IO进程线程day8(2023.8.6)
一、Xmind整理: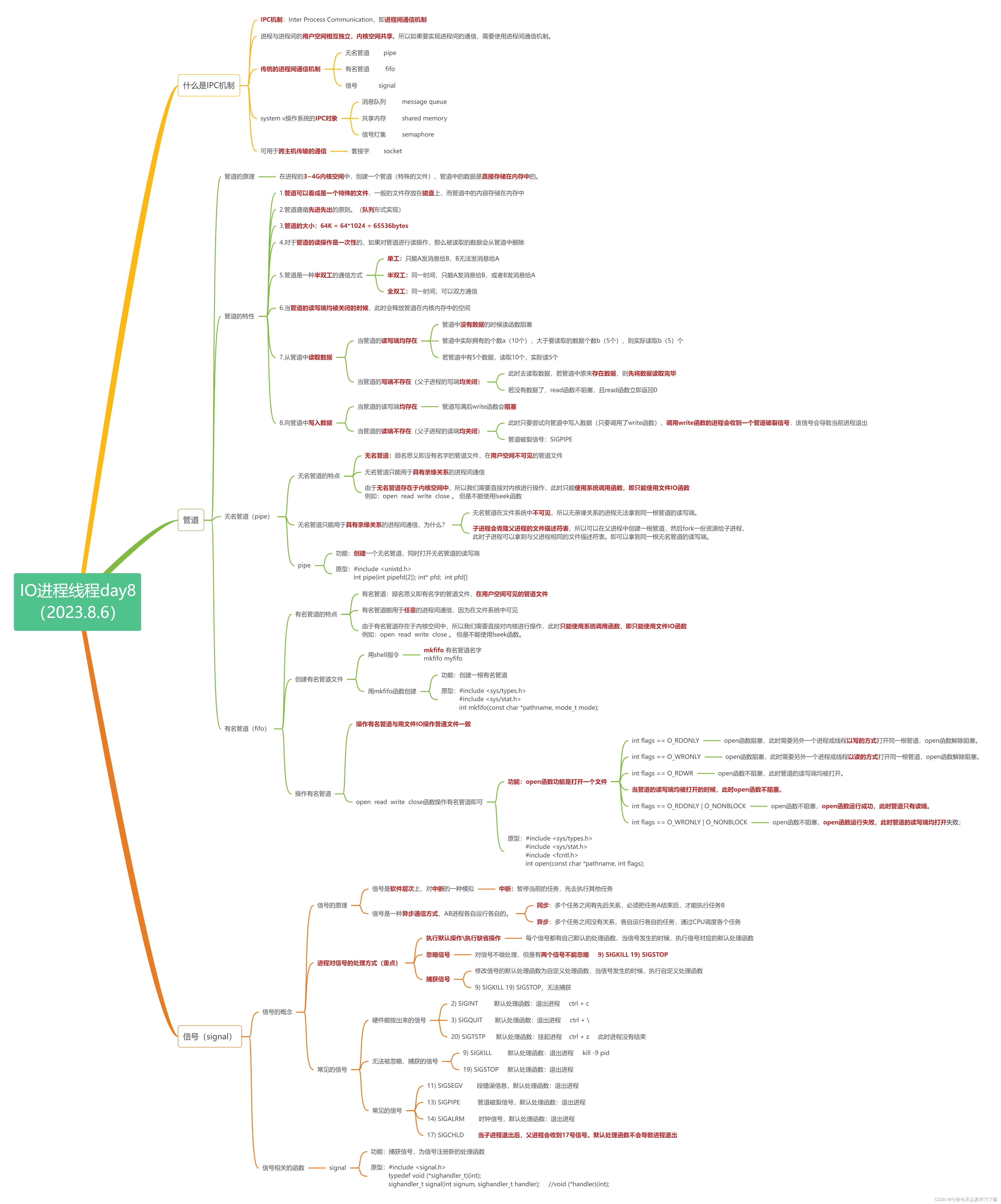
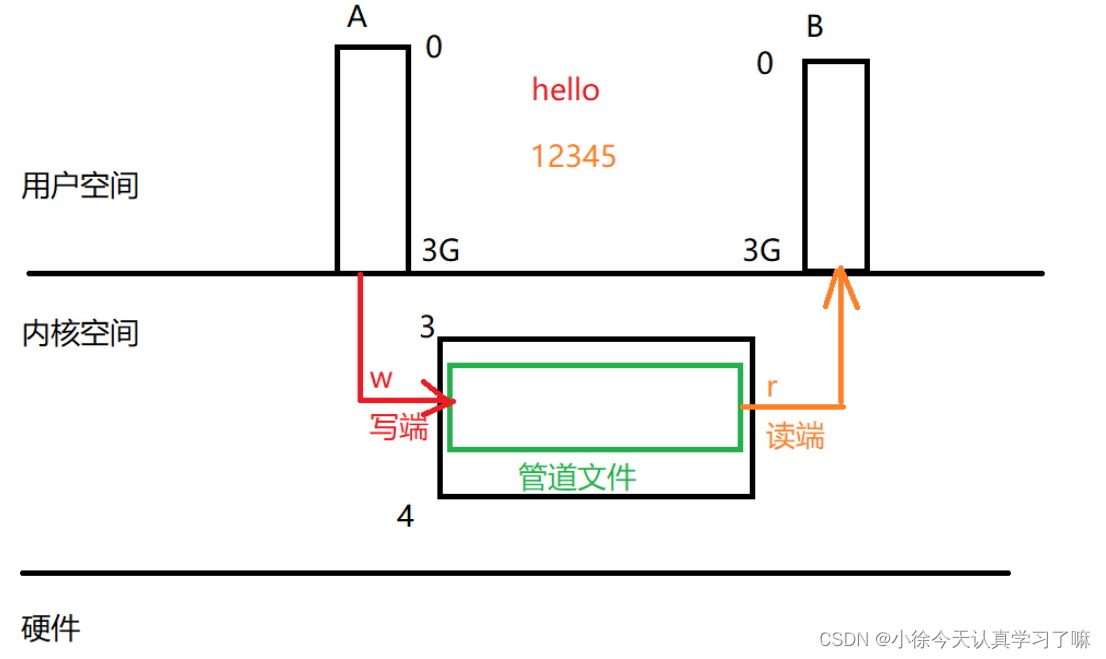
管道的原理:
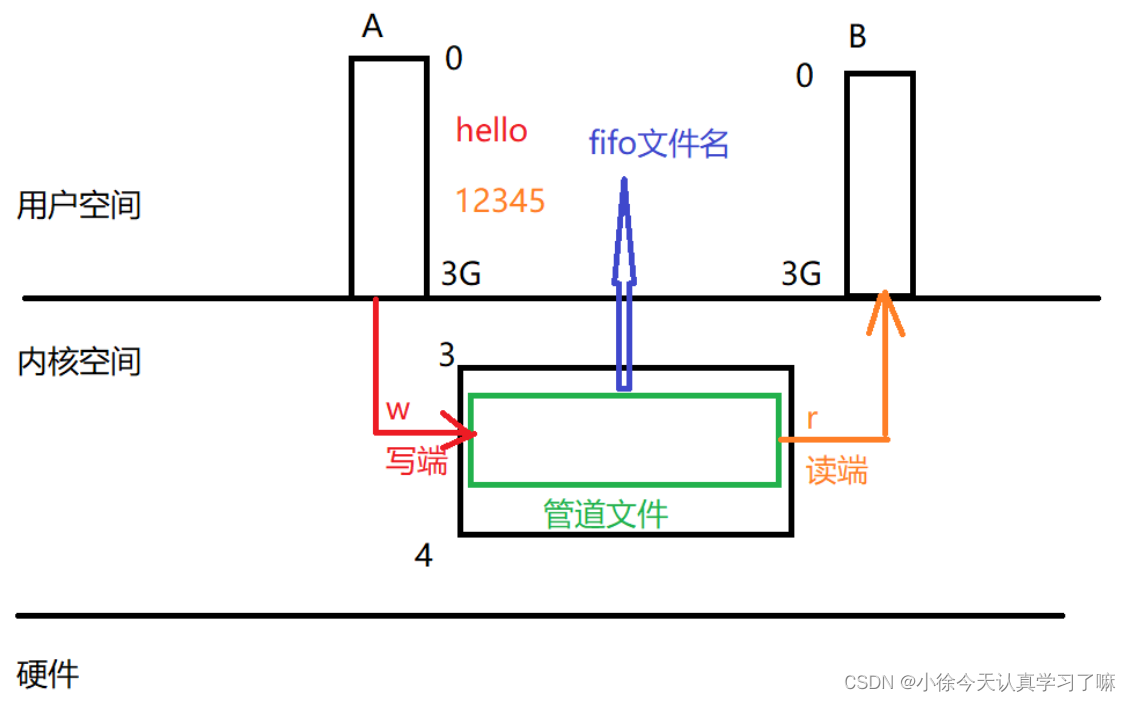
有名管道的特点:
信号的原理:

二、课上练习:
练习1:pipe
功能:创建一个无名管道,同时打开无名管道的读写端
原型:
#include <unistd.h>
int pipe(int pipefd[2]); int* pfd; int pfd[]参数:
int pipefd[2]:函数运行完毕后,该参数指向的数组中会存储两个文件描述符;
pipefd[0]: 读端文件描述符;
pipefd[1]: 写端文件描述符;返回值:
成功,返回0;
失败,返回-1,更新errno;小练:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <head.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//管道的创建必须放在fork函数前//若放在fork函数后,会导致父子进程各自创建一根管道//此时会导致父子进程各自操作各自的管道,无法进行通信int pfd[2] = {0};if(pipe(pfd) < 0){perror("pfd");return -1;}printf("pipe success pfd[0]=%d pfd[1]=%d\n",pfd[0],pfd[1]);pid_t cpid = fork();if(cpid > 0) //父进程中为真{//父进程发送数据给子进程char buf[128]="";while(1){fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1] = 0; //从终端获取数据,最后会拿到\n字符,将\n字符修改成0//将数据写入到管道文件中if(write(pfd[1],buf,sizeof(buf)) < 0){perror("write");return -1;}printf("写入成功\n");}}else if(0 == cpid) //子进程中为真{//子进程读取父进程发送过来的数据char buf[128] = "";ssize_t res = 0;while(1){bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));printf("__%d__\n",__LINE__);//当管道中没有数据的时候,read函数阻塞res = read(pfd[0],buf,sizeof(buf));printf("res=%ld : %s\n",res,buf); }}else{perror("fork");return -1;}return 0;
}

练习2:mkfifo
功能:创建一根有名管道
原型:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);参数:
char *pathname:指定要创建的有名管道的路径以及名字;
mode_t mode:有名管道的权限:0664 0777,真实的权限 (mode & ~umask)
the permissions of the created file are (mode & ~umask)返回值:
成功,返回0;
失败,返回-1,更新errno;
errno == 17,文件已经存在的错误,这是一个允许存在的错误,忽略该错误练习3:操作有名管道
功能:操作有名管道与用文件IO操作普通文件一致
原型:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int open(const char *pathname, int flags);参数:
int flags:O_RDONLY 只读O_WRONLY 只写O_RDWR 读写---上述三种必须,且只能包含一种---O_NONBLOCK 非阻塞1.int flags == O_RDONLY
open函数阻塞,此时需要另外一个进程或线程以写的方式打开同一根管道,open函数解除阻塞
2.int flags == O_WRONLY
open函数阻塞,此时需要另外一个进程或线程以读的方式打开同一根管道,open函数解除阻塞
3.int flags == O_RDWR
open函数不阻塞,此时管道的读写端均被打开
当管道的读写端均被打开的时候,此时open函数不阻塞
4.int flags == O_RDONLY | O_NONBLOCK
open函数不阻塞,open函数运行成功,此时管道只有读端
5.int flags == O_WRONLY | O_NONBLOCK
open函数不阻塞,open函数运行失败,此时管道的读写端均打开失败
示例:
读端:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{umask(0);if(mkfifo("./fifo", 0777) < 0){//printf("errno = %d\n", errno);if(errno != 17) //17 == EEXIST{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("create FIFO success\n");//open函数阻塞int fd = open("./fifo", O_RDONLY);if(fd < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open FIFO rdonly success fd=%d\n", fd);char buf[128] = "";ssize_t res = 0;while(1){bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));res = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));if(res < 0){perror("read");return -1; }else if(0 == res){printf("对端关闭\n");break;}printf("%ld :%s\n", res, buf);}close(fd);return 0;
}写端:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{umask(0);if(mkfifo("./fifo", 0777) < 0){ //printf("errno = %d\n", errno);if(errno != 17) //17 == EEXIST{perror("mkfifo");return -1; }} printf("create FIFO success\n");//open函数阻塞int fd = open("./fifo", O_WRONLY);if(fd < 0){ perror("open");return -1; } printf("open FIFO wronly success fd=%d\n", fd);char buf[128] = ""; while(1){ printf("请输入>>>");fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1] = 0;if(write(fd, buf, sizeof(buf)) < 0){perror("write");return -1; }printf("写入成功\n");} close(fd);return 0;
}小练:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <head.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//创建有名管道if(mkfifo("./fifo",0664) < 0){//printf("%d\n",errno);if(errno != 17) //17:文件已经存在错误,这是一个允许存在的错误,忽略该错误{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("mkfifo success\n");/*int fd = open("./fifo",O_RDWR);if(fd < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open success fd = %d\n",fd);
*/int fd_r = open("./fifo",O_RDONLY|O_NONBLOCK);if(fd_r < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open success fd_r = %d\n",fd_r);int fd_w = open("./fifo",O_WRONLY|O_NONBLOCK);if(fd_w < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open success fd_w = %d\n",fd_w);return 0;
}

练习4:常见的信号
练习5:signal
功能:捕获信号,为信号注册新的处理函数
原型:
#include <signal.h>
typedef void (*sighandler_t)(int);
sighandler_t signal(int signum, sighandler_t handler); //void (*handler)(int);参数:
int signum:指定要捕获的信号对应的编号。可以填编号,也可以填对应的宏。2) SIGINT
sighandler_t handler:函数指针,回调函数;
1) SIG_IGN:忽略信号; 9) 19)号信号无法忽略;
2) SIG_DFL:执行默认操作;
3) 传入一个函数的首地址,代表捕获信号,且该函数的返回值必须是void类型,参数列表必须是int类型,例如:void handler(int sig){ }typedef void (*sighandler_t)(int); typedef void (*)(int) sighandler_t;
typedef 旧的类型名 新的类型名;
typedef int uint32_t; int a ----> uint32_t a;
typedef int* pint; int* pa ---> pint pa;
typedef void (*)(int) sighandler_t; void (*ptr)(int) ----> sighandler_t ptr;返回值:
成功,返回该信号的上一个信号处理函数的首地址; 默认处理函数的首地址获取不到,返回NULL;
失败,返回SIG_ERR ((__sighandler_t)-1),更新errno; 小练:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <head.h>
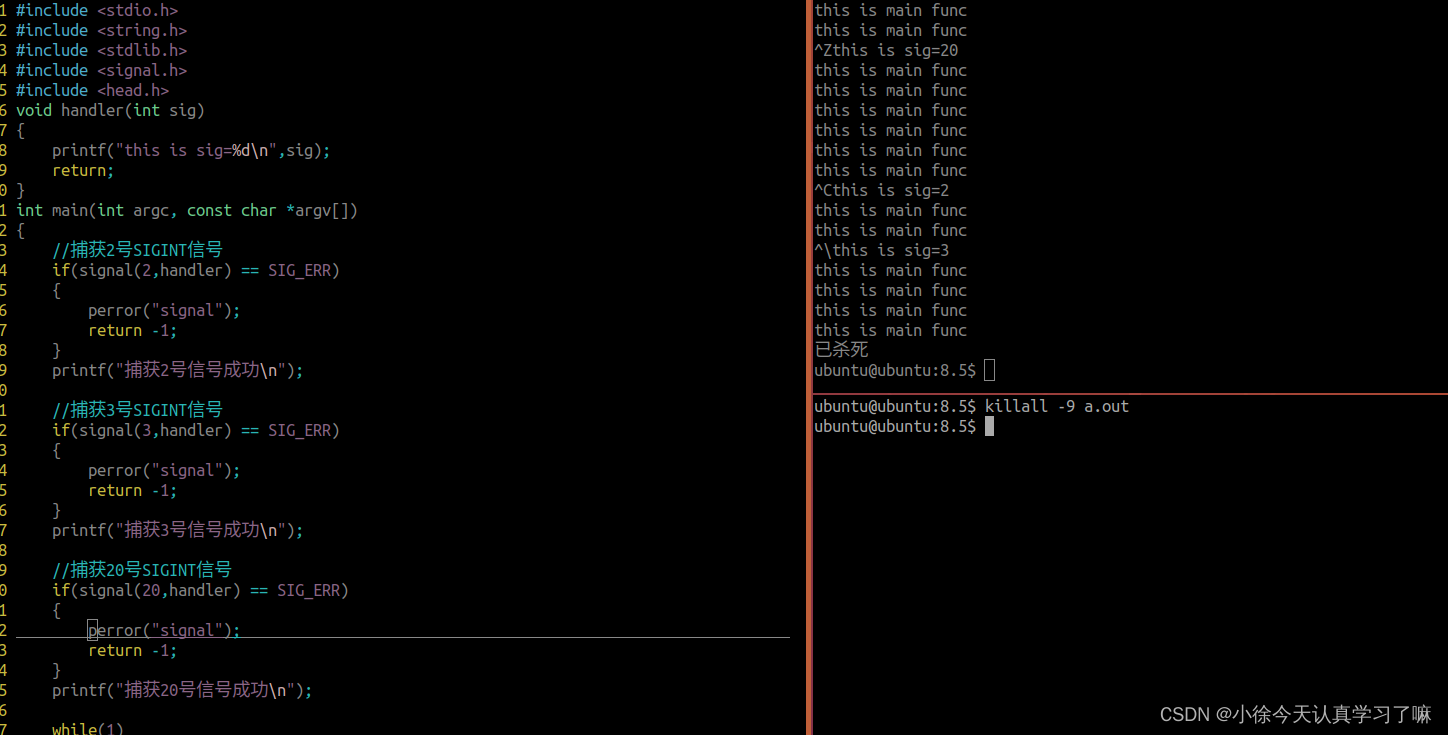
void handler(int sig)
{printf("this is sig=%d\n",sig);return;
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//捕获2号SIGINT信号if(signal(2,handler) == SIG_ERR){perror("signal");return -1;}printf("捕获2号信号成功\n");//捕获3号SIGINT信号if(signal(3,handler) == SIG_ERR){perror("signal");return -1;}printf("捕获3号信号成功\n");//捕获20号SIGINT信号if(signal(20,handler) == SIG_ERR){perror("signal");return -1;}printf("捕获20号信号成功\n");while(1){printf("this is main func\n");sleep(1);}return 0;
}
三、课后作业:
1.要求实现AB进程对话
A进程先发送一句话给B进程,B进程接收后打印
B进程再回复一句话给A进程,A进程接收后打印
重复1.2步骤,当收到quit后,要结束AB进程
提示:两根管道
A进程:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <head.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//创建有名管道if(mkfifo("./fifo",0664) < 0){//printf("%d\n",errno);if(errno != 17) //17:文件已经存在错误,这是一个允许存在的错误,忽略该错误{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("mkfifo success\n");if(mkfifo("./fifo1",0664) < 0){//printf("%d\n",errno);if(errno != 17) //17:文件已经存在错误,这是一个允许存在的错误,忽略该错误{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("mkfifo1 success\n");int fd_r= open("./fifo",O_RDONLY);if(fd_r < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open success fd_r = %d\n",fd_r);int fd_w = open("./fifo1",O_WRONLY);if(fd_w < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open success fd_w= %d\n",fd_w);//从管道中读取数据,打印到终端上char buf[128]="";ssize_t res = 0;while(1){bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));//当管道的读写端均存在,若管道中没有数据,则read函数阻塞res = read(fd_r,buf,sizeof(buf));if(strcmp(buf,"quit") == 0){write(fd_w,buf,sizeof(buf));break;}if(res < 0){perror("read");return -1;}if(0 == res){printf("写端关闭\n");break;}printf("res =%ld\n输出:%s\n",res,buf);bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));printf("请输入:");fgets(buf, sizeof(buf),stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0';if(write(fd_w,buf,sizeof(buf))< 0){perror("write");return -1;}printf("写入数据成功 res =%ld\n",res);}close(fd_r);close(fd_w);return 0;
}
B进程:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <head.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//创建有名管道if(mkfifo("./fifo",0664) < 0){//printf("%d\n",errno);if(errno != 17) //17:文件已经存在错误,这是一个允许存在的错误,忽略该错误{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("mkfifo success\n");if(mkfifo("./fifo1",0664) < 0){//printf("%d\n",errno);if(errno != 17) //17:文件已经存在错误,这是一个允许存在的错误,忽略该错误{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("mkfifo1 success\n");int fd_w = open("./fifo",O_WRONLY);if(fd_w < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open success fd_w= %d\n",fd_w);int fd_r= open("./fifo1",O_RDONLY); if(fd_r < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open success fd_r = %d\n",fd_r);//从终端获取数据,写到管道中char buf[128]="";ssize_t res = 0;while(1){bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));printf("请输入:");fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0';if(strcmp(buf,"quit") == 0){write(fd_w,buf,sizeof(buf));break;}if(write(fd_w,buf,sizeof(buf)) < 0){perror("write");return -1;}printf("写入数据成功 res =%ld\n",res);bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));//当管道的读写端均存在,若管道中没有数据,则read函数阻塞res = read(fd_r,buf,sizeof(buf));if(res < 0){perror("read");return -1;}if(0 == res){printf("写端关闭\n");break;}printf("res =%ld\n输出:%s\n",res,buf);}close(fd_w);close(fd_r);return 0;
}
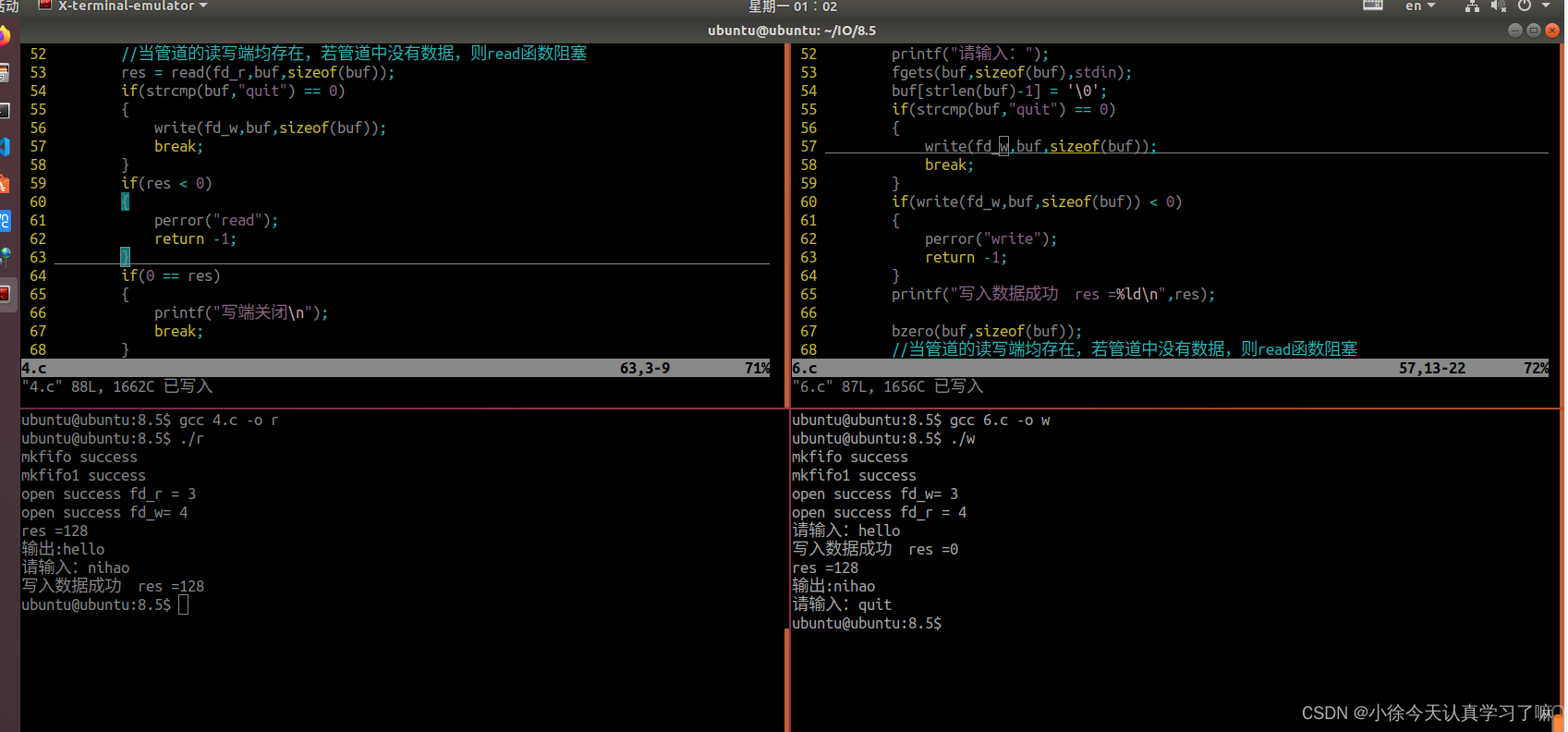
2.在第1题的基础上实现,A能随时发信息给B,B能随时接收A发送的数据,反之亦然。
A进程:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <signal.h>int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{if(mkfifo("./fifo", 0775) < 0) //当前进程写该管道{if(17 != errno) //#define EEXIST 17{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("fifo create success\n");if(mkfifo("./fifo1", 0775) < 0) //当前进程读该管道{if(17 != errno) //#define EEXIST 17{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("fifo1 create success\n");//创建一个子进程pid_t cpid = fork();if(cpid > 0){//读 fifo1int fd_r = open("./fifo1", O_RDONLY); //阻塞if(fd_r < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open fifo rdonly success __%d__\n", __LINE__);ssize_t res = 0;char buf[128] = "";while(1){bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));//读写段均存在,且管道中没有数据,该函数阻塞res = read(fd_r, buf, sizeof(buf));if(res < 0){perror("read");return -1;}else if(0 == res){printf("对端进程退出\n");break; }printf("res=%ld : buf=%s\n", res, buf);if(!strcmp(buf, "quit"))break;}close(fd_r);kill(cpid, 9);wait(NULL);}else if(0 == cpid){//写 fifoint fd_w = open("./fifo", O_WRONLY); //阻塞if(fd_w < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open fifo wronly success __%d__\n", __LINE__);char buf[128] = "";while(1){bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));// printf("请输入>>>");fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1] = 0;if(write(fd_w, buf, sizeof(buf)) < 0){perror("write");return -1;}// printf("写入成功\n");if(!strcmp(buf, "quit"))break;}close(fd_w);kill(getppid() , 9);}else{perror("fork");return -1;}return 0;
}
B进程:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <signal.h>int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{if(mkfifo("./fifo", 0775) < 0) //当前进程写该管道{if(17 != errno) //#define EEXIST 17{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("fifo create success\n");if(mkfifo("./fifo1", 0775) < 0) //当前进程读该管道{if(17 != errno) //#define EEXIST 17{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("fifo1 create success\n");//创建一个子进程pid_t cpid = fork();if(cpid > 0){//读 fifoint fd_r = open("./fifo", O_RDONLY); //阻塞if(fd_r < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open fifo rdonly success __%d__\n", __LINE__);ssize_t res = 0;char buf[128] = "";while(1){bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));//读写段均存在,且管道中没有数据,该函数阻塞res = read(fd_r, buf, sizeof(buf));if(res < 0){perror("read");return -1;}else if(0 == res){printf("对端进程退出\n");break; }printf("res=%ld : buf=%s\n", res, buf);if(!strcmp(buf, "quit"))break;}close(fd_r);kill(cpid, 9);wait(NULL);}else if(0 == cpid){//写 fifo1int fd_w = open("./fifo1", O_WRONLY); //阻塞if(fd_w < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open fifo wronly success __%d__\n", __LINE__);char buf[128] = "";while(1){bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));//printf("请输入>>>");fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1] = 0;if(write(fd_w, buf, sizeof(buf)) < 0){perror("write");return -1;}// printf("写入成功\n");if(!strcmp(buf, "quit"))break;}close(fd_w);kill(getppid() , 9);}else{perror("fork");return -1;}return 0;
}

相关文章:

IO进程线程day8(2023.8.6)
一、Xmind整理: 管道的原理: 有名管道的特点: 信号的原理: 二、课上练习: 练习1:pipe 功能:创建一个无名管道,同时打开无名管道的读写端 原型: #include <unist…...
【5G NR】逻辑信道、传输信道和物理信道的映射关系
博主未授权任何人或组织机构转载博主任何原创文章,感谢各位对原创的支持! 博主链接 本人就职于国际知名终端厂商,负责modem芯片研发。 在5G早期负责终端数据业务层、核心网相关的开发工作,目前牵头6G算力网络技术标准研究。 博客…...

tmux基础教程
tmux基础教程 Mac安装 brew install tmuxubuntu安装 sudo apt-get install tmux入门使用 会话 (Session) Ctrlb d: 分离当前会话。Ctrlb s: 列出所有会话。Ctrlb $: 重命名当前会话。 窗口(Window) Ctrlb c: 创建一个新窗口, 状态栏会显示多个窗…...
项目实战 — 消息队列(4){消息持久化}
目录 一、消息存储格式设计 🍅 1、queue_data.txt:保存消息的内容 🍅 2、queue_stat.txt:保存消息的统计信息 二、消息序列化 三、自定义异常类 四、创建MessageFileManger类 🍅 1、约定消息文件所在的目录和文件名…...

AI编程工具Copilot与Codeium的实测对比
csdn原创谢绝转载 简介 现在没有AI编程工具,效率会打一个折扣,如果还没有,赶紧装起来. GitHub Copilot是OpenAi与github等共同开发的的AI辅助编程工具,基于ChatGPT驱动,功能强大,这个没人怀疑…...
webpack基础知识六:说说webpack的热更新是如何做到的?原理是什么?
一、是什么 HMR全称 Hot Module Replacement,可以理解为模块热替换,指在应用程序运行过程中,替换、添加、删除模块,而无需重新刷新整个应用 例如,我们在应用运行过程中修改了某个模块,通过自动刷新会导致…...

Linux从安装到实战 常用命令 Bash常用功能 用户和组管理
1.0初识Linux 1.1虚拟机介绍 1.2VMware Workstation虚拟化软件 下载CentOS; 1.3远程链接Linux系统 &FinalShell 链接finalshell半天没连接进去 他说ip adress 看IP地址是在虚拟机上 win11主机是 终端输入: ifconfig VMware虚拟机的设置 & ssh连接_snge…...
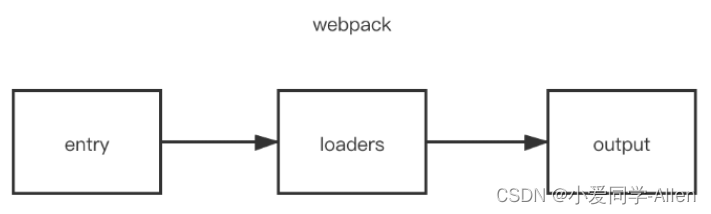
webpack基础知识三:说说webpack中常见的Loader?解决了什么问题?
一、是什么 loader 用于对模块的"源代码"进行转换,在 import 或"加载"模块时预处理文件 webpack做的事情,仅仅是分析出各种模块的依赖关系,然后形成资源列表,最终打包生成到指定的文件中。如下图所示&#…...

深度学习:Pytorch常见损失函数Loss简介
深度学习:Pytorch常见损失函数Loss简介 L1 LossMSE LossSmoothL1 LossCrossEntropy LossFocal Loss 此篇博客主要对深度学习中常用的损失函数进行介绍,并结合Pytorch的函数进行分析,讲解其用法。 L1 Loss L1 Loss计算预测值和真值的平均绝对…...

【Android-java】Parcelable 是什么?
Parcelable 是 Android 中的一个接口,用于实现将对象序列化为字节流的功能,以便在不同组件之间传递。与 Java 的 Serializable 接口不同,Parcelable 的性能更高,适用于 Android 平台。 要实现 Parcelable 接口,我们需…...
)
Spring整合MyBatis小实例(转账功能)
实现步骤 一,引入依赖 <!--仓库--><repositories><!--spring里程碑版本的仓库--><repository><id>repository.spring.milestone</id><name>Spring Milestone Repository</name><url>https://repo.spring.i…...
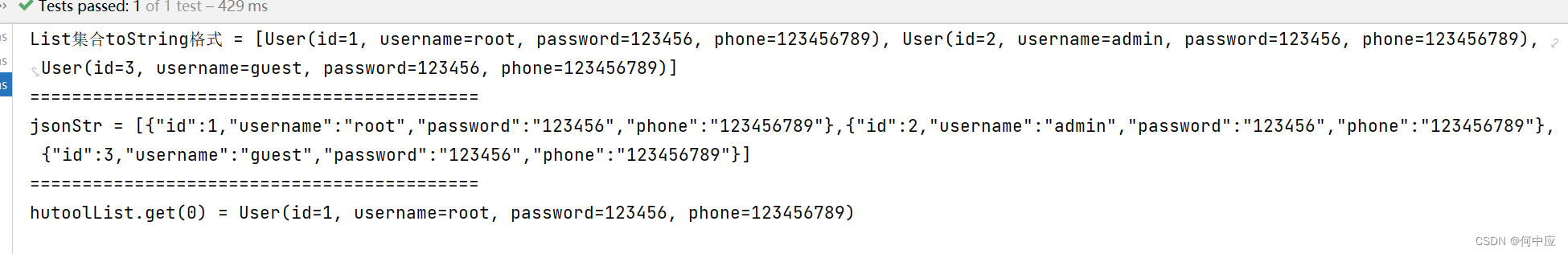
List集合的对象传输的两种方式
说明:在一些特定的情况,我们需要把对象中的List集合属性存入到数据库中,之后把该字段取出来转为List集合的对象使用(如下图) 自定义对象 public class User implements Serializable {/*** ID*/private Integer id;/*…...

海外媒体发稿:软文写作方法方式?一篇好的软文理应合理规划?
不同种类的软文会有不同的方式,下面小编就来来给大家分析一下: 方法一、要选定文章的突破点: 所说突破点就是这篇文章文章软文理应以什么样的视角、什么样的见解、什么样的语言设计理念、如何文章文章的标题来写。不同种类的传播效果&#…...
【秋招】算法岗的八股文之机器学习
目录 机器学习特征工程常见的计算模型总览线性回归模型与逻辑回归模型线性回归模型逻辑回归模型区别 朴素贝叶斯分类器模型 (Naive Bayes)决策树模型随机森林模型支持向量机模型 (Support Vector Machine)K近邻模型神经网络模型卷积神经网络(CNN)循环神经…...
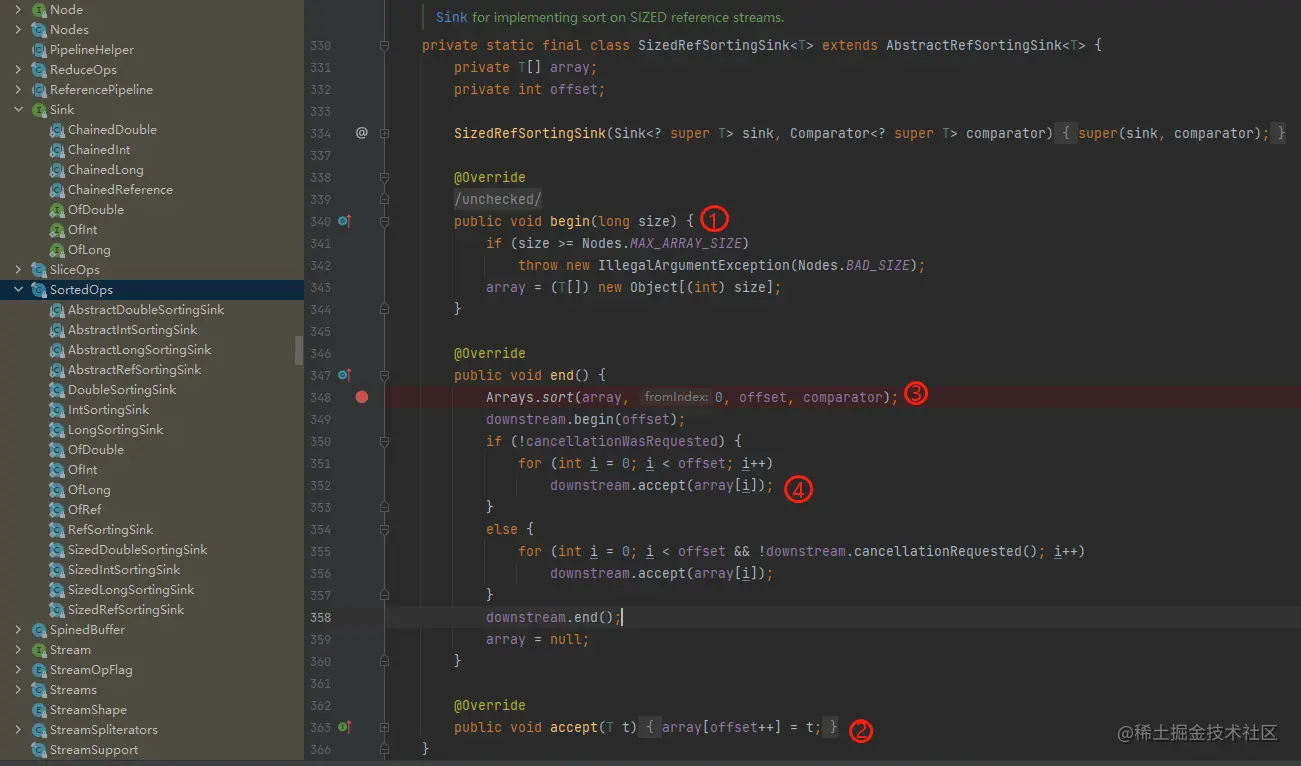
为什么list.sort()比Stream().sorted()更快?
真的更好吗? 先简单写个demo List<Integer> userList new ArrayList<>();Random rand new Random();for (int i 0; i < 10000 ; i) {userList.add(rand.nextInt(1000));}List<Integer> userList2 new ArrayList<>();userList2.add…...

SQL账户SA登录失败,提示错误:18456
错误代码 18456 表示 SQL Server 登录失败。这个错误通常表示提供的凭据(用户名和密码)无法成功验证或者没有权限访问所请求的数据库。以下是一些常见的可能原因和解决方法: 1.错误的凭据:请确认提供的SA账户的用户名和密码是否正…...
Linux 终端操作命令(1)
Linux 命令 终端命令格式 command [-options] [parameter] 说明: command:命令名,相应功能的英文单词或单词的缩写[-options]:选项,可用来对命令进行控制,也可以省略parameter:传给命令的参…...

java与javaw运行jar程序
运行jar程序 一、java.exe启动jar程序 (会显示console黑窗口) 1、一般用法: java -jar myJar.jar2、重命名进程名称启动: echo off copy "%JAVA_HOME%\bin\java.exe" "%JAVA_HOME%\bin\myProcess.exe" myProcess -jar myJar.jar e…...

安装和配置 Home Assistant 教程 HACS Homkit 米家等智能设备接入
安装和配置 Home Assistant 教程 简介 Home Assistant 是一款开源的智能家居自动化平台,可以帮助你集成和控制各种智能设备,从灯光到温度调节器,从摄像头到媒体播放器。本教程将引导你如何在 Docker 环境中安装和配置 Home Assistant&#…...

解决 Android Studio 的 Gradle 面板上只有关于测试的 task 的问题
文章目录 问题描述解决办法 笔者出问题时的运行环境: Android Studio Flamingo | 2022.2.1 Android SDK 33 Gradle 8.0.1 JDK 17 问题描述 笔者最近发现一个奇怪的事情。笔者的 Android Studio 的 Gradle 面板上居然除了用于测试的 task 之外,其它什…...
使用VSCode开发Django指南
使用VSCode开发Django指南 一、概述 Django 是一个高级 Python 框架,专为快速、安全和可扩展的 Web 开发而设计。Django 包含对 URL 路由、页面模板和数据处理的丰富支持。 本文将创建一个简单的 Django 应用,其中包含三个使用通用基本模板的页面。在此…...

【杂谈】-递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战
递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战 文章目录 递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战1、自我改进型人工智能的崛起2、人工智能如何挑战人类监管?3、确保人工智能受控的策略4、人类在人工智能发展中的角色5、平衡自主性与控制力6、总结与…...

【SpringBoot】100、SpringBoot中使用自定义注解+AOP实现参数自动解密
在实际项目中,用户注册、登录、修改密码等操作,都涉及到参数传输安全问题。所以我们需要在前端对账户、密码等敏感信息加密传输,在后端接收到数据后能自动解密。 1、引入依赖 <dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId...

Python爬虫实战:研究feedparser库相关技术
1. 引言 1.1 研究背景与意义 在当今信息爆炸的时代,互联网上存在着海量的信息资源。RSS(Really Simple Syndication)作为一种标准化的信息聚合技术,被广泛用于网站内容的发布和订阅。通过 RSS,用户可以方便地获取网站更新的内容,而无需频繁访问各个网站。 然而,互联网…...
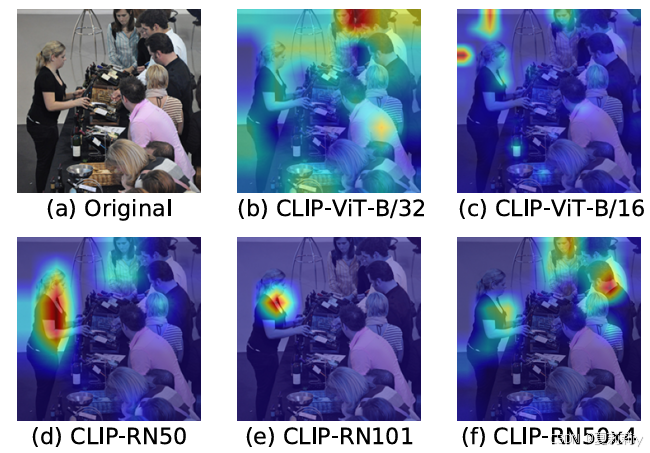

[ICLR 2022]How Much Can CLIP Benefit Vision-and-Language Tasks?
论文网址:pdf 英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用 目录 1. 心得 2. 论文逐段精读 2.1. Abstract 2…...
微信小程序云开发平台MySQL的连接方式
注:微信小程序云开发平台指的是腾讯云开发 先给结论:微信小程序云开发平台的MySQL,无法通过获取数据库连接信息的方式进行连接,连接只能通过云开发的SDK连接,具体要参考官方文档: 为什么? 因为…...

【JavaSE】绘图与事件入门学习笔记
-Java绘图坐标体系 坐标体系-介绍 坐标原点位于左上角,以像素为单位。 在Java坐标系中,第一个是x坐标,表示当前位置为水平方向,距离坐标原点x个像素;第二个是y坐标,表示当前位置为垂直方向,距离坐标原点y个像素。 坐标体系-像素 …...
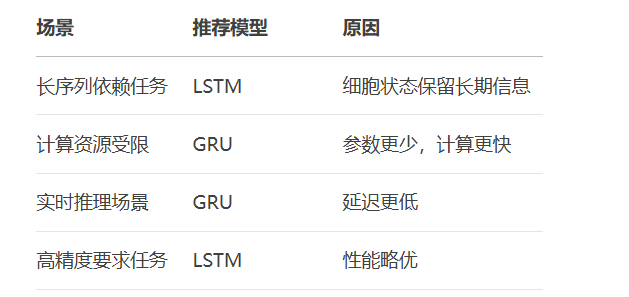
RNN避坑指南:从数学推导到LSTM/GRU工业级部署实战流程
本文较长,建议点赞收藏,以免遗失。更多AI大模型应用开发学习视频及资料,尽在聚客AI学院。 本文全面剖析RNN核心原理,深入讲解梯度消失/爆炸问题,并通过LSTM/GRU结构实现解决方案,提供时间序列预测和文本生成…...
SiFli 52把Imagie图片,Font字体资源放在指定位置,编译成指定img.bin和font.bin的问题
分区配置 (ptab.json) img 属性介绍: img 属性指定分区存放的 image 名称,指定的 image 名称必须是当前工程生成的 binary 。 如果 binary 有多个文件,则以 proj_name:binary_name 格式指定文件名, proj_name 为工程 名&…...

Go 语言并发编程基础:无缓冲与有缓冲通道
在上一章节中,我们了解了 Channel 的基本用法。本章将重点分析 Go 中通道的两种类型 —— 无缓冲通道与有缓冲通道,它们在并发编程中各具特点和应用场景。 一、通道的基本分类 类型定义形式特点无缓冲通道make(chan T)发送和接收都必须准备好࿰…...

