R3LIVE源码解析(9) — R3LIVE中r3live_lio.cpp文件
目录
1 r3live_lio.cpp文件简介
2 r3live_lio.cpp源码解析
1 r3live_lio.cpp文件简介
在r3live.cpp文件中创建LIO线程后,R3LIVE中的LIO线程本质上整体流程和FAST-LIO2基本一致。
2 r3live_lio.cpp源码解析
函数最开始会进行一系列的声明和定义,发布的lidar路径,协方差矩阵,kalman增益矩阵和4个重要的点云容器,IMU前向/后向传播处理器等
/*** ===================================================================================================* @note (1) 定义用到的变量 : 发布的lidar路径,协方差矩阵,kalman增益矩阵和4个重要的点云容器,IMU前向/后向传播处理器等.* ===================================================================================================*/nav_msgs::Path path; // Lidar的路径 : 主要有两个成员变量: header和posepath.header.stamp = ros::Time::now(); // header的时间path.header.frame_id = "/world"; // header的id/*** variables definition ***/// DIM_OF_STATES=29. G:, H_T_H, I_STATE:// G : 用于传递协方差用的矩阵, H_T_H : 用于计算kalman增益用的, I_STATE : 单位阵Eigen::Matrix< double, DIM_OF_STATES, DIM_OF_STATES > G, H_T_H, I_STATE;G.setZero();H_T_H.setZero();I_STATE.setIdentity();cv::Mat matA1( 3, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all( 0 ) ); // 后面没用到cv::Mat matD1( 1, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all( 0 ) ); // 后面没用到cv::Mat matV1( 3, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all( 0 ) ); // 后面没用到cv::Mat matP( 6, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all( 0 ) ); // 后面没用到PointCloudXYZINormal::Ptr feats_undistort( new PointCloudXYZINormal() );//去除畸变后的点云PointCloudXYZINormal::Ptr feats_down( new PointCloudXYZINormal() ); // 保存下采样后的点云// 有M个特征点找到了M个对应的最近平面Si,则coeffSel存储Si的平面方程系数,和点到平面的残差PointCloudXYZINormal::Ptr coeffSel( new PointCloudXYZINormal() );// 存放M个最近平面信息的容器: 平面方程,点-面残差PointCloudXYZINormal::Ptr laserCloudOri( new PointCloudXYZINormal() );// 存放找到了最近平面的M个点的容器/*** variables initialize ***/FOV_DEG = fov_deg + 10; // fov_deg=360HALF_FOV_COS = std::cos( ( fov_deg + 10.0 ) * 0.5 * PI_M / 180.0 );// cos(185)for ( int i = 0; i < laserCloudNum; i++ ) // laserCloudNum = 48x48x48{// featsArray[48x48x48]featsArray[ i ].reset( new PointCloudXYZINormal() );}std::shared_ptr< ImuProcess > p_imu( new ImuProcess() ); // 定义用于前向/后向传播的IMU处理器m_imu_process = p_imu;//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ros::Rate rate( 5000 );bool status = ros::ok();g_camera_lidar_queue.m_liar_frame_buf = &lidar_buffer;//取出lidar数据set_initial_state_cov( g_lio_state ); //初始化g_lio_state的状态协方差矩阵然后开始LIO线程的主循环。首先会对比相机和lidar队列头的时间戳,如果camera的时间戳更早则等待vio线程把更早的图像处理完。
- td::this_thread::yield()函数的作用是让出当前线程的执行权,让其他线程有机会执行。它可以用来提高多线程程序的效率,避免某个线程长时间占用CPU资源。
- std::this_thread::sleep_for()函数的作用是让当前线程暂停执行一段时间。它接受一个时间间隔作为参数,参数类型为std::chrono::milliseconds,表示以毫秒为单位的时间间隔。在代码中,THREAD_SLEEP_TIM是一个时间间隔的变量,它的值可以根据需要进行设置,代码中设置为1s。
while ( g_camera_lidar_queue.if_lidar_can_process() == false )
{ // 考虑camera和lidar在频率上的时间对齐关系// 判断当前时间是否可以处理lidar数据, 不可以则sleep一会ros::spinOnce();std::this_thread::yield();std::this_thread::sleep_for( std::chrono::milliseconds( THREAD_SLEEP_TIM ) );
}从lidar_buffer和imu_buffer_lio中分别获取雷达和imu数据,存放至Measures中,如果没有读取到数据则退出。
/**
* @note (2-2) 从lidar_buffer和imu_buffer_lio中分别获取雷达和imu数据,存放至Measures中
* MeasureGroup Measures; // 存放雷达数据和IMU数据的结构体全局变量
*/
if ( sync_packages( Measures ) == 0 )
{continue; // 提取数据失败
}然后下一步就是调用Process 函数补偿点云畸变,并用imu数据进行系统状态预测。
- 如果没有成功去除点云运动畸变,则重置当前处理lidar帧的起始时间。
- 接着进行时间判断, 当前帧中lidar的开始时间,必须<=记录的帧开始时间,如果时间满足关系,开始EKF过程
/**
* @note (2-3) 通过测量数据Measures(IMU数据和Lidar数据)计算LIO的状态和去畸变后的Lidar点云数据
* 前向传播 + 后向传播
* LIO状态结果保存在g_lio_state,去运动畸变后的点保存在feats_undistort中
*/
p_imu->Process( Measures, g_lio_state, feats_undistort );
g_camera_lidar_queue.g_noise_cov_acc = p_imu->cov_acc; // 获取加速度误差状态传递的协方差
g_camera_lidar_queue.g_noise_cov_gyro = p_imu->cov_gyr; // 获取角速度误差状态传递的协方差
StatesGroup state_propagate( g_lio_state ); // 状态传播值(先验):通过计算得到的状态实例化一个StatesGroup变量// 输出lio上一帧更新的时间 : 上一帧更新记录时间 - lidar开始时间
// cout << "G_lio_state.last_update_time = " << std::setprecision(10) << g_lio_state.last_update_time -g_lidar_star_tim << endl;
if ( feats_undistort->empty() || ( feats_undistort == NULL ) ) // 没有成功去除点云运动畸变
{// 重置当前处理lidar帧的起始时间 : 比如当前处理t1-t2间的lidar但失败了// 因此后面处理时间为t1-t3,所以需要把t1保存进frame_first_pt_timeframe_first_pt_time = Measures.lidar_beg_time;std::cout << "not ready for odometry" << std::endl;continue;
}// 当前帧中lidar的开始时间,必须<=记录的帧开始时间
// 按理应该相等,这里的判断估计是实际使用中发生的问题(从理解的角度-不一定正确:如果lidar中损失了初始点,那么
// 当前最开始的lidar点的时间就<记录下来的帧开始时间)
if ( ( Measures.lidar_beg_time - frame_first_pt_time ) < INIT_TIME ) // INIT_TIME=0
{flg_EKF_inited = false;std::cout << "||||||||||Initiallizing LiDAR||||||||||" << std::endl;
}
else // 时间满足关系,开始EKF过程
{flg_EKF_inited = true;
}p_imu->Process() 函数的主要作用是通过测量数据meas(IMU数据和Lidar数据)计算LIO的状态和去畸变后的Lidar点云数据。
/*** @note 通过测量数据meas(IMU数据和Lidar数据)计算LIO的状态和去畸变后的Lidar点云数据* @param meas : 输入的Lidar和IMU数据* @param stat : Lidar状态* @param cur_pcl_un_ : 去畸变后的点云*/
void ImuProcess::Process( const MeasureGroup &meas, StatesGroup &stat, PointCloudXYZINormal::Ptr cur_pcl_un_ )
{// double t1, t2, t3;// t1 = omp_get_wtime();if ( meas.imu.empty() ) // 判断IMU数据{// std::cout << "no imu data" << std::endl;return;};ROS_ASSERT( meas.lidar != nullptr ); // 判断Lidar数据if ( imu_need_init_ ) // 初始化IMU数据{/// The very first lidar frame 初始化第一帧雷达数据帧// 初始化重力,陀螺仪bias,加速度和陀螺仪协方差// 归一化加速度测量值到单位重力下IMU_Initial( meas, stat, init_iter_num );imu_need_init_ = true;last_imu_ = meas.imu.back(); // 获取当前处理的最后一个imu数据if ( init_iter_num > MAX_INI_COUNT ) // (1 > 20) : 默认不进入if{imu_need_init_ = false;// std::cout<<"mean acc: "<<mean_acc<<" acc measures in word frame:"<<state.rot_end.transpose()*mean_acc<<std::endl;ROS_INFO("IMU Initials: Gravity: %.4f %.4f %.4f; state.bias_g: %.4f %.4f %.4f; acc covarience: %.8f %.8f %.8f; gry covarience: %.8f %.8f %.8f",stat.gravity[ 0 ], stat.gravity[ 1 ], stat.gravity[ 2 ], stat.bias_g[ 0 ], stat.bias_g[ 1 ], stat.bias_g[ 2 ], cov_acc[ 0 ],cov_acc[ 1 ], cov_acc[ 2 ], cov_gyr[ 0 ], cov_gyr[ 1 ], cov_gyr[ 2 ] );}return;}// 去畸变: 第一个点看作为基坐标,使用IMU旋转矩阵补偿Lidar点(仅使用旋转)// if ( 0 || (stat.last_update_time < 0.1))if ( 0 ){// UndistortPcl(meas, stat, *cur_pcl_un_);}else{// ***IMU前向传播计算,Lidar点后向传播去畸变***if ( 1 ) {lic_point_cloud_undistort( meas, stat, *cur_pcl_un_ );}else{*cur_pcl_un_ = *meas.lidar;}// ***状态传播***lic_state_propagate( meas, stat );}// t2 = omp_get_wtime();last_imu_ = meas.imu.back();// t3 = omp_get_wtime();// std::cout<<"[ IMU Process ]: Time: "<<t3 - t1<<std::endl;
}然后就是完成localmap边界更新,便于完成降采样当前帧点云。
lasermap_fov_segment();
// 降采样
downSizeFilterSurf.setInputCloud( feats_undistort );
downSizeFilterSurf.filter( *feats_down );然后就是使用下采样后得到的特征点云构造ikd树。
ikdtree.set_downsample_param(filter_size_map_min)是设置IKD树的下采样参数。filter_size_map_min用于指定下采样的大小。ikdtree.Build(feats_down->points)是构建IKD树的操作。feats_down->points表示输入的特征点。
/**
* @note (2-6)initialize the map kdtree 使用下采样后得到的特征点云构造ikd树**
* @note 判断条件 : if(下采样后特征点数量大于1) && (ikd树根节点为空) :
* 重点:判断条件表明这里只进来一次,且第一帧lidar数据用来构造了ikd树后,就进入下一次循环了
* 所以可知,第一帧Lidar数据直接用来构造ikd树,第>=2帧Lidar数据不再直接添加到树上,而
* 是找与树上最近点,由最近点构成平面,然后计算点到平面的残差,并运用EKF迭代更新后,才加
* 到树上
*/
if ( ( feats_down->points.size() > 1 ) && ( ikdtree.Root_Node == nullptr ) )
{// std::vector<PointType> points_init = feats_down->points;ikdtree.set_downsample_param( filter_size_map_min ); // filter_size_map_min默认=0.4ikdtree.Build( feats_down->points ); // 构造idk树flg_map_initialized = true;continue; // 进入下一次循环
}if ( ikdtree.Root_Node == nullptr ) // 构造ikd树失败
{flg_map_initialized = false;std::cout << "~~~~~~~ Initialize Map iKD-Tree Failed! ~~~~~~~" << std::endl;continue;
}
int featsFromMapNum = ikdtree.size(); // ikd树的节点数
int feats_down_size = feats_down->points.size(); // 下采样过滤后的点数在拿到ikd-tree构建的树后就是使用激光信息进行ESIKF状态更新。
- 在ros上发布ikd特征点云数据,默认不发布
- 遍历所有(下采样后)特征点,搜索每个点在树上的最近点集(5个点), 由最近点集通过PCA方法拟合最近平面,再计算点-面残差,残差定义为点到平面的距离。
- 从找到平面的点中筛选满足条件的点,用新的变量保存该点和对应平面(下标对齐)
- 计算测量Jacobian矩阵和测量向量.
- Iterative Kalman Filter Update
- 收敛判断和协方差更新
- 更新维持的固定大小的map立方体
- 将Kalman更新后的新lidar帧特征点先转世界坐标系,再加入ikd树
- ICP迭代+Kalman更新完成
if ( featsFromMapNum >= 5 ) // ***重点*** : 正式开始ICP和迭代Kalman : ikd树上至少有5个点才进行操作{t1 = omp_get_wtime();/*** @note (2-7-1) : 在ros上发布特征点云数据 - 默认不发布*/ if ( m_if_publish_feature_map ) {PointVector().swap( ikdtree.PCL_Storage );// flatten会将需要删除的点放入Points_deleted或Multithread_Points_deleted中ikdtree.flatten( ikdtree.Root_Node, ikdtree.PCL_Storage, NOT_RECORD );featsFromMap->clear();featsFromMap->points = ikdtree.PCL_Storage;sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 laserCloudMap;pcl::toROSMsg( *featsFromMap, laserCloudMap ); // 将点云数据格式转换为发布的消息格式laserCloudMap.header.stamp = ros::Time::now(); // ros::Time().fromSec(last_timestamp_lidar);// laserCloudMap.header.stamp.fromSec(Measures.lidar_end_time); // ros::Time().fromSec(last_timestamp_lidar);laserCloudMap.header.frame_id = "world";pubLaserCloudMap.publish( laserCloudMap );}/*** @note (2-7-2) : 定义后面点-面计算时需要用到的变量* 变量的理解举例: E为所有特征点,P点属于E,现在为P点找平面S:* 当成功为P点找到平面S,则point_selected_surf[P] = true, 否则=false* 平面S由m个点构成:pointSearchInd_surf[0]到pointSearchInd_surf[m]* E中离P点按距离排序后的点放在Nearest_Points[]中:* Nearest_Points是二维数组(PointVector是一维),存储每个点的最近点集合*/ std::vector< bool > point_selected_surf( feats_down_size, true ); // 记录有那些点成功找到了平面std::vector< std::vector< int > > pointSearchInd_surf( feats_down_size ); // 构成平面的点的indexstd::vector< PointVector > Nearest_Points( feats_down_size ); // 二维数组,存点i的最近点排序后的集合int rematch_num = 0;bool rematch_en = 0;flg_EKF_converged = 0;deltaR = 0.0;deltaT = 0.0;t2 = omp_get_wtime();double maximum_pt_range = 0.0;// cout <<"Preprocess 2 cost time: " << tim.toc("Preprocess") << endl;/*** @note (2-7-3) 进行误差Kalman迭代* //TODO*/ for ( iterCount = 0; iterCount < NUM_MAX_ITERATIONS; iterCount++ ) // NUM_MAX_ITERATIONS默认为4{tim.tic( "Iter" ); // 本次迭代起始时间match_start = omp_get_wtime();laserCloudOri->clear(); // 清空存放找到了最近平面的点的容器coeffSel->clear(); // 清空存放最近平面信息的容器/*** @note (2-7-3-1) : closest surface search and residual computation ** 遍历所有(下采样后)特征点,搜索每个点在树上的最近点集(5个点),* 由最近点集通过PCA方法拟合最近平面,再计算点-面残差*/for ( int i = 0; i < feats_down_size; i += m_lio_update_point_step ) // m_lio_update_point_step默认为1{double search_start = omp_get_wtime();PointType &pointOri_tmpt = feats_down->points[ i ]; // 获取当前下标的特征点 - 原始点// 计算特征点与原点的距离double ori_pt_dis =sqrt( pointOri_tmpt.x * pointOri_tmpt.x + pointOri_tmpt.y * pointOri_tmpt.y + pointOri_tmpt.z * pointOri_tmpt.z );maximum_pt_range = std::max( ori_pt_dis, maximum_pt_range );// 保存离原点最远的点产生的最远距离PointType &pointSel_tmpt = feats_down_updated->points[ i ]; // 获取当前下标的特征点 - 更新后的点/* transform to world frame */pointBodyToWorld( &pointOri_tmpt, &pointSel_tmpt );// 将特征点转到世界坐标下,并保存至可变点pointSel_tmpt中std::vector< float > pointSearchSqDis_surf; // 搜索点-平面时产生的距离序列auto &points_near = Nearest_Points[ i ]; // 下标i的特征点的最近点集合(一维数组)/*** @note (2-7-3-1-1) : 搜索与点最近平面上的5个点* ***注意*** 只有第一次迭代时才进入,后面都用迭代的方法,就不找平面了* (猜测应该是寻找平面耗时,后面直接用第一次找到的平面迭代优化就好了)*/if ( iterCount == 0 || rematch_en ) // 第一次迭代或者重匹配使能时才在ikd树上搜索最近平面{point_selected_surf[ i ] = true;/** Find the closest surfaces in the map 在地图中找到最近的平面**/// NUM_MATCH_POINTS=5ikdtree.Nearest_Search( pointSel_tmpt, NUM_MATCH_POINTS, points_near, pointSearchSqDis_surf );float max_distance = pointSearchSqDis_surf[ NUM_MATCH_POINTS - 1 ];//最近点集的最后一个元素自然最远// max_distance to add residuals// ANCHOR - Long range pt stragetryif ( max_distance > m_maximum_pt_kdtree_dis ) // 超出限定距离,放弃为这个点寻找平面{point_selected_surf[ i ] = false; // 当前点寻找平面失败}}kdtree_search_time += omp_get_wtime() - search_start;if ( point_selected_surf[ i ] == false ) // 当前点寻找平面失败,进入下一个点的寻找流程continue;// match_time += omp_get_wtime() - match_start;double pca_start = omp_get_wtime();/*** @note (2-7-3-2) : 使用PCA方法拟合平面 (using minimum square method)* ***注意*** : 具体PCA解释待补充*/cv::Mat matA0( NUM_MATCH_POINTS, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all( 0 ) );cv::Mat matB0( NUM_MATCH_POINTS, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all( -1 ) );cv::Mat matX0( NUM_MATCH_POINTS, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all( 0 ) );for ( int j = 0; j < NUM_MATCH_POINTS; j++ ){matA0.at< float >( j, 0 ) = points_near[ j ].x;matA0.at< float >( j, 1 ) = points_near[ j ].y;matA0.at< float >( j, 2 ) = points_near[ j ].z;}cv::solve( matA0, matB0, matX0, cv::DECOMP_QR ); // TODOfloat pa = matX0.at< float >( 0, 0 );float pb = matX0.at< float >( 1, 0 );float pc = matX0.at< float >( 2, 0 );float pd = 1;float ps = sqrt( pa * pa + pb * pb + pc * pc );pa /= ps;pb /= ps;pc /= ps;pd /= ps;/*** @note (2-7-3-1-3) : 检测计算平面的有效性 - 将最近点集合带入平面方程中求残差做判断*/bool planeValid = true;for ( int j = 0; j < NUM_MATCH_POINTS; j++ ) // NUM_MATCH_POINTS=5{// ANCHOR - Planar check : 将特征点在平面上的最近5个点带入平面公式中,得到的结果>0.05 (表明当前点不在拟合平面上)if ( fabs( pa * points_near[ j ].x + pb * points_near[ j ].y + pc * points_near[ j ].z + pd ) >m_planar_check_dis ) // Raw 0.05{// ANCHOR - Far distance pt processing// ori_pt_dis:当前点到原点的距离, maximum_pt_range:特征点云中的最远点离原点的距离// m_long_rang_pt_dis:lidar点最远有效距离(默认500)if ( ori_pt_dis < maximum_pt_range * 0.90 || ( ori_pt_dis < m_long_rang_pt_dis ) )// if(1){planeValid = false;point_selected_surf[ i ] = false; // 当前特征点寻找平面失败break;}}}/*** @note (2-7-3-1-4) : 前面计算平面有效时,计算残差res_last[] : 残差定义为点到平面的距离* 对应FAST-LIO公式(12)*/ if ( planeValid ){// 将特征点(世界坐标系下) 代入平面方程,计算残差 (在平面的点代入=0,不在平面的点代入会产生残差)// 按照点到平面的距离公式,这里省略了除以分母的内容 : 对应FAST-LIO公式(12)float pd2 = pa * pointSel_tmpt.x + pb * pointSel_tmpt.y + pc * pointSel_tmpt.z + pd;// s计算了后面没用 : s考虑了除以分母的步骤.float s = 1 - 0.9 * fabs( pd2 ) /sqrt( sqrt( pointSel_tmpt.x * pointSel_tmpt.x + pointSel_tmpt.y * pointSel_tmpt.y +pointSel_tmpt.z * pointSel_tmpt.z ) );// ANCHOR - Point to plane distance// 点到原点的距离<500 ? 0.3 : 1.0double acc_distance = ( ori_pt_dis < m_long_rang_pt_dis ) ? m_maximum_res_dis : 1.0;if ( pd2 < acc_distance ) // 残差小于0.3或者1.0{{// if(std::abs(pd2) > 5 * res_mean_last)// {// point_selected_surf[i] = false;// res_last[i] = 0.0;// continue;// }}point_selected_surf[ i ] = true; // 当前点寻找平面成功coeffSel_tmpt->points[ i ].x = pa; // 记录当前特征点对应最近平面的平面方程coeffSel_tmpt->points[ i ].y = pb;coeffSel_tmpt->points[ i ].z = pc;coeffSel_tmpt->points[ i ].intensity = pd2;res_last[ i ] = std::abs( pd2 ); // 当前特征点代入平面方程产生的残差}else{point_selected_surf[ i ] = false;// 当前点寻找平面失败}}pca_time += omp_get_wtime() - pca_start;} // 遍历所有特征点寻找平面,计算点-面残差完成tim.tic( "Stack" );double total_residual = 0.0;laserCloudSelNum = 0;/*** @note (2-7-3-2) : 从找到平面的点中筛选满足条件的点,用新的变量保存该点和对应平面(下标对齐)* 后面进行Kalman等计算时,都使用这里得到的"laserCloudOri"和"coeffSel"*/ for ( int i = 0; i < coeffSel_tmpt->points.size(); i++ ) // 遍历找到了对应平面的特征点{// 平面有效 && 点到面的残差小于2 (这里的残差条件按理都满足,因为前面存入的残差值小于1.0)if ( point_selected_surf[ i ] && ( res_last[ i ] <= 2.0 ) ){ // 下面重新放入容器是为了对齐点-面的索引laserCloudOri->push_back( feats_down->points[ i ] ); // 将找到最近平面的点放入laserCloudOri中coeffSel->push_back( coeffSel_tmpt->points[ i ] ); // 将最近平面容器放入coeffSel中total_residual += res_last[ i ]; // 总残差 - 从最小二乘的角度,优化的就是让这个总残差最小laserCloudSelNum++; // 找到平面的点的数量}}res_mean_last = total_residual / laserCloudSelNum; // 均值-期望, 后面没用此变量match_time += omp_get_wtime() - match_start;solve_start = omp_get_wtime();/*** @note (2-7-3-3) Computation of Measuremnt Jacobian matrix H and measurents vector* 计算测量Jacobian矩阵和测量向量. 猜测对应FAST-LIO的公式(14)(15)(16)(17)*/ Eigen::MatrixXd Hsub( laserCloudSelNum, 6 ); // Hsub(n x 6)Eigen::VectorXd meas_vec( laserCloudSelNum ); // meas_vec(n x 1)Hsub.setZero();for ( int i = 0; i < laserCloudSelNum; i++ ){const PointType &laser_p = laserCloudOri->points[ i ];// 获取当前点Eigen::Vector3d point_this( laser_p.x, laser_p.y, laser_p.z );// 点坐标point_this += Lidar_offset_to_IMU; // Lidar和IMU的偏移Eigen::Matrix3d point_crossmat;point_crossmat << SKEW_SYM_MATRIX( point_this ); // 将点转为反对称矩阵用于叉乘/*** get the normal vector of closest surface/corner 获取最近平面的法向量***/const PointType &norm_p = coeffSel->points[ i ]; // 当前点的最近平面方程系数Eigen::Vector3d norm_vec( norm_p.x, norm_p.y, norm_p.z );// 平面法向量/*** calculate the Measuremnt Jacobian matrix H ***/// A = 当前点的反对称矩阵 * (lidar帧最后时刻时的旋转)转置 * 最近平面法向量// ?TODO : 这里可能又是一个近似,猜测是因为直接计算H矩阵太耗时Eigen::Vector3d A( point_crossmat * g_lio_state.rot_end.transpose() * norm_vec );Hsub.row( i ) << VEC_FROM_ARRAY( A ), norm_p.x, norm_p.y, norm_p.z;// row(i)=A[0],A[1],A[2],norm_p.x, norm_p.y, norm_p.z/*** Measuremnt: distance to the closest surface/corner ***/meas_vec( i ) = -norm_p.intensity; }Eigen::Vector3d rot_add, t_add, v_add, bg_add, ba_add, g_add; //更新量:旋转,平移,速度,偏置等Eigen::Matrix< double, DIM_OF_STATES, 1 > solution; // 最终解 : 29维Eigen::MatrixXd K( DIM_OF_STATES, laserCloudSelNum );// kalman增益/*** @note (2-7-3-4) : Iterative Kalman Filter Update * 对应(有出入)FAST-LIO中公式(18)(19)(20)*/if ( !flg_EKF_inited ) // 未初始化时初始化 - 前面已经初始化了{cout << ANSI_COLOR_RED_BOLD << "Run EKF init" << ANSI_COLOR_RESET << endl;/*** only run in initialization period ***/set_initial_state_cov( g_lio_state );} else{// cout << ANSI_COLOR_RED_BOLD << "Run EKF uph" << ANSI_COLOR_RESET << endl;//1>:求公式中需要用到的 H 和 H^T*Tauto &&Hsub_T = Hsub.transpose(); // H转置 : 6xn = (nx6)^TH_T_H.block< 6, 6 >( 0, 0 ) = Hsub_T * Hsub;//(0,0)处6x6块.H^T*T//2>:求公式(20)中的Kalman增益的前面部分(省略R) : (H^T * R^-1 * H + P^-1)^-1Eigen::Matrix< double, DIM_OF_STATES, DIM_OF_STATES > &&K_1 =( H_T_H + ( g_lio_state.cov / LASER_POINT_COV ).inverse() ).inverse();//3>:结合2>求的前面部分,求公式(20)Kalman增益(省略R)K = K_1.block< DIM_OF_STATES, 6 >( 0, 0 ) * Hsub_T;// K = (29x6) * (6xn) = (29xn)//4>:求公式(18)中的最右边部分 : x^kk-x^k : Kalman迭代时的传播状态-预估(也是更新)状态auto vec = state_propagate - g_lio_state;//state_propagate初始=g_lio_state//5>:求公式(18)的中间和右边部分(有出入:I什么的都省略了)solution = K * ( meas_vec - Hsub * vec.block< 6, 1 >( 0, 0 ) ); // kalman增益// double speed_delta = solution.block( 0, 6, 3, 1 ).norm();// if(solution.block( 0, 6, 3, 1 ).norm() > 0.05 )// {// solution.block( 0, 6, 3, 1 ) = solution.block( 0, 6, 3, 1 ) / speed_delta * 0.05;// }//6>:结合5>中结果,求公式18计算结果,得到k+1次kalman的迭代更新值g_lio_state = state_propagate + solution; // kalman增益后的状态结果print_dash_board();// cout << ANSI_COLOR_RED_BOLD << "Run EKF uph, vec = " << vec.head<9>().transpose() << ANSI_COLOR_RESET << endl;rot_add = solution.block< 3, 1 >( 0, 0 ); // 旋转增量t_add = solution.block< 3, 1 >( 3, 0 ); // 平移增量flg_EKF_converged = false; // 收敛标识//7>:判断是否收敛if ( ( ( rot_add.norm() * 57.3 - deltaR ) < 0.01 ) && ( ( t_add.norm() * 100 - deltaT ) < 0.015 ) ){flg_EKF_converged = true; // 通过旋转和平移增量与上一次迭代的差值,判断是否收敛// ? : 收敛了为啥不加break,而是继续进行迭代}//8>:旋转和平移增量转换单位deltaR = rot_add.norm() * 57.3; // 角度单位deltaT = t_add.norm() * 100; // 厘米单位}// printf_line;g_lio_state.last_update_time = Measures.lidar_end_time;euler_cur = RotMtoEuler( g_lio_state.rot_end ); // 获得当前lidar的里程计信息,最后这个需要发布到ros中去dump_lio_state_to_log( m_lio_state_fp );/*** Rematch Judgement 重匹配判断 ***/rematch_en = false;if ( flg_EKF_converged || ( ( rematch_num == 0 ) && ( iterCount == ( NUM_MAX_ITERATIONS - 2 ) ) ) ){rematch_en = true;rematch_num++;}/*** @note (2-7-3-5) Convergence Judgements and Covariance Update * 收敛判断和协方差更新 : 对应FAST-LIO公式(19)*/// if (rematch_num >= 10 || (iterCount == NUM_MAX_ITERATIONS - 1))if ( rematch_num >= 2 || ( iterCount == NUM_MAX_ITERATIONS - 1 ) ) // Fast lio ori version.{if ( flg_EKF_inited ){/*** Covariance Update ***/G.block< DIM_OF_STATES, 6 >( 0, 0 ) = K * Hsub; // 对应公式(19)中 : K * Hg_lio_state.cov = ( I_STATE - G ) * g_lio_state.cov;//公式(19): (单位阵-K*H)*Cur_协方差total_distance += ( g_lio_state.pos_end - position_last ).norm();// 两次state间的距离position_last = g_lio_state.pos_end;// std::cout << "position: " << g_lio_state.pos_end.transpose() << " total distance: " << total_distance << std::endl;}solve_time += omp_get_wtime() - solve_start;break;}solve_time += omp_get_wtime() - solve_start;// cout << "Match cost time: " << match_time * 1000.0// << ", search cost time: " << kdtree_search_time*1000.0// << ", PCA cost time: " << pca_time*1000.0// << ", solver_cost: " << solve_time * 1000.0 << endl;// cout <<"Iter cost time: " << tim.toc("Iter") << endl;} // (2-7-3) : Kalman滤波迭代完成t3 = omp_get_wtime();/*** @note (2-7-4):add new frame points to map ikdtree * 1> : 更新维持的固定大小的map立方体 (参考FAST-LIO2:V.A地图管理)* 2> : 将Kalman更新后的新lidar帧特征点先转世界坐标系,再加入ikd树*/PointVector points_history; // 将ikd树中需要移除的点放入points_history中ikdtree.acquire_removed_points( points_history );// 从Points_deleted和Multithread_Points_deleted获取点memset( cube_updated, 0, sizeof( cube_updated ) );//1> : 更新维持的固定大小的map立方体 (参考FAST-LIO2:V.A地图管理)for ( int i = 0; i < points_history.size(); i++ ){PointType &pointSel = points_history[ i ];int cubeI = int( ( pointSel.x + 0.5 * cube_len ) / cube_len ) + laserCloudCenWidth;int cubeJ = int( ( pointSel.y + 0.5 * cube_len ) / cube_len ) + laserCloudCenHeight;int cubeK = int( ( pointSel.z + 0.5 * cube_len ) / cube_len ) + laserCloudCenDepth;if ( pointSel.x + 0.5 * cube_len < 0 )cubeI--;if ( pointSel.y + 0.5 * cube_len < 0 )cubeJ--;if ( pointSel.z + 0.5 * cube_len < 0 )cubeK--;if ( cubeI >= 0 && cubeI < laserCloudWidth && cubeJ >= 0 && cubeJ < laserCloudHeight && cubeK >= 0 && cubeK < laserCloudDepth ){int cubeInd = cubeI + laserCloudWidth * cubeJ + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * cubeK;featsArray[ cubeInd ]->push_back( pointSel );}}//2-1> : 将Kalman更新后的新lidar帧特征点先转世界坐标系for ( int i = 0; i < feats_down_size; i++ ){/* transform to world frame */pointBodyToWorld( &( feats_down->points[ i ] ), &( feats_down_updated->points[ i ] ) );}t4 = omp_get_wtime();//2-2> : 将特征点加入世界坐标中ikdtree.Add_Points( feats_down_updated->points, true ); // 存入ikd树中kdtree_incremental_time = omp_get_wtime() - t4 + readd_time + readd_box_time + delete_box_time;t5 = omp_get_wtime();} // (2-7) ICP迭代+Kalman更新完成最后就是向rgb点云地图中加入新点,并发布laserCloudFullResColor、Maps、Odometry、Path等信息。
/*** @note (2-9) : append point cloud to global map.* 将点云添加至世界地图中 */ if ( 1 ){static std::vector< double > stastic_cost_time;Common_tools::Timer tim;// tim.tic();// ANCHOR - RGB maps updatewait_render_thread_finish();if ( m_if_record_mvs ){std::vector< std::shared_ptr< RGB_pts > > pts_last_hitted;pts_last_hitted.reserve( 1e6 );m_number_of_new_visited_voxel = m_map_rgb_pts.append_points_to_global_map(*laserCloudFullResColor, Measures.lidar_end_time - g_camera_lidar_queue.m_first_imu_time, &pts_last_hitted,m_append_global_map_point_step );m_map_rgb_pts.m_mutex_pts_last_visited->lock();m_map_rgb_pts.m_pts_last_hitted = pts_last_hitted;m_map_rgb_pts.m_mutex_pts_last_visited->unlock();}else{m_number_of_new_visited_voxel = m_map_rgb_pts.append_points_to_global_map(*laserCloudFullResColor, Measures.lidar_end_time - g_camera_lidar_queue.m_first_imu_time, nullptr,m_append_global_map_point_step );}stastic_cost_time.push_back( tim.toc( " ", 0 ) );}/*** @note (2-10) : 仅发布找到了最近平面的有效点*/ if(0) // Uncomment this code scope to enable the publish of effective points. {/******* Publish effective points *******/laserCloudFullResColor->clear();pcl::PointXYZI temp_point;for ( int i = 0; i < laserCloudSelNum; i++ ){RGBpointBodyToWorld( &laserCloudOri->points[ i ], &temp_point );laserCloudFullResColor->push_back( temp_point );}sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 laserCloudFullRes3;pcl::toROSMsg( *laserCloudFullResColor, laserCloudFullRes3 );// laserCloudFullRes3.header.stamp = ros::Time::now(); //.fromSec(last_timestamp_lidar);laserCloudFullRes3.header.stamp.fromSec( Measures.lidar_end_time ); //.fromSec(last_timestamp_lidar);laserCloudFullRes3.header.frame_id = "world";pubLaserCloudEffect.publish( laserCloudFullRes3 );}/*** @note (2-11)***** Publish Maps: 发布地图*******/sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 laserCloudMap;pcl::toROSMsg( *featsFromMap, laserCloudMap );laserCloudMap.header.stamp.fromSec( Measures.lidar_end_time ); // ros::Time().fromSec(last_timestamp_lidar);laserCloudMap.header.frame_id = "world";pubLaserCloudMap.publish( laserCloudMap );/*** @note (2-12)***** Publish Odometry 发布里程计******/geometry_msgs::Quaternion geoQuat = tf::createQuaternionMsgFromRollPitchYaw( euler_cur( 0 ), euler_cur( 1 ), euler_cur( 2 ) );odomAftMapped.header.frame_id = "world";odomAftMapped.child_frame_id = "/aft_mapped";odomAftMapped.header.stamp = ros::Time::now(); // ros::Time().fromSec(last_timestamp_lidar);odomAftMapped.pose.pose.orientation.x = geoQuat.x;odomAftMapped.pose.pose.orientation.y = geoQuat.y;odomAftMapped.pose.pose.orientation.z = geoQuat.z;odomAftMapped.pose.pose.orientation.w = geoQuat.w;odomAftMapped.pose.pose.position.x = g_lio_state.pos_end( 0 );odomAftMapped.pose.pose.position.y = g_lio_state.pos_end( 1 );odomAftMapped.pose.pose.position.z = g_lio_state.pos_end( 2 );pubOdomAftMapped.publish( odomAftMapped );static tf::TransformBroadcaster br;tf::Transform transform;tf::Quaternion q;transform.setOrigin(tf::Vector3( odomAftMapped.pose.pose.position.x, odomAftMapped.pose.pose.position.y, odomAftMapped.pose.pose.position.z ) );q.setW( odomAftMapped.pose.pose.orientation.w );q.setX( odomAftMapped.pose.pose.orientation.x );q.setY( odomAftMapped.pose.pose.orientation.y );q.setZ( odomAftMapped.pose.pose.orientation.z );transform.setRotation( q );br.sendTransform( tf::StampedTransform( transform, ros::Time().fromSec( Measures.lidar_end_time ), "world", "/aft_mapped" ) );msg_body_pose.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();msg_body_pose.header.frame_id = "/camera_odom_frame";msg_body_pose.pose.position.x = g_lio_state.pos_end( 0 );msg_body_pose.pose.position.y = g_lio_state.pos_end( 1 );msg_body_pose.pose.position.z = g_lio_state.pos_end( 2 );msg_body_pose.pose.orientation.x = geoQuat.x;msg_body_pose.pose.orientation.y = geoQuat.y;msg_body_pose.pose.orientation.z = geoQuat.z;msg_body_pose.pose.orientation.w = geoQuat.w;/*** @note (2-13)***** Publish Path 发布路径********/msg_body_pose.header.frame_id = "world";if ( frame_num > 10 ){path.poses.push_back( msg_body_pose );}pubPath.publish( path );/*** @note (2-14)* save debug variables 保存debug变量***/frame_num++;aver_time_consu = aver_time_consu * ( frame_num - 1 ) / frame_num + ( t5 - t0 ) / frame_num;// aver_time_consu = aver_time_consu * 0.8 + (t5 - t0) * 0.2;T1[ time_log_counter ] = Measures.lidar_beg_time;s_plot[ time_log_counter ] = aver_time_consu;s_plot2[ time_log_counter ] = kdtree_incremental_time;s_plot3[ time_log_counter ] = kdtree_search_time;s_plot4[ time_log_counter ] = fov_check_time;s_plot5[ time_log_counter ] = t5 - t0;s_plot6[ time_log_counter ] = readd_box_time;time_log_counter++;fprintf( m_lio_costtime_fp, "%.5f %.5f\r\n", g_lio_state.last_update_time - g_camera_lidar_queue.m_first_imu_time, t5 - t0 );fflush( m_lio_costtime_fp );相关文章:
 — R3LIVE中r3live_lio.cpp文件)
R3LIVE源码解析(9) — R3LIVE中r3live_lio.cpp文件
目录 1 r3live_lio.cpp文件简介 2 r3live_lio.cpp源码解析 1 r3live_lio.cpp文件简介 在r3live.cpp文件中创建LIO线程后,R3LIVE中的LIO线程本质上整体流程和FAST-LIO2基本一致。 2 r3live_lio.cpp源码解析 函数最开始会进行一系列的声明和定义,发布的…...
如何高效的解析Json?
Json介绍 Json是一种数据格式,广泛应用在需要数据交互的场景Json由键值对组成每一个键值对的key是字符串类型每一个键值对的value是值类型(boo1值数字值字符串值)Array类型object类型Json灵活性他可以不断嵌套,数组的每个元素还可以是数组或者键值对键值…...

MySQL——分组查询
2023.9.4 MySQL 分组查询的学习笔记如下: #分组查询 /* 分组查询中的筛选条件分为两类:数据源 位置 关键字 分组前筛选 原始表 group by前面 where 分组后筛选 分组后的结果集 group by后面 having */ #查询每…...

thinkphp 使用 easypay 和 easywechat
easypay 是3.x easywechat 是6.x 引入: use Yansongda\Pay\Pay;//easypayuse EasyWeChat\MiniApp\Application as MiniApp;//easywechat use EasyWeChat\Pay\Application as Payapp;//easywechat public function suborder(){$order [out_trade_no > time(…...

无涯教程-JavaScript - DVARP函数
描述 DVARP函数通过使用列表或数据库中符合您指定条件的记录的字段(列)中的数字,基于整个总体计算总体的方差。 语法 DVARP (database, field, criteria)争论 Argument描述Required/Optionaldatabase 组成列表或数据库的单元格范围。 数据库是相关数据的列表,其中相关信息的…...

Databend 开源周报第 108 期
Databend 是一款现代云数仓。专为弹性和高效设计,为您的大规模分析需求保驾护航。自由且开源。即刻体验云服务:https://app.databend.cn 。 Whats On In Databend 探索 Databend 本周新进展,遇到更贴近你心意的 Databend 。 多源数据目录 …...

Android-Intent实现数据传递
在activityA中使用putExtras(bundle)传递数据,在activityB中使用getExtras()获取数据 MainActivity.java及其xml package com.example.intentactivity;import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;import android.content.ComponentName; import android.co…...
系统学习Linux-zabbix监控平台
一、zabbix的基本概述 zabbix是一个监控软件,其可以监控各种网络参数,保证企业服务架构安全运营,同时支持灵活的告警机制,可以使得运维人员快速定位故障、解决问题。zabbix支持分布式功能,支持复杂架构下的监控解决方…...

基于MediaPipe的人体摔倒检测
1 简介 1.1 研究背景及意义 现如今随着经济等各方面飞速发展,社会安全随之也成为必不可少的话题。而校园安全则是社会安全的重中之重,而在我们的校园中,湿滑的地面、楼梯等位置通常会发生摔倒,尽管有“小心脚下”的告示牌…...

WebDAV之π-Disk派盘 + 无忧日记
无忧日记,生活无忧无虑。 给用户专业的手机记录工具,用户可以很轻松地通过软件进行每天发生事情的记录,可以为用户提供优质的工具与帮助,用户还可以通过软件来将地理位置,天气都记录在日记上,用户也可以通过软件来进行图片的导入,创建长图日记, 心情报表:用户写日记…...

Docker 相关操作,及其一键安装Docker脚本
一、模拟CentOS 7.5上安装Docker: 创建一个CentOS 7.5的虚拟机或使用其他方式准备一个CentOS 7.5的环境。 在CentOS 7.5上执行以下命令,以安装Docker的依赖项: sudo yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 添加Doc…...
【Microsoft Edge】如何彻底卸载 Edge
目录 一、问题描述 二、卸载 Edge 2.1 卸载正式版 Edge 2.2 卸载非正式版 Edge 2.2.1 卸载通用的 WebView2 2.2.2 卸载 Canary 版 Edge 2.2.3 卸载其他版本 2.3 卸载 Edge Update 2.4 卸载 Edge 的 Appx 额外安装残留 2.5 删除日志文件 2.6 我就是想全把 Edge 都删了…...

2023-09-04力扣每日一题
链接: 449. 序列化和反序列化二叉搜索树 题意: 把一个二叉搜索树变成字符串,还要能变回来 解: 和剑指 Offer 37. 序列化二叉树差不多,那个是二叉树的序列化/反序列化-Hard 直接CV了,懒: ( 如果是二叉…...
jQuery成功之路——jQuery事件和插件概述
一、jQuery的事件 1.1常用事件 jQuery绑定事件,事件名字没有on。 事件名称事件说明blur事件源失去焦点click单击事件源change内容改变keydown接受键盘上的所有键(键盘按下)keypress接受键盘上的部分键(ctrl,alt,shift等无效)(键盘按下)key…...

Java ArrayList类详解
基本定义 ArrayList 是 Java 中的一个动态数组数据结构,属于 Java 集合框架的一部分(java.util 包中的类)。它提供了一个基于数组的可变长度列表,允许你在运行时添加、删除和访问元素,而不需要提前指定数组的大小。 简…...

快速排序学习
由于之前做有一题看到题解用了快排提升效率,就浅学了一下快速排序,还是似懂非懂。 首先快排的核心有两点,哨兵划分和递归。 哨兵划分:以数组中的某个数(一般为首位)为基准数,将数组划分为两个部…...
【Vue3 知识第二讲】Vue3新特性、vue-devtools 调试工具、脚手架搭建
文章目录 一、Vue3 新特性1.1 重写双向数据绑定1.1.1 Vue2 基于Object.defineProperty() 实现1.1.2 Vue3 基于Proxy 实现 1.2 优化 虚拟DOM1.3 Fragments1.4 Tree shaking1.5 Composition API 二、 vue-devtools 调试工具三、环境配置四、脚手架目录介绍五、SFC 语法规范解析附…...

pytorch 基于masking对元素进行替换
描述 pytorch 基于masking对元素进行替换. 代码如下. 先展平再赋值. 代码 # map.shape [64,60,128] # infill.shape [64,17,128] # mask_indices.shape [64,60]map map.reshape(map.shape[0] * map.shape[1],map.shape[2]) [mask_indices.reshape(mask_indices.shape[0]*ma…...
Cyber RT学习笔记---7、Component组件认知与实践
7、Component组件认知与实践 前言 本文是对Cyber RT的学习记录,文章可能存在不严谨、不完善、有缺漏的部分,还请大家多多指出。 课程地址: https://apollo.baidu.com/community/course/outline/329?activeId10200 更多还请参考: [1] Apollo星火计划学习笔记——第…...

常见配置文件格式INI/XML/YAML/JSON/Properties/TOML/HCL/YAML Front Matter/.env介绍及实例
1. 常见配置文件INI XML YAML JSON Properties介绍 以下是常见配置文件格式(INI、XML、YAML、JSON、Properties、TOML、HCL、YAML Front Matter、.env)的比较: 配置文件格式简介语法定义优点缺点常见使用场景常见编程语言INI简单的文本文件…...

未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?
编辑:陈萍萍的公主一点人工一点智能 未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?RWM通过双自回归机制有效解决了复合误差、部分可观测性和随机动力学等关键挑战,在不依赖领域特定归纳偏见的条件下实现了卓越的预测准…...
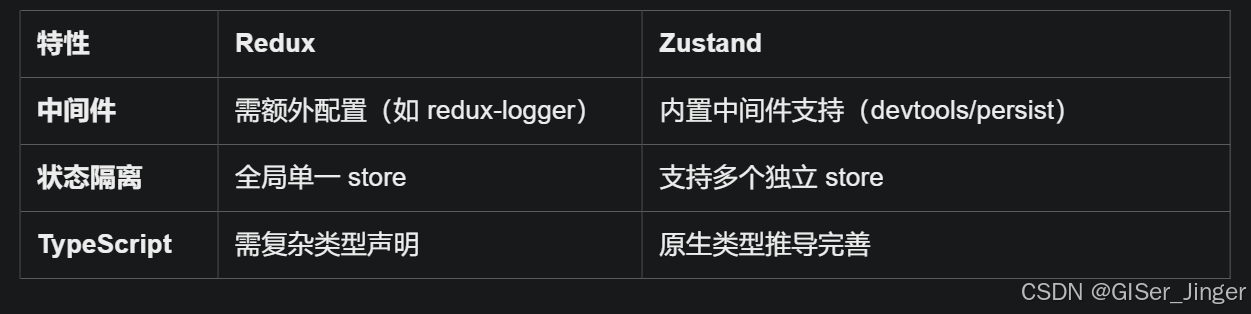
Zustand 状态管理库:极简而强大的解决方案
Zustand 是一个轻量级、快速和可扩展的状态管理库,特别适合 React 应用。它以简洁的 API 和高效的性能解决了 Redux 等状态管理方案中的繁琐问题。 核心优势对比 基本使用指南 1. 创建 Store // store.js import create from zustandconst useStore create((set)…...

五年级数学知识边界总结思考-下册
目录 一、背景二、过程1.观察物体小学五年级下册“观察物体”知识点详解:由来、作用与意义**一、知识点核心内容****二、知识点的由来:从生活实践到数学抽象****三、知识的作用:解决实际问题的工具****四、学习的意义:培养核心素养…...

OkHttp 中实现断点续传 demo
在 OkHttp 中实现断点续传主要通过以下步骤完成,核心是利用 HTTP 协议的 Range 请求头指定下载范围: 实现原理 Range 请求头:向服务器请求文件的特定字节范围(如 Range: bytes1024-) 本地文件记录:保存已…...
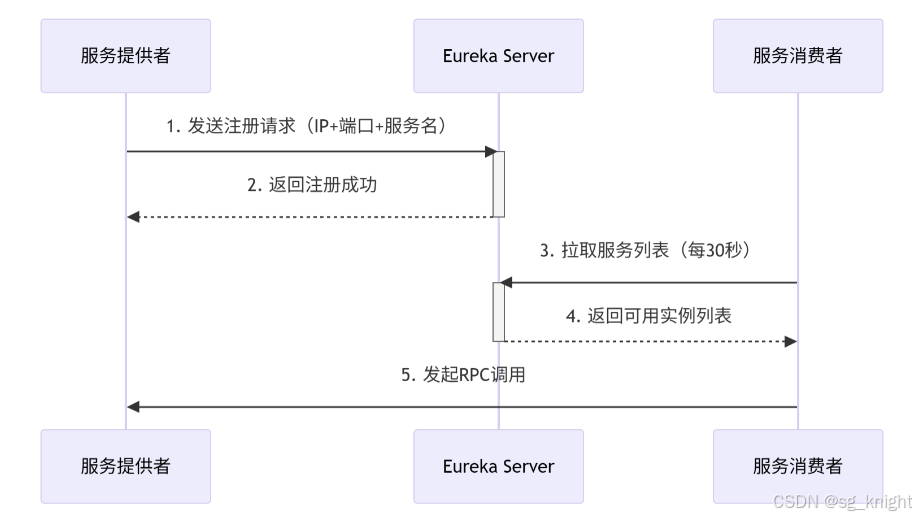
Springcloud:Eureka 高可用集群搭建实战(服务注册与发现的底层原理与避坑指南)
引言:为什么 Eureka 依然是存量系统的核心? 尽管 Nacos 等新注册中心崛起,但金融、电力等保守行业仍有大量系统运行在 Eureka 上。理解其高可用设计与自我保护机制,是保障分布式系统稳定的必修课。本文将手把手带你搭建生产级 Eur…...
Linux-07 ubuntu 的 chrome 启动不了
文章目录 问题原因解决步骤一、卸载旧版chrome二、重新安装chorme三、启动不了,报错如下四、启动不了,解决如下 总结 问题原因 在应用中可以看到chrome,但是打不开(说明:原来的ubuntu系统出问题了,这个是备用的硬盘&a…...

IoT/HCIP实验-3/LiteOS操作系统内核实验(任务、内存、信号量、CMSIS..)
文章目录 概述HelloWorld 工程C/C配置编译器主配置Makefile脚本烧录器主配置运行结果程序调用栈 任务管理实验实验结果osal 系统适配层osal_task_create 其他实验实验源码内存管理实验互斥锁实验信号量实验 CMISIS接口实验还是得JlINKCMSIS 简介LiteOS->CMSIS任务间消息交互…...

重启Eureka集群中的节点,对已经注册的服务有什么影响
先看答案,如果正确地操作,重启Eureka集群中的节点,对已经注册的服务影响非常小,甚至可以做到无感知。 但如果操作不当,可能会引发短暂的服务发现问题。 下面我们从Eureka的核心工作原理来详细分析这个问题。 Eureka的…...

Python 包管理器 uv 介绍
Python 包管理器 uv 全面介绍 uv 是由 Astral(热门工具 Ruff 的开发者)推出的下一代高性能 Python 包管理器和构建工具,用 Rust 编写。它旨在解决传统工具(如 pip、virtualenv、pip-tools)的性能瓶颈,同时…...
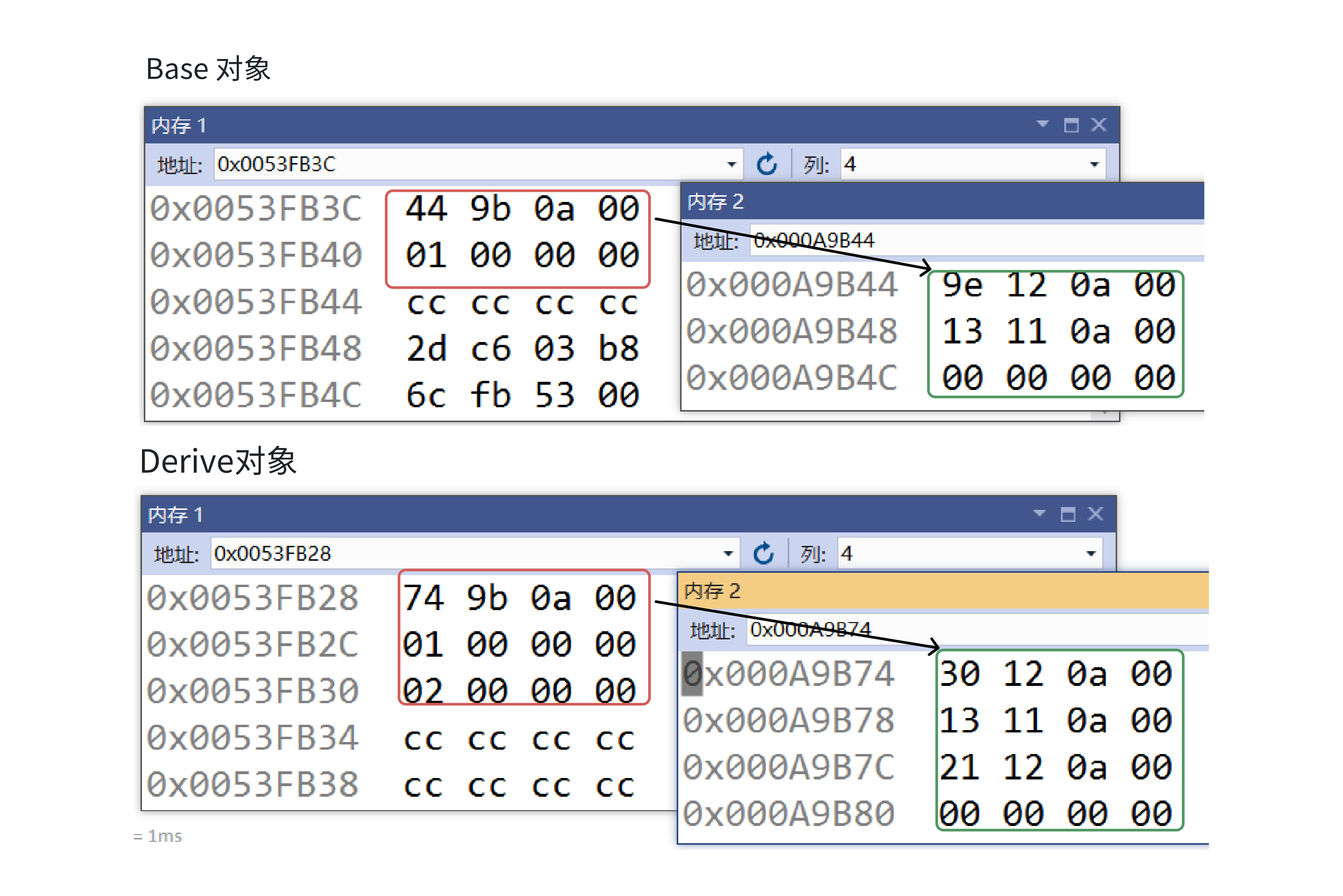
C++:多态机制详解
目录 一. 多态的概念 1.静态多态(编译时多态) 二.动态多态的定义及实现 1.多态的构成条件 2.虚函数 3.虚函数的重写/覆盖 4.虚函数重写的一些其他问题 1).协变 2).析构函数的重写 5.override 和 final关键字 1&#…...
