Handler详解
跟Handler有关系的,包括Thread,Looper,Handler,MessageQueue
Looper:
由于Looper是android包加入的类,而Thread是java包的类,所以,想要为Thread创建一个Looper,需要在线程内部调用Looper.prepare
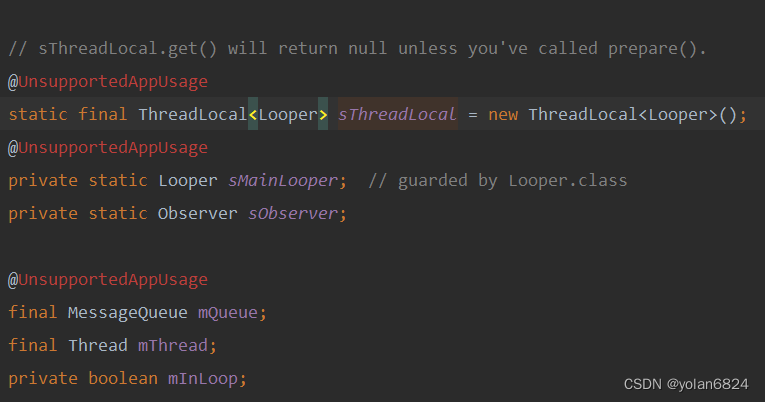
Looper内部会存储一个ThreadLocal,因此每个线程都会有自己的一个Looper。
Looper内部有自己存储了一个MessageQueue,以及主线程的MainLooper。
调用Looper一般会有两个方法:Looper.prepare以及Looper.loop方法
Looper.prepare
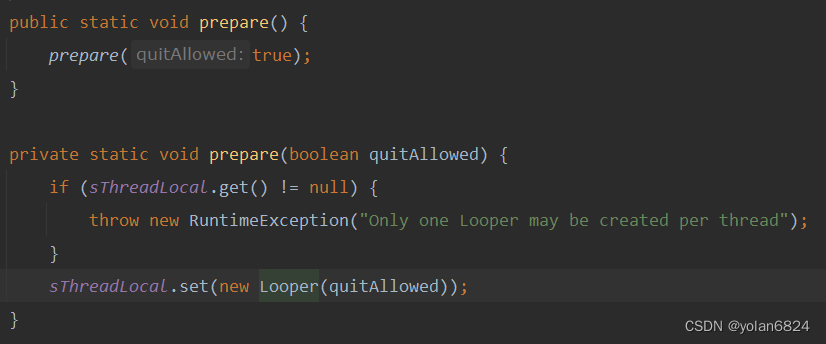
prepare会新创建一个Looper,塞进ThreadLocal,因此prepare必须在线程内部调用,才能将线程本身作为key。
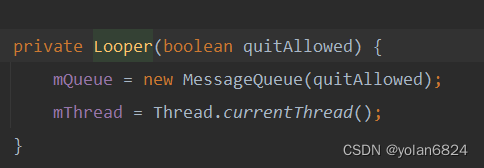
同时,会创建MessageQueue,以及存储当前线程。
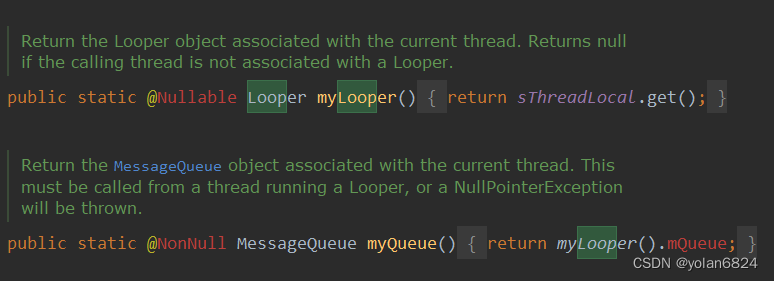
顺便看下两个比较常用的方法:
myLooper是从ThreadLocal中获取的当前线程所属的Looper。
myQueue对应的是当前线程的Looper中存储的MessageQueue。
Looper.loop
从Looper.loop方法,可以看出几个细节:
- 通过调用MessageQueue.next获取下一个要处理的Message
- 通过Message.target.dispatchMessage,将Message提交给Message中存储的Handler去处理,Handler调用dispatchMessage
- 可以创建一个进程唯一的Observer去监听Message的分配以及处理结束的进度。
public static void loop() {final Looper me = myLooper();if (me == null) {throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");}if (me.mInLoop) {Slog.w(TAG, "Loop again would have the queued messages be executed"+ " before this one completed.");}me.mInLoop = true;final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;for (;;) {Message msg = queue.next(); // might blockif (msg == null) {// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.return;}// This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the loggerfinal Printer logging = me.mLogging;if (logging != null) {logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);}// Make sure the observer won't change while processing a transaction.final Observer observer = sObserver;final long traceTag = me.mTraceTag;long slowDispatchThresholdMs = me.mSlowDispatchThresholdMs;long slowDeliveryThresholdMs = me.mSlowDeliveryThresholdMs;if (thresholdOverride > 0) {slowDispatchThresholdMs = thresholdOverride;slowDeliveryThresholdMs = thresholdOverride;}final boolean logSlowDelivery = (slowDeliveryThresholdMs > 0) && (msg.when > 0);final boolean logSlowDispatch = (slowDispatchThresholdMs > 0);final boolean needStartTime = logSlowDelivery || logSlowDispatch;final boolean needEndTime = logSlowDispatch;if (traceTag != 0 && Trace.isTagEnabled(traceTag)) {Trace.traceBegin(traceTag, msg.target.getTraceName(msg));}final long dispatchStart = needStartTime ? SystemClock.uptimeMillis() : 0;final long dispatchEnd;Object token = null;if (observer != null) {token = observer.messageDispatchStarting();}long origWorkSource = ThreadLocalWorkSource.setUid(msg.workSourceUid);try {msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);if (observer != null) {observer.messageDispatched(token, msg);}dispatchEnd = needEndTime ? SystemClock.uptimeMillis() : 0;} catch (Exception exception) {if (observer != null) {observer.dispatchingThrewException(token, msg, exception);}throw exception;} finally {ThreadLocalWorkSource.restore(origWorkSource);if (traceTag != 0) {Trace.traceEnd(traceTag);}}if (logSlowDelivery) {if (slowDeliveryDetected) {if ((dispatchStart - msg.when) <= 10) {Slog.w(TAG, "Drained");slowDeliveryDetected = false;}} else {if (showSlowLog(slowDeliveryThresholdMs, msg.when, dispatchStart, "delivery",msg)) {// Once we write a slow delivery log, suppress until the queue drains.slowDeliveryDetected = true;}}}if (logSlowDispatch) {showSlowLog(slowDispatchThresholdMs, dispatchStart, dispatchEnd, "dispatch", msg);}if (logging != null) {logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback);}// Make sure that during the course of dispatching the// identity of the thread wasn't corrupted.final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();if (ident != newIdent) {Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x"+ Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x"+ Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to "+ msg.target.getClass().getName() + " "+ msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what);}msg.recycleUnchecked();}
}Message
从Looper.loop方法可以看出,会对Looper的MessageQueue遍历,不断取出Message,然后调用Message.target.dispatchMessage方法。
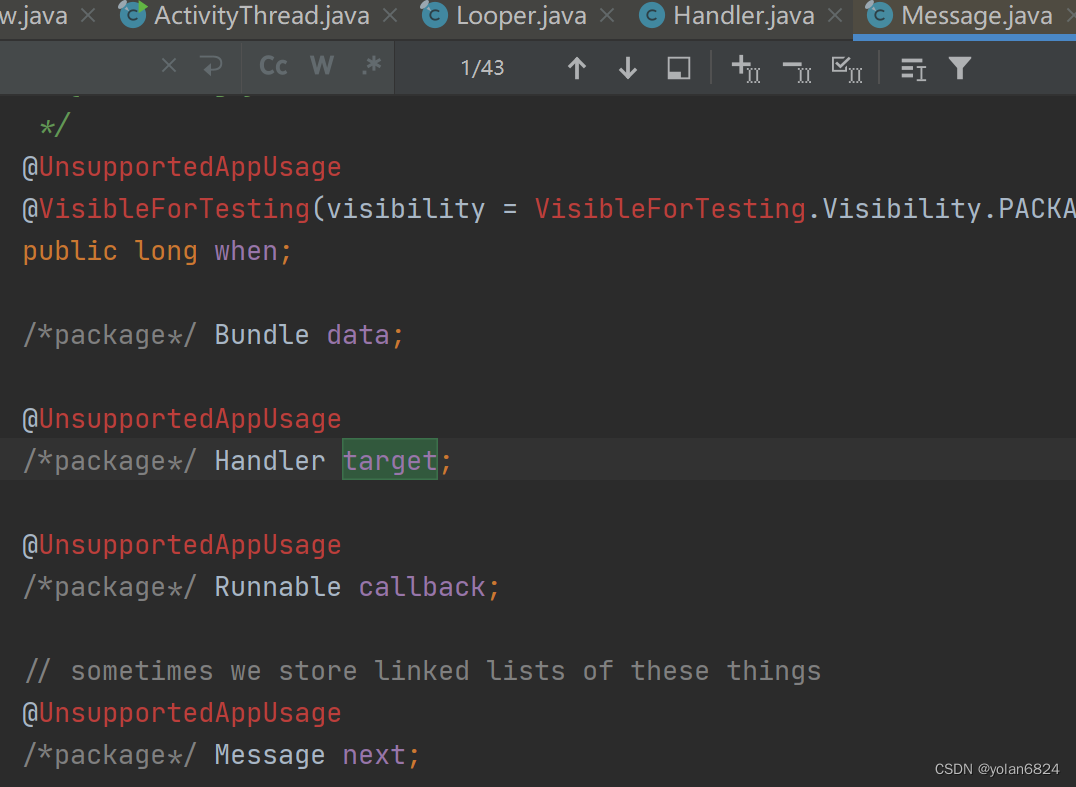
从Message的变量可以看出,target实际是Message所属的Handler。
同时Message存储了一个next,说明MessageQueue是一个链式结构。
MessageQueue
https://www.cnblogs.com/jiy-for-you/p/11707356.html
从MessageQueue.next可以获取几个有效信息:
- nativePollOnce:MessageQueue中没有Message的时候会卡在这个方法,类似于object.wait,当有人调用MessageQueue.enqueueMessage方法的时候,会将线程唤醒。
- msg.target == null,代表该msg是一个同步屏障(即阻拦同步消息的执行)。遇到同步屏障时,会往后遍历,优先执行异步消息(触发view的绘制的那个消息就是异步消息)。
- 如果获取到一个msg,msg.when代表的执行时间还没到,会先去执行IdleHandler里面的消息(或MessageQueue队列为空)。
// MessageQueue.next
Message next() {// Return here if the message loop has already quit and been disposed.// This can happen if the application tries to restart a looper after quit// which is not supported.final long ptr = mPtr;if (ptr == 0) {return null;}int pendingIdleHandlerCount = -1; // -1 only during first iterationint nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;for (;;) {if (nextPollTimeoutMillis != 0) {Binder.flushPendingCommands();}// 如果没有消息,会卡在这个方法nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);synchronized (this) {// Try to retrieve the next message. Return if found.final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();Message prevMsg = null;Message msg = mMessages;if (msg != null && msg.target == null) {// 同步屏障,当遇到同步屏障,会往后寻找异步消息(isAsynchronous)执行// Stalled by a barrier. Find the next asynchronous message in the queue.do {// 遍历,直到找到一个异步的msgprevMsg = msg;// 这一步,prevMsg!=null,这会导致msg = msg.next;} while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous());}if (msg != null) {if (now < msg.when) {// msg.when是这个message的执行时间,如果message的执行时间在now之后// Next message is not ready. Set a timeout to wake up when it is ready.nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(msg.when - now, Integer.MAX_VALUE);} else {// Got a message.mBlocked = false;if (prevMsg != null) {prevMsg.next = msg.next;} else {mMessages = msg.next;}msg.next = null;if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Returning message: " + msg);msg.markInUse();return msg;}} else {// No more messages.nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;}// Process the quit message now that all pending messages have been handled.if (mQuitting) {dispose();return null;}// If first time idle, then get the number of idlers to run.// Idle handles only run if the queue is empty or if the first message// in the queue (possibly a barrier) is due to be handled in the future.// 走到这,说明消息队列是空的,或队首是一个延迟执行的Messageif (pendingIdleHandlerCount < 0&& (mMessages == null || now < mMessages.when)) {pendingIdleHandlerCount = mIdleHandlers.size();}if (pendingIdleHandlerCount <= 0) {// No idle handlers to run. Loop and wait some more.mBlocked = true;continue;}if (mPendingIdleHandlers == null) {mPendingIdleHandlers = new IdleHandler[Math.max(pendingIdleHandlerCount, 4)];}mPendingIdleHandlers = mIdleHandlers.toArray(mPendingIdleHandlers);}// Run the idle handlers.// We only ever reach this code block during the first iteration.for (int i = 0; i < pendingIdleHandlerCount; i++) {final IdleHandler idler = mPendingIdleHandlers[i];mPendingIdleHandlers[i] = null; // release the reference to the handlerboolean keep = false;try {keep = idler.queueIdle();} catch (Throwable t) {Log.wtf(TAG, "IdleHandler threw exception", t);}if (!keep) {synchronized (this) {mIdleHandlers.remove(idler);}}}// Reset the idle handler count to 0 so we do not run them again.pendingIdleHandlerCount = 0;// While calling an idle handler, a new message could have been delivered// so go back and look again for a pending message without waiting.nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;}
}
Handler的总结:
- Handler内部一定会有一个Looper。Looper跟线程一一绑定。绑定的关系存在Looper的sThreadLocal中。所以如果Handler想要监听哪个线程上的消息,可以直接给Handler传那个线程的Looper即可。
- Looper实际上是一个轮询消息的机制,所以内部一定会存在一个MessageQueue。当Looper开始轮询的时候(调用Looper.loop),会每次调用MessageQueue.next取一个Message出来执行。
- Looper获取到Message之后,会调用Message.target.dispatchMessage方法。即实际调用的是Handler.dispatchMessage的方法。
- Message中有几个比较重要的参数:
- target:这个Message从属于哪个handler(从哪个handler post过去的)。
- callback:当调用handler.postRunnable,即创建了一个Message,msg.callBack = runnable。
- what:这个Message的唯一标识id。当Handler.handleMessage方法中,会接收多个message,通过what区分这个Message的类别。
- when:通过handler.postDelayed,设置这个Message实际应该执行的时间:curTime+delay。MessageQueue的入队实际是通过when去进行Message的排序的。
- handler.dispatchMessage方法,
- 如果Message.callback != null,直接执行Message.callback.run(即post(Runnable))中Runnable的执行。
- 否则如果给handler设置了Callback,就调用Callback.handleMessage
- 否则,调用Handler本身的handleMessage方法(空实现),需要重写。
关于barrier
// MessageQueue
private int postSyncBarrier(long when) {// Enqueue a new sync barrier token.// We don't need to wake the queue because the purpose of a barrier is to stall it.synchronized (this) {final int token = mNextBarrierToken++;final Message msg = Message.obtain();msg.markInUse();msg.when = when;msg.arg1 = token;// 代表Message的barrier,特征是target == nullMessage prev = null;Message p = mMessages;if (when != 0) {// 根据when,将代表barrier的msg插入MessageQueuewhile (p != null && p.when <= when) {prev = p;p = p.next;}}if (prev != null) { // invariant: p == prev.nextmsg.next = p;prev.next = msg;} else {msg.next = p;mMessages = msg;}return token;}
}postSyncBarrier,生成一个target == null的Message,根据when,插入MessageQueue中。返回的token是barrier的唯一标识。只要postSyncBarrier,就要根据这个token,后面移除barrier。否则会导致同步消息一直无法执行。
看下有了barrier的MessageQueue取Message的时候是怎么表现的。
Message next() {// Return here if the message loop has already quit and been disposed.// This can happen if the application tries to restart a looper after quit// which is not supported.final long ptr = mPtr;if (ptr == 0) {return null;}int pendingIdleHandlerCount = -1; // -1 only during first iterationint nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;for (;;) {if (nextPollTimeoutMillis != 0) {Binder.flushPendingCommands();}nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);// nextPollTimeoutMillis:等待的时间synchronized (this) {// Try to retrieve the next message. Return if found.final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();Message prevMsg = null;Message msg = mMessages;if (msg != null && msg.target == null) {// 如果取msg的时候,队首的Msg是Barrier// Stalled by a barrier. Find the next asynchronous message in the queue.do {prevMsg = msg;msg = msg.next;// 就一直往后遍历,寻找一个异步的msg} while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous());}if (msg != null) {if (now < msg.when) {// 如果还没到msg的执行时间,就设置nextPollTimeoutMillis// Next message is not ready. Set a timeout to wake up when it is ready.nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(msg.when - now, Integer.MAX_VALUE);} else {// Got a message.mBlocked = false;if (prevMsg != null) {prevMsg.next = msg.next;} else {mMessages = msg.next;}msg.next = null;if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Returning message: " + msg);msg.markInUse();return msg;}} else {// 如果mMessages队列为空,或有Barrier的时候,异步msg为空,就设置等待时间为-1// 为-1代表等待被唤醒// No more messages.nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;}// Process the quit message now that all pending messages have been handled.if (mQuitting) {dispose();return null;}// If first time idle, then get the number of idlers to run.// Idle handles only run if the queue is empty or if the first message// in the queue (possibly a barrier) is due to be handled in the future.if (pendingIdleHandlerCount < 0&& (mMessages == null || now < mMessages.when)) {pendingIdleHandlerCount = mIdleHandlers.size();}// 如果队列为空,或者还没到message的执行时间,开始执行IdleHandlerif (pendingIdleHandlerCount <= 0) {// No idle handlers to run. Loop and wait some more.mBlocked = true;continue;}if (mPendingIdleHandlers == null) {mPendingIdleHandlers = new IdleHandler[Math.max(pendingIdleHandlerCount, 4)];}mPendingIdleHandlers = mIdleHandlers.toArray(mPendingIdleHandlers);}// Run the idle handlers.// We only ever reach this code block during the first iteration.for (int i = 0; i < pendingIdleHandlerCount; i++) {final IdleHandler idler = mPendingIdleHandlers[i];mPendingIdleHandlers[i] = null; // release the reference to the handlerboolean keep = false;try {keep = idler.queueIdle();} catch (Throwable t) {Log.wtf(TAG, "IdleHandler threw exception", t);}if (!keep) {synchronized (this) {mIdleHandlers.remove(idler);}}}// Reset the idle handler count to 0 so we do not run them again.// 防止下次再走一遍IdleHandlerpendingIdleHandlerCount = 0;// While calling an idle handler, a new message could have been delivered// so go back and look again for a pending message without waiting.// 经过IdleHandler之后,可能已经有Message入队了,再遍历一遍,第二次就直接等待了。nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;}
}总结下next的逻辑:
- 如果mMessages的队首是barrier(msg.target == null),就遍历messages,优先执行异步消息(异步消息一般是优先级最高的信息:比如响应input事件或是view刷新。)。
- 如果不是barrier,就直接取队首的message执行。
- 如果1,2步骤取到的message != null,先看message的when < now,大于则直接返回message给Looper.loop方法。小于,则设置nextPollTimeoutMillis,用来设置线程的等待时间:nativePollOnce。
- 如果messageQueue为空,或message.when > now(即要等待),那么这个时候,就去执行IdleHandler。
总结下上面,nativePollOnce其实代表,线程在等待下一个消息的执行,或者messages队列为空。或者是设置了barrier情况下,没有异步消息的时候。
下一步,看下MessageQueue的具体打出日志代表什么。
相关文章:

Handler详解
跟Handler有关系的,包括Thread,Looper,Handler,MessageQueue Looper: 由于Looper是android包加入的类,而Thread是java包的类,所以,想要为Thread创建一个Looper,需要在线程内部调用…...
)
Feign忽略Https的SSL最佳方案(且保证负载均衡将失效)
同时解决Https的SSL证书验证问题和feign不支持Patch请求方法的问题 代码 1. 工具类 OkHttpUtils.java import javax.net.ssl.*; import java.security.KeyManagementException; import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; import java.security.SecureRandom; import j…...

Neo4j之SET基础
在 Neo4j 中,SET 语句用于更新节点或关系的属性。它允许你修改节点或关系的属性值,可以单独使用,也可以与其他查询语句(如 MATCH、CREATE、MERGE 等)一起使用。以下是一些使用 SET 语句的常见例子,以及它们…...

Redis 缓存过期及删除
一、Redis缓存过期策略 物理内存达到上限后,像磁盘空间申请虚拟内存(硬盘与内存的swap),甚至崩溃。 内存与硬盘交换 (swap) 虚拟内存,频繁I0 性能急剧下降,会造成redis内存急剧下降; 一般设置物理内存的3/4,在redis…...

万字长文·通俗易懂·一篇包掌握——输入/输出·文件操作(c语言超详细系列)(二)
前言:Hello,大家好😘,我是心跳sy,上一节我们主要学习了格式化输入输出的基本内容,这一节我们对格式化进行更加深入的了解,对文件概念进行介绍,并且对输入、输出与文件读写的基本概念…...
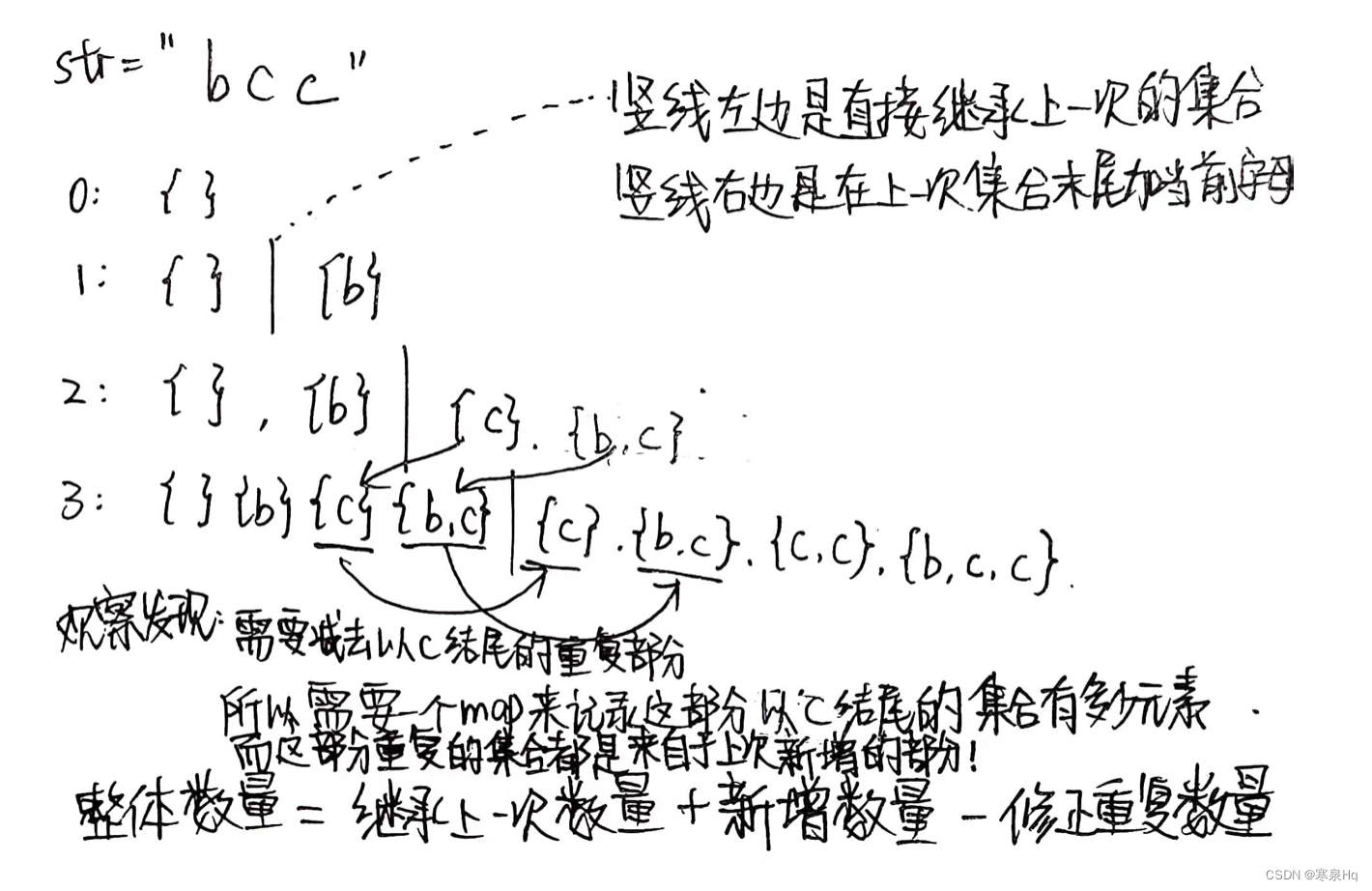
【左神算法刷题班】第17节:在有序二维数组中查找目标值、等于目标字符串的子序列个数
第17节 题目1:在有序二维数组中查找目标值 给定一个每一行有序、每一列也有序,整体可能无序的二维数组 再给定一个数num, 返回二维数组中有没有num这个数 例子 数组如下,找 6 是否存在。 1 3 5 7 2 4 6 13 3 9 14 …...
)
【Terraform学习】本地变量(Terraform配置语言学习)
背景: 关于如何在机器上拉terraform代码,初始化就不重复了,需要的可以查看前面的文章: 【Terraform学习】Terraform-AWS部署快速入门(快速入门)_向往风的男子的博客-CSDN博客 使用本地变量命名资源 将每…...
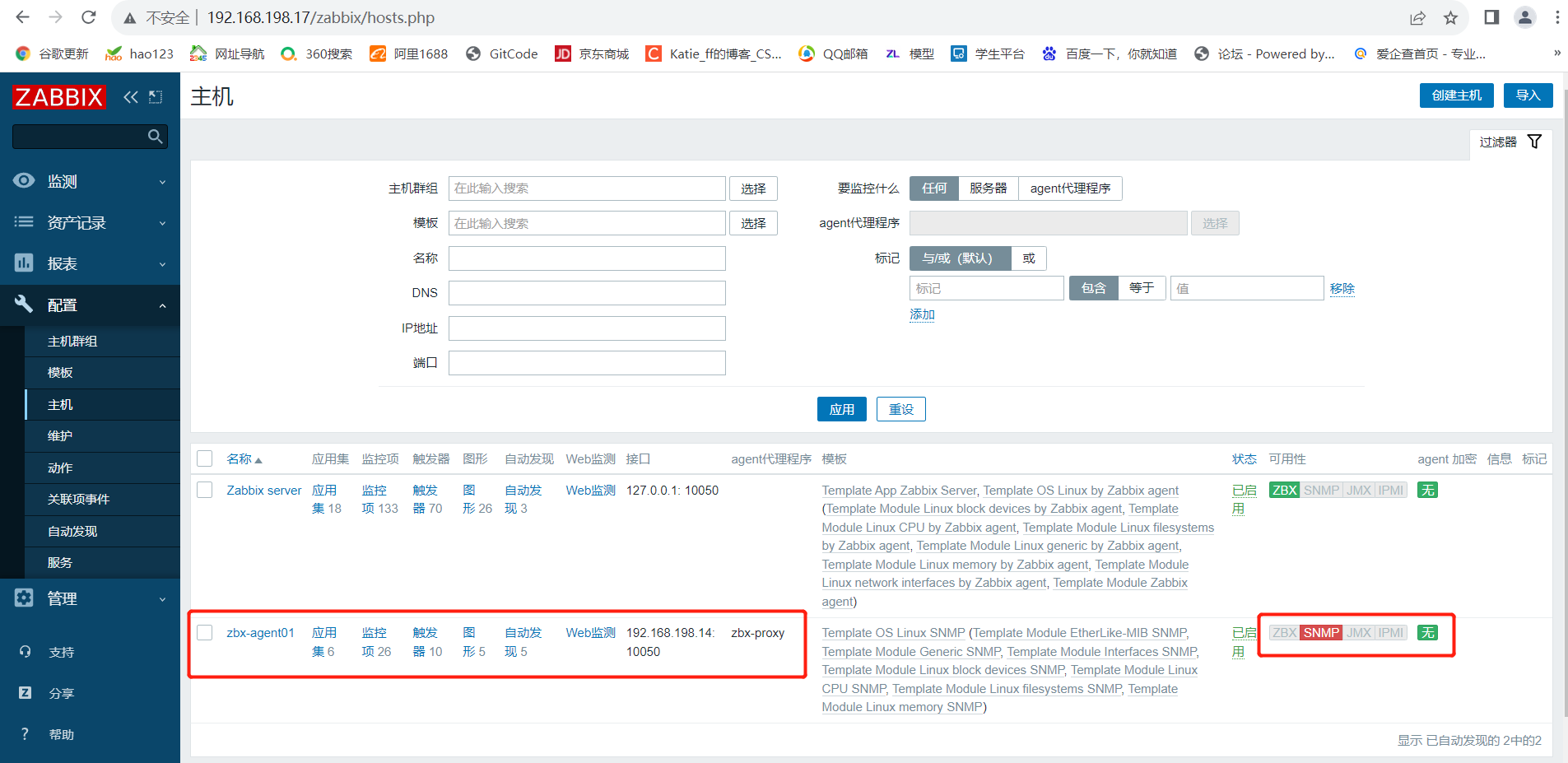
zabbix自动注册服务器以及部署代理服务器
文章目录 Zabbix自动注册服务器及部署代理服务器一.zabbix自动注册1.什么是自动注册2.环境准备3.zabbix客户端配置4.在 Web 页面配置自动注册5.验证自动注册 二.部署 zabbix 代理服务器1.分布式监控的作用:2.环境部署3.代理服务器配置4.客户端配置5.web页面配置5.1 …...

掌握Python的X篇_32_使用python编辑pdf文件_pdfrw
本篇介绍利用python操作pdf文件,我们平时也会有合并和拆分pdf的需求,此时我们就可以使用本节内容。 文章目录 1. pdfrw的安装2. 切分pdf文件3. pdfrw官网及实现一版四面的实例 1. pdfrw的安装 pip install pdfrw官网地址:https://github.co…...
【软件工程】软件测试
软件测试的对象 软件程序文档 测试对象:各个阶段产生的源程序和文档。 软件测试的目的 基于不同的立场,对软件测试的目的存在着两种完全对立的观点。 (1)一种观点是通过测试暴露出软件中所包含的故障和缺陷(从用户的角度)…...
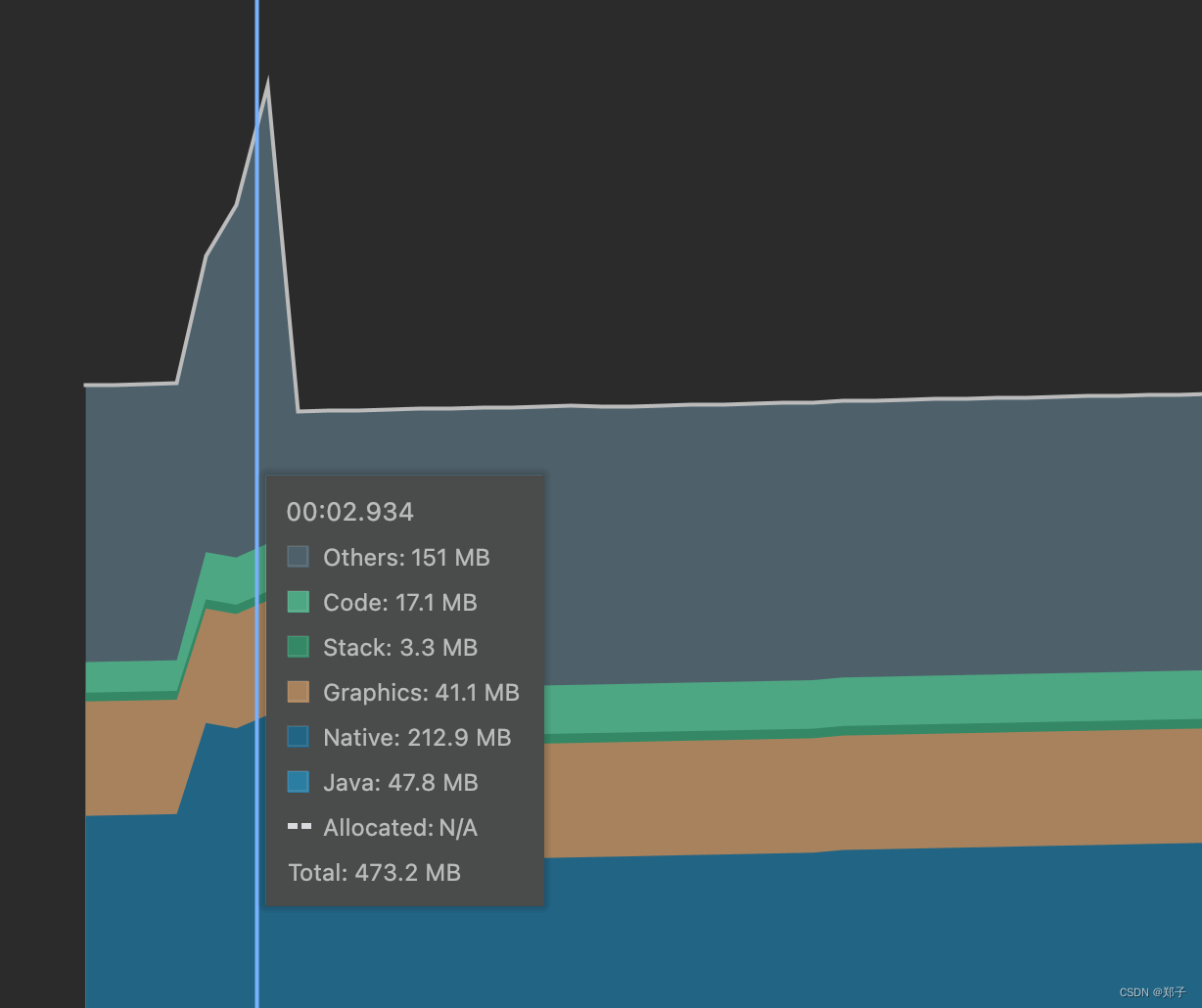
Android性能优化——内存优化
一、内存问题 内存抖动,锯齿状,GC导致卡顿内存泄漏,可用内存减少,频繁GC 内存溢出,OOM,程序异常 二、内存分析工具 Memory ProfilerMemory Analyzer LeakCanary Memory Profiler 实时图表展示应用内存使…...

Android Studio实现图形验证码
源代码 源代码MainActivity 效果图32行需要修改,不修改会报错:需要常量表达式,我的代码已修改 点击后 MainActivity import static com.example.graphicverificationcode.RxCaptcha.TYPE.NUMBER;import android.annotation.SuppressLint; …...

JAVA面试数据库篇
目录 一.优化 1.MYSQL中,如何定位慢查询? 2.SQL语句执行慢,如何分析呢? 3.索引 了解过索引吗?(什么是索引) 索引的底层数据结构了解过吗? B树和B树的区别是什么呢? 什么是聚…...

Android高手进阶教程(三)之----Android 中自定义View的应用.
大家好我们今天的教程是在Android 教程中自定义View 的学习,对于初学着来说,他们习惯了Android 传统的页面布局方式,如下代码: <?xml version"1.0" encoding"utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android"htt…...

第一百一十三回 dart中的getter/setter方法
文章目录 概念介绍使用方法示例代码使用扩展 我们在上一章回中介绍了 flutter_screenutil包相关的内容,本章回中将介绍 dart中的setter/getter方法.闲话休提,让我们一起Talk Flutter吧。 概念介绍 我们在这里介绍的setter/getter方法属于编程语言中的…...

搭建Docker环境
目录 一、docker环境搭建 1、卸载旧版本docker 2、安装依赖和设置仓库 3、安装docker 4、启动并加入开机启动 5、验证是否安装成功 二、利用docker搭建nginx 1、拉取镜像 2、启动容器,部署nginx 一、docker环境搭建 1、卸载旧版本docker yum remove docke…...
微服务08-多级缓存
1.什么是多级缓存 传统的缓存策略一般是请求到达Tomcat后,先查询Redis,如果未命中则查询数据库,如图: 存在下面的问题: •请求要经过Tomcat处理,Tomcat的性能成为整个系统的瓶颈 •Redis缓存失效时,会对数据库产生冲击 多级缓存就是充分利用请求处理的每个环节,分…...

Intel汇编和ATT汇编的区别?
一、前缀不同 在 Intel 语法中,没有寄存器前缀或立即前缀。 然而,在 AT&T 中,寄存器的前缀是“%”,而 immed 的前缀是“$”。 Intel 语法十六进制或二进制即时数据分别带有“h”和“b”后缀。 此外,如果第一个十六…...
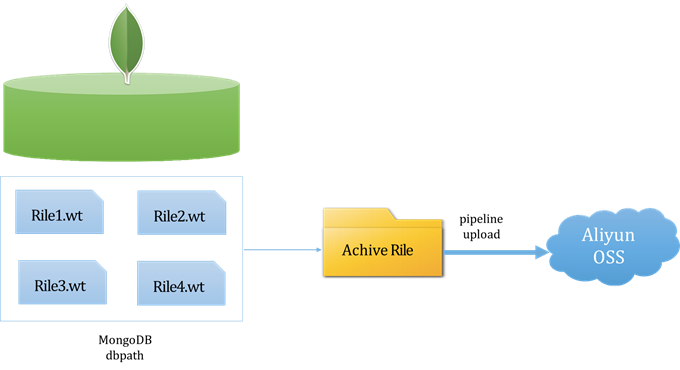
MongoDB 备份与恢复
1.1 MongoDB的常用命令 mongoexport / mongoimport mongodump / mongorestore 有以上两组命令在备份与恢复中进行使用。 1.1.1 导出工具mongoexport Mongodb中的mongoexport工具可以把一个collection导出成JSON格式或CSV格式的文件。可以通过参数指定导出的数据项,…...
探讨uniapp的网络通信问题
uni-app 中有很多原生的 API,其中我们经常会用到的肯定有:uni.request(OBJECT) method 有效值 注意:method有效值必须大写,每个平台支持的method有效值不同,详细见下表。 success 返回参数说明 data 数据说明 最终…...

零门槛NAS搭建:WinNAS如何让普通电脑秒变私有云?
一、核心优势:专为Windows用户设计的极简NAS WinNAS由深圳耘想存储科技开发,是一款收费低廉但功能全面的Windows NAS工具,主打“无学习成本部署” 。与其他NAS软件相比,其优势在于: 无需硬件改造:将任意W…...
【HarmonyOS 5.0】DevEco Testing:鸿蒙应用质量保障的终极武器
——全方位测试解决方案与代码实战 一、工具定位与核心能力 DevEco Testing是HarmonyOS官方推出的一体化测试平台,覆盖应用全生命周期测试需求,主要提供五大核心能力: 测试类型检测目标关键指标功能体验基…...

pam_env.so模块配置解析
在PAM(Pluggable Authentication Modules)配置中, /etc/pam.d/su 文件相关配置含义如下: 配置解析 auth required pam_env.so1. 字段分解 字段值说明模块类型auth认证类模块,负责验证用户身份&am…...
)
python爬虫:Newspaper3k 的详细使用(好用的新闻网站文章抓取和解析的Python库)
更多内容请见: 爬虫和逆向教程-专栏介绍和目录 文章目录 一、Newspaper3k 概述1.1 Newspaper3k 介绍1.2 主要功能1.3 典型应用场景1.4 安装二、基本用法2.2 提取单篇文章的内容2.2 处理多篇文档三、高级选项3.1 自定义配置3.2 分析文章情感四、实战案例4.1 构建新闻摘要聚合器…...

python如何将word的doc另存为docx
将 DOCX 文件另存为 DOCX 格式(Python 实现) 在 Python 中,你可以使用 python-docx 库来操作 Word 文档。不过需要注意的是,.doc 是旧的 Word 格式,而 .docx 是新的基于 XML 的格式。python-docx 只能处理 .docx 格式…...
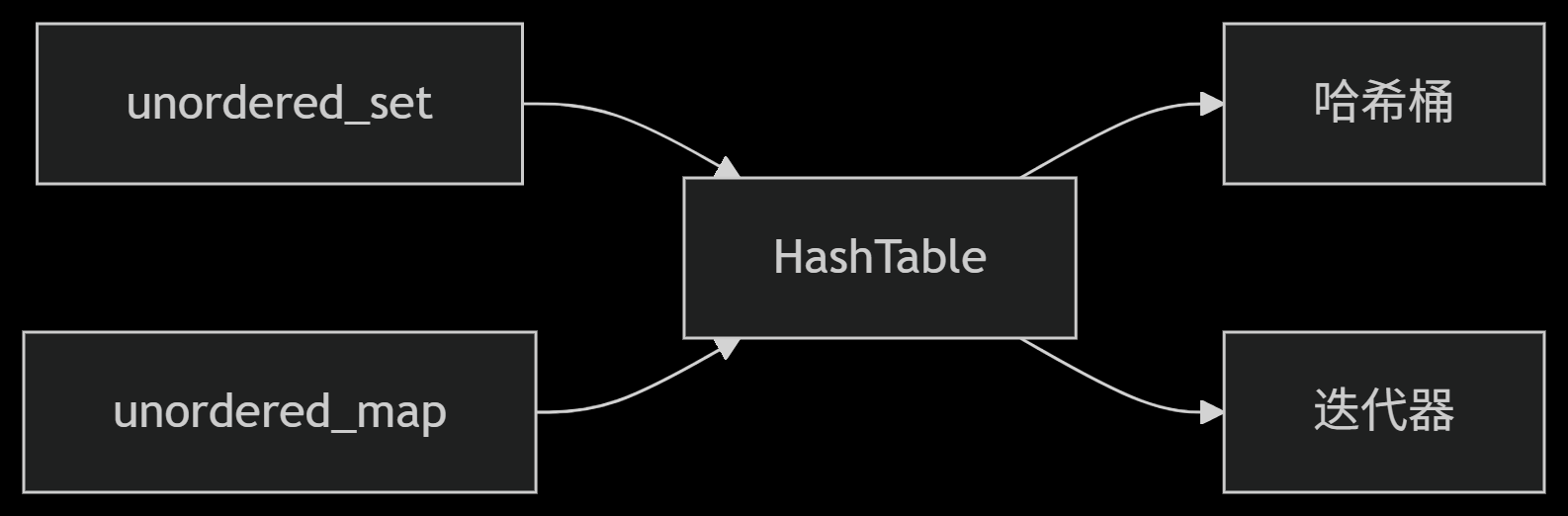
从零实现STL哈希容器:unordered_map/unordered_set封装详解
本篇文章是对C学习的STL哈希容器自主实现部分的学习分享 希望也能为你带来些帮助~ 那咱们废话不多说,直接开始吧! 一、源码结构分析 1. SGISTL30实现剖析 // hash_set核心结构 template <class Value, class HashFcn, ...> class hash_set {ty…...

Spring AI 入门:Java 开发者的生成式 AI 实践之路
一、Spring AI 简介 在人工智能技术快速迭代的今天,Spring AI 作为 Spring 生态系统的新生力量,正在成为 Java 开发者拥抱生成式 AI 的最佳选择。该框架通过模块化设计实现了与主流 AI 服务(如 OpenAI、Anthropic)的无缝对接&…...

【OSG学习笔记】Day 16: 骨骼动画与蒙皮(osgAnimation)
骨骼动画基础 骨骼动画是 3D 计算机图形中常用的技术,它通过以下两个主要组件实现角色动画。 骨骼系统 (Skeleton):由层级结构的骨头组成,类似于人体骨骼蒙皮 (Mesh Skinning):将模型网格顶点绑定到骨骼上,使骨骼移动…...

关于 WASM:1. WASM 基础原理
一、WASM 简介 1.1 WebAssembly 是什么? WebAssembly(WASM) 是一种能在现代浏览器中高效运行的二进制指令格式,它不是传统的编程语言,而是一种 低级字节码格式,可由高级语言(如 C、C、Rust&am…...
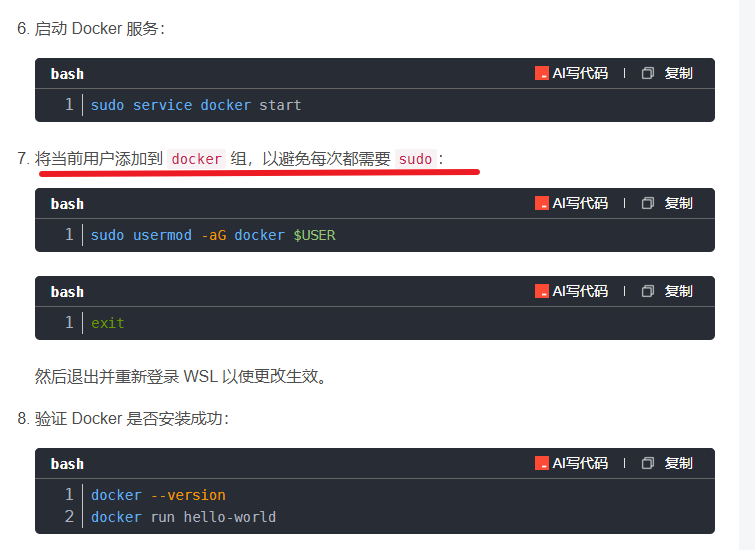
在WSL2的Ubuntu镜像中安装Docker
Docker官网链接: https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ubuntu/ 1、运行以下命令卸载所有冲突的软件包: for pkg in docker.io docker-doc docker-compose docker-compose-v2 podman-docker containerd runc; do sudo apt-get remove $pkg; done2、设置Docker…...
