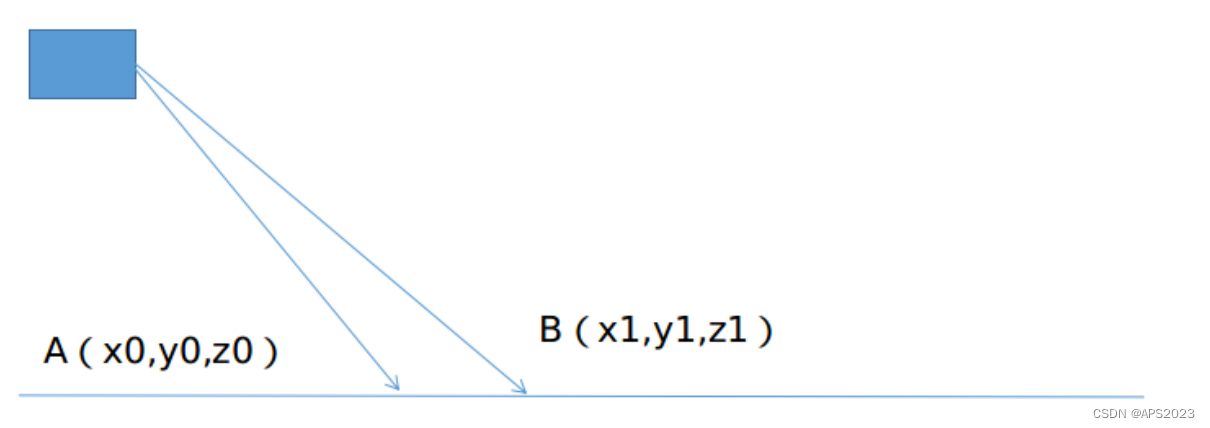LeGO-Loam代码解析(二)--- Lego-LOAM的地面点分离、聚类、两步优化方法
1 地面点分离剔除方法
1.1 数学推导
LeGO-LOAM 中前端改进中很重要的一点就是充分利用了地面点,那首先自然是提取
对地面点的提取。
如上图,相邻的两个扫描线束的同一列打在地面上如
点所示,他们的垂直高度差
,水平距离差
,计算垂直高度差和水平高度差的角度
。(这里
为AB到水平面的夹角)理想情况下,
应该接近 0,考虑到一方面激光雷达安装也无法做到绝对水平。另一方面,地面也不是绝对水平。因此,这个角度会略微大于 0,考虑到作者实际在草坪之类的场景下运动,因此这个值被设置成 10 度。
实际上此种地面分离算法有一些简单,我们可以结合激光雷达安装高度等其他先验信息进行优化。
1.2 Lego-LOAM代码实现
版本1:LegoLOAM改版
void ImageProjection::groundRemoval() {// _ground_mat// -1, no valid info to check if ground of not// 0, initial value, after validation, means not ground// 1, ground// 同一列由下到上 _horizontal_scans = 1800 _ground_scan_index=7(地面点的上限)16线设置为7 因为水平地面点不可能在天上面对把for (size_t j = 0; j < _horizontal_scans; ++j){for (size_t i = 0; i < _ground_scan_index; ++i){// 取出同一列相邻点的索引size_t lowerInd = j + (i)*_horizontal_scans;size_t upperInd = j + (i + 1) * _horizontal_scans;// 非有效点if (_full_cloud->points[lowerInd].intensity == -1 ||_full_cloud->points[upperInd].intensity == -1) {// no info to check, invalid points_ground_mat(i, j) = -1;continue;}float dX =_full_cloud->points[upperInd].x - _full_cloud->points[lowerInd].x;float dY =_full_cloud->points[upperInd].y - _full_cloud->points[lowerInd].y;float dZ =_full_cloud->points[upperInd].z - _full_cloud->points[lowerInd].z;float vertical_angle = std::atan2(dZ , sqrt(dX * dX + dY * dY + dZ * dZ));// TODO: review this change// 和上文的公式相同 _sensor_mount_angle设置为(_sensor_mount_angle *= DEG_TO_RAD) (DEG_TO_RAD = M_PI / 180.0)if ( (vertical_angle - _sensor_mount_angle) <= 10 * DEG_TO_RAD){_ground_mat(i, j) = 1;_ground_mat(i + 1, j) = 1;}}}// extract ground cloud (_ground_mat == 1)// mark entry that doesn't need to label (ground and invalid point) for// segmentation note that ground remove is from 0~_N_scan-1, need _range_mat// for mark label matrix for the 16th scan// 遍历特征矩阵 1800 * 16 如果是地面点/无效点的话 设置为-1 不参与线特征面特征的提取for (size_t i = 0; i < _vertical_scans; ++i){for (size_t j = 0; j < _horizontal_scans; ++j){if (_ground_mat(i, j) == 1 ||_range_mat(i, j) == FLT_MAX){_label_mat(i, j) = -1;}}}// RVIZ可视化的操作for (size_t i = 0; i <= _ground_scan_index; ++i){for (size_t j = 0; j < _horizontal_scans; ++j){if (_ground_mat(i, j) == 1)_ground_cloud->push_back(_full_cloud->points[j + i * _horizontal_scans]);}} }版本2:Lego-LOAM原生
void groundRemoval(){size_t lowerInd, upperInd;float diffX, diffY, diffZ, angle;// groundMat// -1, no valid info to check if ground of not// 0, initial value, after validation, means not ground// 1, groundfor (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j){for (size_t i = 0; i < groundScanInd; ++i){lowerInd = j + ( i )*Horizon_SCAN;upperInd = j + (i+1)*Horizon_SCAN;if (fullCloud->points[lowerInd].intensity == -1 ||fullCloud->points[upperInd].intensity == -1){// no info to check, invalid pointsgroundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) = -1;continue;}diffX = fullCloud->points[upperInd].x - fullCloud->points[lowerInd].x;diffY = fullCloud->points[upperInd].y - fullCloud->points[lowerInd].y;diffZ = fullCloud->points[upperInd].z - fullCloud->points[lowerInd].z;angle = atan2(diffZ, sqrt(diffX*diffX + diffY*diffY) ) * 180 / M_PI;if (abs(angle - sensorMountAngle) <= 10){groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) = 1;groundMat.at<int8_t>(i+1,j) = 1;}}}// extract ground cloud (groundMat == 1)// mark entry that doesn't need to label (ground and invalid point) for segmentation// note that ground remove is from 0~N_SCAN-1, need rangeMat for mark label matrix for the 16th scanfor (size_t i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i){for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j){if (groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) == 1 || rangeMat.at<float>(i,j) == FLT_MAX){labelMat.at<int>(i,j) = -1;}}}if (pubGroundCloud.getNumSubscribers() != 0){for (size_t i = 0; i <= groundScanInd; ++i){for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j){if (groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) == 1)groundCloud->push_back(fullCloud->points[j + i*Horizon_SCAN]);}}}}
2 基于BFS的点云聚类和外点剔除、树干点云提取算法
2.1 数学推导
广度优先遍历(BFS)和深度优先遍历(DFS)同属于两种经典的图遍历的算法。
具体到广度优先遍历算法来说,首先从某个节点出发,一层一层地遍历,下一层必须等到上一层节点全部遍历完成之后才会开始遍历。
比如在上面这个无向图中,如果我们从 A 节点开始遍历,那么首先访问和 A 节点相邻
的节点,这里就是 S、B、D,然后在访问和 S、B、D 相邻的其他节点,这里就是 C。
因此,遍历的顺序是 A->S->B->D->C;如果我们从 S 开始遍历,则顺序就是 S->A->B-
>C->D;可以看到,不同的起始点对应的遍历顺序是不同的。
通常我们使用 BFS 遍历图结构的时候,会借助一个队列 std::queue 来帮助我们实现,
其基本步骤如下:1. 将起始顶点 S 加入队列
2. 访问 S,同时把 S 标记为已访问
3. 循环从队列中取出节
1.如果队列为空,则访问结束
2.否则类似 S,将该节点标记为已访问,同时将其子节点加入队列。
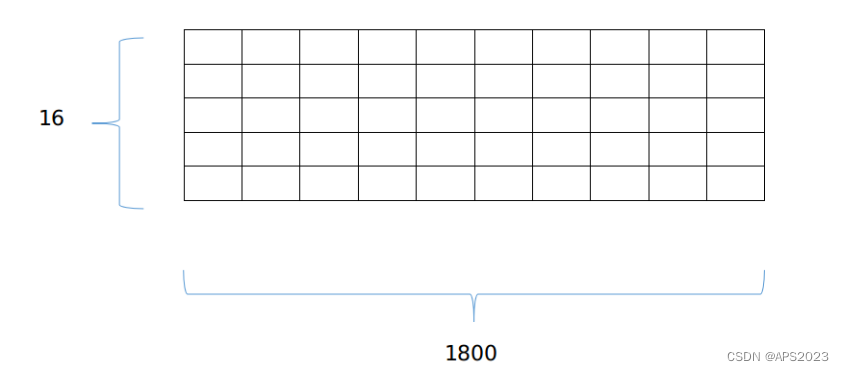
在 LeGO-LOAM 中,BFS 算法用于实现一个简单的点云聚类功能。BFS 算法适用于图数据结构,为了把单帧 lidar 点云运用上 BFS 算法,首先需要将其建模成一个图模型,一个很简单有效的办法就是将其投影到一个平面图上,以velodyne-16 为例,我们将其投影到一个 16×1800 大小的图上(这里 16 是一共有 16跟线束,1800 是因为水平分辨率是 0.2 度,一个扫描周期有 1800 个点)如图:
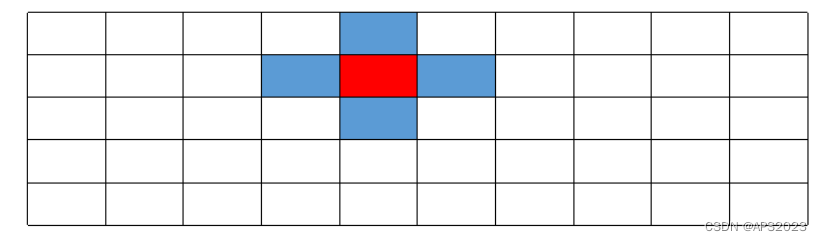
对于任何一个珊格点,其上下左右四个相邻点视为图结构中的邻接节点,这里要注意的是,左右边界的点和边界另一侧也构成邻接,因为水平方向是同一个扫描周期,具有物理意义上的连续性。我们可以以任意一个点开始执行 BFS 搜索,直到遍历完这部分近邻点,聚类点数过少的就认为是 outlier,可以被剔除。
具体实现
1. 遍历每个点,如果该点已经被处理过了就不再处理
2. 如果没有被处理就说明这是一个新的聚类,然后执行 BFS 的步骤
1.将队列里的首元素弹出,然后将该元素近邻塞入队列末尾(这里没有使用std::queue,使用的普通数组,所以就使用双指针来替代)这里的近邻就是上下左右:
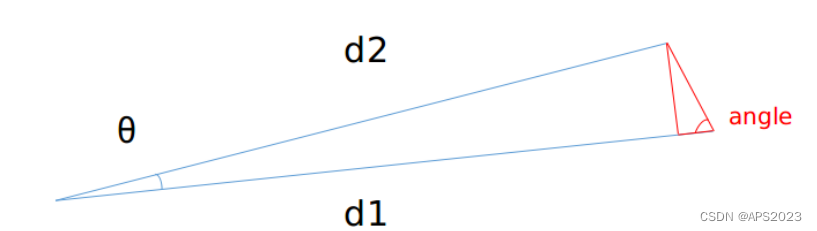
2.分别判断近邻和自身距离是否足够近
angle 越大则认为两点越可能是同一个聚类物体上的点,则打上同样的 label。
3.如此循环
2.2 代码实现
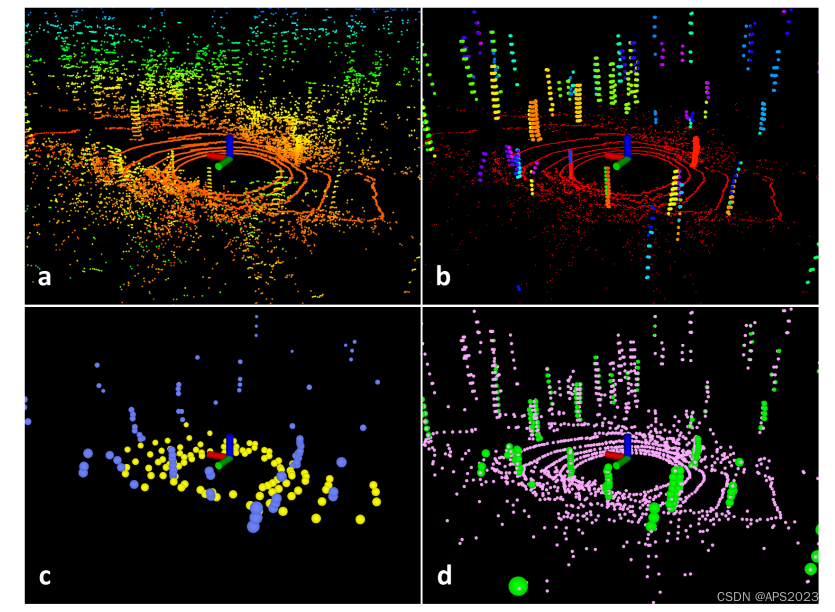
在嘈杂环境中的扫描的特征提取过程。原始点云如图(a)所示。在图(b)中,红色点被标记为地面点。其余的点是分割后保留的点。只保留树干..树叶点都被剔除掉了在图(c)中,蓝色和黄色点表示F e 和 F p 中的边缘和平面特征。在图(d)中,绿色和粉色点分别代表F e 和 F p 中的边缘和平面特征。 广度优先遍历代码:
// 广度优先遍历void labelComponents(int row, int col){// use std::queue std::vector std::deque will slow the program down greatlyfloat d1, d2, alpha, angle;int fromIndX, fromIndY, thisIndX, thisIndY; bool lineCountFlag[N_SCAN] = {false};// 用一个数组保存X坐标,一个数组保存Y坐标queueIndX[0] = row;queueIndY[0] = col;// 队列里面有多少个点int queueSize = 1;// 指向前端int queueStartInd = 0;// 指向即将要加入的位置int queueEndInd = 1;// 将这个点的(X,Y)坐标赋予给allPushedIndX[0]allPushedIndX[0] = row;allPushedIndY[0] = col;int allPushedIndSize = 1;while(queueSize > 0){// 将队列的首元素去除,完成广度优先的操作fromIndX = queueIndX[queueStartInd];fromIndY = queueIndY[queueStartInd];// 队列中一共有多少点--queueSize;// 将指向队列首部的指针向前移动1++queueStartInd;// 标记这个点云属于哪一类,当前聚类的ID,当前物体属于同一个ID在确定当前可以聚类的情况下更新 labelCount,labelCount++labelMat.at<int>(fromIndX, fromIndY) = labelCount;// 遍历这个结点的邻接顶点,其实就是上下左右四个元素// std::vector<std::pair<int8_t, int8_t> > neighborIterator;// std::pair<int8_t, int8_t> neighbor;// neighbor.first = -1; neighbor.second = 0; neighborIterator.push_back(neighbor);// neighbor.first = 0; neighbor.second = 1; neighborIterator.push_back(neighbor);// neighbor.first = 0; neighbor.second = -1; neighborIterator.push_back(neighbor);// neighbor.first = 1; neighbor.second = 0; neighborIterator.push_back(neighbor);for (auto iter = neighborIterator.begin(); iter != neighborIterator.end(); ++iter){// 四个可能的邻接顶点的(X,Y)值thisIndX = fromIndX + (*iter).first;thisIndY = fromIndY + (*iter).second;// 索引必须在(N_SCAN * HORIZON_SCAN = 16 * 1600中)// 行数不在 0 - 16 间(最上面最下面的点 第1根线或者第8根线的点)if (thisIndX < 0 || thisIndX >= N_SCAN)continue;// 同一根线相距360度且左右相邻if (thisIndY < 0)thisIndY = Horizon_SCAN - 1;if (thisIndY >= Horizon_SCAN)thisIndY = 0;// 这个顶点是否被访问过if (labelMat.at<int>(thisIndX, thisIndY) != 0)continue;// 将两个点距离雷达较远的点的距离赋值为d1,较近的点赋值为d2d1 = std::max(rangeMat.at<float>(fromIndX, fromIndY), rangeMat.at<float>(thisIndX, thisIndY));d2 = std::min(rangeMat.at<float>(fromIndX, fromIndY), rangeMat.at<float>(thisIndX, thisIndY));// (0,1) (0,-1) 角分辨率为0.2度--左右糯if ((*iter).first == 0)alpha = segmentAlphaX;// (1,0) (-1,0) 角分辨率为2度--上下挪动elsealpha = segmentAlphaY;// d2*sin(alpha)为垂线距离 d2*cos(alpha))为垂线的对边 d1 -d2*cos(alpha))为小边 求tan值为angle角度angle = atan2(d2*sin(alpha), (d1 -d2*cos(alpha)));// 60度(弧度制) 60.0/180.0*M_PI; ----减少这个值会增大精度if (angle > segmentTheta){// 丁真 添加到队列中 queueEndInd指向即将要插入的位置中queueIndX[queueEndInd] = thisIndX;queueIndY[queueEndInd] = thisIndY;++queueSize;++queueEndInd;// 标记和前面一种的类型labelMat.at<int>(thisIndX, thisIndY) = labelCount;// 标志位 : 是否这个点被遍历过设置为truelineCountFlag[thisIndX] = true;// 保存聚类结果allPushedIndX[allPushedIndSize] = thisIndX;allPushedIndY[allPushedIndSize] = thisIndY;++allPushedIndSize;}}}// check if this segment is validbool feasibleSegment = false;// 如果聚类的点大于30,小于30认为是叶子点/噪声点if (allPushedIndSize >= 30)feasibleSegment = true;// 可能是树杆(垂直于LIDAR扫描方向的)else if (allPushedIndSize >= segmentValidPointNum){int lineCount = 0;for (size_t i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i)if (lineCountFlag[i] == true)++lineCount;if (lineCount >= segmentValidLineNum)feasibleSegment = true; }// segment is valid, mark these pointsif (feasibleSegment == true){// 更新标签值,表示下次是新的一陀东西++labelCount;}else{// 聚类无效for (size_t i = 0; i < allPushedIndSize; ++i){labelMat.at<int>(allPushedIndX[i], allPushedIndY[i]) = 999999;}}}特征提取前预处理代码:
// 对非地面点聚类void cloudSegmentation(){// 对所有点进行遍历 N_SCAN=16线 Horizon_SCAN=1800(每根线有1800个点)for (size_t i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i)for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j)if (labelMat.at<int>(i,j) == 0)// 地面点会是-1我们不处理(在上面的代码讲解中已经说过了)// 以这个点为顶点进行广度优先遍历labelComponents(i, j);int sizeOfSegCloud = 0;// 遍历本帧所有激光点for (size_t i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i){segMsg.startRingIndex[i] = sizeOfSegCloud-1 + 5;for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j){// 要不是有效的距离点 要不是有效的地面点if (labelMat.at<int>(i,j) > 0 || groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) == 1){// 聚类无效的点if (labelMat.at<int>(i,j) == 999999){if (i > groundScanInd && j % 5 == 0){outlierCloud->push_back(fullCloud->points[j + i*Horizon_SCAN]);continue;}else{continue;}}// 1800列 做一个下采样 点云加密的时候可以用// groundMat// -1, no valid info to check if ground of not// 0, initial value, after validation, means not ground// 1, groundif (groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) == 1){if (j%5!=0 && j>5 && j<Horizon_SCAN-5)continue;}// 标记地面点,这样在后续提取特征的时候不会被当作角点提取segMsg.segmentedCloudGroundFlag[sizeOfSegCloud] = (groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) == 1);// mark the points' column index for marking occlusion latersegMsg.segmentedCloudColInd[sizeOfSegCloud] = j;// 保存距离激光雷达的距离segMsg.segmentedCloudRange[sizeOfSegCloud] = rangeMat.at<float>(i,j);// 保存点云segmentedCloud->push_back(fullCloud->points[j + i*Horizon_SCAN]);// 更新下一帧的点的索引++sizeOfSegCloud;}}// 同LIO-SAM特征提取的边界segMsg.endRingIndex[i] = sizeOfSegCloud-1 - 5;}// 发布给RVIZif (pubSegmentedCloudPure.getNumSubscribers() != 0){for (size_t i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i){for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j){if (labelMat.at<int>(i,j) > 0 && labelMat.at<int>(i,j) != 999999){segmentedCloudPure->push_back(fullCloud->points[j + i*Horizon_SCAN]);segmentedCloudPure->points.back().intensity = labelMat.at<int>(i,j);}}}}}
3 两步优化的帧间里程计
3.1 理论推导
和原始 LOAM (或者 A-LOAM )一样,通过前后两帧点云来估计两帧之间的运动,从而累加得到前端里程记的输出,和上述方法使用线面约束同时优化六自由度帧间位姿不同,LeGO-LOAM 的前端分成两个步骤,每个步骤估计三自由度的变量:
第一步 利用地面点优化
地面点更符合面特征的性质。因此,地面点的优化问题就使用点到面的约束来构建,同时我们注意到,地面点之间的约束对 x , y 和 yaw 这三个自由度是不能观的。换句话说,当这三个自由度的值发生变化时,点到面的残差不会发生显著变化。所以,地面点之间的优化只会对 pitch , roll 以及 z 进行约束和优化
第二步 利用角点优化
第一步优化完 pitch 、 roll 以及 z 之后,我们仍需对另外三个自由度的变量进行估计,此时,我们选用提取的角点进行优化,由于多线激光雷达提取的角点通常是垂直的边缘特征。因此,这些特征对 x 、 y 以及yaw 有着比较好的能观性,通过角点的优化结合上地面点的结果可以得到六自由度的帧间优化结果。
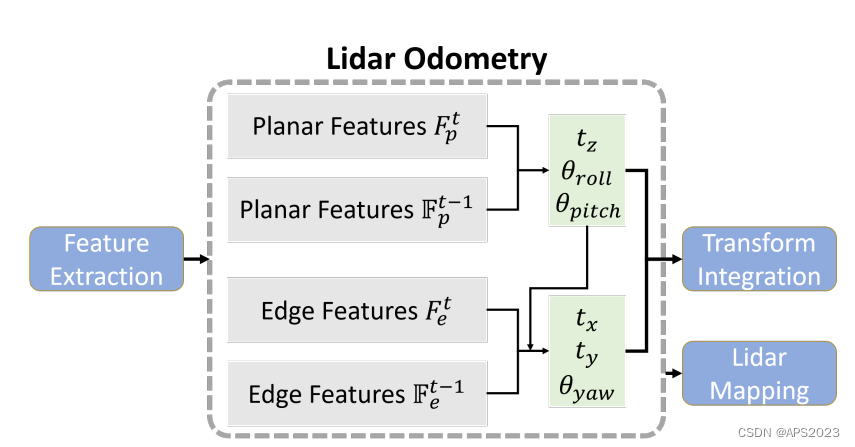
激光里程计模块的两步优化。首先通过匹配从地面点提取的平面特征获得 [t z , θ roll , θ pitch ]。然后,使用从分割点提取的边缘特征来估计 [t x , t y , θ yaw ],同时将 [t z , θ roll , θ pitch ] 作为约束。
3.2 代码实现
void updateTransformation(){if (laserCloudCornerLastNum < 10 || laserCloudSurfLastNum < 100)return;for (int iterCount1 = 0; iterCount1 < 25; iterCount1++) {laserCloudOri->clear();coeffSel->clear();// 平面点优化findCorrespondingSurfFeatures(iterCount1);if (laserCloudOri->points.size() < 10)continue;if (calculateTransformationSurf(iterCount1) == false)break;}for (int iterCount2 = 0; iterCount2 < 25; iterCount2++) {laserCloudOri->clear();coeffSel->clear();// 角点优化findCorrespondingCornerFeatures(iterCount2);if (laserCloudOri->points.size() < 10)continue;if (calculateTransformationCorner(iterCount2) == false)break;}}每一个部分和LOAM一致,请移步我的多传感器融合的博客。
void findCorrespondingSurfFeatures(int iterCount){int surfPointsFlatNum = surfPointsFlat->points.size();for (int i = 0; i < surfPointsFlatNum; i++) {TransformToStart(&surfPointsFlat->points[i], &pointSel);if (iterCount % 5 == 0) {kdtreeSurfLast->nearestKSearch(pointSel, 1, pointSearchInd, pointSearchSqDis);int closestPointInd = -1, minPointInd2 = -1, minPointInd3 = -1;if (pointSearchSqDis[0] < nearestFeatureSearchSqDist) {closestPointInd = pointSearchInd[0];int closestPointScan = int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[closestPointInd].intensity);float pointSqDis, minPointSqDis2 = nearestFeatureSearchSqDist, minPointSqDis3 = nearestFeatureSearchSqDist;for (int j = closestPointInd + 1; j < surfPointsFlatNum; j++) {if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) > closestPointScan + 2.5) {break;}pointSqDis = (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) * (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) + (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) * (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) + (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z) * (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z);if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) <= closestPointScan) {if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis2) {minPointSqDis2 = pointSqDis;minPointInd2 = j;}} else {if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis3) {minPointSqDis3 = pointSqDis;minPointInd3 = j;}}}for (int j = closestPointInd - 1; j >= 0; j--) {if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) < closestPointScan - 2.5) {break;}pointSqDis = (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) * (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) + (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) * (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) + (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z) * (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z);if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) >= closestPointScan) {if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis2) {minPointSqDis2 = pointSqDis;minPointInd2 = j;}} else {if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis3) {minPointSqDis3 = pointSqDis;minPointInd3 = j;}}}}pointSearchSurfInd1[i] = closestPointInd;pointSearchSurfInd2[i] = minPointInd2;pointSearchSurfInd3[i] = minPointInd3;}if (pointSearchSurfInd2[i] >= 0 && pointSearchSurfInd3[i] >= 0) {tripod1 = laserCloudSurfLast->points[pointSearchSurfInd1[i]];tripod2 = laserCloudSurfLast->points[pointSearchSurfInd2[i]];tripod3 = laserCloudSurfLast->points[pointSearchSurfInd3[i]];float pa = (tripod2.y - tripod1.y) * (tripod3.z - tripod1.z) - (tripod3.y - tripod1.y) * (tripod2.z - tripod1.z);float pb = (tripod2.z - tripod1.z) * (tripod3.x - tripod1.x) - (tripod3.z - tripod1.z) * (tripod2.x - tripod1.x);float pc = (tripod2.x - tripod1.x) * (tripod3.y - tripod1.y) - (tripod3.x - tripod1.x) * (tripod2.y - tripod1.y);float pd = -(pa * tripod1.x + pb * tripod1.y + pc * tripod1.z);float ps = sqrt(pa * pa + pb * pb + pc * pc);pa /= ps;pb /= ps;pc /= ps;pd /= ps;float pd2 = pa * pointSel.x + pb * pointSel.y + pc * pointSel.z + pd;float s = 1;if (iterCount >= 5) {s = 1 - 1.8 * fabs(pd2) / sqrt(sqrt(pointSel.x * pointSel.x+ pointSel.y * pointSel.y + pointSel.z * pointSel.z));}if (s > 0.1 && pd2 != 0) {coeff.x = s * pa;coeff.y = s * pb;coeff.z = s * pc;coeff.intensity = s * pd2;laserCloudOri->push_back(surfPointsFlat->points[i]);coeffSel->push_back(coeff);}}}}void findCorrespondingCornerFeatures(int iterCount){int cornerPointsSharpNum = cornerPointsSharp->points.size();for (int i = 0; i < cornerPointsSharpNum; i++) {TransformToStart(&cornerPointsSharp->points[i], &pointSel);if (iterCount % 5 == 0) {kdtreeCornerLast->nearestKSearch(pointSel, 1, pointSearchInd, pointSearchSqDis);int closestPointInd = -1, minPointInd2 = -1;if (pointSearchSqDis[0] < nearestFeatureSearchSqDist) {closestPointInd = pointSearchInd[0];int closestPointScan = int(laserCloudCornerLast->points[closestPointInd].intensity);float pointSqDis, minPointSqDis2 = nearestFeatureSearchSqDist;for (int j = closestPointInd + 1; j < cornerPointsSharpNum; j++) {if (int(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].intensity) > closestPointScan + 2.5) {break;}pointSqDis = (laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) * (laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) + (laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) * (laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) + (laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z) * (laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z);if (int(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].intensity) > closestPointScan) {if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis2) {minPointSqDis2 = pointSqDis;minPointInd2 = j;}}}for (int j = closestPointInd - 1; j >= 0; j--) {if (int(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].intensity) < closestPointScan - 2.5) {break;}pointSqDis = (laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) * (laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) + (laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) * (laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) + (laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z) * (laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z);if (int(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].intensity) < closestPointScan) {if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis2) {minPointSqDis2 = pointSqDis;minPointInd2 = j;}}}}pointSearchCornerInd1[i] = closestPointInd;pointSearchCornerInd2[i] = minPointInd2;}if (pointSearchCornerInd2[i] >= 0) {tripod1 = laserCloudCornerLast->points[pointSearchCornerInd1[i]];tripod2 = laserCloudCornerLast->points[pointSearchCornerInd2[i]];float x0 = pointSel.x;float y0 = pointSel.y;float z0 = pointSel.z;float x1 = tripod1.x;float y1 = tripod1.y;float z1 = tripod1.z;float x2 = tripod2.x;float y2 = tripod2.y;float z2 = tripod2.z;float m11 = ((x0 - x1)*(y0 - y2) - (x0 - x2)*(y0 - y1));float m22 = ((x0 - x1)*(z0 - z2) - (x0 - x2)*(z0 - z1));float m33 = ((y0 - y1)*(z0 - z2) - (y0 - y2)*(z0 - z1));float a012 = sqrt(m11 * m11 + m22 * m22 + m33 * m33);float l12 = sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2)*(y1 - y2) + (z1 - z2)*(z1 - z2));float la = ((y1 - y2)*m11 + (z1 - z2)*m22) / a012 / l12;float lb = -((x1 - x2)*m11 - (z1 - z2)*m33) / a012 / l12;float lc = -((x1 - x2)*m22 + (y1 - y2)*m33) / a012 / l12;float ld2 = a012 / l12;float s = 1;if (iterCount >= 5) {s = 1 - 1.8 * fabs(ld2);}if (s > 0.1 && ld2 != 0) {coeff.x = s * la; coeff.y = s * lb;coeff.z = s * lc;coeff.intensity = s * ld2;laserCloudOri->push_back(cornerPointsSharp->points[i]);coeffSel->push_back(coeff);}}}}
相关文章:

LeGO-Loam代码解析(二)--- Lego-LOAM的地面点分离、聚类、两步优化方法
1 地面点分离剔除方法 1.1 数学推导 LeGO-LOAM 中前端改进中很重要的一点就是充分利用了地面点,那首先自然是提取 对地面点的提取。 如上图,相邻的两个扫描线束的同一列打在地面上如 点所示,他们的垂直高度差 ,水平距离差 ,计算垂直高度差和水平高度差…...

程序员如何利用公网打造低成本轻量化的搜索和下载平台【内网穿透】
🎬 鸽芷咕:个人主页 🔥 个人专栏: 《高效编程技巧》《cpolar》 ⛺️生活的理想,就是为了理想的生活! 公网远程访问本地硬盘文件【内网穿透】 文章目录 公网远程访问本地硬盘文件【内网穿透】前言1. 下载cpolar和Everything软件1.…...
构建可远程访问的企业内部论坛
文章目录 前言1.cpolar、PHPStudy2.Discuz3.打开PHPStudy,安装网页论坛所需软件4.进行网页运行环境的构建5.运行Discuz网页程序6.使用cpolar建立穿透内网的数据隧道,发布到公网7.对云端保留的空白数据隧道进行配置8.Discuz论坛搭建完毕 前言 企业在发展…...
场:河南理工大学-C 旅游)
2023河南萌新联赛第(六)场:河南理工大学-C 旅游
2023河南萌新联赛第(六)场:河南理工大学 https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/63602/C 文章目录 2023河南萌新联赛第(六)场:河南理工大学题意解题思路代码 题意 小C喜欢旅游,现在他要去DSH旅…...
)
C语言 常用工具型API ----------strchr()
函数原型 char *strchr(const char *str, int c) 参数 str-- 要被检索的 C 字符串。 c-- 在 str 中要搜索的字符。 功能 在参数str所指向的字符串中搜索第一次出现字符c(一个无符号字符)的位置 头文件 #include <string.h> 返回值 返回一…...

建造者模式的理论与实现
本文实践代码仓库:https://github.com/goSilver/my_practice 文章目录 一、定义二、作用三、实现四、总结 一、定义 建造者模式是一种创建复杂对象的设计模式。它将一个复杂对象的构建过程分解为多个简单的步骤,并且允许按照特定的顺序来构建对象。通过…...

非计算机科班如何顺利转码进入计算机领域?
文章目录 如何规划才能实现转码?计算机岗位发展前景?现阶段转码 总结 🎉欢迎来到Java学习路线专栏~探索非计算机科班如何顺利转码进入计算机领域 ☆* o(≧▽≦)o *☆嗨~我是IT陈寒🍹✨博客主页:IT陈寒的博客dz…...
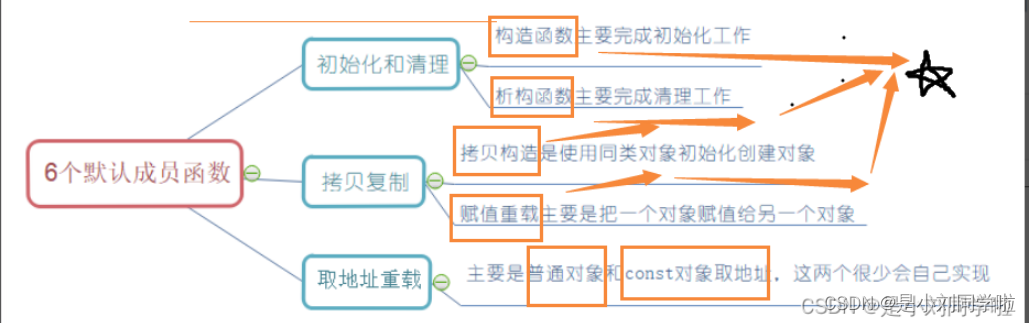
【C++类和对象】类有哪些默认成员函数呢?(下)
文章目录 一、类的6个默认成员函数二、日期类的实现2.1 运算符重载部分2.2 日期之间的运算2.3 整体代码1.Date.h部分2. Date.cpp部分 三. const成员函数四. 取地址及const取地址操作符重载扩展内容 总结 ヾ(๑╹◡╹)ノ" 人总要为过去的懒惰而付出代价ヾ(๑╹◡…...

springboot自定义banner的输出与源码解析
文章目录 一、介绍二、演示环境三、自定义banner1. 文本2. 图片3. placeholder占位符4. 关闭banner 四、源码分析1. 关闭banner2. banner模式3. banner打印器4. 打印banner① 获取banner② 打印banner 5. 版本号占位符的解析器6. 文本格式占位符的解析器7. 应用标题占位符的解析…...

LeetCode 141.环形链表
文章目录 💡题目分析💡解题思路🔔接口源码💡深度思考❓思考1❓思考2 题目链接👉 LeetCode 141.环形链表👈 💡题目分析 给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。 如果链表中…...
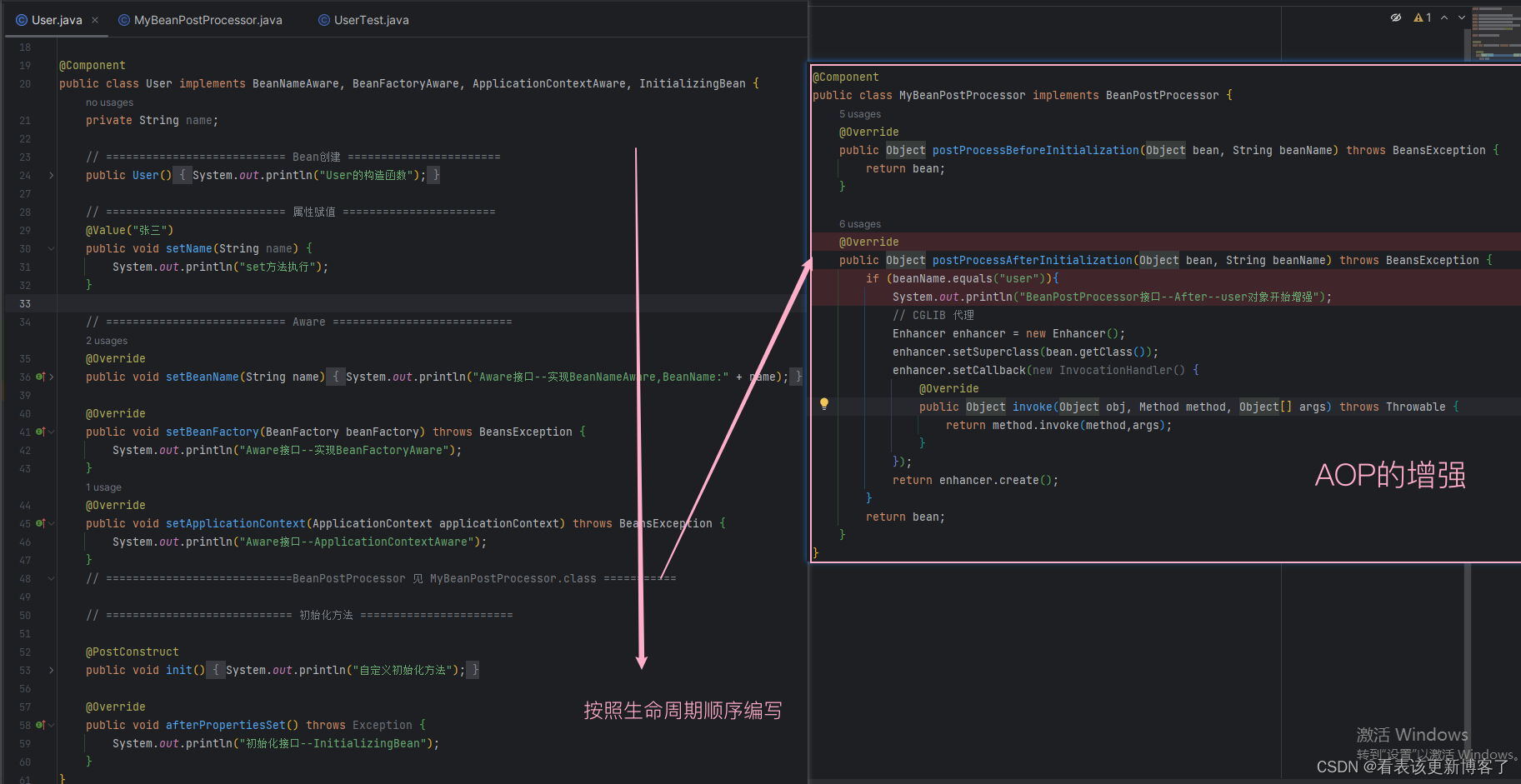
Spring-Bean的生命周期
目录 生命周期汇总 细分生命周期 1.实例化 2.属性赋值(依赖注入) 3.Aware接口 4.BeanPostProcessor接口 5.初始化 6.销毁 测试验证 类结构 业务类 测试类 生命周期汇总 Spring Bean 的生命周期见下图 (一定记忆好下图&#x…...
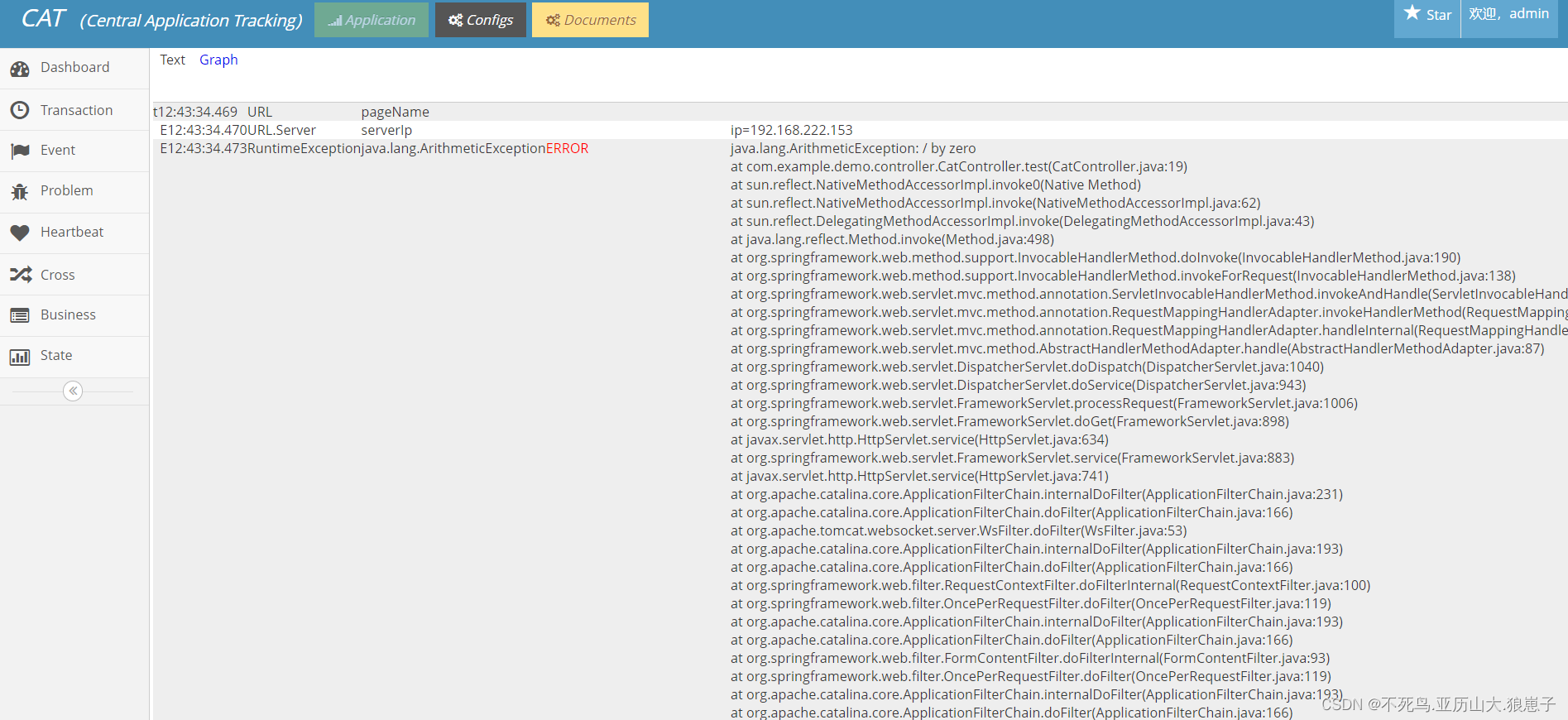
Cat(3):客户端集成—简单案例
接下来编写一个简单的springboot与Cat整合的案例 1 新建springboot项目 首先创建一个Spring Boot的初始化工程。只需要勾选web依赖即可。 2 添加 Maven 添加依赖 <dependency><groupId>com.dianping.cat</groupId><artifactId>cat-client</artifa…...

虚拟机/双系统Ubuntu扩容
虚拟机Ubuntu扩容 1.需要删除所有的快照 2.扩展虚拟机磁盘大小 虚拟机(M)→设置(s)→硬盘(SCSI)→扩展磁盘容量 3.Ubuntu内调整分区大小 安装gparted分区工具:sudo apt-get install gparted 启动gparted并resize分区 4.最后最好建一个快照,不然gg了…...
Nginx搭建本地服务器,无需购买服务器即可测试vue项目打包后的效果
一.前言 本文是在windows环境(Linux环境下其实也大同小异)下基于Nginx实现搭建本地服务器,手把手教你部署vue项目。 二.Nginx入门 1)下载安装 进入Nginx官网下载,选择stable版本下的windows版本下载即可 2)…...

SpringBoot 接口调用出现乱码解决 中文乱码
SpringBoot 接口调用出现乱码解决 package com.cxjg.mvc.util;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter; import org.springfra…...

JDBC封装与设计模式
什么是 DAO ? Data Access Object(数据存取对象) 位于业务逻辑和持久化数据之间实现对持久化数据的访问 DAO起着转换器的作用,将数据在实体类和数据库记录之间进行转换。 ----------------------------------------------------- DAO模式的组成部分 …...

小程序扫描二维码获取网址,通过Jsoup进行解析
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档 目录 文章目录 前言 一、Jsoup是什么? 二、使用步骤 1.引入库 2.读入数据 总结 前言 vx开发小程序使用扫一扫时不同二维码展示的东西不一样,需要进行解析 提示&a…...
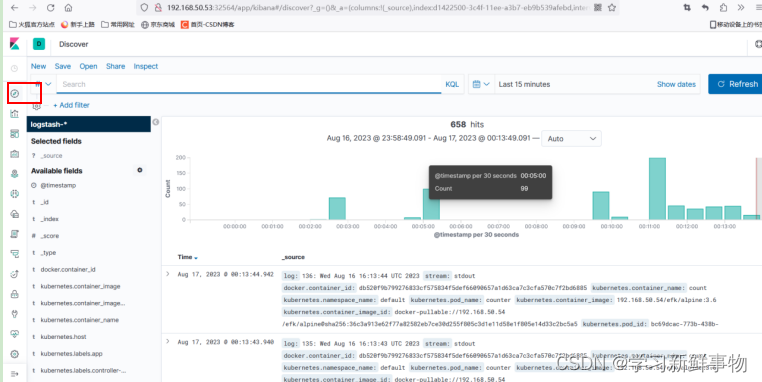
Kubernetes+EFK构建日志分析平台
目录 Elasticsearch产品介绍 Fluentd 工作原理 Kibana产品介绍 一、环境准备 前三个主机都要操作 1、主机初始化配置 2、部署docker环境 2、部署kubernetes集群 2.1、组件介绍 2.2、配置阿里云yum源 2.3、安装kubelet kubeadm kubectl 2.4、配置init-config.yaml …...
客服如何减轻工作压力?浅析客服压力管理方法
在现代商业领域中,客服是一项非常重要的工作,负责根据客户需求提供解决方案。客服工作不仅需要一定的专业知识和技能,还需要面对各种复杂、多变的情况,并拥有强大的应对压力的能力。客服从业人员的工作压力往往非常大,…...
知识储备--基础算法篇-二分搜索
1.前言 最近准备开始刷算法题了,搜了很多相关的帖子,下面三个很不错, 计算机视觉秋招准备过程看这个:计算机视觉算法工程师-秋招面经 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/399813916 复习深度学习相关…...
Linux 文件类型,目录与路径,文件与目录管理
文件类型 后面的字符表示文件类型标志 普通文件:-(纯文本文件,二进制文件,数据格式文件) 如文本文件、图片、程序文件等。 目录文件:d(directory) 用来存放其他文件或子目录。 设备…...

Cesium1.95中高性能加载1500个点
一、基本方式: 图标使用.png比.svg性能要好 <template><div id"cesiumContainer"></div><div class"toolbar"><button id"resetButton">重新生成点</button><span id"countDisplay&qu…...
YSYX学习记录(八)
C语言,练习0: 先创建一个文件夹,我用的是物理机: 安装build-essential 练习1: 我注释掉了 #include <stdio.h> 出现下面错误 在你的文本编辑器中打开ex1文件,随机修改或删除一部分,之后…...

MySQL账号权限管理指南:安全创建账户与精细授权技巧
在MySQL数据库管理中,合理创建用户账号并分配精确权限是保障数据安全的核心环节。直接使用root账号进行所有操作不仅危险且难以审计操作行为。今天我们来全面解析MySQL账号创建与权限分配的专业方法。 一、为何需要创建独立账号? 最小权限原则…...

动态 Web 开发技术入门篇
一、HTTP 协议核心 1.1 HTTP 基础 协议全称 :HyperText Transfer Protocol(超文本传输协议) 默认端口 :HTTP 使用 80 端口,HTTPS 使用 443 端口。 请求方法 : GET :用于获取资源,…...
 Module Federation:Webpack.config.js文件中每个属性的含义解释)
MFE(微前端) Module Federation:Webpack.config.js文件中每个属性的含义解释
以Module Federation 插件详为例,Webpack.config.js它可能的配置和含义如下: 前言 Module Federation 的Webpack.config.js核心配置包括: name filename(定义应用标识) remotes(引用远程模块࿰…...

WebRTC调研
WebRTC是什么,为什么,如何使用 WebRTC有什么优势 WebRTC Architecture Amazon KVS WebRTC 其它厂商WebRTC 海康门禁WebRTC 海康门禁其他界面整理 威视通WebRTC 局域网 Google浏览器 Microsoft Edge 公网 RTSP RTMP NVR ONVIF SIP SRT WebRTC协…...
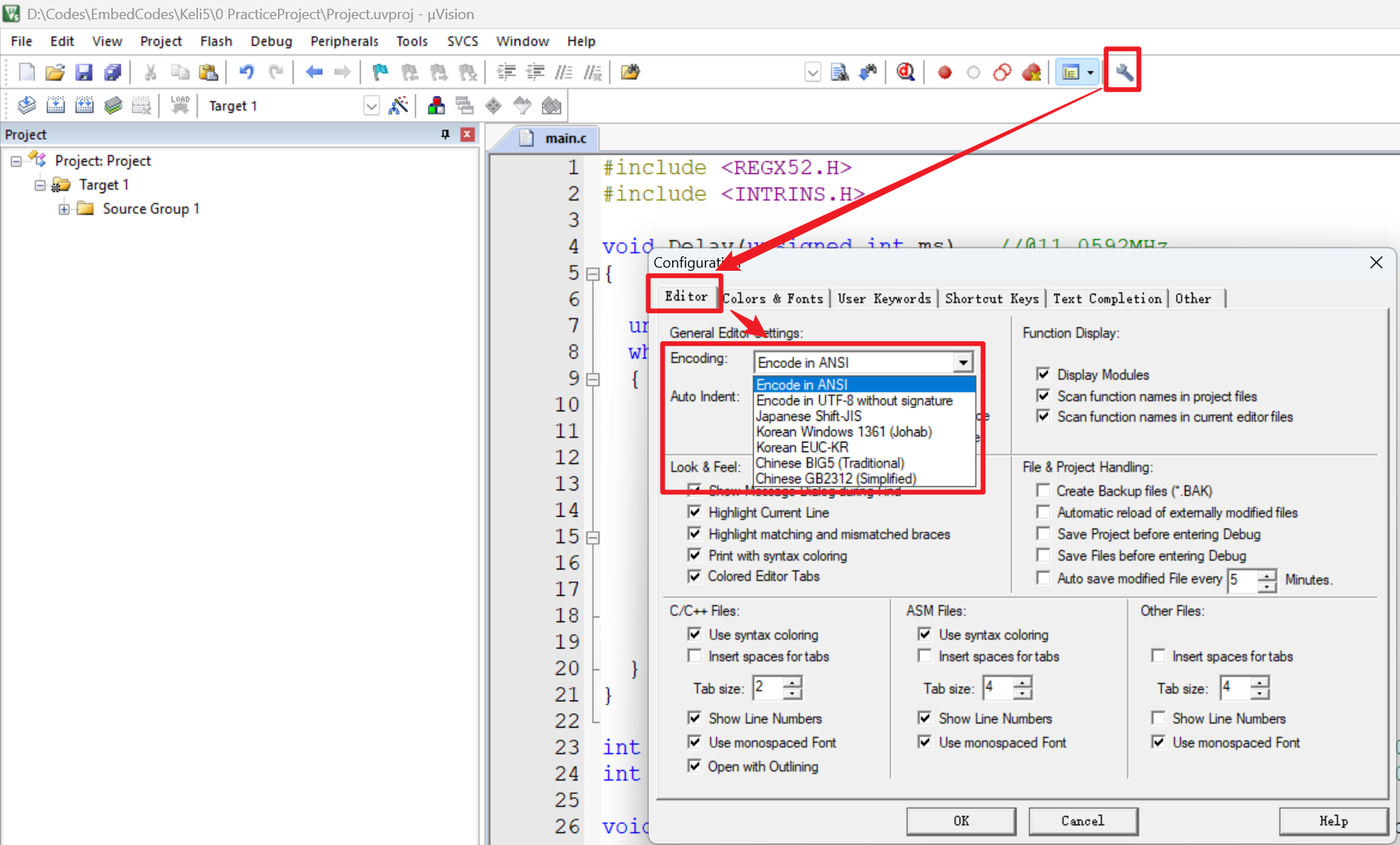
【51单片机】4. 模块化编程与LCD1602Debug
1. 什么是模块化编程 传统编程会将所有函数放在main.c中,如果使用的模块多,一个文件内会有很多代码,不利于组织和管理 模块化编程则是将各个模块的代码放在不同的.c文件里,在.h文件里提供外部可调用函数声明,其他.c文…...

数据分析六部曲?
引言 上一章我们说到了数据分析六部曲,何谓六部曲呢? 其实啊,数据分析没那么难,只要掌握了下面这六个步骤,也就是数据分析六部曲,就算你是个啥都不懂的小白,也能慢慢上手做数据分析啦。 第一…...
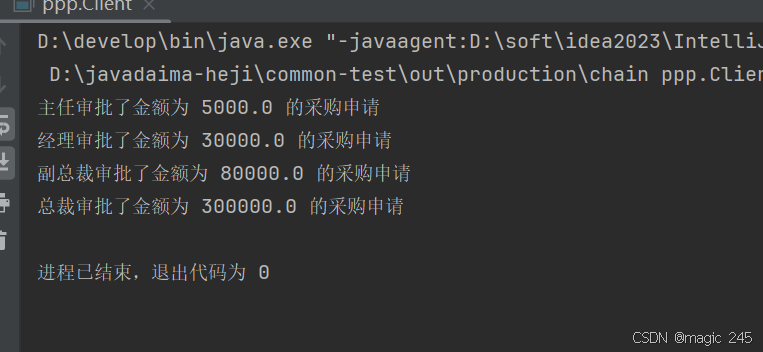
Java设计模式:责任链模式
一、什么是责任链模式? 责任链模式(Chain of Responsibility Pattern) 是一种 行为型设计模式,它通过将请求沿着一条处理链传递,直到某个对象处理它为止。这种模式的核心思想是 解耦请求的发送者和接收者,…...