Reinforcement Learning with Code 【Code 1. Tabular Q-learning】
Reinforcement Learning with Code 【Code 1. Tabular Q-learning】
This note records how the author begin to learn RL. Both theoretical understanding and code practice are presented. Many material are referenced such as ZhaoShiyu’s Mathematical Foundation of Reinforcement Learning.
This code refers to Mofan’s reinforcement learning course.
文章目录
- Reinforcement Learning with Code 【Code 1. Tabular Q-learning】
- 1.1 Problem and result
- 1.2 Environment
- 1.3 Tabular Q-learning Algorithm
- 1.4 Run this main
- 1.5 Check the Q table
- Reference
1.1 Problem and result
Please consider the problem that a little mouse (denoted by red block) wants to avoid trap (denoted by black block) to get the cheese (denoted by yellow circle). As the figure shows.
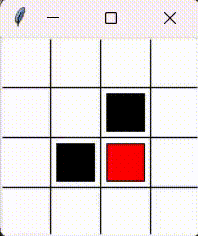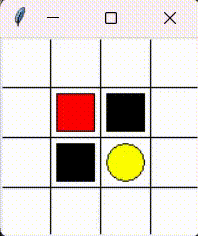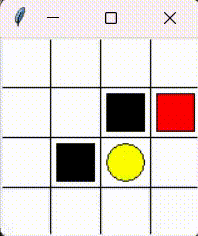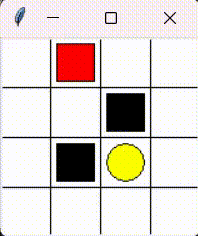
This chapter aims to realize tabular Q-learning algorithm sovle this problem.
1.2 Environment
We use the tkinter package of python to build our environment to interact with agent.
import numpy as np
import time
import sys
import tkinter as tk
# if sys.version_info.major == 2: # 检查python版本是否是python2
# import Tkinter as tk
# else:
# import tkinter as tkUNIT = 40 # pixels
MAZE_H = 4 # grid height
MAZE_W = 4 # grid widthclass Maze(tk.Tk, object):def __init__(self):super(Maze, self).__init__()# Action Spaceself.action_space = ['up', 'down', 'right', 'left'] # action space self.n_actions = len(self.action_space)# 绘制GUIself.title('Maze env')self.geometry('{0}x{1}'.format(MAZE_W * UNIT, MAZE_H * UNIT)) # 指定窗口大小 "width x height"self._build_maze()def _build_maze(self):self.canvas = tk.Canvas(self, bg='white',height=MAZE_H * UNIT,width=MAZE_W * UNIT) # 创建背景画布# create gridsfor c in range(UNIT, MAZE_W * UNIT, UNIT): # 绘制列分隔线x0, y0, x1, y1 = c, 0, c, MAZE_H * UNITself.canvas.create_line(x0, y0, x1, y1)for r in range(UNIT, MAZE_H * UNIT, UNIT): # 绘制行分隔线x0, y0, x1, y1 = 0, r, MAZE_W * UNIT, rself.canvas.create_line(x0, y0, x1, y1)# create origin 第一个方格的中心,origin = np.array([UNIT/2, UNIT/2]) # hell1hell1_center = origin + np.array([UNIT * 2, UNIT])self.hell1 = self.canvas.create_rectangle(hell1_center[0] - (UNIT/2 - 5), hell1_center[1] - (UNIT/2 - 5),hell1_center[0] + (UNIT/2 - 5), hell1_center[1] + (UNIT/2 - 5),fill='black')# hell2hell2_center = origin + np.array([UNIT, UNIT * 2])self.hell2 = self.canvas.create_rectangle(hell2_center[0] - (UNIT/2 - 5), hell2_center[1] - (UNIT/2 - 5),hell2_center[0] + (UNIT/2 - 5), hell2_center[1] + (UNIT/2 - 5),fill='black')# create oval 绘制终点圆形oval_center = origin + np.array([UNIT*2, UNIT*2])self.oval = self.canvas.create_oval(oval_center[0] - (UNIT/2 - 5), oval_center[1] - (UNIT/2 - 5),oval_center[0] + (UNIT/2 - 5), oval_center[1] + (UNIT/2 - 5),fill='yellow')# create red rect 绘制agent红色方块,初始在方格左上角self.rect = self.canvas.create_rectangle(origin[0] - (UNIT/2 - 5), origin[1] - (UNIT/2 - 5),origin[0] + (UNIT/2 - 5), origin[1] + (UNIT/2 - 5),fill='red')# pack all 显示所有canvasself.canvas.pack()def get_state(self, rect):# convert the coordinate observation to state tuple# use the uniformed center as the state such as # |(1,1)|(2,1)|(3,1)|...# |(1,2)|(2,2)|(3,2)|...# |(1,3)|(2,3)|(3,3)|...# |....x0,y0,x1,y1 = self.canvas.coords(rect)x_center = (x0+x1)/2y_center = (y0+y1)/2state = ((x_center-(UNIT/2))/UNIT + 1, (y_center-(UNIT/2))/UNIT + 1)return statedef reset(self):self.update()self.after(500) # delay 500msself.canvas.delete(self.rect) # delete origin rectangleorigin = np.array([UNIT/2, UNIT/2])self.rect = self.canvas.create_rectangle(origin[0] - (UNIT/2 - 5), origin[1] - (UNIT/2 - 5),origin[0] + (UNIT/2 - 5), origin[1] + (UNIT/2 - 5),fill='red')# return observation return self.get_state(self.rect) def step(self, action):# agent和环境进行一次交互s = self.get_state(self.rect) # 获得智能体的坐标base_action = np.array([0, 0])reach_boundary = Falseif action == self.action_space[0]: # upif s[1] > 1:base_action[1] -= UNITelse: # 触碰到边界reward=-1并停留在原地reach_boundary = Trueelif action == self.action_space[1]: # downif s[1] < MAZE_H:base_action[1] += UNITelse:reach_boundary = True elif action == self.action_space[2]: # rightif s[0] < MAZE_W:base_action[0] += UNITelse:reach_boundary = Trueelif action == self.action_space[3]: # leftif s[0] > 1:base_action[0] -= UNITelse:reach_boundary = Trueself.canvas.move(self.rect, base_action[0], base_action[1]) # move agents_ = self.get_state(self.rect) # next state# reward functionif s_ == self.get_state(self.oval): # reach the terminalreward = 1done = Trues_ = 'success'elif s_ == self.get_state(self.hell1): # reach the blockreward = -1s_ = 'block_1'done = Falseelif s_ == self.get_state(self.hell2):reward = -1s_ = 'block_2'done = Falseelse:reward = 0done = Falseif reach_boundary:reward = -1return s_, reward, donedef render(self):time.sleep(0.15)self.update()if __name__ == '__main__':def test():for t in range(10):s = env.reset()print(s)while True:env.render()a = 'right's, r, done = env.step(a)print(s)if done:breakenv = Maze()env.after(100, test) # 在延迟100ms后调用函数testenv.mainloop()This part is important that the reward function design is include, which is as follows
reward = { 1 , if reach the cheese − 1 , if reach the trap or reach the boundary 0 , others \text{reward} = \left \{ \begin{aligned} & 1, \quad \text{if reach the cheese} \\ & -1, \quad \text{if reach the trap or reach the boundary} \\ & 0, \quad \text{others} \end{aligned} \right. reward=⎩ ⎨ ⎧1,if reach the cheese−1,if reach the trap or reach the boundary0,others
We need to explan some function of the class Maze.
- First, the function
_build_mazecreates the inital maze location.
In this example we use the left up coordination of each grid as the state of each block. - Second, the function
get_stateconverts the coordination of each grid to numerical representation such as ( 1 , 1 ) , ( 1 , 2 ) , ⋯ (1,1),(1,2),\cdots (1,1),(1,2),⋯. - Third, the function
resetrenew the state which means placing the mouse in the original grid. - Then, the function
stepwe let the agent interact with envrionment for one step, ang get the reward after the action. - Then, the function
rendercontrols updating the window.
1.3 Tabular Q-learning Algorithm
import numpy as np
import pandas as pdclass QLearningTable():def __init__(self, actions, learning_rate=0.05, reward_decay=0.9, e_greedy=0.9):self.actions = actions # action listself.lr = learning_rateself.gamma = reward_decayself.epsilon = e_greedy # epsilon greedy update policyself.q_table = pd.DataFrame(columns=self.actions, dtype=np.float64)def check_state_exist(self, state):if state not in self.q_table.index:# append new state to q table, use the coordinate as the observation# self.q_table = self.q_table.append( # DataFrame.append is invalid# pd.Series(# [0]*len(self.actions),# index=self.q_table.columns,# name=state,# )# )self.q_table = pd.concat([self.q_table,pd.DataFrame(data=np.zeros((1,len(self.actions))),columns = self.q_table.columns,index = [state])])def choose_action(self, observation):self.check_state_exist(observation)# action selection# epsilon greedy algorithmif np.random.uniform() < self.epsilon:state_action = self.q_table.loc[observation, :]# some actions may have the same value, randomly choose on in these actions# state_action == np.max(state_action) generate bool mask# choose best actionaction = np.random.choice(state_action[state_action == np.max(state_action)].index)else:# choose random actionaction = np.random.choice(self.actions)return actiondef learn(self, s, a, r, s_):self.check_state_exist(s_)q_predict = self.q_table.loc[s, a]if s_ != 'success':q_target = r + self.gamma * self.q_table.loc[s_, :].max() # next state is not terminalelse:q_target = r # next state is terminalself.q_table.loc[s, a] += self.lr * (q_target - q_predict) # update
We store the Q-table as a DataFrame of pandas. The explanation of the functions are as follows.
- First, the function
check_state_existcheck the existence of one state, if not we append it to the Q-table. This is because once the state-action pair is visited, then we update it into the Q-table. - Second, the function
choose_actionis following the ϵ \epsilon ϵ-greedy algorithm
π ( a ∣ s ) = { 1 − ϵ ∣ A ( s ) ∣ ( ∣ A ( s ) ∣ − 1 ) , for the geedy action ϵ ∣ A ( s ) ∣ , for the other ∣ A ( s ) ∣ − 1 actions \pi(a|s) = \left \{ \begin{aligned} 1 - \frac{\epsilon}{|\mathcal{A}(s)|}(|\mathcal{A(s)}|-1), & \quad \text{for the geedy action} \\ \frac{\epsilon}{|\mathcal{A}(s)|}, & \quad \text{for the other } |\mathcal{A}(s)|-1 \text{ actions} \end{aligned} \right. π(a∣s)=⎩ ⎨ ⎧1−∣A(s)∣ϵ(∣A(s)∣−1),∣A(s)∣ϵ,for the geedy actionfor the other ∣A(s)∣−1 actions
- Third, the function
learnis update the q value as Q-learning algorithm purposed.
Q-learning : { q t + 1 ( s t , a t ) = q t ( s t , a t ) − α t ( s t , a t ) [ q t ( s t , a t ) − ( r t + 1 + γ max a ∈ A ( s t + 1 ) q t ( s t + 1 , a ) ) ] q t + 1 ( s , a ) = q t ( s , a ) , for all ( s , a ) ≠ ( s t , a t ) \text{Q-learning} : \left \{ \begin{aligned} \textcolor{red}{q_{t+1}(s_t,a_t)} & \textcolor{red}{= q_t(s_t,a_t) - \alpha_t(s_t,a_t) \Big[q_t(s_t,a_t) - (r_{t+1}+ \gamma \max_{a\in\mathcal{A}(s_{t+1})} q_t(s_{t+1},a)) \Big]} \\ \textcolor{red}{q_{t+1}(s,a)} & \textcolor{red}{= q_t(s,a)}, \quad \text{for all } (s,a) \ne (s_t,a_t) \end{aligned} \right. Q-learning:⎩ ⎨ ⎧qt+1(st,at)qt+1(s,a)=qt(st,at)−αt(st,at)[qt(st,at)−(rt+1+γa∈A(st+1)maxqt(st+1,a))]=qt(s,a),for all (s,a)=(st,at)
1.4 Run this main
Run this main script that we can run the all codes.
from maze_env_custom import Maze
from RL_brain import QLearningTableMAX_EPISODE = 30def update():for episode in range(MAX_EPISODE):# initial observation, observation is the rect's coordiante# observation is [x0,y0, x1,y1]observation = env.reset() while True:# fresh envenv.render()# RL choose action based on observation ['up', 'down', 'right', 'left']action = RL.choose_action(str(observation))# RL take action and get next observation and rewardobservation_, reward, done = env.step(action)# RL learn from this transitionRL.learn(str(observation), action, reward, str(observation_))# swap observationobservation = observation_# break while loop when end of this episodeif done:break# show q_tableprint(RL.q_table)print('\n')# end of gameprint('game over')env.destroy()if __name__ == "__main__":env = Maze()RL = QLearningTable(env.action_space)env.after(100, update)env.mainloop()1.5 Check the Q table
After a long run we can check the q-table to judge wheter the learning is reasonable. The q-table is as follows:
up down right left
(1.0, 1.0) -0.226208 0.000963 0.000000 -9.750000e-02
(1.0, 2.0) 0.000024 0.005773 0.000000 -5.000000e-02
(2.0, 1.0) -0.050000 0.000000 0.000000 5.247904e-07
(2.0, 2.0) 0.000000 -0.050000 -0.050000 0.000000e+00
block_2 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 1.793534e-04
(2.0, 4.0) -0.097500 -0.050000 0.336315 2.916072e-03
(1.0, 4.0) 0.002162 -0.140781 0.112337 -5.000000e-02
(1.0, 3.0) 0.000008 0.033479 -0.050000 -9.739821e-02
block_1 0.000000 0.097500 0.000000 0.000000e+00
(4.0, 2.0) 0.000000 0.006525 -0.050000 -5.000000e-02
success 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000e+00
(3.0, 1.0) -0.050000 -0.047750 0.000000 0.000000e+00
(3.0, 4.0) 0.722610 -0.050000 0.000000 1.298347e-02
(4.0, 1.0) -0.050000 0.000101 -0.050000 0.000000e+00
(4.0, 3.0) 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 1.426250e-01
For example, when at the original place if the mouse wants to move up or move left it will reach the boundary and get reward − 1 -1 −1. Hence the state value in q-table is minus.
Reference
赵世钰老师的课程
莫烦ReinforcementLearning course
相关文章:

Reinforcement Learning with Code 【Code 1. Tabular Q-learning】
Reinforcement Learning with Code 【Code 1. Tabular Q-learning】 This note records how the author begin to learn RL. Both theoretical understanding and code practice are presented. Many material are referenced such as ZhaoShiyu’s Mathematical Foundation o…...
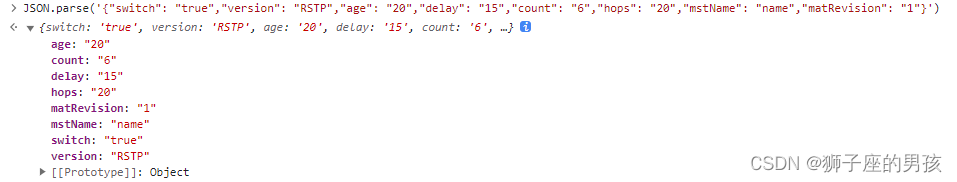
解决:Uncaught (in promise) SyntaxError: “[object Object]“ is not valid JSON 问题的过程
1、问题描述: 其一、报错为: Uncaught (in promise) SyntaxError: "[object Object]" is not valid JSON 中文为: 未捕获(承诺中)语法错误:“[object Object]”不是有效的 JSON 其二、问题描…...

机器学习-New Optimization
机器学习(New Optimization) 前言: 学习资料 videopptblog 下面的PPT里面有一些符号错误,但是我还是按照PPT的内容编写公式,自己直到符号表示什么含义就好了 Notation 符号解释 θ t \theta_t θt第 t 步时,模型的参数 Δ L …...

3d虚拟vr汽车实景展厅吸引更多潜在消费者
随着人们对生活品质的追求,越来越多的消费者开始关注汽车的外观设计、内饰配置等方面。传统的展示方式已经不能满足消费者的需求,车辆VR虚拟漫游展示应运而生。借助VR虚拟现实和web3d开发建模技术,对汽车的外观、造型及信息数据进行数字化处理…...

Java里的static import使用小结
Java里的static import使用小结 换了工作要把Java重新捡起来了,这个在大学里用过的语言,虽然不复杂,还是有一些奇怪的地方的。比如static Slgluimport。 Static import是JDK 1.5中引进的特性,不过读大学那会还真没注意到。它的作…...
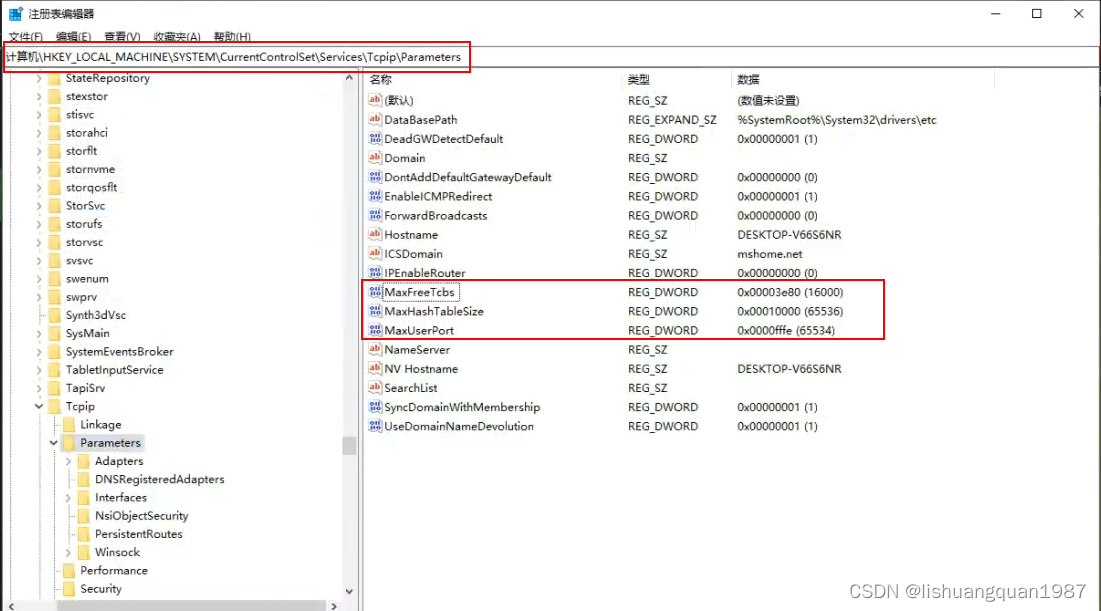
go程序使用tcp短连接报:only one usage of each socket address
环境及现象 Win10上位机(C#,WPF)后台使用go作为服务。 连接情况 C#连接大概60个TCP长连接(设备)。 后台go服务连接60个UDP短连接(设备附属硬件), 10个TCP短连接(PLC,modbus通讯&a…...
十分钟配置好Neovim go开发环境(其他语言一样)
文章目录 前言仓库地址用法快捷键问题反馈 前言 这篇文章的目的是为了分享下我自己的Neovim配置。 本人是Golang程序员,最开始使用的IDE是JetBrains Goland。有一说一这个ide适配度很高,认识的很多人都使用这个。但是它也有几个对我来说的缺点…...
Linux第八章之进程概念
一、冯诺依曼体系结构 关于冯诺依曼,必须强调几点: 这里的存储器指的是内存不考虑缓存情况,这里的CPU能且只能对内存进行读写,不能访问外设(输入或输出设备)外设(输入或输出设备)要输入或者输出数据,也只能写入内存或…...

怎么学习Java并发编程相关技术? - 易智编译EaseEditing
学习Java并发编程可以通过多种方式进行,包括但不限于以下几种: 在线教程和学习平台: 网上有许多免费和付费的Java并发编程教程和学习平台,如Coursera、Udemy、edX、Codecademy等。这些平台提供结构化的课程和练习,适…...

vue3 +element动态表单实现
可以直接复制,接口看后端 父页面 <schedulesref"schedulesRef":dxbz"props.dxbz":jdlx"props.jdlx":woId"myWoId":addendumList"formInline.addendumList"v-if"addendumShow"addendum"addendu…...

Linux部署jar包,隐藏命令行参数
Linux部署jar包,隐藏命令行参数 一、背景需求二、查阅资料三、实现隐藏库3.1、测试test.c3.2、设置隐藏库3.3、验证 四、应用jar启动命令五、直接应用结果 最新项目安全检测,发现配置文件中数据库密码,redis密码仍处理明文状态 于是整理了一篇…...
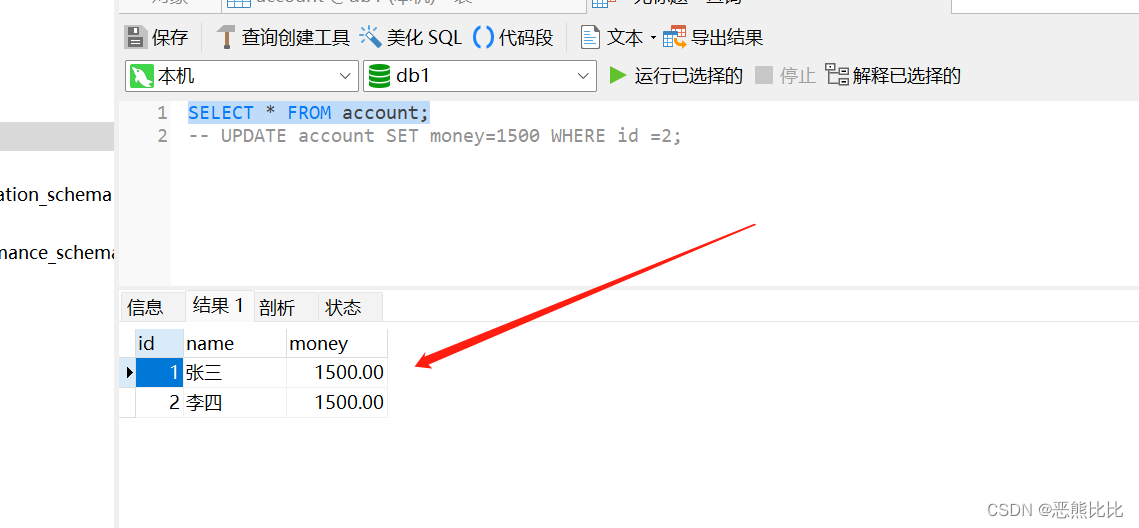
JDBC-笔记
JDBC 1. JDBC介绍 JDBC(Java Database Connectivity)是一种用于连接和操作数据库的 Java API。 通过Java操作数据库的流程 第一步:编写Java代码 第二步:Java代码将SQL发送到MySQL服务端 第三步:MySQL服务端接收到SQ…...
)
Rust的入门篇(中)
Rust的入门篇(中) 这是接上面一篇rust入门篇(上)文章 22. 包管理一 mod nation {pub mod government {pub fn govern() {}}mod congress {pub fn legislate() {}}mod court {fn judicial() {super::congress::legislate();}} }fn main() {nation::government::govern(); }23.…...

手机设置全局代理ip步骤
在互联网时代,隐私和安全问题备受关注。使用全局代理能够帮助我们保护个人信息,突破地理限制,并提高网络速度。但是,你是否对全局代理的安全性存有疑虑?而且,如何在手机上设置全局代理呢?今天就…...

spring boot+thymeleaf+semantic ui 分页
参考: https://my.oschina.net/ayyao/blog/898041 后端 springboot 使用: com.github.pagehelper.PageInfo,作为分页对象 <!--引入分页插件--> <dependency><groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId><artifa…...
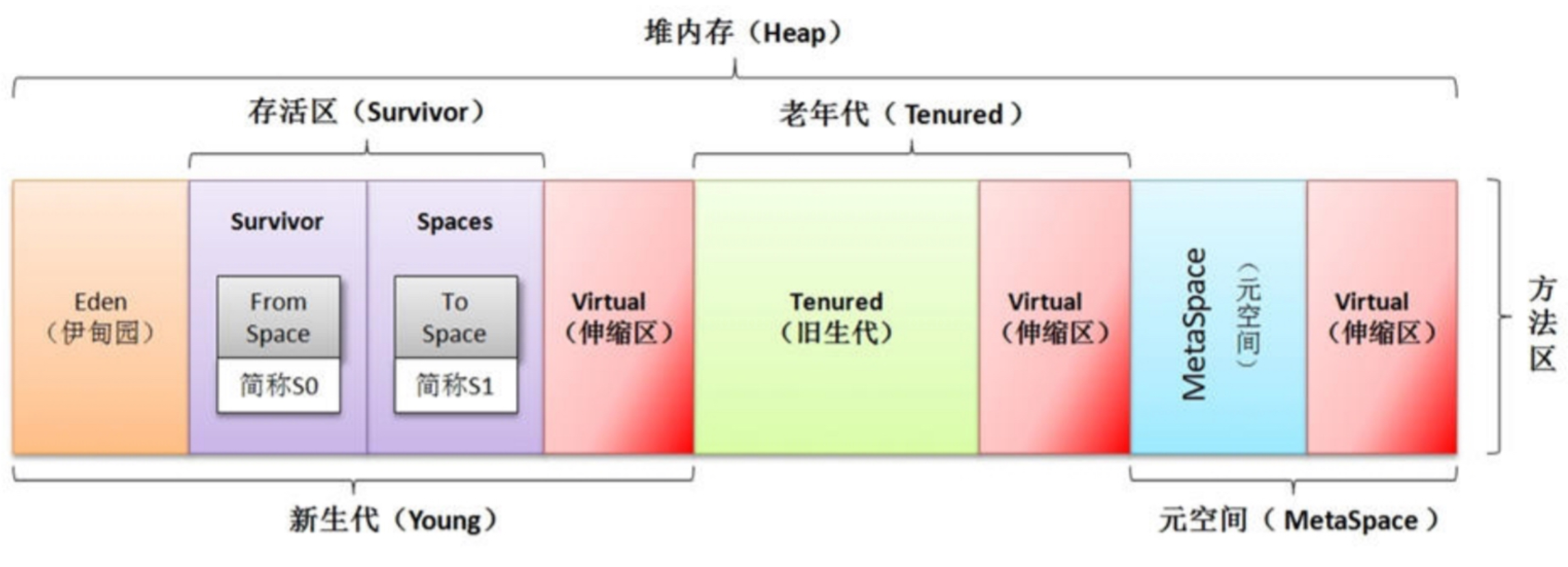
【JVM】(一)深入理解JVM运行时数据区
文章目录 一、JVM 运行流程二、虚拟机栈(线程私有)三、本地方法栈 (线程私有)四、方法区(元数据区)五、堆(线程共享)六、程序计数器(线程私有) 一、JVM 运行流…...

C++ QRegExpValidator
//正在表达式限制输入 QString str "\\b(?:(?:25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)\\.){3}(?:25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)\\b"; ui->lineEdit->setValidator(new QRegExpValidator(QRegExp(str))); //用于占位 ui->lineEdit->setI…...
备战秋招 | 笔试强训19
目录 一、选择题 二、编程题 三、选择题题解 四、编程题题解 一、选择题 1、二分查找的时间复杂度() A. O(N*log(N)) B. O(N) C. O(log(N)) D. O(N^2) 2、有一个单向链表中有一个A、B两个相邻元素,有一个指针p指向元素A,现将…...

第一章 计算机网络概述
第一章 计算机网络概述 1.1 计算机网络在信息时代的作用 1.2 因特网概述 网络分类: 网络:许多计算机连接在一起的的局域网; 互联网:internet许多网络连接在一起; 因特网:Internet 全球最大的互联网&…...
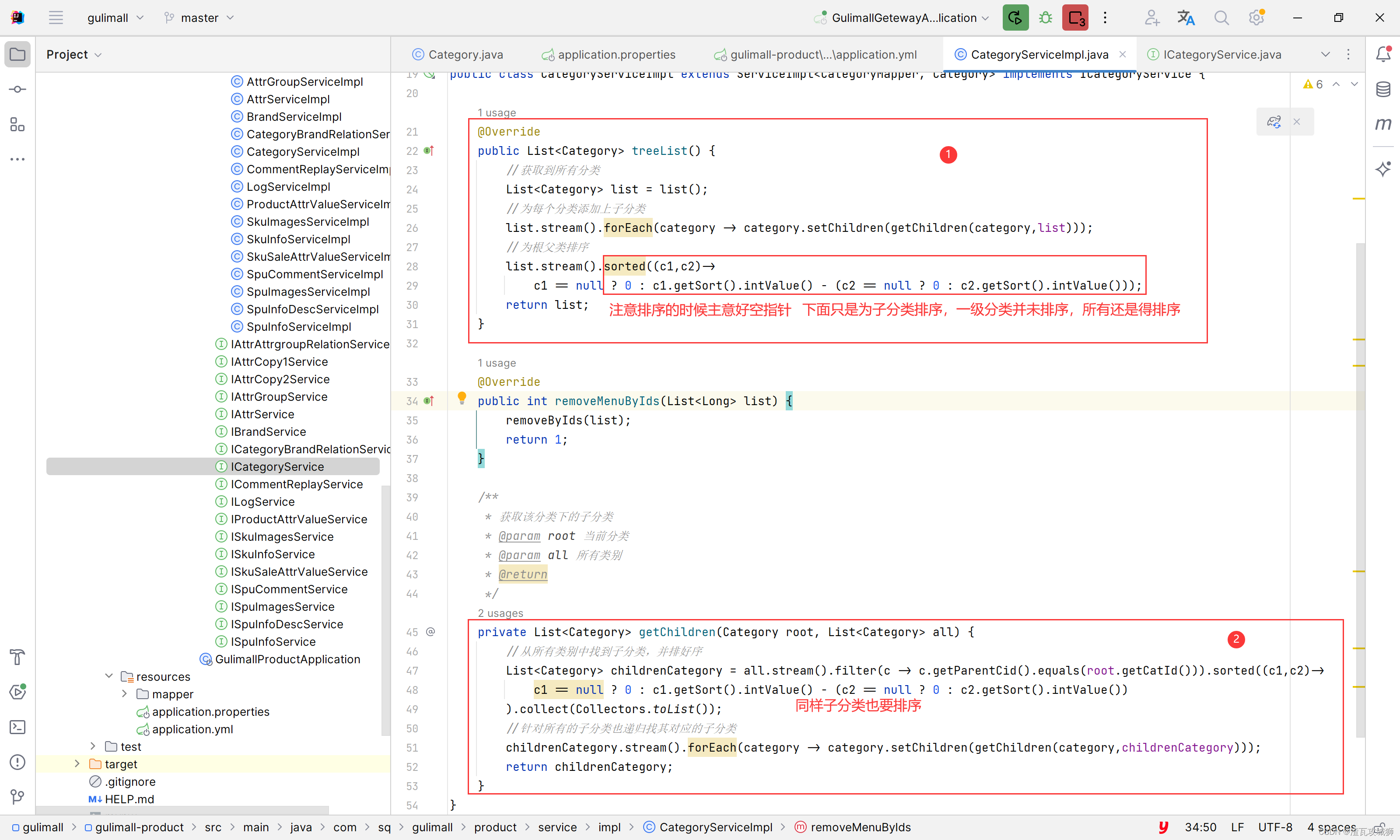
谷粒商城第六天-商品服务之分类管理下的获取三级分类树形列表
目录 一、总述 1.1 前端思路 1.2 后端思路 二、前端部分 2.1 在网页中建好目录及菜单 2.1.1 建好商品目录 2.1.2 建好分类管理菜单 编辑 2.2 编写组件 2.2.1 先完成组件文件的创建 2.2.2 编写组件 2.2.2.1 显示三级分类树形列表 三、后端部分 3.1 编写商品分类…...
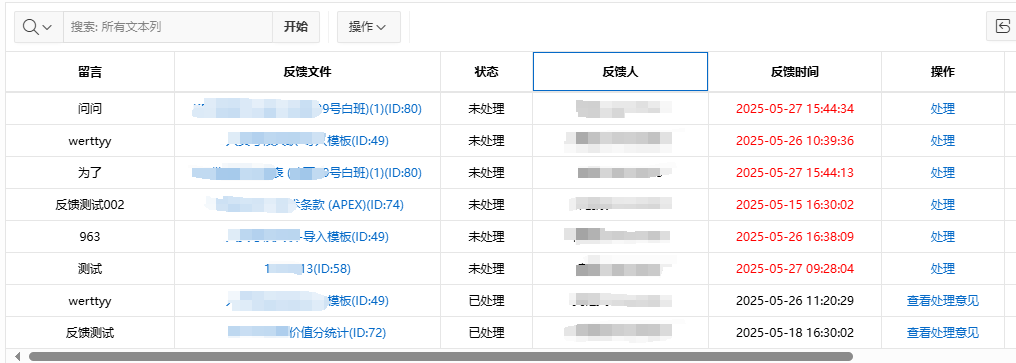
【Oracle APEX开发小技巧12】
有如下需求: 有一个问题反馈页面,要实现在apex页面展示能直观看到反馈时间超过7天未处理的数据,方便管理员及时处理反馈。 我的方法:直接将逻辑写在SQL中,这样可以直接在页面展示 完整代码: SELECTSF.FE…...
)
React Native 导航系统实战(React Navigation)
导航系统实战(React Navigation) React Navigation 是 React Native 应用中最常用的导航库之一,它提供了多种导航模式,如堆栈导航(Stack Navigator)、标签导航(Tab Navigator)和抽屉…...

【Linux】C语言执行shell指令
在C语言中执行Shell指令 在C语言中,有几种方法可以执行Shell指令: 1. 使用system()函数 这是最简单的方法,包含在stdlib.h头文件中: #include <stdlib.h>int main() {system("ls -l"); // 执行ls -l命令retu…...
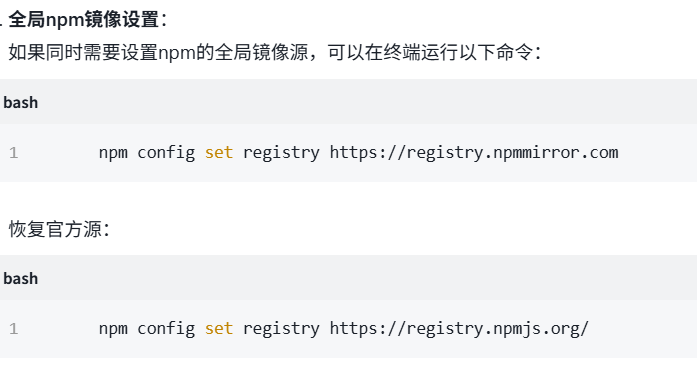
关于nvm与node.js
1 安装nvm 安装过程中手动修改 nvm的安装路径, 以及修改 通过nvm安装node后正在使用的node的存放目录【这句话可能难以理解,但接着往下看你就了然了】 2 修改nvm中settings.txt文件配置 nvm安装成功后,通常在该文件中会出现以下配置&…...

Leetcode 3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations
Leetcode 3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations 1. 解题思路2. 代码实现 题目链接:3577. Count the Number of Computer Unlocking Permutations 1. 解题思路 这一题其实就是一个脑筋急转弯,要想要能够将所有的电脑解锁&#x…...

376. Wiggle Subsequence
376. Wiggle Subsequence 代码 class Solution { public:int wiggleMaxLength(vector<int>& nums) {int n nums.size();int res 1;int prediff 0;int curdiff 0;for(int i 0;i < n-1;i){curdiff nums[i1] - nums[i];if( (prediff > 0 && curdif…...

Unit 1 深度强化学习简介
Deep RL Course ——Unit 1 Introduction 从理论和实践层面深入学习深度强化学习。学会使用知名的深度强化学习库,例如 Stable Baselines3、RL Baselines3 Zoo、Sample Factory 和 CleanRL。在独特的环境中训练智能体,比如 SnowballFight、Huggy the Do…...

多模态大语言模型arxiv论文略读(108)
CROME: Cross-Modal Adapters for Efficient Multimodal LLM ➡️ 论文标题:CROME: Cross-Modal Adapters for Efficient Multimodal LLM ➡️ 论文作者:Sayna Ebrahimi, Sercan O. Arik, Tejas Nama, Tomas Pfister ➡️ 研究机构: Google Cloud AI Re…...

CSS设置元素的宽度根据其内容自动调整
width: fit-content 是 CSS 中的一个属性值,用于设置元素的宽度根据其内容自动调整,确保宽度刚好容纳内容而不会超出。 效果对比 默认情况(width: auto): 块级元素(如 <div>)会占满父容器…...
淘宝扭蛋机小程序系统开发:打造互动性强的购物平台
淘宝扭蛋机小程序系统的开发,旨在打造一个互动性强的购物平台,让用户在购物的同时,能够享受到更多的乐趣和惊喜。 淘宝扭蛋机小程序系统拥有丰富的互动功能。用户可以通过虚拟摇杆操作扭蛋机,实现旋转、抽拉等动作,增…...
