2023牛客第七场补题报告C F L M
2023牛客第七场补题报告C F L M
C-Beautiful Sequence_2023牛客暑期多校训练营7 (nowcoder.com)
思路
观察到数组一定是递增的,所以从最高位往下考虑每位的1最多只有一个,然后按位枚举贪心即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
void solve();
signed main(){cin.sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);int T = 1;cin >> T;while(T--){solve();}return 0;
}const int N = 1e6 + 5;
bool bit[N][32];
int nok[32][2];
void dfs(int l, int r, int d){//cout << " " << d << " " << l << " " << r << "\n";if(d < 0 || l >= r)return;int conv = 0;int id = l - 1;for(int i = l;i < r;i++){if(bit[i][d] != bit[i + 1][d]){id = i;conv++;}}if(conv > 1){nok[d][0] = 1;nok[d][1] = 1;return;} else if(conv == 1){if(bit[l][d] == 0){nok[d][1] = 1;}else{nok[d][0] = 1;}dfs(l, id, d - 1);dfs(id + 1, r, d - 1);}else{dfs(l, r, d - 1);}}
void solve(){int n,k;cin >> n >> k;vector<int> b(n + 1);for(int i = 1;i < n;i ++) {cin >> b[i];} for(int i = 0;i <= 30;i++){nok[i][0] = 0;nok[i][1] = 0;}for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++) {for(int j = 0;j <= 30;j ++) {if(i == 1){bit[i][j] = 0;}else{bit[i][j] = (bit[i - 1][j] ^ ((b[i - 1] >> j) & 1));}}}dfs(1, n, 30);for(int i = 0;i < 30;i++){if(nok[i][0] == 1 && nok[i][1] == 1){cout << "-1\n";return;}}long long rag = 1;for(int i = 0;i <= 30;i++){if(nok[i][0] == 0 && nok[i][1] == 0){rag <<= 1;}}if(rag < k){cout << "-1\n";}else{k--;long long ans = 0;for(int i = 0, kk = 0;i <= 30;i++){if(nok[i][0] == 0 && nok[i][1] == 0){if((k >> kk) & 1){ans |= 1 << i;}kk++;}else if(nok[i][1] == 0){ans |= 1 << i;}}if(ans >= (1ll << 30)){cout << "-1\n";}else{cout << ans << " ";for(int i = 1;i < n;i++){ans = ans ^ b[i];cout << ans << " ";}cout << "\n";}}
}
F-Counting Sequences_2023牛客暑期多校训练营7 (nowcoder.com)
思路
考虑到数据范围很大,先想的dp会t,可以使用多项式乘法,n次幂乘以m次幂就可以变换为n+m,此时直接输出多项式幂次的第k项即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;void solve();int main(){cin.sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);int T = 1;//cin >> T;while(T--){solve();}return 0;
}constexpr int P = 998244353;
using i64 = long long;
// assume -P <= x < 2P
int norm(int x) {if (x < 0) {x += P;}if (x >= P) {x -= P;}return x;
}
template<class T>
T power(T a, int b) {T res = 1;for (; b; b /= 2, a *= a) {if (b % 2) {res *= a;}}return res;
}struct Z {int x;Z(int x = 0) : x(norm(x)) {}int val() const {return x;}Z operator-() const {return Z(norm(P - x));}Z inv() const {assert(x != 0);return power(*this, P - 2);}Z &operator*=(const Z &rhs) {x = i64(x) * rhs.x % P;return *this;}Z &operator+=(const Z &rhs) {x = norm(x + rhs.x);return *this;}Z &operator-=(const Z &rhs) {x = norm(x - rhs.x);return *this;}Z &operator/=(const Z &rhs) {return *this *= rhs.inv();}friend Z operator*(const Z &lhs, const Z &rhs) {Z res = lhs;res *= rhs;return res;}friend Z operator+(const Z &lhs, const Z &rhs) {Z res = lhs;res += rhs;return res;}friend Z operator-(const Z &lhs, const Z &rhs) {Z res = lhs;res -= rhs;return res;}friend Z operator/(const Z &lhs, const Z &rhs) {Z res = lhs;res /= rhs;return res;}friend std::istream &operator>>(std::istream &is, Z &a) {i64 v;is >> v;a = Z(v);return is;}friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Z &a) {return os << a.val();}
};std::vector<int> rev;
std::vector<Z> roots{0, 1};
void dft(std::vector<Z> &a) {int n = a.size();if (int(rev.size()) != n) {int k = __builtin_ctz(n) - 1;rev.resize(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {rev[i] = rev[i >> 1] >> 1 | (i & 1) << k;}}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if (rev[i] < i) {std::swap(a[i], a[rev[i]]);}}if (int(roots.size()) < n) {int k = __builtin_ctz(roots.size());roots.resize(n);while ((1 << k) < n) {Z e = power(Z(3), (P - 1) >> (k + 1));for (int i = 1 << (k - 1); i < (1 << k); i++) {roots[2 * i] = roots[i];roots[2 * i + 1] = roots[i] * e;}k++;}}for (int k = 1; k < n; k *= 2) {for (int i = 0; i < n; i += 2 * k) {for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {Z u = a[i + j];Z v = a[i + j + k] * roots[k + j];a[i + j] = u + v;a[i + j + k] = u - v;}}}
}
void idft(std::vector<Z> &a) {int n = a.size();std::reverse(a.begin() + 1, a.end());dft(a);Z inv = (1 - P) / n;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {a[i] *= inv;}
}
struct Poly {std::vector<Z> a;Poly() {}Poly(const std::vector<Z> &a) : a(a) {}Poly(const std::initializer_list<Z> &a) : a(a) {}int size() const {return a.size();}void resize(int n) {a.resize(n);}Z operator[](int idx) const {if (idx < size()) {return a[idx];} else {return 0;}}Z &operator[](int idx) {return a[idx];}Poly mulxk(int k) const {auto b = a;b.insert(b.begin(), k, 0);return Poly(b);}Poly modxk(int k) const {k = std::min(k, size());return Poly(std::vector<Z>(a.begin(), a.begin() + k));}Poly divxk(int k) const {if (size() <= k) {return Poly();}return Poly(std::vector<Z>(a.begin() + k, a.end()));}friend Poly operator+(const Poly &a, const Poly &b) {std::vector<Z> res(std::max(a.size(), b.size()));for (int i = 0; i < int(res.size()); i++) {res[i] = a[i] + b[i];}return Poly(res);}friend Poly operator-(const Poly &a, const Poly &b) {std::vector<Z> res(std::max(a.size(), b.size()));for (int i = 0; i < int(res.size()); i++) {res[i] = a[i] - b[i];}return Poly(res);}friend Poly operator*(Poly a, Poly b) {if (a.size() == 0 || b.size() == 0) {return Poly();}int sz = 1, tot = a.size() + b.size() - 1;while (sz < tot) {sz *= 2;}a.a.resize(sz);b.a.resize(sz);dft(a.a);dft(b.a);for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) {a.a[i] = a[i] * b[i];}idft(a.a);a.resize(tot);return a;}friend Poly operator*(Z a, Poly b) {for (int i = 0; i < int(b.size()); i++) {b[i] *= a;}return b;}friend Poly operator*(Poly a, Z b) {for (int i = 0; i < int(a.size()); i++) {a[i] *= b;}return a;}Poly &operator+=(Poly b) {return (*this) = (*this) + b;}Poly &operator-=(Poly b) {return (*this) = (*this) - b;}Poly &operator*=(Poly b) {return (*this) = (*this) * b;}Poly deriv() const {if (a.empty()) {return Poly();}std::vector<Z> res(size() - 1);for (int i = 0; i < size() - 1; ++i) {res[i] = (i + 1) * a[i + 1];}return Poly(res);}Poly integr() const {std::vector<Z> res(size() + 1);for (int i = 0; i < size(); ++i) {res[i + 1] = a[i] / (i + 1);}return Poly(res);}Poly inv(int m) const {Poly x{a[0].inv()};int k = 1;while (k < m) {k *= 2;x = (x * (Poly{2} - modxk(k) * x)).modxk(k);}return x.modxk(m);}Poly log(int m) const {return (deriv() * inv(m)).integr().modxk(m);}Poly exp(int m) const {Poly x{1};int k = 1;while (k < m) {k *= 2;x = (x * (Poly{1} - x.log(k) + modxk(k))).modxk(k);}return x.modxk(m);}Poly pow(int k, int m) const {int i = 0;while (i < size() && a[i].val() == 0) {i++;}if (i == size() || 1LL * i * k >= m) {return Poly(std::vector<Z>(m));}Z v = a[i];auto f = divxk(i) * v.inv();return (f.log(m - i * k) * k).exp(m - i * k).mulxk(i * k) * power(v, k);}Poly sqrt(int m) const {Poly x{1};int k = 1;while (k < m) {k *= 2;x = (x + (modxk(k) * x.inv(k)).modxk(k)) * ((P + 1) / 2);}return x.modxk(m);}Poly mulT(Poly b) const {if (b.size() == 0) {return Poly();}int n = b.size(); // eb + 1std::reverse(b.a.begin(), b.a.end());return ((*this) * b).divxk(n - 1); //保留系数(x ^ eb)及以上的}std::vector<Z> eval(std::vector<Z> x) const {if (size() == 0) {return std::vector<Z>(x.size(), 0);}const int n = std::max(int(x.size()), size());std::vector<Poly> q(4 * n);std::vector<Z> ans(x.size());x.resize(n);std::function<void(int, int, int)> build = [&](int p, int l, int r) {if (r - l == 1) {q[p] = Poly{1, -x[l]};} else {int m = (l + r) / 2;build(2 * p, l, m);build(2 * p + 1, m, r);q[p] = q[2 * p] * q[2 * p + 1];}};build(1, 0, n);std::function<void(int, int, int, const Poly &)> work = [&](int p, int l, int r, const Poly &num) {if (r - l == 1) {if (l < int(ans.size())) {ans[l] = num[0];}} else {int m = (l + r) / 2;work(2 * p, l, m, num.mulT(q[2 * p + 1]).modxk(m - l));work(2 * p + 1, m, r, num.mulT(q[2 * p]).modxk(r - m));}};work(1, 0, n, mulT(q[1].inv(n)));return ans;}
};void solve(){int n, m, k;cin >> n >> m >> k;vector<Z> a(k + 1);a[0] = 1;int R = min(n, k);for(int i = 1;i <= R;i++){a[i] = a[i - 1] * (n - i + 1) / i;}for(int i = 1;i <= R;i+=2){a[i] = 0;}for(int i = 0;i <= R;i+=2){a[i] *= 2;}auto c = Poly(a).pow(m,k + 1);cout << c[k] << "\n";
}
L-Misaka Mikoto’s Dynamic KMP Problem_2023牛客暑期多校训练营7 (nowcoder.com)
思路
注意到|s|>|t|时出现次数必定为0,所以该询问的 x i × y i = 0 x_i×y_i=0 xi×yi=0。而当 ∣ s ∣ ≤ ∣ t ∣ |s| \leq |t| ∣s∣≤∣t∣直接暴力跑KMP求出现次数和最长border即可。单轮复杂度O(t)。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;template<class T>
class KMP {int m;T p;public:vector<int> nxt;KMP() {}KMP(const T &_p) { init(_p); }void init(const T &_p) {m = _p.size() - 1;p = _p;nxt.assign(m + 1, 0);for (int i = 2;i <= m;i++) {nxt[i] = nxt[i - 1];while (nxt[i] && p[i] != p[nxt[i] + 1]) nxt[i] = nxt[nxt[i]];nxt[i] += p[i] == p[nxt[i] + 1];}}vector<int> find(const T &s) {int n = s.size() - 1;vector<int> pos;for (int i = 1, j = 0;i <= n;i++) {while (j && s[i] != p[j + 1]) j = nxt[j];j += s[i] == p[j + 1];if (j == m) {pos.push_back(i - j + 1);j = nxt[j];}}return pos;}vector<int> get_cycle_time() {vector<int> res;int pos = m;while (pos) {pos = nxt[pos];res.push_back(m - pos);}return res;}vector<int> get_cycle_loop() {vector<int> res;for (auto val : get_cycle_time())if (!(m % val)) res.push_back(val);return res;}int min_cycle_loop() { return get_cycle_loop()[0]; }void debug() {for (int i = 1;i <= m;i++)cout << nxt[i] << " \n"[i == m];}
};
/// KMP,前缀函数O(|P|)、查找O(|S|+|P|)、循环相关O(|P|),维护字符串前缀函数int main() {std::ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);int n, q, b, p;cin >> n >> q >> b >> p;vector<int> s(n + 1);for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++) cin >> s[i];ll z = 0;int mul = 1, ans = 0;while (q--) {int op;cin >> op;if (op == 1) {ll x, c;cin >> x >> c;x = (x ^ z) % n + 1;c ^= z;s[x] = c;}else {int m;cin >> m;vector<int> t(m + 1);for (int i = 1;i <= m;i++) {ll val;cin >> val;t[i] = val ^ z;}mul = 1LL * mul * b % p;if (m < n) z = 0;else {KMP<vector<int>> kmp(s);z = 1LL * kmp.nxt[n] * kmp.find(t).size();}ans = (ans + z % p * mul % p) % p;}}cout << ans << '\n';return 0;
}
M-Writing Books_2023牛客暑期多校训练营7 (nowcoder.com)
思路
直接枚举位数。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0)
#define fi first
#define sc secondusing namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int n;
int a[N];void solve() {cin >> n;int tmp = 1;int res = 0;int cnt = 1;while (n >= tmp) {int x = tmp;tmp *= 10;res += (min(n, tmp - 1) - x + 1) * cnt;cnt++;}cout << res << "\n";
}signed main() {IOS;int t = 1;cin >> t;for (int i = 1; i <= t; i++) {solve();}
}
相关文章:

2023牛客第七场补题报告C F L M
2023牛客第七场补题报告C F L M C-Beautiful Sequence_2023牛客暑期多校训练营7 (nowcoder.com) 思路 观察到数组一定是递增的,所以从最高位往下考虑每位的1最多只有一个,然后按位枚举贪心即可。 代码 #include <bits/stdc.h> using namespac…...
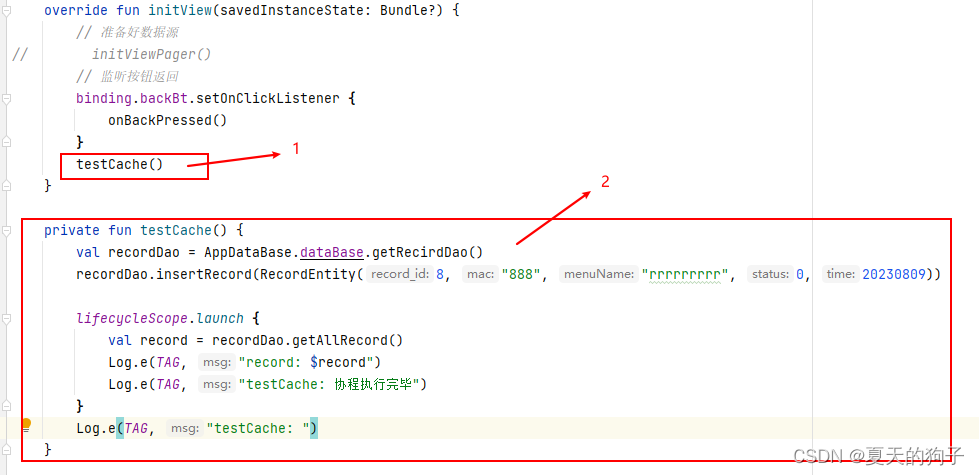
Android使用kotlin+协程+room数据库的简单应用
前言:一般主线程(UI线程)中是不能执行创建数据这些操作的,因为等待时间长。所以协程就是为了解决这个问题出现。 第一步:在模块级的build.gradle中引入 id com.android.application// roomid kotlin-androidid kotlin…...
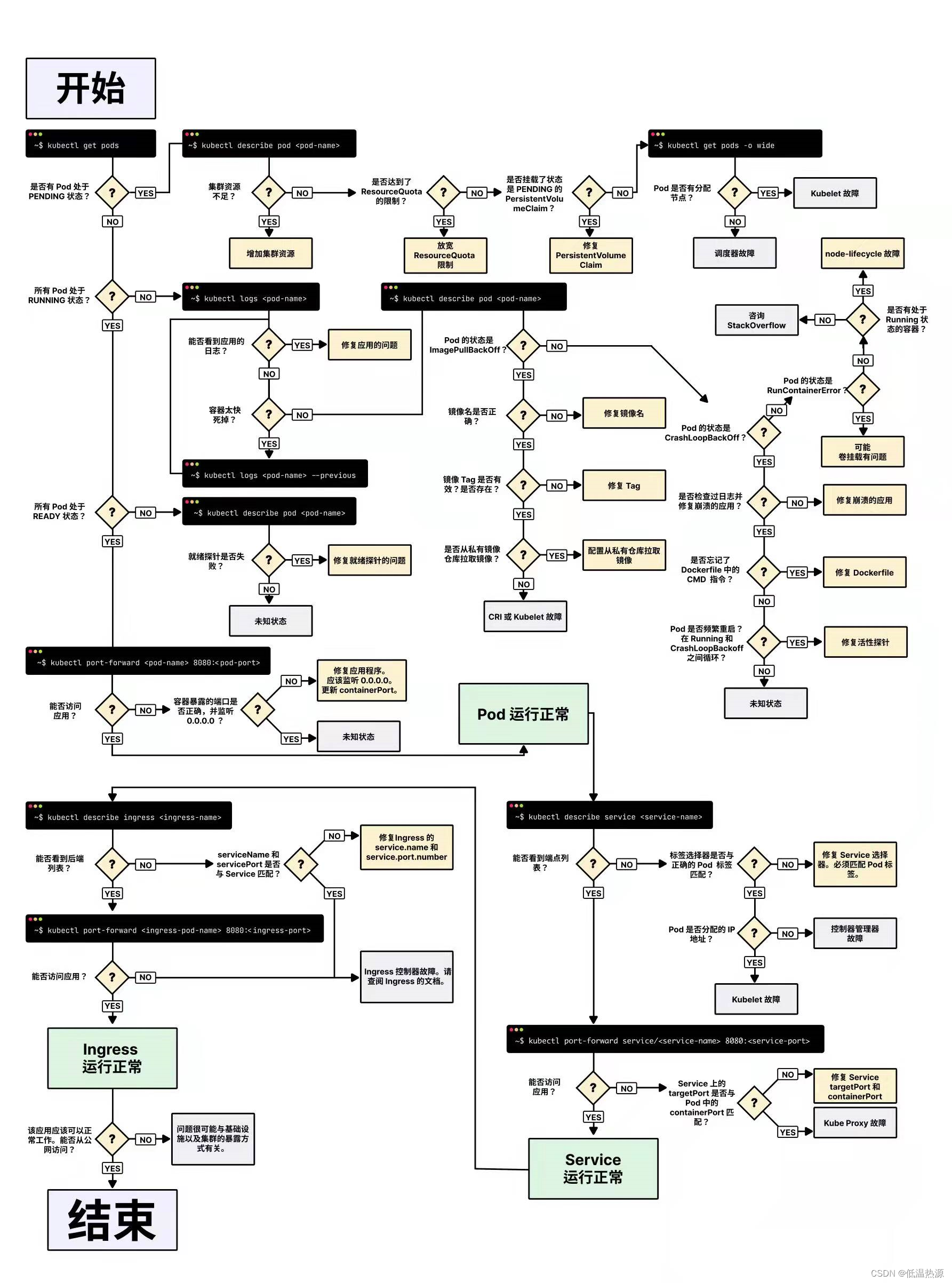
Kubernetes pod调度约束[亲和性 污点] 生命阶段 排障手段
调度约束 Kubernetes 是通过 List-Watch 的机制进行每个组件的协作,保持数据同步的,每个组件之间的设计实现了解耦。 用户是通过 kubectl 根据配置文件,向 APIServer 发送命令,在 Node 节点上面建立 Pod 和 Container。 APIServer…...
)
Matlab实现模拟退火算法(附上多个完整源码)
模拟退火算法(Simulated Annealing)是一种全局优化算法,其基本思想是通过模拟物理退火过程来寻找最优解。该算法可以应用于各种优化问题,如函数优化、组合优化、图形优化等。 文章目录 步骤简单案例完整仿真源码下载 步骤 在Mat…...
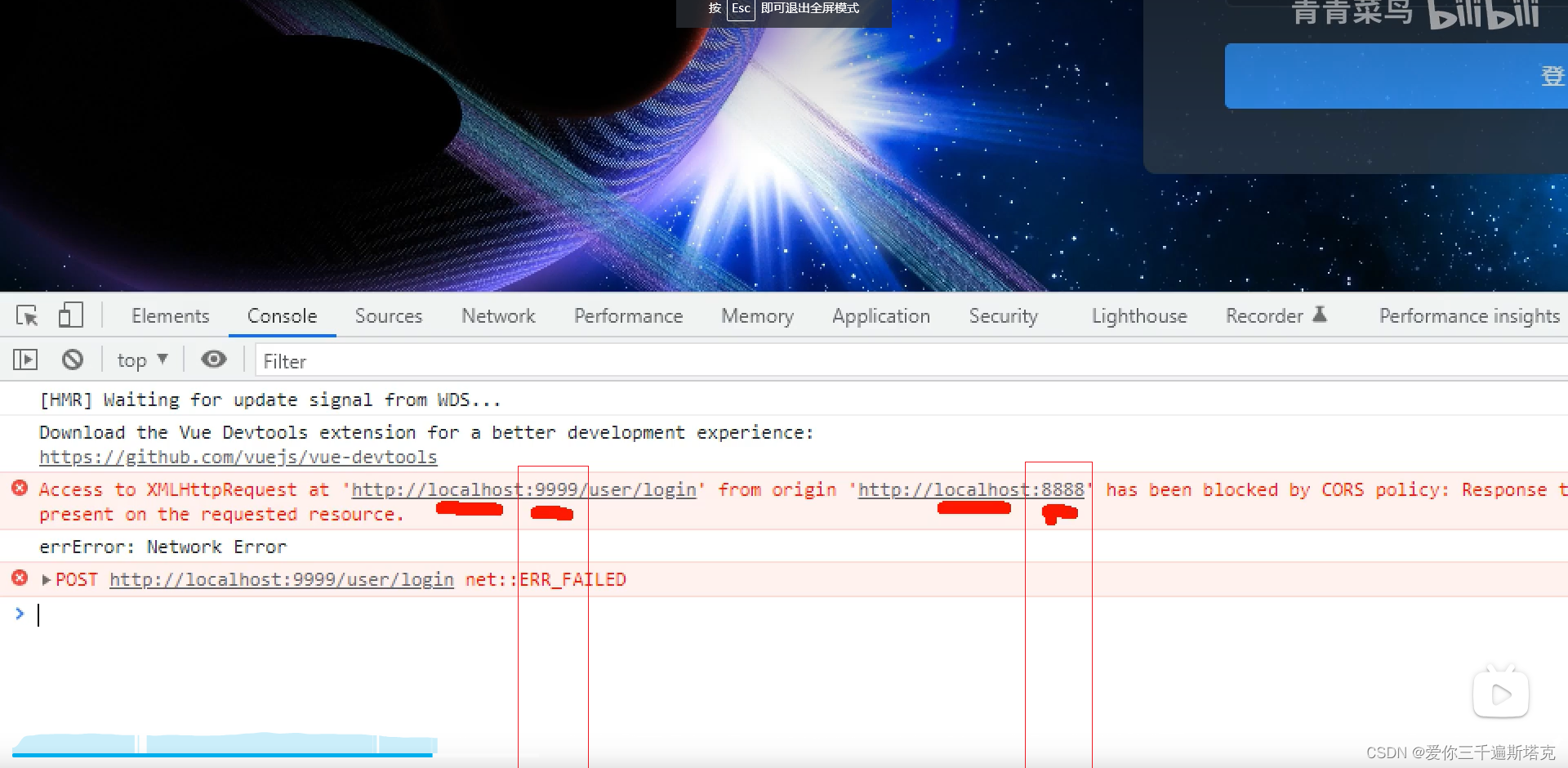
前后端分离------后端创建笔记(03)前后端对接(上)
本文章转载于【SpringBootVue】全网最简单但实用的前后端分离项目实战笔记 - 前端_大菜007的博客-CSDN博客 仅用于学习和讨论,如有侵权请联系 源码:https://gitee.com/green_vegetables/x-admin-project.git 素材:https://pan.baidu.com/s/…...

stable diffusion安装包和超火使用文档及提示词,数字人网址
一:文生图、图生图 1:stable diffusion:对喜欢二次元、美女小姐姐、大眼萌妹的人及其友好哈哈(o^^o) 1):关于安装包和模型包: 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/11_kguofh76gwhTBPUipepw 提取码…...

训练营:贪心篇
贪心就是:局部最优 1、455. 分发饼干 按照饼干分,从大到小,最大的给胃口最大能满足的 def findContentChildren455(g, s):g sorted(g,reverseTrue)s sorted(s,reverseTrue)j0c 0i0while(i<len(s) and j<len(g)):if s[i]>g[j]:c…...
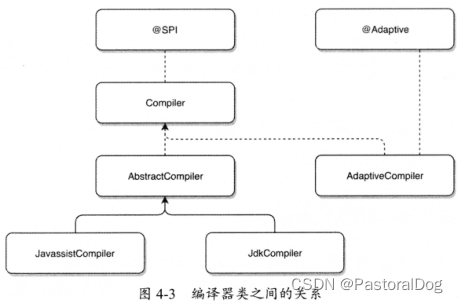
四、Dubbo扩展点加载机制
四、Dubbo扩展点加载机制 4.1 加载机制概述 Dubbo良好的扩展性与框架中针对不同场景使用合适设计模式、加载机制密不可分 Dubbo几乎所有功能组件都是基于扩展机制(SPI)实现的 Dubbo SPI 没有直接使用 Java SPI,在它思想上进行改进ÿ…...
[保研/考研机试] KY103 2的幂次方 上海交通大学复试上机题 C++实现
题目链接: KY103 2的幂次方 https://www.nowcoder.com/share/jump/437195121691999575955 描述 Every positive number can be presented by the exponential form.For example, 137 2^7 2^3 2^0。 Lets present a^b by the form a(b).Then 137 is present…...

时序预测 | MATLAB实现基于BP神经网络的时间序列预测-递归预测未来(多指标评价)
时序预测 | MATLAB实现基于BP神经网络的时间序列预测-递归预测未来(多指标评价) 目录 时序预测 | MATLAB实现基于BP神经网络的时间序列预测-递归预测未来(多指标评价)预测结果基本介绍程序设计参考资料 预测结果 基本介绍 Matlab实现BP神经网络时间序列预测未来(完整…...

组合模式(C++)
定义 将对象组合成树形结构以表示部分-整体’的层次结构。Composite使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性(稳定)。 应用场景 在软件在某些情况下,客户代码过多地依赖于对象容器复杂的内部实现结构,对象容器内部实现结构(而非抽象接口)的变化…...

git上传问题记录
unable to access ‘https://github.com/songjiahao-wq/untitled.git/’: Failed to connect to github.com port 443 after 21086 ms: Couldn’t connect to serve 解决办法:修改 Git 的网络设置 打开git Bash运行,clash代理一般是下面的端口 # 注意…...

通过动态IP解决网络数据采集问题
动态地址的作用 说到Python网络爬虫,很多人都会遇到困难。最常见的就是爬取过程中IP地址被屏蔽。虽然大部分都是几个小时内自动解封的,但这对于分秒必争的python网络爬虫来说,是一个关键性的打击!当一个爬虫被阻塞时,…...

可重入锁,不可重入锁,死锁的多种情况,以及产生的原因,如何解决,synchronized采用的锁策略(渣女圣经)自适应的底层,锁清除,锁粗化,CAS的部分应用
一、💛 锁策略——接上一篇 6.分为可重入锁,不可重入锁 如果一个线程,针对一把锁,连续加锁两次,会出现死锁,就是不可重入锁,不会出现死锁,就是可重入锁。 如果一个线程,针…...
和JSON.stringify()用法)
JSON.parse()和JSON.stringify()用法
JSON.parse() 方法用于将 JSON 格式的字符串转换为 JavaScript 对象,而 JSON.stringify() 方法用于将 JavaScript 对象转换为 JSON 字符串。这两个方法可以组合使用来实现将数据从对象到字符串再到对象的转换。 示例 // 创建一个包含属性的 JavaScript 对象 var pe…...
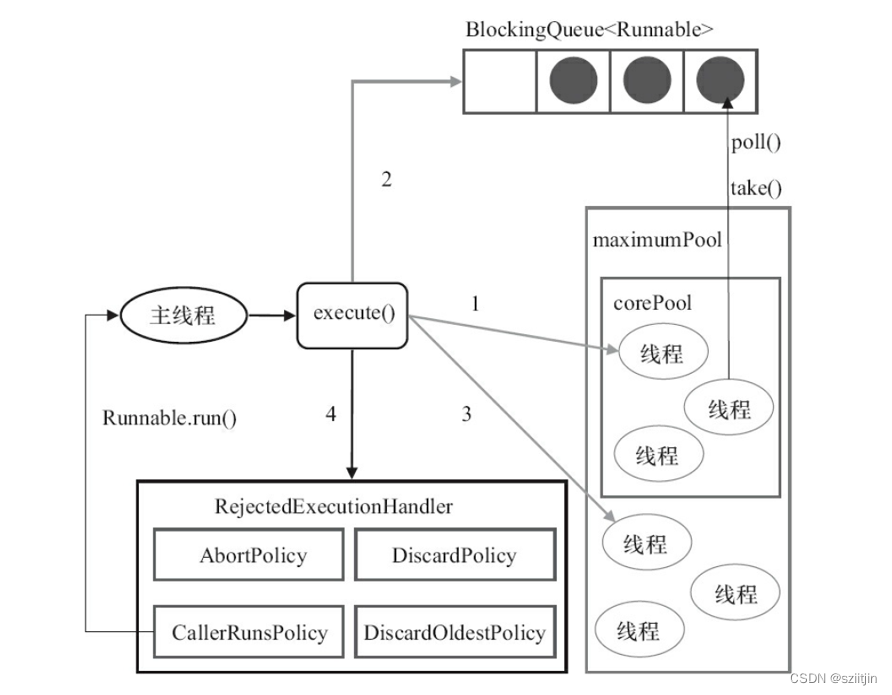
Android 并发编程--阻塞队列和线程池
一、阻塞队列 队列是一种特殊的线性表,特殊之处在于它只允许在表的前端(front)进行删除操作,而在表的后端(rear)进行插入操作,和栈一样,队列是一种操作受限制的线性表。进行插入操作…...

Playwright快速上手-1
前言 随着近年来对UI自动化测试的要求越来越高,,功能强大的测试框架也不断的涌现。本系列主讲的Playwright作为一款新兴的端到端测试框架,凭借其独特优势,正在逐渐成为测试工程师的热门选择。 本系列文章将着重通过示例讲解 Playwright python开发环境的搭建 …...
PPT颜色又丑又乱怎么办?
一、设计一套PPT时,可以从这5个方面进行设计 二、PPT颜色 (一)、PPT常用颜色分类 一个ppt需要主色、辅助色、字体色、背景色即可。 (二)、搭建PPT色彩系统 设计ppt时,根据如下几个步骤,依次选…...

python计算相关系数R
方法一: import numpy as np# 计算相关系数R def r(y_true, y_pred):y_true np.array(y_true)y_pred np.array(y_pred)corr np.corrcoef(y_true, y_pred)[0][1]return corrcorr r(yture, ypred)方法二 import scipy.stats # 计算皮尔逊相关指数,并…...

黑马项目一阶段面试 自我介绍篇
面试官你好,我叫xxx,是来自xxxx的本科毕业生。我通过招聘网站/内推/线下招聘了解到的贵司,我具有扎实的Java后端的基础功底,基本掌握JavaSE、JavaEE流行技术的使用,并且我比较好学,心态也很乐观积极&#x…...
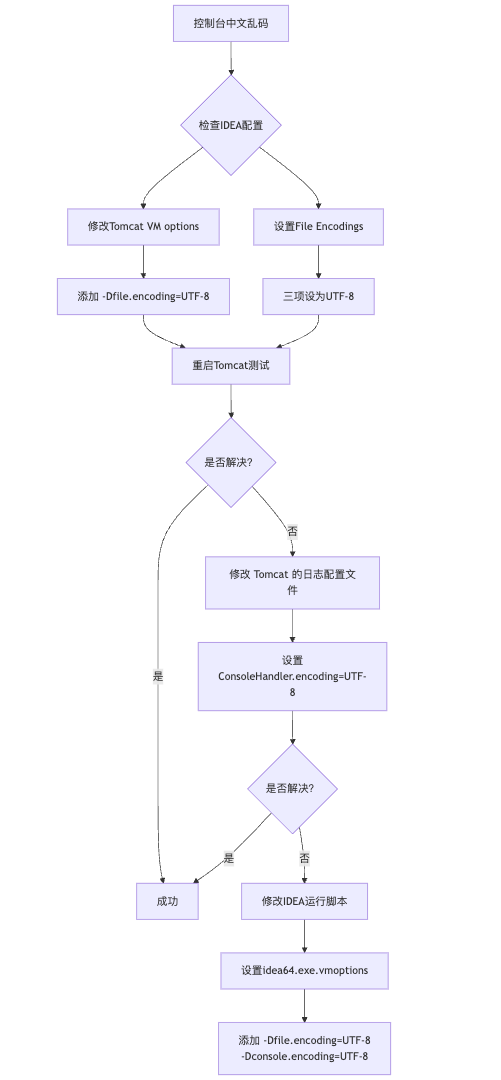
IDEA运行Tomcat出现乱码问题解决汇总
最近正值期末周,有很多同学在写期末Java web作业时,运行tomcat出现乱码问题,经过多次解决与研究,我做了如下整理: 原因: IDEA本身编码与tomcat的编码与Windows编码不同导致,Windows 系统控制台…...
)
论文解读:交大港大上海AI Lab开源论文 | 宇树机器人多姿态起立控制强化学习框架(二)
HoST框架核心实现方法详解 - 论文深度解读(第二部分) 《Learning Humanoid Standing-up Control across Diverse Postures》 系列文章: 论文深度解读 + 算法与代码分析(二) 作者机构: 上海AI Lab, 上海交通大学, 香港大学, 浙江大学, 香港中文大学 论文主题: 人形机器人…...
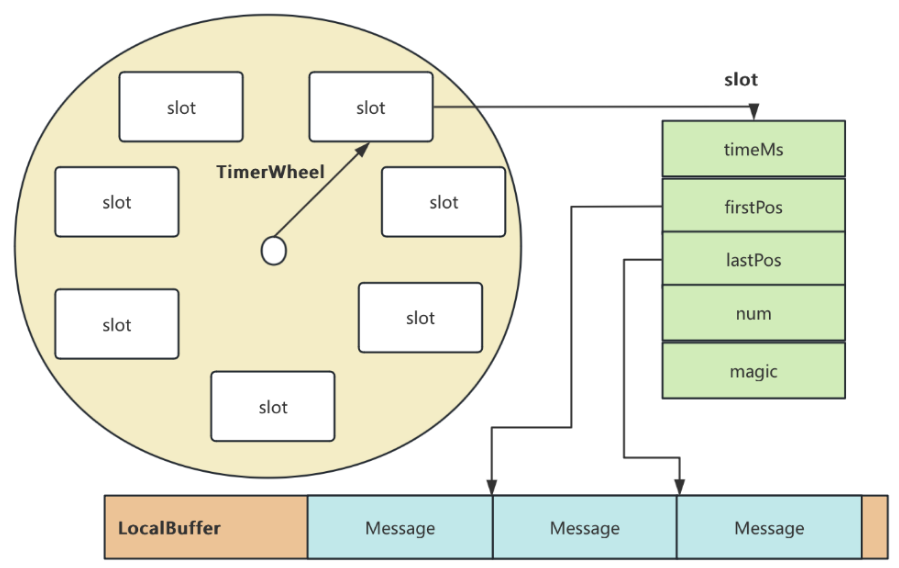
RocketMQ延迟消息机制
两种延迟消息 RocketMQ中提供了两种延迟消息机制 指定固定的延迟级别 通过在Message中设定一个MessageDelayLevel参数,对应18个预设的延迟级别指定时间点的延迟级别 通过在Message中设定一个DeliverTimeMS指定一个Long类型表示的具体时间点。到了时间点后…...
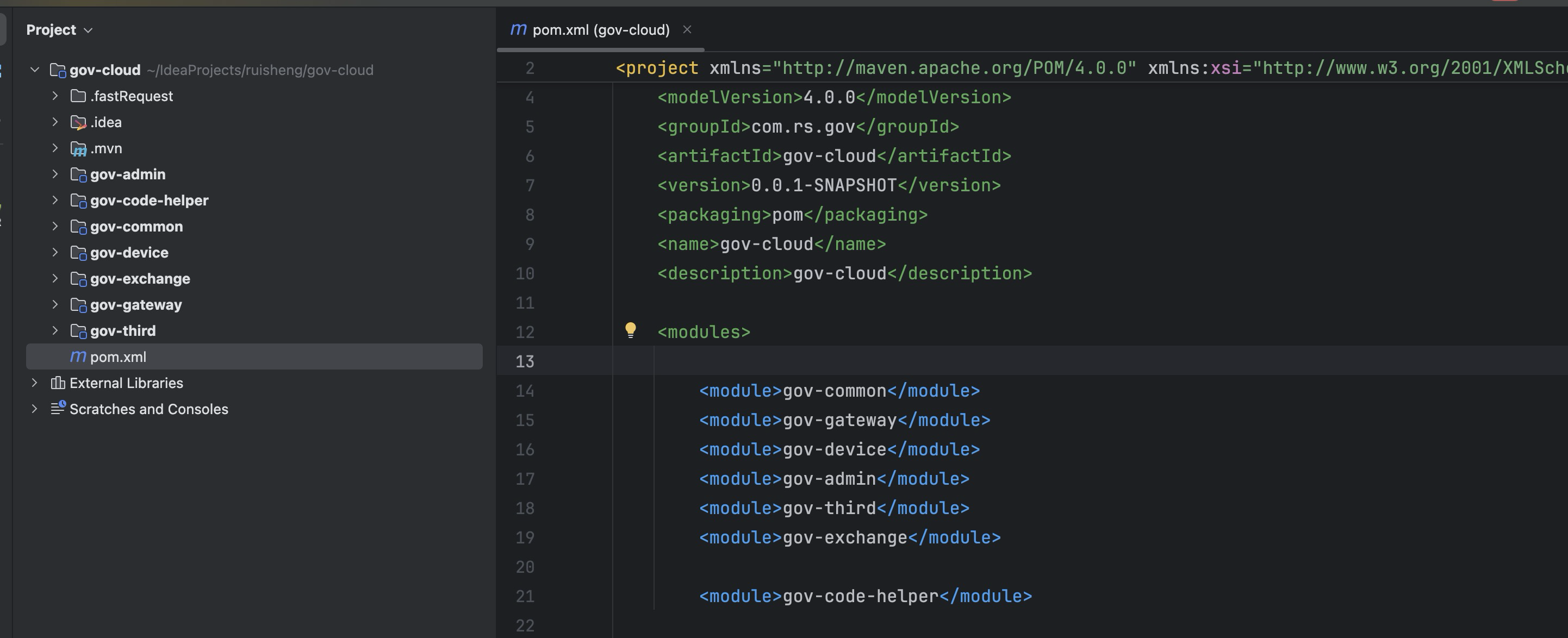
最新SpringBoot+SpringCloud+Nacos微服务框架分享
文章目录 前言一、服务规划二、架构核心1.cloud的pom2.gateway的异常handler3.gateway的filter4、admin的pom5、admin的登录核心 三、code-helper分享总结 前言 最近有个活蛮赶的,根据Excel列的需求预估的工时直接打骨折,不要问我为什么,主要…...

智能在线客服平台:数字化时代企业连接用户的 AI 中枢
随着互联网技术的飞速发展,消费者期望能够随时随地与企业进行交流。在线客服平台作为连接企业与客户的重要桥梁,不仅优化了客户体验,还提升了企业的服务效率和市场竞争力。本文将探讨在线客服平台的重要性、技术进展、实际应用,并…...

【C语言练习】080. 使用C语言实现简单的数据库操作
080. 使用C语言实现简单的数据库操作 080. 使用C语言实现简单的数据库操作使用原生APIODBC接口第三方库ORM框架文件模拟1. 安装SQLite2. 示例代码:使用SQLite创建数据库、表和插入数据3. 编译和运行4. 示例运行输出:5. 注意事项6. 总结080. 使用C语言实现简单的数据库操作 在…...
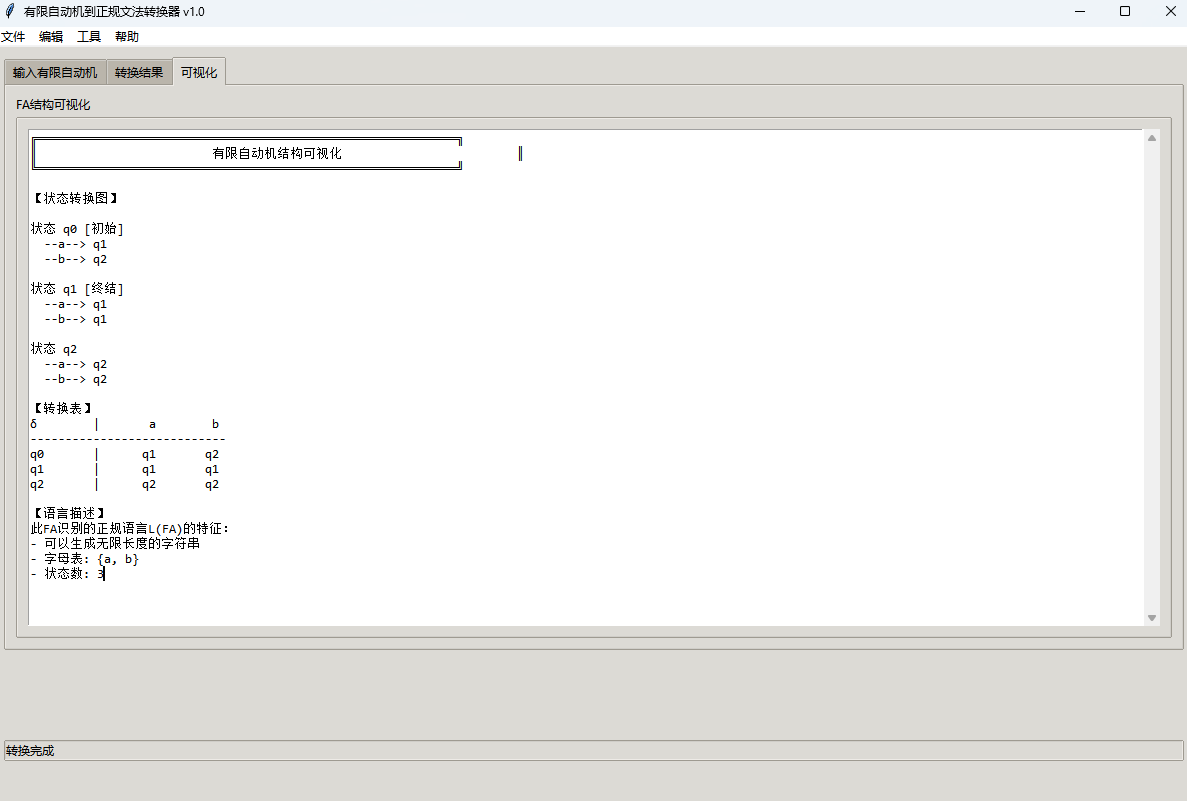
有限自动机到正规文法转换器v1.0
1 项目简介 这是一个功能强大的有限自动机(Finite Automaton, FA)到正规文法(Regular Grammar)转换器,它配备了一个直观且完整的图形用户界面,使用户能够轻松地进行操作和观察。该程序基于编译原理中的经典…...
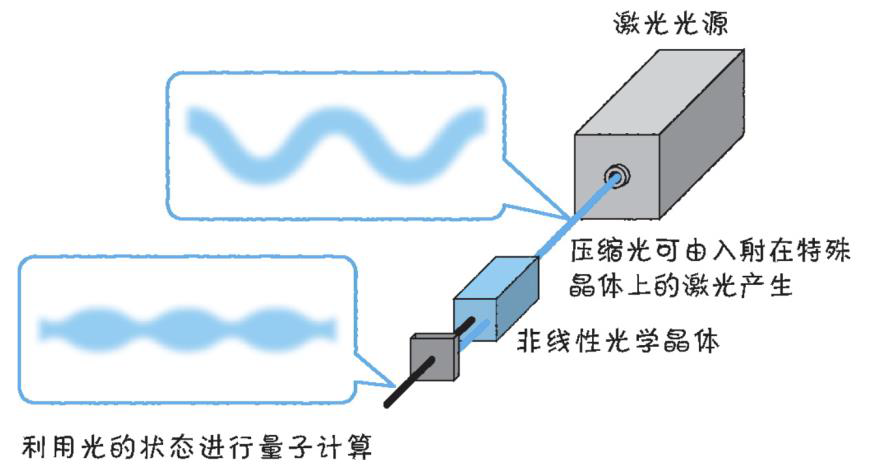
以光量子为例,详解量子获取方式
光量子技术获取量子比特可在室温下进行。该方式有望通过与名为硅光子学(silicon photonics)的光波导(optical waveguide)芯片制造技术和光纤等光通信技术相结合来实现量子计算机。量子力学中,光既是波又是粒子。光子本…...

提升移动端网页调试效率:WebDebugX 与常见工具组合实践
在日常移动端开发中,网页调试始终是一个高频但又极具挑战的环节。尤其在面对 iOS 与 Android 的混合技术栈、各种设备差异化行为时,开发者迫切需要一套高效、可靠且跨平台的调试方案。过去,我们或多或少使用过 Chrome DevTools、Remote Debug…...

Vue 模板语句的数据来源
🧩 Vue 模板语句的数据来源:全方位解析 Vue 模板(<template> 部分)中的表达式、指令绑定(如 v-bind, v-on)和插值({{ }})都在一个特定的作用域内求值。这个作用域由当前 组件…...
