【数据结构】---几分钟简单几步学会手撕链式二叉树(下)
文章目录
- 前言
- 🌟一、二叉树链式结构的实现
- 🌏1.1 二叉树叶子节点个数
- 💫代码:
- 💫流程图:
- 🌏1.2 二叉树的高度
- 💫第一种写法(不支持):
- 📒代码:
- 📒流程图:
- 💫第二种写法:
- 📒代码:
- 📒流程图:
- 🌏1.3 二叉树第K层的节点个数
- 💫代码:
- 💫流程图:
- 🌏1.4 二叉树查找值为x的节点
- 💫第一种写法(错误示范):
- 📒代码:
- 📒流程图:
- 💫第二种写法(正确写法):
- 📒代码:
- 📒流程图:
- 🌏1.5 层序遍历
- 📒代码:
- 📒思路流程(多种嵌套):
- 🌏1.6 二叉树销毁(采用后序)
- 📒代码:
- 📒流程图:
- 🌏1.7 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
- 📒代码:
- 📒思路流程:
- 🌟二、二叉树链式结构完整代码
- 😽总结
前言
👧个人主页:@小沈熬夜秃头中୧⍤⃝❅
😚小编介绍:欢迎来到我的乱七八糟小星球🌝
📋专栏:数据结构
🔑本章内容:手撕链式二叉树
送给各位💌:成为更好的自己才是应该做的事
记得 评论📝 +点赞👍 +收藏😽 +关注💞哦~
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
🌟一、二叉树链式结构的实现
🌏1.1 二叉树叶子节点个数
💫代码:
int BTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL)return 0;if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)return 1;return BTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BTreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
💫流程图:
🌏1.2 二叉树的高度
💫第一种写法(不支持):
📒代码:
int BTreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL)return 0;return BTreeHeight(root->left) > BTreeHeight(root->right) ?BTreeHeight(root->left) + 1 : BTreeHeight(root->right) + 1;
}
📒流程图:
由图可知,每次比较完后并没有记录数据而是再次调用当树跃高底层最大的那个函数调用的次数就越多,所以这种方法虽然对但是耗时太长,而底层也就变成了所谓的天选打工人
💫第二种写法:
📒代码:
int BTreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL)return 0;int leftHeight = BTreeHeight(root->left);int rightHeight = BTreeHeight(root->right );return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
📒流程图:
每次调用都记录上数据,这样比较完直接返回大的那个+1;
🌏1.3 二叉树第K层的节点个数
💫代码:
int BTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root,int k)
{if (root == NULL)return 0;if (k == 1)return 1;return BTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1) + BTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
💫流程图:
🌏1.4 二叉树查找值为x的节点
💫第一种写法(错误示范):
📒代码:
BTNode* BTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{if (root == NULL)return NULL;if (root->data == x)return root;BTreeFind(root->left, x);BTreeFind(root->right, x);
}
📒流程图:
💫第二种写法(正确写法):
📒代码:
BTNode* BTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{if (root == NULL)return NULL;if (root->data == x)return root;BTNode* ret1 = BTreeFind(root->left, x);if (ret1)return ret1;BTNode* ret2 = BTreeFind(root->left, x);if (ret2)return ret2;return NULL;
}
📒流程图:
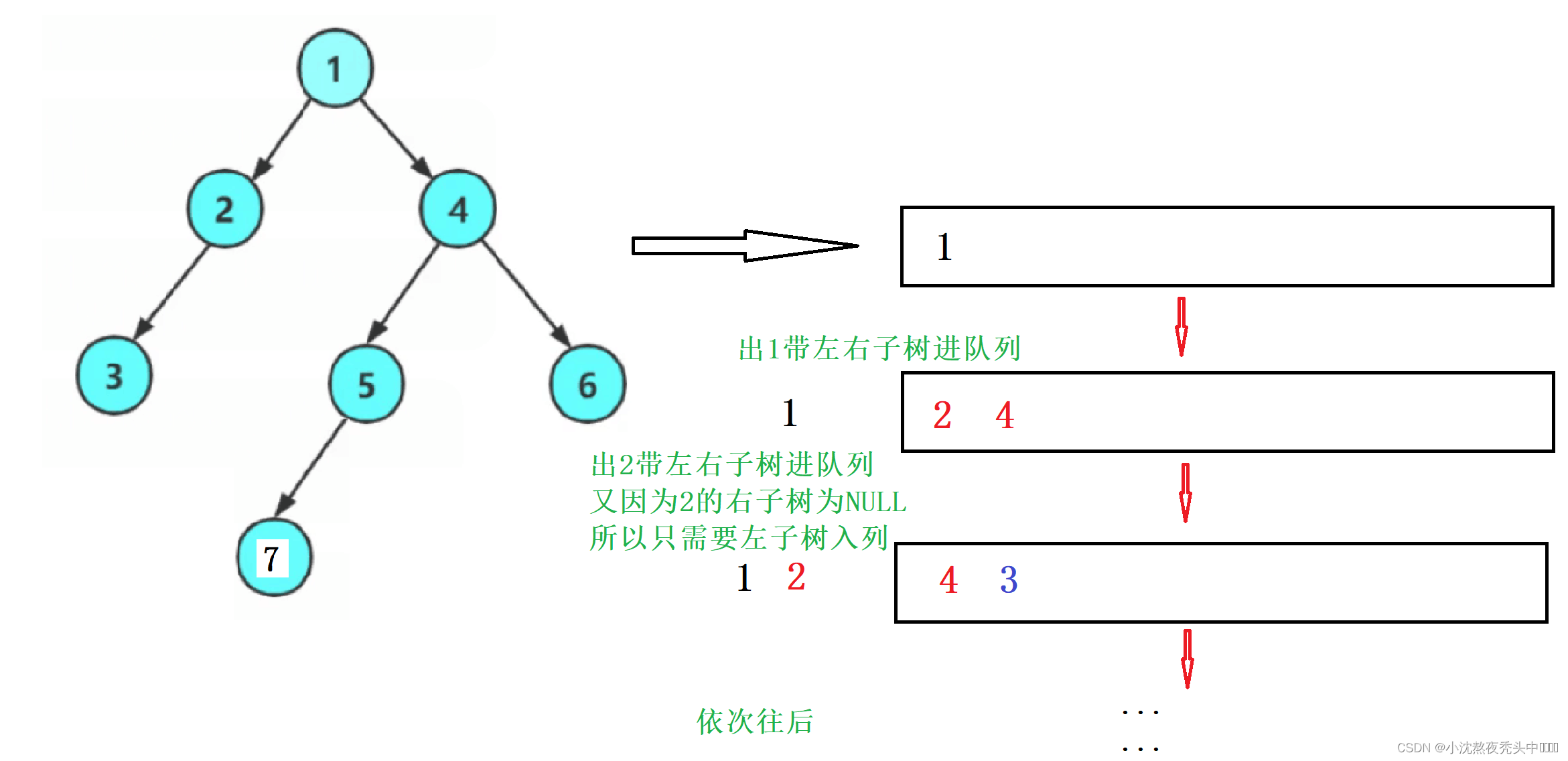
🌏1.5 层序遍历
📒代码:
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{Queue q;QueueInit(&q);if (root)QueuePush(&q, root);while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);printf("%d ", front->data);if (front->left)QueuePush(&q, front->left);if (front->right)QueuePush(&q, front->right);}printf("\n");QueueDestroy(&q);
}
📒思路流程(多种嵌套):
对于层序遍历,可以采用队列的思想(先进先出)
具体核心思想:上一层出时带下一层进队列所以进入时不能存储树节点的值而是存储树节点指针
🌏1.6 二叉树销毁(采用后序)
📒代码:
void BTreeDestroy(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL)return;BTreeDestroy(root->left);BTreeDestroy(root->right);free(root);
}
📒流程图:
🌏1.7 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
📒代码:
bool BTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{Queue q;QueueInit(&q);if (root)QueuePush(&q, root);while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);//遇到空就跳出if (front == NULL)break;QueuePush(&q, front->left);QueuePush(&q, front->right);}//检查后面的节点有没有非空//有非空不是完全二叉树while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);if (front != NULL)//往外拿数出现非空就不是完全二叉树{return false;QueueDestroy(&q);}}return true;QueueDestroy(&q);
}
📒思路流程:
和上述层序遍历一样,采用队列思想,上一层出时带下一层进入,出现NULL时跳出然后将里面的数字往外拿,出现非空不是完全二叉树
>N代表空
🌟二、二叉树链式结构完整代码
//Queue.h
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>typedef struct BinaryTreeNode* QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode//每个节点的结构
{struct QueueNode* next;QDataType data;
}QNode;typedef struct Queue
{QNode* phead;QNode* ptail;int size;
}Queue;//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
//释放
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
//尾插(入队)
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
//头删(出队)
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
//队头数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
//队尾数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
//数据个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
//判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);//Queue.c
#include"Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->phead = NULL;pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->phead;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail\n");return;}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->ptail == NULL){assert(pq->phead == NULL);pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;}else{pq->ptail->next = newnode;pq->ptail = newnode;}pq->size++;
}void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//一个队列if (pq->phead->next == NULL){free(pq->phead);pq->phead = NULL;pq->ptail = NULL;}//多个队列else{QNode* next = pq->phead->next;free(pq->phead);pq->phead = next;}pq->size--;
}QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->phead->data;
}QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->ptail->data;
}int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size == 0;/*return pq->phead == NULL && pq->ptail == NULL;*/return pq->size == 0;
}//Test.c
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include"Queue.h"typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{BTDataType data;struct BinaryTreeNode* left;struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));if (node == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return NULL;}node->data = x;node->left = NULL;node->right = NULL;return node;
}
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);BTNode* node7 = BuyNode(7);node1->left = node2;node1->right = node4;node2->left = node3;node4->left = node5;node4->right = node6;node5->left = node7;return node1;
}void PrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("NULL ");return;}printf("%d ", root->data);PrevOrder(root->left);PrevOrder(root->right);
}void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("NULL ");return;}InOrder(root->left);printf("%d ", root->data);InOrder(root->right);
}void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("NULL ");return;}PostOrder(root->left);PostOrder(root->right);printf("%d ", root->data);
}//二叉树节点个数 --- 遍历计数
//int size = 0;
//void BTreeSzie(BTNode* root)
//{
// if (root == NULL)
// {
// return size;
// }
// size++;
// BTreeSzie(root->left);
// BTreeSzie(root->right);
// return size;
//}//int BTreeSzie(BTNode* root)
//{
// static int size = 0;
// //printf("%p,%d\n", &size,size);
// if (root == NULL)
// {
// return size;
// }
// size++;
// BTreeSzie(root->left );
// BTreeSzie(root->right );
// return size;
//}int BTreeSzie(BTNode* root)
{return root == NULL ? 0 :BTreeSzie(root->left)+ BTreeSzie(root->right) + 1;
}//二叉树叶子节点个数
int BTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL)return 0;if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)return 1;return BTreeLeafSize(root->left)+ BTreeLeafSize(root->right);
}//二叉树树的高度
int BTreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL)return 0;int leftHeight = BTreeHeight(root->left);int rightHeight = BTreeHeight(root->right);return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}//二叉树第k层的节点个数
int BTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{assert(k >= 1);if (root == NULL)return 0;if (k == 1)return 1;return BTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1)+ BTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}//二叉树查找值为x的节点
BTNode* BTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{if (root == NULL)return NULL;if (root->data == x)return root;/*BTNode* ret1 = BTreeFind(root->left, x);if (ret1)return ret1;BTNode* ret2 = BTreeFind(root->left, x);if (ret2)return ret2;return NULL;*///BTreeFind(root->left, x);//BTreeFind(root->right, x);//return NULL;BTNode* ret1 = BTreeFind(root->left, x);if (ret1)return ret1;return BTreeFind(root->left, x);
}//层序遍历---用队列
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{Queue q;QueueInit(&q);if (root)QueuePush(&q, root);while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);printf("%d ", front->data);if (front->left)QueuePush(&q, front->left);if (front->right)QueuePush(&q, front->right);}printf("\n");QueueDestroy(&q);
}void BTreeDestroy(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL)return;BTreeDestroy(root->left);BTreeDestroy(root->right);free(root);
}//判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
bool BTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{Queue q;QueueInit(&q);if (root)QueuePush(&q, root);while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);//遇到空就跳出if (front == NULL)break;QueuePush(&q, front->left);QueuePush(&q, front->right);}//检查后面的节点有没有非空//有非空不是完全二叉树while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);if (front != NULL){return false;QueueDestroy(&q);}}return true;QueueDestroy(&q);
}int main()
{BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();PrevOrder(root);printf("\n");InOrder(root);printf("\n");PostOrder(root);printf("\n");//printf("BTreeSize:%d\n", BTreeSzie(root));//printf("BTreeSize:%d\n", BTreeSzie(root));//printf("BTreeSize:%d\n", BTreeSzie(root));/*BTreeSzie(root);printf("BTreeSize:%d\n", size);size = 0;BTreeSzie(root);printf("BTreeSize:%d\n", size);size = 0;BTreeSzie(root);printf("BTreeSize:%d\n", size);*/printf("BTreeSize:%d\n", BTreeSzie(root));printf("BTreeLeafSize: % d\n", BTreeLeafSize(root));printf("BTreeHeight: % d\n", BTreeHeight(root));printf("BTreeLevelKSize: % d\n", BTreeLevelKSize(root, 3));printf("BTreeLevelKSize: % d\n", BTreeLevelKSize(root, 2));LevelOrder(root);printf("BTreeComplete: % d\n", BTreeComplete(root));BTreeDestroy(root);root = NULL;return 0;
}
😽总结
😽Ending,今天的链式二叉树的内容就到此结束啦~,如果后续想了解更多,就请关注我吧,一键三连哦 ~
相关文章:

【数据结构】---几分钟简单几步学会手撕链式二叉树(下)
文章目录 前言🌟一、二叉树链式结构的实现🌏1.1 二叉树叶子节点个数💫代码:💫流程图: 🌏1.2 二叉树的高度💫第一种写法(不支持):📒代码:…...
用户验证FTP实验
用户FTP实验 目录 匿名用户验证: 本地用户验证: 本地用户访问控制: 匿名用户验证: 例:(前提配置,防火墙关闭,yum安装,同模式vmware11) 现有一台计算机huy…...

App 软件开发《单选4》试卷答案及解析
App 软件开发《单选4》试卷答案及解析 注:本文章所有答案的解析来自 ChatGPT 的回答(给出正确答案让其解释原因),正确性请自行甄辨。 文章目录 App 软件开发《单选4》试卷答案及解析单选题(共计0分)1&#…...

代码随想录算法训练营第三十七天 | 力扣 738.单调递增的数字, 968.监控二叉树
738.单调递增的数字 题目 738. 单调递增的数字 当且仅当每个相邻位数上的数字 x 和 y 满足 x < y 时,我们称这个整数是单调递增的。 给定一个整数 n ,返回 小于或等于 n 的最大数字,且数字呈 单调递增 。 解析 从后向前遍历…...
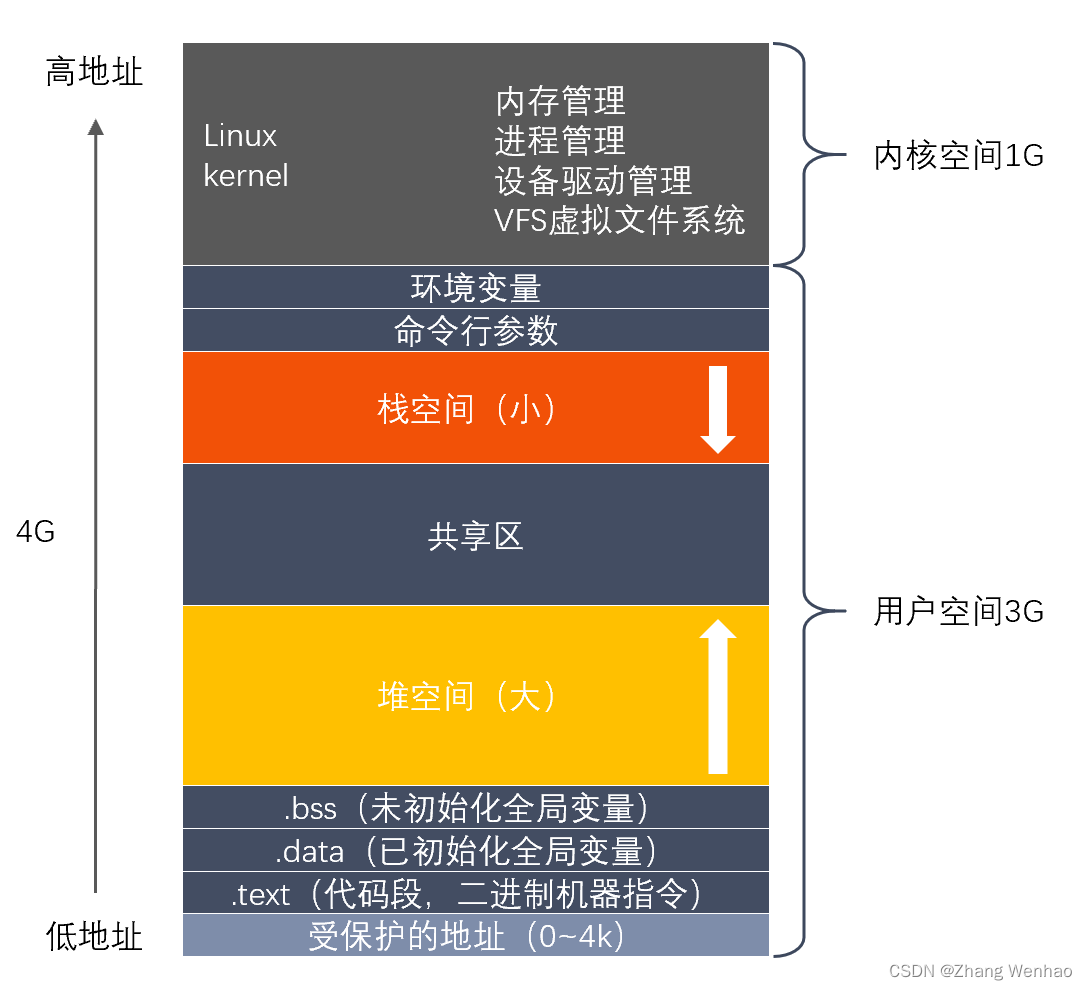
C++内存总结
1.2 C内存 参考 https://www.nowcoder.com/issue/tutorial?tutorialId93&uuid8f38bec08f974de192275e5366d8ae24 1.2.1 简述一下堆和栈的区别 参考回答 区别: 堆栈空间分配不同。栈由操作系统自动分配释放 ,存放函数的参数值,局部变…...
开发移动端官网总结_Vue2.x
目录 1、自定义加载中效果 2、HTML页面注入环境变量 / 加载CDN和本地库 3、在 Vue 中使用 wow.js 4、过渡路由 5、全局监听当前设备,切换PC端和移动端 6、移动端常用初始化样式 7、官网默认入口文件 8、回到顶部滑动过渡效果(显示与隐藏、滑动置…...
Zookeeper+消息队列Kafka
一、Zookeeper 概述 官方下载地址:Index of /dist/zookeeper 1.1 Zookeeper 定义 Zookeeper是一个开源的分布式的,为分布式框架提供协调服务的Apache项目。 1.2 Zookeeper 工作机制 Zookeeper从设计模式角度来理解:是一个基于观察者模式设…...

【滤波】设计卡尔曼滤波器
本文主要翻译自rlabbe/Kalman-and-Bayesian-Filters-in-Python的第8章节08-Designing-Kalman-Filters(设计卡尔曼滤波器)。 %matplotlib inline#format the book import book_format book_format.set_style()简介 在上一章节中,我们讨论了教…...

redis主备切换,哨兵模式,缓存穿透、缓存击穿、缓存雪崩问题
主备切换 主从复制指的是把一台Redis服务器的数据复制到其他Redis服务器上,前者称为主节点Master,后者称为从节点Slave,只能从Master单向复制到Slave,一般Master以写操作为主,Slave以读操作为主,实现读写分…...

2023山东icpc省赛总结
距离比赛结束已经一天多了,现在的感觉就是三个字:意难平。 这是我们第一次打现场赛,去之前真的是很激动。因为我们比赛前做了很多其他省的省赛模拟,也做了几套今年别的省的题目,做完会去搜题解,会看到别人写…...

linux0.12-12-fs
[606页] 第12章 文件系统 606–12-1-总体功能 607–12-1-1-MINIX文件系统 611–12-1-2-文件类型、属性和目录项 615–12-1-3-高速缓冲区 616–12-1-4-文件系统底层函数 616–12-1-5-文件中数据的访问操作 618–12-1-6-文件和目录管理系统调用 619–12-1-7-360KB软盘中文件系统…...
快速入门SpringMVC 学习
目录 SpringMVC 定义 MVC定义 创建SpringMVC项目 SpringMVC掌握功能 一、连接功能 RequestMapping(请求映射) GetMapping 和 PostMapping 二、获取参数功能 传递单个参数/多个参数 注意点: RequestParam(前后端参数映射) 前后端参数映射 RequestParam特…...

leetcode96--不同的二叉搜索树[java]
不同的二叉搜索树 leetcode 96 题 不同的二叉搜索树题目描述暴力递归解题思路代码演示执行效率 递归 缓存解题思路代码演示执行效率 动态规划专题 leetcode 96 题 不同的二叉搜索树 原题链接: 难度—中等 https://leetcode.cn/problems/unique-binary-search-trees/ 题目描述 …...

【Spring 项目的创建和使用】
🎉🎉🎉点进来你就是我的人了博主主页:🙈🙈🙈戳一戳,欢迎大佬指点! 欢迎志同道合的朋友一起加油喔🤺🤺🤺 目录 1. 创建 Spring 项目 2. 创建一个 普通 Maven…...
数据类型.
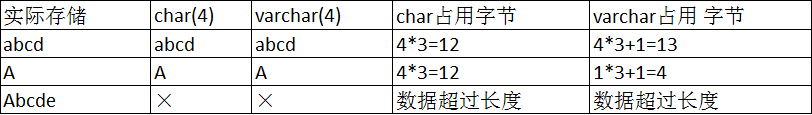
数据类型 数据类型分类 数值类型 tinyint类型 数值越界测试: mysql> create table tt1(num tinyint); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)mysql> insert into tt1 values(1); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> insert into tt1 values(128…...

深入了解JavaScript中的Promise
在JavaScript中,异步编程是必不可少的。过去,我们通常使用回调函数来处理异步操作,但回调地狱(callback hell)和复杂的错误处理使得代码难以维护。为了解决这些问题,ES6引入了Promise,它是一种更…...
Solidity基础六
生活本来就是平凡琐碎的,哪有那么多惊天动地的大事,快乐的秘诀就是不管对大事小事都要保持热情 目录 一、Solidity的特殊变量(全局) 二、Solidity的不可变量 immutable的赋值方式 三、Solidity的事件与日志 事件和日志加深理解 四、Solidity的异常…...

自学网络安全解决问题方法
自学网络安全很容易学着学着就迷茫了,找到源头问题,解决它就可以了,所以首先咱们聊聊,学习网络安全方向通常会有哪些问题,看到后面有惊喜哦 1、打基础时间太长 学基础花费很长时间,光语言都有几门…...
)
Java之旅(七)
Java 异常 Java异常(Exception)是在程序运行过程中出现错误或异常情况时,由程序自动抛出,导致程序无法正常运行,用于向上层调用程序传递错误信息或中断程序执行的一种机制。 异常与错误不同,错误是由于程…...

测试报告模板二
项目名称 系统测试报告 平台测试小组 2023年x月xx日 文档信息 文档名称: 作者:...

Docker 离线安装指南
参考文章 1、确认操作系统类型及内核版本 Docker依赖于Linux内核的一些特性,不同版本的Docker对内核版本有不同要求。例如,Docker 17.06及之后的版本通常需要Linux内核3.10及以上版本,Docker17.09及更高版本对应Linux内核4.9.x及更高版本。…...

高频面试之3Zookeeper
高频面试之3Zookeeper 文章目录 高频面试之3Zookeeper3.1 常用命令3.2 选举机制3.3 Zookeeper符合法则中哪两个?3.4 Zookeeper脑裂3.5 Zookeeper用来干嘛了 3.1 常用命令 ls、get、create、delete、deleteall3.2 选举机制 半数机制(过半机制࿰…...

基于Uniapp开发HarmonyOS 5.0旅游应用技术实践
一、技术选型背景 1.跨平台优势 Uniapp采用Vue.js框架,支持"一次开发,多端部署",可同步生成HarmonyOS、iOS、Android等多平台应用。 2.鸿蒙特性融合 HarmonyOS 5.0的分布式能力与原子化服务,为旅游应用带来…...

多模态商品数据接口:融合图像、语音与文字的下一代商品详情体验
一、多模态商品数据接口的技术架构 (一)多模态数据融合引擎 跨模态语义对齐 通过Transformer架构实现图像、语音、文字的语义关联。例如,当用户上传一张“蓝色连衣裙”的图片时,接口可自动提取图像中的颜色(RGB值&…...
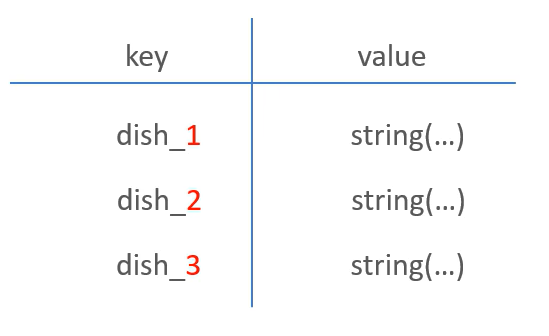
苍穹外卖--缓存菜品
1.问题说明 用户端小程序展示的菜品数据都是通过查询数据库获得,如果用户端访问量比较大,数据库访问压力随之增大 2.实现思路 通过Redis来缓存菜品数据,减少数据库查询操作。 缓存逻辑分析: ①每个分类下的菜品保持一份缓存数据…...

uniapp中使用aixos 报错
问题: 在uniapp中使用aixos,运行后报如下错误: AxiosError: There is no suitable adapter to dispatch the request since : - adapter xhr is not supported by the environment - adapter http is not available in the build 解决方案&…...
selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】
selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】 文章目录 selenium学习实战【Python爬虫】一、声明二、学习目标三、安装依赖3.1 安装selenium库3.2 安装浏览器驱动3.2.1 查看Edge版本3.2.2 驱动安装 四、代码讲解4.1 配置浏览器4.2 加载更多4.3 寻找内容4.4 完整代码 五、报告文件爬取5.1 提…...
【开发技术】.Net使用FFmpeg视频特定帧上绘制内容
目录 一、目的 二、解决方案 2.1 什么是FFmpeg 2.2 FFmpeg主要功能 2.3 使用Xabe.FFmpeg调用FFmpeg功能 2.4 使用 FFmpeg 的 drawbox 滤镜来绘制 ROI 三、总结 一、目的 当前市场上有很多目标检测智能识别的相关算法,当前调用一个医疗行业的AI识别算法后返回…...

分布式增量爬虫实现方案
之前我们在讨论的是分布式爬虫如何实现增量爬取。增量爬虫的目标是只爬取新产生或发生变化的页面,避免重复抓取,以节省资源和时间。 在分布式环境下,增量爬虫的实现需要考虑多个爬虫节点之间的协调和去重。 另一种思路:将增量判…...

安宝特案例丨Vuzix AR智能眼镜集成专业软件,助力卢森堡医院药房转型,赢得辉瑞创新奖
在Vuzix M400 AR智能眼镜的助力下,卢森堡罗伯特舒曼医院(the Robert Schuman Hospitals, HRS)凭借在无菌制剂生产流程中引入增强现实技术(AR)创新项目,荣获了2024年6月7日由卢森堡医院药剂师协会࿰…...