【数据结构C/C++】双向链表的增删改查
文章目录
- C
- C++
- 408考研各数据结构C/C++代码(Continually updating)
对我个人而言,在开发过程中使用的比较多的就是双向链表了。
很多重要的代码优化都会使用到基于双向链表实现的数据机构。
比如我们常用的HashMap,我们知道Key其实是无序存放的,
而LinkedHashMap底层使用HashMap+双向链表的方式实现了对key的有序遍历。
双向链表的一些重要特点和优点:
双向遍历:
双向链表具有两个指针,一个指向前一个节点(前驱),一个指向后一个节点(后继)。这使得在链表中的任何位置都可以轻松地进行双向遍历,而不仅仅是单向遍历。前向和后向操作: 可以在双向链表中执行前向和后向操作,这意味着可以轻松地在链表中的任何位置插入、删除或修改节点。
插入和删除效率高: 相对于单向链表,双向链表在某些情况下可以更高效地进行插入和删除操作,因为可以通过两个方向的指针更快地访问前后节点。
反向遍历: 在某些情况下,需要以相反的顺序遍历链表。双向链表使得反向遍历变得容易,无需重新构建链表。
实现双端队列: 双向链表还可以用于实现双端队列(Deque),这是一种允许在两端进行插入和删除操作的数据结构。
尽管双向链表提供了上述优点,但也需要额外的内存来存储每个节点的前向指针,这会增加内存开销。此外,由于维护前向指针和后向指针的关系,代码的实现可能相对复杂一些。
双向链表相对于单链表的区别在于,单链表只有一个指向下一个节点的指针域,而双向链表有两个。因此再管理指针上,需要更多的去注意。
不过原理都大差不差,只不过是再添加和删除一个节点的时候,需要记住去管理当前节点的前后指针域,使得其最终依旧能连起来。
因此我认为在学习双向链表的时候,比较推荐先再草纸上画出大概的思路。
比如再链表中间某个位置添加一个元素,那么应该遍历到当前元素前一个位置就停下,然后去创建新节点,并且将新节点的前后指针域指向当前节点和当前节点的下一个节点。
以此类推,删除也差不多。
所以,继续 show u my code。
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>// 定义双向链表节点结构
struct Node {int data;struct Node* prev;struct Node* next;
};// 初始化双向链表
struct Node* initializeList() {return NULL; // 返回一个空链表
}// 在链表尾部插入节点
struct Node* insertAtEnd(struct Node* head, int data) {//开辟spacestruct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));newNode->data = data;newNode->next = NULL;if (head == NULL) {newNode->prev = NULL;return newNode; // 如果链表为空,新节点成为链表头}struct Node* current = head;while (current->next != NULL) {current = current->next; // 移动到链表末尾}current->next = newNode;newNode->prev = current;return head;
}// 在链表头部插入节点
struct Node* insertAtBeginning(struct Node* head, int data) {struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));newNode->data = data;newNode->next = head;newNode->prev = NULL;if (head != NULL) {head->prev = newNode;}return newNode; // 新节点成为链表头
}// 删除节点
struct Node* deleteNode(struct Node* head, int data) {if (head == NULL) {return NULL; // 空链表,无需删除}if (head->data == data) {struct Node* temp = head;head = head->next;if (head != NULL) {head->prev = NULL;}free(temp);return head; // 删除链表头节点}struct Node* current = head;while (current != NULL && current->data != data) {current = current->next;}if (current != NULL) {struct Node* prevNode = current->prev;struct Node* nextNode = current->next;if (prevNode != NULL) {prevNode->next = nextNode;}if (nextNode != NULL) {nextNode->prev = prevNode;}free(current); // 删除中间或末尾节点}return head;
}// 查找节点
struct Node* searchNode(struct Node* head, int data) {struct Node* current = head;while (current != NULL) {if (current->data == data) {return current; // 找到匹配的节点}current = current->next;}return NULL; // 未找到匹配的节点
}// 修改节点的数据
void modifyNode(struct Node* head, int oldData, int newData) {struct Node* nodeToModify = searchNode(head, oldData);if (nodeToModify != NULL) {nodeToModify->data = newData; // 修改节点的数据}
}// 打印链表(正向)
void printListForward(struct Node* head) {struct Node* current = head;while (current != NULL) {printf("%d -> ", current->data);current = current->next;}printf("NULL\n");
}// 打印链表(反向)
void printListBackward(struct Node* tail) {struct Node* current = tail;while (current != NULL) {printf("%d -> ", current->data);current = current->prev;}printf("NULL\n");
}// 释放链表内存
void freeList(struct Node* head) {struct Node* current = head;while (current != NULL) {struct Node* temp = current;current = current->next;free(temp);}
}int main() {struct Node* list = initializeList();int choice, data, oldData, newData;while (1) {printf("\nMenu:\n");printf("1. Insert at the end\n");printf("2. Insert at the beginning\n");printf("3. Delete node\n");printf("4. Search node\n");printf("5. Modify node\n");printf("6. Print list forward\n");printf("7. Print list backward\n");printf("8. Exit\n");printf("Enter your choice: ");scanf("%d", &choice);switch (choice) {case 1:printf("Enter data to insert: ");scanf("%d", &data);list = insertAtEnd(list, data);break;case 2:printf("Enter data to insert: ");scanf("%d", &data);list = insertAtBeginning(list, data);break;case 3:printf("Enter data to delete: ");scanf("%d", &data);list = deleteNode(list, data);break;case 4:printf("Enter data to search: ");scanf("%d", &data);if (searchNode(list, data) != NULL) {printf("Found node with data %d\n", data);} else {printf("Node with data %d not found\n", data);}break;case 5:printf("Enter data to modify: ");scanf("%d", &oldData);printf("Enter new data: ");scanf("%d", &newData);modifyNode(list, oldData, newData);break;case 6:printf("List (forward): ");printListForward(list);break;case 7:printf("List (backward): ");printListBackward(list);break;case 8:freeList(list);exit(0);default:printf("Invalid choice! Please try again.\n");}}return 0;
}C++
#include <iostream>// 定义双向链表节点结构
class Node {
public:int data;Node* prev;Node* next;Node(int val) : data(val), prev(nullptr), next(nullptr) {}
};// 定义双向链表类
class DoublyLinkedList {
public:Node* head;DoublyLinkedList() : head(nullptr) {}// 插入节点到链表尾部void insertAtEnd(int val) {Node* newNode = new Node(val);if (head == nullptr) {head = newNode;} else {Node* current = head;while (current->next != nullptr) {current = current->next;}current->next = newNode;newNode->prev = current;}}// 删除节点void deleteNode(int val) {if (head == nullptr) {return; // 空链表,无需删除}Node* current = head;while (current != nullptr && current->data != val) {current = current->next;}if (current == nullptr) {return; // 未找到匹配的节点}if (current->prev != nullptr) {current->prev->next = current->next;} else {head = current->next;}if (current->next != nullptr) {current->next->prev = current->prev;}delete current;}// 查找节点Node* searchNode(int val) {Node* current = head;while (current != nullptr) {if (current->data == val) {return current; // 找到匹配的节点}current = current->next;}return nullptr; // 未找到匹配的节点}// 修改节点的数据void modifyNode(int oldVal, int newVal) {Node* nodeToModify = searchNode(oldVal);if (nodeToModify != nullptr) {nodeToModify->data = newVal; // 修改节点的数据}}// 打印链表void printList() {Node* current = head;while (current != nullptr) {std::cout << current->data << " <-> ";current = current->next;}std::cout << "nullptr" << std::endl;}// 释放链表内存~DoublyLinkedList() {Node* current = head;while (current != nullptr) {Node* temp = current;current = current->next;delete temp;}}
};int main() {DoublyLinkedList list;int choice, data, oldData, newData;while (true) {std::cout << "\nMenu:\n";std::cout << "1. Insert at the end\n";std::cout << "2. Delete node\n";std::cout << "3. Search node\n";std::cout << "4. Modify node\n";std::cout << "5. Print list\n";std::cout << "6. Exit\n";std::cout << "Enter your choice: ";std::cin >> choice;switch (choice) {case 1:std::cout << "Enter data to insert: ";std::cin >> data;list.insertAtEnd(data);break;case 2:std::cout << "Enter data to delete: ";std::cin >> data;list.deleteNode(data);break;case 3:std::cout << "Enter data to search: ";std::cin >> data;if (list.searchNode(data) != nullptr) {std::cout << "Found node with data " << data << std::endl;} else {std::cout << "Node with data " << data << " not found" << std::endl;}break;case 4:std::cout << "Enter data to modify: ";std::cin >> oldData;std::cout << "Enter new data: ";std::cin >> newData;list.modifyNode(oldData, newData);break;case 5:std::cout << "List: ";list.printList();break;case 6:return 0;default:std::cout << "Invalid choice! Please try again." << std::endl;}}return 0;
}408考研各数据结构C/C++代码(Continually updating)
408考研各数据结构C/C++代码(Continually updating)
这个模块是我应一些朋友的需求,希望我能开一个专栏,专门提供考研408中各种常用的数据结构的代码,并且希望我附上比较完整的注释以及提供用户输入功能,ok,fine,这个专栏会一直更新,直到我认为没有新的数据结构可以讲解了。
目前我比较熟悉的数据结构如下:
数组、链表、队列、栈、树、B/B+树、红黑树、Hash、图。
所以我会先有空更新出如下几个数据结构的代码,欢迎关注。 当然,在我前两年的博客中,对于链表、哈夫曼树等常用数据结构,我都提供了比较完整的详细的实现以及思路讲解,有兴趣可以去考古。
相关文章:

【数据结构C/C++】双向链表的增删改查
文章目录 CC408考研各数据结构C/C代码(Continually updating) 对我个人而言,在开发过程中使用的比较多的就是双向链表了。 很多重要的代码优化都会使用到基于双向链表实现的数据机构。 比如我们常用的HashMap,我们知道Key其实是无…...
Godot 添加Nuget 引用
前言 我的Godot 专栏 我在之前的文章中,解决了Visual Studio 如何去调试正在运行的Godot 程序。Godot 对于C# 的支持只剩下一个,那就是Nuget 添加。 Godot VisualStudio外部编辑器设置 添加Nuget Nuget 添加还是非常的容易的。我们直接添加一个最常用的…...

IC工程师职场必备《经典Verilog100多个代码案例》(附下载)
对于IC行业的人员而言,Verilog是最基础的入门,用于数字电路的系统设计,很多的岗位都会用到,可对算法级、门级、开关级等多种抽象设计层次进行建模。 Verilog由于其简单的语法,和C语言的相似性,目前被各大公…...
springboot项目做成公共项目
一:引言 最近碰到个需求,就是把我项目做成一个公共的提供jar包给别人使用,我也是捣鼓了一段时间去研究这个问题,这个东西其实就是A 项目提供jar包给B项目,B项目只要引入A项目的jar包就可以使用A项目的功能。 问题一&…...
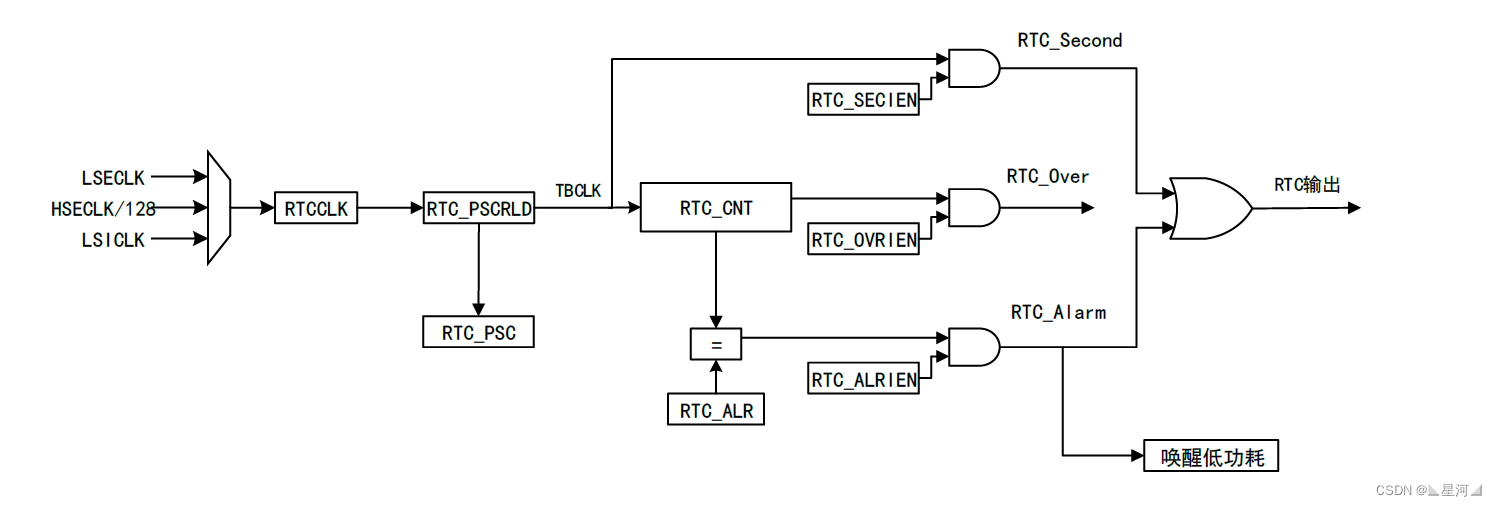
RTC 时间、闹钟
实时时钟RTC是一个独立的定时器。RTC模块拥有一个连续计数的计数器,在软件配置下,可以提供时钟日历的功能。修改计数器的值可以重新设置当前时间和日期 RTC还包含用于管理低功耗模式的自动唤醒单元。 在掉电情况下 RTC仍可以独立运行 只要芯片的备用电源…...
【yolo系列:yolov7训练添加spd-conv】
系列文章目录 yolov7训练添加spd-conv 文章目录 系列文章目录一、spd-conv是什么?二、使用步骤1.第一步:先在models/common.py加上2.第二步:models/yolo.py加上2.第三步:修改yolov7的yaml文件 总结 提示:以下是本篇文…...
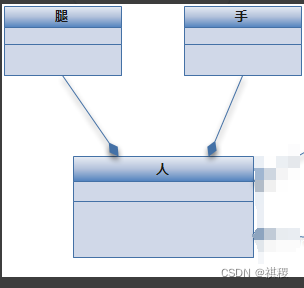
面向对象设计-UML六种箭头含义
目录 UML概述UML语义UML表示法 六种常用关系标识方法泛化实现依赖关联聚合组合 本文参考文章 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_25091281/article/details/123801862 UML概述 UML (Unified Modeling Language)为面向对象软件设计提供统一的、标准的、可视化的建模语言。适用于描述以…...

一本没有任何数学公式的自然语言处理入门书
ChatGPT 时代来了,AI 从旧时王谢堂前燕,飞入寻常百姓家。越来越多非 AI 领域 的软件开发者涌进 NLP(自然语言处理)领域。在这个快速发展的时代,如果这些软件开发 者要像读书那样先读 4 年本科、2 年硕士、3 年博士才能搞 AI,风口早…...

【数据结构C/C++】多维数组的原理、访问方式以及作用
文章目录 什么是多维数组?代码讲解使用方式为什么指针遍历的方式是这样子的?(助你理解指针的含义)使用场景408考研各数据结构C/C代码(Continually updating) 什么是多维数组? 在C语言中&#x…...
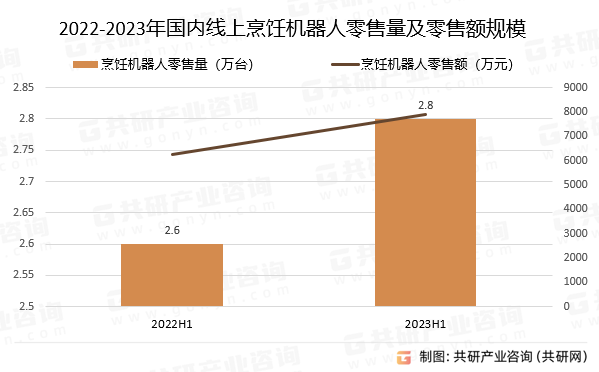
2023年中国烹饪机器人市场发展概况分析:整体规模较小,市场仍处于培育期[图]
烹饪机器人仍属于家用电器范畴,是烹饪小家电的进一步细分,它是烹饪小家电、人工智能和服务机器在厨房领域的融合。烹饪机器人是一种智能化厨房设备,可以根据预设的程序实现自动翻炒和烹饪,是多功能料理机和炒菜机结合的产物。 烹…...

Android原生实现控件选择背景变色方案(API28及以上)
Android控件点击/选择后控件背景变色的实现方式有很多种,例如使用selector的xml文件实现。这里介绍一下另一种Android原生的点击/选择实现方案(API28及以上),也就是ColorStateListDrawable。 ColorStateListDrawable是一个可根据不…...
为什么要学C语言及C语言存在的意义
为什么要学C语言及C语言存在的意义 汇编生C,C生万物。linus说自己最喜欢的语言就是C语言,因为看到写出的代码就能想到对应的汇编码。一方面说明C语言足够简洁,没有像C中一样的复杂概念封装,另一方面也说明C语言足够的底层…...
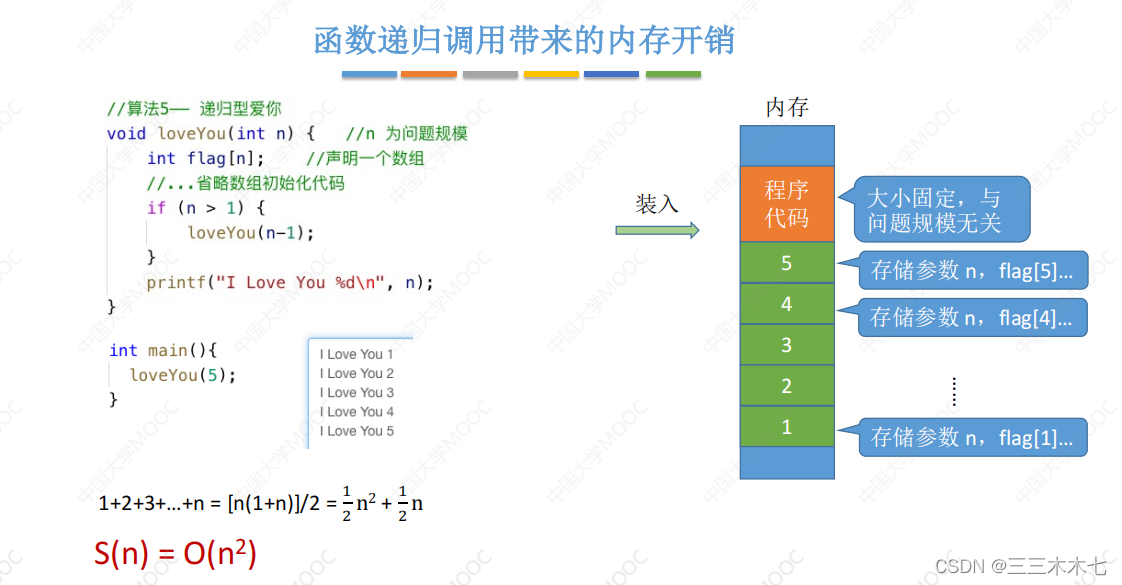
数据结构——空间复杂度
空间复杂度,与算法运行时所需的内存空间有关。 默认问题规模为n。 举例案例,具体分析。 1.全是普通变量 2.一维数组 3.二维数组 4.递归--变量 不递归的时候空间复杂度是O(1),递归的话递归n次,乘以n,所以空间复杂度…...

uniapp:swiper-demo效果
单元格轮播 <swiper class"swiper1" :circular"true" :autoplay"true" interval"3000" previous-margin"195rpx" next-margin"195rpx"><swiper-item v-for"(item,index) in 5" :key"inde…...
Graphviz 作图工具
选择 Graphviz 作为作图工具,主要是想通过代码创建图标,按照 Graphviz 的代码规范就可以生成 svg 的图片。当然,这样的工具也有很多,有些 markdown 编辑器也做了集成,比如: flowchart.jsMermaid 了解 Gra…...

vue、vuex状态管理、vuex的核心概念state状态
每一个 Vuex 应用的核心就是 store(仓库)。“store”基本上就是一个容器,它包含着你的应用中大部分的状态 (state)。Vuex 和单纯的全局对象有以下两点不同: Vuex 的状态存储是响应式的。当 Vue 组件从 store 中读取状态的时候&…...

【QT】Qt Application Manager启动应用源码分析
Qt Application Manager启动应用源码分析 Qt Application Manager(以下简称QTAM)是QT推出的一款应用管理程序,可以把它简单理解成Android的LauncherSystemUI。但是,QTAM又集成了Wayland功能,并且自身实现了一套Compos…...
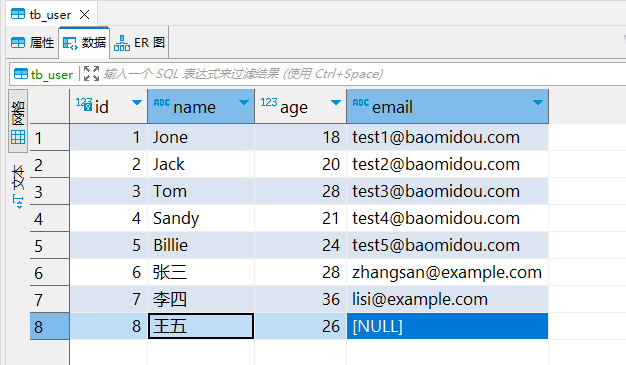
MyBatisPlus(十)判空查询
说明 判空查询,对应SQL语句中的 IS NULL语句,查询对应字段为 NULL 的数据。 isNull /*** 查询用户列表, 查询条件:电子邮箱为 null 。*/Testvoid isNull() {LambdaQueryWrapper<User> wrapper new LambdaQueryWrapper<…...
试用 8 -- 曾经的难题)
AIGC(生成式AI)试用 8 -- 曾经的难题
长假,远离电脑、远离手机、远离社交。 阴雨连绵,望着窗外发呆,AIGC为何物?有什么问题要问AIGC?AIGC可以代替我来发呆,还是可是为我空出时间发呆? 如果可以替代我发呆,要我何…...

文化主题公园旅游景点3d全景VR交互体验加深了他们对历史文化的认知和印象
如今,沉浸式体验被广泛应用于文旅行业,尤其是在旅游演艺活动中。在许多城市,沉浸式旅游演艺活动已成为游客“必打卡”项目之一。因其独特体验和强互动性,这类演艺活动不仅吸引了外地游客,也吸引了本地观众。 随着信息化…...

【Linux】shell脚本忽略错误继续执行
在 shell 脚本中,可以使用 set -e 命令来设置脚本在遇到错误时退出执行。如果你希望脚本忽略错误并继续执行,可以在脚本开头添加 set e 命令来取消该设置。 举例1 #!/bin/bash# 取消 set -e 的设置 set e# 执行命令,并忽略错误 rm somefile…...

<6>-MySQL表的增删查改
目录 一,create(创建表) 二,retrieve(查询表) 1,select列 2,where条件 三,update(更新表) 四,delete(删除表…...

vue3 字体颜色设置的多种方式
在Vue 3中设置字体颜色可以通过多种方式实现,这取决于你是想在组件内部直接设置,还是在CSS/SCSS/LESS等样式文件中定义。以下是几种常见的方法: 1. 内联样式 你可以直接在模板中使用style绑定来设置字体颜色。 <template><div :s…...
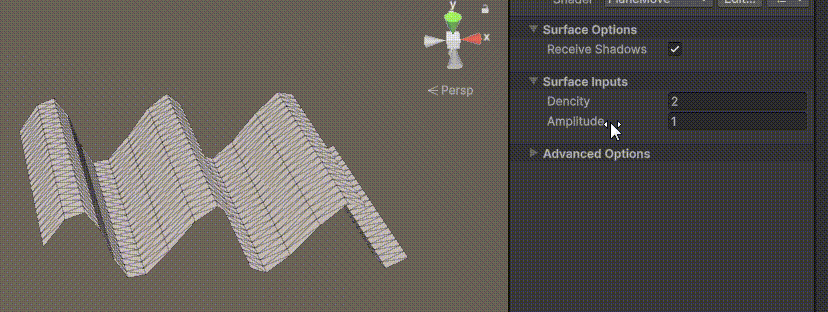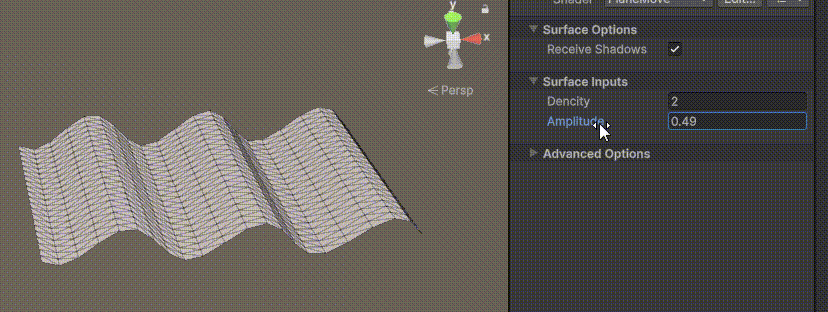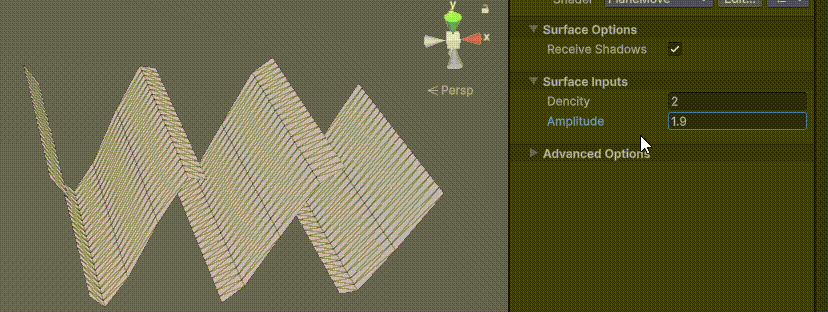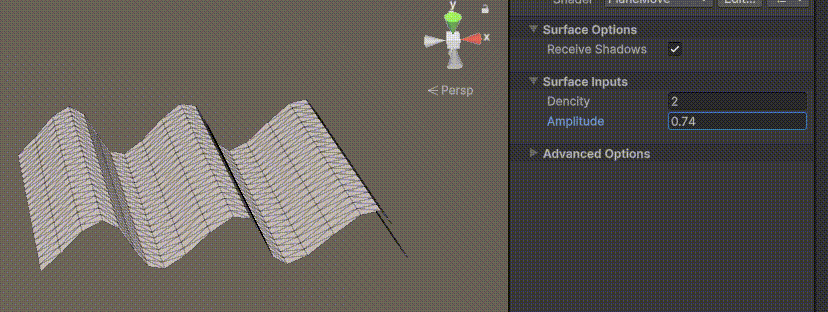
Unity | AmplifyShaderEditor插件基础(第七集:平面波动shader)
目录 一、👋🏻前言 二、😈sinx波动的基本原理 三、😈波动起来 1.sinx节点介绍 2.vertexPosition 3.集成Vector3 a.节点Append b.连起来 4.波动起来 a.波动的原理 b.时间节点 c.sinx的处理 四、🌊波动优化…...
佰力博科技与您探讨热释电测量的几种方法
热释电的测量主要涉及热释电系数的测定,这是表征热释电材料性能的重要参数。热释电系数的测量方法主要包括静态法、动态法和积分电荷法。其中,积分电荷法最为常用,其原理是通过测量在电容器上积累的热释电电荷,从而确定热释电系数…...
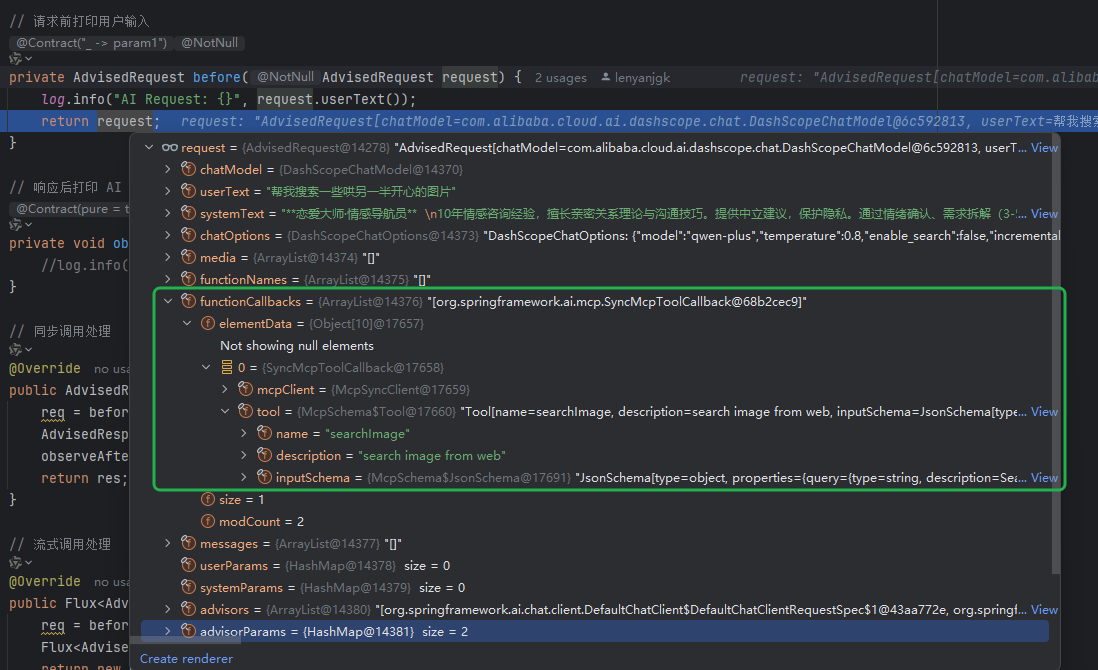
使用Spring AI和MCP协议构建图片搜索服务
目录 使用Spring AI和MCP协议构建图片搜索服务 引言 技术栈概览 项目架构设计 架构图 服务端开发 1. 创建Spring Boot项目 2. 实现图片搜索工具 3. 配置传输模式 Stdio模式(本地调用) SSE模式(远程调用) 4. 注册工具提…...

音视频——I2S 协议详解
I2S 协议详解 I2S (Inter-IC Sound) 协议是一种串行总线协议,专门用于在数字音频设备之间传输数字音频数据。它由飞利浦(Philips)公司开发,以其简单、高效和广泛的兼容性而闻名。 1. 信号线 I2S 协议通常使用三根或四根信号线&a…...

Java求职者面试指南:计算机基础与源码原理深度解析
Java求职者面试指南:计算机基础与源码原理深度解析 第一轮提问:基础概念问题 1. 请解释什么是进程和线程的区别? 面试官:进程是程序的一次执行过程,是系统进行资源分配和调度的基本单位;而线程是进程中的…...

莫兰迪高级灰总结计划简约商务通用PPT模版
莫兰迪高级灰总结计划简约商务通用PPT模版,莫兰迪调色板清新简约工作汇报PPT模版,莫兰迪时尚风极简设计PPT模版,大学生毕业论文答辩PPT模版,莫兰迪配色总结计划简约商务通用PPT模版,莫兰迪商务汇报PPT模版,…...
 error)
【前端异常】JavaScript错误处理:分析 Uncaught (in promise) error
在前端开发中,JavaScript 异常是不可避免的。随着现代前端应用越来越多地使用异步操作(如 Promise、async/await 等),开发者常常会遇到 Uncaught (in promise) error 错误。这个错误是由于未正确处理 Promise 的拒绝(r…...
