北邮22信通:二叉树显示路径的两种方法 递归函数保存现场返回现场的实例
北邮22信通一枚~
跟随课程进度每周更新数据结构与算法的代码和文章
持续关注作者 解锁更多邮苑信通专属代码~
获取更多文章 请访问专栏~
北邮22信通_青山如墨雨如画的博客-CSDN博客
一.讲解
要想实现二叉树的路径显示,我们要按照先后顺序做这样几件事:
1.判断是否能够找到路径;
2.如果能找到路径,则将路径存储起来,如果不能找到路径,则返回查询失败的信息;
3.将路径按照一定的方法打印出来;
1.递归详解:是否能够找到路径并将找到的可行路径存储起来的实现函数
template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r, stack <binnode<temp>>& stk)
{if (r == NULL)return false;stk.push(*r);if (r->data == target)return true;else if (stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk))return true;else if (stl_search_path(target, r->rightchild, stk))return true;stk.pop();return false;
}首先我们向这个函数中传入3个参数,分别是待查找的目标,二叉树的根节点,一个空栈(用来存储路径);实现的具体过程运用了递归思想:对整个查找过程中的某次查找如果父节点数据域就是要查找的目标,返回真值;如果沿着他的左孩子找下去能找到目标,返回真值,如果沿着他的右孩子找下去能找到目标,返回真值。如果父节点不是目标并且沿着左孩子右孩子都找不到目标的话,弹出父节点返回假值。
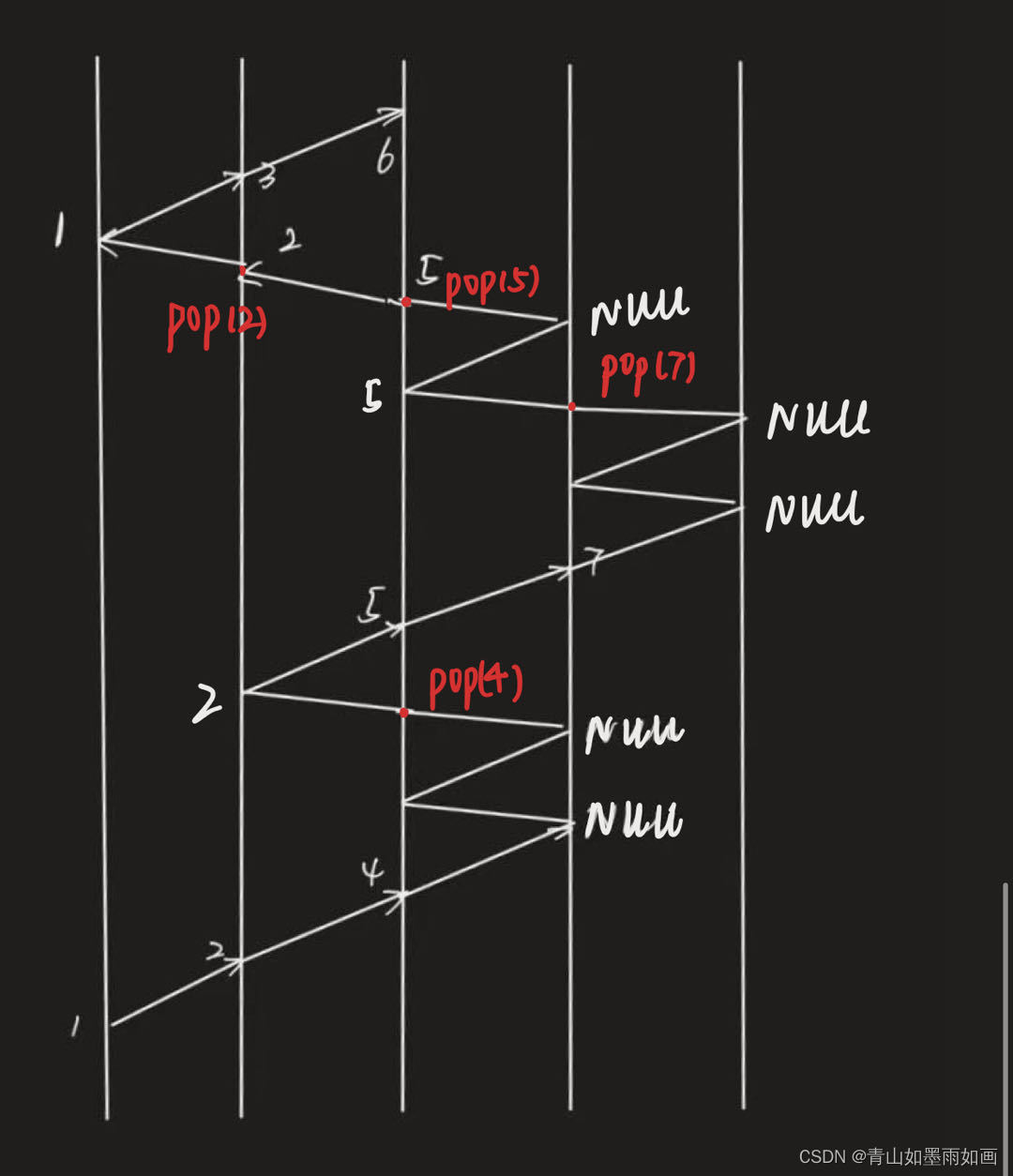
这里用例子重新讲解递归函数保存现场返回现场的运行过程:

如上图,我们要查找到结点6的路径:
按照函数编写顺序:
1首先入栈,判断1不是6(函数第5、6行),继续执行;
template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r, stack <binnode<temp>>& stk)
{if (r == NULL)return false;stk.push(*r);if (r->data == target)//现在是1,不是9return true;//执行完毕,继续向下执行;
}执行到第7行,需要判断沿着1的左孩子2能不能找到合适路径,保存现场;
template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r, stack <binnode<temp>>& stk)
{if (r == NULL)return false;stk.push(*r);if (r->data == target)return true;else if (stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk))return true;/*执行到这一步,需要重新判断stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk)是否为真值;函数保存现场不继续向下执行,将r->leftchild==2作为参数替代r==1,重新开始执行函数;*/
}重新从第一行开始执行函数,2入栈,2不是6,向下执行;
template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r, stack <binnode<temp>>& stk)
{if (r == NULL)return false;stk.push(*r);if (r->data == target)return true;//r==2不是9,继续向下执行;
}执行到第7行,需要判断沿着2的左孩子4能不能找到合适路径,保存现场;
template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r, stack <binnode<temp>>& stk)
{if (r == NULL)return false;stk.push(*r);if (r->data == target)return true;else if (stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk))return true;/*执行到这一步,需要重新判断stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk)是否为真值;函数保存现场不继续向下执行,将r->leftchild->leftchild==4作为参数替代r->leftchild==2,重新开始执行函数;*/
}重新从第一行开始执行函数,4入栈,4不是6,向下执行;
template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r, stack <binnode<temp>>& stk)
{if (r == NULL)return false;stk.push(*r);if (r->data == target)return true;else if (stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk))return true;/*执行到这一步,需要重新判断stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk)是否为真值;函数保存现场不继续向下执行,将r->leftchild->leftchild->leftchild==NULL作为参数替代r->leftchild->leftchild==4,重新开始执行函数;*/
}发现4的左孩子是空,返回假值;
返回上一级现场,执行函数第8、9行,需要判断沿着4的右孩子能不能找到合适路径,保存现场;
template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r, stack <binnode<temp>>& stk)
{if (r == NULL)return false;stk.push(*r);if (r->data == target)return true;else if (stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk))return true;else if (stl_search_path(target, r->rightchild, stk))return true;/*执行到这一步,需要重新判断stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk)是否为真值;函数保存现场不继续向下执行,将r->leftchild->leftchild->rightchild==NULL作为参数替代r->leftchild->leftchild==4,重新开始执行函数;*/
}右孩子为空;
返回上一级现场,判断沿着2的右孩子5能不能找到可行的路径,保存现场,以此类推……
示意图如下:
2.打印路径的函数
template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::stl_node_root_path(temp target)
{stack<binnode<temp>>stk;stl_search_path(target, this->root, stk);if (stk.empty())cout << target << "未能找到目标" << endl;else{cout << target << "结点到根节点的路径为:" << endl;binnode<temp>out;while (!stk.empty()){out = stk.top();if (stk.size() == 1)cout << out.data;elsecout << out.data << "->";stk.pop();}cout << endl;}
}对于给定的二叉树,首先调用上面讲解过的函数,如果有可行路径就将可行路径通过函数存储到本函数的栈空间中,然后通过控制条件输出,最终可以实现打印的效果。
3.另一种存储方式
使用模板类定义的栈存储也未尝不可。
代码如下:
template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::linkstack_node_root_path(temp target)
{linkstack<binnode<temp>>stk;linkstack_search_path(target, this->root, stk);if (stk.empty())cout << target << "未能找到目标" << endl;else{cout << target << "结点到根节点的路径为:" << endl;binnode<temp>out;while (!stk.empty()){out = stk.gettop();if (stk.getsize() == 1)cout << out.data;elsecout << out.data << "->";stk.pop();}cout << endl;}
}template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::linkstack_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r, linkstack<binnode<temp>>& stk)
{if (r == NULL)return false;stk.push(*r);if (r->data == target)return true;else if (linkstack_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk))return true;else if (linkstack_search_path(target, r->rightchild, stk))return true;stk.pop();return false;
}二.完整代码:
2.1使用STL栈实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;class student
{
private:int ID;string name;
public:int existence;student(){this->ID = 0;this->name = "unknown name";this->existence = 0;}student(int ID, string name){this->ID = ID;this->name = name;this->existence = 1;}bool operator == (student& s){return ((this->ID == s.ID) && (this->name == s.name)) ? true : false;}friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& output, student& s){output << "\"" << s.ID << " " << s.name << "\"";return output;}
};template<class temp>
struct binnode
{temp data;binnode* leftchild;binnode* rightchild;
};template<class temp>
class bintree
{
private:void create(binnode<temp>*& r, temp data[], int i, int n);void release(binnode<temp>* r);
public:binnode<temp>* root;bintree(temp data[], int n);void stl_node_root_path(temp target);bool stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r, stack <binnode<temp>>& stk);~bintree();
};template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::create(binnode<temp>*& r, temp data[], int i, int n)
{if (i <= n && data[i - 1].existence != 0){r = new binnode<temp>;r->data = data[i - 1];r->leftchild = NULL;r->rightchild = NULL;create(r->leftchild, data, 2 * i, n);create(r->rightchild, data, 2 * i + 1, n);}
}template<class temp>
bintree<temp>::bintree(temp data[], int n)
{create(this->root, data, 1, n);
}template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::release(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r != NULL){release(r->leftchild);release(r->rightchild);delete r;}
}template<class temp>
bintree<temp>::~bintree()
{release(this->root);
}template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::stl_node_root_path(temp target)
{stack<binnode<temp>>stk;stl_search_path(target, this->root, stk);if (stk.empty())cout << target << "未能找到目标" << endl;else{cout << target << "结点到根节点的路径为:" << endl;binnode<temp>out;while (!stk.empty()){out = stk.top();if (stk.size() == 1)cout << out.data;elsecout << out.data << "->";stk.pop();}cout << endl;}
}template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::stl_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r, stack <binnode<temp>>& stk)
{if (r == NULL)return false;stk.push(*r);if (r->data == target)return true;else if (stl_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk))return true;else if (stl_search_path(target, r->rightchild, stk))return true;stk.pop();return false;
}int main()
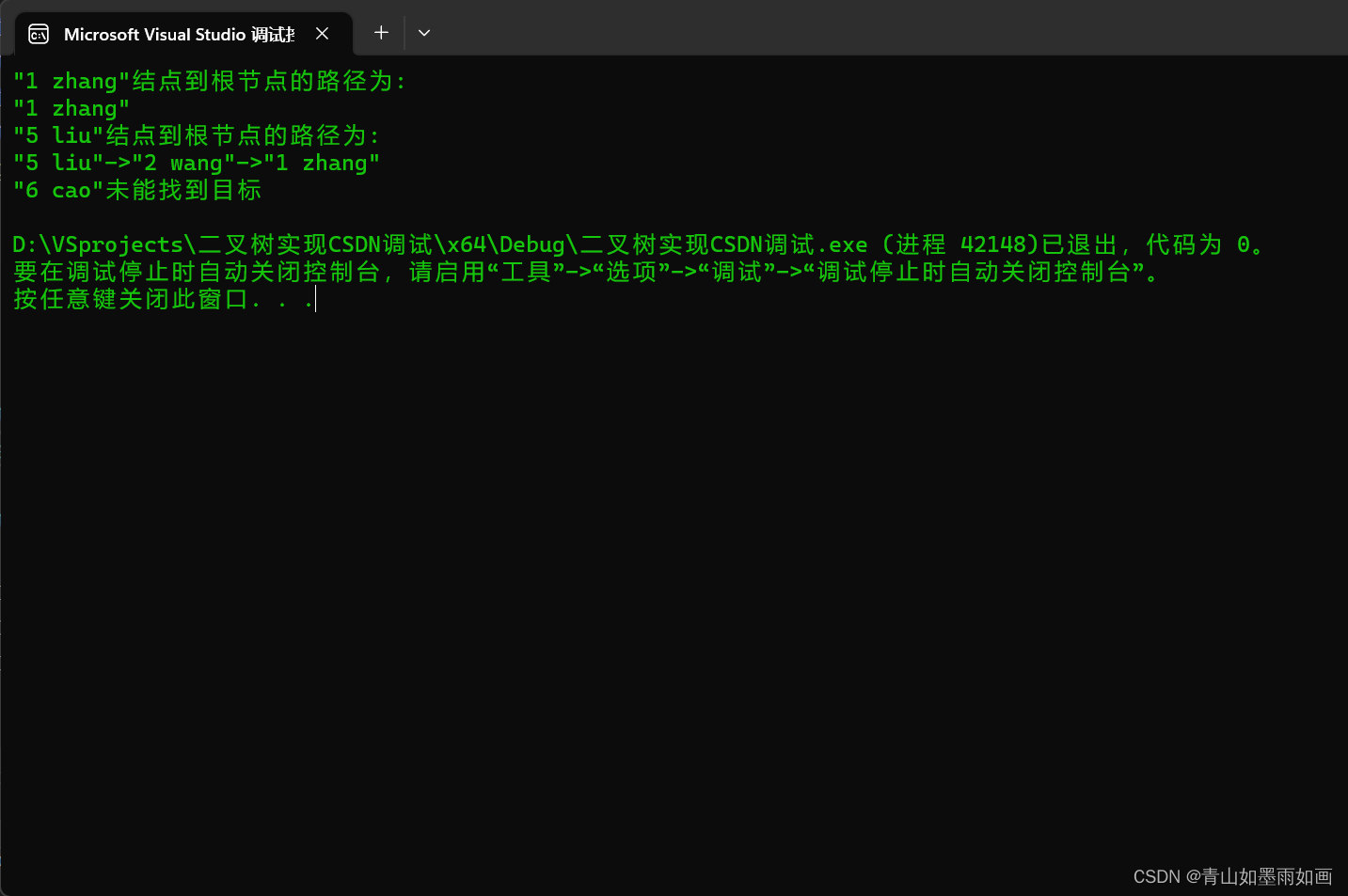
{system("color 0A");student stu[5] = { {1,"zhang"},{2,"wang"},{3,"li"},{4,"zhao"},{5,"liu"} };bintree<student>tree(stu, 5);student stu1(1, "zhang"), stu2(5, "liu"), stu3(6, "cao");tree.stl_node_root_path(stu1);tree.stl_node_root_path(stu2);tree.stl_node_root_path(stu3);return 0;
}2.2使用模板类定义的栈实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class student
{
private:int ID;string name;
public:int existence;student(){this->ID = 0;this->name = "unknown name";this->existence = 0;}student(int ID, string name){this->ID = ID;this->name = name;this->existence = 1;}bool operator == (student& s){return ((this->ID == s.ID) && (this->name == s.name)) ? true : false;}friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& output, student& s){output << "\"" << s.ID << " " << s.name << "\"";return output;}
};
//二叉树声明部分
template<class temp>
struct binnode;
//栈
template <class temp>
struct node
{temp data;node<temp>* next;
};template <class temp>
class linkstack
{
public:binnode<temp>* r;int tag;linkstack() { top = NULL; }~linkstack();void push(temp x);temp pop();temp gettop();int getsize();bool empty(){return top == NULL ? true : false;}
private:node<temp>* top;
};template <class temp>
void linkstack<temp>::push(temp x)
{node<temp>* p = new node<temp>;p->data = x;p->next = this->top;this->top = p;
}template<class temp>
temp linkstack<temp>::pop()
{if (empty())throw "下溢";temp x = this->top->data;node<temp>* p = this->top;this->top = this->top->next;delete p;return x;
}template<class temp>
linkstack<temp>::~linkstack()
{while (this->top != NULL){node<temp>* p = this->top;this->top = this->top->next;delete p;}
}template<class temp>
temp linkstack<temp>::gettop()
{if (empty())throw"下溢";return this->top->data;
}template<class temp>
int linkstack<temp>::getsize()
{int num = 0;node<temp>* p = this->top;while (p != NULL){num++;p = p->next;}return num;
}template<class temp>
struct binnode
{temp data;binnode* leftchild;binnode* rightchild;
};template<class temp>
class bintree
{
private:void create(binnode<temp>*& r, temp data[], int i, int n);void release(binnode<temp>* r);
public:binnode<temp>* root;bintree(temp data[], int n);void linkstack_node_root_path(temp target);bool linkstack_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r, linkstack<binnode<temp>>& stk);~bintree();
};template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::create(binnode<temp>*& r, temp data[], int i, int n)
{if (i <= n && data[i - 1].existence != 0){r = new binnode<temp>;r->data = data[i - 1];r->leftchild = NULL;r->rightchild = NULL;create(r->leftchild, data, 2 * i, n);create(r->rightchild, data, 2 * i + 1, n);}
}template<class temp>
bintree<temp>::bintree(temp data[], int n)
{create(this->root, data, 1, n);
}template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::release(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r != NULL){release(r->leftchild);release(r->rightchild);delete r;}
}template<class temp>
bintree<temp>::~bintree()
{release(this->root);
}template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::linkstack_node_root_path(temp target)
{linkstack<binnode<temp>>stk;linkstack_search_path(target, this->root, stk);if (stk.empty())cout << target << "未能找到目标" << endl;else{cout << target << "结点到根节点的路径为:" << endl;binnode<temp>out;while (!stk.empty()){out = stk.gettop();if (stk.getsize() == 1)cout << out.data;elsecout << out.data << "->";stk.pop();}cout << endl;}
}template<class temp>
bool bintree<temp>::linkstack_search_path(temp target, binnode<temp>*& r, linkstack<binnode<temp>>& stk)
{if (r == NULL)return false;stk.push(*r);if (r->data == target)return true;else if (linkstack_search_path(target, r->leftchild, stk))return true;else if (linkstack_search_path(target, r->rightchild, stk))return true;stk.pop();return false;
}int main()
{system("color 0A");student stu[5] = { {1,"zhang"},{2,"wang"},{3,"li"},{4,"zhao"},{5,"liu"} };bintree<student>tree(stu, 5);student stu1(1, "zhang"), stu2(5, "liu"), stu3(6, "cao");tree.linkstack_node_root_path(stu1);tree.linkstack_node_root_path(stu2);tree.linkstack_node_root_path(stu3);return 0;
}2.3运行效果:
相关文章:

北邮22信通:二叉树显示路径的两种方法 递归函数保存现场返回现场的实例
北邮22信通一枚~ 跟随课程进度每周更新数据结构与算法的代码和文章 持续关注作者 解锁更多邮苑信通专属代码~ 获取更多文章 请访问专栏~ 北邮22信通_青山如墨雨如画的博客-CSDN博客 一.讲解 要想实现二叉树的路径显示,我们要按照…...
)
vue 3 第二十八章:组件十二(组件的v-model、多v-model)
文章目录 1. 基本使用2. 使用conputed实现3. v-model 的参数4. 多 v-model 的使用5. v-model 修饰符 在 Vue 3 中, v-model 指令的使用更加灵活,可以绑定任意属性和事件。例如,我们可以使用 v-model:checked 指令来绑定单选框或复选框的 c…...
LCD 显示
概述 LCD显示控制模块接收 MCU 送过来的数据,按一定规律储存在显示 RAM 中,并根据显示 RAM 中的数据驱动 LCD 显示屏来实现期望的字符显示功能。 主要特点: ⚫ 最大支持 840 、 642 、 444 的显示段数 ⚫ 1/3bias 、 1/4bia s ⚫ 16 级灰度可…...
互联网医院开发|在线问诊系统架构设计功能有哪些?
互联网医院会增加更多的医疗业务,电话问诊、视频问诊、个性化的医疗套餐等,未来互联网医院会建成围绕健康主题的深度大数据平台和多元化医疗服务生态体系,丰富人工智能、物联网等应用场景,为用户提供更好的服务体验、更低的成本、…...
)
数据安全运营有效管理-数据安全复合治理框架和模型解读(1)
数据治理,数据安全治理行业在发展,在实践,所以很多东西是实践出来的,哪有什么神仙理论指导,即使有也是一家之说,但为了提高企业投产比,必要的认知是必须的,落地运营管理水平差异直接决定产品和项目是否可持续性,当前和未来更需要专业和有效创新。数据安全治理要充分考…...

【刷题之路】LeetCode 面试题 03.02. 栈的最小值
【刷题之路】LeetCode 面试题 03.02. 栈的最小值 一、题目描述二、解题1、方法1——“辅助栈”1.1、思路分析1.2、代码实现 一、题目描述 原题连接: 面试题 03.02. 栈的最小值 题目描述: 请设计一个栈,除了常规栈支持的pop与push函数以外&am…...

如何处理图片排重(精准排重,相似排重)
图片相似度对比 1、需求 假如有一个图片池,存有1亿图片。给一张目标图片,在图片池中做匹配。 判断一张图片是否在图片池中出现过。(完全一样)判断有没有相似的出现过。比如两张图相似度90,两张图片是在描述一件事情。 …...

盐城北大青鸟“北大青鸟杯”IT精英挑战赛设中心评审隆重开赛
为积极响应北大青鸟总部开展第十届“北大青鸟杯”全国IT精英挑战赛的号召,成就学员们的IT梦想,“北大青鸟杯”IT精英挑战赛(设计组)盐城卓晨中心评审于2023年5月25日下午1:00在人才大厦306教室正式开赛! 赛前&a…...
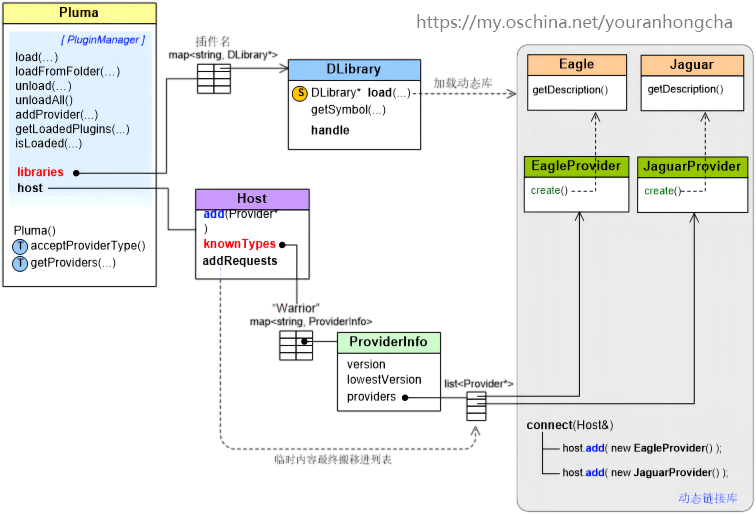
Pluma 插件管理框架
1. 概述 Pluma 是一个用 C 开发的可用于管理插件的开源架构,其官网地址为:http://pluma-framework.sourceforge.net/。该架构是个轻量级架构,非常易于理解。 Pluma 架构有以下基本概念: 1)插件的外在行为体现为一个…...
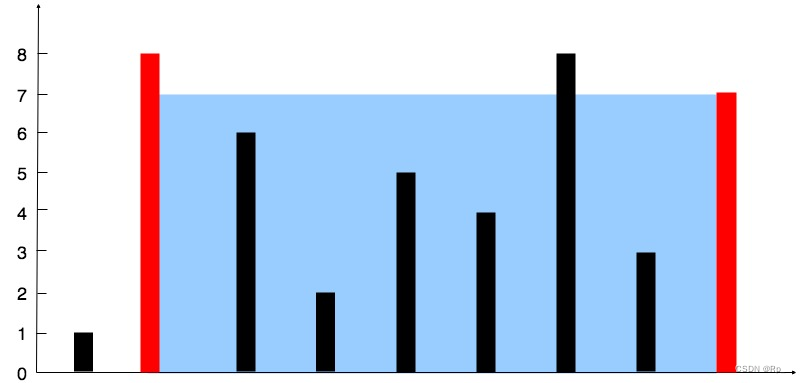
Leetcode11 盛最多水的容器
Leetcode11 盛最多水的容器 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/container-with-most-water/description 博主Github:https://github.com/GDUT-Rp/LeetCode 题目: 给定一个长度为 n…...

Java
FileOutputStream写数据的3种方式 void write(int b) //一次写一个字节的数据 void write(byte[] b) //一次写一个字节数组数据 void write(byte[] b, int off,int len) //一次写一个字节数组的部分数据 参数一:数组;参数二:起始索引 0;参数三:个数换行: windows:“\r\n” lin…...
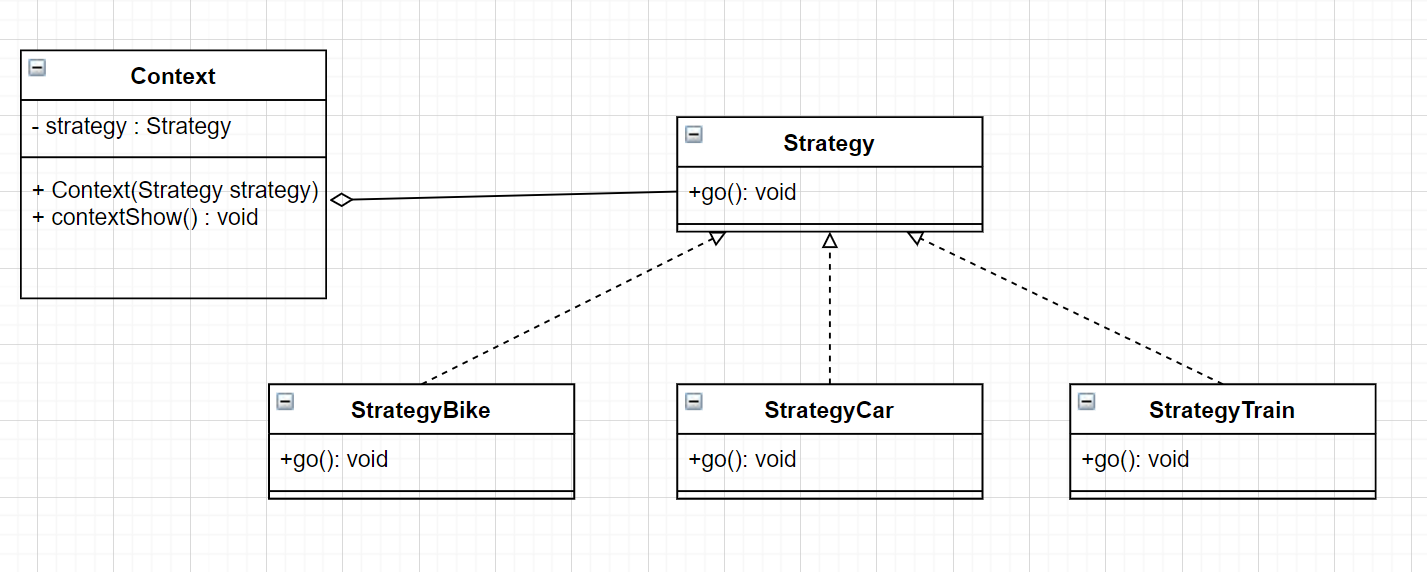
第十四章行为性模式—策略模式
文章目录 命令模式解决的问题结构实例存在的问题适用场景 JDK源码解析 行为型模式用于描述程序在运行时复杂的流程控制,即描述多个类或对象之间怎样相互协作共同完成单个对象无法单独完成的任务,它涉及算法与对象间职责的分配。行为型模式分为类行为模式…...
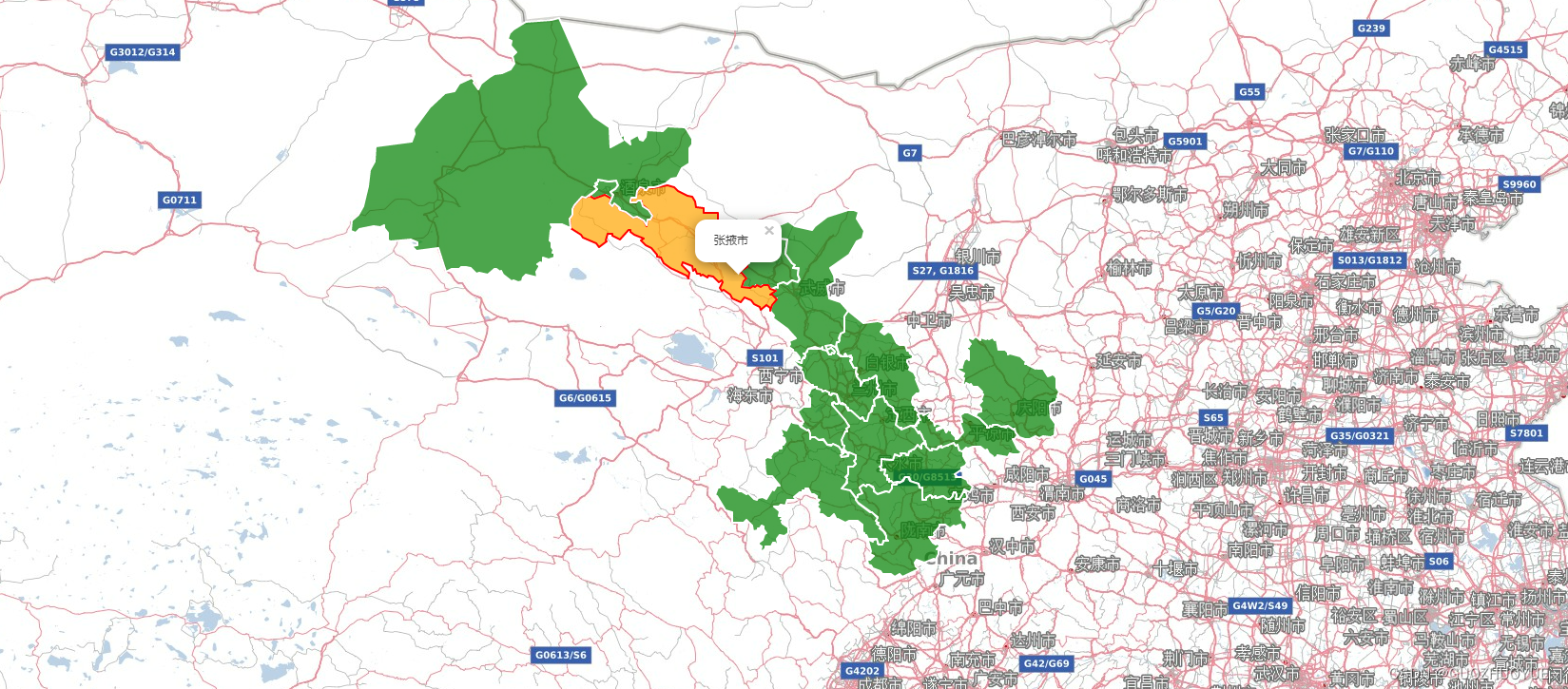
Leaflet基本用法
使用 阿里云地理工具 获取相应的地理JSON数据,用于对地图边界绘制。 如何使用leaflet? 这里用HTML5进行操作; 因为我是用的是Leaflet库,所以要引入JavaScript 和 CSS 文件(可参考官网https://leafletjs.com/&#x…...
Unity | HDRP高清渲染管线学习笔记:示例场景解析
目录 一、HDRP入门 1.HDRP设置 1.1 HDRP配置文件中的全部设置项 1.1.1 Rendering下的Lit Shader Mode 1.1.2 Lighting 下的Volumetrics(体积光)和Screen Space Reflection(屏幕空间反射) 2.离线渲染VS实时渲染 3.Volume组件 …...
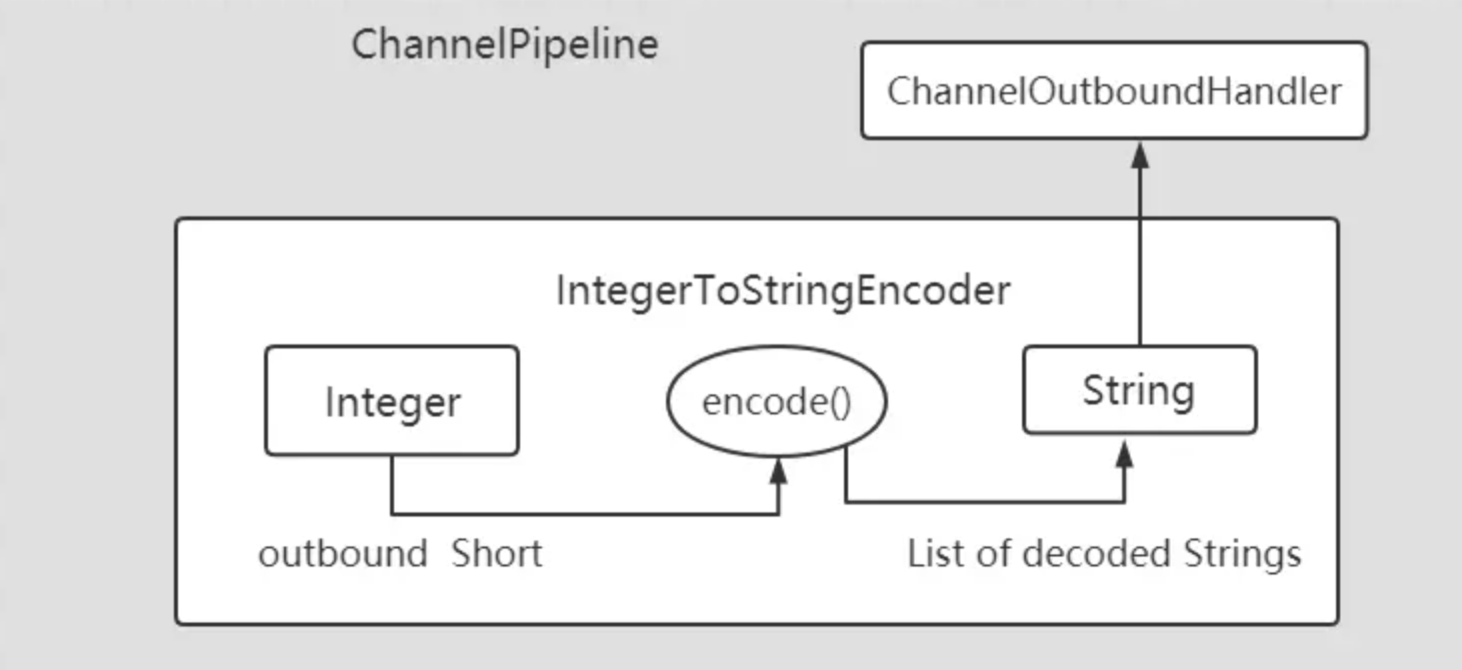
【Netty】Netty 编码器(十三)
文章目录 前言一、MessageToByteEncoder 抽象类二、MessageToMessageEncoder 抽象类总结 前言 回顾Netty系列文章: Netty 概述(一)Netty 架构设计(二)Netty Channel 概述(三)Netty ChannelHan…...

Netty和Tomcat的区别、性能对比
文章目录 一、Netty和Tomcat有什么区别?二、为什么Netty受欢迎?三、Netty为什么并发高 ? 一、Netty和Tomcat有什么区别? Netty和Tomcat最大的区别就在于通信协议,Tomcat是基于Http协议的,他的实质是一个基…...

chatgpt赋能python:Python函数调用局部变量-深入了解
Python函数调用局部变量-深入了解 函数调用局部变量是Python中的一个重要概念,特别是在大型项目中,其中多个函数共享相同变量时。在本文中,我们将深入探讨Python函数调用局部变量,并为您介绍一些实用技巧。 什么是Python函数调用…...

Android 12.0 NavigationBarView 导航栏 左边显示的修改
1.概述 在12.0定制化开发中,要求导航栏左边显示的定制化,这时需要了解导航栏的显示控制方向,然后修改显示方向 在10.0以后关于导航栏显示位置都是在DisplayPolicy.java中处理的所以查询相关的设置方法,然后修改导航栏显示方向2.NavigationBarView 导航栏 左边显示的修改的…...

Mybatis源码细节探究:二级缓存Cache对象是在什么时候创建的?
给自己的每日一句 不从恶人的计谋,不站罪人的道路,不坐亵慢人的座位,惟喜爱耶和华的律法,昼夜思想,这人便为有福!他要像一棵树栽在溪水旁,按时候结果子,叶子也不枯干。凡他所做的尽…...

【数据库】无效数据:软件测试对无效数据的处理
目录 一、无效数据的常见场景 (1)测试阶段 (2)测试方法 二、无效数据的概念 三、无效数据的影响 四、无效数据的识别 五、无效数据的处理方法 (1)拒绝无效数据 ① 拒绝无效数据的概念 ② 拒绝…...

C++_核心编程_多态案例二-制作饮品
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;/*制作饮品的大致流程为:煮水 - 冲泡 - 倒入杯中 - 加入辅料 利用多态技术实现本案例,提供抽象制作饮品基类,提供子类制作咖啡和茶叶*//*基类*/ class AbstractDr…...
理解 MCP 工作流:使用 Ollama 和 LangChain 构建本地 MCP 客户端
🌟 什么是 MCP? 模型控制协议 (MCP) 是一种创新的协议,旨在无缝连接 AI 模型与应用程序。 MCP 是一个开源协议,它标准化了我们的 LLM 应用程序连接所需工具和数据源并与之协作的方式。 可以把它想象成你的 AI 模型 和想要使用它…...

鸿蒙中用HarmonyOS SDK应用服务 HarmonyOS5开发一个医院挂号小程序
一、开发准备 环境搭建: 安装DevEco Studio 3.0或更高版本配置HarmonyOS SDK申请开发者账号 项目创建: File > New > Create Project > Application (选择"Empty Ability") 二、核心功能实现 1. 医院科室展示 /…...

vue3 字体颜色设置的多种方式
在Vue 3中设置字体颜色可以通过多种方式实现,这取决于你是想在组件内部直接设置,还是在CSS/SCSS/LESS等样式文件中定义。以下是几种常见的方法: 1. 内联样式 你可以直接在模板中使用style绑定来设置字体颜色。 <template><div :s…...
相机从app启动流程
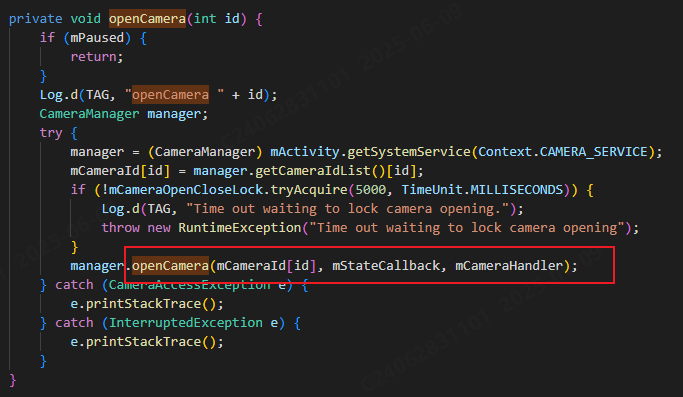
一、流程框架图 二、具体流程分析 1、得到cameralist和对应的静态信息 目录如下: 重点代码分析: 启动相机前,先要通过getCameraIdList获取camera的个数以及id,然后可以通过getCameraCharacteristics获取对应id camera的capabilities(静态信息)进行一些openCamera前的…...

论文浅尝 | 基于判别指令微调生成式大语言模型的知识图谱补全方法(ISWC2024)
笔记整理:刘治强,浙江大学硕士生,研究方向为知识图谱表示学习,大语言模型 论文链接:http://arxiv.org/abs/2407.16127 发表会议:ISWC 2024 1. 动机 传统的知识图谱补全(KGC)模型通过…...
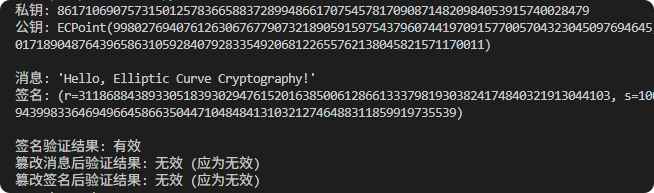
现代密码学 | 椭圆曲线密码学—附py代码
Elliptic Curve Cryptography 椭圆曲线密码学(ECC)是一种基于有限域上椭圆曲线数学特性的公钥加密技术。其核心原理涉及椭圆曲线的代数性质、离散对数问题以及有限域上的运算。 椭圆曲线密码学是多种数字签名算法的基础,例如椭圆曲线数字签…...

【git】把本地更改提交远程新分支feature_g
创建并切换新分支 git checkout -b feature_g 添加并提交更改 git add . git commit -m “实现图片上传功能” 推送到远程 git push -u origin feature_g...

BCS 2025|百度副总裁陈洋:智能体在安全领域的应用实践
6月5日,2025全球数字经济大会数字安全主论坛暨北京网络安全大会在国家会议中心隆重开幕。百度副总裁陈洋受邀出席,并作《智能体在安全领域的应用实践》主题演讲,分享了在智能体在安全领域的突破性实践。他指出,百度通过将安全能力…...

Axios请求超时重发机制
Axios 超时重新请求实现方案 在 Axios 中实现超时重新请求可以通过以下几种方式: 1. 使用拦截器实现自动重试 import axios from axios;// 创建axios实例 const instance axios.create();// 设置超时时间 instance.defaults.timeout 5000;// 最大重试次数 cons…...
