CompletableFuture异步任务编排使用
CompletableFuture异步任务编排使用
- runAsync 和 supplyAsync
- allOf 和 anyOf
- join 和 get
- whenComplete 和 whenCompleteAsync 和 exceptionally
- handle 和 handleAsync
- 串行编排
- runAsync().thenRunAsync()
- supplyAsync().thenAcceptAsync((res) ->{})
- supplyAsync().thenApplyAsync((res) ->{return}
- 两个任务都完成,再做其他事
- runAfterBothAsync
- thenAcceptBothAsync
- thenCombine
- 任意一个任务完成,再做其他事
- runAfterEitherAsync
- acceptEitherAsync
- applyToEitherAsync
- 总结
runAsync 和 supplyAsync
- runAsync(runnable):无返回值
- runAsync(runnable, executor):无返回值,可自定义线程池
- supplyAsync(runnable):有返回值
- supplyAsync(runnable, executor):有回值,可自定义线程池
相关代码演示:
public static void testOne(){CompletableFuture<Void> oneFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start1");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("end1");});CompletableFuture<String> twoFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start2");try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("end2");return "this is twoFuture";});CompletableFuture.allOf(oneFuture, twoFuture).join();System.out.println(oneFuture.join());System.out.println(twoFuture.join());}
start1
start2
end1
end2
null
this is twoFuture
解析:oneFuture.join()获取的执行结果为null,因为runAsync是没有返回结果的。
allOf 和 anyOf
- allOf(future1,future2,future3…):等待所有future任务都完成,才可以做接下来的事。无返回值
- anyOf(future1,future2,future3…):任意一个任务完成,就可以做接下来的事。返回object
allOf用法示例:
public static void testTwo(){long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();CompletableFuture<Void> oneFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start1");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("end1");});CompletableFuture<String> twoFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start2");try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("end2");return "this is twoFuture";});CompletableFuture<Integer> threeFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start3");try {Thread.sleep(1500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("end3");return 100;});CompletableFuture.allOf(oneFuture, twoFuture, threeFuture).join();System.out.println(twoFuture.join() + threeFuture.join());System.out.println("cost:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");}
start1
start2
start3
end1
end3
end2
this is twoFuture100
cost:2067ms
解析:allOf后的join起阻塞主线程作用。从结果可以看出,所有future执行完成后,再执行的主线程逻辑。
anyOf用法示例:
public static void testThree(){long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();CompletableFuture<Void> oneFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start1");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("end1");});CompletableFuture<String> twoFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start2");try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("end2");return "this is twoFuture";});CompletableFuture<Integer> threeFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start3");try {Thread.sleep(1500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("end3");return 100;});Object result = CompletableFuture.anyOf(oneFuture, twoFuture, threeFuture).join();System.out.println("result:" + result);System.out.println("cost:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");}
start1
start2
start3
end1
result:null
cost:1058ms
解析:oneFuture 最先完成,因为没有返回值,所以获得的结果是null
join 和 get
都是用于获取Completable的返回值的
- join方法可能会抛出未检验的异常
- get方法强制用户手动处理异常
whenComplete 和 whenCompleteAsync 和 exceptionally
- whenComplete:执行当前线程的任务继续执行whenComplete的任务
- whenCompleteAsync:whenCompleteAsync的任务是由线程池来执行
- CompleableFuture即使发生异常也会执行whenComplete、whenCompleteAsync
- exceptionally是用来处理异常的
以whenComplete举例
正常逻辑:
public static void testFour() {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();CompletableFuture<Integer> oneFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start1");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("end1");return 100;}).whenComplete((res, e) ->{System.out.println("res:" + res);System.out.println("e:" + e);}).exceptionally((e) ->{System.out.println("error:" + e);return -1;});System.out.println("result:" + oneFuture.join());System.out.println("cost:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");}
start1
end1
res:100
e:null
result:100
cost:1084ms
捕获和处理异常:
public static void testFive() {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();CompletableFuture<Integer> oneFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start1");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("end1");return 100/0;}).whenComplete((res, e) ->{System.out.println("res:" + res);System.out.println("e:" + e);}).exceptionally((e) ->{System.out.println("error:" + e);return -1;});System.out.println("result:" + oneFuture.join());System.out.println("cost:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");}
start1
end1
res:null
e:java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
error:java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
result:-1
cost:1073ms
handle 和 handleAsync
- handle和handleAsync的区别是后者用线程池管理
- handle相当于whenComplete和exceptionally的组合,能够对异常捕获和处理
handle捕获和处理异常:
public static void testSix() {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();CompletableFuture<Integer> oneFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start1");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("end1");return 100/0;}).handle((res, e) ->{System.out.println("res:" + res);System.out.println("e:" + e);return -1;});System.out.println("result:" + oneFuture.join());System.out.println("cost:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");}
start1
end1
res:null
e:java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
result:-1
cost:1081ms
串行编排
- 该模块用到的api都有普通版和async版本,这里不做赘述。async版本可以传入线程池,用线程池管理逻辑。
runAsync().thenRunAsync()
- runAsync没有返回值,thenRunAsync也没有返回值
public static void testSeven(){long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();CompletableFuture<Void> oneFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start1");System.out.println("end1");}).thenRunAsync(() ->{System.out.println("do something");});oneFuture.join();System.out.println("cost:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");}
start1
end1
do something
cost:72ms
supplyAsync().thenAcceptAsync((res) ->{})
- thenAcceptAsync取supplyAsync的返回值,自身没有返回值
public static void testEight(){long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();CompletableFuture<Void> oneFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start1");System.out.println("end1");return 100;}).thenAcceptAsync((res) ->{System.out.println("res:"+ res);});oneFuture.join();System.out.println("cost:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");}
start1
end1
res:100
cost:83ms
supplyAsync().thenApplyAsync((res) ->{return}
- thenApplyAsync取supplyAsync的返回值,自身也有返回值
public static void testNine(){long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();CompletableFuture<Integer> oneFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start1");System.out.println("end1");return 100;}).thenApplyAsync((res) ->{return 100* 10;});System.out.println("result:" + oneFuture.join());System.out.println("cost:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");}
start1
end1
result:1000
cost:75ms
两个任务都完成,再做其他事
runAfterBothAsync
- 无入参、无出参
public static void testTen(){CompletableFuture<Integer> oneFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start1");System.out.println("end1");return 100;});CompletableFuture<Void> twoFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start2");System.out.println("end2");});oneFuture.runAfterBothAsync(twoFuture, ()->{System.out.println("do something");});System.out.println("result:" + oneFuture.join());}
start1
end1
start2
end2
do something
result:100
thenAcceptBothAsync
- 有入参、无出参
public static void testEleven(){CompletableFuture<Integer> oneFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start1");System.out.println("end1");return 100;});CompletableFuture<Void> twoFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start2");System.out.println("end2");});oneFuture.thenAcceptBothAsync(twoFuture, (res1, res2)->{System.out.println("res1:" + res1);System.out.println("res2:" + res2);});System.out.println("result:" + oneFuture.join());}
start1
end1
start2
end2
result:100
res1:100
res2:null
thenCombine
- 有入参、有出参
public static void testTwelve(){CompletableFuture<Integer> oneFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start1");System.out.println("end1");return 100;});CompletableFuture<Void> twoFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start2");System.out.println("end2");});CompletableFuture<Integer> combineFuture = oneFuture.thenCombine(twoFuture, (res1, res2) -> {System.out.println("res1:" + res1);System.out.println("res2:" + res2);return res1 == 100 ? res1 : -1;});System.out.println("result1:" + oneFuture.join());System.out.println("combine:" + combineFuture.join());}
start1
end1
start2
end2
res1:100
res2:null
result1:100
combine:100
任意一个任务完成,再做其他事
runAfterEitherAsync
- 无入参、无出参
public static void testThirteen(){CompletableFuture<Integer> oneFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start1");System.out.println("end1");return 100;});CompletableFuture<Void> twoFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start2");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("end2");});oneFuture.runAfterEitherAsync(twoFuture, ()->{System.out.println("do something");});System.out.println("result:" + oneFuture.join());}
start1
end1
start2
result:100
do something
acceptEitherAsync
- 有入参、无出参
public static void testFourteen(){CompletableFuture<Integer> oneFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start1");System.out.println("end1");return 100;});CompletableFuture<Integer> twoFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start2");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("end2");return 10;});oneFuture.acceptEitherAsync(twoFuture, (res)->{System.out.println("res:"+ res);});System.out.println("result:" + oneFuture.join());}
start1
end1
start2
result:100
res:100
applyToEitherAsync
- 有入参、有出参
public static void testFifteen(){CompletableFuture<Integer> oneFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start1");System.out.println("end1");return 100;});CompletableFuture<Integer> twoFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("start2");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("end2");return 10;});CompletableFuture<Integer> applyFuture = oneFuture.applyToEitherAsync(twoFuture, (res) -> {System.out.println("res:" + res);return res * 10;});System.out.println("result:" + oneFuture.join());System.out.println("applyFuture:" + applyFuture.join());}
start1
end1
start2
result:100
res:100
applyFuture:1000
总结
根据以上api,在多任务的情况下可以实现任意组合,实现异步执行逻辑,并提高了代码的执行效率。
相关文章:

CompletableFuture异步任务编排使用
CompletableFuture异步任务编排使用 runAsync 和 supplyAsyncallOf 和 anyOfjoin 和 getwhenComplete 和 whenCompleteAsync 和 exceptionallyhandle 和 handleAsync 串行编排runAsync().thenRunAsync()supplyAsync().thenAcceptAsync((res) ->{})supplyAsync().thenApplyAs…...

Scala的高级用法
文章目录 1. 默认参数值1.1 方法默认参数1.2 类默认参数 2. 特质 (Traits)2.1 子类型2.2 扩展特征,当做接口来使用 3.元组3.1 定义与取值3.2 元组用于模式匹配3.3 用于for循环 4 高阶函数4.1 常见的高阶函数map4.2 简化涨薪策略代码 5.嵌套方法6.多参数列表…...

【31.在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置】
给你一个按照非递减顺序排列的整数数组 nums,和一个目标值 target。请你找出给定目标值在数组中的开始位置和结束位置。 如果数组中不存在目标值 target,返回 [-1, -1]。 你必须设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的算法解决此问题。 示例 1:…...

如何构建“Buy Me a Coffee”DeFi dApp
🥸 本教程来自官网:https://docs.alchemy.com/docs。对原文部分内容进行了修改。教程中所有实例经过本人实践,代码可见:https://github.com/ChuXiaoYi/web3Study 区块链技术令人惊叹,因为它使我们能够使用代码和软件编…...
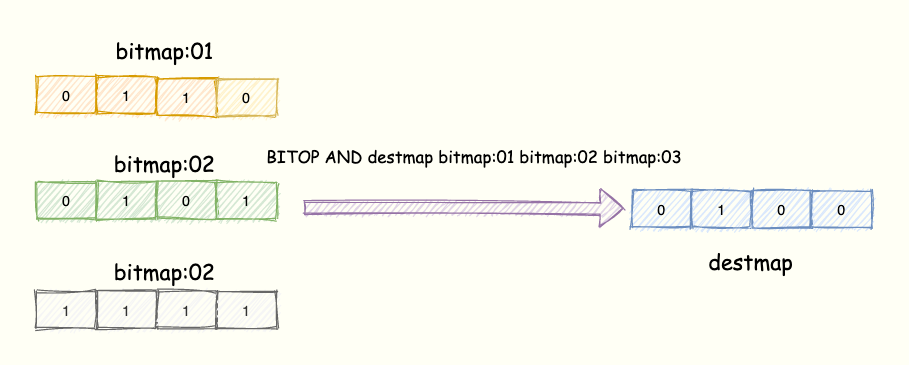
Redis 实战篇:巧用 Bitmap 实现亿级海量数据统计
目录 二值状态统计判断用户登陆态SETBIT 命令GETBIT 命令第一步,执行以下指令,表示用户已登录。第二步,检查该用户是否登陆,返回值 1 表示已登录。第三步,登出,将 offset 对应的 value 设置成 0。 用户每个…...

3 天,入门 TAURI 并开发一个跨平台 ChatGPT 客户端
TAURI 是什么 TAURI 是一个使用 Rust 编写的程序框架,它允许我们使用 Web 技术和 Rust 语言构建跨端应用。它提供了大量特性,例如系统通知、网络请求、全局快捷键、本地文件处理等,它们都可以在前端通过 JavaScript 便捷的调用。 TAURI 应用…...

14个最佳创业企业WordPress主题
要创建免费网站?从易服客建站平台免费开始 500M免费空间,可升级为20GB电子商务网站 创建免费网站 您网站的设计使您能够展示产品的独特卖点。通过正确的主题,您将能够解释为什么客户应该选择您的品牌而不是其他品牌。 在本文中࿰…...
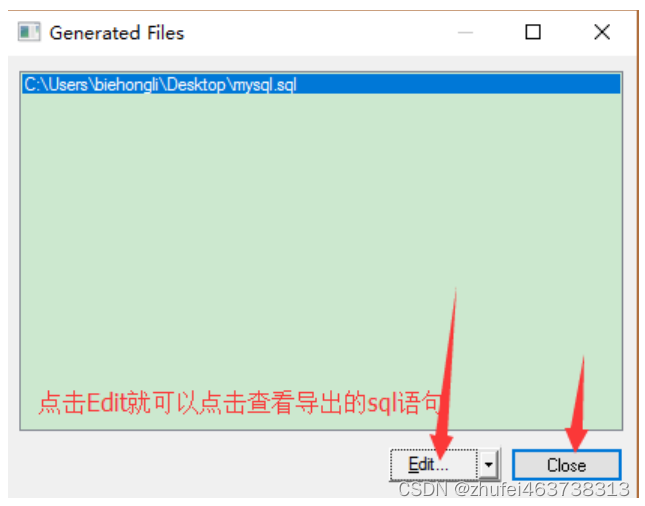
MySQL基础(三十)PowerDesigner的使用
1 PowerDesigner的使用 PowerDesigner是一款开发人员常用的数据库建模工具,用户利用该软件可以方便地制作 数据流程图 、概念数据模型 、 物理数据模型,它几乎包括了数据库模型设计的全过程,是Sybase公司为企业建模和设计提供的一套完整的集…...
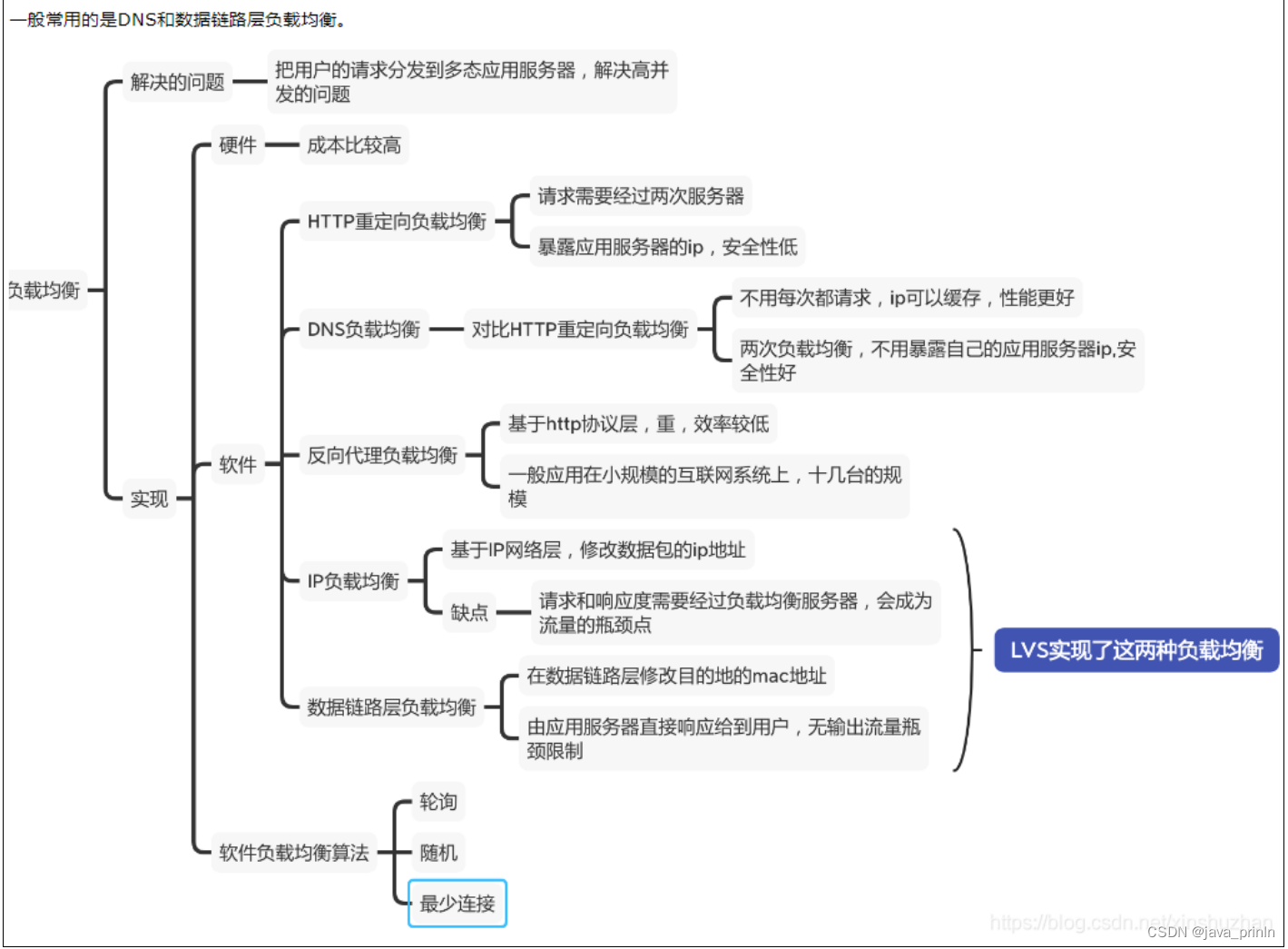
nginx 服务器总结
一. 负载均衡的作用有哪些? 1、转发功能 按照一定的算法【权重、轮询】,将客户端请求转发到不同应用服务器上,减轻单个服务器压力,提高 系统并发量。 2、故障移除 通过心跳检测的方式,判断应用服务器当前是否可以正常…...
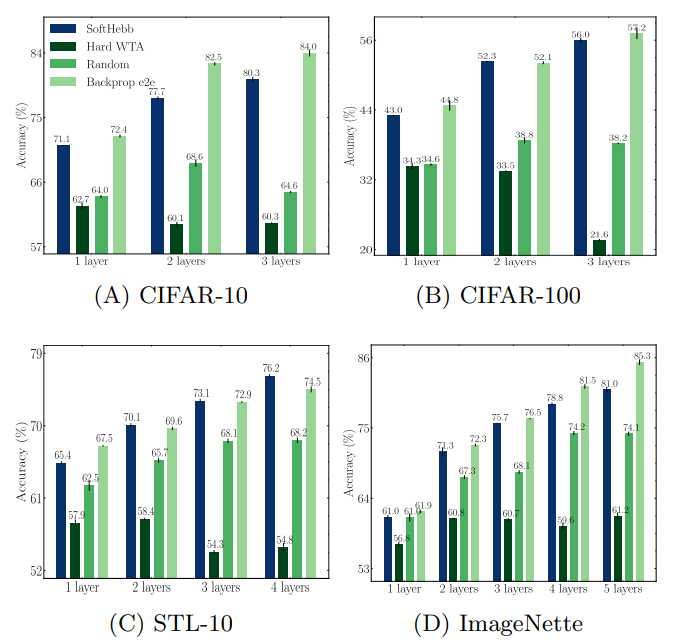
基于Hebb学习的深度学习方法总结
基于Hebb学习的深度学习方法总结 0 引言1 前置知识1.1 Hebb学习规则1.2 Delta学习规则 2 SoftHebb学习算法2.1 WTA(Winner Take All)2.2 SoftHebb2.3 多层Hebb网络2.4 Hebb学习的性能测评 3 参考文献 0 引言 总所周知,反向传播算法(back-propagating, B…...

思科模拟器 | 访问控制列表ACL实现网段精准隔绝
文章目录 一、ACL工作原理二、ACL分类初步介绍三、标准ACL1、标准ACL的决策过程2、标通配符掩码关键字3、标准ACL网络拓扑4、标准ACL演示5、实战讲解 四、扩展ACL1、基础语法明细2、扩展ACL示例3、扩展ACL网络拓扑4、实战讲解 五、总结与提炼 一、ACL工作原理 ACL(A…...

Python os模块详解
1. 简介 os就是“operating system”的缩写,顾名思义,os模块提供的就是各种 Python 程序与操作系统进行交互的接口。通过使用os模块,一方面可以方便地与操作系统进行交互,另一方面页也可以极大增强代码的可移植性。如果该模块中相…...

Oracle PL/SQL基础语法学习13:比较运算符
系列文章目录 Oracle PL/SQL基础语法学习12:短路求值 Oracle PL/SQL基础语法学习13:比较运算符 Oracle PL/SQL基础语法学习14:BOOLEAN表达式 文章目录 系列文章目录Oracle PL/SQL基础语法学习13:比较运算符比较运算符介绍官方文档…...

金仓数据库适配记录
金仓数据库适配记录 人大金仓数据库管理系统KingbaseES(简称:金仓数据库或KingbaseES)是北京人大金仓信息技术股份有限公司自主研制开发的具有自主知识产权的通用关系型数据库管理系统。 金仓数据库主要面向事务处理类应用,兼顾各类数据分析类应用,可用做管理信息系统、…...

ElasticSearch 学习 ==ELK== 进阶
二、ElasticSearch 学习 ELK 进阶 (1)文档局部更新 我们也说过文档是不可变的——它们不能被更改,只能被替换。 update API必须遵循相同的规则。表面看来,我们似乎是局部更新了文档的位置,内部却是像我们之前说的一样…...
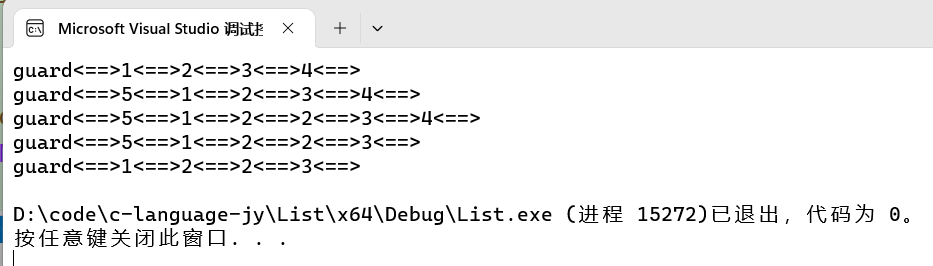
【数据结构 -- C语言】 双向带头循环链表的实现
目录 1、双向带头循环链表的介绍 2、双向带头循环链表的接口 3、接口实现 3.1 开辟结点 3.2 创建返回链表的头结点 3.3 判断链表是否为空 3.4 打印 3.5 双向链表查找 3.6 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入 3.6.1 头插 3.6.2 尾插 3.6.3 更新头插、尾插写法 3.7 双向链…...
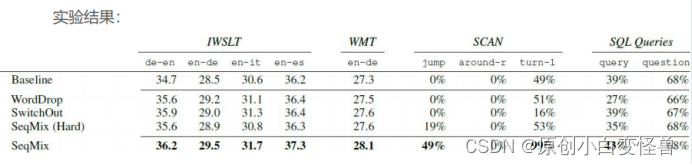
自然语言处理与其Mix-up数据增强方法报告
自然语言处理与其Mix-up数据增强方法 1绪论1.课题背景与意义1.2国内外研究现状 2 自然语言经典知识简介2.1 贝叶斯算法2.2 最大熵模型2.3神经网络模型 3 Data Augmentation for Neural Machine Translation with Mix-up3.1 数据增强3.2 对于神经机器翻译的软上下文的数据增强3.…...

Vue(组件化编程:非单文件组件、单文件组件)
一、组件化编程 1. 对比传统编写与组件化编程(下面两个解释图对比可以直观了解) 传统组件编写:不同的HTML引入不同的样式和行为文件 组件方式编写:组件单独,复用率高(前提组件拆分十分细致) 理…...
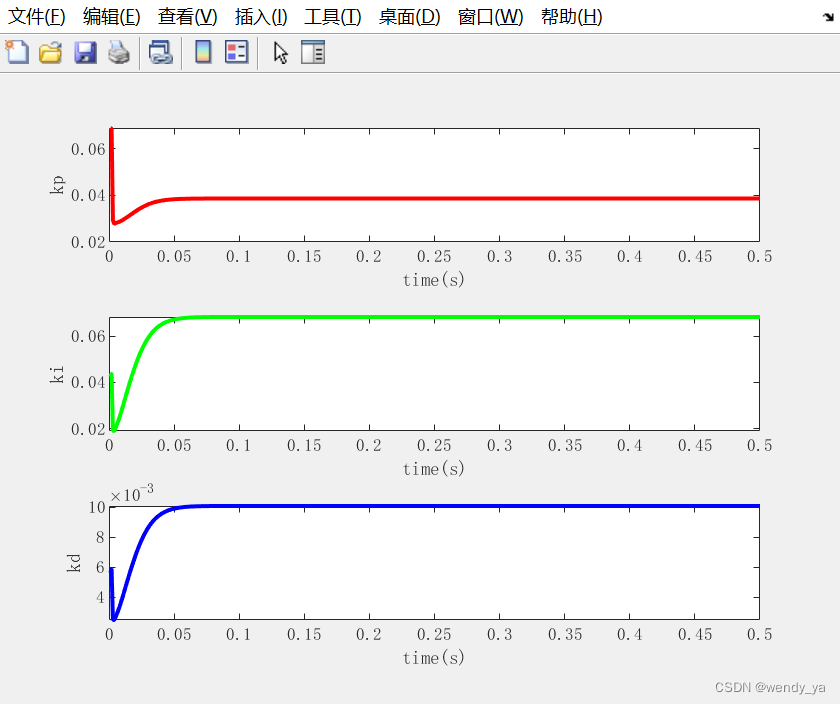
【MATLAB数据处理实用案例详解(22)】——基于BP神经网络的PID参数整定
目录 一、问题描述二、算法仿真2.1 BP_PID参数整定初始化2.2 优化PID2.3 绘制图像 三、运行结果四、完整程序 一、问题描述 基于BP神经网络的PID控制的系统结构如下图所示: 考虑仿真对象,输入为r(k)1.0,输入层为4,隐藏层为5&…...

第11章 项目人力资源管理
文章目录 项目人力资源管理 过程11.2.1 编制项目人力资源计划的工具与技术(1)层次结构图(工作、组织、资源 分解结构)(2)矩阵图(责任分配矩阵,RAM)(3…...

Chapter03-Authentication vulnerabilities
文章目录 1. 身份验证简介1.1 What is authentication1.2 difference between authentication and authorization1.3 身份验证机制失效的原因1.4 身份验证机制失效的影响 2. 基于登录功能的漏洞2.1 密码爆破2.2 用户名枚举2.3 有缺陷的暴力破解防护2.3.1 如果用户登录尝试失败次…...

基于ASP.NET+ SQL Server实现(Web)医院信息管理系统
医院信息管理系统 1. 课程设计内容 在 visual studio 2017 平台上,开发一个“医院信息管理系统”Web 程序。 2. 课程设计目的 综合运用 c#.net 知识,在 vs 2017 平台上,进行 ASP.NET 应用程序和简易网站的开发;初步熟悉开发一…...

iPhone密码忘记了办?iPhoneUnlocker,iPhone解锁工具Aiseesoft iPhone Unlocker 高级注册版分享
平时用 iPhone 的时候,难免会碰到解锁的麻烦事。比如密码忘了、人脸识别 / 指纹识别突然不灵,或者买了二手 iPhone 却被原来的 iCloud 账号锁住,这时候就需要靠谱的解锁工具来帮忙了。Aiseesoft iPhone Unlocker 就是专门解决这些问题的软件&…...

django filter 统计数量 按属性去重
在Django中,如果你想要根据某个属性对查询集进行去重并统计数量,你可以使用values()方法配合annotate()方法来实现。这里有两种常见的方法来完成这个需求: 方法1:使用annotate()和Count 假设你有一个模型Item,并且你想…...
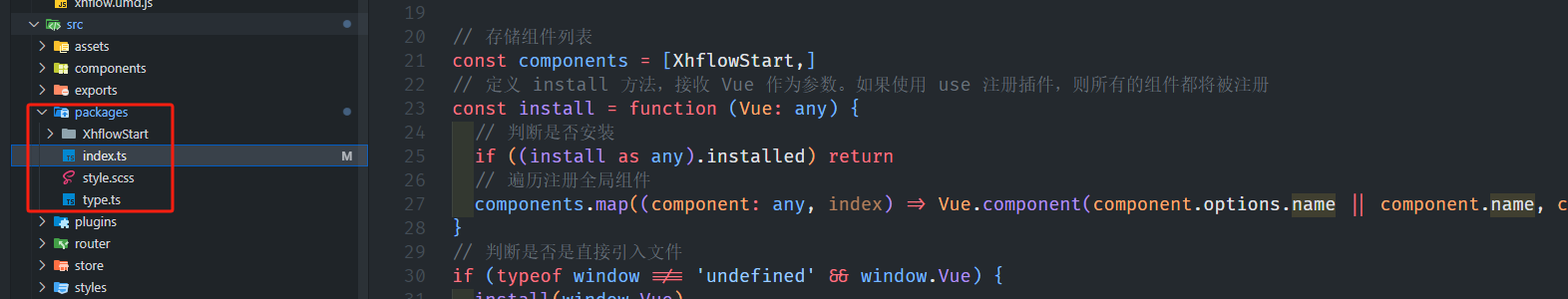
基于当前项目通过npm包形式暴露公共组件
1.package.sjon文件配置 其中xh-flowable就是暴露出去的npm包名 2.创建tpyes文件夹,并新增内容 3.创建package文件夹...

【AI学习】三、AI算法中的向量
在人工智能(AI)算法中,向量(Vector)是一种将现实世界中的数据(如图像、文本、音频等)转化为计算机可处理的数值型特征表示的工具。它是连接人类认知(如语义、视觉特征)与…...
JUC笔记(上)-复习 涉及死锁 volatile synchronized CAS 原子操作
一、上下文切换 即使单核CPU也可以进行多线程执行代码,CPU会给每个线程分配CPU时间片来实现这个机制。时间片非常短,所以CPU会不断地切换线程执行,从而让我们感觉多个线程是同时执行的。时间片一般是十几毫秒(ms)。通过时间片分配算法执行。…...

Unit 1 深度强化学习简介
Deep RL Course ——Unit 1 Introduction 从理论和实践层面深入学习深度强化学习。学会使用知名的深度强化学习库,例如 Stable Baselines3、RL Baselines3 Zoo、Sample Factory 和 CleanRL。在独特的环境中训练智能体,比如 SnowballFight、Huggy the Do…...

Java面试专项一-准备篇
一、企业简历筛选规则 一般企业的简历筛选流程:首先由HR先筛选一部分简历后,在将简历给到对应的项目负责人后再进行下一步的操作。 HR如何筛选简历 例如:Boss直聘(招聘方平台) 直接按照条件进行筛选 例如:…...
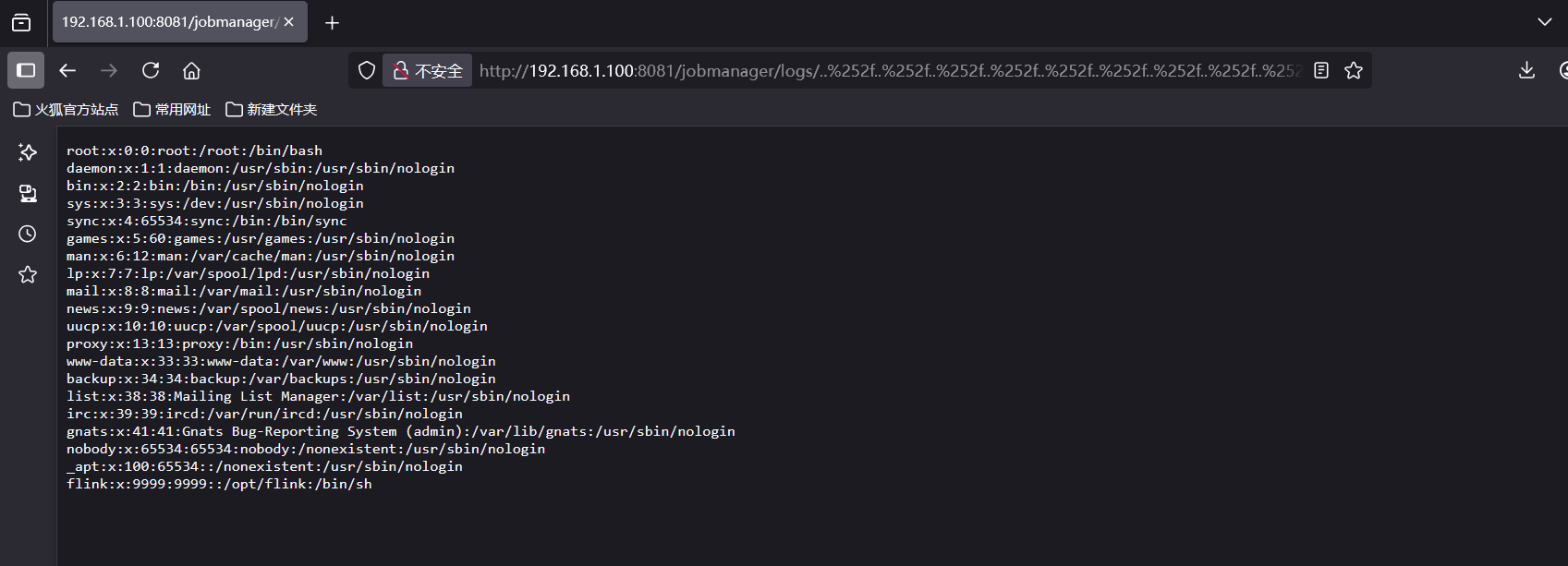
CVE-2020-17519源码分析与漏洞复现(Flink 任意文件读取)
漏洞概览 漏洞名称:Apache Flink REST API 任意文件读取漏洞CVE编号:CVE-2020-17519CVSS评分:7.5影响版本:Apache Flink 1.11.0、1.11.1、1.11.2修复版本:≥ 1.11.3 或 ≥ 1.12.0漏洞类型:路径遍历&#x…...
