STL- 常用算法
概述:
-
算法主要是由头文件
<algorithm><functional><numeric>组成。 -
<algorithm>是所有STL头文件中最大的一个,范围涉及到比较、 交换、查找、遍历操作、复制、修改等等 -
<numeric>体积很小,只包括几个在序列上面进行简单数学运算的模板函数 -
<functional>定义了一些模板类,用以声明函数对象。
1 常用遍历算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的遍历算法
算法简介:
for_each//遍历容器transform//搬运容器到另一个容器中
1.1 for_each
功能描述:
- 实现遍历容器
函数原型:
-
for_each(iterator beg, iterator end, _func);// 遍历算法 遍历容器元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _func 函数或者函数对象
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>//普通函数
void print01(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}
//函数对象
class print02
{public:void operator()(int val) {cout << val << " ";}
};//for_each算法基本用法
void test01() {vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v.push_back(i);}//遍历算法for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print01);cout << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
总结:for_each在实际开发中是最常用遍历算法,需要熟练掌握
1.2 transform
功能描述:
- 搬运容器到另一个容器中
函数原型:
transform(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, _func);
//beg1 源容器开始迭代器
//end1 源容器结束迭代器
//beg2 目标容器开始迭代器
//_func 函数或者函数对象
示例:
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>//常用遍历算法 搬运 transformclass TransForm
{
public:int operator()(int val){return val;}};class MyPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}vector<int>vTarget; //目标容器vTarget.resize(v.size()); // 目标容器需要提前开辟空间transform(v.begin(), v.end(), vTarget.begin(), TransForm());for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), MyPrint());
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
总结: 搬运的目标容器必须要提前开辟空间,否则无法正常搬运
2 常用查找算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的查找算法
算法简介:
find//查找元素find_if//按条件查找元素adjacent_find//查找相邻重复元素binary_search//二分查找法count//统计元素个数count_if//按条件统计元素个数
2.1 find
功能描述:
- 查找指定元素,找到返回指定元素的迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器end()
函数原型:
-
find(iterator beg, iterator end, value);// 按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 查找的元素
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
void test01() {vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v.push_back(i + 1);}//查找容器中是否有 5 这个元素vector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 5);if (it == v.end()) {cout << "没有找到!" << endl;}else {cout << "找到:" << *it << endl;}
}class Person {
public:Person(string name, int age) {this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}//重载==bool operator==(const Person& p) {if (this->m_Name == p.m_Name && this->m_Age == p.m_Age) {return true;}return false;}public:string m_Name;int m_Age;
};void test02() {vector<Person> v;//创建数据Person p1("aaa", 10);Person p2("bbb", 20);Person p3("ccc", 30);Person p4("ddd", 40);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);vector<Person>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), p2);if (it == v.end()) {cout << "没有找到!" << endl;}else {cout << "找到姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄: " << it->m_Age << endl;}
}
总结: 利用find可以在容器中找指定的元素,返回值是迭代器
2.2 find_if
功能描述:
- 按条件查找元素
函数原型:
-
find_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);// 按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _Pred 函数或者谓词(返回bool类型的仿函数)
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <string>//内置数据类型
class GreaterFive
{
public:bool operator()(int val){return val > 5;}
};void test01() {vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v.push_back(i + 1);}vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive());if (it == v.end()) {cout << "没有找到!" << endl;}else {cout << "找到大于5的数字:" << *it << endl;}
}//自定义数据类型
class Person {
public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}
public:string m_Name;int m_Age;
};class Greater20
{
public:bool operator()(Person &p){return p.m_Age > 20;}};void test02() {vector<Person> v;//创建数据Person p1("aaa", 10);Person p2("bbb", 20);Person p3("ccc", 30);Person p4("ddd", 40);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);vector<Person>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater20());if (it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到!" << endl;}else{cout << "找到姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄: " << it->m_Age << endl;}
}int main() {//test01();test02();system("pause");return 0;
}
总结:find_if按条件查找使查找更加灵活,提供的仿函数可以改变不同的策略
2.3 adjacent_find
功能描述:
- 查找相邻重复元素
函数原型:
-
adjacent_find(iterator beg, iterator end);// 查找相邻重复元素,返回相邻元素的第一个位置的迭代器
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(5);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(3);//查找相邻重复元素vector<int>::iterator it = adjacent_find(v.begin(), v.end());if (it == v.end()) {cout << "找不到!" << endl;}else {cout << "找到相邻重复元素为:" << *it << endl;}
}
总结:面试题中如果出现查找相邻重复元素,记得用STL中的adjacent_find算法
2.4 binary_search
功能描述:
- 查找指定元素是否存在
函数原型:
-
bool binary_search(iterator beg, iterator end, value);// 查找指定的元素,查到 返回true 否则false
// 注意: 在无序序列中不可用
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 查找的元素
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}//二分查找bool ret = binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(),2);if (ret){cout << "找到了" << endl;}else{cout << "未找到" << endl;}
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
**总结:**二分查找法查找效率很高,值得注意的是查找的容器中元素必须的有序序列
2.5 count
功能描述:
- 统计元素个数
函数原型:
-
count(iterator beg, iterator end, value);// 统计元素出现次数
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 统计的元素
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>//内置数据类型
void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(5);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(4);int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), 4);cout << "4的个数为: " << num << endl;
}//自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}bool operator==(const Person & p){if (this->m_Age == p.m_Age){return true;}else{return false;}}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};void test02()
{vector<Person> v;Person p1("刘备", 35);Person p2("关羽", 35);Person p3("张飞", 35);Person p4("赵云", 30);Person p5("曹操", 25);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);v.push_back(p5);Person p("诸葛亮",35);int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), p);cout << "num = " << num << endl;
}
int main() {//test01();test02();system("pause");return 0;
}
总结: 统计自定义数据类型时候,需要配合重载 operator==
2.6 count_if
功能描述:
- 按条件统计元素个数
函数原型:
-
count_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);// 按条件统计元素出现次数
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _Pred 谓词
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>class Greater4
{
public:bool operator()(int val){return val >= 4;}
};//内置数据类型
void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(5);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(4);int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater4());cout << "大于4的个数为: " << num << endl;
}//自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};class AgeLess35
{
public:bool operator()(const Person &p){return p.m_Age < 35;}
};
void test02()
{vector<Person> v;Person p1("刘备", 35);Person p2("关羽", 35);Person p3("张飞", 35);Person p4("赵云", 30);Person p5("曹操", 25);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);v.push_back(p5);int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), AgeLess35());cout << "小于35岁的个数:" << num << endl;
}int main() {//test01();test02();system("pause");return 0;
}
**总结:**按值统计用count,按条件统计用count_if
3 常用排序算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的排序算法
算法简介:
sort//对容器内元素进行排序random_shuffle//洗牌 指定范围内的元素随机调整次序merge// 容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中reverse// 反转指定范围的元素
3.1 sort
功能描述:
- 对容器内元素进行排序
函数原型:
-
sort(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);// 按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _Pred 谓词
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>void myPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}void test01() {vector<int> v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);//sort默认从小到大排序sort(v.begin(), v.end());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;//从大到小排序sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
**总结:**sort属于开发中最常用的算法之一,需熟练掌握
3.2 random_shuffle
功能描述:
- 洗牌 指定范围内的元素随机调整次序
函数原型:
-
random_shuffle(iterator beg, iterator end);// 指定范围内的元素随机调整次序
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <ctime>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));vector<int> v;for(int i = 0 ; i < 10;i++){v.push_back(i);}for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;//打乱顺序random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
总结:random_shuffle洗牌算法比较实用,使用时记得加随机数种子
3.3 merge
功能描述:
- 两个容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中
函数原型:
-
merge(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);// 容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中
// 注意: 两个容器必须是有序的
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10 ; i++) {v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i + 1);}vector<int> vtarget;//目标容器需要提前开辟空间vtarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());//合并 需要两个有序序列merge(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vtarget.begin());for_each(vtarget.begin(), vtarget.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
总结:merge合并的两个容器必须的有序序列
3.4 reverse
功能描述:
- 将容器内元素进行反转
函数原型:
-
reverse(iterator beg, iterator end);// 反转指定范围的元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);cout << "反转前: " << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;cout << "反转后: " << endl;reverse(v.begin(), v.end());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
**总结:**reverse反转区间内元素,面试题可能涉及到
4 常用拷贝和替换算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的拷贝和替换算法
算法简介:
copy// 容器内指定范围的元素拷贝到另一容器中replace// 将容器内指定范围的旧元素修改为新元素replace_if// 容器内指定范围满足条件的元素替换为新元素swap// 互换两个容器的元素
4.1 copy
功能描述:
- 容器内指定范围的元素拷贝到另一容器中
函数原型:
-
copy(iterator beg, iterator end, iterator dest);// 按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// dest 目标起始迭代器
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v1;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v1.push_back(i + 1);}vector<int> v2;v2.resize(v1.size());copy(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin());for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
总结:利用copy算法在拷贝时,目标容器记得提前开辟空间
4.2 replace
功能描述:
- 将容器内指定范围的旧元素修改为新元素
函数原型:
-
replace(iterator beg, iterator end, oldvalue, newvalue);// 将区间内旧元素 替换成 新元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// oldvalue 旧元素
// newvalue 新元素
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(20);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(10);v.push_back(20);cout << "替换前:" << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;//将容器中的20 替换成 2000cout << "替换后:" << endl;replace(v.begin(), v.end(), 20,2000);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
总结:replace会替换区间内满足条件的元素
4.3 replace_if
功能描述:
- 将区间内满足条件的元素,替换成指定元素
函数原型:
-
replace_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _pred, newvalue);// 按条件替换元素,满足条件的替换成指定元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _pred 谓词
// newvalue 替换的新元素
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};class ReplaceGreater30
{
public:bool operator()(int val){return val >= 30;}};void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(20);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(10);v.push_back(20);cout << "替换前:" << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;//将容器中大于等于的30 替换成 3000cout << "替换后:" << endl;replace_if(v.begin(), v.end(), ReplaceGreater30(), 3000);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
总结:replace_if按条件查找,可以利用仿函数灵活筛选满足的条件
4.4 swap
功能描述:
- 互换两个容器的元素
函数原型:
-
swap(container c1, container c2);// 互换两个容器的元素
// c1容器1
// c2容器2
示例:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i+100);}cout << "交换前: " << endl;for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;cout << "交换后: " << endl;swap(v1, v2);for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
总结:swap交换容器时,注意交换的容器要同种类型
5 常用算术生成算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的算术生成算法
注意:
- 算术生成算法属于小型算法,使用时包含的头文件为
#include <numeric>
算法简介:
-
accumulate// 计算容器元素累计总和 -
fill// 向容器中添加元素
5.1 accumulate
功能描述:
- 计算区间内 容器元素累计总和
函数原型:
-
accumulate(iterator beg, iterator end, value);// 计算容器元素累计总和
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 起始值
示例:
#include <numeric>
#include <vector>
void test01()
{vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {v.push_back(i);}int total = accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 0);cout << "total = " << total << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
总结:accumulate使用时头文件注意是 numeric,这个算法很实用
5.2 fill
功能描述:
- 向容器中填充指定的元素
函数原型:
-
fill(iterator beg, iterator end, value);// 向容器中填充元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 填充的值
示例:
#include <numeric>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v;v.resize(10);//填充fill(v.begin(), v.end(), 100);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
总结:利用fill可以将容器区间内元素填充为 指定的值
6 常用集合算法
学习目标:
- 掌握常用的集合算法
算法简介:
-
set_intersection// 求两个容器的交集 -
set_union// 求两个容器的并集 -
set_difference// 求两个容器的差集
6.1 set_intersection
功能描述:
- 求两个容器的交集
函数原型:
-
set_intersection(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);// 求两个集合的交集
// 注意:两个集合必须是有序序列
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
示例:
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i+5);}vector<int> vTarget;//取两个里面较小的值给目标容器开辟空间vTarget.resize(min(v1.size(), v2.size()));//返回目标容器的最后一个元素的迭代器地址vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_intersection(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
总结:
- 求交集的两个集合必须的有序序列
- 目标容器开辟空间需要从两个容器中取小值
- set_intersection返回值既是交集中最后一个元素的位置
6.2 set_union
功能描述:
- 求两个集合的并集
函数原型:
-
set_union(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);// 求两个集合的并集
// 注意:两个集合必须是有序序列
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
示例:
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i+5);}vector<int> vTarget;//取两个容器的和给目标容器开辟空间vTarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());//返回目标容器的最后一个元素的迭代器地址vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_union(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
总结:
- 求并集的两个集合必须的有序序列
- 目标容器开辟空间需要两个容器相加
- set_union返回值既是并集中最后一个元素的位置
6.3 set_difference
功能描述:
- 求两个集合的差集
函数原型:
-
set_difference(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);// 求两个集合的差集
// 注意:两个集合必须是有序序列
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
示例:
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>class myPrint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int> v1;vector<int> v2;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i+5);}vector<int> vTarget;//取两个里面较大的值给目标容器开辟空间vTarget.resize( max(v1.size() , v2.size()));//返回目标容器的最后一个元素的迭代器地址cout << "v1与v2的差集为: " << endl;vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_difference(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint());cout << endl;cout << "v2与v1的差集为: " << endl;itEnd = set_difference(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v1.begin(), v1.end(), vTarget.begin());for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint());cout << endl;
}int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
总结:
- 求差集的两个集合必须的有序序列
- 目标容器开辟空间需要从两个容器取较大值
- set_difference返回值既是差集中最后一个元素的位置
相关文章:

STL- 常用算法
概述: 算法主要是由头文件<algorithm> <functional> <numeric>组成。 <algorithm>是所有STL头文件中最大的一个,范围涉及到比较、 交换、查找、遍历操作、复制、修改等等 <numeric>体积很小,只包括几个在序列上面进行简…...
苹果铃声怎么设置?3招教你设置个性化铃声!
苹果手机因其颜值、性能与生态吸引了一大批粉丝用户。在拿到新手机后,大家第一时间就是给手机设置好听的铃声。那么,苹果铃声怎么设置呢?手机铃声能设置成自己喜欢的歌曲吗?当然可以了!本文将给大家介绍3种轻松设置苹果…...

LRTimelapse 6 for Mac(延时摄影视频制作软件)
LRTimelapse 是一款适用于macOS 系统的延时摄影视频制作软件,可以帮助用户创建高质量的延时摄影视频。该软件提供了直观的界面和丰富的功能,支持多种时间轴摄影工具和文件格式,并具有高度的可定制性和扩展性。 LRTimelapse 的主要特点如下&am…...
:栈与队列)
数据结构和算法(4):栈与队列
栈 ADT 及实现 栈(stack)是存放数据对象的一种特殊容器,其中的数据元素按线性的逻辑次序排列,故也可定义首、末元素。 尽管栈结构也支持对象的插入和删除操作,但其操作的范围仅限于栈的某一特定端。 也就是说…...
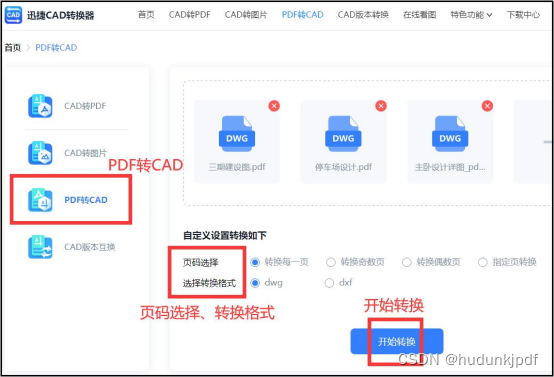
pdf怎么转换成dwg格式?简单转换方法分享
当我们需要在CAD中编辑PDF文件中的向量图形时,将PDF转换成DWG格式是一个非常好的选择。因为PDF是一种非常流行的文档格式,很多时候我们会接收到PDF文件,但是PDF文件中的向量图形无法直接在CAD中编辑。而将PDF转换成DWG格式后,就可…...
uniapp使用H5实现预览pdf文件
下载后把压缩包解压到自己的项目的static文件夹下的pdf文件下,如图 新建一个文件名为filePreview.vue <template><view><web-view :src"allUrl"></web-view></view> </template><script>export default {dat…...

Studio 3T for MongoDB的介绍及语法简单介绍
用法介绍 Studio 3T是一款用于MongoDB数据库管理和开发的图形化工具,它提供了许多功能来简化MongoDB的操作和开发过程。以下是一些常见的Studio 3T用法: 连接到MongoDB服务器: 打开Studio 3T并创建一个新连接配置。输入MongoDB服务器的主机名…...
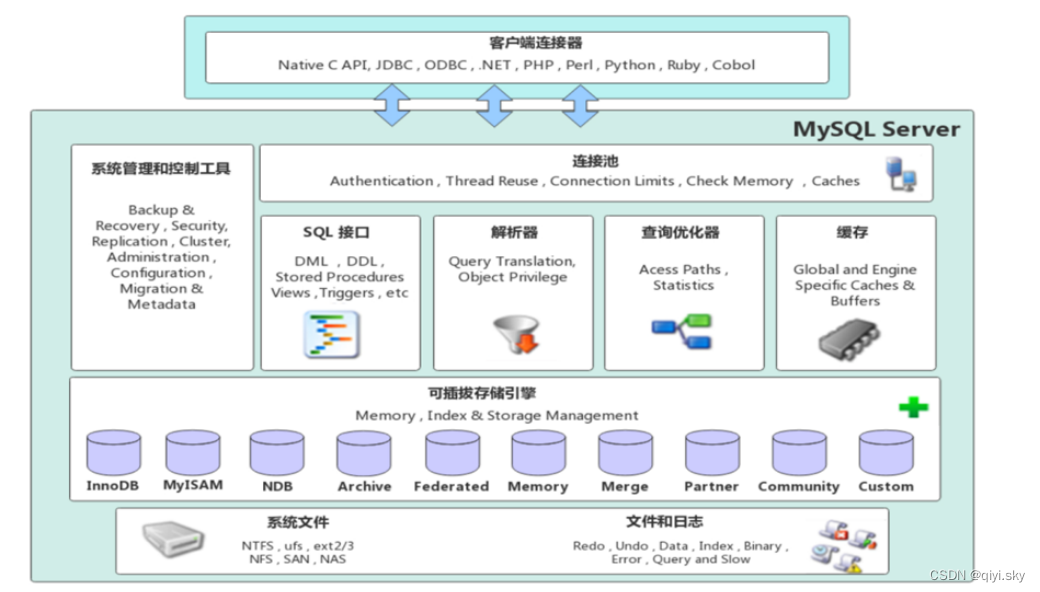
MySQL数据库——存储引擎(1)-MySQL体系结构、存储引擎简介
目录 MySQL体系结构 连接层 服务层 引擎层 存储层 存储引擎简介 概念 语句 演示 下面开始学习进阶篇的第一个内容——存储引擎 分为四点学习: MySQL体系结构存储引擎简介存储引擎特点存储引擎选择 MySQL体系结构 连接层 最上层是一些客户端和链接服务&am…...

211. 添加与搜索单词 - 数据结构设计
211. 添加与搜索单词 - 数据结构设计 class WordDictionary { public:struct Node{Node *node[26];bool is_end;Node(){is_endfalse;for(int i0;i< 26;i){node[i]NULL;}}};Node *root;WordDictionary() {root new Node();}void addWord(string word) {auto p root;for(aut…...
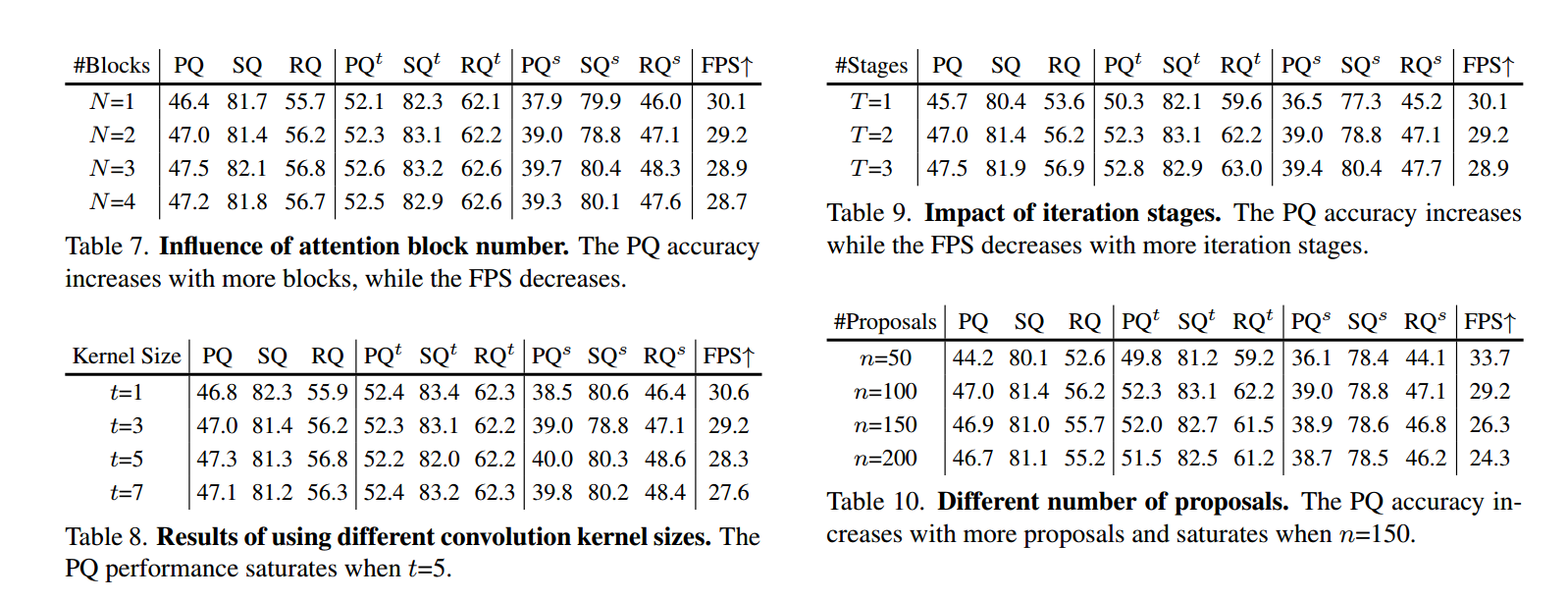
【深度学习】You Only Segment Once: Towards Real-Time Panoptic Segmentation,YOSO全景分割
论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.14651 代码:https://github.com/hujiecpp/YOSO 文章目录 Abstract1. Introduction2. Related Work3. Method3.1. Task Formulation3.2. Feature Pyramid Aggregator3.3. Separable Dynamic Decoder 4. Experiments4.1. …...
ping与Traceroute是如何工作的
ping 是基于 ICMP 协议工作的。ICMP 全称 Internet Control Message Protocol,就是互联网控制报文协议。 ICMP 报文是封装在 IP 包里面的。因为传输指令的时候,肯定需要源地址和目标地址。它本身非常简单。 ICMP 报文有很多的类型,不同的类型…...

CentOS Python环境搭建
安装依赖 yum install -y libffi-devel wget gcc make zlib-devel openssl openssl-devel ncurses-devel openldap-devel gettext bzip2-devel xz-devel下载安装包 wget "https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.9.10/Python-3.9.10.tar.xz" 编译安装 # 3.1、解压安装包…...
亚马逊云科技与伊克罗德推出AI绘画解决方案——imAgine
在过去的数月中,亚马逊云科技已经推出了多篇介绍如何在亚马逊云科技上部署Stable Diffusion,或是如何结合Amazon SageMaker与Stable Diffusion进行模型训练和推理任务的内容。 为了帮助客户快速、安全地在亚马逊云科技上构建、部署和管理应用程序&#x…...

机器学习课后习题 --- 逻辑回归
(一)单选题 1.一监狱人脸识别准入系统用来识别待进入人员的身份,此系统一共包括识别4种不同的人员:狱警,小偷,送餐员,其他。下面哪种学习方法最适合此种应用需求: A:二分类问题 …...
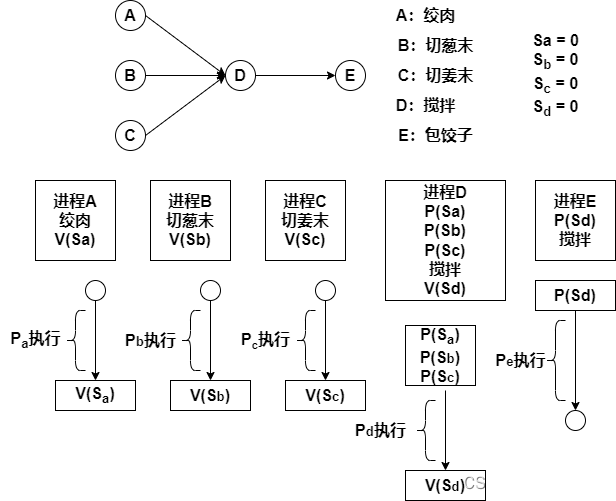
软件设计师学习笔记9-进程调度
目录 1. PV操作 1.1进程的同步与互斥 1.1.1互斥 1.1.2同步 1.2 PV操作 1.2.1信号量 1.2.2 PV操作的概念 2.信号量与PV操作 2.1 PV操作与互斥模型 2.2 PV操作与同步模型 2.3 互斥与同步模型结合 3.前趋图与PV操作 1. PV操作 1.1进程的同步与互斥 1.1.1互斥 互斥&…...
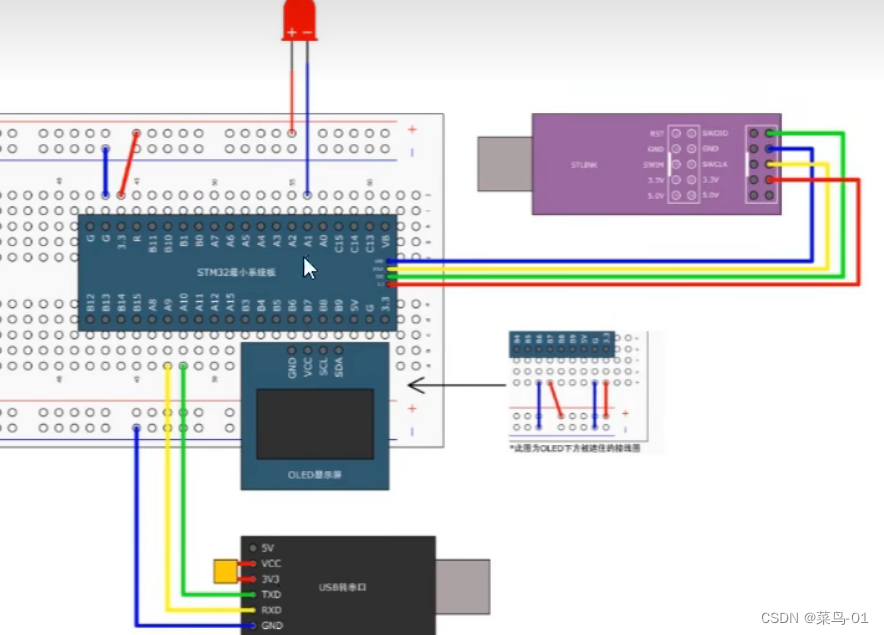
09:STM32-------USART串口通信+串口数据包
目录 一:串口协议 1:通信接口 2:串口通信 3:硬件电路 4:电平标准 5:串口参数及其时序 二:USART介绍 1:简历 2:USART框图 3:USART的基本结构 4:数据帧 5: 波特率发生器 6:数据模式 三:案例 A:串口发送--单发送 1:连接图 2:函数介绍 3:代码 B:串口发送接收 1…...

“安全即服务”为网络安全推开一道门
8月30日,三六零(下称“360”)集团发布了2023年半年报,其中安全业务第二季度收入6.54亿元,同比增长98.76%,环比增长157.16%,安全第二增长曲线已完全成型!特别值得一提的是,…...
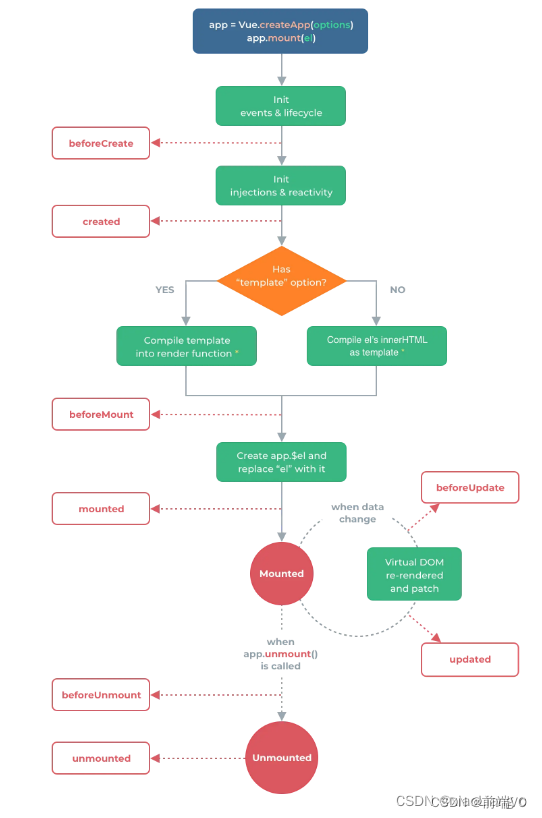
vue3的生命周期
1.vue3生命周期官方流程图 2.vue3中的选项式生命周期 vue3中的选项式生命周期钩子基本与vue2中的大体相同,它们都是定义在 vue实例的对象参数中的函数,它们在vue中实例的生命周期的不同阶段被调用。生命周期函数钩子会在我们的实例挂载,更新…...
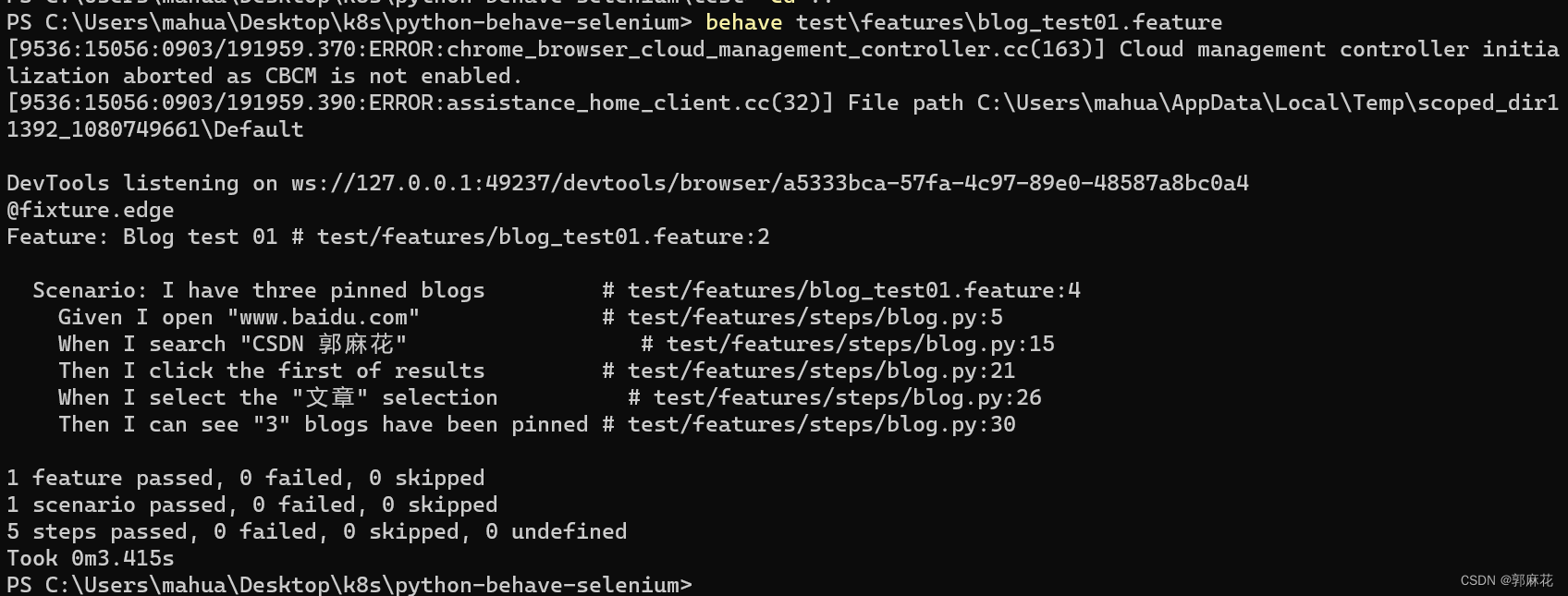
[E2E Test] Python Behave Selenium 一文学会自动化测试
前言 本文将使用Python Behave与Selenium,和同学们一起认识自动化测试,并附上完整的实践教程。 项目源码已上传:CSDN 郭麻花 Azure Repo python-behave-selenium 核心概念 1. 什么是E2E Test E2E即End-to-end,意思是从头到尾…...

Knowledge Graph Prompting for Multi-Document Question Answering
本文是LLM系列文章,针对《Knowledge Graph Prompting for Multi-Document Question Answering》的翻译。 多文档问答中的知识图谱提示 摘要1 引言2 符号3 知识图谱构建4 LM引导的图形遍历器5 实验6 相关工作7 结论 摘要 大型语言模型的“预训练、提示、预测”范式…...
51c自动驾驶~合集58
我自己的原文哦~ https://blog.51cto.com/whaosoft/13967107 #CCA-Attention 全局池化局部保留,CCA-Attention为LLM长文本建模带来突破性进展 琶洲实验室、华南理工大学联合推出关键上下文感知注意力机制(CCA-Attention),…...
从深圳崛起的“机器之眼”:赴港乐动机器人的万亿赛道赶考路
进入2025年以来,尽管围绕人形机器人、具身智能等机器人赛道的质疑声不断,但全球市场热度依然高涨,入局者持续增加。 以国内市场为例,天眼查专业版数据显示,截至5月底,我国现存在业、存续状态的机器人相关企…...
DIY|Mac 搭建 ESP-IDF 开发环境及编译小智 AI
前一阵子在百度 AI 开发者大会上,看到基于小智 AI DIY 玩具的演示,感觉有点意思,想着自己也来试试。 如果只是想烧录现成的固件,乐鑫官方除了提供了 Windows 版本的 Flash 下载工具 之外,还提供了基于网页版的 ESP LA…...

【git】把本地更改提交远程新分支feature_g
创建并切换新分支 git checkout -b feature_g 添加并提交更改 git add . git commit -m “实现图片上传功能” 推送到远程 git push -u origin feature_g...

MySQL中【正则表达式】用法
MySQL 中正则表达式通过 REGEXP 或 RLIKE 操作符实现(两者等价),用于在 WHERE 子句中进行复杂的字符串模式匹配。以下是核心用法和示例: 一、基础语法 SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE column_name REGEXP pattern; …...

Java 二维码
Java 二维码 **技术:**谷歌 ZXing 实现 首先添加依赖 <!-- 二维码依赖 --><dependency><groupId>com.google.zxing</groupId><artifactId>core</artifactId><version>3.5.1</version></dependency><de…...

LeetCode - 199. 二叉树的右视图
题目 199. 二叉树的右视图 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路 右视图是指从树的右侧看,对于每一层,只能看到该层最右边的节点。实现思路是: 使用深度优先搜索(DFS)按照"根-右-左"的顺序遍历树记录每个节点的深度对于…...
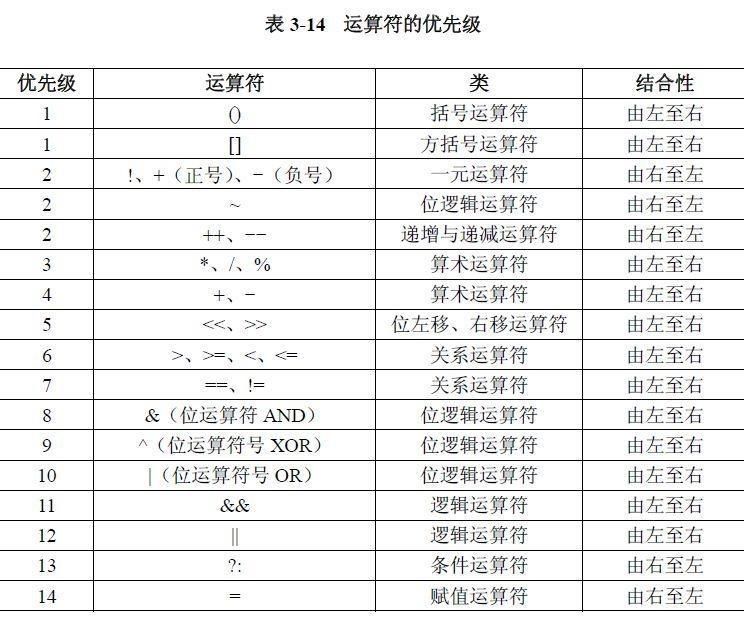
02.运算符
目录 什么是运算符 算术运算符 1.基本四则运算符 2.增量运算符 3.自增/自减运算符 关系运算符 逻辑运算符 &&:逻辑与 ||:逻辑或 !:逻辑非 短路求值 位运算符 按位与&: 按位或 | 按位取反~ …...

在RK3588上搭建ROS1环境:创建节点与数据可视化实战指南
在RK3588上搭建ROS1环境:创建节点与数据可视化实战指南 背景介绍完整操作步骤1. 创建Docker容器环境2. 验证GUI显示功能3. 安装ROS Noetic4. 配置环境变量5. 创建ROS节点(小球运动模拟)6. 配置RVIZ默认视图7. 创建启动脚本8. 运行可视化系统效果展示与交互技术解析ROS节点通…...

C++--string的模拟实现
一,引言 string的模拟实现是只对string对象中给的主要功能经行模拟实现,其目的是加强对string的底层了解,以便于在以后的学习或者工作中更加熟练的使用string。本文中的代码仅供参考并不唯一。 二,默认成员函数 string主要有三个成员变量,…...
