C++ - 仿 RabbitMQ 实现消息队列(3)(详解使用muduo库)
C++ - 仿 RabbitMQ 实现消息队列(3)(详解使用muduo库)
- muduo库的基层原理
- 核心概念总结:
- 通俗例子:餐厅模型
- 优势体现
- 典型场景
- muduo库中的主要类
- Eventloop
- Muduo 的 `EventLoop` 核心解析
- 1. 核心机制:事件循环(Reactor 模式)
- 2. 线程绑定:One Loop Per Thread
- 3. 跨线程任务调度
- 4. 定时器功能
- 5. 唤醒机制
- 6. Channel 管理
- 核心设计思想
- TcpServer
- Muduo 的 `TcpServer` 核心解析
- 1. 核心机制:主从 Reactor 模型
- (1)`Acceptor` 处理新连接
- (2)`EventLoopThreadPool` 线程池管理
- 2. 连接管理
- (1)`TcpConnection` 封装 TCP 连接
- (2)连接移除
- 3. 服务器控制
- (1)启动服务器
- (2)`ReusePort` 支持
- 1. 三大核心回调函数
- (1)`setConnectionCallback` —— 连接建立/关闭回调
- (2)`setMessageCallback` —— 数据到达回调(最常用!)
- (3)`setWriteCompleteCallback` —— 数据发送完成回调
- 2. 回调函数的底层机制
- (1)回调存
- (2)回调触发流程
- 3. 完整示例代码
- 服务器的大致结构
- TcpClient
- 1. 核心功能
- 2. 关键成员变量
- 3. 连接生命周期管理
- (1) 连接建立流程
- (2) 连接断开处理
- 4. 回调函数
- 5. 线程安全性
- 6. 断线重连机制
- 7. 典型使用场景
- (1) 简单客户端
- (2) 带重连的客户端
- Buffer
- 1. 核心回调类型总览
- 客户端大致结构
- 为什么使用 `EventLoopThread` 而不是 `EventLoop`?
- 1. `EventLoopThread` 的核心作用
- 2. 与直接使用 `EventLoop` 的关键区别
- 3. 在 `TranslateClient` 中的必要性
- `muduo::CountDownLatch _latch` 的作用
- 1. `CountDownLatch` 的核心功能
- 2. 在 `TranslateClient` 中的用途
- 3. 典型工作流程
我们前面简单介绍了一下protobuf和muduo库,对他们有了一个基本的了解,如果还不熟悉的小伙伴可以点击这里:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_67693066/article/details/147979379?spm=1011.2415.3001.5331
我们今天的任务就是对muduo库进行比较细致的了解,然后搭建一个简单的翻译服务器。
muduo库的基层原理
muduo库的基层是基于主从Reactor模型的网络库:

核心概念总结:
-
主从 Reactor 模型
- 主 Reactor(通常由
main EventLoop负责):监听新连接(accept),将新连接分发给从 Reactor。 - 从 Reactor(每个线程一个
EventLoop):负责已建立连接的读写事件(read/write)和定时任务。
- 主 Reactor(通常由
-
One Loop Per Thread
- 每个线程独立运行一个事件循环(
EventLoop),处理自己的 IO 和定时事件。 - 一个 TCP 连接从建立到销毁,全程由同一个线程管理,避免多线程竞争。
- 每个线程独立运行一个事件循环(
-
非阻塞 IO + 事件驱动
- 通过
epoll(Linux)监听文件描述符(FD)事件,数据到来时触发回调,不阻塞线程。
- 通过
通俗例子:餐厅模型
想象一个高并发的餐厅(服务器),采用 Muduo 的工作模式:
-
主 Reactor(前台经理)
- 专职站在门口接待新顾客(
accept新连接)。 - 每来一个新顾客,经理分配一个专属服务员(从 Reactor 线程)全程服务。
- 专职站在门口接待新顾客(
-
从 Reactor(专属服务员)
- 每个服务员(线程)负责固定几桌顾客(TCP 连接),全程处理点菜、上菜、结账(
read/write)。 - 服务员在自己的工作区(
EventLoop)循环检查负责的餐桌是否有需求(事件驱动)。 - 如果某桌顾客长时间不点菜(空闲连接),服务员会主动检查(定时任务)。
- 每个服务员(线程)负责固定几桌顾客(TCP 连接),全程处理点菜、上菜、结账(
-
为什么不用多服务员服务一桌?
- 避免两个服务员同时给同一桌上菜时撞翻盘子(多线程竞争 FD)。
- 专属服务员更熟悉顾客的需求(连接状态管理更简单)。
优势体现
- 高并发:前台经理快速分配,每个服务员专注自己的餐桌,不互相干扰。
- 低延迟:服务员非阻塞工作,没菜上时就去做其他事(如清理餐具)。
- 线程安全:每桌数据由专属服务员处理,无需加锁。
典型场景
- 聊天服务器:每个用户连接固定由一个线程处理消息。
- 游戏服务器:玩家 TCP 连接的读写和逻辑在同一线程中完成。
Muduo 的设计,简单来说就是开了一家餐馆,门口会有一个负责揽客的(主Reactor),把客人招进来之后,会有专门的服务员(从Reactor)对客人进行服务。
muduo库中的主要类
Eventloop
// Copyright 2010, Shuo Chen. All rights reserved.
// http://code.google.com/p/muduo/
//
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
// that can be found in the License file.// Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com)
//
// This is a public header file, it must only include public header files.#ifndef MUDUO_NET_EVENTLOOP_H
#define MUDUO_NET_EVENTLOOP_H#include <atomic>
#include <functional>
#include <vector>#include <boost/any.hpp>#include "muduo/base/Mutex.h"
#include "muduo/base/CurrentThread.h"
#include "muduo/base/Timestamp.h"
#include "muduo/net/Callbacks.h"
#include "muduo/net/TimerId.h"namespace muduo
{
namespace net
{class Channel;
class Poller;
class TimerQueue;///
/// Reactor, at most one per thread.
///
/// This is an interface class, so don't expose too much details.
class EventLoop : noncopyable
{public:typedef std::function<void()> Functor;EventLoop();~EventLoop(); // force out-line dtor, for std::unique_ptr members.////// Loops forever.////// Must be called in the same thread as creation of the object.///void loop();/// Quits loop.////// This is not 100% thread safe, if you call through a raw pointer,/// better to call through shared_ptr<EventLoop> for 100% safety.void quit();////// Time when poll returns, usually means data arrival.///Timestamp pollReturnTime() const { return pollReturnTime_; }int64_t iteration() const { return iteration_; }/// Runs callback immediately in the loop thread./// It wakes up the loop, and run the cb./// If in the same loop thread, cb is run within the function./// Safe to call from other threads.void runInLoop(Functor cb);/// Queues callback in the loop thread./// Runs after finish pooling./// Safe to call from other threads.void queueInLoop(Functor cb);size_t queueSize() const;// timers////// Runs callback at 'time'./// Safe to call from other threads.///TimerId runAt(Timestamp time, TimerCallback cb);////// Runs callback after @c delay seconds./// Safe to call from other threads.///TimerId runAfter(double delay, TimerCallback cb);////// Runs callback every @c interval seconds./// Safe to call from other threads.///TimerId runEvery(double interval, TimerCallback cb);////// Cancels the timer./// Safe to call from other threads.///void cancel(TimerId timerId);// internal usagevoid wakeup();void updateChannel(Channel* channel);void removeChannel(Channel* channel);bool hasChannel(Channel* channel);// pid_t threadId() const { return threadId_; }void assertInLoopThread(){if (!isInLoopThread()){abortNotInLoopThread();}}bool isInLoopThread() const { return threadId_ == CurrentThread::tid(); }// bool callingPendingFunctors() const { return callingPendingFunctors_; }bool eventHandling() const { return eventHandling_; }void setContext(const boost::any& context){ context_ = context; }const boost::any& getContext() const{ return context_; }boost::any* getMutableContext(){ return &context_; }static EventLoop* getEventLoopOfCurrentThread();private:void abortNotInLoopThread();void handleRead(); // waked upvoid doPendingFunctors();void printActiveChannels() const; // DEBUGtypedef std::vector<Channel*> ChannelList;bool looping_; /* atomic */std::atomic<bool> quit_;bool eventHandling_; /* atomic */bool callingPendingFunctors_; /* atomic */int64_t iteration_;const pid_t threadId_;Timestamp pollReturnTime_;std::unique_ptr<Poller> poller_;std::unique_ptr<TimerQueue> timerQueue_;int wakeupFd_;// unlike in TimerQueue, which is an internal class,// we don't expose Channel to client.std::unique_ptr<Channel> wakeupChannel_;boost::any context_;// scratch variablesChannelList activeChannels_;Channel* currentActiveChannel_;mutable MutexLock mutex_;std::vector<Functor> pendingFunctors_ GUARDED_BY(mutex_);
};} // namespace net
} // namespace muduo#endif // MUDUO_NET_EVENTLOOP_HMuduo 的 EventLoop 核心解析
EventLoop 是 Muduo 网络库的核心,实现了 Reactor 模式的事件循环,采用 one loop per thread 模型。以下是其最核心的部分:
1. 核心机制:事件循环(Reactor 模式)
loop()方法:
核心事件循环,通过Poller(底层用epoll/poll)监听文件描述符(FD)事件,触发回调。void loop(); // 永不退出,直到调用 quit()quit()方法:
安全退出事件循环(通过原子变量quit_控制)。std::atomic<bool> quit_; // 线程安全标志
2. 线程绑定:One Loop Per Thread
- 每个
EventLoop仅属于一个线程:const pid_t threadId_; // 创建 EventLoop 的线程 ID bool isInLoopThread() const; // 检查当前线程是否属于该 EventLoop- 通过
assertInLoopThread()确保线程安全,禁止跨线程操作。
- 通过
3. 跨线程任务调度
runInLoop(Functor cb):
立即在EventLoop所在线程执行回调(如果当前线程是EventLoop线程,直接执行;否则唤醒EventLoop并排队)。queueInLoop(Functor cb):
将回调函数加入任务队列(通过pendingFunctors_),由事件循环下次迭代时执行。std::vector<Functor> pendingFunctors_; // 待执行任务队列 MutexLock mutex_; // 保护任务队列的互斥锁
4. 定时器功能
TimerQueue定时器管理:
通过runAt、runAfter、runEvery注册定时任务,底层用timerfd或时间堆实现。std::unique_ptr<TimerQueue> timerQueue_; // 定时器队列 TimerId runAt(Timestamp time, TimerCallback cb); // 在指定时间触发回调
5. 唤醒机制
wakeup()方法:
通过eventfd(或管道)唤醒阻塞在epoll上的EventLoop,用于处理跨线程任务或立即退出。int wakeupFd_; // 用于唤醒的文件描述符 std::unique_ptr<Channel> wakeupChannel_; // 封装 wakeupFd_ 的 Channel
6. Channel 管理
Channel是事件处理的封装:
每个 FD 对应一个Channel,注册读写事件回调。void updateChannel(Channel* channel); // 更新监听事件 void removeChannel(Channel* channel); // 移除监听
核心设计思想
-
线程隔离:
- 一个
EventLoop仅由一个线程操作,避免锁竞争。 - 跨线程调用通过
runInLoop/queueInLoop安全派发任务。
- 一个
-
事件驱动:
- 所有 IO 和定时任务均由
Poller监听,回调在事件循环中触发。
- 所有 IO 和定时任务均由
-
高效唤醒:
- 通过
wakeupFd_打破epoll阻塞,及时处理新任务。
- 通过
TcpServer
// Copyright 2010, Shuo Chen. All rights reserved.
// http://code.google.com/p/muduo/
//
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
// that can be found in the License file.// Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com)
//
// This is a public header file, it must only include public header files.#ifndef MUDUO_NET_TCPSERVER_H
#define MUDUO_NET_TCPSERVER_H#include "muduo/base/Atomic.h"
#include "muduo/base/Types.h"
#include "muduo/net/TcpConnection.h"#include <map>namespace muduo
{
namespace net
{class Acceptor;
class EventLoop;
class EventLoopThreadPool;///
/// TCP server, supports single-threaded and thread-pool models.
///
/// This is an interface class, so don't expose too much details.
class TcpServer : noncopyable
{public:typedef std::function<void(EventLoop*)> ThreadInitCallback;enum Option{kNoReusePort,kReusePort,};//TcpServer(EventLoop* loop, const InetAddress& listenAddr);TcpServer(EventLoop* loop,const InetAddress& listenAddr,const string& nameArg,Option option = kNoReusePort);~TcpServer(); // force out-line dtor, for std::unique_ptr members.const string& ipPort() const { return ipPort_; }const string& name() const { return name_; }EventLoop* getLoop() const { return loop_; }/// Set the number of threads for handling input.////// Always accepts new connection in loop's thread./// Must be called before @c start/// @param numThreads/// - 0 means all I/O in loop's thread, no thread will created./// this is the default value./// - 1 means all I/O in another thread./// - N means a thread pool with N threads, new connections/// are assigned on a round-robin basis.void setThreadNum(int numThreads);void setThreadInitCallback(const ThreadInitCallback& cb){ threadInitCallback_ = cb; }/// valid after calling start()std::shared_ptr<EventLoopThreadPool> threadPool(){ return threadPool_; }/// Starts the server if it's not listening.////// It's harmless to call it multiple times./// Thread safe.void start();/// Set connection callback./// Not thread safe.void setConnectionCallback(const ConnectionCallback& cb){ connectionCallback_ = cb; }/// Set message callback./// Not thread safe.void setMessageCallback(const MessageCallback& cb){ messageCallback_ = cb; }/// Set write complete callback./// Not thread safe.void setWriteCompleteCallback(const WriteCompleteCallback& cb){ writeCompleteCallback_ = cb; }private:/// Not thread safe, but in loopvoid newConnection(int sockfd, const InetAddress& peerAddr);/// Thread safe.void removeConnection(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn);/// Not thread safe, but in loopvoid removeConnectionInLoop(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn);typedef std::map<string, TcpConnectionPtr> ConnectionMap;EventLoop* loop_; // the acceptor loopconst string ipPort_;const string name_;std::unique_ptr<Acceptor> acceptor_; // avoid revealing Acceptorstd::shared_ptr<EventLoopThreadPool> threadPool_;ConnectionCallback connectionCallback_;MessageCallback messageCallback_;WriteCompleteCallback writeCompleteCallback_;ThreadInitCallback threadInitCallback_;AtomicInt32 started_;// always in loop threadint nextConnId_;ConnectionMap connections_;
};} // namespace net
} // namespace muduo#endif // MUDUO_NET_TCPSERVER_HMuduo 的 TcpServer 核心解析
TcpServer 是 Muduo 网络库的核心类,用于构建 TCP 服务器,支持 单线程 和 线程池 两种模型。以下是其最核心的部分:
1. 核心机制:主从 Reactor 模型
(1)Acceptor 处理新连接
Acceptor:
负责监听新连接(listen+accept),通过Channel封装listen_fd,将新连接分发给EventLoop。std::unique_ptr<Acceptor> acceptor_; // 监听新连接的组件newConnection回调:
当新连接到达时,Acceptor调用newConnection(),创建TcpConnection并分配 IO 线程。void newConnection(int sockfd, const InetAddress& peerAddr); // 在新连接到达时调用
(2)EventLoopThreadPool 线程池管理
threadPool_:
管理多个EventLoop线程(从 Reactor),用于处理已建立的连接。std::shared_ptr<EventLoopThreadPool> threadPool_; // IO 线程池- 线程数量设置:
setThreadNum(0):所有连接由主线程(acceptor_loop)处理(单线程)。setThreadNum(1):单独一个 IO 线程处理所有连接。setThreadNum(N):线程池模式,轮询分配连接。
void setThreadNum(int numThreads); // 必须在 start() 前调用
2. 连接管理
(1)TcpConnection 封装 TCP 连接
ConnectionMap:
存储所有活跃的TcpConnection,以name为键。typedef std::map<string, TcpConnectionPtr> ConnectionMap; ConnectionMap connections_; // 当前所有连接- 连接生命周期回调:
connectionCallback_:连接建立/关闭时触发。messageCallback_:收到数据时触发。writeCompleteCallback_:数据发送完成时触发。
ConnectionCallback connectionCallback_; // 连接状态变化回调 MessageCallback messageCallback_; // 数据到达回调 WriteCompleteCallback writeCompleteCallback_; // 数据发送完成回调
(2)连接移除
removeConnection:
线程安全地移除连接(可能跨线程调用)。void removeConnection(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn); // 线程安全removeConnectionInLoop:
在正确的EventLoop线程中销毁连接。void removeConnectionInLoop(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn); // 必须在 IO 线程执行
3. 服务器控制
(1)启动服务器
start():
开始监听端口,启动Acceptor。void start(); // 启动服务器(线程安全)started_原子标志:
防止重复启动。AtomicInt32 started_; // 是否已启动
(2)ReusePort 支持
Option选项:
支持SO_REUSEPORT,允许多个进程/线程绑定相同端口(提高 accept 性能)。enum Option { kNoReusePort, kReusePort }; TcpServer(..., Option option = kNoReusePort); // 构造函数选项
TcpServer中最重要的是三个回调函数,用来处理不同情况下的消息处理:
1. 三大核心回调函数
(1)setConnectionCallback —— 连接建立/关闭回调
- 触发时机:
- 当新连接建立时(
onConnection)。 - 当连接关闭时(
onClose)。
- 当新连接建立时(
- 典型用途:
- 记录连接日志。
- 管理连接状态(如用户上线/下线)。
- 示例:
server.setConnectionCallback([](const TcpConnectionPtr& conn) {if (conn->connected()) {LOG_INFO << "New connection: " << conn->peerAddress().toIpPort();} else {LOG_INFO << "Connection closed: " << conn->peerAddress().toIpPort();} });
(2)setMessageCallback —— 数据到达回调(最常用!)
- 触发时机:
- 当收到对端发送的数据时(
onMessage)。
- 当收到对端发送的数据时(
- 典型用途:
- 解析协议(如 HTTP、Redis 命令)。
- 业务逻辑处理(如聊天消息转发)。
- 示例:
server.setMessageCallback([](const TcpConnectionPtr& conn, Buffer* buf, Timestamp receiveTime) {// 从 buf 中读取数据string msg = buf->retrieveAllAsString();LOG_INFO << "Received " << msg.size() << " bytes: " << msg;conn->send(msg); // 回显数据 });
(3)setWriteCompleteCallback —— 数据发送完成回调
- 触发时机:
- 当数据全部写入内核缓冲区(
send完成)时。
- 当数据全部写入内核缓冲区(
- 典型用途:
- 流量控制(如高水位回调配合使用)。
- 发送完成后的日志记录。
- 示例:
server.setWriteCompleteCallback([](const TcpConnectionPtr& conn) {LOG_INFO << "Data sent to " << conn->peerAddress().toIpPort(); });
2. 回调函数的底层机制
(1)回调存
在 TcpServer 中,这三个回调通过成员变量保存:
ConnectionCallback connectionCallback_; // 连接回调
MessageCallback messageCallback_; // 数据回调
WriteCompleteCallback writeCompleteCallback_; // 发送完成回调
(2)回调触发流程
- 连接建立:
Acceptor接受新连接 → 创建TcpConnection→ 调用connectionCallback_。
- 数据到达:
EventLoop监听到sockfd可读 →TcpConnection::handleRead()→ 调用messageCallback_。
- 数据发送完成:
TcpConnection::sendInLoop()完成写入 → 调用writeCompleteCallback_。
3. 完整示例代码
#include <muduo/net/TcpServer.h>
#include <muduo/net/EventLoop.h>
#include <muduo/base/Logging.h>using namespace muduo;
using namespace muduo::net;int main() {EventLoop loop;InetAddress listenAddr(8888);TcpServer server(&loop, listenAddr, "EchoServer");// 设置回调server.setConnectionCallback([](const TcpConnectionPtr& conn) {if (conn->connected()) {LOG_INFO << "New connection from " << conn->peerAddress().toIpPort();} else {LOG_INFO << "Connection closed: " << conn->peerAddress().toIpPort();}});server.setMessageCallback([](const TcpConnectionPtr& conn, Buffer* buf, Timestamp time) {string msg = buf->retrieveAllAsString();LOG_INFO << "Received: " << msg;conn->send(msg); // 回显});server.setThreadNum(4); // 4个IO线程server.start();loop.loop(); // 启动事件循环
}
服务器的大致结构
如果我们想要通过muduo库来搭建一个简单的服务器,大概的框架就是这样的:
#include <muduo/net/TcpServer.h>
#include <muduo/net/EventLoop.h>
#include <muduo/net/TcpConnection.h>class TranslateServer{public:TranslateServer(int port):_sever(&_baseloop,muduo::net::InetAddress("0.0.0.0",port),"TranslateSever",muduo::net::TcpServer::kNoReusePort){}//开始运行void start(){}private:void onConnection(const muduo::net::TcpConnectionPtr& conn){//新建链接时的回调函数}void onMessage(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn,Buffer*buffer,muduo::Timestamp){//收到消息时的回调函数}private:muduo::net::EventLoop _baseloop; //基本事件循环muduo::net::TcpServer _server; //翻译服务器
};int main()
{TranslateServer server(8085);server.start(); //开始运行
}
添加完整应该是这个样子:
#include <muduo/net/TcpServer.h>
#include <muduo/net/EventLoop.h>
#include <muduo/net/TcpConnection.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <unordered_map>class TranslateServer
{
public:TranslateServer(int port): _server(&_baseloop, muduo::net::InetAddress("0.0.0.0", port),"TranslateSever", muduo::net::TcpServer::kNoReusePort){// 绑定std::bind// 类的成员设定为服务器的回调处理函数_server.setConnectionCallback(std::bind(&TranslateServer::onConnection, this, std::placeholders::_1));_server.setMessageCallback(std::bind(&TranslateServer::onMessage, this, std::placeholders::_1,std::placeholders::_2, std::placeholders::_3));}// 开始运行void start(){_server.start(); // 开始事件监听_baseloop.loop(); // 开启事件监控}private:void onConnection(const muduo::net::TcpConnectionPtr &conn){// 新建链接时的回调函数if (conn->connected() == true){std::cout << "新连接建立成功" << std::endl;}else{std::cout << "新连接关闭" << std::endl;}}std::string translate(const std::string &str){static const std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> dict_map = {{"Hello", "你好"},{"hello", "你好"},{"你好", "Hello"},{"hi", "嗨"} // 扩展示例};auto it = dict_map.find(str);if (it == dict_map.end()){std::cout << "未识别的输入: " << str << std::endl;return "未识别的输入"; // 必须返回默认值!}return it->second;}void onMessage(const muduo::net::TcpConnectionPtr &conn, muduo::net::Buffer *buffer, muduo::Timestamp){// 收到消息时的回调函数// 1.从buffer中把请求的数据拿出来std::string str = buffer->retrieveAllAsString();// 2.调用接口std::string resp = translate(str);// 3.对客户端进行响应conn->send(resp);}private:muduo::net::EventLoop _baseloop; // 基本事件循环muduo::net::TcpServer _server; // 翻译服务器
};int main()
{TranslateServer server(8085);server.start(); // 开始运行
}
TcpClient
// Copyright 2010, Shuo Chen. All rights reserved.
// http://code.google.com/p/muduo/
//
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
// that can be found in the License file.// Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com)
//
// This is a public header file, it must only include public header files.#ifndef MUDUO_NET_TCPCLIENT_H
#define MUDUO_NET_TCPCLIENT_H#include "muduo/base/Mutex.h"
#include "muduo/net/TcpConnection.h"namespace muduo
{
namespace net
{class Connector;
typedef std::shared_ptr<Connector> ConnectorPtr;class TcpClient : noncopyable
{public:// TcpClient(EventLoop* loop);// TcpClient(EventLoop* loop, const string& host, uint16_t port);TcpClient(EventLoop* loop,const InetAddress& serverAddr,const string& nameArg);~TcpClient(); // force out-line dtor, for std::unique_ptr members.void connect();void disconnect();void stop();TcpConnectionPtr connection() const{MutexLockGuard lock(mutex_);return connection_;}EventLoop* getLoop() const { return loop_; }bool retry() const { return retry_; }void enableRetry() { retry_ = true; }const string& name() const{ return name_; }/// Set connection callback./// Not thread safe.void setConnectionCallback(ConnectionCallback cb){ connectionCallback_ = std::move(cb); }/// Set message callback./// Not thread safe.void setMessageCallback(MessageCallback cb){ messageCallback_ = std::move(cb); }/// Set write complete callback./// Not thread safe.void setWriteCompleteCallback(WriteCompleteCallback cb){ writeCompleteCallback_ = std::move(cb); }private:/// Not thread safe, but in loopvoid newConnection(int sockfd);/// Not thread safe, but in loopvoid removeConnection(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn);EventLoop* loop_;ConnectorPtr connector_; // avoid revealing Connectorconst string name_;ConnectionCallback connectionCallback_;MessageCallback messageCallback_;WriteCompleteCallback writeCompleteCallback_;bool retry_; // atomicbool connect_; // atomic// always in loop threadint nextConnId_;mutable MutexLock mutex_;TcpConnectionPtr connection_ GUARDED_BY(mutex_);
};} // namespace net
} // namespace muduo#endif // MUDUO_NET_TCPCLIENT_H1. 核心功能
| 方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
connect() | 发起连接(非阻塞,异步完成) |
disconnect() | 断开当前连接 |
stop() | 停止客户端(不再重连) |
connection() | 获取当前连接的 TcpConnectionPtr(线程安全) |
setXXXCallback() | 设置连接、消息、写完成的回调函数 |
2. 关键成员变量
| 变量 | 作用 |
|---|---|
connector_ | 负责实际连接操作的 Connector 对象(内部用 socket + non-blocking connect) |
connection_ | 当前活跃的 TcpConnection 对象(受互斥锁保护) |
retry_ | 是否启用断线自动重连(默认关闭) |
nextConnId_ | 为每个连接分配唯一 ID(用于日志跟踪) |
3. 连接生命周期管理
(1) 连接建立流程
TcpClient client(loop, serverAddr, "Client1");
client.setConnectionCallback(onConnection);
client.setMessageCallback(onMessage);
client.connect(); // 触发连接
connect()- 调用
connector_->start(),开始异步连接(非阻塞)。
- 调用
newConnection(int sockfd)(回调)- 连接成功后,创建
TcpConnection对象。 - 设置用户回调(
connectionCallback_、messageCallback_)。
- 连接成功后,创建
- 连接就绪
- 通过
connectionCallback_通知用户。
- 通过
(2) 连接断开处理
void removeConnection(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn);
- 当连接关闭时,由
TcpConnection回调触发。 - 如果
retry_=true,会自动重新发起连接。
4. 回调函数
| 回调类型 | 触发时机 | 典型用途 |
|---|---|---|
ConnectionCallback | 连接建立或关闭时 | 记录日志、状态管理 |
MessageCallback | 收到数据时(Buffer* 包含数据) | 解析协议、业务处理 |
WriteCompleteCallback | 数据完全写入内核缓冲区时 | 流量控制、发送完成通知 |
示例:设置回调
client.setMessageCallback([](const TcpConnectionPtr& conn, Buffer* buf, Timestamp) {std::string msg = buf->retrieveAllAsString();LOG_INFO << "Received: " << msg;
});
5. 线程安全性
connection()方法通过mutex_保证线程安全。- 回调函数 的执行始终在
EventLoop绑定的线程中(无竞态条件)。 connect()/disconnect()可在任意线程调用,但实际操作会派发到EventLoop线程。
6. 断线重连机制
- 默认关闭:需调用
enableRetry()启用。 - 重试逻辑:由
Connector实现,采用指数退避策略(避免频繁重连)。
7. 典型使用场景
(1) 简单客户端
EventLoop loop;
InetAddress serverAddr("127.0.0.1", 8888);
TcpClient client(&loop, serverAddr, "DemoClient");client.setConnectionCallback(onConnection);
client.setMessageCallback(onMessage);
client.connect();loop.loop(); // 启动事件循环
(2) 带重连的客户端
client.enableRetry(); // 启用断线重连
client.connect();
Buffer
// Copyright 2010, Shuo Chen. All rights reserved.
// http://code.google.com/p/muduo/
//
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
// that can be found in the License file.// Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com)
//
// This is a public header file, it must only include public header files.#ifndef MUDUO_NET_CALLBACKS_H
#define MUDUO_NET_CALLBACKS_H#include "muduo/base/Timestamp.h"#include <functional>
#include <memory>namespace muduo
{using std::placeholders::_1;
using std::placeholders::_2;
using std::placeholders::_3;// should really belong to base/Types.h, but <memory> is not included there.template<typename T>
inline T* get_pointer(const std::shared_ptr<T>& ptr)
{return ptr.get();
}template<typename T>
inline T* get_pointer(const std::unique_ptr<T>& ptr)
{return ptr.get();
}// Adapted from google-protobuf stubs/common.h
// see License in muduo/base/Types.h
template<typename To, typename From>
inline ::std::shared_ptr<To> down_pointer_cast(const ::std::shared_ptr<From>& f) {if (false){implicit_cast<From*, To*>(0);}#ifndef NDEBUGassert(f == NULL || dynamic_cast<To*>(get_pointer(f)) != NULL);
#endifreturn ::std::static_pointer_cast<To>(f);
}namespace net
{// All client visible callbacks go here.class Buffer;
class TcpConnection;
typedef std::shared_ptr<TcpConnection> TcpConnectionPtr;
typedef std::function<void()> TimerCallback;
typedef std::function<void (const TcpConnectionPtr&)> ConnectionCallback;
typedef std::function<void (const TcpConnectionPtr&)> CloseCallback;
typedef std::function<void (const TcpConnectionPtr&)> WriteCompleteCallback;
typedef std::function<void (const TcpConnectionPtr&, size_t)> HighWaterMarkCallback;// the data has been read to (buf, len)
typedef std::function<void (const TcpConnectionPtr&,Buffer*,Timestamp)> MessageCallback;void defaultConnectionCallback(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn);
void defaultMessageCallback(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn,Buffer* buffer,Timestamp receiveTime);} // namespace net
} // namespace muduo#endif // MUDUO_NET_CALLBACKS_H1. 核心回调类型总览
| 回调类型 | 触发时机 | 参数说明 |
|---|---|---|
ConnectionCallback | 连接建立/关闭时 | TcpConnectionPtr& |
MessageCallback | 收到数据时 | TcpConnectionPtr&, Buffer*, Timestamp |
WriteCompleteCallback | 数据完全写入内核缓冲区时 | TcpConnectionPtr& |
HighWaterMarkCallback | 发送缓冲区超过高水位线时 | TcpConnectionPtr&, size_t(水位值) |
CloseCallback | 连接关闭时(更精细的控制) | TcpConnectionPtr& |
简单了解之后,我们可以理清客户端的一个基本框架了:
客户端大致结构
#include <muduo/net/TcpClient.h>
#include <muduo/net/EventLoop.h>
#include <muduo/net/TcpConnection.h>
#include "../base/CountDownLatch.h"
#include <muduo/net/EventLoopThread.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>class TranslateClient{public:TranslateClient(const std::string& sip,int port){}void connect() //连接服务器{}void send(const std::string& msg) //发送数据{}private:void onConnection(const muduo::net::TcpConnectionPtr& conn);void onMessage(const muduo::net::TcpConnectionPtr& conn,muduo::net::Buffer*buffer,muduo::Timestamp)private:muduo::net::EventLoopThread _loopthread; //客户端的Event对象muduo::CountDownLatch _latch;muduo::net::TcpClient _client; //客户端对象muduo::net::TcpConnection _conn; //连接对象
};int main()
{TranslateClient client("127.0.0.1",8085);client.connect();while(1){std::string buf;std::cin >> buf;client.send(buf);}return 0;
}这里给解答两个疑点:

为什么使用 EventLoopThread 而不是 EventLoop?
1. EventLoopThread 的核心作用
EventLoopThread 是 Muduo 提供的一个封装类,它:
- 自动创建并管理一个
EventLoop(在独立线程中运行) - 提供线程安全的
EventLoop获取接口(通过startLoop())
2. 与直接使用 EventLoop 的关键区别
| 对比项 | EventLoop | EventLoopThread |
|---|---|---|
| 线程模型 | 必须在当前线程创建和运行 | 自动在新线程中创建和运行 EventLoop |
| 线程安全性 | 非线程安全(只能在其所属线程操作) | 通过 startLoop() 安全获取 EventLoop |
| 典型用途 | 单线程程序 | 需要后台运行事件循环的多线程程序 |
3. 在 TranslateClient 中的必要性
- 客户端需要非阻塞:如果直接在主线程使用
EventLoop,loop.loop()会阻塞主线程,导致无法响应终端输入。 - 自动线程管理:
EventLoopThread简化了多线程下EventLoop的生命周期管理。
muduo::CountDownLatch _latch 的作用
1. CountDownLatch 的核心功能
- 线程同步工具:允许一个或多个线程等待,直到其他线程完成某些操作。
- 关键方法:
countDown():计数器减1wait():阻塞直到计数器归零
2. 在 TranslateClient 中的用途
通常用于确保 EventLoopThread 的 EventLoop 已初始化完成:
TranslateClient::TranslateClient(...) : _loopthread([](EventLoop* loop) { /* 初始化代码 */ }),_latch(1) // 初始计数器为1
{// 启动 EventLoop 线程_loopthread.startLoop();// 等待 EventLoop 初始化完成_latch.wait();
}
3. 典型工作流程
- 主线程创建
EventLoopThread并启动 EventLoopThread在新线程中初始化EventLoop- 初始化完成后调用
_latch.countDown() - 主线程通过
_latch.wait()解除阻塞
客户端补充完之后应该是这样的:
#include <muduo/net/TcpClient.h>
#include <muduo/net/EventLoop.h>
#include <muduo/net/TcpConnection.h>
#include "../base/CountDownLatch.h"
#include "../net/EventLoopThread.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>class TranslateClient {
public:TranslateClient(const std::string& sip, int port): _latch(1),_client(_loopthread.startLoop(), muduo::net::InetAddress(sip, port), "TranslateClient"){_client.setConnectionCallback(std::bind(&TranslateClient::onConnection, this, std::placeholders::_1));_client.setMessageCallback(std::bind(&TranslateClient::onMessage, this, std::placeholders::_1, std::placeholders::_2, std::placeholders::_3));}void connect() // 连接服务器{_client.connect();_latch.wait(); // 阻塞等待,直到连接建立成功}bool send(const std::string& msg) // 发送数据{if (_conn && _conn->connected()) // 检查连接是否有效{_conn->send(msg);return true;}return false;}private:void onConnection(const muduo::net::TcpConnectionPtr& conn){if (conn->connected()){_latch.countDown(); // 唤醒主线程中的阻塞_conn = conn;}else{// 连接关闭std::cout << "新连接关闭" << std::endl;_conn.reset();}}void onMessage(const muduo::net::TcpConnectionPtr& conn, muduo::net::Buffer* buffer, muduo::Timestamp){std::string msg = buffer->retrieveAllAsString();std::cout << "翻译结果:" << msg << std::endl;}private:muduo::net::EventLoopThread _loopthread; // 客户端的 EventLoop 线程muduo::CountDownLatch _latch;muduo::net::TcpClient _client; // 客户端对象muduo::net::TcpConnectionPtr _conn; // 连接对象
};int main()
{TranslateClient client("127.0.0.1", 8085);client.connect();while (true){std::string buf;std::getline(std::cin, buf); // 使用 getline 读取整行输入if (!client.send(buf)){std::cerr << "发送失败" << std::endl;}}return 0;
}
最后效果展示:


附上CMakeLists.txt:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10)
project(TranslateServer)# 设置 C++ 标准
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON)# 查找 muduo 网络库
set(MUDUO_INCLUDE_DIRS ./include)
set(MUDUO_LIBRARY_DIR ./lib)# 添加可执行文件
add_executable(translate_server./server/server.cpp # 假设你的代码保存在 main.cpp 文件中
)add_executable(translate_client./client/client.cpp # 假设你的代码保存在 main.cpp 文件中
)# 链接 muduo 库
target_link_libraries(translate_servermuduo_netmuduo_basepthread # muduo 需要 pthread 库
)# 链接 muduo 库
target_link_libraries(translate_clientmuduo_netmuduo_basepthread # muduo 需要 pthread 库
)
相关文章:

C++ - 仿 RabbitMQ 实现消息队列(3)(详解使用muduo库)
C - 仿 RabbitMQ 实现消息队列(3)(详解使用muduo库) muduo库的基层原理核心概念总结:通俗例子:餐厅模型优势体现典型场景 muduo库中的主要类EventloopMuduo 的 EventLoop 核心解析1. 核心机制:事…...

docker部署XTdrone
目录 一、前置准备 二、依赖安装 三、ros安装 四、gazebo安装 五、mavros安装 六、PX4的配置 七、Xtdrone源码下载 八、xtdrone与gazebo(实际上应该是第四步之后做这件事) 九、键盘控制 参考链接:仿真平台基础配置 语雀 一、前置准…...

图解 | 大模型智能体LLM Agents
文章目录 正文1. 存储 Memory1.1 短期记忆 Short-Term Memory1.1.1 模型的上下文窗口1.1.2 对话历史1.1.3 总结对话历史 1.2 长期记忆Long-term Memory 2. 工具Tools2.1 工具的类型2.2 function calling2.3 Toolformer2.3.1 大模型调研工具的过程2.3.2 生成工具调用数据集 2.4 …...

Lambda表达式的方法引用详解
Lambda表达式的方法引用详解 1. 方法引用的概念与作用 定义:方法引用(Method Reference)是Lambda表达式的一种简化写法,允许直接通过方法名引用已有的方法。核心目的:减少冗余代码,提升可读性,尤其在Lambda仅调用一个现有方法时。语法符号:双冒号 ::。2. 方法引用的四种…...

echarts设置标线和最大值最小值
echarts设置标线和最大值最小值 基本ECharts图表初始化配置 设置动态的y轴范围(min/max值) 通过markPoint标记最大值和最小值点 使用markLine添加水平参考线 配置双y轴图表 自定义标记点和线的样式(颜色、符号等) 响应式调整图表大…...

gcc编译构建流程
0. 项目结构 /home/pi/test/ ├── src/ │ ├── add/ │ │ ├── add.cpp │ │ ├── add.h │ └── log/ │ ├── log.cpp │ ├── log.h │ ├── data.h ├── main.cppmain.cpp代码 // main.cpp #include "log.h&quo…...

Maven 中央仓库操作指南
Maven 中央仓库操作指南 登录注册 在 Maven Central 登录(注册)账号。 添加命名空间 注册 通过右上角用户菜单跳转到命名空间管理页面: 注册命名空间: 填入你拥有的域名并注册: 刚提交的命名空间状态是Unverified…...

BUUCTF——RCE ME
BUUCTF——RCE ME 进入靶场 <?php error_reporting(0); if(isset($_GET[code])){$code$_GET[code];if(strlen($code)>40){die("This is too Long.");}if(preg_match("/[A-Za-z0-9]/",$code)){die("NO.");}eval($code); } else{highlight…...

clickhouse-1-特性及docker化安装
clickhouse-1-特性及docker化安装 1.核心特性1.1.列式存储与高效压缩1.2.向量化执行引擎1.3.分布式架构与高可用性1.4.多样化的表引擎1.5.实时处理能力2.安装2.1 拉取镜像2.2 创建容器3.连接4.使用4.1.创建数据库5.其他5.1 primary key5.2 ENG…...

Docker核心笔记
一、概述 1、架构 Docker容器基于镜像运行,容器共享宿主机的内核,不会加载额外内核,通过Namespaces(环境隔离)和Cgroups(资源控制)实现隔离,Cgroups会限容器使用资源并控制优先级和统计数据。隔离后的容器仅包含应用所需的用户态依赖 2、安装 安装先卸载再安装,使用的yum…...

log日志最佳实践
log日志最佳实践 1、占位符的使用2、延迟计算 1、占位符的使用 在进行日志打印的时候,推荐使用占位符进行字符串打印,而不是直接使用字符串拼接。原因: 这样可以避免不必要的字符串拼接。使用占位符时,实际字符串拼接由日志框架…...

FreeRTOS--消息队列
一、简介 消息队列是FreeRTOS中用于任务与任务或任务与中断之间数据交换的一种机制,采用FIFO(先进先出)方式管理数据,也可以采用LIFO(后进先出)方式。有点类似全局变量。 1.1 那为什么不直接使用全局变量&a…...

三步快速部署一个本地Windows/Linux大语言模型ChatGLM(环境配置+权重下载+运行)
前言: 最近刚拿到实验室一个装了3张3090显卡的服务器账号,感觉不用来霍霍有点浪费,于是有了部署一个大语言模型的想法,除去下载权重和传文件到服务器上可能也就用了十分钟不到(这下看懂为啥python受众现在这么广了&…...

深入解析Spring Boot与Redis的缓存集成实践
深入解析Spring Boot与Redis的缓存集成实践 引言 在现代Web应用开发中,缓存技术是提升系统性能的重要手段之一。Redis作为一种高性能的内存数据库,广泛应用于缓存场景。本文将详细介绍如何在Spring Boot项目中集成Redis,并探讨其在实际开发…...

leetcode105.从中序与前序遍历序列构造二叉树:前序定根与中序分治的递归重建术
一、题目深度解析与核心挑战 在二叉树的重建问题中,"从中序与前序遍历序列构造二叉树"是一道考察递归分治思想的经典题目。题目要求我们根据一棵二叉树的前序遍历序列和中序遍历序列,重建出该二叉树的原始结构。这道题的核心难点在于如何利用…...

Python二级考试
目录 一、核心知识模块 1. 程序结构 2. 循环结构 3. 组合数据类型 4. 函数与模块 二、重点算法 1. 排序算法 2. 查找算法 三、文件操作 1. 基础文件处理 四、备考建议 五、典型易错点 以下是Python二级考试的复习要点整理,分为知识模块和备考建议&#…...

DeepSeek联网Google搜索引擎
目录: 1、使用背景2、实现代码3、Gradio 的 yield 机制 1、使用背景 比如所有易建联是什么时候退役的?使用大模型对这种实事回答不准确,需要通过联网搜索处理。 正确答案应该是2023年8月29日退役。 2、实现代码 # import gradio as gr# d…...
时,经典理论失效?)
理论物理:为什么在极低温(接近绝对零度)时,经典理论失效?
经典理论应该是指经典力学和经典统计物理吧,比如牛顿力学、麦克斯韦-玻尔兹曼分布这些。而到了接近绝对零度的时候,物质的状态会发生什么变化呢?比如说超流性、超导性,或者玻色-爱因斯坦凝聚这些现象,这些在经典理论里好像没法解释。 因为在极低温下,粒子的热运动减弱,…...

奈雪小程序任务脚本
功能概述 该脚本用于自动完成奈雪点单小程序的每日任务,包括: 自动检测 Token 有效性自动签到(如果未签到)获取用户基础信息(昵称、手机号)查询当前奈雪币余额记录连续签到天数支持多账号执行,…...

上海医日健集团物联网专利技术领跑智慧药房赛道
在智慧医疗蓬勃发展的浪潮中,上海医日健集团凭借其卓越的创新能力与强大的技术实力,在智慧药房领域崭露头角。集团自主研发的物联网专利技术,正以前所未有的优势,重塑智慧药房运营模式,引领行业迈向新的发展高度。 上…...

基于Java+MySQL实现(Web)图书借阅管理系统
图书借阅管理系统(前后台) 1 需求分析 图书借阅管理系统是模拟学校图书馆实现的一个具有前后台的 Web 系统.对于读者,能够提供全文检索,个性化推荐,借阅等功能.对于管理员,能够提供可视化数据分析,信息管理等功能. 2 技术栈 前端: Layui,jQuery,echarts 后端:Spring Boot,…...

SAR ADC的功耗设计
SAR ADC 由比较器、逻辑和DAC组成,功耗比可能是3:6:1,对于低功耗设计来说,我们需要尽量让DAC的功耗最小,这里来探讨一下CDAC的功耗计算方法。 CDAC从状态1切换到状态2时,需要从Vref buffer上抽拉电荷。C是状态2时连接Vref的总电容,V2就是状态2时接Vref的电容上的电压…...

PP-OCRv5
目录 PP-OCRv5官方效果如下 C封装、C#调用效果 项目 代码 下载 PP-OCRv5官方效果如下 C封装、C#调用效果 项目 代码 using Newtonsoft.Json; using OpenCvSharp; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Diagnostics; using System.Drawing; usi…...
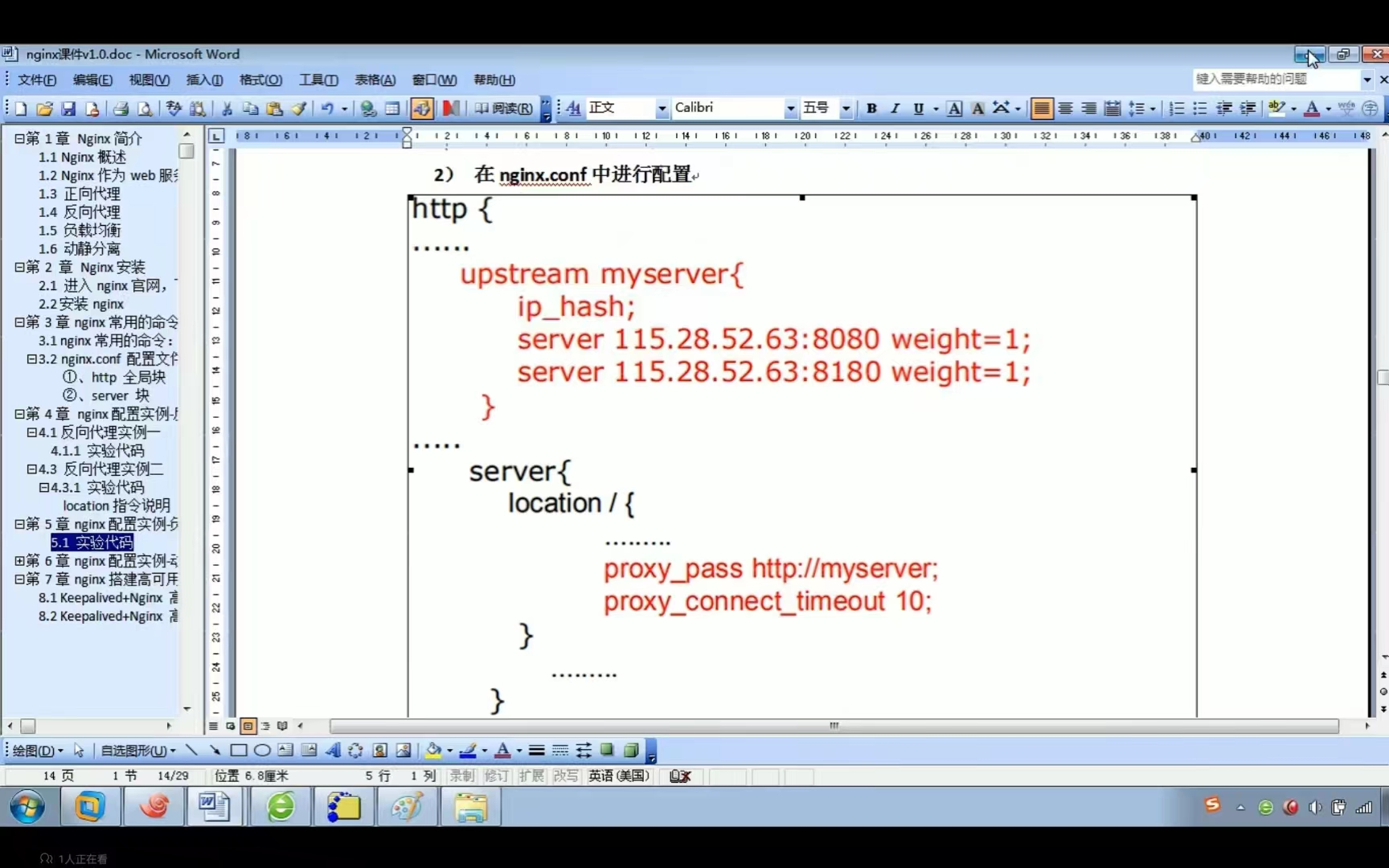
nginx的一些配置的意思
1.用这个端口可以访问到nginx 2.工作进程,设置成和cpu核心数一样即可 3.每个工作进程的最大网络连接数。 4.主机名称 设置反向代理时,把server_name设置成ip。 5.反向代理进行转发,localhost指的是nginx所在的机器。 关键字proxy_pass。 …...

Agent模型微调
这篇文章讲解: 把 Agent 和 Fine-Tuning 的知识串起来,在更高的技术视角看大模型应用;加深对 Agent 工作原理的理解;加深对 Fine-Tuning 训练数据处理的理解。 1. 认识大模型 Agent 1.1 大模型 Agent 的应用场景 揭秘Agent核心…...

Android-OkHttp与Retrofit学习总结
OkHttp核心机制与工作流程 面试官:能简单介绍一下OkHttp的工作流程吗? 候选人: 好的,OkHttp的工作流程大致可以分为几个步骤。首先,我们需要创建一个OkHttpClient实例,通常会用建造者模式来配置…...

移远三款主流5G模块RM500U,RM520N,RG200U比较
文章目录 概要一、技术架构差异1. 3GPP协议版本2. 芯片平台与性能3. 频段覆盖与区域适配4. 协议增强与特殊功能 二、功能与应用定位1. 网络兼容性2. 封装与接口扩展 三、典型应用场景总结 概要 本文介绍下移远两款主流5G模块RM500U RM520N RG200U。 一…...

C++引用以及和指针的区别
C++ 引用 引用(reference)是 C++ 中的一种变量类型,是另一个变量的别名。一旦引用被初始化,就不能再改变它所指向的对象。 引用的特点 必须初始化:声明引用时必须立即对其进行初始化。不可更改绑定:一旦引用绑定到某个变量,就不能再指向其他变量。语法简洁:使用引用不…...

firfox 国外版和国内版本账号不互通问题处理
https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_37891718/article/details/147445621 现在国际服的火狐浏览器修改使用国内的账号服务器,需要先在搜索框输入about:config 中改变三项配置,然后重启浏览器,才能正常使用国内的火狐账号服务器 identity.fxaccount…...

Linux基本指令篇 —— whoami指令
whoami 是 Linux 和 Unix 系统中一个简单但实用的命令,全称 Who Am I(我是谁)。它的功能是显示当前登录用户的用户名。以下是关于 whoami 的详细解析: 目录 1. 基本用法 2. 命令特点 3. 实际应用场景 场景 1:脚本中…...
