30. 利用linprog 解决 生产决策问题(matlab程序)
1.简述
线线规划的几个基本性质:【文献[1]第46页】
(1)线性规划问题的可行域如果非空,则是一个凸集-凸多面体;
(2)如果线性规划问题有最优解,那么最优解可在可行域的顶点中确定;
(3)如果可行域有界,且可行域只有有限个顶点,则问题的最优解必存在,并在这有限个顶点中确定;
(4)最优解可由最优顶点处的有效约束形成的方程组的解确定。
常用的线性规划求解方法有单纯形法和内点法。
1、单纯形法(simplex method)
单纯形法是由G.B. Dantzig在1947年提出来的,这是20世纪数学界最重大的成果之一。单纯形法是一种迭代法,它根据线性规划问题的特点在问题可行域的顶点中逐步确定问题的最优解。在每一个是基本可行解的迭代点(即顶点),如果它不是最优的,单纯形法从与该顶点相连结的边中确定一个使目标函数值下降的边,沿该边移动可以确定一个与该顶点相邻且目标函数又优于该顶点的新顶点(新的基本可行解)。由于可行域的顶点数是有限的,如果每一次的移动都能使目标函数值下降,则经过有限次的移动方法必终止于问题的一个最优顶点。【文献[1]第57页】
单纯形法要求线性规划具有标准形式,即
即约束函数都是等式约束,且决策变量均是非负的。
任何线性规划问题使用单纯形法时都需要通过变换转换为线性规划的标准形。转换方法参见文献[1]第51页例2.1.6。
2、从单纯形法到内点法
由于单纯形法的有效性,几十年来得到了广泛的应用。近年来,对于大规模的线性规划问题,尽管单纯形法受到了内点法的挑战,但单纯形法还是受到广大用户的青睐。
一个算法如果其求得问题的解所用的运算工作量是问题的参数m和n的多项式,则称这一算法的复杂多项式时间算法;如果所需运算工作量的阶数是以m或n为幂的指数2m或2n,则称复杂性是指数时间的算法。
单纯形算法的平均运算工作量是多项式时间的,但对于一个具体的问题其算法的复杂性并不一定是多项式的。1972年,Klee和Minty给出了一个复杂性为指数时间的例子。那么对线性规划问题是否存在时间复杂性是多项式的算法呢?如果存在多项式时间算法,如何设计这样的算法?
1979年,前苏联数学家Khachiyan回答了第1个问题,他提出了一个椭球算法求不等式问题的解,并证明了算法的时间复杂性是多项式的。利用对偶理论,线性规划问题可以转换成不等式问题,这就明确回答了对线性规划存在多项式时间算法。但是计算的实际表明,椭球算法的效果要比单纯形方法差得多,并不是一个有实际应用价值的算法。
1984年,在美国贝尔实验室工作的印度数学家Karmarkar回答了第2个问题,它对线性规划的求解提出了一个具有多项式时间复杂性的内点算法。
3、内点法(interior point method)
求线性规划问题的单纯形方法在问题的基本可行解中确定最优解,在几何上,每次迭代它是沿着可行域的边界从一个顶点向另一个更好的顶点移动来实现的。内点算法则完全不同,它是从可行域的一个严格内点开始,产生一个使目标函数值逐步改善的严格内点序列,并最终收敛于问题的最优解。通过下图可以清晰的看出单纯形法与内点法的区别。
单纯形法与内战法轨迹(文献[1]图2.4.4)
经过近20年的研究与发展,如今已有大量求解线性规划问题的内点算法,它们可以分成三类:路径跟踪算法,仿射调比算法,和原始对偶内点算法(primal-dual interior point method)。
4、线性规划问题的MATLAB求解
在MATLAB中求解线性规划问题的函数是linprog,该函数集中了几种求线性规划的算法,如内点法和单纯形法,根据问题的规模或用户指定的算法进行求解。具体使用方法可查询帮助文件。
2.代码
主程序:
%% 生产决策问题
f=[-5;-7]; %线性方程系数
A=[4,2;5,4;2,7;-6,-5;]; %线性不等式约束系数矩阵
b=[90;200;210;0];
l=[0 0]; %变量上限
[xo,fo,exitflag]=linprog(f,A,b,[],[],l)
子程序:
function [x,fval,exitflag,output,lambda]=linprog(f,A,B,Aeq,Beq,lb,ub,x0,options)
%LINPROG Linear programming.
% X = LINPROG(f,A,b) attempts to solve the linear programming problem:
%
% min f'*x subject to: A*x <= b
% x
%
% X = LINPROG(f,A,b,Aeq,beq) solves the problem above while additionally
% satisfying the equality constraints Aeq*x = beq. (Set A=[] and B=[] if
% no inequalities exist.)
%
% X = LINPROG(f,A,b,Aeq,beq,LB,UB) defines a set of lower and upper
% bounds on the design variables, X, so that the solution is in
% the range LB <= X <= UB. Use empty matrices for LB and UB
% if no bounds exist. Set LB(i) = -Inf if X(i) is unbounded below;
% set UB(i) = Inf if X(i) is unbounded above.
%
% X = LINPROG(f,A,b,Aeq,beq,LB,UB,X0) sets the starting point to X0. This
% option is only available with the active-set algorithm. The default
% interior point algorithm will ignore any non-empty starting point.
%
% X = LINPROG(PROBLEM) finds the minimum for PROBLEM. PROBLEM is a
% structure with the vector 'f' in PROBLEM.f, the linear inequality
% constraints in PROBLEM.Aineq and PROBLEM.bineq, the linear equality
% constraints in PROBLEM.Aeq and PROBLEM.beq, the lower bounds in
% PROBLEM.lb, the upper bounds in PROBLEM.ub, the start point
% in PROBLEM.x0, the options structure in PROBLEM.options, and solver
% name 'linprog' in PROBLEM.solver. Use this syntax to solve at the
% command line a problem exported from OPTIMTOOL.
%
% [X,FVAL] = LINPROG(f,A,b) returns the value of the objective function
% at X: FVAL = f'*X.
%
% [X,FVAL,EXITFLAG] = LINPROG(f,A,b) returns an EXITFLAG that describes
% the exit condition. Possible values of EXITFLAG and the corresponding
% exit conditions are
%
% 3 LINPROG converged to a solution X with poor constraint feasibility.
% 1 LINPROG converged to a solution X.
% 0 Maximum number of iterations reached.
% -2 No feasible point found.
% -3 Problem is unbounded.
% -4 NaN value encountered during execution of algorithm.
% -5 Both primal and dual problems are infeasible.
% -7 Magnitude of search direction became too small; no further
% progress can be made. The problem is ill-posed or badly
% conditioned.
% -9 LINPROG lost feasibility probably due to ill-conditioned matrix.
%
% [X,FVAL,EXITFLAG,OUTPUT] = LINPROG(f,A,b) returns a structure OUTPUT
% with the number of iterations taken in OUTPUT.iterations, maximum of
% constraint violations in OUTPUT.constrviolation, the type of
% algorithm used in OUTPUT.algorithm, the number of conjugate gradient
% iterations in OUTPUT.cgiterations (= 0, included for backward
% compatibility), and the exit message in OUTPUT.message.
%
% [X,FVAL,EXITFLAG,OUTPUT,LAMBDA] = LINPROG(f,A,b) returns the set of
% Lagrangian multipliers LAMBDA, at the solution: LAMBDA.ineqlin for the
% linear inequalities A, LAMBDA.eqlin for the linear equalities Aeq,
% LAMBDA.lower for LB, and LAMBDA.upper for UB.
%
% NOTE: the interior-point (the default) algorithm of LINPROG uses a
% primal-dual method. Both the primal problem and the dual problem
% must be feasible for convergence. Infeasibility messages of
% either the primal or dual, or both, are given as appropriate. The
% primal problem in standard form is
% min f'*x such that A*x = b, x >= 0.
% The dual problem is
% max b'*y such that A'*y + s = f, s >= 0.
%
% See also QUADPROG.
% Copyright 1990-2018 The MathWorks, Inc.
% If just 'defaults' passed in, return the default options in X
% Default MaxIter, TolCon and TolFun is set to [] because its value depends
% on the algorithm.
defaultopt = struct( ...
'Algorithm','dual-simplex', ...
'Diagnostics','off', ...
'Display','final', ...
'LargeScale','on', ...
'MaxIter',[], ...
'MaxTime', Inf, ...
'Preprocess','basic', ...
'TolCon',[],...
'TolFun',[]);
if nargin==1 && nargout <= 1 && strcmpi(f,'defaults')
x = defaultopt;
return
end
% Handle missing arguments
if nargin < 9
options = [];
% Check if x0 was omitted and options were passed instead
if nargin == 8
if isa(x0, 'struct') || isa(x0, 'optim.options.SolverOptions')
options = x0;
x0 = [];
end
else
x0 = [];
if nargin < 7
ub = [];
if nargin < 6
lb = [];
if nargin < 5
Beq = [];
if nargin < 4
Aeq = [];
end
end
end
end
end
end
% Detect problem structure input
problemInput = false;
if nargin == 1
if isa(f,'struct')
problemInput = true;
[f,A,B,Aeq,Beq,lb,ub,x0,options] = separateOptimStruct(f);
else % Single input and non-structure.
error(message('optim:linprog:InputArg'));
end
end
% No options passed. Set options directly to defaultopt after
allDefaultOpts = isempty(options);
% Prepare the options for the solver
options = prepareOptionsForSolver(options, 'linprog');
if nargin < 3 && ~problemInput
error(message('optim:linprog:NotEnoughInputs'))
end
% Define algorithm strings
thisFcn = 'linprog';
algIP = 'interior-point-legacy';
algDSX = 'dual-simplex';
algIP15b = 'interior-point';
% Check for non-double inputs
msg = isoptimargdbl(upper(thisFcn), {'f','A','b','Aeq','beq','LB','UB', 'X0'}, ...
f, A, B, Aeq, Beq, lb, ub, x0);
if ~isempty(msg)
error('optim:linprog:NonDoubleInput',msg);
end
% After processing options for optionFeedback, etc., set options to default
% if no options were passed.
if allDefaultOpts
% Options are all default
options = defaultopt;
end
if nargout > 3
computeConstrViolation = true;
computeFirstOrderOpt = true;
% Lagrange multipliers are needed to compute first-order optimality
computeLambda = true;
else
computeConstrViolation = false;
computeFirstOrderOpt = false;
computeLambda = false;
end
% Algorithm check:
% If Algorithm is empty, it is set to its default value.
algIsEmpty = ~isfield(options,'Algorithm') || isempty(options.Algorithm);
if ~algIsEmpty
Algorithm = optimget(options,'Algorithm',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts);
OUTPUT.algorithm = Algorithm;
% Make sure the algorithm choice is valid
if ~any(strcmp({algIP; algDSX; algIP15b},Algorithm))
error(message('optim:linprog:InvalidAlgorithm'));
end
else
Algorithm = algDSX;
OUTPUT.algorithm = Algorithm;
end
% Option LargeScale = 'off' is ignored
largescaleOn = strcmpi(optimget(options,'LargeScale',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts),'on');
if ~largescaleOn
[linkTag, endLinkTag] = linkToAlgDefaultChangeCsh('linprog_warn_largescale');
warning(message('optim:linprog:AlgOptsConflict', Algorithm, linkTag, endLinkTag));
end
% Options setup
diagnostics = strcmpi(optimget(options,'Diagnostics',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts),'on');
switch optimget(options,'Display',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts)
case {'final','final-detailed'}
verbosity = 1;
case {'off','none'}
verbosity = 0;
case {'iter','iter-detailed'}
verbosity = 2;
case {'testing'}
verbosity = 3;
otherwise
verbosity = 1;
end
% Set the constraints up: defaults and check size
[nineqcstr,nvarsineq] = size(A);
[neqcstr,nvarseq] = size(Aeq);
nvars = max([length(f),nvarsineq,nvarseq]); % In case A is empty
if nvars == 0
% The problem is empty possibly due to some error in input.
error(message('optim:linprog:EmptyProblem'));
end
if isempty(f), f=zeros(nvars,1); end
if isempty(A), A=zeros(0,nvars); end
if isempty(B), B=zeros(0,1); end
if isempty(Aeq), Aeq=zeros(0,nvars); end
if isempty(Beq), Beq=zeros(0,1); end
% Set to column vectors
f = f(:);
B = B(:);
Beq = Beq(:);
if ~isequal(length(B),nineqcstr)
error(message('optim:linprog:SizeMismatchRowsOfA'));
elseif ~isequal(length(Beq),neqcstr)
error(message('optim:linprog:SizeMismatchRowsOfAeq'));
elseif ~isequal(length(f),nvarsineq) && ~isempty(A)
error(message('optim:linprog:SizeMismatchColsOfA'));
elseif ~isequal(length(f),nvarseq) && ~isempty(Aeq)
error(message('optim:linprog:SizeMismatchColsOfAeq'));
end
[x0,lb,ub,msg] = checkbounds(x0,lb,ub,nvars);
if ~isempty(msg)
exitflag = -2;
x = x0; fval = []; lambda = [];
output.iterations = 0;
output.constrviolation = [];
output.firstorderopt = [];
output.algorithm = ''; % not known at this stage
output.cgiterations = [];
output.message = msg;
if verbosity > 0
disp(msg)
end
return
end
if diagnostics
% Do diagnostics on information so far
gradflag = []; hessflag = []; constflag = false; gradconstflag = false;
non_eq=0;non_ineq=0; lin_eq=size(Aeq,1); lin_ineq=size(A,1); XOUT=ones(nvars,1);
funfcn{1} = []; confcn{1}=[];
diagnose('linprog',OUTPUT,gradflag,hessflag,constflag,gradconstflag,...
XOUT,non_eq,non_ineq,lin_eq,lin_ineq,lb,ub,funfcn,confcn);
end
% Throw warning that x0 is ignored (true for all algorithms)
if ~isempty(x0) && verbosity > 0
fprintf(getString(message('optim:linprog:IgnoreX0',Algorithm)));
end
if strcmpi(Algorithm,algIP)
% Set the default values of TolFun and MaxIter for this algorithm
defaultopt.TolFun = 1e-8;
defaultopt.MaxIter = 85;
[x,fval,lambda,exitflag,output] = lipsol(f,A,B,Aeq,Beq,lb,ub,options,defaultopt,computeLambda);
elseif strcmpi(Algorithm,algDSX) || strcmpi(Algorithm,algIP15b)
% Create linprog options object
algoptions = optimoptions('linprog', 'Algorithm', Algorithm);
% Set some algorithm specific options
if isfield(options, 'InternalOptions')
algoptions = setInternalOptions(algoptions, options.InternalOptions);
end
thisMaxIter = optimget(options,'MaxIter',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts);
if strcmpi(Algorithm,algIP15b)
if ischar(thisMaxIter)
error(message('optim:linprog:InvalidMaxIter'));
end
end
if strcmpi(Algorithm,algDSX)
algoptions.Preprocess = optimget(options,'Preprocess',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts);
algoptions.MaxTime = optimget(options,'MaxTime',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts);
if ischar(thisMaxIter) && ...
~strcmpi(thisMaxIter,'10*(numberofequalities+numberofinequalities+numberofvariables)')
error(message('optim:linprog:InvalidMaxIter'));
end
end
% Set options common to dual-simplex and interior-point-r2015b
algoptions.Diagnostics = optimget(options,'Diagnostics',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts);
algoptions.Display = optimget(options,'Display',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts);
thisTolCon = optimget(options,'TolCon',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts);
if ~isempty(thisTolCon)
algoptions.TolCon = thisTolCon;
end
thisTolFun = optimget(options,'TolFun',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts);
if ~isempty(thisTolFun)
algoptions.TolFun = thisTolFun;
end
if ~isempty(thisMaxIter) && ~ischar(thisMaxIter)
% At this point, thisMaxIter is either
% * a double that we can set in the options object or
% * the default string, which we do not have to set as algoptions
% is constructed with MaxIter at its default value
algoptions.MaxIter = thisMaxIter;
end
% Create a problem structure. Individually creating each field is quicker
% than one call to struct
problem.f = f;
problem.Aineq = A;
problem.bineq = B;
problem.Aeq = Aeq;
problem.beq = Beq;
problem.lb = lb;
problem.ub = ub;
problem.options = algoptions;
problem.solver = 'linprog';
% Create the algorithm from the options.
algorithm = createAlgorithm(problem.options);
% Check that we can run the problem.
try
problem = checkRun(algorithm, problem, 'linprog');
catch ME
throw(ME);
end
% Run the algorithm
[x, fval, exitflag, output, lambda] = run(algorithm, problem);
% If exitflag is {NaN, <aString>}, this means an internal error has been
% thrown. The internal exit code is held in exitflag{2}.
if iscell(exitflag) && isnan(exitflag{1})
handleInternalError(exitflag{2}, 'linprog');
end
end
output.algorithm = Algorithm;
% Compute constraint violation when x is not empty (interior-point/simplex presolve
% can return empty x).
if computeConstrViolation && ~isempty(x)
output.constrviolation = max([0; norm(Aeq*x-Beq, inf); (lb-x); (x-ub); (A*x-B)]);
else
output.constrviolation = [];
end
% Compute first order optimality if needed. This information does not come
% from either qpsub, lipsol, or simplex.
if exitflag ~= -9 && computeFirstOrderOpt && ~isempty(lambda)
output.firstorderopt = computeKKTErrorForQPLP([],f,A,B,Aeq,Beq,lb,ub,lambda,x);
else
output.firstorderopt = [];
end
3.运行结果

相关文章:

30. 利用linprog 解决 生产决策问题(matlab程序)
1.简述 线线规划的几个基本性质:【文献[1]第46页】 (1)线性规划问题的可行域如果非空,则是一个凸集-凸多面体; (2)如果线性规划问题有最优解,那么最优解可在可行域的顶点中确定; (3)如果可行域有界,且可行域…...
一百三十九、Kettle——Linux安装Kettle8.2
一、目的 为了方便海豚调度kettle任务,在Linux上安装kettle 二、kettle版本与前提 版本:kettle8.2 pdi-ce-8.2.0.0-342 前提:Linux已经安装好jdk 三、安装步骤 (一)打开安装包所在地 [roothurys22 ~]# cd …...

react路由在layout中的监听
业务中需要在layout里来监听路由的变化,但是layout并不是一个路由组件,所以layout组件内的props并没有location,history等属性,(路由组件:由Route组件处理的才是路由组件)所以我们需要将layout组件转变成路…...
Java反射(三)
目录 1.反射与代理设计模式 2.反射与Annotation 3.自定义Annotation 4.Annotation整合工厂设计模式和代理设计模式 1.反射与代理设计模式 代理模式是指通过业务真实类实现业务接口,再通过设置代理类创建业务真实类子类从而间接访问业务真实类。但是这存在一个弊…...

ansible-playbook roles编写lnmp剧本
目录 集中式编写lnmp剧本 执行 分布式编写lnmp剧本 一定要设置ssh免交互 nginx mysql php 执行 集中式编写lnmp剧本 vim /etc/ansible/lnmp.yml - name: lnmp playhosts: dbserversremote_user: roottasks:- name: perpare condifurecopy: src/etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.r…...

相机可用性变化监听AvailabilityCallback流程分析
相机可用性变化监听及流程分析 一、接口说明 相机可用性变化监听可以通过CameraManager中的接口registerAvailabilityCallback()来设置回调,接口如下: /** *注册一个回调以获得有关相机设备可用性的通知。 * *<p>再次注册相同的回调将用提供…...

使用Python多线程实现生产者消费者模型
“Talk is cheap, show me the code.” 废话不多说,直接上代码: """ 生产者消费者模型 Python实现 """ import queue import threading import random import timeclass ConsProd:# 队列参数_que None # 队列# 生产者…...

Notepad++工具通过正则表达式批量替换内容
1.每行末尾新增特定字符串 CtrlH弹出小窗口;查找目标输入$,替换为输入特定字符串;选中循环查找,查找模式选正则表达式;最后点击全部替换 2.每行行首新增特定字符串 CtrlH弹出小窗口;查找目标输入^&…...
从零构建深度学习推理框架-3 手写算子relu
Relu介绍: relu是一个非线性激活函数,可以避免梯度消失,过拟合等情况。我们一般将thresh设为0。 operator类: #ifndef KUIPER_COURSE_INCLUDE_OPS_OP_HPP_ #define KUIPER_COURSE_INCLUDE_OPS_OP_HPP_ namespace kuiper_infer {…...
想做上位机,学C#还是QT?
学习C#还是Qt,取决于你的具体需求和偏好。 如果你计划开发跨平台的桌面应用程序,并且希望使用一种更轻量级、直观的界面框架,那么Qt可能是一个不错的选择。Qt是一个功能丰富且成熟的跨平台框架,支持多种开发语言(包括…...

Ansible —— playbook 剧本
Ansible —— playbook 剧本 一、playbook的概述1.playbook简介2.什么是Ansible playbook剧本?3.Ansible playbook剧本的特点4.如何使用Ansible playbook剧本?5.playbooks 本身由以下各部分组成 二、playbook示例1.运行playbook2.定义、引用变量3.指定远…...

ARM寻址方式
寻址方式 寻址方式是根据指令中给出的地址码字段来实现寻找操作数地址的方式,ARM中有以下8种基本的寻址方式。 1、寄存器寻址 将寄存器中的值作为操作数,指令中的地址码字段是寄存器编号。 MOV R1,R2 ;R1 R2 ADD R0,R1,R2 ;R0 R1 R22、立即寻…...

【JAVA】String ,StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 三者有何联系?
个人主页:【😊个人主页】 系列专栏:【❤️初识JAVA】 文章目录 前言StringBufferStringBuffer方法 StringBuilderStringBuilder方法 String ,StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder的区别String和StringBuffer互相转换 前言 在之前的文章…...
)
关于计数以及Index返回订单号升级版(控制字符长度,控制年月标记)
数据库表操作: EXEC sys.sp_dropextendedproperty nameNName , level0typeNSCHEMA,level0nameNdbo, level1typeNTABLE,level1nameNSetNoIndexGOEXEC sys.sp_dropextendedproperty nameNMS_Description , level0typeNSCHEMA,level0nameNdbo, level1typeNTABLE,level…...
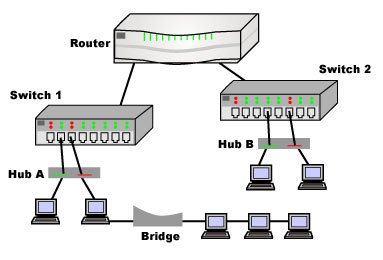
【计算机网络】11、网桥(bridge)、集线器(hub)、交换机(switch)、路由器(router)、网关(gateway)
文章目录 一、网桥(bridge)二、集线器(hub)三、交换机(switch)四、路由器(router)五、网关(gateway) 对于hub,一个包过来后,直接将包转发到其他口。 对于桥&…...

第九篇-自我任务数据准备
格式化自我意识数据用于ChatGLM微调 准备数据源 https://github.com/hiyouga/ChatGLM-Efficient-Tuning cd data self_cognition.json代码self_process.py #!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # 读取self_cognition自我认知解析并写入转换新文件import json# 读取se…...
2023.8.1号论文阅读
文章目录 MCPA: Multi-scale Cross Perceptron Attention Network for 2D Medical Image Segmentation摘要本文方法实验结果 SwinMM: Masked Multi-view with SwinTransformers for 3D Medical Image Segmentation摘要本文方法实验结果 MCPA: Multi-scale Cross Perceptron Att…...

webpack优化前端框架性能
webpack优化目的 webpack优化目的1. 提升开发体验提升开发体验使用 SourceMap 2. 提升打包构建速度提升打包构建速度(开发模式)提升打包速度 oneOf提升打包速度 include(包含)/exclude(排除)提升第二次打包…...
组件的介绍及使用)
Unity UGUI的Outline(描边)组件的介绍及使用
Unity UGUI的Outline(描边)组件的介绍及使用 1. 什么是Outline(描边)组件? Outline(描边)组件是Unity UGUI中的一种特效组件,用于给UI元素添加描边效果。通过设置描边的颜色、宽度和模糊程度,可以使UI元素在视觉上更加突出。 2. Outline(描…...

爆改vue3 setup naiveui可编辑table
使用naiveui官网的可编辑table总是报错,所以手写了一个 思路:table数据数组unitMsgArr对应一个布尔的数组isEditArr ,点击table可编辑的行数据的时候,更改对应的isEdit为true,此时渲染组件EditCom,在EditC…...

浅谈 React Hooks
React Hooks 是 React 16.8 引入的一组 API,用于在函数组件中使用 state 和其他 React 特性(例如生命周期方法、context 等)。Hooks 通过简洁的函数接口,解决了状态与 UI 的高度解耦,通过函数式编程范式实现更灵活 Rea…...

C++初阶-list的底层
目录 1.std::list实现的所有代码 2.list的简单介绍 2.1实现list的类 2.2_list_iterator的实现 2.2.1_list_iterator实现的原因和好处 2.2.2_list_iterator实现 2.3_list_node的实现 2.3.1. 避免递归的模板依赖 2.3.2. 内存布局一致性 2.3.3. 类型安全的替代方案 2.3.…...
(二)TensorRT-LLM | 模型导出(v0.20.0rc3)
0. 概述 上一节 对安装和使用有个基本介绍。根据这个 issue 的描述,后续 TensorRT-LLM 团队可能更专注于更新和维护 pytorch backend。但 tensorrt backend 作为先前一直开发的工作,其中包含了大量可以学习的地方。本文主要看看它导出模型的部分&#x…...

转转集团旗下首家二手多品类循环仓店“超级转转”开业
6月9日,国内领先的循环经济企业转转集团旗下首家二手多品类循环仓店“超级转转”正式开业。 转转集团创始人兼CEO黄炜、转转循环时尚发起人朱珠、转转集团COO兼红布林CEO胡伟琨、王府井集团副总裁祝捷等出席了开业剪彩仪式。 据「TMT星球」了解,“超级…...

Nginx server_name 配置说明
Nginx 是一个高性能的反向代理和负载均衡服务器,其核心配置之一是 server 块中的 server_name 指令。server_name 决定了 Nginx 如何根据客户端请求的 Host 头匹配对应的虚拟主机(Virtual Host)。 1. 简介 Nginx 使用 server_name 指令来确定…...

Axios请求超时重发机制
Axios 超时重新请求实现方案 在 Axios 中实现超时重新请求可以通过以下几种方式: 1. 使用拦截器实现自动重试 import axios from axios;// 创建axios实例 const instance axios.create();// 设置超时时间 instance.defaults.timeout 5000;// 最大重试次数 cons…...

06 Deep learning神经网络编程基础 激活函数 --吴恩达
深度学习激活函数详解 一、核心作用 引入非线性:使神经网络可学习复杂模式控制输出范围:如Sigmoid将输出限制在(0,1)梯度传递:影响反向传播的稳定性二、常见类型及数学表达 Sigmoid σ ( x ) = 1 1 +...

今日学习:Spring线程池|并发修改异常|链路丢失|登录续期|VIP过期策略|数值类缓存
文章目录 优雅版线程池ThreadPoolTaskExecutor和ThreadPoolTaskExecutor的装饰器并发修改异常并发修改异常简介实现机制设计原因及意义 使用线程池造成的链路丢失问题线程池导致的链路丢失问题发生原因 常见解决方法更好的解决方法设计精妙之处 登录续期登录续期常见实现方式特…...
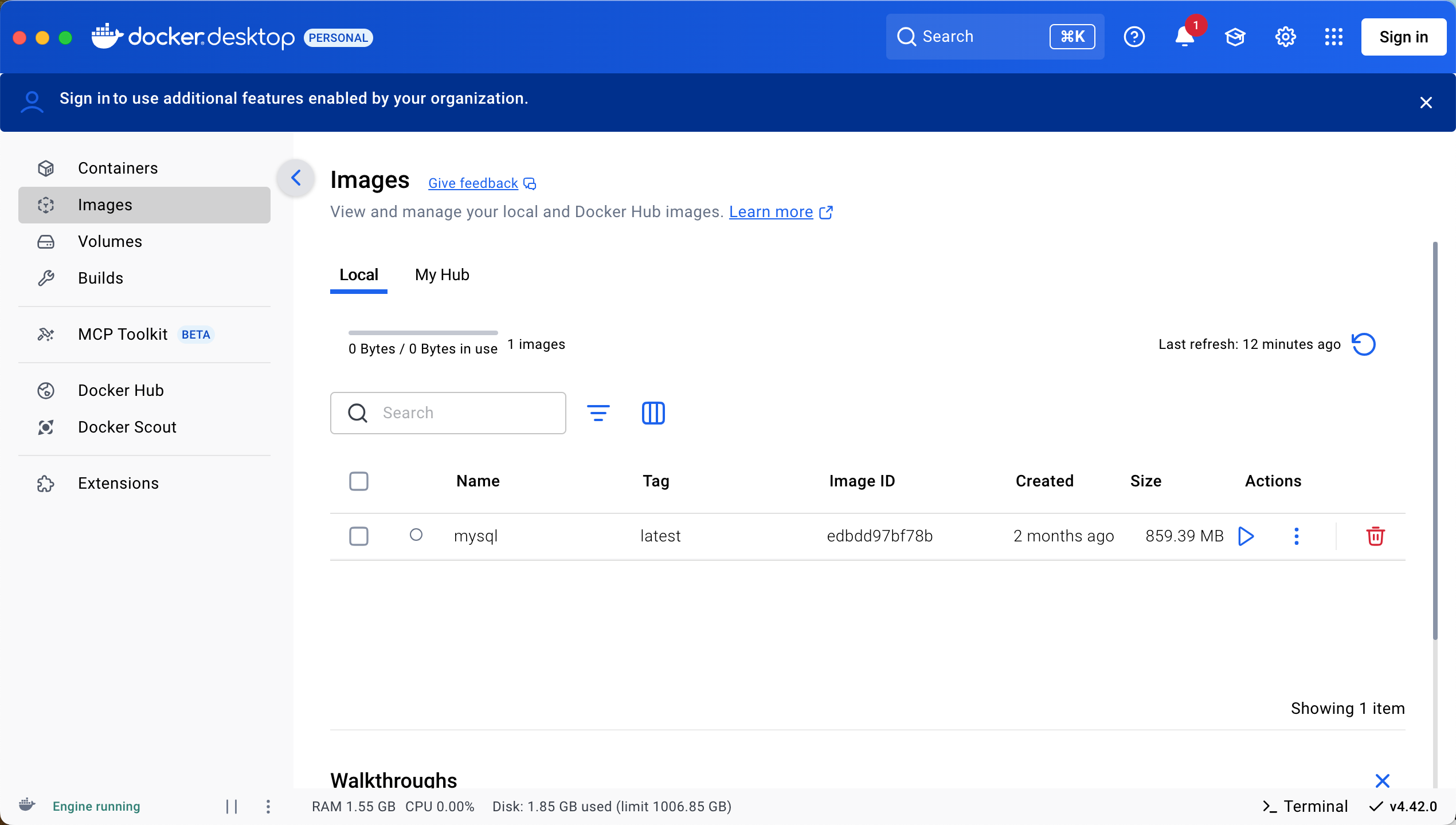
Docker 本地安装 mysql 数据库
Docker: Accelerated Container Application Development 下载对应操作系统版本的 docker ;并安装。 基础操作不再赘述。 打开 macOS 终端,开始 docker 安装mysql之旅 第一步 docker search mysql 》〉docker search mysql NAME DE…...
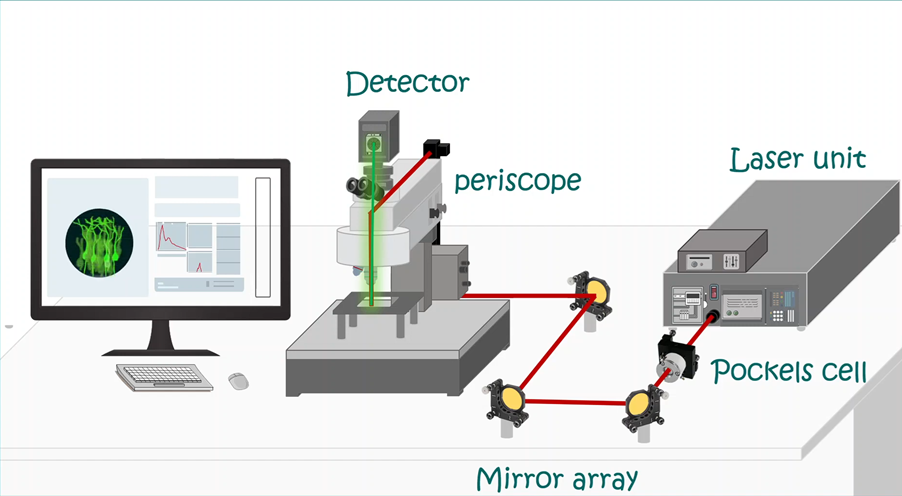
LabVIEW双光子成像系统技术
双光子成像技术的核心特性 双光子成像通过双低能量光子协同激发机制,展现出显著的技术优势: 深层组织穿透能力:适用于活体组织深度成像 高分辨率观测性能:满足微观结构的精细研究需求 低光毒性特点:减少对样本的损伤…...
