Rust vs Go:常用语法对比(四)

题图来自 Go vs. Rust performance comparison: The basics
61. Get current date
获取当前时间
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
d := time.Now()
fmt.Println("Now is", d)
// The Playground has a special sandbox, so you may get a Time value fixed in the past.
}
Now is 2009-11-10 23:00:00 +0000 UTC m=+0.000000001
extern crate time;
let d = time::now();
or
use std::time::SystemTime;
fn main() {
let d = SystemTime::now();
println!("{:?}", d);
}
SystemTime { tv_sec: 1526318418, tv_nsec: 699329521 }
62. Find substring position
字符串查找
查找子字符串位置
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
x := "été chaud"
{
y := "chaud"
i := strings.Index(x, y)
fmt.Println(i)
}
{
y := "froid"
i := strings.Index(x, y)
fmt.Println(i)
}
}
i is the byte index of y in x, not the character (rune) index. i will be -1 if y is not found in x.
6
-1
fn main() {
let x = "été chaud";
let y = "chaud";
let i = x.find(y);
println!("{:?}", i);
let y = "froid";
let i = x.find(y);
println!("{:?}", i);
}
Some(6)
None
63. Replace fragment of a string
替换字符串片段
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
x := "oink oink oink"
y := "oink"
z := "moo"
x2 := strings.Replace(x, y, z, -1)
fmt.Println(x2)
}
moo moo moo
fn main() {
let x = "lorem ipsum dolor lorem ipsum";
let y = "lorem";
let z = "LOREM";
let x2 = x.replace(&y, &z);
println!("{}", x2);
}
LOREM ipsum dolor LOREM ipsum
64. Big integer : value 3 power 247
超大整数
package main
import "fmt"
import "math/big"
func main() {
x := new(big.Int)
x.Exp(big.NewInt(3), big.NewInt(247), nil)
fmt.Println(x)
}
7062361041362837614435796717454722507454089864783271756927542774477268334591598635421519542453366332460075473278915787
extern crate num;
use num::bigint::ToBigInt;
fn main() {
let a = 3.to_bigint().unwrap();
let x = num::pow(a, 247);
println!("{}", x)
}
7062361041362837614435796717454722507454089864783271756927542774477268334591598635421519542453366332460075473278915787
65. Format decimal number
格式化十进制数
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
x := 0.15625
s := fmt.Sprintf("%.1f%%", 100.0*x)
fmt.Println(s)
}
15.6%
fn main() {
let x = 0.15625f64;
let s = format!("{:.1}%", 100.0 * x);
println!("{}", s);
}
15.6%
66. Big integer exponentiation
大整数幂运算
package main
import "fmt"
import "math/big"
func exp(x *big.Int, n int) *big.Int {
nb := big.NewInt(int64(n))
var z big.Int
z.Exp(x, nb, nil)
return &z
}
func main() {
x := big.NewInt(3)
n := 5
z := exp(x, n)
fmt.Println(z)
}
243
extern crate num;
use num::bigint::BigInt;
fn main() {
let x = BigInt::parse_bytes(b"600000000000", 10).unwrap();
let n = 42%
67. Binomial coefficient "n choose k"
Calculate binom(n, k) = n! / (k! * (n-k)!). Use an integer type able to handle huge numbers.
二项式系数“n选择k”
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math/big"
)
func main() {
z := new(big.Int)
z.Binomial(4, 2)
fmt.Println(z)
z.Binomial(133, 71)
fmt.Println(z)
}
6
555687036928510235891585199545206017600
extern crate num;
use num::bigint::BigInt;
use num::bigint::ToBigInt;
use num::traits::One;
fn binom(n: u64, k: u64) -> BigInt {
let mut res = BigInt::one();
for i in 0..k {
res = (res * (n - i).to_bigint().unwrap()) /
(i + 1).to_bigint().unwrap();
}
res
}
fn main() {
let n = 133;
let k = 71;
println!("{}", binom(n, k));
}
555687036928510235891585199545206017600
68. Create a bitset
创建位集合
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math/big"
)
func main() {
var x *big.Int = new(big.Int)
x.SetBit(x, 42, 1)
for _, y := range []int{13, 42} {
fmt.Println("x has bit", y, "set to", x.Bit(y))
}
}
x has bit 13 set to 0
x has bit 42 set to 1
or
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
const n = 1024
func main() {
x := make([]bool, n)
x[42] = true
for _, y := range []int{13, 42} {
fmt.Println("x has bit", y, "set to", x[y])
}
}
x has bit 13 set to false
x has bit 42 set to true
or
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
const n = 1024
x := NewBitset(n)
x.SetBit(13)
x.SetBit(42)
x.ClearBit(13)
for _, y := range []int{13, 42} {
fmt.Println("x has bit", y, "set to", x.GetBit(y))
}
}
type Bitset []uint64
func NewBitset(n int) Bitset {
return make(Bitset, (n+63)/64)
}
func (b Bitset) GetBit(index int) bool {
pos := index / 64
j := index % 64
return (b[pos] & (uint64(1) << j)) != 0
}
func (b Bitset) SetBit(index int) {
pos := index / 64
j := index % 64
b[pos] |= (uint64(1) << j)
}
func (b Bitset) ClearBit(index int) {
pos := index / 64
j := index % 64
b[pos] ^= (uint64(1) << j)
}
x has bit 13 set to false
x has bit 42 set to true
fn main() {
let n = 20;
let mut x = vec![false; n];
x[3] = true;
println!("{:?}", x);
}
[false, false, false, true, false, false, false, false, false, false, false, false, false, false, false, false, false, false, false, false]
69. Seed random generator
Use seed s to initialize a random generator.
If s is constant, the generator output will be the same each time the program runs. If s is based on the current value of the system clock, the generator output will be different each time.
随机种子生成器
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
)
func main() {
var s int64 = 42
rand.Seed(s)
fmt.Println(rand.Int())
}
3440579354231278675
or
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
)
func main() {
var s int64 = 42
r := rand.New(rand.NewSource(s))
fmt.Println(r.Int())
}
3440579354231278675
use rand::{Rng, SeedableRng, rngs::StdRng};
fn main() {
let s = 32;
let mut rng = StdRng::seed_from_u64(s);
println!("{:?}", rng.gen::<f32>());
}
0.35038823
70. Use clock as random generator seed
Get the current datetime and provide it as a seed to a random generator. The generator sequence will be different at each run.
使用时钟作为随机生成器的种子
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"time"
)
func main() {
rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano())
// Well, the playground date is actually fixed in the past, and the
// output is cached.
// But if you run this on your workstation, the output will vary.
fmt.Println(rand.Intn(999))
}
524
or
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"time"
)
func main() {
r := rand.New(rand.NewSource(time.Now().UnixNano()))
// Well, the playground date is actually fixed in the past, and the
// output is cached.
// But if you run this on your workstation, the output will vary.
fmt.Println(r.Intn(999))
}
524
use rand::{Rng, SeedableRng, rngs::StdRng};
use std::time::SystemTime;
fn main() {
let d = SystemTime::now()
.duration_since(SystemTime::UNIX_EPOCH)
.expect("Duration since UNIX_EPOCH failed");
let mut rng = StdRng::seed_from_u64(d.as_secs());
println!("{:?}", rng.gen::<f32>());
}
0.7326781
71. Echo program implementation
Basic implementation of the Echo program: Print all arguments except the program name, separated by space, followed by newline.
The idiom demonstrates how to skip the first argument if necessary, concatenate arguments as strings, append newline and print it to stdout.
实现 Echo 程序
package main
import "fmt"
import "os"
import "strings"
func main() {
fmt.Println(strings.Join(os.Args[1:], " "))
}
use std::env;
fn main() {
println!("{}", env::args().skip(1).collect::<Vec<_>>().join(" "));
}
or
use itertools::Itertools;
println!("{}", std::env::args().skip(1).format(" "));
74. Compute GCD
Compute the greatest common divisor x of big integers a and b. Use an integer type able to handle huge numbers.
计算大整数a和b的最大公约数x。使用能够处理大数的整数类型。
package main
import "fmt"
import "math/big"
func main() {
a, b, x := new(big.Int), new(big.Int), new(big.Int)
a.SetString("6000000000000", 10)
b.SetString("9000000000000", 10)
x.GCD(nil, nil, a, b)
fmt.Println(x)
}
3000000000000
extern crate num;
use num::Integer;
use num::bigint::BigInt;
fn main() {
let a = BigInt::parse_bytes(b"6000000000000", 10).unwrap();
let b = BigInt::parse_bytes(b"9000000000000", 10).unwrap();
let x = a.gcd(&b);
println!("{}", x);
}
3000000000000
75. Compute LCM
计算大整数a和b的最小公倍数x。使用能够处理大数的整数类型。
Compute the least common multiple x of big integers a and b. Use an integer type able to handle huge numbers.
package main
import "fmt"
import "math/big"
func main() {
a, b, gcd, x := new(big.Int), new(big.Int), new(big.Int), new(big.Int)
a.SetString("6000000000000", 10)
b.SetString("9000000000000", 10)
gcd.GCD(nil, nil, a, b)
x.Div(a, gcd).Mul(x, b)
fmt.Println(x)
}
18000000000000
extern crate num;
use num::bigint::BigInt;
use num::Integer;
fn main() {
let a = BigInt::parse_bytes(b"6000000000000", 10).unwrap();
let b = BigInt::parse_bytes(b"9000000000000", 10).unwrap();
let x = a.lcm(&b);
println!("x = {}", x);
}
x = 18000000000000
76. Binary digits from an integer
Create the string s of integer x written in base 2.
E.g. 13 -> "1101"
将十进制整数转换为二进制数字
package main
import "fmt"
import "strconv"
func main() {
x := int64(13)
s := strconv.FormatInt(x, 2)
fmt.Println(s)
}
1101
or
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math/big"
)
func main() {
x := big.NewInt(13)
s := fmt.Sprintf("%b", x)
fmt.Println(s)
}
1101
fn main() {
let x = 13;
let s = format!("{:b}", x);
println!("{}", s);
}
1101
77. SComplex number
Declare a complex x and initialize it with value (3i - 2). Then multiply it by i.
复数
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
)
func main() {
x := 3i - 2
x *= 1i
fmt.Println(x)
fmt.Print(reflect.TypeOf(x))
}
(-3-2i)
complex128
extern crate num;
use num::Complex;
fn main() {
let mut x = Complex::new(-2, 3);
x *= Complex::i();
println!("{}", x);
}
-3-2i
78. "do while" loop
Execute a block once, then execute it again as long as boolean condition c is true.
循环执行
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
)
func main() {
for {
x := rollDice()
fmt.Println("Got", x)
if x == 3 {
break
}
}
}
func rollDice() int {
return 1 + rand.Intn(6)
}
Go has no do while loop, use the for loop, instead.
Got 6
Got 4
Got 6
Got 6
Got 2
Got 1
Got 2
Got 3
or
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
)
func main() {
for done := false; !done; {
x := rollDice()
fmt.Println("Got", x)
done = x == 3
}
}
func rollDice() int {
return 1 + rand.Intn(6)
}
Got 6
Got 4
Got 6
Got 6
Got 2
Got 1
Got 2
Got 3
loop {
doStuff();
if !c { break; }
}
Rust has no do-while loop with syntax sugar. Use loop and break.
79. Convert integer to floating point number
Declare floating point number y and initialize it with the value of integer x .
整型转浮点型
声明浮点数y并用整数x的值初始化它。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
)
func main() {
x := 5
y := float64(x)
fmt.Println(y)
fmt.Printf("%.2f\n", y)
fmt.Println(reflect.TypeOf(y))
}
5
5.00
float64
fn main() {
let i = 5;
let f = i as f64;
println!("int {:?}, float {:?}", i, f);
}
int 5, float 5.0
80. Truncate floating point number to integer
Declare integer y and initialize it with the value of floating point number x . Ignore non-integer digits of x . Make sure to truncate towards zero: a negative x must yield the closest greater integer (not lesser).
浮点型转整型
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
a := -6.4
b := 6.4
c := 6.6
fmt.Println(int(a))
fmt.Println(int(b))
fmt.Println(int(c))
}
-6
6
6
fn main() {
let x = 41.59999999f64;
let y = x as i32;
println!("{}", y);
}
41
本文由 mdnice 多平台发布
相关文章:

Rust vs Go:常用语法对比(四)
题图来自 Go vs. Rust performance comparison: The basics 61. Get current date 获取当前时间 package mainimport ( "fmt" "time")func main() { d : time.Now() fmt.Println("Now is", d) // The Playground has a special sandbox, so you …...

c++ 派生类 文本查询程序再探
Query_base类和Query类 //这是一个抽象基类,具体的查询类型从中派生,所有成员都是private的 class Query_base {friend class Query;protected:using line_no TextQuery::line_no;//用于level函数virtual ~Query_base() default;private://eval返回与…...

17. 电话号码的字母组合
题目描述 给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。答案可以按 任意顺序 返回。 给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。 示例 1: 输入:digits "23" …...

Redis 基础知识和核心概念解析:理解 Redis 的键值操作和过期策略
🌷🍁 博主 libin9iOak带您 Go to New World.✨🍁 🦄 个人主页——libin9iOak的博客🎐 🐳 《面试题大全》 文章图文并茂🦕生动形象🦖简单易学!欢迎大家来踩踩~ἳ…...
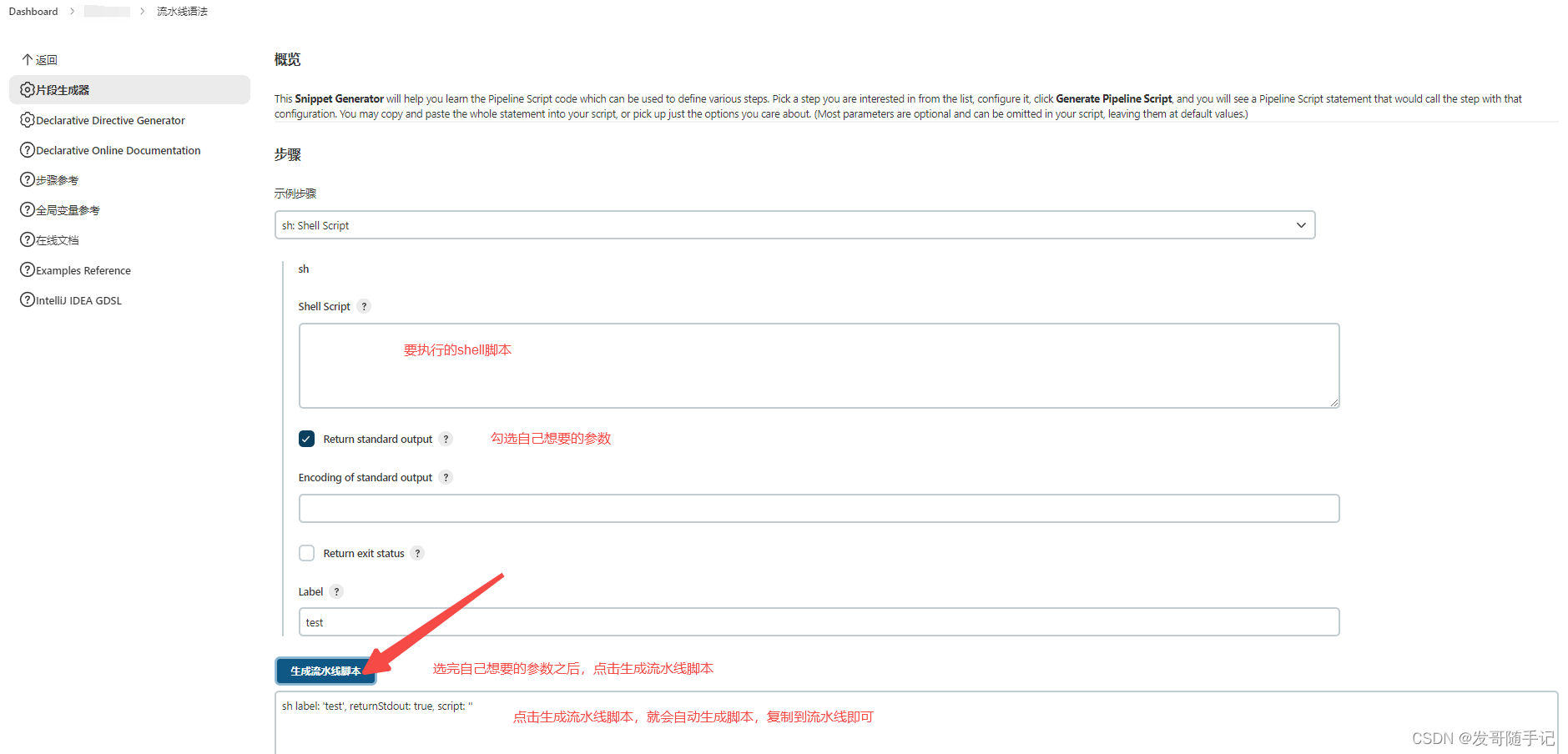
Jenkins中sh函数的用法
在Jenkins的Pipeline中,sh函数的用法 用法一 单个命令字符串包括使用,示例如下: sh echo "Hello, Jenkins!"用法二 多个命令字符串包括命令列表使用,示例如下: sh echo "Step 1" echo "…...
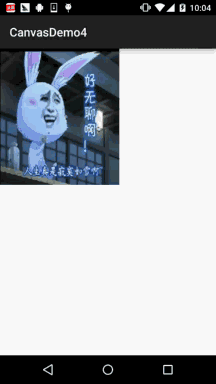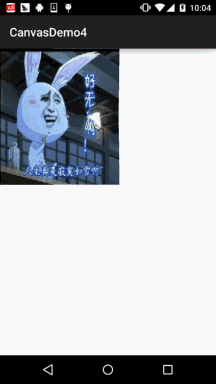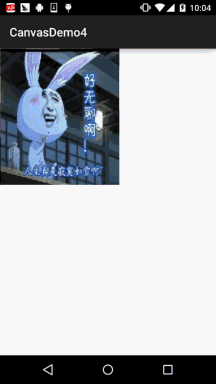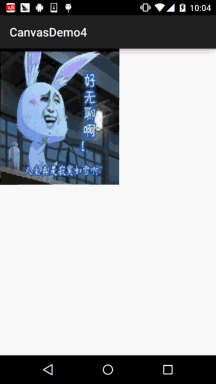
Android 之 Canvas API 详解 (Part 3) Matrix 和 drawBitmapMesh
本节引言: 在Canvas的API文档中,我们看到这样一个方法:drawBitmap(Bitmap bitmap, Matrix matrix, Paint paint) 这个Matrix可是有大文章的,前面我们在学Paint的API中的ColorFilter中曾讲过ColorMatrix 颜色矩阵,一个4…...
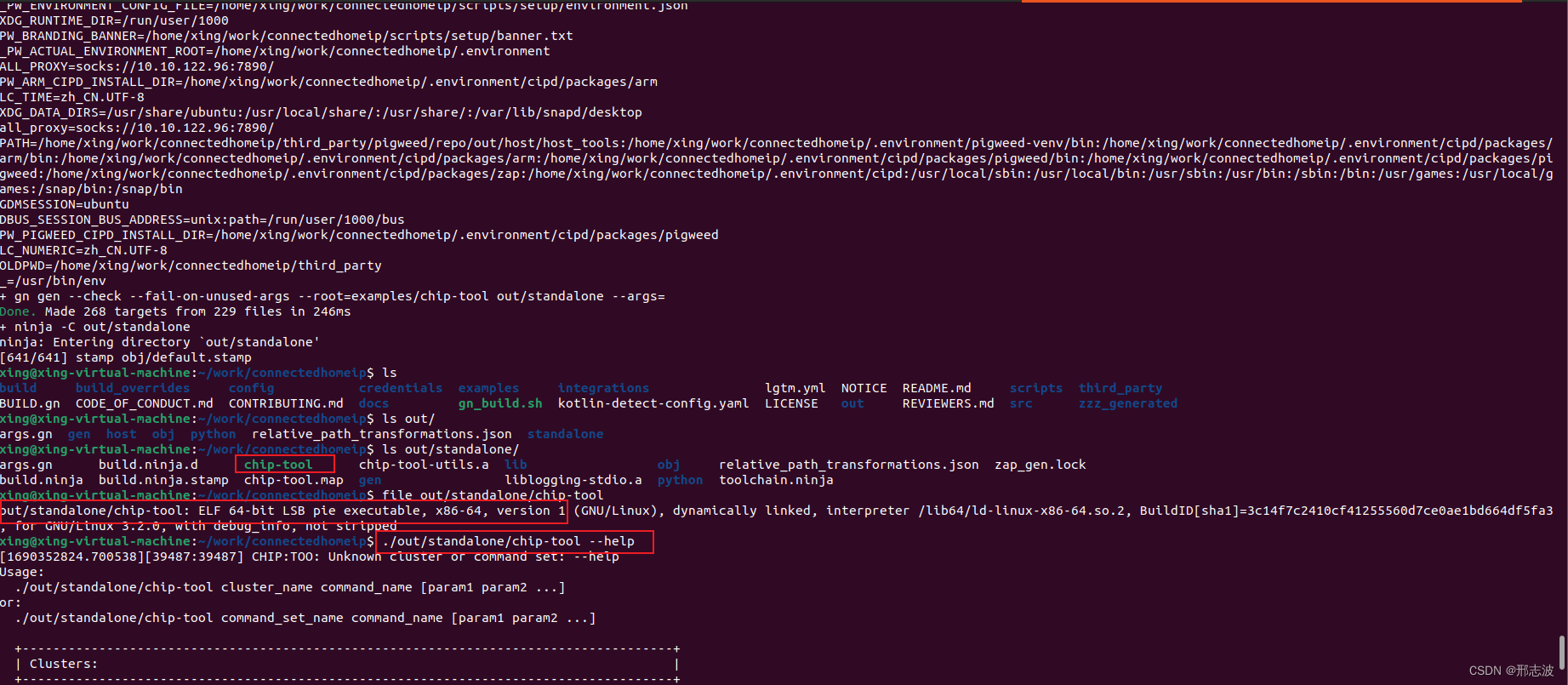
基于Ubuntu 22.04 编译chip-tool工具
前言 编译过程有点曲折,做下记录,过程中,有参考别人写的博客,也看github 官方介绍,终于跑通了~ 环境说明: 首先需要稳定的梯子,可以访问“外网”ubuntu 环境,最终成功实验在Ubunt…...
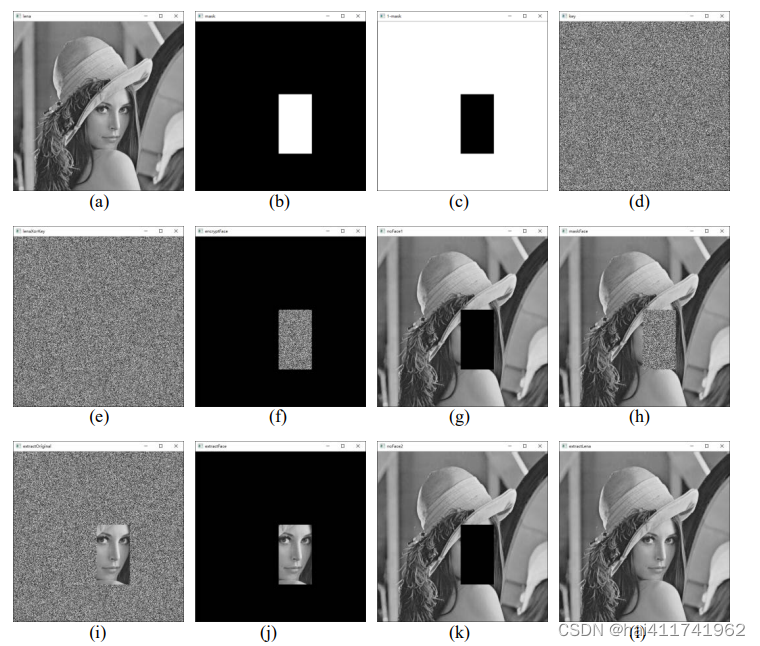
opencv-17 脸部打码及解码
使用掩模和按位运算方式实现的对脸部打码、解码实例 代码如下: import cv2 import numpy as np #读取原始载体图像 lenacv2.imread("lena.png",0) #读取原始载体图像的 shape 值 r,clena.shape masknp.zeros((r,c),dtypenp.uint8) mask[220:400,250:350…...

JVM分享
JVM分享 官网:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jvms/se8/html/index.html Java代码的执行流程 我们编写完之后的java文件如果要运行,java文件会编译成class文件,在jvm中运行时ClassLoader会加载class文件,加载进来之后&a…...
Apache Dubbo CVE-2021-36162 挖掘过程
01 漏洞背景 发现该漏洞的起因是在分析 CVE-2021-30181 的脚本注入补丁的时候,意外发现了几个已被修复的 yaml 反序列化漏洞,还以为是未公开的Nday,查询后发现其实对应的是 CVE-2021-30180 漏洞的修复代码。通过查看补丁可以知道,…...

开源框架面试题目整理
目录 SpringIOC SpringAOP Spring的生命周期 Spring Bean作用域 Spring Bean作用域并发安全 Spring循环依赖...
Mr. Cappuccino的第52杯咖啡——Mybatis环境搭建与使用
Mybatis环境搭建与使用 Mybatis介绍Mybatis环境搭建与使用基于XML方式-原生方式开发创建数据库表项目准备项目结构项目代码实体类中添加有参构造方法产生的问题 基于XML方式-mapper代理开发项目准备项目结构项目代码SQL映射文件中namespace未设置为接口全限定名产生的问题 基于…...
了解Unity编辑器之组件篇Tilemap(五)
Tilemap:用于创建和编辑2D网格地图的工具。Tilemap的主要作用是简化2D游戏中地图的创建、编辑和渲染过程。以下是一些Tilemap的主要用途: 2D地图绘制:Tilemap提供了一个可视化的编辑器界面,可以快速绘制2D地图,例如迷…...

Linux字符设备操作函数
Linux字符设备操作函数是指对字符设备进行打开、关闭、读取、写入、控制等基本操作的函数,它们通过字符设备结构体中的 file_operations 结构体来定义。常用的字符设备操作函数包括: 1、open: 当一个进程试图打开设备文件时,调用这个函数。开…...

吉林大学计算机软件考研经验贴
文章目录 简介政治英语数学专业课 简介 本人23考研,一战上岸吉林大学软件工程专硕,政治72分,英一71分,数二144分,专业课967综合146分,总分433分,上图: 如果学弟学妹需要专业课资料…...

2023-07-26力扣每日一题-区间翻转线段树
链接: 2569. 更新数组后处理求和查询 题意: 给两个等长数组nums1和nums2,三个操作: 操作1:将nums1的[l,r]翻转(0变1,1变0) 操作2:将nums2[any]变成nums2[any]nums1[any]*p&…...

Java设计模式之 -- 桥接模式
什么是桥接模式 桥接模式是一种结构型设计模式,也被称为“Handle/Body”。这种设计模式主要用于将抽象部分与它的实现部分分离,使它们可以独立地变化。这种方式有助于减少系统中的耦合性,增加了扩展性。 主要解决什么问题 桥接模式主要解决…...

【node.js】02-path模块
目录 1. path.join() 2. path.basename() 3. path.extname() 1. path.join() 使用 path.join() 方法,可以把多个路径片段拼接为完整的路径字符串,语法格式如下: path.join([...paths]) 例子: const path require(path)co…...

攻防世界-Reverse-re1
题目描述:菜鸡开始学习逆向工程,首先是最简单的题目 下载附件,执行程序,如下界面 1. 思路分析 没啥说的,既然题目都说是一道简单的逆向题,那么直接使用ida逆向即可,看逆向出的结果是否能写入到…...

AES加密的基本常识和封装类
AES加密的基本常识和封装类 AES(Advanced Encryption Standard)是一种对称密钥加密算法,被广泛用于保护敏感数据的安全性。它是一种块加密算法,意味着它将明文数据分成固定大小的块,并使用相同的密钥对每个块进行独立…...
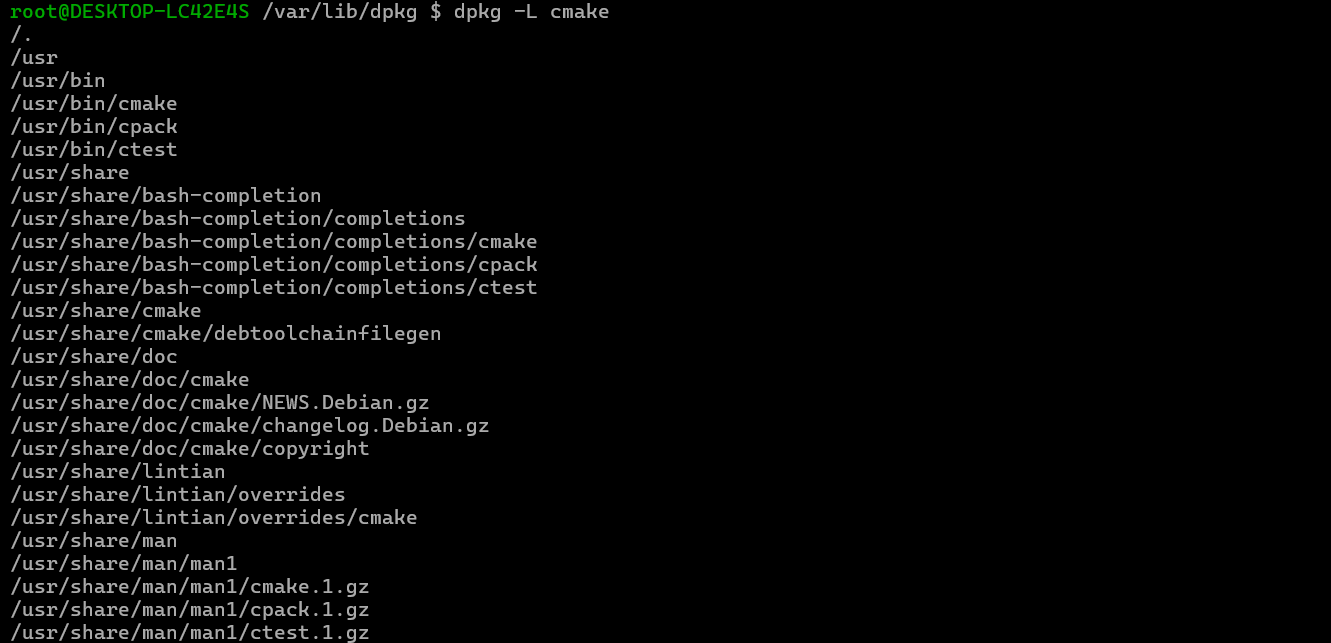
Debian系统简介
目录 Debian系统介绍 Debian版本介绍 Debian软件源介绍 软件包管理工具dpkg dpkg核心指令详解 安装软件包 卸载软件包 查询软件包状态 验证软件包完整性 手动处理依赖关系 dpkg vs apt Debian系统介绍 Debian 和 Ubuntu 都是基于 Debian内核 的 Linux 发行版ÿ…...
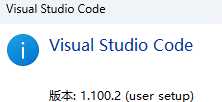
无法与IP建立连接,未能下载VSCode服务器
如题,在远程连接服务器的时候突然遇到了这个提示。 查阅了一圈,发现是VSCode版本自动更新惹的祸!!! 在VSCode的帮助->关于这里发现前几天VSCode自动更新了,我的版本号变成了1.100.3 才导致了远程连接出…...

关于iview组件中使用 table , 绑定序号分页后序号从1开始的解决方案
问题描述:iview使用table 中type: "index",分页之后 ,索引还是从1开始,试过绑定后台返回数据的id, 这种方法可行,就是后台返回数据的每个页面id都不完全是按照从1开始的升序,因此百度了下,找到了…...
:爬虫完整流程)
Python爬虫(二):爬虫完整流程
爬虫完整流程详解(7大核心步骤实战技巧) 一、爬虫完整工作流程 以下是爬虫开发的完整流程,我将结合具体技术点和实战经验展开说明: 1. 目标分析与前期准备 网站技术分析: 使用浏览器开发者工具(F12&…...
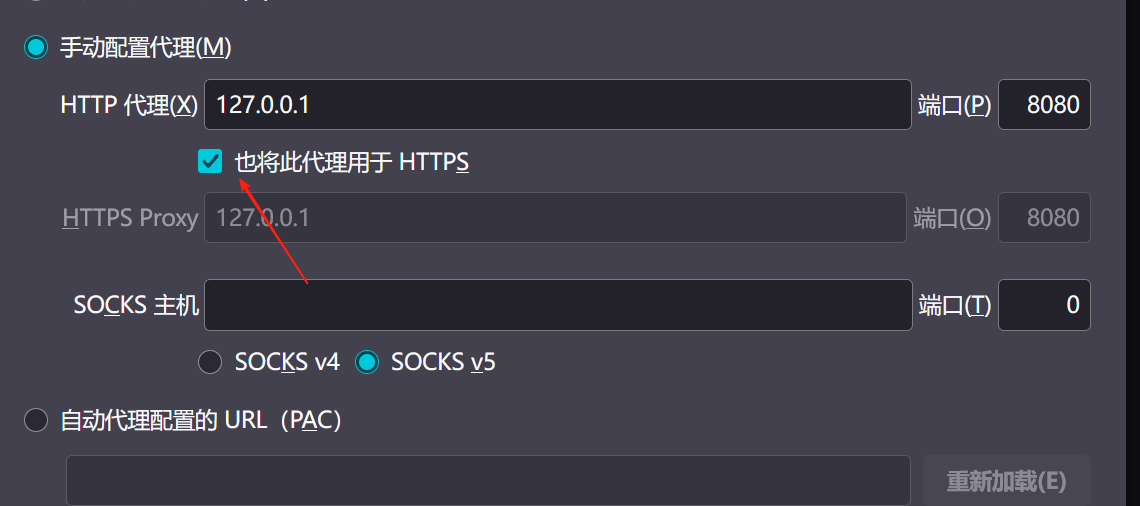
【2025年】解决Burpsuite抓不到https包的问题
环境:windows11 burpsuite:2025.5 在抓取https网站时,burpsuite抓取不到https数据包,只显示: 解决该问题只需如下三个步骤: 1、浏览器中访问 http://burp 2、下载 CA certificate 证书 3、在设置--隐私与安全--…...

鸿蒙DevEco Studio HarmonyOS 5跑酷小游戏实现指南
1. 项目概述 本跑酷小游戏基于鸿蒙HarmonyOS 5开发,使用DevEco Studio作为开发工具,采用Java语言实现,包含角色控制、障碍物生成和分数计算系统。 2. 项目结构 /src/main/java/com/example/runner/├── MainAbilitySlice.java // 主界…...

零基础在实践中学习网络安全-皮卡丘靶场(第九期-Unsafe Fileupload模块)(yakit方式)
本期内容并不是很难,相信大家会学的很愉快,当然对于有后端基础的朋友来说,本期内容更加容易了解,当然没有基础的也别担心,本期内容会详细解释有关内容 本期用到的软件:yakit(因为经过之前好多期…...

AI,如何重构理解、匹配与决策?
AI 时代,我们如何理解消费? 作者|王彬 封面|Unplash 人们通过信息理解世界。 曾几何时,PC 与移动互联网重塑了人们的购物路径:信息变得唾手可得,商品决策变得高度依赖内容。 但 AI 时代的来…...
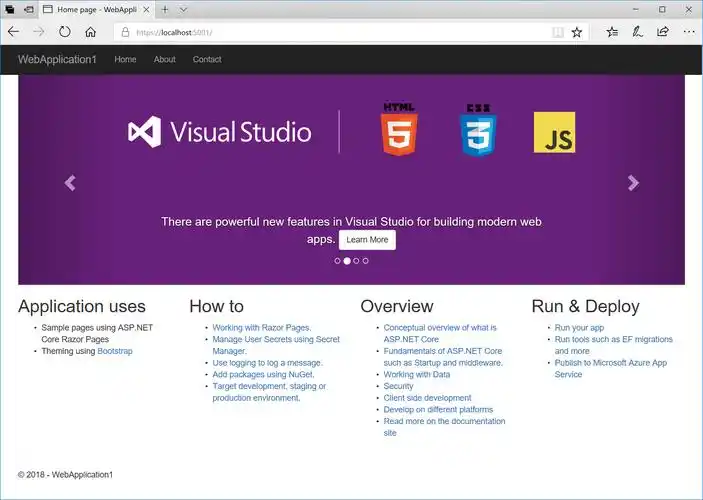
Razor编程中@Html的方法使用大全
文章目录 1. 基础HTML辅助方法1.1 Html.ActionLink()1.2 Html.RouteLink()1.3 Html.Display() / Html.DisplayFor()1.4 Html.Editor() / Html.EditorFor()1.5 Html.Label() / Html.LabelFor()1.6 Html.TextBox() / Html.TextBoxFor() 2. 表单相关辅助方法2.1 Html.BeginForm() …...
ubuntu22.04有线网络无法连接,图标也没了
今天突然无法有线网络无法连接任何设备,并且图标都没了 错误案例 往上一顿搜索,试了很多博客都不行,比如 Ubuntu22.04右上角网络图标消失 最后解决的办法 下载网卡驱动,重新安装 操作步骤 查看自己网卡的型号 lspci | gre…...
