angle_{FSA}=\frac{Rshiftbit(FSA, 1)}{64} AngleFSA=64Rshiftbit(FSA,1)
End angle solution formula: A n g l e L S A = R s h i f t b i t ( L S A , 1 ) 64 Angle_{LSA}=\frac{Rshiftbit(LSA, 1)}{64} AngleLSA=64Rshiftbit(LSA,1)
Intermediate angle solution formula:
A n g l e i = d i f f ( A n g l e ) L S N − 1 ∗ i + A n g l e F S A ( 0 , 1 , … , L S N − 1 ) Angle_{i}=\frac{diff(Angle)}{LSN - 1}*i + Angle_{FSA} (0,1,\ldots,LSN-1) Anglei=LSN−1diff(Angle)∗i+AngleFSA(0,1,…,LSN−1)
A n g l e 0 : A n g l e F S A Angle_{0} : Angle_{FSA} Angle0:AngleFSA;
A n g l e L S N − 1 : A n g l e L S A Angle_{LSN-1} : Angle_{LSA} AngleLSN−1:AngleLSA;
Rshiftbit(data,1) means shifting the data to the right by one bit.
diff Angle means the clockwise angle difference from the starting angle (uncorrected value) to the ending angle (uncorrected value),and LSN represents the number of packet samples in this frame.
diff(Angle): ( A n g l e ( L S A ) − A n g l e ( F S A ) ) (Angle(LSA) - Angle(FSA)) (Angle(LSA)−Angle(FSA));
If less than zero, d i f f ( A n g l e ) = ( A n g l e ( L S A ) − A n g l e ( F S A ) ) + 360 diff(Angle) = (Angle(LSA)- Angle(FSA)) + 360 diff(Angle)=(Angle(LSA)−Angle(FSA))+360 ,
otherwise
d i f f ( A n g l e ) = ( A n g l e ( L S A ) − A n g l e ( F S A ) ) diff(Angle) = (Angle(LSA)- Angle(FSA)) diff(Angle)=(Angle(LSA)−Angle(FSA)).
double Angle_FSA = (FSA >> 1) / 64;
double Angle_LSA = (LSA >> 1) / 64;
double angle_diff = Angle_LSA - Angle_FSA;
if(angle_diff < 0) {angle_diff += 360;
}
double Angle[LSN];
for(int i = 0; i < LSN; i++) {if(LSN > 1) {Angle[i] = i* angle_diff / (LSN - 1) + Angle_FSA;} else {Angle[i] = Angle_FSA;}
}Second-level analysis:
Triangle Lidar only has current Second-level analysis, TOF Lidar does not need.
Angle correction formula:
A n g l e i = A n g l e i + A n g C o r r e c t i Angle_{i} = Angle_{i} + AngCorrect_{i} Anglei=Anglei+AngCorrecti; ( 1 , 2 , … , L S N 1,2,\ldots,LSN 1,2,…,LSN)
AngCorrect is the angle correction value, and its calculation formula is as follows, t a n − 1 tan^{-1} tan−1 is an inverse trigonometric function. and the return angle value is:
if( D i s t a n c e i Distance_{i} Distancei == 0)
{
A n g C o r r e c t i AngCorrect_{i} AngCorrecti = 0;
}
else
{
A n g C o r r e c t i = a t a n ( 21.8 ∗ 155.3 − D i s t a n c e i 155.3 ∗ D i s t a n c e i ) ∗ ( 180 / 3.1415926 ) AngCorrect_{i} = atan(21.8 * \frac{155.3 - Distance_{i}}{155.3*Distance_{i}}) * (180/3.1415926) AngCorrecti=atan(21.8∗155.3∗Distancei155.3−Distancei)∗(180/3.1415926);
}
For example, In the data packet, the 4th to 8th bytes are 28 E5 6F BD 79, so LSN = 0x28 = 40(dec), FSA = 0x6FE5, LSA = 0x79BD, and bring in the first-level solution formula, and get:
A n g l e F S A = 223.7 8 ° Angle_{FSA} = 223.78^{°} AngleFSA=223.78°
A n g l e L S A = 243.4 7 ° Angle_{LSA} = 243.47^{°} AngleLSA=243.47°
d i f f ( A n g l e ) = A n g l e L S A − A n g l e F S A = 243.4 7 ° − 223.7 8 ° = 19.6 9 ° diff(Angle) = Angle_{LSA} - Angle_{FSA} = 243.47^{°} - 223.78^{°} = 19.69^{°} diff(Angle)=AngleLSA−AngleFSA=243.47°−223.78°=19.69°
A n g l e i = 19.6 9 ° 39 ∗ ( i − 1 ) + 223.7 8 ° Angle_{i} = \frac{19.69^{°}}{39}*(i -1) + 223.78^{°} Anglei=3919.69°∗(i−1)+223.78° ( 1 , 2 , … , L S N 1,2,\ldots,LSN 1,2,…,LSN)
Assume that in the frame data:
D i s t a n c e 1 = 1000 Distance_{1} = 1000 Distance1=1000
D i s t a n c e L S N = 8000 Distance_{LSN} = 8000 DistanceLSN=8000
bring in the second-level solution formula, you get:
A n g C o r r e c t 1 = − 6.762 2 ° AngCorrect_{1} = -6.7622^{°} AngCorrect1=−6.7622°
A n g C o r r e c t L S N = − 7.837 4 ° AngCorrect_{LSN} = -7.8374^{°} AngCorrectLSN=−7.8374°
A n g l e F S A = A n g l e 1 + A n g C o r r e c t 1 = 217.017 8 ° Angle_{FSA} = Angle_{1} + AngCorrect_{1} = 217.0178^{°} AngleFSA=Angle1+AngCorrect1=217.0178°
A n g l e L S A = A n g l e L S A + A n g C o r r e c t L S A = 235.632 6 ° Angle_{LSA} = Angle_{LSA} + AngCorrect_{LSA} = 235.6326^{°} AngleLSA=AngleLSA+AngCorrectLSA=235.6326°
Similarly, A n g l e i ( 2 , 3 , … , L S N − 1 ) Angle_{i}(2,3, \ldots,LSN-1) Anglei(2,3,…,LSN−1), can be obtained sequentially.
for(int i = 0; i < LSN; i++) {if(Distance[i] > 0) {double AngCorrect = atan(21.8 * (155.3 - Distance[i]) / (155.3 * Distance[i]));Angle[i] += AngCorrect * 180 / M_PI;//degree}if(Angle[i] >= 360) {Angle[i] -= 360;}
}Note: TOF LiDAR does not neeed second-level analysis.
Check code parsing:
The check code uses a two-byte exclusive OR to verify the
current data packet. The check code itself does not participate in
XOR operations, and the XOR order is not strictly in byte order.
Therefore, the check code solution formula is:
C S = X O R ∑ i = 1 n ( C i ) CS = XOR \sum_{i=1}^{n}(C^i) CS=XORi=1∑n(Ci)
No intensity Si(2B):
uint16_t checksumcal = PH;
checksumcal ^= FSA;
for(int i = 0; i < 2 * LSN; i = i +2 ) {checksumcal ^= uint16_t(data[i+1] <<8 | data[i]);
}
checksumcal ^= uint16_t(LSN << 8 | CT);
checksumcal ^= LSA;## uint16_t : unsigned short Intensity Si(3B):
uint16_t checksumcal = PH;
checksumcal ^= FSA;
for(int i = 0; i < 3 * LSN; i = i + 3) {checksumcal ^= data[i];checksumcal ^= uint16_t(data[i+2] <<8 | data[i + 1]);
}
checksumcal ^= uint16_t(LSN << 8 | CT);
checksumcal ^= LSA;## uint16_t : unsigned short example
No Intensity:

uint8_t Buffer[12];
Buffer[0] = 0xAA;
Buffer[1] = 0x55;
Buffer[2] = 0x01;
Buffer[3] = 0x01;
Buffer[4] = 0x53;
Buffer[5] = 0xAE;
Buffer[6] = 0x53;
Buffer[7] = 0xAE;
Buffer[8] = 0xAB;
Buffer[9] = 0x54;
Buffer[10] = 0x00;
Buffer[11] = 0x00;uint16_t check_code = 0x55AA;
uint8_t CT = Buffer[2] & 0x01;
uin8_t LSN = Buffer[3];
uint16_t FSA = uint16_t(Buffer[5] << 8 | Buffer[4]);
check_code ^= FSA;
uint16_t LSA = uint16_t(Buffer[7] << 8 | Buffer[6]);
uint16_t CS = uint16_t(Buffer[9] << 8 | Buffer[8]);double Distance[LSN];
for(int i = 0; i < 2 * LSN; i = i + 2) {uint16_t data = uint16_t(Buffer[10 + i + 1] << 8 | Buffer[10 + i]);check_code ^= data;Distance[i / 2 ] = data / 4;
}
check_code ^= uint16_t(LSN << 8 | CT);
check_code ^= LSA;double Angle[LSN];if(check_code == CS) {double Angle_FSA = (FSA >> 1) / 64;double Angle_LSA = (LSA >> 1) / 64;double Angle_Diff = (Angle_LSA - Angle_FSA);if(Angle_Diff < 0) {Angle_Diff = Angle_Diff + 360;}for(int i = 0; i < LSN; i++) {if(LSN > 1) {Angle[i] = i * Angle_Diff/ (LSN- 1) + Angle_FSA;} else {Angle[i] = Angle_FSA;}if(Distance[i] > 0) {double AngCorrect = atan(21.8 * (155.3 - Distance[i]) / (155.3 * Distance[i]));Angle[i] = Angle[i] + AngCorrect * 180 / M_PI;}if(Angle[i] >= 360) {Angle[i] -= 360;}}
}Intensity:

uint8_t Buffer[13];
Buffer[0] = 0xAA;
Buffer[1] = 0x55;
Buffer[2] = 0x01;
Buffer[3] = 0x01;
Buffer[4] = 0x53;
Buffer[5] = 0xAE;
Buffer[6] = 0x53;
Buffer[7] = 0xAE;
Buffer[8] = 0xAB;
Buffer[9] = 0x54;
Buffer[10] = 0x00;
Buffer[11] = 0x00;
Buffer[12] = 0x00;uint16_t check_code = 0x55AA;
uint8_t CT = Buffer[2] & 0x01;
uin8_t LSN = Buffer[3];
uint16_t FSA = uint16_t(Buffer[5] << 8 | Buffer[4]);
check_code ^= FSA;
uint16_t LSA = uint16_t(Buffer[7] << 8 | Buffer[6]);
uint16_t CS = uint16_t(Buffer[9] << 8 | Buffer[8]);double Distance[LSN];
uin16_t Itensity[LSN];
for(int i = 0; i < 3 * LSN; i = i + 3) {check_code ^= Buffer[10 + i];uint16_t data = uint16_t(Buffer[10 + i + 2] << 8 | Buffer[10 + i + 1]);check_code ^= data;Itensity[i / 3] = uint16_t((Buffer[10 + i + 1] & 0x03) <<8 | Buffer[10 + i]);Distance[i / 3] = data >> 2;
}
check_code ^= uint16_t(LSN << 8 | CT);
check_code ^= LSA;double Angle[LSN];if(check_code == CS) {double Angle_FSA = (FSA >> 1) / 64;double Angle_LSA = (LSA >> 1) / 64;double Angle_Diff = (Angle_LSA - Angle_FSA);if(Angle_Diff < 0) {Angle_Diff = Angle_Diff + 360;}for(int i = 0; i < LSN; i++) {if(LSN > 1) {Angle[i] = i * Angle_Diff/ (LSN- 1) + Angle_FSA;} else {Angle[i] = Angle_FSA;}if(Distance[i] > 0) {double AngCorrect = atan(21.8 * (155.3 - Distance[i]) / (155.3 * Distance[i]));Angle[i] = Angle[i] + AngCorrect * 180 / M_PI;}}
}1 )编译过程
创建一个工作空间,把雷达SDK驱动和雷达ROS功能包下载到工作空间的src目录。然后catkin_make编译安装。
mkdir -p ydlidar_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/YDLIDAR/YDLidar-SDK.git
git clone https://github.com/YDLIDAR/ydlidar_ros_driver.git
cd ..
catkin_make
由于SDK驱动支持C++外,还支持PYTHON语言,所以,编译前可能需要先安装swig、python3-pip和python。
编译后,生成 ydlidar_ros_driver包中的ydlidar_ros_driver_node。
然后,环境变量设置:
echo "source ~/ydlidar_ws/devel/setup.bash">> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
运行(对于 YDLidar-G4):
roslaunch ydlidar_ros2_driver ydlidar_view.launch
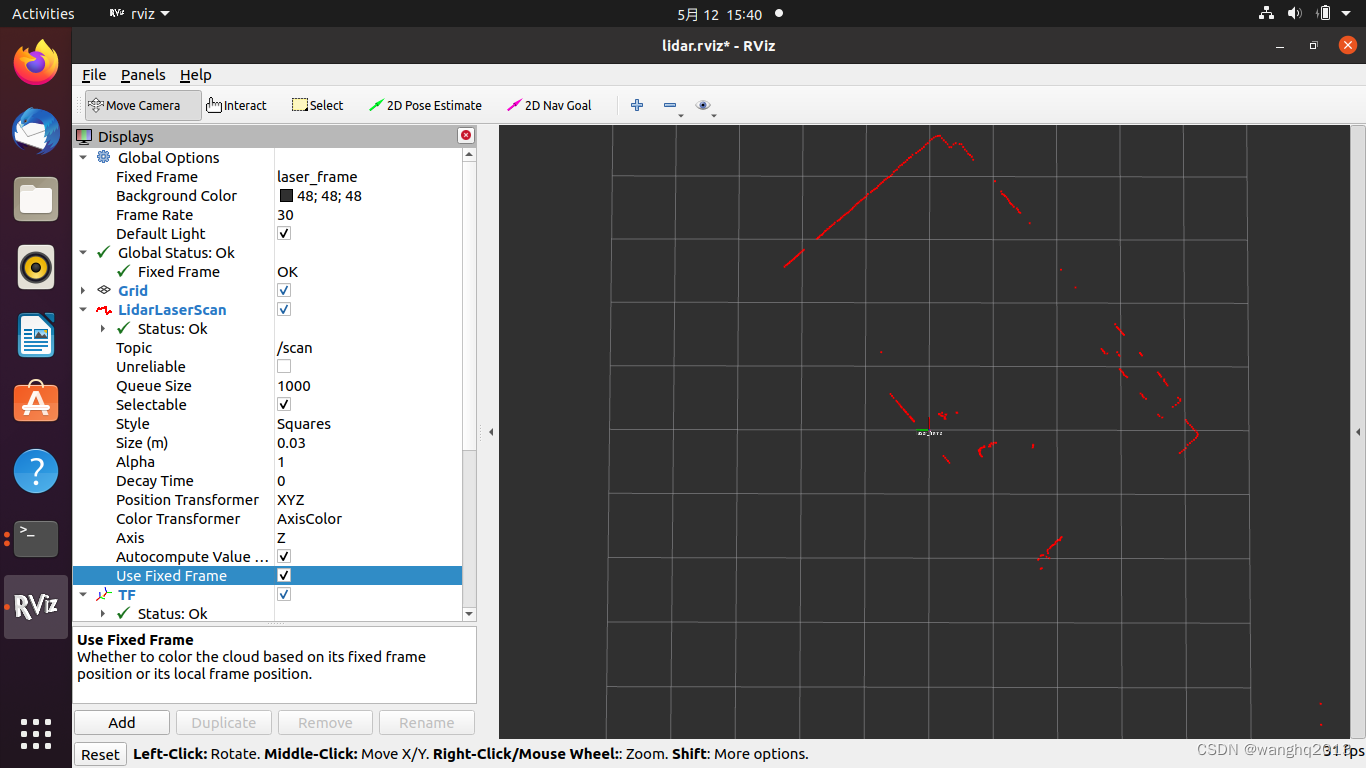 2) 源码分析
2) 源码分析
SDK的驱动源码由core/base|common|math|network|serial 几个部分组成:
core
│ ├── base
│ │ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ │ ├── datatype.h
│ │ ├── locker.h
│ │ ├── thread.h
│ │ ├── timer.cpp
│ │ ├── timer.h
│ │ ├── typedef.h
│ │ ├── utils.h
│ │ ├── v8stdint.h
│ │ └── ydlidar.h
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── common
│ │ ├── ChannelDevice.h
│ │ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ │ ├── DriverInterface.h
│ │ ├── ydlidar_datatype.h
│ │ ├── ydlidar_def.cpp
│ │ ├── ydlidar_def.h
│ │ ├── ydlidar_help.h
│ │ └── ydlidar_protocol.h
│ ├── math
│ │ ├── angles.h
│ │ └── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── network
│ │ ├── ActiveSocket.cpp
│ │ ├── ActiveSocket.h
│ │ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ │ ├── PassiveSocket.cpp
│ │ ├── PassiveSocket.h
│ │ ├── SimpleSocket.cpp
│ │ ├── SimpleSocket.h
│ │ └── StatTimer.h
│ └── serial
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── common.h
│ ├── impl
│ │ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ │ ├── unix
│ │ │ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ │ │ ├── list_ports_linux.cpp
│ │ │ ├── lock.c
│ │ │ ├── lock.h
│ │ │ ├── unix.h
│ │ │ ├── unix_serial.cpp
│ │ │ └── unix_serial.h
│ │ └── windows
│ │ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ │ ├── list_ports_win.cpp
│ │ ├── win.h
│ │ ├── win_serial.cpp
│ │ └── win_serial.h
│ ├── serial.cpp
│ └── serial.hSDK驱动编译安装后,按照CMakeLists.txt配置,将被安装在/usr/local/目录下,包括头文件,库文件,文档和测试程序等。
.
├── bin
│ ├── etlidar_test.py
│ ├── et_test
│ ├── gs_test
│ ├── lidar_c_api_test
│ ├── plot_tof_test.py
│ ├── plot_ydlidar_test.py
│ ├── rosdepc
│ ├── sdm_test
│ ├── test.py
│ ├── tmini_test
│ ├── tof_test
│ ├── tof_test.py
│ ├── tri_and_gs_test
│ ├── tri_restart
│ ├── tri_test
│ └── ydlidar_test.py
├── etc
├── games
├── include
│ ├── core
│ │ ├── base
│ │ │ ├── datatype.h
│ │ │ ├── locker.h
│ │ │ ├── thread.h
│ │ │ ├── timer.h
│ │ │ ├── typedef.h
│ │ │ ├── utils.h
│ │ │ ├── v8stdint.h
│ │ │ └── ydlidar.h
│ │ ├── common
│ │ │ ├── ChannelDevice.h
│ │ │ ├── DriverInterface.h
│ │ │ ├── ydlidar_datatype.h
│ │ │ ├── ydlidar_def.h
│ │ │ ├── ydlidar_help.h
│ │ │ └── ydlidar_protocol.h
│ │ ├── math
│ │ │ └── angles.h
│ │ ├── network
│ │ │ ├── ActiveSocket.h
│ │ │ ├── PassiveSocket.h
│ │ │ ├── SimpleSocket.h
│ │ │ └── StatTimer.h
│ │ └── serial
│ │ ├── common.h
│ │ ├── impl
│ │ │ └── unix
│ │ │ ├── lock.h
│ │ │ ├── unix.h
│ │ │ └── unix_serial.h
│ │ └── serial.h
│ ├── src
│ │ ├── CYdLidar.h
│ │ ├── ETLidarDriver.h
│ │ ├── filters
│ │ │ ├── FilterInterface.h
│ │ │ └── NoiseFilter.h
│ │ ├── GS1LidarDriver.h
│ │ ├── GS2LidarDriver.h
│ │ ├── SDMLidarDriver.h
│ │ ├── YDlidarDriver.h
│ │ └── ydlidar_sdk.h
│ └── ydlidar_config.h
├── lib
│ ├── cmake
│ │ └── ydlidar_sdk
│ │ ├── ydlidar_sdkConfig.cmake
│ │ ├── ydlidar_sdkConfigVersion.cmake
│ │ └── ydlidar_sdkTargets.cmake
│ ├── libydlidar_sdk.a
│ ├── pkgconfig
│ │ └── YDLIDAR_SDK.pc
│ ├── python2.7
│ │ ├── dist-packages
│ │ │ ├── ydlidar.py
│ │ │ └── _ydlidar.so
│ │ └── site-packages
│ └── python3.8
│ └── dist-packages
│ ├── rosdepc
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── __pycache__
│ │ │ ├── __init__.cpython-38.pyc
│ │ │ └── rosdepc.cpython-38.pyc
│ │ └── rosdepc.py
│ └── rosdepc-1.0.2.dist-info
│ ├── entry_points.txt
│ ├── INSTALLER
│ ├── LICENSE
│ ├── METADATA
│ ├── RECORD
│ ├── top_level.txt
│ └── WHEEL其中,startup目录下的initenv.sh,涉及/dev/ttyUSB*的识别,出问题较多。
#!/bin/bash
echo 'KERNEL=="ttyUSB*", ATTRS{idVendor}=="10c4", ATTRS{idProduct}=="ea60", MODE:="0666", GROUP:="dialout", SYMLINK+="ydlidar"' >/etc/udev/rules.d/ydlidar.rulesecho 'KERNEL=="ttyACM*", ATTRS{idVendor}=="0483", ATTRS{idProduct}=="5740", MODE:="0666", GROUP:="dialout", SYMLINK+="ydlidar"' >/etc/udev/rules.d/ydlidar-V2.rulesecho 'KERNEL=="ttyUSB*", ATTRS{idVendor}=="067b", ATTRS{idProduct}=="2303", MODE:="0666", GROUP:="dialout", SYMLINK+="ydlidar"' >/etc/udev/rules.d/ydlidar-2303.rulesservice udev reload
sleep 2
service udev restart
编译安装后,对于G4雷达生成对应的文件 “/etc/udev/rules.d/ydlidar.rules”,一般的,/dev/ttyUSB0对应于雷达ROS功能包中串口通信中的“port”参数,即:“dev/ydlidar”
vscode 调试源码时,配置文件:
{"configurations": [{"name": "Linux","includePath": ["${workspaceFolder}/**", #功能包头文件路径"/usr/local/include/**", #SDK头文件路径"/opt/ros/noetic/include/**" #ROS系统及消息头文件路径],"defines": [],"compilerPath": "/usr/bin/gcc","cStandard": "c17","cppStandard": "gnu++14","intelliSenseMode": "linux-gcc-x64"}],"version": 4
}
雷达数据类型(LaserFan.msg):
std_msgs/Header header
float32 angle_min
float32 angle_max
float32 time_increment
float32 scan_time
float32 range_min
float32 range_max
float32[] angles
float32[] ranges
float32[] intensities节点源码:
//ydlidar_ros_driver.cpp
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include "sensor_msgs/LaserScan.h"
#include "sensor_msgs/PointCloud.h"
//#include "ydlidar_ros_driver/LaserFan.h"
#include "std_srvs/Empty.h"
#include "src/CYdLidar.h"
#include "ydlidar_config.h"
#include <limits> // std::numeric_limits#define SDKROSVerision "1.0.2"CYdLidar laser;bool stop_scan(std_srvs::Empty::Request &req,std_srvs::Empty::Response &res) {ROS_DEBUG("Stop scan");return laser.turnOff();
}bool start_scan(std_srvs::Empty::Request &req,std_srvs::Empty::Response &res) {ROS_DEBUG("Start scan");return laser.turnOn();
}int main(int argc, char **argv) {ros::init(argc, argv, "ydlidar_ros_driver"); //节点初始化ROS_INFO("YDLIDAR ROS Driver Version: %s", SDKROSVerision);ros::NodeHandle nh; //声明一个ROS句柄ros::Publisher scan_pub = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::LaserScan>("scan", 1); //注册一个/scan话题的消息发布者ros::Publisher pc_pub = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud>("point_cloud",1);//注册一个/point_cloud话题的消息发布者ros::NodeHandle nh_private("~"); //利用函数模板进行ROS对象的雷达属性设置std::string str_optvalue = "/dev/ydlidar";nh_private.param<std::string>("port", str_optvalue,"/dev/ydlidar");///lidar port //雷达属性设置,对应于lidar.launch(For G4)中的参数laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropSerialPort, str_optvalue.c_str(),str_optvalue.size());///ignore arraynh_private.param<std::string>("ignore_array", str_optvalue, "");laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropIgnoreArray, str_optvalue.c_str(),str_optvalue.size());std::string frame_id = "laser_frame";nh_private.param<std::string>("frame_id", frame_id, "laser_frame");//int property//// lidar baudrateint optval = 230400;nh_private.param<int>("baudrate", optval, 230400);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropSerialBaudrate, &optval, sizeof(int));/// tof lidaroptval = TYPE_TRIANGLE;nh_private.param<int>("lidar_type", optval, TYPE_TRIANGLE);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropLidarType, &optval, sizeof(int));/// device typeoptval = YDLIDAR_TYPE_SERIAL;nh_private.param<int>("device_type", optval, YDLIDAR_TYPE_SERIAL);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropDeviceType, &optval, sizeof(int));/// sample rateoptval = 9;nh_private.param<int>("sample_rate", optval, 9);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropSampleRate, &optval, sizeof(int));/// abnormal countoptval = 4;nh_private.param<int>("abnormal_check_count", optval, 4);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropAbnormalCheckCount, &optval, sizeof(int));//intensity bit countoptval = 10;nh_private.param<int>("intensity_bit", optval, 10);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropIntenstiyBit, &optval, sizeof(int));//bool property//// fixed angle resolutionbool b_optvalue = false;nh_private.param<bool>("resolution_fixed", b_optvalue, true);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropFixedResolution, &b_optvalue, sizeof(bool));/// rotate 180nh_private.param<bool>("reversion", b_optvalue, true);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropReversion, &b_optvalue, sizeof(bool));/// Counterclockwisenh_private.param<bool>("inverted", b_optvalue, true);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropInverted, &b_optvalue, sizeof(bool));b_optvalue = true;nh_private.param<bool>("auto_reconnect", b_optvalue, true);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropAutoReconnect, &b_optvalue, sizeof(bool));/// one-way communicationb_optvalue = false;nh_private.param<bool>("isSingleChannel", b_optvalue, false);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropSingleChannel, &b_optvalue, sizeof(bool));/// intensityb_optvalue = false;nh_private.param<bool>("intensity", b_optvalue, false);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropIntenstiy, &b_optvalue, sizeof(bool));/// Motor DTRb_optvalue = false;nh_private.param<bool>("support_motor_dtr", b_optvalue, false);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropSupportMotorDtrCtrl, &b_optvalue, sizeof(bool));//float property//// unit: °float f_optvalue = 180.0f;nh_private.param<float>("angle_max", f_optvalue, 180.f);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropMaxAngle, &f_optvalue, sizeof(float));f_optvalue = -180.0f;nh_private.param<float>("angle_min", f_optvalue, -180.f);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropMinAngle, &f_optvalue, sizeof(float));/// unit: mf_optvalue = 16.f;nh_private.param<float>("range_max", f_optvalue, 16.f);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropMaxRange, &f_optvalue, sizeof(float));f_optvalue = 0.1f;nh_private.param<float>("range_min", f_optvalue, 0.1f);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropMinRange, &f_optvalue, sizeof(float));/// unit: Hzf_optvalue = 10.f;nh_private.param<float>("frequency", f_optvalue, 10.f);laser.setlidaropt(LidarPropScanFrequency, &f_optvalue, sizeof(float));bool invalid_range_is_inf = false;nh_private.param<bool>("invalid_range_is_inf", invalid_range_is_inf,invalid_range_is_inf);bool point_cloud_preservative = false;nh_private.param<bool>("point_cloud_preservative", point_cloud_preservative,point_cloud_preservative);//注册启停服务,绑定雷达启停回调函数ros::ServiceServer stop_scan_service = nh.advertiseService("stop_scan",stop_scan);ros::ServiceServer start_scan_service = nh.advertiseService("start_scan",start_scan);// initialize SDK and LiDARbool ret = laser.initialize();//雷达初始化if (ret) {//success//Start the device scanning routine which runs on a separate thread and enable motor.ret = laser.turnOn();} else {ROS_ERROR("%s\n", laser.DescribeError());}ros::Rate r(30);while (ret && ros::ok()) {LaserScan scan;
//雷达扫描和点云消息数据处理if (laser.doProcessSimple(scan)) {sensor_msgs::LaserScan scan_msg;sensor_msgs::PointCloud pc_msg;
// ydlidar_ros_driver::LaserFan fan;ros::Time start_scan_time;start_scan_time.sec = scan.stamp / 1000000000ul;start_scan_time.nsec = scan.stamp % 1000000000ul;scan_msg.header.stamp = start_scan_time;scan_msg.header.frame_id = frame_id;pc_msg.header = scan_msg.header;
// fan.header = scan_msg.header;scan_msg.angle_min = (scan.config.min_angle);scan_msg.angle_max = (scan.config.max_angle);scan_msg.angle_increment = (scan.config.angle_increment);scan_msg.scan_time = scan.config.scan_time;scan_msg.time_increment = scan.config.time_increment;scan_msg.range_min = (scan.config.min_range);scan_msg.range_max = (scan.config.max_range);int size = (scan.config.max_angle - scan.config.min_angle) /scan.config.angle_increment + 1;scan_msg.ranges.resize(size,invalid_range_is_inf ? std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity() : 0.0);scan_msg.intensities.resize(size);pc_msg.channels.resize(2);int idx_intensity = 0;pc_msg.channels[idx_intensity].name = "intensities";int idx_timestamp = 1;pc_msg.channels[idx_timestamp].name = "stamps";for (size_t i = 0; i < scan.points.size(); i++) {int index = std::ceil((scan.points[i].angle - scan.config.min_angle) /scan.config.angle_increment);if (index >= 0 && index < size) {if (scan.points[i].range >= scan.config.min_range) {scan_msg.ranges[index] = scan.points[i].range;scan_msg.intensities[index] = scan.points[i].intensity;}}if (point_cloud_preservative ||(scan.points[i].range >= scan.config.min_range &&scan.points[i].range <= scan.config.max_range)) {geometry_msgs::Point32 point;point.x = scan.points[i].range * cos(scan.points[i].angle);point.y = scan.points[i].range * sin(scan.points[i].angle);point.z = 0.0;pc_msg.points.push_back(point);pc_msg.channels[idx_intensity].values.push_back(scan.points[i].intensity);pc_msg.channels[idx_timestamp].values.push_back(i * scan.config.time_increment);}}scan_pub.publish(scan_msg);pc_pub.publish(pc_msg);
// laser_fan_pub.publish(fan);} else {ROS_ERROR("Failed to get Lidar Data");}r.sleep();ros::spinOnce();}laser.turnOff();ROS_INFO("[YDLIDAR INFO] Now YDLIDAR is stopping .......");laser.disconnecting();return 0;
}- 问题及解决
在调试G4雷达功能包时,用“ls -l /dev/ttyUSB*”指令,一直显示找不到串口。后来,转而顺利调试了SLD-1雷达,返回来调试G4时,无论在ROS2版本的还是ROS版本的都出现同一个问题。后来在同事的帮助下,换了根C-USB数据线,再试,问题解决了,找到了串口/dev/ttyUSB0。信号线电源线很重要。
如果还不行,用下面的命令映射/dev/ttyUSB0的别名:
cd startup
sudo sh initenv.sh
执行上面命令后,在/etc/udev/rule.d目录下生成与ydlidr对应的端口映射文件。
参考文献: 【1】YDLidar-SDK Communication Protocol
【2】ydlidar激光雷达的安装与驱动
【3】驱动EAI的激光雷达YDLIDAR-X4
相关文章:

ROS 下 激光扫描仪 YDLidar-G4 使用
环境配置: ubuntu20.04 LTS ROS noetic 编程工具:vs code,远程通过ssh访问 扫描仪:YDLidar-G4 YDLidar驱动: YDLidar SDK YDLidar ROS 功能包 此环境包含树莓派,以下过程在树莓派3B上测试通过,…...

智能边缘:数字化时代的关键战略之一
随着物联网、云计算和人工智能等技术的快速发展,智能边缘已经成为了许多企业和组织中的重要部分。智能边缘旨在将物联网设备、应用程序和数据存储集成到一个统一的、移动的计算环境中,以提高效率、降低成本并增强数据安全性。在本文中,我们将…...

EasyRecovery16中文最新版电脑数据恢复软件下载使用教程
EasyRecovery如果需要使用它来恢复数据,请注意,尤其是当需要恢复的数据文件非常重要时,建议使用软件EasyRecovery以保障数据安全。共有三个版本,分别是个人版、专业版、企业版,这三种都可以免费下载并使用,…...
什么是鉴权?这些postman鉴权方式你又知道多少?
一、什么是鉴权? 鉴权也就是身份认证,就是验证您是否有权限从服务器访问或操作相关数据。发送请求时,通常必须包含相应的检验参数以确保请求具有访问权限并返回所需数据。通俗的讲就是一个门禁,您想要进入室内,必须通过…...

最新的经典mysql面试题及答案
互联网产品必然是需要有架构的,架构包含接入层、储蓄层、逻辑处理等等,其中存储层承载着数据落地和持久化的任务,同时给逻辑处理层提供数据查询功能支持。而一提到储蓄层必然就要说数据库了,对于数据库的掌握也是软件工程师面试时…...

算法修炼之练气篇——练气十九层
博主:命运之光 专栏:算法修炼之练气篇 前言:每天练习五道题,炼气篇大概会练习200道题左右,题目有C语言网上的题,也有洛谷上面的题,题目简单适合新手入门。(代码都是命运之光自己写的…...
记录一次Windows7操作系统渗透测试
#本文档仅用于实验,请勿用来使用恶意攻击! 《中华人民共和国网络安全法》中,恶意破坏计算机信息系统罪在第二十七条被明确规定,规定内容为: 第二十七条 任何单位和个人不得为达到破坏计算机信息系统安全的目的&#x…...

承诺协议:定义 构造
文章目录 安全性定义方案构造基于 OWP 存在性基于 DL 假设基于 OWF 存在性基于 DDH 假设 总结 安全性定义 承诺协议(Commitment Scheme)是一个两阶段的两方协议。一方是承诺者(Committer) C C C,另一方是接收者&#…...

二、easyUI中的layout(布局)组件
1.layout(布局)组件的概述 布局容器有5个区域:北、南、东、西和中间。中间区域面板是必须的,边缘的面板都是可选的。每个边缘区域面板都可以通过拖拽其边框改变大小,也可以点击折叠按钮将面板折叠起来。布局可以进行嵌…...

MySQL---聚合函数、字符串函数、数学函数、日期函数
1. 聚合函数 数据准备: create database mydb4; use mydb4;create table emp(emp_id int primary key auto_increment comment 编号,emp_name char(20) not null default comment 姓名,salary decimal(10,2) not null default 0 comment 工资,department char(20…...

边缘计算盒子有哪些?边缘计算应用场景
边缘计算(Edge Computing)是一种分布式计算模型,旨在将数据处理和计算功能从中心数据中心移到数据源附近的边缘设备上。它的目标是在接近数据生成的地方进行实时数据处理和分析,减少数据传输延迟和网络拥塞,提高应用程…...
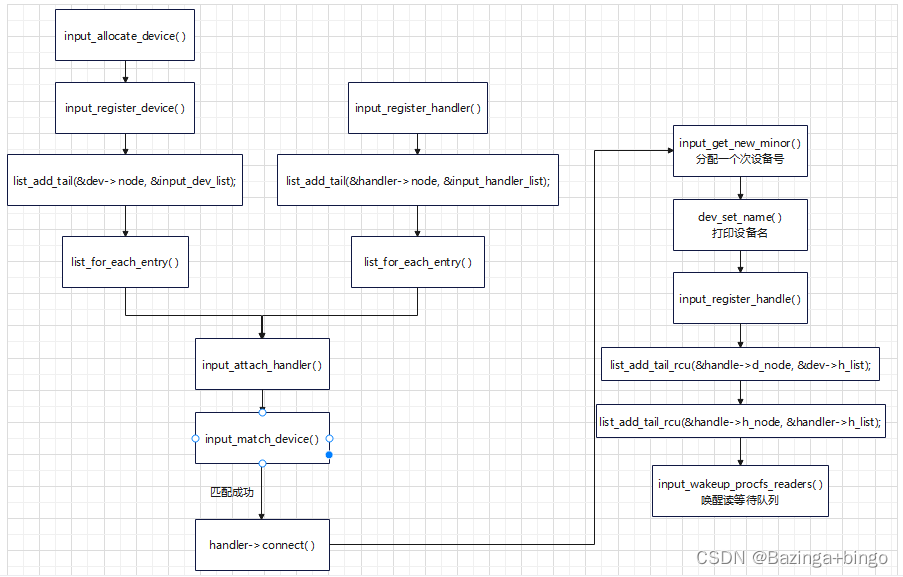
Linux内核(十四)Input 子系统详解 IV —— 配对的input设备与input事件处理器 input_register_handle
文章目录 input_handle结构体详解配对的input设备与input事件处理器实例input核心层对驱动层和事件层之间的框架建立流程图 本文章中与input子系统相关的结构体可参考input子系统结构体解析 input函数路径:drivers/input/input.c input_handle结构体详解 input_ha…...
)
Vue2.x源码解析(三)
Platform 函数 Platform 函数是用于与各种浏览器和平台进行交互的函数,它为 Vue 提供了跨平台的支持,例如浏览器、Node.js 等。Platform 函数提供了一些常用的工具和配置项,例如事件的托管、资源请求和异步更新等。下面是 Platform 函数的伪…...
)
全面理解守护进程的基础概念,以及如何创建一个守护进程(系列文章第三篇)
前言 这个系列的文章有四篇,其目的是为了搞清楚: 进程,shell,shell进程,终端,控制终端,前台进程,后台进程,控制进程,前台进程组,后台进程组&#…...

Leetcode刷题日志5.0
目录 前言: 1.两数相加 2.无重复字符的最长子串 3.整数反转 4.删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 前言: 今天我又来继续分享最近做的题了,现在开始进入我们快乐的刷题时间吧!(编程语言Python3.0,难度…...

母亲节:向世界上最伟大的母爱致敬
在这世间众多的亲情关系中,有一种关系无与伦比,毫不费力地凌驾于其他任何已知的地球关系之上。这种非凡的关系就是母亲与子女之间的关系。 母亲对家庭无尽的爱、奉献和忠诚使这份感情无价。为了向全球所有母亲表示敬意,母亲节在世界46个国家庆…...
Springboot +Flowable,各种历史信息如何查询(二)
一.简介 正在执行的流程信息是保存在以 ACT_RU_ 为前缀的表中,执行完毕的流程信息则保存在以 ACT_HI_ 为前缀的表中,也就是流程历史信息表。 假设有一个流程,流程图如下: 当这个流程执行完毕后,以 ACT_RU_ 为前缀的…...

DataX下载安装使用
文章目录 01.Clickhouse到HBase(Phoenix)数据导入 DataX介绍下载执行同步的组件配置数据同步查看官方读写配置样例创建Hbase和Phoenix表创建ClickHouse表写入ClickHouse测试数据编写ClickHouse2Hbase配置文件执行同步命令 拓展ClickHouse同步到MySQL配置文件 01.Clickhouse到HB…...
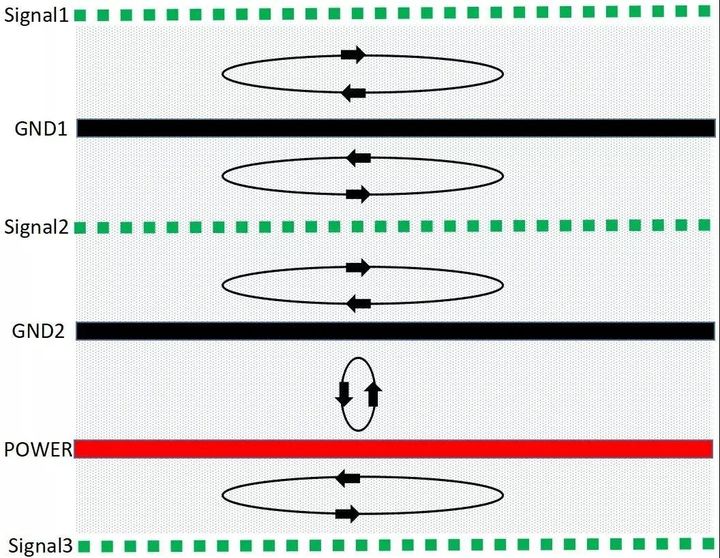
PCB多层板 : 磁通对消法有效控制EMC
在PCB的EMC设计考虑中,首先涉及的便是层的设置;单板的层数由电源、地的层数和信号层数组成;在产品的EMC设计中,除了元器件的选择和电路设计之外,良好的PCB设计也是一个非常重要的因素。 PCB的EMC设计的关键࿰…...

基于正点原子电机实验的pid调试助手代码解析(速度环控制)
这里写目录标题 下位机与PID调试助手传输的原理代码讲解(基于正点原子)解析数据接受和数据发送的底层函数数据接受数据帧格式环形数组以及怎么找到它的帧头位置crc校验 数据发送数据上传函数 通过前两节文章,我已经了解了基本的pid算法,现在在完成了电机…...
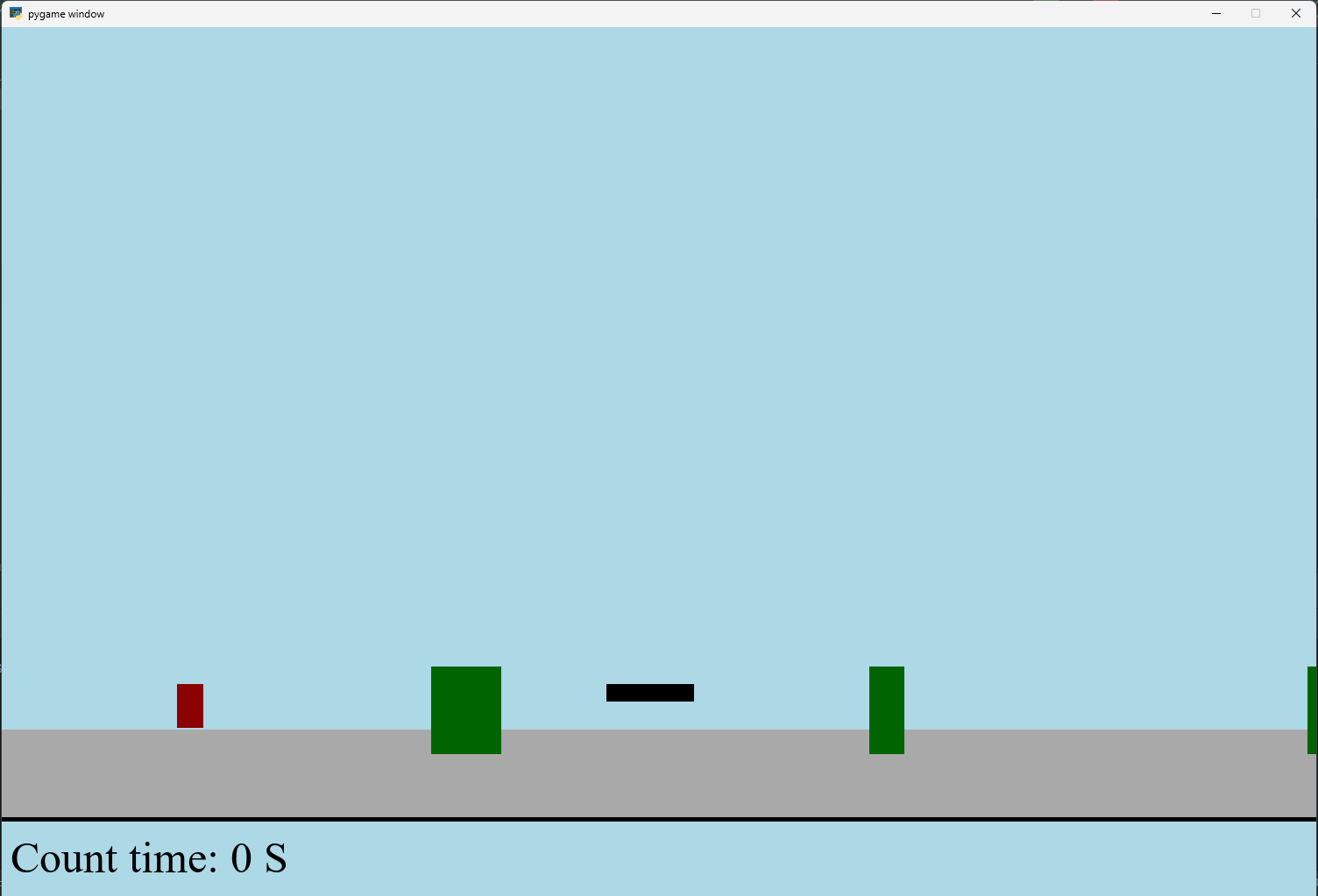
【Python】 -- 趣味代码 - 小恐龙游戏
文章目录 文章目录 00 小恐龙游戏程序设计框架代码结构和功能游戏流程总结01 小恐龙游戏程序设计02 百度网盘地址00 小恐龙游戏程序设计框架 这段代码是一个基于 Pygame 的简易跑酷游戏的完整实现,玩家控制一个角色(龙)躲避障碍物(仙人掌和乌鸦)。以下是代码的详细介绍:…...

Java 8 Stream API 入门到实践详解
一、告别 for 循环! 传统痛点: Java 8 之前,集合操作离不开冗长的 for 循环和匿名类。例如,过滤列表中的偶数: List<Integer> list Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); List<Integer> evens new ArrayList…...
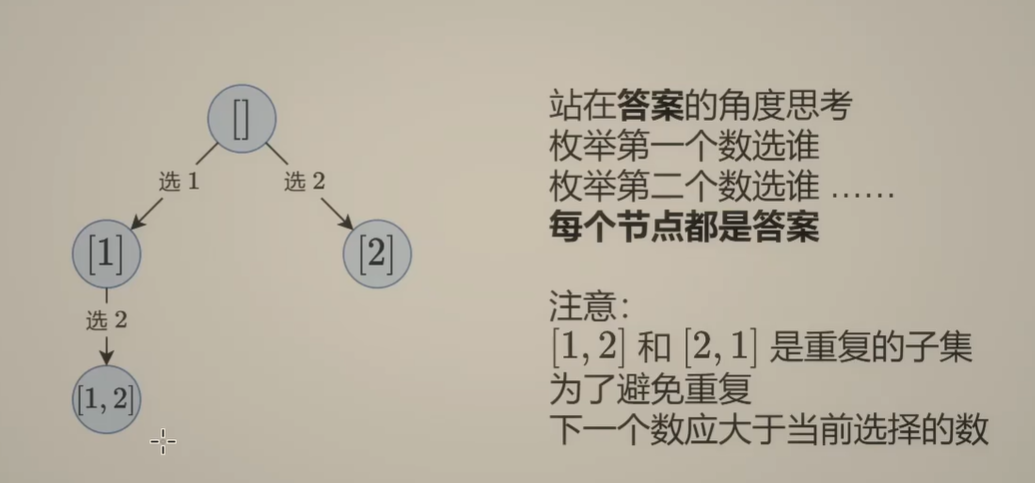
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集 78.子集 78. 子集 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路: 笔者写过很多次这道题了,不想写题解了,大家看灵神讲解吧 回溯算法套路①子集型回溯【基础算法精讲 14】_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 完…...

服务器硬防的应用场景都有哪些?
服务器硬防是指一种通过硬件设备层面的安全措施来防御服务器系统受到网络攻击的方式,避免服务器受到各种恶意攻击和网络威胁,那么,服务器硬防通常都会应用在哪些场景当中呢? 硬防服务器中一般会配备入侵检测系统和预防系统&#x…...
Linux-07 ubuntu 的 chrome 启动不了
文章目录 问题原因解决步骤一、卸载旧版chrome二、重新安装chorme三、启动不了,报错如下四、启动不了,解决如下 总结 问题原因 在应用中可以看到chrome,但是打不开(说明:原来的ubuntu系统出问题了,这个是备用的硬盘&a…...
(转)什么是DockerCompose?它有什么作用?
一、什么是DockerCompose? DockerCompose可以基于Compose文件帮我们快速的部署分布式应用,而无需手动一个个创建和运行容器。 Compose文件是一个文本文件,通过指令定义集群中的每个容器如何运行。 DockerCompose就是把DockerFile转换成指令去运行。 …...

AGain DB和倍数增益的关系
我在设置一款索尼CMOS芯片时,Again增益0db变化为6DB,画面的变化只有2倍DN的增益,比如10变为20。 这与dB和线性增益的关系以及传感器处理流程有关。以下是具体原因分析: 1. dB与线性增益的换算关系 6dB对应的理论线性增益应为&…...

十九、【用户管理与权限 - 篇一】后端基础:用户列表与角色模型的初步构建
【用户管理与权限 - 篇一】后端基础:用户列表与角色模型的初步构建 前言准备工作第一部分:回顾 Django 内置的 `User` 模型第二部分:设计并创建 `Role` 和 `UserProfile` 模型第三部分:创建 Serializers第四部分:创建 ViewSets第五部分:注册 API 路由第六部分:后端初步测…...

rm视觉学习1-自瞄部分
首先先感谢中南大学的开源,提供了很全面的思路,减少了很多基础性的开发研究 我看的阅读的是中南大学FYT战队开源视觉代码 链接:https://github.com/CSU-FYT-Vision/FYT2024_vision.git 1.框架: 代码框架结构:readme有…...

起重机起升机构的安全装置有哪些?
起重机起升机构的安全装置是保障吊装作业安全的关键部件,主要用于防止超载、失控、断绳等危险情况。以下是常见的安全装置及其功能和原理: 一、超载保护装置(核心安全装置) 1. 起重量限制器 功能:实时监测起升载荷&a…...
