matplotlib绘制三维图
目录
- 线状堆积图 PolygonPlot
- 三维表面图 SurfacePlot
- 散点图ScatterPlot
- 柱形图 BarPlot
- 三维直方图
- 螺旋曲线图 LinePlot
- ContourPlot
- 轮廓图
- 网状图 WireframePlot
- 箭头图
- 二维三维合并
- 文本图Text
- 三维多个子图
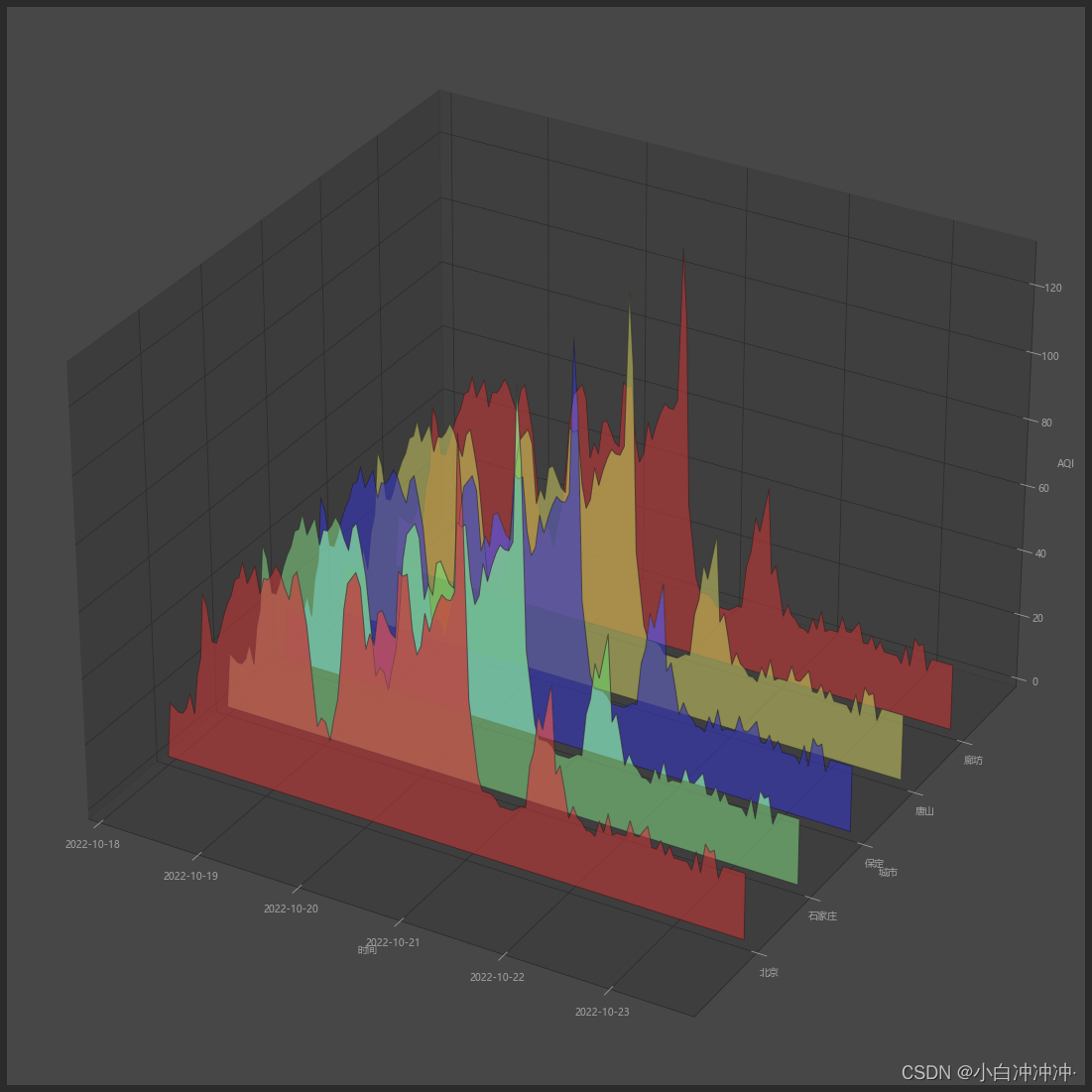
线状堆积图 PolygonPlot
Axes3D.add_collection3d(col, zs=0, zdir=‘z’)
这个函数可以将三维 collection对象或二维collection对象加入到一个图形中,包括:
- PolyCollection
- LineCollection
- PatchCollection
import pandas as pd
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from matplotlib.collections import PolyCollection
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import colors as mcolors
import numpy as np
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'Microsoft YaHei' # 字体设置
plt.rcParams['font.size'] = 10 # 字体大小设置fig = plt.figure(figsize=(30,20))
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')def cc(arg):return mcolors.to_rgba(arg, alpha=0.6)
def polygon_under_graph(xlist, ylist):'''Construct the vertex list which defines the polygon filling the space underthe (xlist, ylist) line graph. Assumes the xs are in ascending order.'''return [(xlist[0], 0.), *zip(xlist, ylist), (xlist[-1], 0.)]xs = np.arange(0,137,1)verts = []zs = [0.0,1.0,2.0, 3.0,4.0]
for z in zs:for i in range(1,6): #读取数据ys = df.iloc[:,i]verts.append(polygon_under_graph(xs,ys))poly = PolyCollection(verts, facecolors=[cc('r'), cc('g'), cc('b'),cc('y'),cc('r')])
poly.set_alpha(0.7) # 图形的透明度
ax.add_collection3d(poly, zs=zs, zdir='y')names_1 = ['2022-10-18', '2022-10-19', '2022-10-20','2022-10-21',
'2022-10-22', '2022-10-23']
plt.xticks(xs[::24], names_1)names = ['北京', '石家庄', '保定','唐山','廊坊']
plt.yticks(zs, names)ax.set_xlabel('时间')
ax.set_ylabel('城市')
ax.set_zlabel('AQI')
ax.set_xlim3d(0, 136)
ax.set_ylim3d(-1, 5)
ax.set_zlim3d(0, 130)
#plt.savefig('三维时间.png',bbox_inches = 'tight',dpi=500)
plt.show()
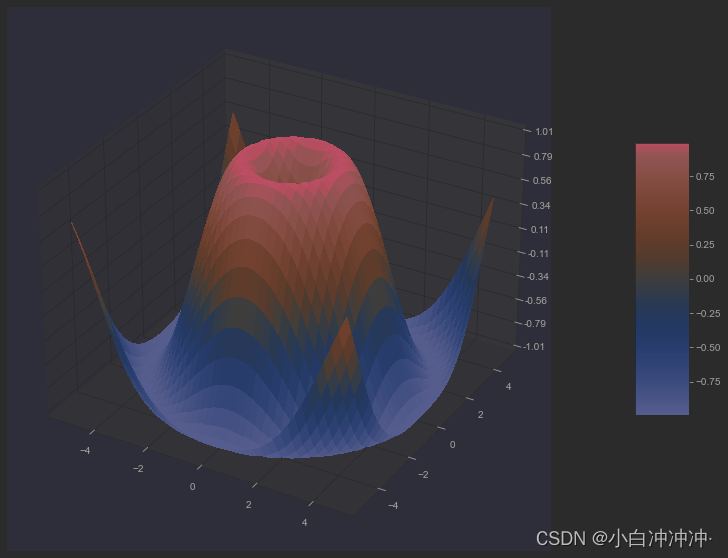
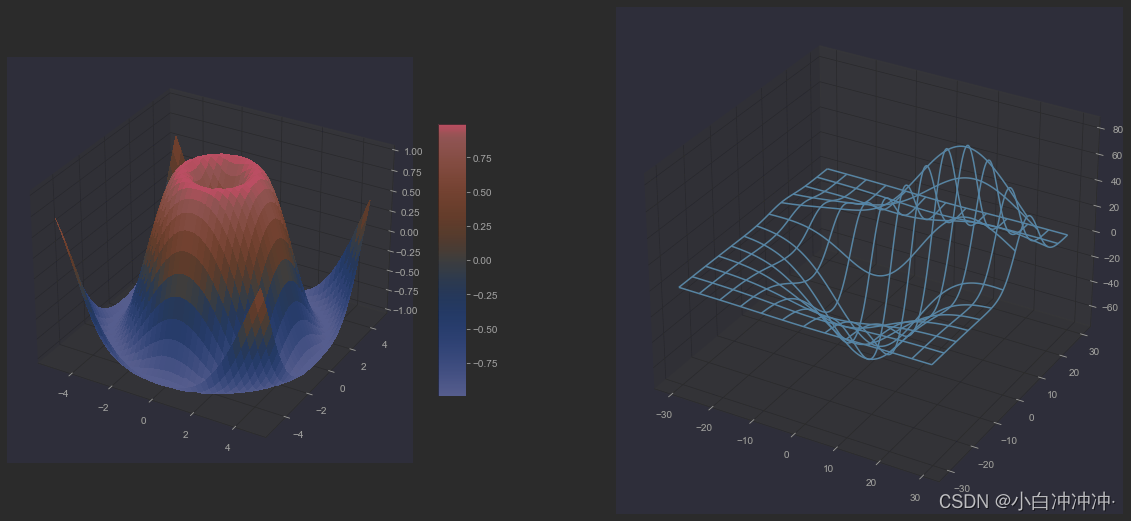
三维表面图 SurfacePlot
Axes3D.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, *args, norm=None, vmin=None, vmax=None, lightsource=None, **kwargs)
这个函数算是比较常用的函数,用于绘制三维表面图,让人惊艳的是它的着色效果。
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| X, Y,Z | 坐标点 |
| rcount,ccount,rstride,cstride | 同上 |
| color | 定义surface patch的颜色,type:color-like |
| cmap | 定义surface patch的颜色,只不过是colorMap,type:colormap |
| facecolors | 指定单个patch的颜色, type:array-like of colors |
| norm | colormap的normalization, type:Normalize |
| shade | 阴影效果,type:boolean |
| vmin, vmax | normalization的边界 |
| **kwargs | 向下传递到Poly3DCollection |
| antialiased | 抗锯齿,type:boolean |
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cmfrom matplotlib.ticker import LinearLocator, FormatStrFormatter
import numpy as npfig = plt.figure(figsize=(30,10))
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')# Make data.
X = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
Y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
R = np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2)
Z = np.sin(R)# Plot the surface.
surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap=cm.coolwarm,linewidth=0, antialiased=False)# Customize the z axis.
ax.set_zlim(-1.01, 1.01)
ax.zaxis.set_major_locator(LinearLocator(10))
ax.zaxis.set_major_formatter(FormatStrFormatter('%.02f'))# Add a color bar which maps values to colors.
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)plt.show()
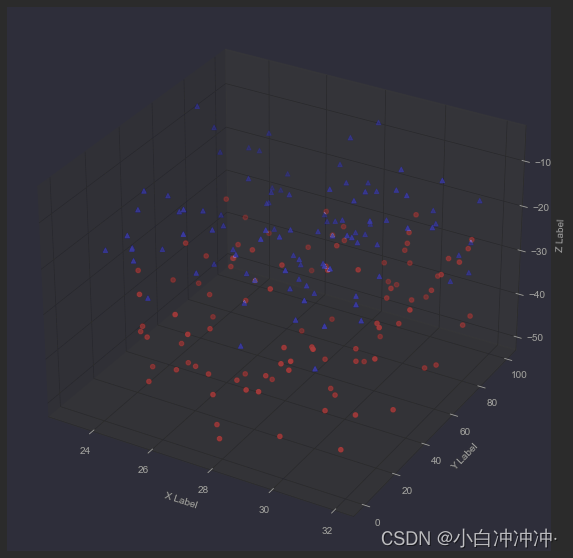
散点图ScatterPlot
Axes3D.scatter(xs, ys, zs=0, zdir=‘z’, s=20, c=None, depthshade=True, *args, **kwargs)
返回Patch3DCollection,
其他参数向下传递给plot函数
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| xs, ys | x,y坐标点 |
| zs | z 坐标,可以是一个标量或一个x*y维矩阵,默认是0. |
| zdir | 当绘制二维图像时的z轴方向 |
| s | size,即散点大小 |
| c | 颜色映射,其取值可以是非常多类型,有时间专门写一篇讲解 |
| depthshade | 是否渲染景深(或则就说阴影吧),默认是True. |
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3Dimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)def randrange(n, vmin, vmax):'''Helper function to make an array of random numbers having shape (n, )with each number distributed Uniform(vmin, vmax).'''return (vmax - vmin)*np.random.rand(n) + vminfig = plt.figure(figsize=(20,10))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')n = 100# For each set of style and range settings, plot n random points in the box
# defined by x in [23, 32], y in [0, 100], z in [zlow, zhigh].
for c, m, zlow, zhigh in [('r', 'o', -50, -25), ('b', '^', -30, -5)]:xs = randrange(n, 23, 32)ys = randrange(n, 0, 100)zs = randrange(n, zlow, zhigh)ax.scatter(xs, ys, zs, c=c, marker=m)ax.set_xlabel('X Label')
ax.set_ylabel('Y Label')
ax.set_zlabel('Z Label')plt.show()
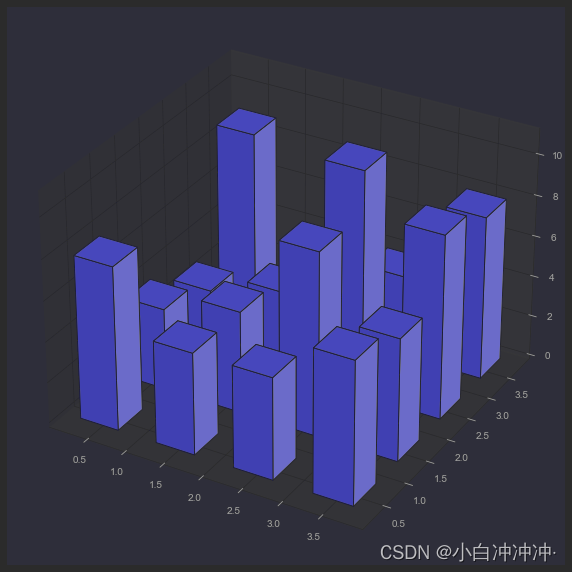
柱形图 BarPlot
Axes3D.bar(left, height, zs=0, zdir=‘z’, *args, **kwargs)
其他参数向下传递给bar函数,返回Patch3DCollection对象
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| left | 条形图水平坐标 |
| height | 条形的高度 |
| zs | Z方向 |
| zdir | 同上 |
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D # noqa: F401 unused importimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,20))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')colors = ['r', 'g', 'b', 'y']
yticks = [3, 2, 1, 0]
for c, k in zip(colors, yticks):# Generate the random data for the y=k 'layer'.xs = np.arange(20)ys = np.random.rand(20)# You can provide either a single color or an array with the same length as# xs and ys. To demonstrate this, we color the first bar of each set cyan.cs = [c] * len(xs)# Plot the bar graph given by xs and ys on the plane y=k with 80% opacity.ax.bar(xs, ys, zs=k, zdir='y', color=cs, alpha=0.8)ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('Z')# On the y axis let's only label the discrete values that we have data for.
ax.set_yticks(yticks)plt.show()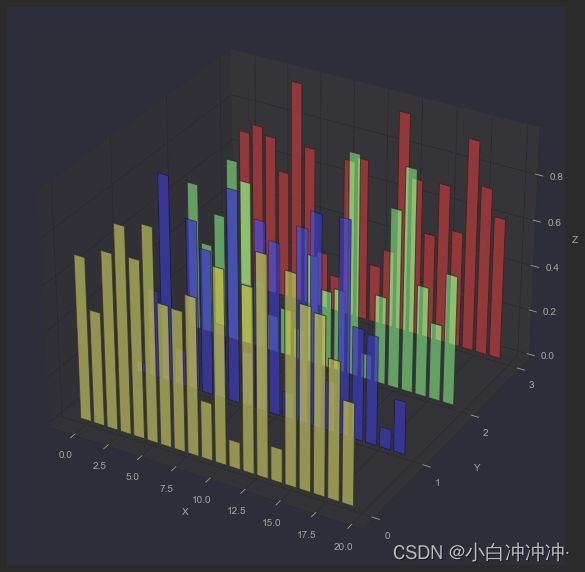
三维直方图
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as npfig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
x, y = np.random.rand(2, 100) * 4
hist, xedges, yedges = np.histogram2d(x, y, bins=4, range=[[0, 4], [0, 4]])# Construct arrays for the anchor positions of the 16 bars.
# Note: np.meshgrid gives arrays in (ny, nx) so we use 'F' to flatten xpos,
# ypos in column-major order. For numpy >= 1.7, we could instead call meshgrid
# with indexing='ij'.
xpos, ypos = np.meshgrid(xedges[:-1] + 0.25, yedges[:-1] + 0.25)
xpos = xpos.flatten('F')
ypos = ypos.flatten('F')
zpos = np.zeros_like(xpos)# Construct arrays with the dimensions for the 16 bars.
dx = 0.5 * np.ones_like(zpos)
dy = dx.copy()
dz = hist.flatten()ax.bar3d(xpos, ypos, zpos, dx, dy, dz, color='b', zsort='average')plt.show()
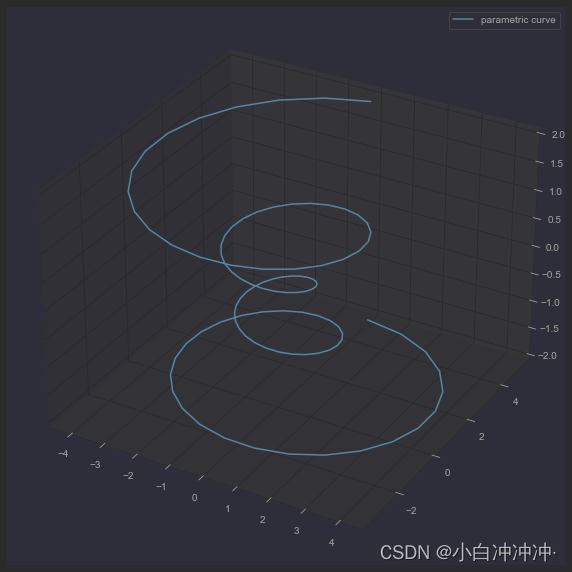
螺旋曲线图 LinePlot
Axes3D.plot(xs, ys, *args, zdir=‘z’, **kwargs)
其他参数向下传递给plot函数
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| xs, ys | x、y 坐标 |
| zs | z 坐标,可以是一个标量或一个x*y维矩阵 |
| zdir | 当绘制二维图像时的z轴方向 |
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3Dimport numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltplt.rcParams['legend.fontsize'] = 10
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,20))
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d') # get current axes# Prepare arrays x, y, z
theta = np.linspace(-4 * np.pi, 4 * np.pi, 100)
z = np.linspace(-2, 2, 100)
r = z**2 + 1
x = r * np.sin(theta)
y = r * np.cos(theta)ax.plot(x, y, z, label='parametric curve')
ax.legend() plt.show()
ContourPlot
Axes3D.contour(X, Y, Z, *args, extend3d=False, stride=5, zdir=‘z’, offset=None, **kwargs)
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| X, Y,Z | Data values as numpy.arrays |
| extend3d | 是否延申到3d空间 (default: False) |
| *stride | (extend3d的)采样步长 |
| zdir | 同上 |
| offset | 绘制轮廓线在zdir垂直的水平面上的投影 |
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cmfig = plt.figure(figsize=(30,10))
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
X, Y, Z = axes3d.get_test_data(0.05)# Plot contour curves
cset = ax.contour(X, Y, Z, cmap=cm.coolwarm)ax.clabel(cset, fontsize=9, inline=1) # function to label a contourplt.show()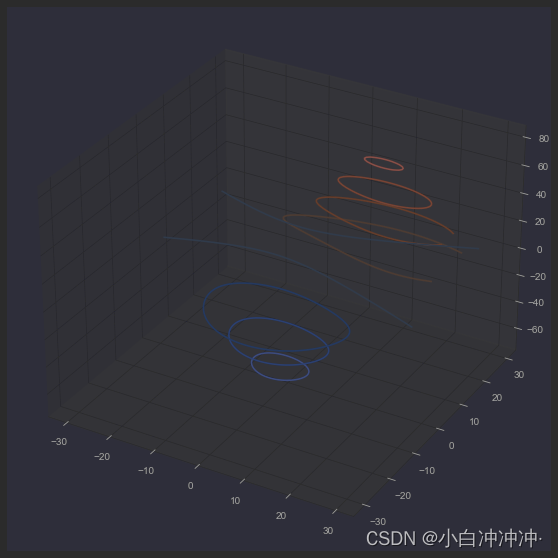
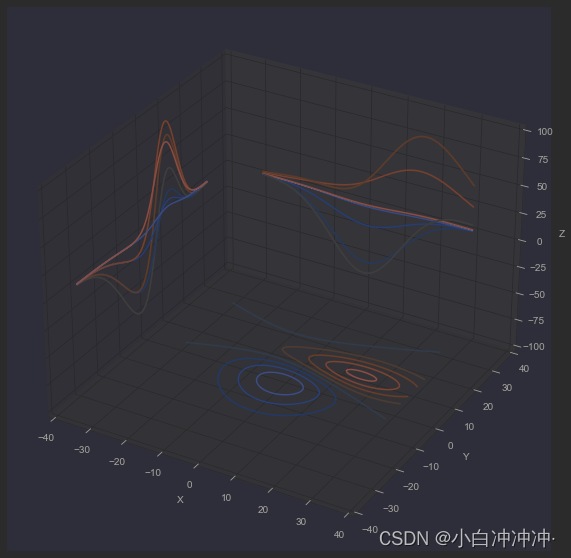
轮廓图
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cmfig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
X, Y, Z = axes3d.get_test_data(0.05)
cset = ax.contour(X, Y, Z, zdir='z', offset=-100, cmap=cm.coolwarm)
cset = ax.contour(X, Y, Z, zdir='x', offset=-40, cmap=cm.coolwarm)
cset = ax.contour(X, Y, Z, zdir='y', offset=40, cmap=cm.coolwarm)ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_xlim(-40, 40)
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_ylim(-40, 40)
ax.set_zlabel('Z')
ax.set_zlim(-100, 100)plt.show()
网状图 WireframePlot
Axes3D.plot_wireframe(X, Y, Z, *args, **kwargs)
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| X, Y,Z | 坐标点 |
| rcount,ccount | 采样数,越大采样越多,默认50 |
| rstride,cstride | 采样步长,越小采样越多 |
| **kwargs | 其他参数向下传入Line3DCollection |
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfig = plt.figure(figsize=(30,10))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')# Grab some test data.
X, Y, Z = axes3d.get_test_data(0.05)# Plot a basic wireframe.
ax.plot_wireframe(X, Y, Z, rstride=10, cstride=10)plt.show()
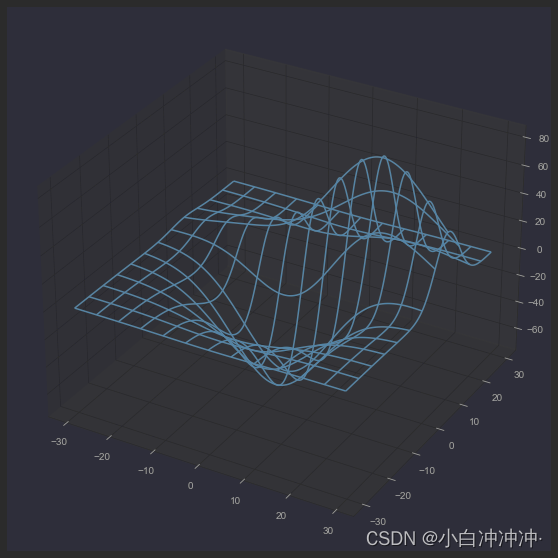
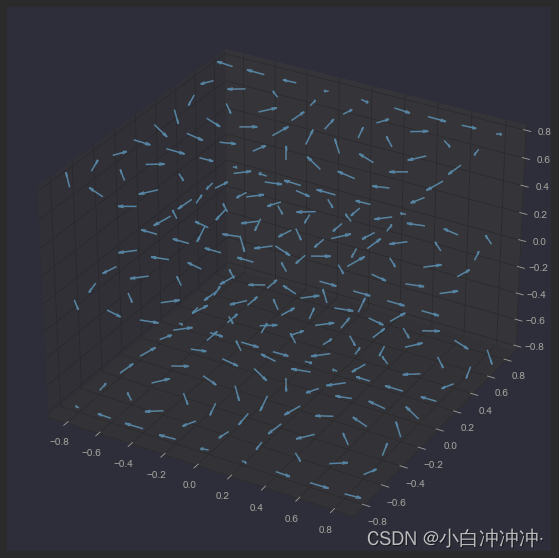
箭头图
Axes3D.quiver(*args, **kwargs)
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| X, Y, Z | The x, y and z coordinates of the arrow locations (default is tail of arrow; see pivot kwarg) |
| U, V, W | The x, y and z components of the arrow vectors |
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as npfig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')# Make the grid
x, y, z = np.meshgrid(np.arange(-0.8, 1, 0.2),np.arange(-0.8, 1, 0.2),np.arange(-0.8, 1, 0.8))# Make the direction data for the arrows
u = np.sin(np.pi * x) * np.cos(np.pi * y) * np.cos(np.pi * z)
v = -np.cos(np.pi * x) * np.sin(np.pi * y) * np.cos(np.pi * z)
w = (np.sqrt(2.0 / 3.0) * np.cos(np.pi * x) * np.cos(np.pi * y) *np.sin(np.pi * z))ax.quiver(x, y, z, u, v, w, length=0.1, normalize=True)plt.show()
二维三维合并
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')# Plot a sin curve using the x and y axes.
x = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
y = np.sin(x * 2 * np.pi) / 2 + 0.5
ax.plot(x, y, zs=0, zdir='z', label='curve in (x,y)')# Plot scatterplot data (20 2D points per colour) on the x and z axes.
colors = ('r', 'g', 'b', 'k')
x = np.random.sample(20 * len(colors))
y = np.random.sample(20 * len(colors))
labels = np.random.randint(3, size=80)# By using zdir='y', the y value of these points is fixed to the zs value 0
# and the (x,y) points are plotted on the x and z axes.
ax.scatter(x, y, zs=0, zdir='y', c=labels, label='points in (x,z)')# Make legend, set axes limits and labels
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlim(0, 1)
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax.set_zlim(0, 1)
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('Z')# Customize the view angle so it's easier to see that the scatter points lie
# on the plane y=0
ax.view_init(elev=20., azim=-35)plt.show()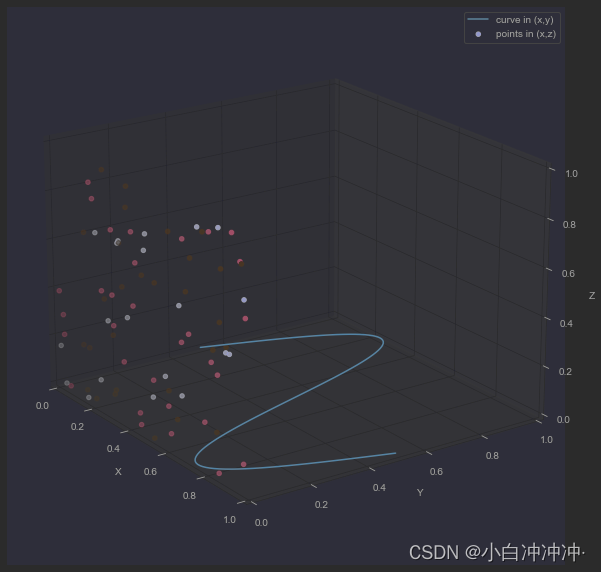
文本图Text
Axes3D.text(x, y, z, s, zdir=None, **kwargs)
text的内容其实也很繁杂,需要用一篇内容去探讨,在三维中很重要的一点是要学会二维、三维文字的添加。
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D # noqa: F401 unused importimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')# Demo 1: zdir
zdirs = (None, 'x', 'y', 'z', (1, 1, 0), (1, 1, 1))
xs = (1, 4, 4, 9, 4, 1)
ys = (2, 5, 8, 10, 1, 2)
zs = (10, 3, 8, 9, 1, 8)for zdir, x, y, z in zip(zdirs, xs, ys, zs):label = '(%d, %d, %d), dir=%s' % (x, y, z, zdir)ax.text(x, y, z, label, zdir)# Demo 2: color
ax.text(9, 0, 0, "red", color='red')# Demo 3: text2D
# Placement 0, 0 would be the bottom left, 1, 1 would be the top right.
ax.text2D(0.05, 0.95, "2D Text", transform=ax.transAxes)# Tweaking display region and labels
ax.set_xlim(0, 10)
ax.set_ylim(0, 10)
ax.set_zlim(0, 10)
ax.set_xlabel('X axis')
ax.set_ylabel('Y axis')
ax.set_zlabel('Z axis')plt.show()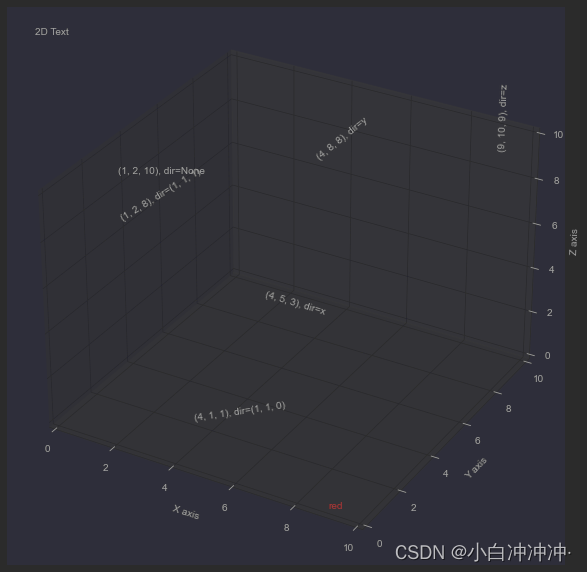
三维多个子图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.axes3d import Axes3D, get_test_data
from matplotlib import cm
import numpy as np# set up a figure twice as wide as it is tall
# fig = plt.figure(figsize=plt.figaspect(0.5))
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20,10))# ===============
# First subplot
# ===============
# set up the axes for the first plot
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1, projection='3d')# plot a 3D surface like in the example mplot3d/surface3d_demo
X = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
Y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
R = np.sqrt(X ** 2 + Y ** 2)
Z = np.sin(R)
surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=cm.coolwarm,linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
ax.set_zlim(-1.01, 1.01)
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=10)# ===============
# Second subplot
# ===============
# set up the axes for the second plot
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2, projection='3d')# plot a 3D wireframe like in the example mplot3d/wire3d_demo
X, Y, Z = get_test_data(0.05)
ax.plot_wireframe(X, Y, Z, rstride=10, cstride=10)plt.show()
相关文章:

matplotlib绘制三维图
目录线状堆积图 PolygonPlot三维表面图 SurfacePlot散点图ScatterPlot柱形图 BarPlot三维直方图螺旋曲线图 LinePlotContourPlot轮廓图网状图 WireframePlot箭头图二维三维合并文本图Text三维多个子图线状堆积图 PolygonPlot Axes3D.add_collection3d(col, zs0, zdir‘z’) …...
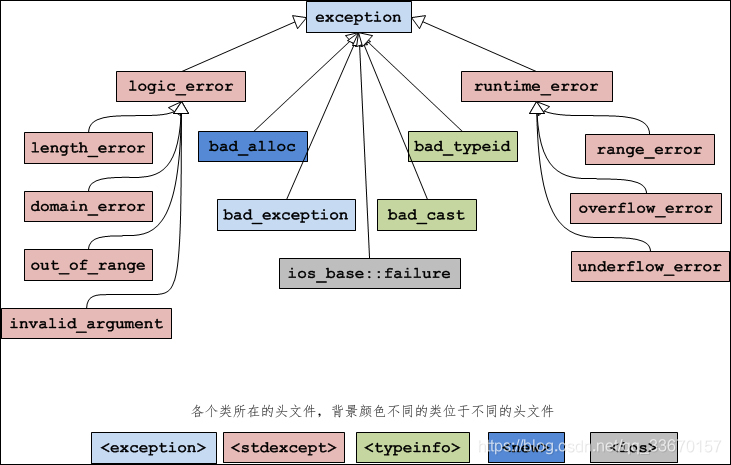
4万字c++讲解+区分c和c++,不来可惜了(含代码+解析)
目录 1 C简介 1.1 起源 1.2 应用范围 1.3 C和C 2开发工具 3 基本语法 3.1 注释 3.2关键字 3.3标识符 4 数据类型 4.1基本数据类型 4.2 数据类型在不同系统中所占空间大小 4.3 typedef声明 4.4 枚举类型 5 变量 5.1 变量的声明和定义 5.2 变量的作用域 6 运算符…...

AcWing 482. 合唱队形
482. 合唱队形N 位同学站成一排,音乐老师要请其中的 (N−K) 位同学出列,使得剩下的 K 位同学排成合唱队形。 合唱队形是指这样的一种队形:设 K位同学从左到右依次编号为 1,2…,K,他们的身高分别为…...
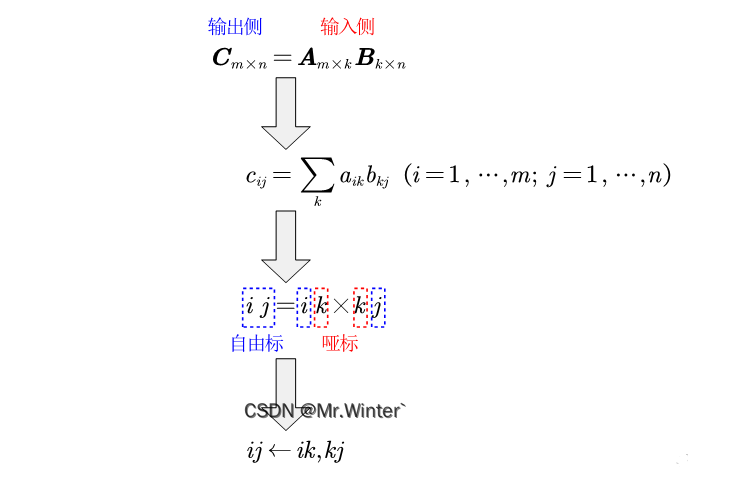
Pytorch深度学习实战3-4:通俗理解张量Tensor的爱因斯坦求和(附实例)
目录1 爱因斯坦求和由来2 爱因斯坦求和原理3 实例:字母表示法3.1 向量运算3.2 矩阵运算3.3 张量运算4 实例:常量表示法4.1 向量运算4.2 矩阵运算4.3 张量运算1 爱因斯坦求和由来 爱因斯坦求和约定(Einstein summation convention)是一种标记的约定&#…...
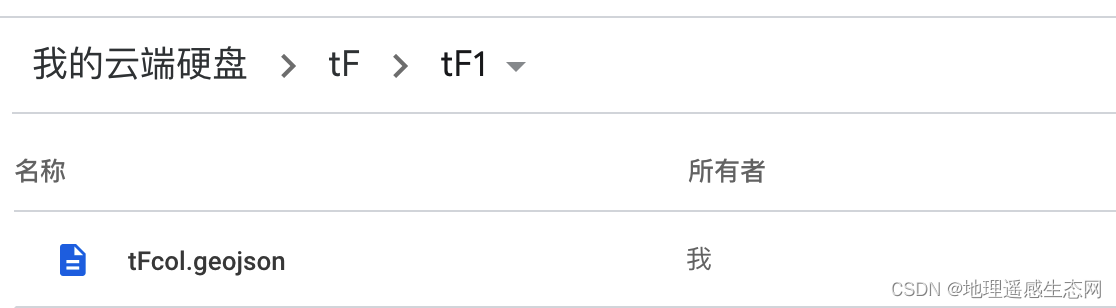
GEE学习笔记 五十六:GEE中如何把文件导出到Google Drive的子目录
今天在群里看到有人在问一个问题,如何使用GEE把文件导出到Google Drive的子目录中?这里我就简单的说一下这个问题。 首先,在GEE中我们都知道了如何将数据导出导出Google Drive的文件夹中,如下面的一个例子: var geome…...

【Go基础】数据库编程
文章目录1. SQL语法简介2. MySQL最佳实践3. Go SQL驱动接口解读4. 数据库增删改查5. stmt6. SQLBuilder6.1 Go-SQLBuilder6.2 Gendry6.3 自行实现SQLBuilder7. GORM8. Go操作MongoDB1. SQL语法简介 SQL(Structured Query Language)是一套语法标准&#…...

【颠覆软件开发】华为自研IDE!未来IDE将不可预测!
IDE是软件开发生态的入口,但目前我们所使用的IDE基本都是由国外巨头提供,比如Visual Studio、Eclipse、JetBrains。这些IDE具有很高的断供风险,与操作系统、芯片、编程语言一样,非常重要。 随着越来越多的软件开始采用云上开发模…...

怎样从零基础学黑客
可以说想学黑客技术,要求你首先是一个“T”字型人才,也就是说电脑的所有领域你都能做的来,而且有一项是精通的。因此作为一个零基础的黑客爱好者来说,没有良好的基础是绝对不行的,下面我就针对想真正学习黑客的零基础朋…...
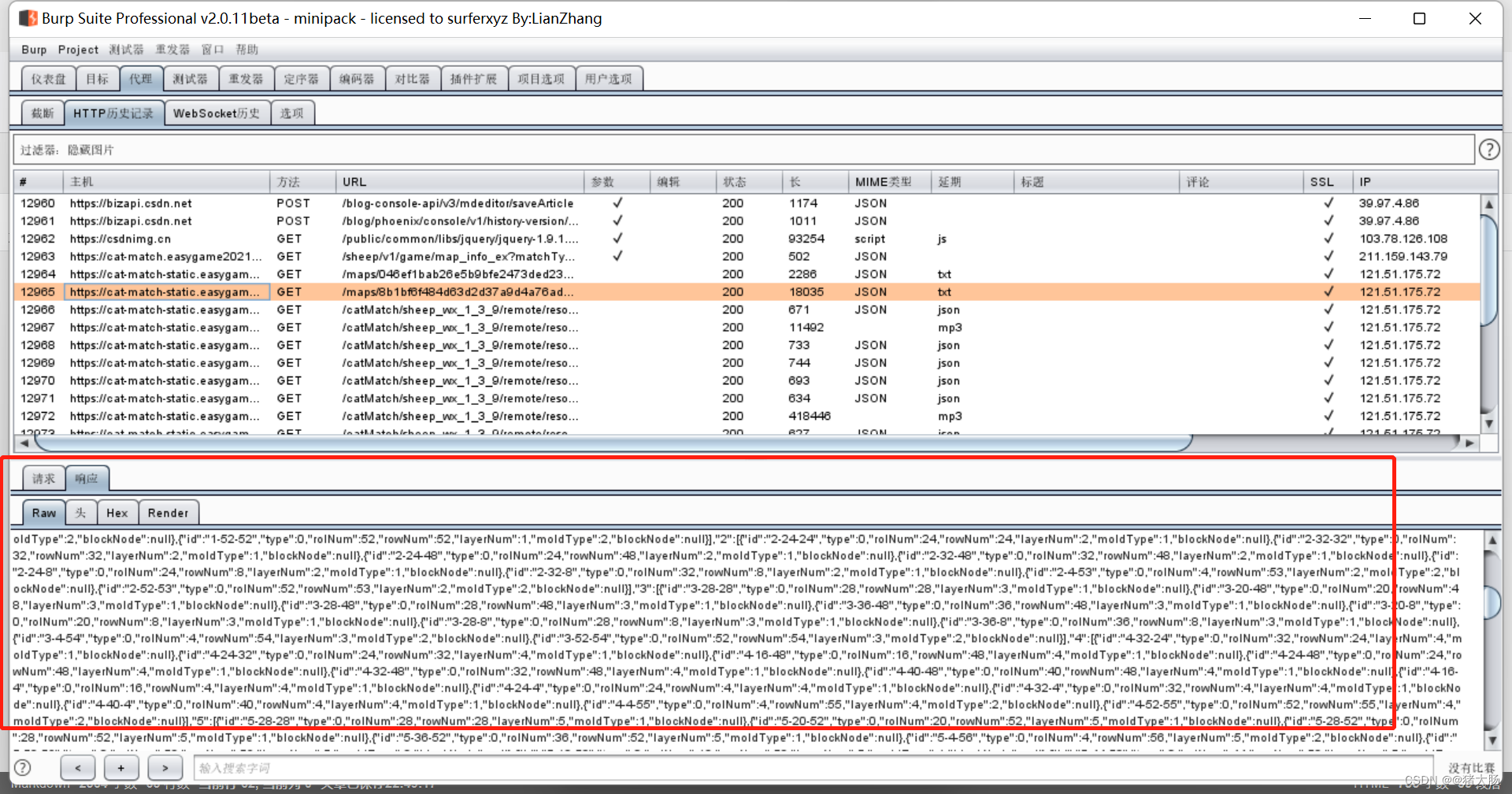
burp小程序抓包
身为一名码农,抓包肯定是一项必备技能。工作中遇到很多次需要对小程序进行抓包排查问题。下面分享一下我的抓包方式,使用的是电脑版小程序抓包,跟手机的方式都差不多的。 一、环境 微信版本:3.6.0.18 Burpsuite版本:…...

文件上传攻击骚操作
允许直接上传shell 只要有文件上传功能,那么就可以尝试上传webshell直接执行恶意代码,获得服务器权限,这是最简单也是最直接的利用。 允许上传压缩包 如果可以上传压缩包,并且服务端会对压缩包解压,那么就可能存在Zip …...
Scala流程控制(第四章:分支控制、嵌套分支、switch分支、for循环控制全、while与do~while、多重与中断)
文章目录第 4 章 流程控制4.1 分支控制 if-else4.1.1 单分支4.1.2 双分支4.1.3 多分支4.2 嵌套分支4.3 Switch 分支结构4.4 For 循环控制4.4.1 范围数据循环(To)4.4.2 范围数据循环(Until)4.4.3 循环守卫4.4.4 循环步长4.4.5 嵌套…...
)
华为OD机试真题Python实现【整理扑克牌】真题+解题思路+代码(20222023)
整理扑克牌 题目 给定一组数字,表示扑克牌的牌面数字,忽略扑克牌的花色,请安如下规则对这一组扑克牌进行整理。 步骤一: 对扑克牌进行分组,规则如下 当牌面数字相同张数大于等于4时,组合牌为炸弹;三张相同牌面数字+两张相同牌面数字,且三张牌与两张牌不相同时,组合牌…...
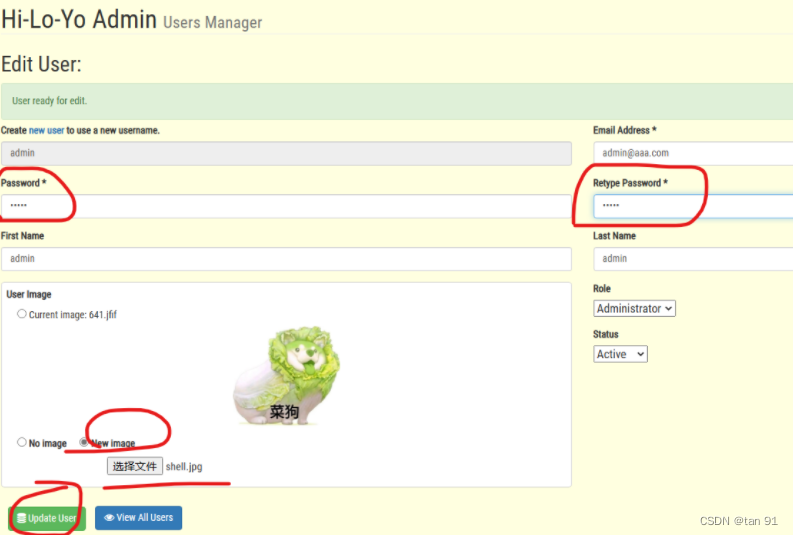
【春秋云境】CVE-2022-28525
靶标介绍: ED01-CMS v20180505 存在任意文件上传漏洞 打开靶场: 盲猜一波弱密码admin:admin就进去了。登录后在图中位置点击进行图片更新,需要将密码等都写上 抓包将图片信息进行替换,并修改文件名: POST /admin…...

Android设置取消系统闹钟
系统闹钟包名:com.android.deskclock 调用系统闹钟,首先在清单文件AndroidManifest.xml中添加权限: <uses-permission android:name"com.android.alarm.permission.SET_ALARM" />设置系统闹钟: public static v…...

使用 Node.js 多进程提高任务执行效率
什么是 Node 多进程? Node 是在单个线程中运行,我们虽然没办法开启额外的线程,但是可以开启进程集群。这样可以让下载任务和上传任务同时进行。 使用多进程进行初步代码优化 const dl require(./download.js) const ul require(./upload…...
[Golang实战]github.io部署个人博客hugo[新手开箱可用][小白教程]
[Golang实战]github.io部署个人博客hugo[新手开箱可用][小白教程]1.新手教程(小白也能学会)2.开始准备2.1myBlog是hugo的项目1.安装Hugo2.创建hugo项目2.2 xxxx.github.io是github.io中规定的pages项目3.成功部署4.TODO自动化workflows部署github.io1.新手教程(小白也能学会) …...

50个 Pandas 高频操作技巧,建议收藏
在数据分析和数据建模的过程中需要对数据进行清洗和整理等工作,有时需要对数据增删字段。 下面为大家介绍Pandas对数据的复杂查询、数据类型转换、数据排序、数据的修改、数据迭代以及函数的使用 文章目录技术交流01、复杂查询1、逻辑运算2、逻辑筛选数据3、函数筛…...

pygraphviz安装教程
0x01. 背景 最近在做casual inference,做实验时候想因果图可视化,遂需要安装pygraphviz,整了一下午,终于捣鼓好了,真头大。 环境: win10操作系统python3.9环境 0x02. 安装Graphviz 传送门:…...
HarmonyOS Connect认证测试
在HarmonyOS Connect生态产品的认证测试过程中,你是否存在这些疑问:认证流程具体包括哪些操作环节?如何根据实际场景选择合适的认证方式?如何选择认证测试标准的版本…… 本期FAQ为大家带来HarmonyOS Connect认证测试的常见问题…...

Datawhale团队第九期录取名单!
Datawhale团队 公示:Datawhale团队成员Datawhale成立四年了,从一开始的12个人,学习互助,到提议成立开源组织,做更多开源的事情,帮助更多学习者,也促使我们更好地成长。于是有了我们的使命&#…...
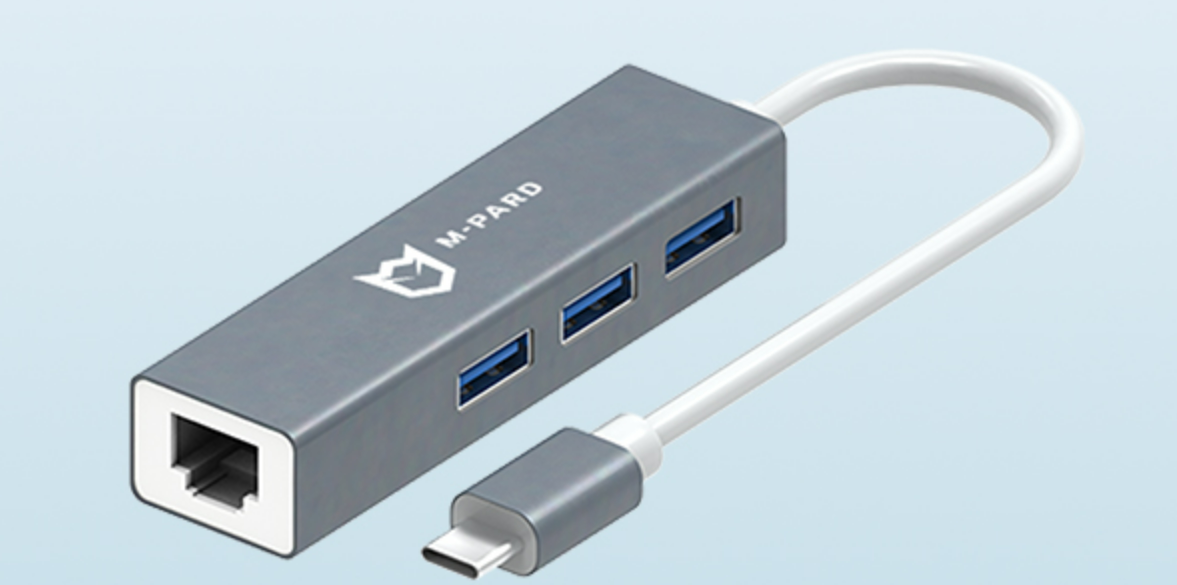

铭豹扩展坞 USB转网口 突然无法识别解决方法
当 USB 转网口扩展坞在一台笔记本上无法识别,但在其他电脑上正常工作时,问题通常出在笔记本自身或其与扩展坞的兼容性上。以下是系统化的定位思路和排查步骤,帮助你快速找到故障原因: 背景: 一个M-pard(铭豹)扩展坞的网卡突然无法识别了,扩展出来的三个USB接口正常。…...
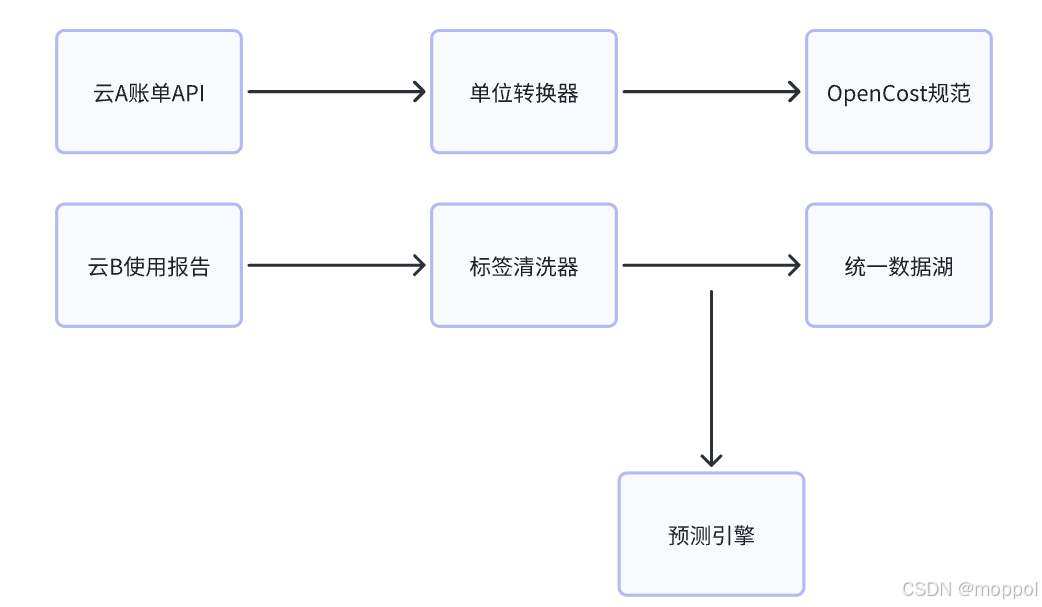
多云管理“拦路虎”:深入解析网络互联、身份同步与成本可视化的技术复杂度
一、引言:多云环境的技术复杂性本质 企业采用多云策略已从技术选型升维至生存刚需。当业务系统分散部署在多个云平台时,基础设施的技术债呈现指数级积累。网络连接、身份认证、成本管理这三大核心挑战相互嵌套:跨云网络构建数据…...
业务系统对接大模型的基础方案:架构设计与关键步骤
业务系统对接大模型:架构设计与关键步骤 在当今数字化转型的浪潮中,大语言模型(LLM)已成为企业提升业务效率和创新能力的关键技术之一。将大模型集成到业务系统中,不仅可以优化用户体验,还能为业务决策提供…...

R语言AI模型部署方案:精准离线运行详解
R语言AI模型部署方案:精准离线运行详解 一、项目概述 本文将构建一个完整的R语言AI部署解决方案,实现鸢尾花分类模型的训练、保存、离线部署和预测功能。核心特点: 100%离线运行能力自包含环境依赖生产级错误处理跨平台兼容性模型版本管理# 文件结构说明 Iris_AI_Deployme…...

大语言模型如何处理长文本?常用文本分割技术详解
为什么需要文本分割? 引言:为什么需要文本分割?一、基础文本分割方法1. 按段落分割(Paragraph Splitting)2. 按句子分割(Sentence Splitting)二、高级文本分割策略3. 重叠分割(Sliding Window)4. 递归分割(Recursive Splitting)三、生产级工具推荐5. 使用LangChain的…...
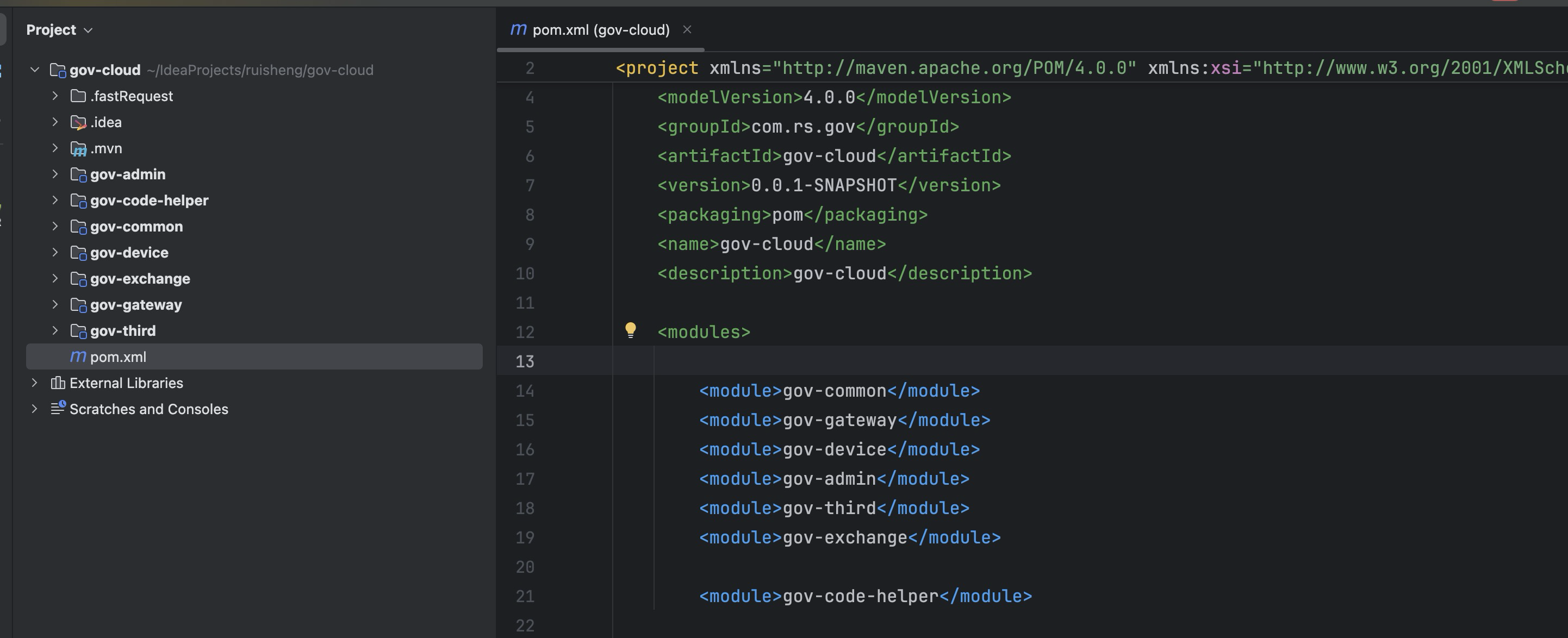
最新SpringBoot+SpringCloud+Nacos微服务框架分享
文章目录 前言一、服务规划二、架构核心1.cloud的pom2.gateway的异常handler3.gateway的filter4、admin的pom5、admin的登录核心 三、code-helper分享总结 前言 最近有个活蛮赶的,根据Excel列的需求预估的工时直接打骨折,不要问我为什么,主要…...

MODBUS TCP转CANopen 技术赋能高效协同作业
在现代工业自动化领域,MODBUS TCP和CANopen两种通讯协议因其稳定性和高效性被广泛应用于各种设备和系统中。而随着科技的不断进步,这两种通讯协议也正在被逐步融合,形成了一种新型的通讯方式——开疆智能MODBUS TCP转CANopen网关KJ-TCPC-CANP…...

Axios请求超时重发机制
Axios 超时重新请求实现方案 在 Axios 中实现超时重新请求可以通过以下几种方式: 1. 使用拦截器实现自动重试 import axios from axios;// 创建axios实例 const instance axios.create();// 设置超时时间 instance.defaults.timeout 5000;// 最大重试次数 cons…...
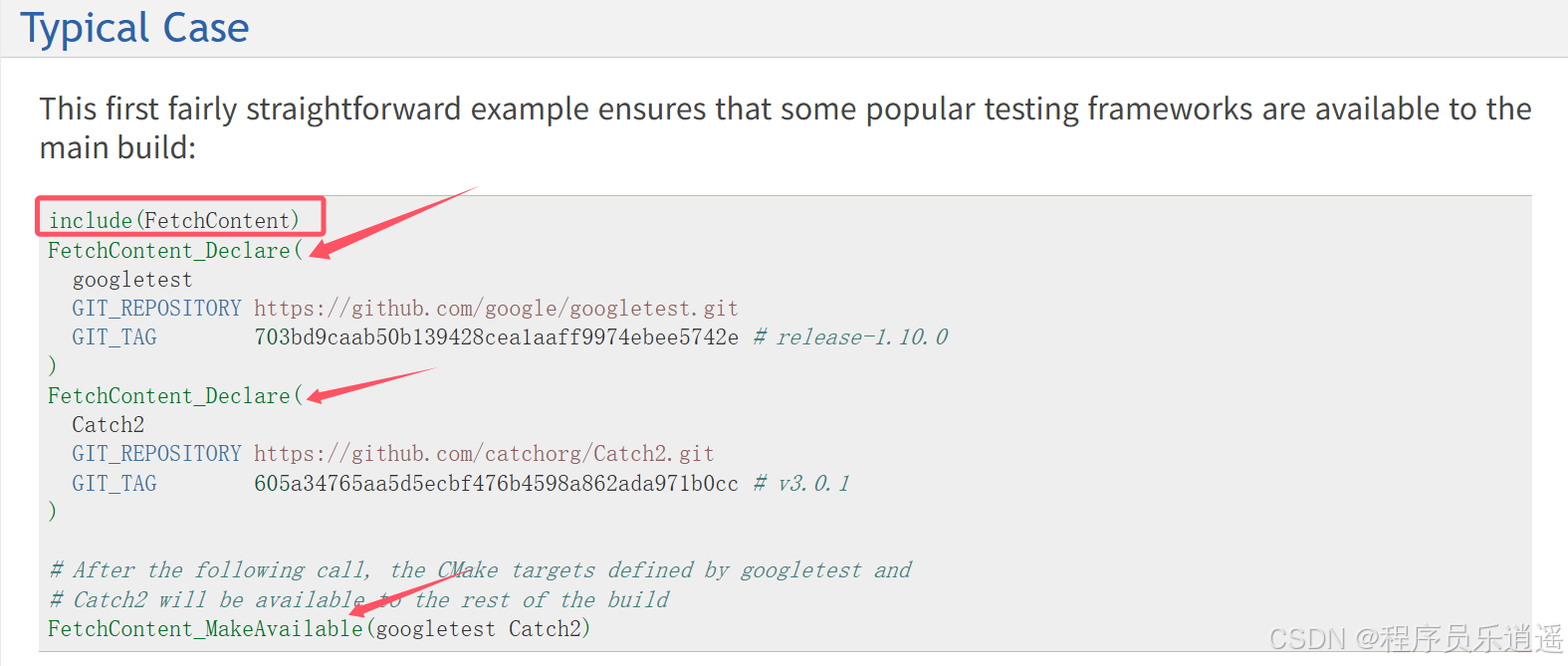
CMake 从 GitHub 下载第三方库并使用
有时我们希望直接使用 GitHub 上的开源库,而不想手动下载、编译和安装。 可以利用 CMake 提供的 FetchContent 模块来实现自动下载、构建和链接第三方库。 FetchContent 命令官方文档✅ 示例代码 我们将以 fmt 这个流行的格式化库为例,演示如何: 使用 FetchContent 从 GitH…...
)
Java入门学习详细版(一)
大家好,Java 学习是一个系统学习的过程,核心原则就是“理论 实践 坚持”,并且需循序渐进,不可过于着急,本篇文章推出的这份详细入门学习资料将带大家从零基础开始,逐步掌握 Java 的核心概念和编程技能。 …...
