SpringBoot运行流程源码分析------阶段三(Spring Boot外化配置源码解析)
Spring Boot外化配置源码解析
外化配置简介
Spring Boot设计了非常特殊的加载指定属性文件(PropertySouce)的顺序,允许属性值合理的覆盖,属性值会以下面的优先级进行配置。
- home目录下的Devtool全局设置属性(~/.spring-boot-devtools.properties,条件是当devtools激活时)
- @TestPropertySource注解的测试用例。
- @SpringBootTest#properties注解的测试用例。
- 命令行参数。
- 来自SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON的属性(内嵌在环境变量或系统属性中的内联JSON)
- ServletConfig初始化参数
- ServletContext初始化参数
- java:comp/env的JNDI属性
- Java系统属性(System.getProperties())
- 操作系统环境变量
- RandomValuePropertySource,只包含random.*中的属性
- jar包外的Profile_specific应用属性(application-{profile}.propertis和YAML变量)
- jar包内的Profile_specific应用属性(application-{profile}.propertis和YAML变量)
- jar包外的应用配置(application.properties和YAML变量)
- jar包内的应用配置(application.properties和YAML变量)
- @Configuration类上的@PropertySource注解
- 默认属性(通过SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties指定)
在以上配置方式中,我们经常使用的包括:命令参数,属性文件,YAML文件等内容,以下将围绕他们的运行及相关代码进行讲解。
ApplicationArguments参数处理
ApplicationArguments提供了针对参数的解析和查询功能。在Spring Boot运行阶段的章节中我们提到过,通过SpringApplication.run(args)传递的参数会被封装在ApplicationArguments接口中。本节我们来详细了解下ApplicationArguments接口。
接口定义及初始化
首先看一下ApplicationArguments接口的具体方法定义及功能介绍。
package org.springframework.boot;import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;public interface ApplicationArguments {//返回原始未处理的参数(通过application传入的)String[] getSourceArgs();//返回所有参数的集合,如参数为:--foo=bar --debug,则返回【"foo","debug"】Set<String> getOptionNames();//选项参数中是否包含指定名称的参数boolean containsOption(String name);//根据选项参数的名称获取选项参数的值列表List<String> getOptionValues(String name);//返回非选项参数列表List<String> getNonOptionArgs();}
通过接口定义可以看出,ApplicationArguments主要提供了针对参数名称和值的查询,以及判断是否存在指定参数的功能。
在Spring Boot的初始化运行过程中,ApplicationArguments接口的实例化操作默认是通过实现类DefaultApplicationArguments来完成的。DefaultApplicationArguments的底层又是基于Spring框架中的命令行配置源SimpleCommandLinePropertySource实现的,SpringCommandLinePropertySource是PropertySource抽象类的派生类。
以下代码中内部类Source便是SimppleCommandLinePropertySource的子类。
public class DefaultApplicationArguments implements ApplicationArguments {private final Source source;private final String[] args;public DefaultApplicationArguments(String... args) {Assert.notNull(args, "Args must not be null");this.source = new Source(args);this.args = args;}......private static class Source extends SimpleCommandLinePropertySource {......}}
我们再来看SimpleCommandLinePropertySource的构造方法,通过代码会发现默认使用spring的SimpleCommandLineArgsParser对args参加进行解析。
public class SimpleCommandLinePropertySource extends CommandLinePropertySource<CommandLineArgs> {public SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(String... args) {super((new SimpleCommandLineArgsParser()).parse(args));}//重载的构造方法public SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(String name, String[] args) {super(name, (new SimpleCommandLineArgsParser()).parse(args));}......
}
除了构造方法之外,SimpleCommandLinePropertySource还提供了不同类型参数信息的获取和检查是否存在的功能,代码如下:
public class SimpleCommandLinePropertySource extends CommandLinePropertySource<CommandLineArgs> {......//获取选项参数数组 public String[] getPropertyNames() {return StringUtils.toStringArray(((CommandLineArgs)this.source).getOptionNames());}//获取是否包含指定name的参数protected boolean containsOption(String name) {return ((CommandLineArgs)this.source).containsOption(name);}//获取指定name的选项参数列表@Nullableprotected List<String> getOptionValues(String name) {return ((CommandLineArgs)this.source).getOptionValues(name);}//获取非选项参数列表protected List<String> getNonOptionArgs() {return ((CommandLineArgs)this.source).getNonOptionArgs();}
}
ApplicatinArguments,或者更进一步说是SimpleCommandLinePropertySource对参数类型是有所区分的,即选项参数和非选项参数。
选项参数必须以“–”为前缀,参数值可为空,该参数可以通过Spring Boot属性处理后使用,比如在执行jar -jar命令时,添加选项参数“–app.name=spring boot start",在代码中可以通过注解@Value属性及其他方式获取到该参数的值。该参数可以通过逗号分隔多个参数值,或者多次使用同一个参数来包含多个参数的值。
非选项参数并不要求以“–”前缀开始,可自行定义。非选项参数可以直接在jar -jar命令中定义参数为“non-option"的参数值。
以上所说的选项参数和非选项参数的解析是在SimpleCommandLinePropertySource构造方法中调用SimpleCommandLineArgsParser中完成的,代码如下:
class SimpleCommandLineArgsParser {SimpleCommandLineArgsParser() {}//解析args参数,返回一个完整的CommandLineArgs对象public CommandLineArgs parse(String... args) {CommandLineArgs commandLineArgs = new CommandLineArgs();String[] var3 = args;int var4 = args.length;//遍历参数for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {String arg = var3[var5];//解析选项参数,以"--"开头if (arg.startsWith("--")) {String optionText = arg.substring(2, arg.length());String optionValue = null;String optionName;//判断是--foo=bar参数格式,还是-foo参数格式,并分别处理获取值if (optionText.contains("=")) {optionName = optionText.substring(0, optionText.indexOf(61));optionValue = optionText.substring(optionText.indexOf(61) + 1, optionText.length());} else {optionName = optionText;}if (optionName.isEmpty() || optionValue != null && optionValue.isEmpty()) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid argument syntax: " + arg);}commandLineArgs.addOptionArg(optionName, optionValue);} else {//处理非选项参数commandLineArgs.addNonOptionArg(arg);}}return commandLineArgs;}
}
通过SimpleCommandLineArgsParser的代码可以看出,Spring对参数的解析是按照指定的参数格式分别解析字符串中的值来实现的。最终,解析的结果均封装在CommandLineArgs中。而CommandLineArgs类只是命令行参数的简单表示形式,内部分为“选项参数”和"非选项参数"
class CommandLineArgs {private final Map<String, List<String>> optionArgs = new HashMap();private final List<String> nonOptionArgs = new ArrayList();CommandLineArgs() {}......
}
CommandLineArgs的核心存储结构包括:存储选项参数的Map<String,List>optionArgs和存储非选项参数的ListnonOptionsArgs。同时,针对这两个核心存储接口,SpringBoot也提供了相关的读写操作的方法。
SimpleCommandLineArgsParser解析获得的CommandLineArgs对象,最终会被SimpleCommandLinePropertySource的构造方法通过parser调用,一层层地传递到PropertySource类的构造方法中,最终封装到相应的属性当中。
public abstract class PropertySource<T> {protected final Log logger;//参数类别名称protected final String name;//参数封装类protected final T source;......
}
以在SimpleCommandLinePropertySource中的使用为例,最终封装在PropertySource中的结构为:name为“commandLineArgs”,source为解析出的CommandLineArgs对象。
而DefaultApplicationArguments的内部类Source作为SimpleCommandLinePropertySource的子类存储了以上解析的数据内容。同时,args参数的原始值储存在DefaultApplicationArguments的String[]args属性中。
命令行参数的获取
命令行参数就是在启动Spring Boot项目时通过命令行传递的参数。比如通过一下命令来启动一个Spring Boot项目。
jar -jar app.jar --name=SpringBoot
那么–name=SpringBoot是如何一步步传递到Spring内部的呢?
默认情况下,SpringApplication会将以上类似name的命令行参数(以“–”开头)解析封装成一个PropertySource对象,并将其添加到Spring-Environment当中,而命令行参数的优先级要高于其他配置源。
下面我们来通过代码来追踪启动过程中整个参数的获取,解析和分装过程。首先,参数是通过SpringApplication的run方法的args传递参数。
在SpringApplication的run方法中,通过以下操作先将args封装于ApplicationArguments中,然后又将封装之后的对象传递入prepareEnvironment方法。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {......try {ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);......}catch (Throwable ex) {handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);throw new IllegalStateException(ex);}......}
在prepareEnvironment方法中,通过applicationArguments.getSourceArgs()获得传递的参数数组,并作为参数调用configureEnvironment方法,此处获得的args依旧是未解析的参数值,代码如下:
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {......configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());......}
在configureEnvironment方法中又将参数传递给configurePropertySource方法。
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {......configurePropertySources(environment, args);configureProfiles(environment, args);}
而在configurePropertySources方法中才对参数进行了真正的解析和封装
protected void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {//获取环境变量中的属性资源信息MutablePropertySources sources = environment.getPropertySources();//如果默认属性配置存在,则将其放置在属性资源的最后位置if (this.defaultProperties != null && !this.defaultProperties.isEmpty()) {sources.addLast(new MapPropertySource("defaultProperties", this.defaultProperties));}//如果命令行属性未被禁用且存在if (this.addCommandLineProperties && args.length > 0) {String name = CommandLinePropertySource.COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;//如果默认属性资源中不包含该命令则将命令行属性放置在第一位//如果包含则通过CompositePropertySource进行处理if (sources.contains(name)) {PropertySource<?> source = sources.get(name);CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(name);composite.addPropertySource(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource("springApplicationCommandLineArgs", args));composite.addPropertySource(source);sources.replace(name, composite);}else {//不存在,则添加并放置在第一位sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args));}}}
因为configurePropertySources方法在之前章节中介绍过,下面针对命令行参数再次进行讲解和深入分析,重点介绍两个内容:参数的优先级和命令行参数的解析。
参数的优先级,从上面的代码注解中可以看到,configurePropertySources方法
- 第一步获得环境变量中存储配置信息的sources;
- 第二步判断默认参数是否为空,如果不为空,则将默认参数放置在sources的最后位置,这里已经明显反应了参数的优先级是通过顺序来体现的;
- 第三步如果命令行参数未被禁用,且不为空,则要么将原有默认参数替换掉,要么直接放在第一位,这一步中的替换操作也是另外一种优先级形式的体现。
在上面代码中,可以通过SpringApplication的setAddCommandLineProperties方法将其设置为false来禁用。命令行参数的解析用到了SimpleCommandLinePropertySource类,而该类的相关使用在上面以详细介绍过。下面将分析配置文件中的参数获取。
配置文件的加载
Spring Boot启动时默认会去加载classpah下的application.yml或application.properties文件。配置文件的加载过程中主要是利用了Spring Boot的事件机制来完成的,也就是我们之前说的SpringApplicationRunListeners中的environmentPrepared方法来启动加载配置文件的事件。通过该方法发布的事件会被注册到ConfigFileApplicationListener监听到,而实现资源的加载。
下面来通过源码的追踪分析这一过程。该事件同样是SpringApplication的run方法来完成的。前半部分的调用过程与上面命令行获取参数的方法调用一样,不同的是当执行到prepareEnvironment中,当执行完configureEnvironment方法之后,便通过事件发布来通知监听器加载资源。
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {// Create and configure the environmentConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();// 配置环境,主要包括PropertySources和activeProfiles的配置configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);//listeners环境准备listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);......}
该事件监听器通过EventPublishingRunListener的environmentPrepared方法发布一个ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件
public class EventPublishingRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener, Ordered {......@Overridepublic void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, environment));}......
}在META-INF/spring.factories中注册的ConfigFileApplicationListener会监听到对应事件,并进行相应的处理。spring.factories中ConfigFileApplicationListener的注册配置如下:
# Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
org.springframework.boot.ClearCachesApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener
在ConfiFileApplicationListener类中我们会看到很多与配置文件加载相关的常量。
public class ConfigFileApplicationListener implements EnvironmentPostProcessor, SmartApplicationListener, Ordered {private static final String DEFAULT_PROPERTIES = "defaultProperties";// 默认的加载配置文件路径private static final String DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS = "classpath:/,classpath:/config/,file:./,file:./config/";//默认的配置文件名称private static final String DEFAULT_NAMES = "application";......//激活配置文件的属性名public static final String ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY = "spring.profiles.active";......
通过这些基本的常量,可以看出默认加载配置文件的路径和默认的名称。再回到刚才的事件监听,入口方法为ConfigFileApplicationListener的onApplicationEvent方法。
@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {//对应当前发布的事件,执行次业务逻辑if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);}if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {onApplicationPreparedEvent(event);}}
上面调用onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent方法如下,该方法会获得注册的处理器,遍历并依次调用postPropcessEnvironment方法。
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();postProcessors.add(this);AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(postProcessors);//遍历并依次调用postProcessEnvironment方法for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication());}}
其中EnvironmentPostProcessor接口的实现类也是在META-INF/spring.factories文件中注册的。
# Environment Post Processors
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\
org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.env.SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.env.SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.reactor.DebugAgentEnvironmentPostProcessor
ConfigFileApplicationListener本身也是EvironmentPostProcessor接口的实现类,可以跟着ConfigFileApplicationListener中postProcessEnvironment的调用链路代码一直往下看,会发现最后在其内部类Loader的load方法进行配置文件的加载操作。其中关于文件路径及其名称的组合代码如下:
// 1接口类,查找实现类ConfiFileApplicationListener
public interface EnvironmentPostProcessor {void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application);
}// 2 ConfiFileApplicationListener实现类
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {addPropertySources(environment, application.getResourceLoader());
}
// 3 addPropertySources
protected void addPropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment(environment);new Loader(environment, resourceLoader).load();
}
// 4 load()
void load() {FilteredPropertySource.apply(this.environment, DEFAULT_PROPERTIES, LOAD_FILTERED_PROPERTY,(defaultProperties) -> {this.profiles = new LinkedList<>();this.processedProfiles = new LinkedList<>();this.activatedProfiles = false;this.loaded = new LinkedHashMap<>();initializeProfiles();while (!this.profiles.isEmpty()) {Profile profile = this.profiles.poll();if (isDefaultProfile(profile)) {addProfileToEnvironment(profile.getName());}load(profile, this::getPositiveProfileFilter,addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addLast, false));this.processedProfiles.add(profile);}load(null, this::getNegativeProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addFirst, true));addLoadedPropertySources();applyActiveProfiles(defaultProperties);});
}
// 5 load()
private void load(Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) {getSearchLocations().forEach((location) -> {boolean isFolder = location.endsWith("/");Set<String> names = isFolder ? getSearchNames() : NO_SEARCH_NAMES;names.forEach((name) -> load(location, name, profile, filterFactory, consumer));});
}
private void load(String location, String name, Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory,DocumentConsumer consumer) {......Set<String> processed = new HashSet<>();for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.propertySourceLoaders) {for (String fileExtension : loader.getFileExtensions()) {if (processed.add(fileExtension)) {loadForFileExtension(loader, location + name, "." + fileExtension, profile, filterFactory,consumer);}}}}
在该方法中可以看到loadForFileExtension的第二个参数"文件路径+名称"和第三个参数"扩展名称"的拼接组成方式。location默认值就是常量DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS的值。
在for循环中遍历的PropertySourceLoader也是在META-INF/spring.factories中注册的,并且在Loader的构造方法中通过SpringFactoriesLoader的loadFactories方法来获得。
# PropertySource Loaders
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=\
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertiesPropertySourceLoader,\
org.springframework.boot.env.YamlPropertySourceLoader
当查看PropertiesPropertySourceLoader和YamlPropertySourceLoader两个加载器代码时,就会发现他们分别定义了所支持文件类型及其加载方法。PropertiesPropertySourceLoader支持配置文件类型的定义代码如下:
public class PropertiesPropertySourceLoader implements PropertySourceLoader {private static final String XML_FILE_EXTENSION = ".xml";@Overridepublic String[] getFileExtensions() {return new String[] { "properties", "xml" };}@Overridepublic List<PropertySource<?>> load(String name, Resource resource) throws IOException {Map<String, ?> properties = loadProperties(resource);if (properties.isEmpty()) {return Collections.emptyList();}return Collections.singletonList(new OriginTrackedMapPropertySource(name, Collections.unmodifiableMap(properties), true));}@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })private Map<String, ?> loadProperties(Resource resource) throws IOException {String filename = resource.getFilename();if (filename != null && filename.endsWith(XML_FILE_EXTENSION)) {return (Map) PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);}return new OriginTrackedPropertiesLoader(resource).load();}}
YamlPropertySourceLoader支持配置文件类型的定义代码如下:
public class YamlPropertySourceLoader implements PropertySourceLoader {@Overridepublic String[] getFileExtensions() {return new String[] { "yml", "yaml" };}@Overridepublic List<PropertySource<?>> load(String name, Resource resource) throws IOException {if (!ClassUtils.isPresent("org.yaml.snakeyaml.Yaml", null)) {throw new IllegalStateException("Attempted to load " + name + " but snakeyaml was not found on the classpath");}List<Map<String, Object>> loaded = new OriginTrackedYamlLoader(resource).load();if (loaded.isEmpty()) {return Collections.emptyList();}List<PropertySource<?>> propertySources = new ArrayList<>(loaded.size());for (int i = 0; i < loaded.size(); i++) {String documentNumber = (loaded.size() != 1) ? " (document #" + i + ")" : "";propertySources.add(new OriginTrackedMapPropertySource(name + documentNumber,Collections.unmodifiableMap(loaded.get(i)), true));}return propertySources;}}
其中PropertiesPropertySourceLoader对文件的加载通过PropertiesLoaderUtils类(加载xml文件)和OriginTrackedYamlLoader类来完成,而YamlPropertySourceLoader对文件的加载主要通过OriginrackedYamlLoader来完成。
下面以PropertiesPropertySourceLoader使用的OriginTrackedPropertiesLoader为例进行源码分析。
PropertiesPropertySourceLoader中加载相关的代码如下:
public class PropertiesPropertySourceLoader implements PropertySourceLoader {private static final String XML_FILE_EXTENSION = ".xml";@Overridepublic String[] getFileExtensions() {return new String[] { "properties", "xml" };}//加载指定的配置文件@Overridepublic List<PropertySource<?>> load(String name, Resource resource) throws IOException {//调用load方法进行加载并返回Map形式的数据Map<String, ?> properties = loadProperties(resource);if (properties.isEmpty()) {return Collections.emptyList();}//对返回结果进行处理和转换return Collections.singletonList(new OriginTrackedMapPropertySource(name, Collections.unmodifiableMap(properties), true));}//具体加载过程@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })private Map<String, ?> loadProperties(Resource resource) throws IOException {String filename = resource.getFilename();//加载xml格式if (filename != null && filename.endsWith(XML_FILE_EXTENSION)) {return (Map) PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);}//加载properties格式return new OriginTrackedPropertiesLoader(resource).load();}}
OriginTrackedPropertiesLoader的构造方法非常简单,只是把resource设置给其成员变量Resource。
class OriginTrackedPropertiesLoader {private final Resource resource;OriginTrackedPropertiesLoader(Resource resource) {Assert.notNull(resource, "Resource must not be null");this.resource = resource;}Map<String, OriginTrackedValue> load() throws IOException {return load(true);}//加载properties文件的数据并返回map类型//其中expandLists用于指定参数为"name[]=a,b,c"的列表是否进行扩展,默认为trueMap<String, OriginTrackedValue> load(boolean expandLists) throws IOException {//创建配置文件的readertry (CharacterReader reader = new CharacterReader(this.resource)) {Map<String, OriginTrackedValue> result = new LinkedHashMap<>();StringBuilder buffer = new StringBuilder();//读取文件中数据while (reader.read()) {//读取文件中的keyString key = loadKey(buffer, reader).trim();//可扩展列表的处理if (expandLists && key.endsWith("[]")) {key = key.substring(0, key.length() - 2);int index = 0;do {OriginTrackedValue value = loadValue(buffer, reader, true);put(result, key + "[" + (index++) + "]", value);if (!reader.isEndOfLine()) {reader.read();}}while (!reader.isEndOfLine());}else {//读取文件中value并封装为OriginTrackedValueOriginTrackedValue value = loadValue(buffer, reader, false);put(result, key, value);}}return result;}}
}
以上代码展示了OriginTrackedPropertiesLoader的load方法的核心功能:创建reader读取配置文件,获得配置文件中配置的key,获取配置文件中的value,封装key-value到map中并返回。
相关文章:
)
SpringBoot运行流程源码分析------阶段三(Spring Boot外化配置源码解析)
Spring Boot外化配置源码解析 外化配置简介 Spring Boot设计了非常特殊的加载指定属性文件(PropertySouce)的顺序,允许属性值合理的覆盖,属性值会以下面的优先级进行配置。home目录下的Devtool全局设置属性(~/.sprin…...
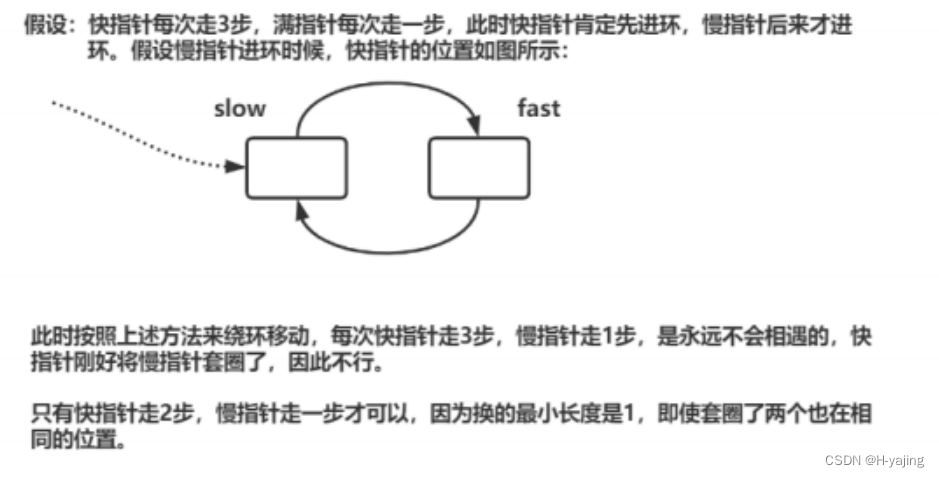
环形链表-力扣
一、题目描述 题目链接:力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台 二、题解 解题思路: 快慢指针,即慢指针一次走一步,快指针一次走两步,两个指针从链表起始位置开始运行,…...

人生岁月年华
人生很长吗?不知道。只知道高中坐在教室里,闹哄哄的很难受。也记得上班时无聊敲着代码也很难受。 可是人生也不长。你没有太多时间去试错,你没有无限的时间精力去追寻你认为的高大上。 人生是何体验呢?人生的感觉很多吧。大多数…...
电脑QQ如何录制视频文件?
听说QQ可以录制视频,还很方便,请问该如何录制呢?是需要先打开QQ才可以录制吗?还是可以直接使用快捷键进行录制呢?录制的质量又如何呢? 不要着急,既然都打开这篇文章看了,那小编今天…...

python:多波段遥感影像分离成单波段影像
作者:CSDN @ _养乐多_ 在遥感图像处理中,我们经常需要将多波段遥感影像拆分成多个单波段图像,以便进行各种分析和后续处理。本篇博客将介绍一个用Python编写的程序,该程序可以读取多波段遥感影像,将其拆分为单波段图像,并保存为单独的文件。本程序使用GDAL库来处理遥感影…...

天堂2游戏出错如何解决
运行游戏时出现以下提示:“the game may not be consistant because AGP is deactivated please activate AGP for consistancy” 这个问题的原因可能是由于您的显示卡的驱动或者主板的显示芯片组的驱动不是新开。或您虽然已经更新了您的显示卡的驱动程序࿰…...
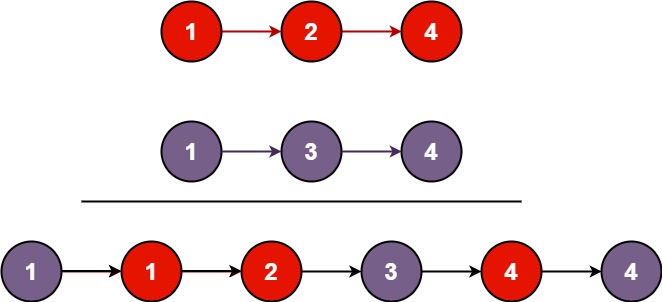
『力扣刷题本』:合并两个有序链表(递归解法)
一、题目 将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。 示例 1: 输入:l1 [1,2,4], l2 [1,3,4] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]示例 2: 输入:l1 [], l2 [] 输出&#x…...
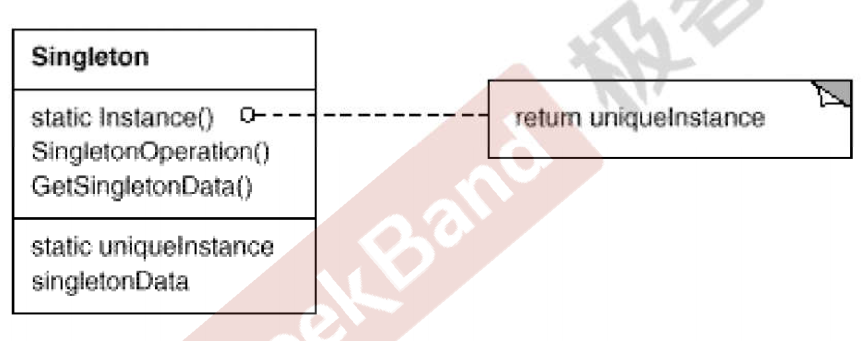
C++设计模式_12_Singleton 单件模式
在之前的博文C57个入门知识点_44:单例的实现与理解中,已经详细介绍了单例模式,并且根据其中内容,单例模式已经可以在日常编码中被使用,本文将会再做梳理。 Singleton 单件模式可以说是最简单的设计模式,但由…...
67 内网安全-域横向smbwmi明文或hash传递
#知识点1: windows2012以上版本默认关闭wdigest,攻击者无法从内存中获取明文密码windows2012以下版本如安装KB2871997补丁,同样也会导致无法获取明文密码针对以上情况,我们提供了4种方式解决此类问题 1.利用哈希hash传递(pth,ptk等…...

面向对象(类/继承/封装/多态)详解
简介: 面向对象编程(Object-Oriented Programming,OOP)是一种广泛应用于软件开发的编程范式。它基于一系列核心概念,包括类、继承、封装和多态。在这篇详细的解释中,我们将探讨这些概念,并说明它们如何在P…...

【Python机器学习】零基础掌握GradientBoostingRegressor集成学习
如何精准预测房价? 当人们提到房价预测时,很多人可能会想到房地产经纪人或专业的评估师。但是,有没有一种更科学、更精确的方法来预测房价呢?答案是有的,这就要用到机器学习中的一种算法——梯度提升回归(Gradient Boosting Regressor)。 假设现在有一组房屋数据,包括…...

【tio-websocket】12、应用层包—Packet
Packet 介绍 Packet 是用于表述业务数据结构的,我们通过继承 Packet 来实现自己的业务数据结构,对于各位而言,把 Packet 看作是一个普通的 VO 对象即可。 public class Packet implements java.io.Serializable, Cloneable {private static Logger log = LoggerFac…...
OpenCV官方教程中文版 —— 模板匹配
OpenCV官方教程中文版 —— 模板匹配 前言一、原理二、OpenCV 中的模板匹配三、多对象的模板匹配 前言 在本节我们要学习: 使用模板匹配在一幅图像中查找目标 函数:cv2.matchTemplate(),cv2.minMaxLoc() 一、原理 模板匹配是用来在一副大…...
如何为3D模型设置自发光材质?
1、自发光贴图的原理 自发光贴图是一种纹理贴图,用于模拟物体自发光的效果。其原理基于光的发射和反射过程。 在真实世界中,物体自发光通常是由于其本身具有能够产生光的属性,如荧光物质、发光材料或光源本身。为了在计算机图形中模拟这种效…...
UI组件库基础
UI组件库 全局组件* 全局注册组件 & 并且使用了require.context 模块化编程 & webpack打包 const install(Vue)>{const contextrequire.context(.,true,/\.vue$/)context.keys().forEach(fileName>{const modulecontext(fileName)Vue.component(module.default.n…...
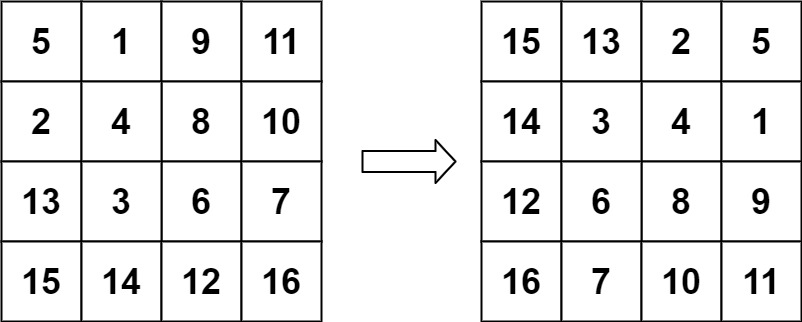
数据结构与算法之矩阵: Leetcode 48. 旋转矩阵 (Typescript版)
旋转图像 https://leetcode.cn/problems/rotate-image/ 描述 给定一个 n n 的二维矩阵 matrix 表示一个图像。请你将图像顺时针旋转 90 度。你必须在 原地 旋转图像,这意味着你需要直接修改输入的二维矩阵。请不要 使用另一个矩阵来旋转图像。 示例 1 输入&…...
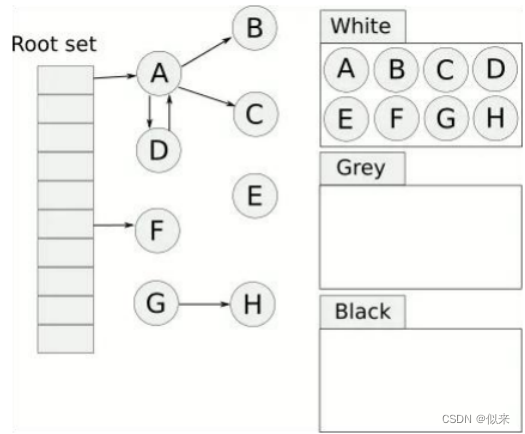
大厂面试题-JVM中的三色标记法是什么?
目录 问题分析 问题答案 问题分析 三色标记法是Java虚拟机(JVM)中垃圾回收算法的一种,主要用来标记内存中存活和需要回收的对象。 它的好处是,可以让JVM不发生或仅短时间发生STW(Stop The World),从而达到清除JVM内存垃圾的目的ÿ…...
Leetcode—121.买卖股票的最佳时机【简单】
2023每日刷题(十一) Leetcode—17.电话号码的字母组合 枚举法题解 参考自灵茶山艾府 枚举法实现代码 int maxProfit(int* prices, int pricesSize){int i;int max 0;int minPrice prices[0];for(i 1; i < pricesSize; i) {int tmp prices[i] -…...
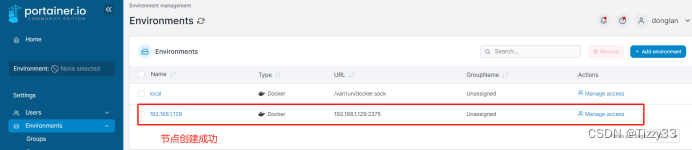
【云原生】portainer管理多个独立docker服务器
目录 一、portainer简介 二、安装Portainer 1.1 内网环境下: 1.1.1 方式1:命令行运行 1.1.2 方式2:通过compose-file来启动 2.1 配置本地主机(node-1) 3.1 配置其他主机(被node-1管理的节点服务器&…...

Command集合
Command集合 mysql相关命令 查看mysql的状态 sudo netstat -tap | grep mysql 启动mysql sudo service mysql start 停止mysql sudo service mysql stop 重启mysql sudo service mysql restart 指定端口号,客户端连接mysql sudo mysql -h127.0.0.1 -uroot -p red…...

<6>-MySQL表的增删查改
目录 一,create(创建表) 二,retrieve(查询表) 1,select列 2,where条件 三,update(更新表) 四,delete(删除表…...

大语言模型如何处理长文本?常用文本分割技术详解
为什么需要文本分割? 引言:为什么需要文本分割?一、基础文本分割方法1. 按段落分割(Paragraph Splitting)2. 按句子分割(Sentence Splitting)二、高级文本分割策略3. 重叠分割(Sliding Window)4. 递归分割(Recursive Splitting)三、生产级工具推荐5. 使用LangChain的…...

Java - Mysql数据类型对应
Mysql数据类型java数据类型备注整型INT/INTEGERint / java.lang.Integer–BIGINTlong/java.lang.Long–––浮点型FLOATfloat/java.lang.FloatDOUBLEdouble/java.lang.Double–DECIMAL/NUMERICjava.math.BigDecimal字符串型CHARjava.lang.String固定长度字符串VARCHARjava.lang…...
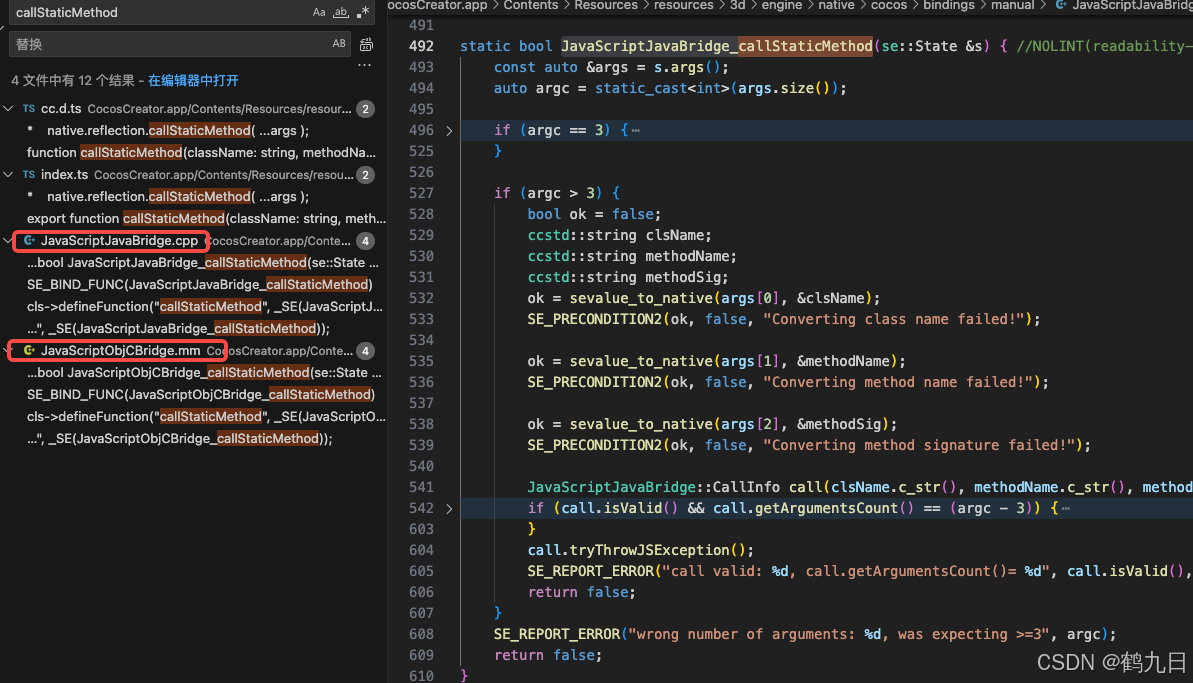
CocosCreator 之 JavaScript/TypeScript和Java的相互交互
引擎版本: 3.8.1 语言: JavaScript/TypeScript、C、Java 环境:Window 参考:Java原生反射机制 您好,我是鹤九日! 回顾 在上篇文章中:CocosCreator Android项目接入UnityAds 广告SDK。 我们简单讲…...

基于Docker Compose部署Java微服务项目
一. 创建根项目 根项目(父项目)主要用于依赖管理 一些需要注意的点: 打包方式需要为 pom<modules>里需要注册子模块不要引入maven的打包插件,否则打包时会出问题 <?xml version"1.0" encoding"UTF-8…...
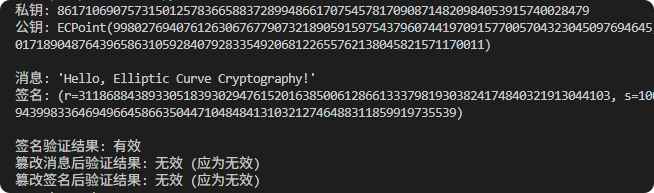
现代密码学 | 椭圆曲线密码学—附py代码
Elliptic Curve Cryptography 椭圆曲线密码学(ECC)是一种基于有限域上椭圆曲线数学特性的公钥加密技术。其核心原理涉及椭圆曲线的代数性质、离散对数问题以及有限域上的运算。 椭圆曲线密码学是多种数字签名算法的基础,例如椭圆曲线数字签…...
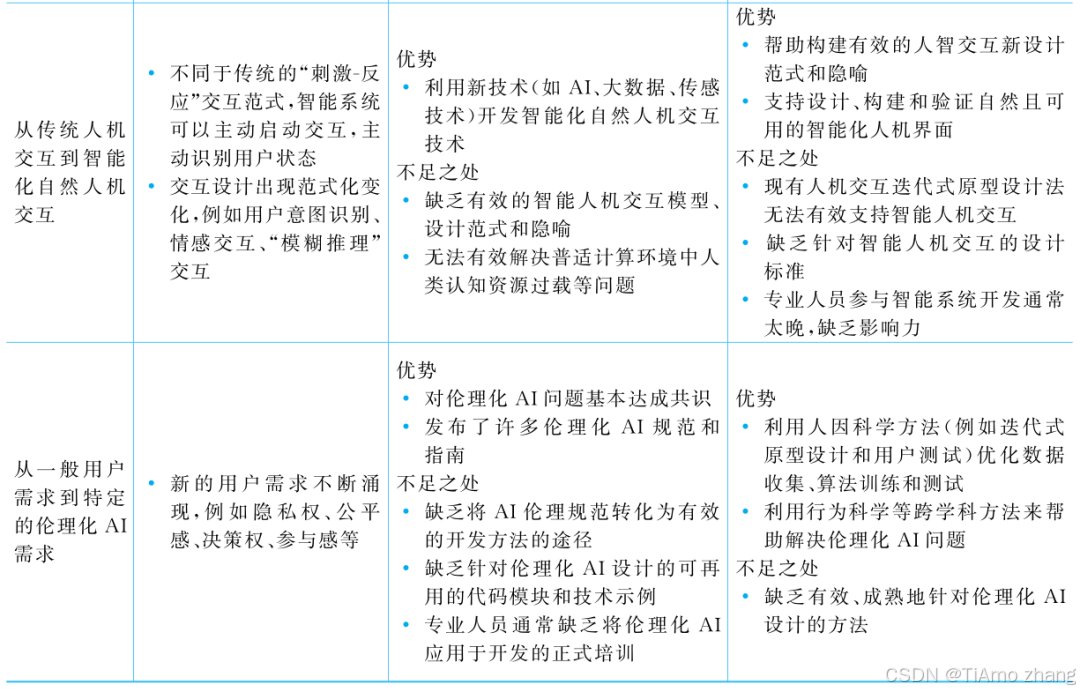
人机融合智能 | “人智交互”跨学科新领域
本文系统地提出基于“以人为中心AI(HCAI)”理念的人-人工智能交互(人智交互)这一跨学科新领域及框架,定义人智交互领域的理念、基本理论和关键问题、方法、开发流程和参与团队等,阐述提出人智交互新领域的意义。然后,提出人智交互研究的三种新范式取向以及它们的意义。最后,总结…...
宇树科技,改名了!
提到国内具身智能和机器人领域的代表企业,那宇树科技(Unitree)必须名列其榜。 最近,宇树科技的一项新变动消息在业界引发了不少关注和讨论,即: 宇树向其合作伙伴发布了一封公司名称变更函称,因…...

NPOI Excel用OLE对象的形式插入文件附件以及插入图片
static void Main(string[] args) {XlsWithObjData();Console.WriteLine("输出完成"); }static void XlsWithObjData() {// 创建工作簿和单元格,只有HSSFWorkbook,XSSFWorkbook不可以HSSFWorkbook workbook new HSSFWorkbook();HSSFSheet sheet (HSSFSheet)workboo…...
详细解析)
Caliper 负载(Workload)详细解析
Caliper 负载(Workload)详细解析 负载(Workload)是 Caliper 性能测试的核心部分,它定义了测试期间要执行的具体合约调用行为和交易模式。下面我将全面深入地讲解负载的各个方面。 一、负载模块基本结构 一个典型的负载模块(如 workload.js)包含以下基本结构: use strict;/…...
