CJSON简单介绍
json简介
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。 易于人阅读和编写。同时也易于机器解析和生成。 它基于JavaScript Programming Language, Standard ECMA-262 3rd Edition - December 1999的一个子集,最新的定义可以参考ECMA-404_2nd_edition_The JSON Data Interchange Syntax,这份标准只有16页,可以一次性读完。
JSON具有以下这些形式:
- 对象是一个无序的“‘名称/值’对”集合。一个对象以 {左括号\{_{左括号}{左括号 开始, }右括号\}_{右括号}}右括号 结束。每个“名称”后跟一个 :冒号:_{冒号}:冒号 ;“‘名称/值’ 对”之间使用 ,逗号,_{逗号},逗号 分隔。
- 数组是值(value)的有序集合。一个数组以 [左中括号[_{左中括号}[左中括号 开始, ]右中括号]_{右中括号}]右中括号 结束。值之间使用 ,逗号 分隔。
- 值(value)可以是双引号括起来的字符串(string)、数值(number)、true、false、 null、对象(object)或者数组(array)。这些结构可以嵌套。
- 字符串(string)是由双引号包围的任意数量Unicode字符的集合,使用反斜线转义。一个字符(character)即一个单独的字符串(character string)。
- 数值(number)也与C或者Java的数值非常相似。除去未曾使用的八进制与十六进制格式。除去一些编码细节。
- 空白可以加入到任何符号之间。
一个典型的json结构如下所示
{"FirstName": "John","LastName": "Doe","Age": 43,"Address": {"Street": "Downing Street 10","City": "London","Country": "Great Britain"},"Phone numbers": ["+44 1234567","+44 2345678"]}
具体可以参考jason官网:http://www.json.org/json-zh.html
CJSON
CJSON是一个基于C语言实现的json库,为了兼容更多的平台,使用ANSI C (C89)标准来编写,其项目地址在http://github.com/DaveGamble/cJSON。
如何在项目中使用CJSON
有两种方式:
- 使用链接库的方式,先编译成库,之后在项目中使用
- 直接将CJSON的源代码(
cJSON.h和cJSON.c)加到项目中,之后和项目一起编译
CJSON提供的接口
CJSON提供的接口都在cJSON.h中声明出来了(以CJSON_PUBLIC的宏开头),还有一些直接是宏
/* returns the version of cJSON as a string */
CJSON_PUBLIC(const char*) cJSON_Version(void);/* Supply malloc, realloc and free functions to cJSON */
CJSON_PUBLIC(void) cJSON_InitHooks(cJSON_Hooks* hooks);/* Memory Management: the caller is always responsible to free the results from all variants of cJSON_Parse (with cJSON_Delete) and cJSON_Print (with stdlib free, cJSON_Hooks.free_fn, or cJSON_free as appropriate). The exception is cJSON_PrintPreallocated, where the caller has full responsibility of the buffer. */
/* Supply a block of JSON, and this returns a cJSON object you can interrogate. */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_Parse(const char *value);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_ParseWithLength(const char *value, size_t buffer_length);
/* ParseWithOpts allows you to require (and check) that the JSON is null terminated, and to retrieve the pointer to the final byte parsed. */
/* If you supply a ptr in return_parse_end and parsing fails, then return_parse_end will contain a pointer to the error so will match cJSON_GetErrorPtr(). */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_ParseWithOpts(const char *value, const char **return_parse_end, cJSON_bool require_null_terminated);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_ParseWithLengthOpts(const char *value, size_t buffer_length, const char **return_parse_end, cJSON_bool require_null_terminated);/* Render a cJSON entity to text for transfer/storage. */
CJSON_PUBLIC(char *) cJSON_Print(const cJSON *item);
/* Render a cJSON entity to text for transfer/storage without any formatting. */
CJSON_PUBLIC(char *) cJSON_PrintUnformatted(const cJSON *item);
/* Render a cJSON entity to text using a buffered strategy. prebuffer is a guess at the final size. guessing well reduces reallocation. fmt=0 gives unformatted, =1 gives formatted */
CJSON_PUBLIC(char *) cJSON_PrintBuffered(const cJSON *item, int prebuffer, cJSON_bool fmt);
/* Render a cJSON entity to text using a buffer already allocated in memory with given length. Returns 1 on success and 0 on failure. */
/* NOTE: cJSON is not always 100% accurate in estimating how much memory it will use, so to be safe allocate 5 bytes more than you actually need */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_PrintPreallocated(cJSON *item, char *buffer, const int length, const cJSON_bool format);
/* Delete a cJSON entity and all subentities. */
CJSON_PUBLIC(void) cJSON_Delete(cJSON *item);/* Returns the number of items in an array (or object). */
CJSON_PUBLIC(int) cJSON_GetArraySize(const cJSON *array);
/* Retrieve item number "index" from array "array". Returns NULL if unsuccessful. */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_GetArrayItem(const cJSON *array, int index);
/* Get item "string" from object. Case insensitive. */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_GetObjectItem(const cJSON * const object, const char * const string);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_GetObjectItemCaseSensitive(const cJSON * const object, const char * const string);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_HasObjectItem(const cJSON *object, const char *string);
/* For analysing failed parses. This returns a pointer to the parse error. You'll probably need to look a few chars back to make sense of it. Defined when cJSON_Parse() returns 0. 0 when cJSON_Parse() succeeds. */
CJSON_PUBLIC(const char *) cJSON_GetErrorPtr(void);/* Check item type and return its value */
CJSON_PUBLIC(char *) cJSON_GetStringValue(const cJSON * const item);
CJSON_PUBLIC(double) cJSON_GetNumberValue(const cJSON * const item);/* These functions check the type of an item */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_IsInvalid(const cJSON * const item);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_IsFalse(const cJSON * const item);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_IsTrue(const cJSON * const item);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_IsBool(const cJSON * const item);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_IsNull(const cJSON * const item);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_IsNumber(const cJSON * const item);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_IsString(const cJSON * const item);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_IsArray(const cJSON * const item);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_IsObject(const cJSON * const item);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_IsRaw(const cJSON * const item);/* These calls create a cJSON item of the appropriate type. */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateNull(void);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateTrue(void);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateFalse(void);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateBool(cJSON_bool boolean);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateNumber(double num);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateString(const char *string);
/* raw json */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateRaw(const char *raw);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateArray(void);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateObject(void);/* Create a string where valuestring references a string so* it will not be freed by cJSON_Delete */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateStringReference(const char *string);
/* Create an object/array that only references it's elements so* they will not be freed by cJSON_Delete */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateObjectReference(const cJSON *child);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateArrayReference(const cJSON *child);/* These utilities create an Array of count items.* The parameter count cannot be greater than the number of elements in the number array, otherwise array access will be out of bounds.*/
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateIntArray(const int *numbers, int count);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateFloatArray(const float *numbers, int count);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateDoubleArray(const double *numbers, int count);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateStringArray(const char *const *strings, int count);/* Append item to the specified array/object. */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_AddItemToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_AddItemToObject(cJSON *object, const char *string, cJSON *item);
/* Use this when string is definitely const (i.e. a literal, or as good as), and will definitely survive the cJSON object.* WARNING: When this function was used, make sure to always check that (item->type & cJSON_StringIsConst) is zero before* writing to `item->string` */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_AddItemToObjectCS(cJSON *object, const char *string, cJSON *item);
/* Append reference to item to the specified array/object. Use this when you want to add an existing cJSON to a new cJSON, but don't want to corrupt your existing cJSON. */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_AddItemReferenceToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_AddItemReferenceToObject(cJSON *object, const char *string, cJSON *item);/* Remove/Detach items from Arrays/Objects. */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_DetachItemViaPointer(cJSON *parent, cJSON * const item);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(cJSON *array, int which);
CJSON_PUBLIC(void) cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(cJSON *array, int which);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_DetachItemFromObject(cJSON *object, const char *string);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_DetachItemFromObjectCaseSensitive(cJSON *object, const char *string);
CJSON_PUBLIC(void) cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(cJSON *object, const char *string);
CJSON_PUBLIC(void) cJSON_DeleteItemFromObjectCaseSensitive(cJSON *object, const char *string);/* Update array items. */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_InsertItemInArray(cJSON *array, int which, cJSON *newitem); /* Shifts pre-existing items to the right. */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_ReplaceItemViaPointer(cJSON * const parent, cJSON * const item, cJSON * replacement);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(cJSON *array, int which, cJSON *newitem);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *newitem);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_ReplaceItemInObjectCaseSensitive(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *newitem);/* Duplicate a cJSON item */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_Duplicate(const cJSON *item, cJSON_bool recurse);
/* Duplicate will create a new, identical cJSON item to the one you pass, in new memory that will* need to be released. With recurse!=0, it will duplicate any children connected to the item.* The item->next and ->prev pointers are always zero on return from Duplicate. */
/* Recursively compare two cJSON items for equality. If either a or b is NULL or invalid, they will be considered unequal.* case_sensitive determines if object keys are treated case sensitive (1) or case insensitive (0) */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_Compare(const cJSON * const a, const cJSON * const b, const cJSON_bool case_sensitive);/* Minify a strings, remove blank characters(such as ' ', '\t', '\r', '\n') from strings.* The input pointer json cannot point to a read-only address area, such as a string constant, * but should point to a readable and writable address area. */
CJSON_PUBLIC(void) cJSON_Minify(char *json);/* Helper functions for creating and adding items to an object at the same time.* They return the added item or NULL on failure. */
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON*) cJSON_AddNullToObject(cJSON * const object, const char * const name);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON*) cJSON_AddTrueToObject(cJSON * const object, const char * const name);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON*) cJSON_AddFalseToObject(cJSON * const object, const char * const name);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON*) cJSON_AddBoolToObject(cJSON * const object, const char * const name, const cJSON_bool boolean);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON*) cJSON_AddNumberToObject(cJSON * const object, const char * const name, const double number);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON*) cJSON_AddStringToObject(cJSON * const object, const char * const name, const char * const string);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON*) cJSON_AddRawToObject(cJSON * const object, const char * const name, const char * const raw);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON*) cJSON_AddObjectToObject(cJSON * const object, const char * const name);
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON*) cJSON_AddArrayToObject(cJSON * const object, const char * const name);/* When assigning an integer value, it needs to be propagated to valuedouble too. */
#define cJSON_SetIntValue(object, number) ((object) ? (object)->valueint = (object)->valuedouble = (number) : (number))
/* helper for the cJSON_SetNumberValue macro */
CJSON_PUBLIC(double) cJSON_SetNumberHelper(cJSON *object, double number);
#define cJSON_SetNumberValue(object, number) ((object != NULL) ? cJSON_SetNumberHelper(object, (double)number) : (number))
/* Change the valuestring of a cJSON_String object, only takes effect when type of object is cJSON_String */
CJSON_PUBLIC(char*) cJSON_SetValuestring(cJSON *object, const char *valuestring);/* If the object is not a boolean type this does nothing and returns cJSON_Invalid else it returns the new type*/
#define cJSON_SetBoolValue(object, boolValue) ( \(object != NULL && ((object)->type & (cJSON_False|cJSON_True))) ? \(object)->type=((object)->type &(~(cJSON_False|cJSON_True)))|((boolValue)?cJSON_True:cJSON_False) : \cJSON_Invalid\
)/* Macro for iterating over an array or object */
#define cJSON_ArrayForEach(element, array) for(element = (array != NULL) ? (array)->child : NULL; element != NULL; element = element->next)/* malloc/free objects using the malloc/free functions that have been set with cJSON_InitHooks */
CJSON_PUBLIC(void *) cJSON_malloc(size_t size);
CJSON_PUBLIC(void) cJSON_free(void *object);
CJSON数据结构
CJSON核心数据结构就只有一个:
typedef struct cJSON
{/* next/prev allow you to walk array/object chains. Alternatively, use GetArraySize/GetArrayItem/GetObjectItem */struct cJSON *next;struct cJSON *prev;/* An array or object item will have a child pointer pointing to a chain of the items in the array/object. */struct cJSON *child;/* The type of the item, as above. */int type;/* The item's string, if type==cJSON_String and type == cJSON_Raw */char *valuestring;/* writing to valueint is DEPRECATED, use cJSON_SetNumberValue instead */int valueint;/* The item's number, if type==cJSON_Number */double valuedouble;/* The item's name string, if this item is the child of, or is in the list of subitems of an object. */char *string;
} cJSON;
可以看出,json是一个嵌套数据结构,这与json的定义所表达的思想一致。
CJSON使用实例
/*** @file simple-cjson.c* @author your name (you@domain.com)* @brief * @version 0.1* @date 2023-02-19* * @copyright Copyright (c) 2023* */
#include "../cJSON.h"
#include <stdio.h>char simple_json[] = "{\\"FirstName\": \"John\",\\"LastName\": \"Doe\",\\"Age\": 43,\\"Address\": {\\"Street\": \"Downing Street 10\",\\"City\": \"London\",\\"Country\": \"Great Britain\"\},\\"Phone numbers\": [\\"+44 1234567\",\\"+44 2345678\"\]\}";int main()
{cJSON* json = cJSON_Parse(simple_json);cJSON_AddStringToObject(json, "ID", "666");char* print_json_str = cJSON_Print(json);printf("simple json: %s", print_json_str);return 0;
}编译运行:
$./simple-cjson
simple json: {"FirstName": "John","LastName": "Doe","Age": 43,"Address": {"Street": "Downing Street 10","City": "London","Country": "Great Britain"},"Phone numbers": ["+44 1234567", "+44 2345678"],"ID": "666"
}
这部分完全可以参考CJSON项目的README。
注意事项
CJSON使用ANSI C编写的,具有很多的指针操作,如果不注意非常容易产生指针操作相关的问题,这点最好阅读下项目的README和源代码。
参考
- https://www.json.org/json-en.html
- https://www.ecma-international.org/wp-content/uploads/ECMA-404_2nd_edition_december_2017.pdf
- https://github.com/DaveGamble/cJSON
相关文章:

CJSON简单介绍
json简介 JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。 易于人阅读和编写。同时也易于机器解析和生成。 它基于JavaScript Programming Language, Standard ECMA-262 3rd Edition - December 1999的一个子集,最新的定义可以参考ECMA-404_2nd_ed…...
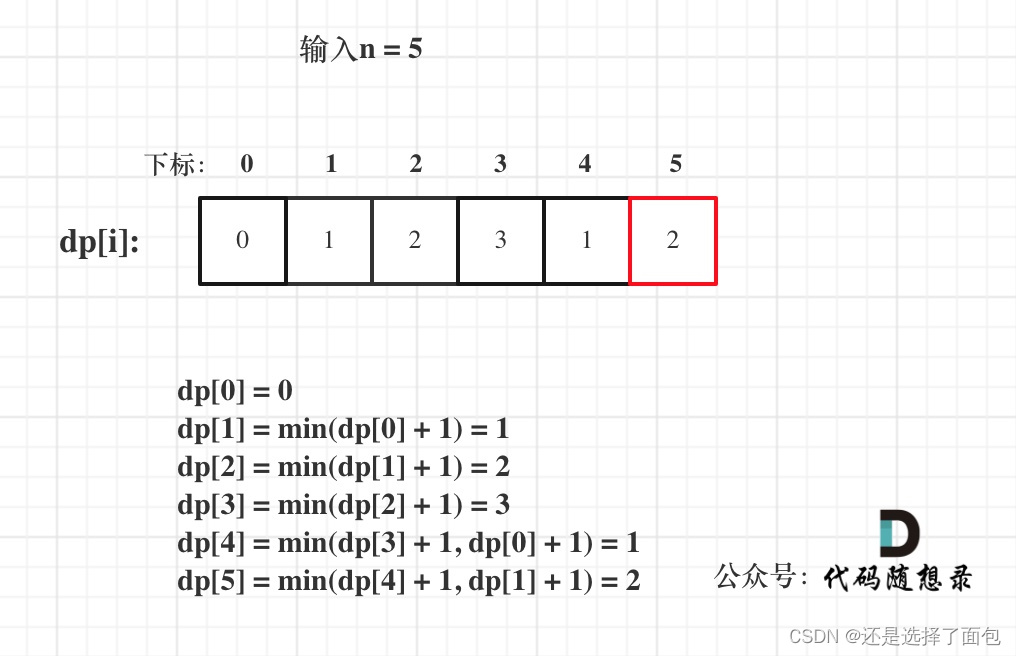
算法训练营 day49 动态规划 爬楼梯 (进阶)零钱兑换 完全平方数
算法训练营 day49 动态规划 爬楼梯 (进阶)零钱兑换 完全平方数 爬楼梯 (进阶) 70. 爬楼梯 - 力扣(LeetCode) 假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。 每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同…...

Vue:extends继承组件复用性
提到extends继承,最先想到的可能是ES6中的class、TS中的interface、面向对象编程语言中中的类和接口概念等等,但是我们今天的关注点在于:如何在Vue中使用extends继承特性。 目录 Vue:创建Vue实例的方式 构造函数方式࿱…...

ChatGPT 的一些思考
最近 ChatGPT3.5 在全世界范围内掀起了一次 AI 的潮流,ChatGPT1.0/ChatGPT2.0 当时也是比较火爆,但是那个当时感觉还是比较初级的应用,相当于是一个进阶版的微软小冰,给人的感觉是有一点智能,但不多。其实从早期版本开…...
GEE学习笔记 六十九:【GEE之Python版教程三】Python基础编程一
环境配置完成后,那么可以开始正式讲解编程知识。之前我在文章中也讲过,GEE的python版接口它是依赖python语言的。目前很多小伙伴是刚开始学习GEE编程,之前或者没有编程基础,或者是没有学习过python。为了照顾这批小伙伴࿰…...
大数据全系安装
内容版本号CentOS7.6.1810ZooKeeper3.4.6Hadoop2.9.1HBase1.2.0MySQL5.6.51HIVE2.3.7Sqoop1.4.6flume1.9.0kafka2.8.1scala2.12davinci3.0.1spark2.4.8flink1.13.5 1. 下载CentOS 7镜像 CentOS官网 2. 安装CentOS 7系统——采用虚拟机方式 2.1 新建虚拟机 2.2.1 [依次选择]-&…...

stable-diffusion-webui 安装使用
文章目录1.github 下载,按教程运行2.安装python 忘记勾选加入环境变量,自行加入(重启生效)3.环境变量添加后,清理tmp ,venv重新运行4.运行报错,无法升级pip,无法下载包,5…...
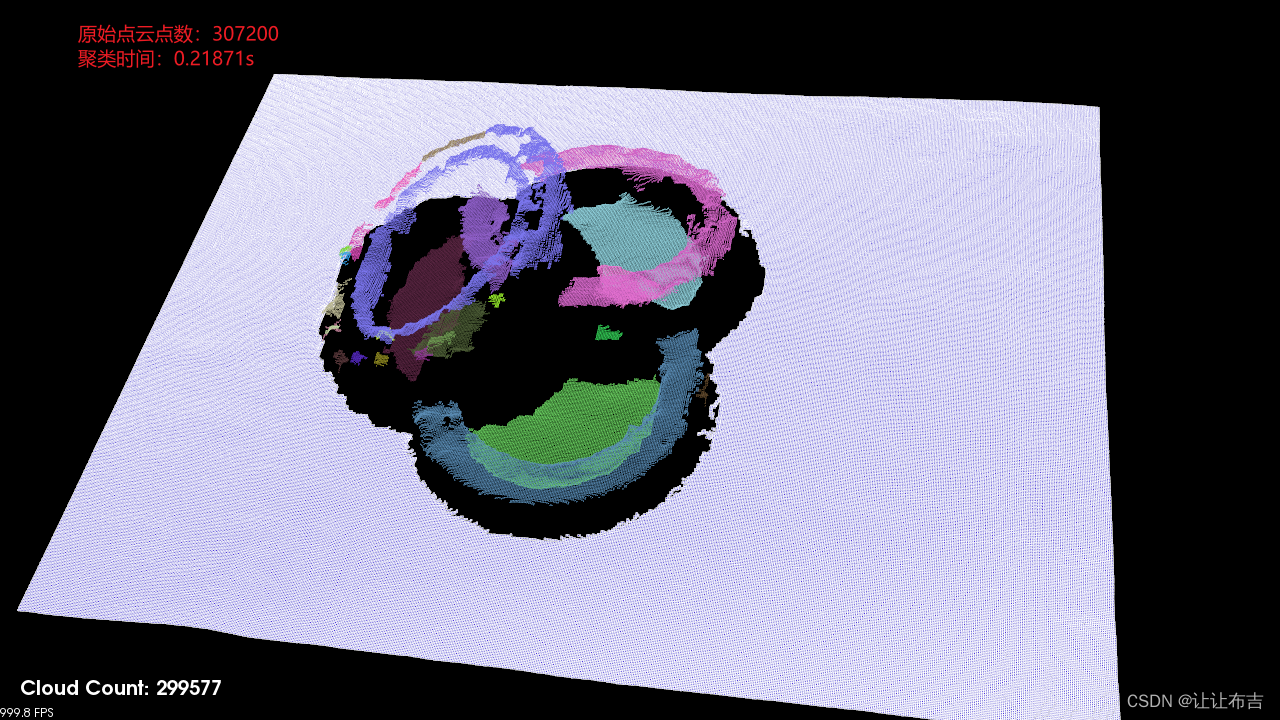
3D点云处理:点云聚类--FEC: Fast Euclidean Clustering for Point Cloud Segmentation
文章目录 聚类结果一、论文内容1.1 Ground Surface Removal1.2 Fast Euclidean Clustering题外:欧几里得聚类Fast Euclidean Clustering二、参考聚类结果 原始代码中采用的是pcl中的搜索方式,替换为另外第三方库,速度得到进一步提升。 一、论文内容 论文中给出的结论:该…...
| 代码+思路+重要知识点)
华为OD机试题 - 射击比赛(JavaScript)| 代码+思路+重要知识点
最近更新的博客 华为OD机试题 - 括号检查(JavaScript) 华为OD机试题 - 最小施肥机能效(JavaScript) 华为OD机试题 - 子序列长度(JavaScript) 华为OD机试题 - 众数和中位数(JavaScript) 华为OD机试题 - 服务依赖(JavaScript) 华为OD机试题 - 字符串加密(JavaScript)…...
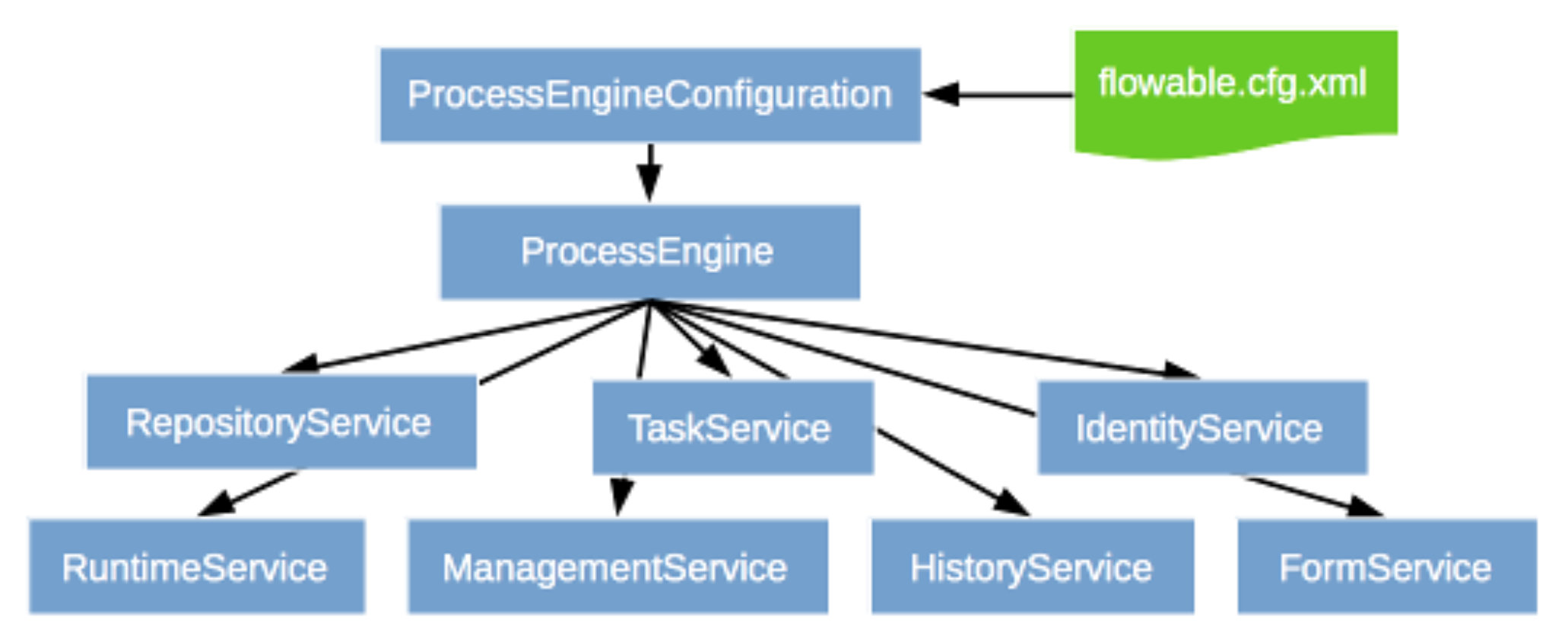
流程引擎之Flowable简介
背景Flowable 是一个流行的轻量级的采用 Java 开发的业务流程引擎,通过 Flowable 流程引擎,我们可以部署遵循 BPMN2.0 协议的流程定义(一般为XML文件)文件,并能创建流程实例,查询和访问流程相关的实例与数据…...
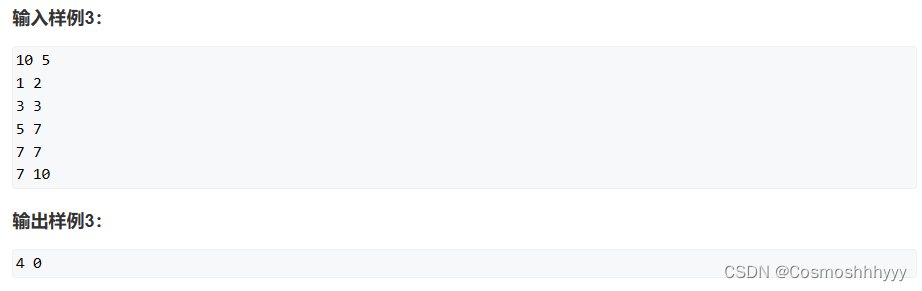
AcWing:4861. 构造数列、4862. 浇花(C++)
目录 4861. 构造数列 问题描述: 实现代码: 4862. 浇花 问题描述: 实现代码: 4861. 构造数列 问题描述: 我们规定如果一个正整数满足除最高位外其它所有数位均为 00,则称该正整数为圆数。 例如&…...
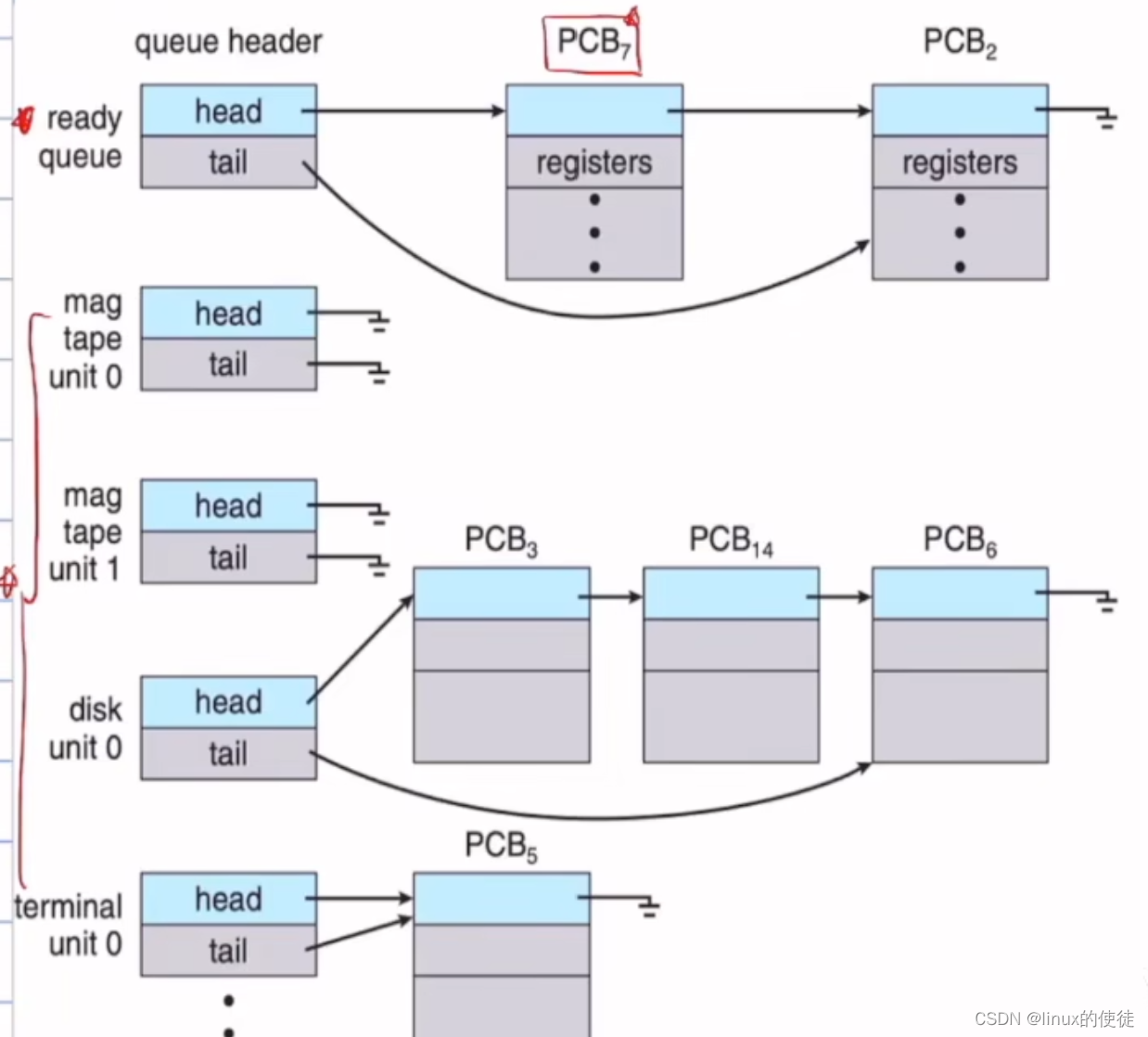
进程的概念
进程的概念 程序的概念 这里说的是一个可执行文件,passive的意思可以理解为我们这个执行文件需要我们进行双击才会被被执行。 双击后,程序入口地址读入寄存器,程序加载入主存,成为一个进程 进程是主动去获取想要的资源࿰…...
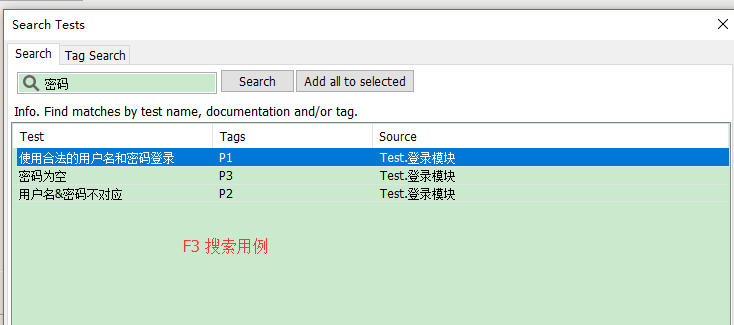
自动化测试5年经验,分享一些心得
自动化测试介绍 自动化测试(Automated Testing),是指把以人为驱动的测试行为转化为机器执行的过程。实际上自动化测试往往通过一些测试工具或框架,编写自动化测试用例,来模拟手工测试过程。比如说,在项目迭代过程中,持…...
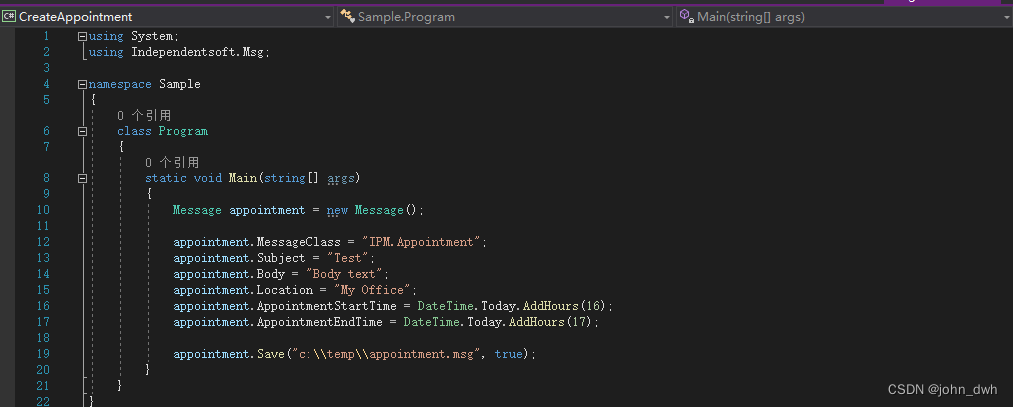
independentsoft.de/MSG .NET Framework Crack
MSG .NET 是用于 .NET Framework / .NET Core 的 Microsoft Outlook .msg 文件 API。API 允许您轻松创建/读取/解析/转换 .msg 文件等。API 不需要在机器上安装 Microsoft Outlook 或任何其他第三方应用程序或库即可工作。 以下示例向您展示了如何打开现有文件并显示消息的某些…...

基于Transformer的NLP处理管线
HuggingFace transformers 是一个整合了跨语言、视觉、音频和多模式模态与最先进的预训练模型并且提供用户友好的 API 的AI开发库。 它由 170 多个预训练模型组成,支持 PyTorch、TensorFlow 和 JAX 等框架,能够在代码之间进行互操作。 这个库还易于部署&…...
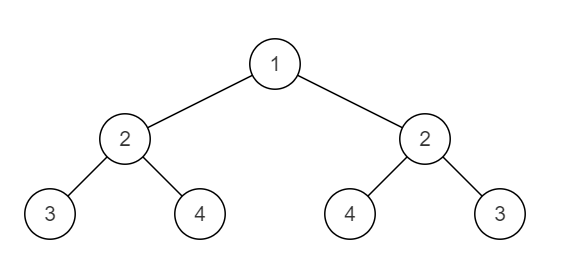
二叉树OJ(一)二叉树的最大深度 二叉搜索树与双向链表 对称的二叉树
二叉树的最大深度 二叉树中和为某一值的路径(一) 二叉搜索树与双向链表 对称的二叉树 二叉树的最大深度 描述 求给定二叉树的最大深度, 深度是指树的根节点到任一叶子节点路径上节点的数量。 最大深度是所有叶子节点的深度的最大值。 (注:…...

使用Fairseq进行Bart预训练
文章目录前言环境流程介绍数据部分分词部分预处理部分训练部分遇到的问题问题1可能遇到的问题问题1问题2前言 本文是使用 fairseq 做 Bart 预训练任务的踩坑记录huggingface没有提供 Bart 预训练的代码 facebookresearch/fairseq: Facebook AI Research Sequence-to-Sequence…...
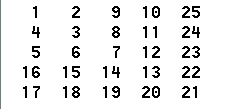
n阶数字回转方阵 ← 模拟法
【问题描述】 请编程输出如下数字回旋方阵。 【算法代码】 #include <bits/stdc.h> using namespace std;const int maxn100; int z[maxn][maxn];void matrix(int n) {int num2;z[0][0]1;int i0,j1;while(i<n && j<n) {while(i<j) z[i][j]num;while(j&…...

【人工智能AI】二、NoSQL 基础知识《NoSQL 企业级基础入门与进阶实战》
写一篇介绍 NoSQL 基础知识的技术文章,分5个章节,每个章节细分到3级目录,重点介绍一下NoSQL 数据模型,NoSQL 数据库架构,NoSQL 数据库特性等,不少于2000字。 NoSQL 基础知识 NoSQL(Not Only SQ…...

Camera Rolling Shutter和Global Shutter的区别
卷帘快门(Rolling Shutter)与全局快门(Global Shutter)的区别 什么是快门 快门是照相机用来控制感光片有效曝光时间的机构。 快门是照相机的一个重要组成部分,它的结构、形式及功能是衡量照相机档次的一个重要因素。 …...
。】2022-5-15)
【根据当天日期输出明天的日期(需对闰年做判定)。】2022-5-15
缘由根据当天日期输出明天的日期(需对闰年做判定)。日期类型结构体如下: struct data{ int year; int month; int day;};-编程语言-CSDN问答 struct mdata{ int year; int month; int day; }mdata; int 天数(int year, int month) {switch (month){case 1: case 3:…...
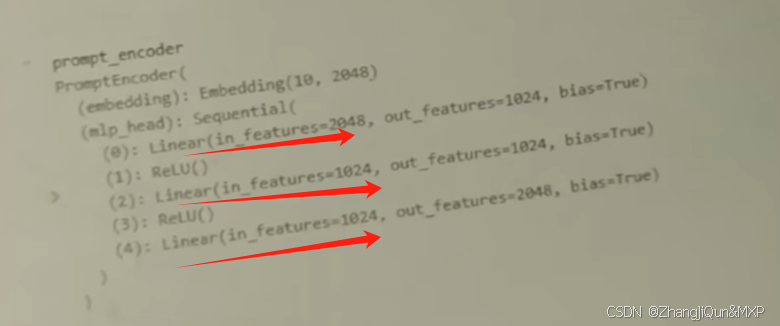
Prompt Tuning、P-Tuning、Prefix Tuning的区别
一、Prompt Tuning、P-Tuning、Prefix Tuning的区别 1. Prompt Tuning(提示调优) 核心思想:固定预训练模型参数,仅学习额外的连续提示向量(通常是嵌入层的一部分)。实现方式:在输入文本前添加可训练的连续向量(软提示),模型只更新这些提示参数。优势:参数量少(仅提…...
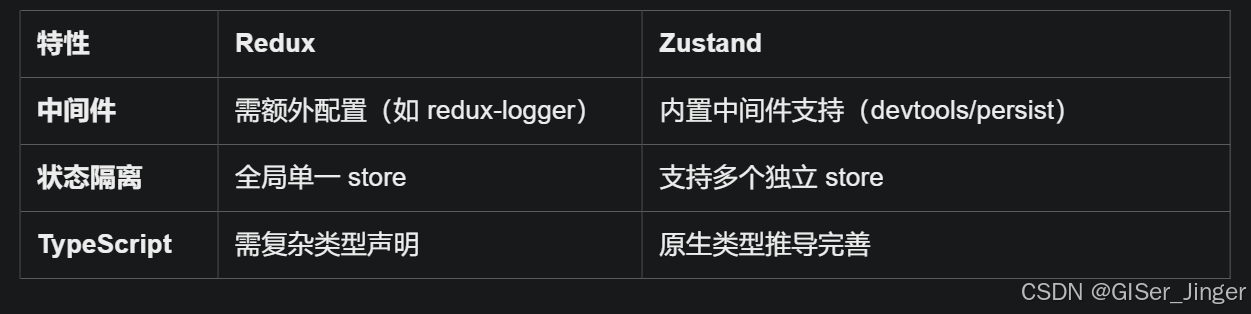
Zustand 状态管理库:极简而强大的解决方案
Zustand 是一个轻量级、快速和可扩展的状态管理库,特别适合 React 应用。它以简洁的 API 和高效的性能解决了 Redux 等状态管理方案中的繁琐问题。 核心优势对比 基本使用指南 1. 创建 Store // store.js import create from zustandconst useStore create((set)…...

逻辑回归:给不确定性划界的分类大师
想象你是一名医生。面对患者的检查报告(肿瘤大小、血液指标),你需要做出一个**决定性判断**:恶性还是良性?这种“非黑即白”的抉择,正是**逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)** 的战场&a…...

Python:操作 Excel 折叠
💖亲爱的技术爱好者们,热烈欢迎来到 Kant2048 的博客!我是 Thomas Kant,很开心能在CSDN上与你们相遇~💖 本博客的精华专栏: 【自动化测试】 【测试经验】 【人工智能】 【Python】 Python 操作 Excel 系列 读取单元格数据按行写入设置行高和列宽自动调整行高和列宽水平…...
苍穹外卖--缓存菜品
1.问题说明 用户端小程序展示的菜品数据都是通过查询数据库获得,如果用户端访问量比较大,数据库访问压力随之增大 2.实现思路 通过Redis来缓存菜品数据,减少数据库查询操作。 缓存逻辑分析: ①每个分类下的菜品保持一份缓存数据…...
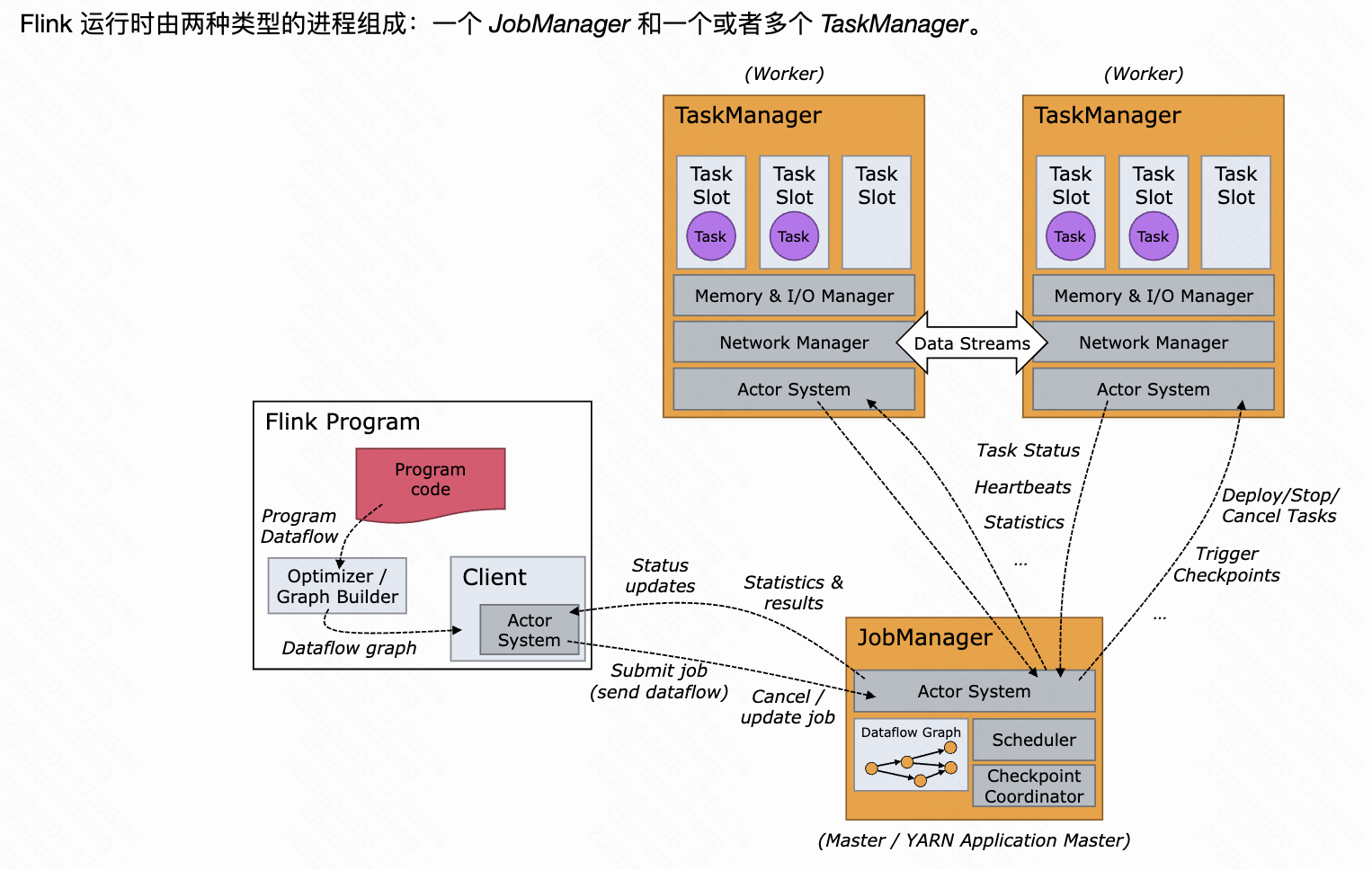
《基于Apache Flink的流处理》笔记
思维导图 1-3 章 4-7章 8-11 章 参考资料 源码: https://github.com/streaming-with-flink 博客 https://flink.apache.org/bloghttps://www.ververica.com/blog 聚会及会议 https://flink-forward.orghttps://www.meetup.com/topics/apache-flink https://n…...

图表类系列各种样式PPT模版分享
图标图表系列PPT模版,柱状图PPT模版,线状图PPT模版,折线图PPT模版,饼状图PPT模版,雷达图PPT模版,树状图PPT模版 图表类系列各种样式PPT模版分享:图表系列PPT模板https://pan.quark.cn/s/20d40aa…...
)
是否存在路径(FIFOBB算法)
题目描述 一个具有 n 个顶点e条边的无向图,该图顶点的编号依次为0到n-1且不存在顶点与自身相连的边。请使用FIFOBB算法编写程序,确定是否存在从顶点 source到顶点 destination的路径。 输入 第一行两个整数,分别表示n 和 e 的值(1…...
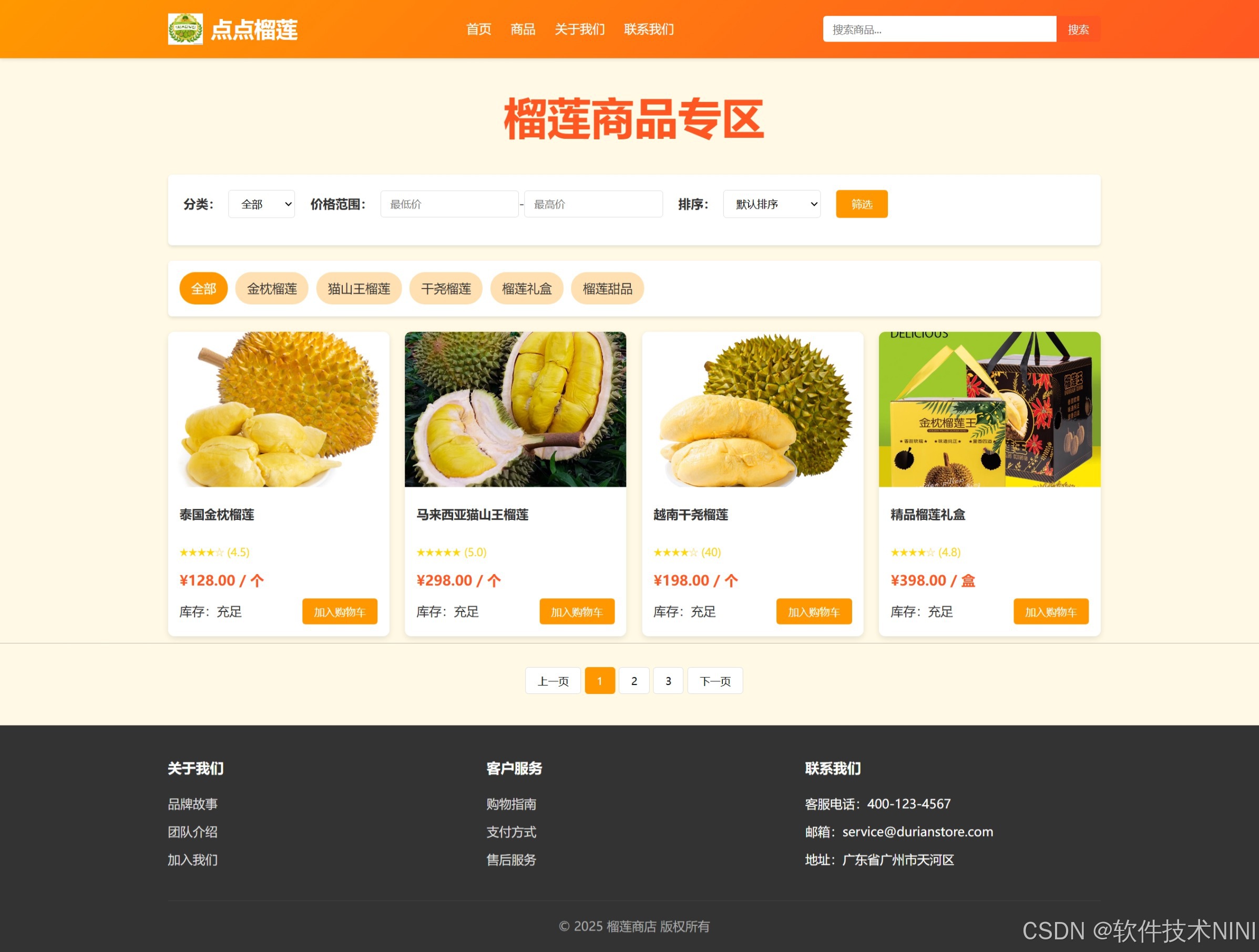
html css js网页制作成品——HTML+CSS榴莲商城网页设计(4页)附源码
目录 一、👨🎓网站题目 二、✍️网站描述 三、📚网站介绍 四、🌐网站效果 五、🪓 代码实现 🧱HTML 六、🥇 如何让学习不再盲目 七、🎁更多干货 一、👨…...
