C++系列之list的模拟实现

💗 💗 博客:小怡同学
💗 💗 个人简介:编程小萌新
💗 💗 如果博客对大家有用的话,请点赞关注再收藏 🌞
list的节点类
template
struct list_Node
{
public:
list_Node* _prev;
list_Node* _next;
T _val;
list_Node(const T& val = T())
{
_prev = _next = nullptr;
_val = val;
}
};`
list的迭代器类
//这里写入多个参数的目的是区分const迭代器
//传入不同的模板就会有不同的类
template<class T,class Ref ,class Ptr>
struct list_iterator
{public:typedef list_Node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> self;list_iterator(Node* node = nullptr){_node = node;}list_iterator(const self& i){_node(i._node);}//const对象不改变原数据T& operator*(){return _node->_val;}T* operator->(){return &_node->val;}self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(_node);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self& operator--(int){self tmp(_node);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const self& l){return _node != l._node;}bool operator==(const self& l){return _node == l._node;}Node* _node;};构造函数
list(int n, const T& value = T())
{_head = new Node();_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;while (n--){push_back(value);}
}
template <class Intiterator>
list(Intiterator first, Intiterator last)
{//这三行代码的作用是制造一个头结点_head = new Node();_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;while (first != last){push_back(*first);first++;}
}
list(const list<T>& l)
{_head = new Node();_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;//这里制造一个list对象,构建与l对象一样的元素,在与*this进行调换。list<T> tmp (l.begin(),l.end());swap(tmp);
}
析构函数
~list()
{clear();//复用clear()函数,如果元素是自定义类型,则一一析构,delete _head;_head = nullptr;
}赋值运算符=
list<T>& operator=(const list<T> l)
{swap(l);return *this;
}
迭代器的使用
iterator begin()
{return iterator(_head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{return itertor(_head);
}
//const对象迭代器的使用返回的是const指针(实际上迭代器是一个模板,只是类型不同)
const_iterator begin()const
{return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator end()const
{return itertor(_head);
}
list的元素大小和判空
size_t size()const//const与非const对象都可调用
{return _size;
}
bool empty()const
{return _size == 0;
}
访问list的头节点与尾节点
T& front()
{return _head->_next->_val;
}
const T& front()const
{return _head->_next->_val;
}
T& back()
{return _head->_prev->_val;
}
const T& back()const
{return _head->_prev->_val;
}
尾插,尾删,头插,尾删,插入,删除,交换,清空
//这里使用了函数的调用
void push_back(const T& val)
{insert(end(), val);
}
void pop_back()
{ erase(--end());
}
void push_front(const T& val)
{ insert(begin(), val);
}
void pop_front()
{ erase(begin());
}
// 在pos位置前插入值为val的节点
//这里不会发生迭代器的失效,迭代器没有被改变,返回时返回pos之前的迭代器
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val)
{Node* newnode = new Node(val);Node* node_pos = pos.Node;Node* prev = node_pos->_prev;Node* next = node_pos->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;return newnode;
}
// 删除pos位置的节点,返回该节点的下一个位置
//这里发生迭代器的失效。指向pos指针变成野指针,返回时需要更新到该节点的下一个位置
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{Node* node_pos = pos.Node;Node* node_next = pos.Node->_next;node_pos->_prev->_next = node_pos->_next;node_next->_prev = node_pos->_prev;delete node_pos;return iterator(node_next);
}
//清除链表,只保留头节点
void clear()
{iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){erase(it);}_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;
}
//交换链表
void swap(const list<T>& L)
{Node* tmp = L._head;L._head = tmp;tmp = _head;
}
#include <assert.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace zjy
{template<class T>struct list_Node{public:list_Node* _prev;list_Node* _next;T _val;list_Node(const T& val = T()){_prev = _next = nullptr;_val = val;}};template<class T,class Ref ,class Ptr>struct list_iterator{public:typedef list_Node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> self;list_iterator(Node* node = nullptr){_node = node;}list_iterator(const self& i){_node(i._node);}T& operator*(){return _node->_val;}T* operator->(){return &_node->val;}self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(_node);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self& operator--(int){self tmp(_node);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const self& l){return _node != l._node;}bool operator==(const self& l){return _node == l._node;}Node* _node;};template<class T>class list{public:typedef list_Node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;list(){_head = new Node();_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;}/*list(int n, const T& value = T()){_head = new Node();_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;while (n--){Node* newnode = new Node(value);Node* tail = _head->_prev;tail -> _next = newnode;newnode->_prev = _head;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;tail = newnode;}}*/list(int n, const T& value = T()){_head = new Node();_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;while (n--){push_back(value);}}/*template <class Intiterator>list(Intiterator first, Intiterator last){_head = new Node();_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;Node* begin= first._node;Node* end = last._node;Node* tail = _head->_prev;while (begin != last){tail->_next = begin;begin->_prev = tail;begin->_next = _head;_head->_prev = begin;tail = begin;begin++;}}*/template <class Intiterator>list(Intiterator first, Intiterator last){_head = new Node();_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;while (first != last){push_back(*first);first++;}}void swap(const list<T>& L){Node* tmp = L._head;L._head = tmp;tmp = _head;}list(const list<T>& l){_head = new Node();_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;list<T> tmp (l.begin(),l.end());swap(tmp);}list<T>& operator=(const list<T> l){swap(l);return *this;}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return itertor(_head);}const_iterator begin()const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end()const{return const_itertor(_head);}size_t size()const{return _size;}bool empty()const{return _size == 0;}T& front(){return _head->_next->_val;}const T& front()const{return _head->_next->_val;}T& back(){return _head->_prev->_val;}const T& back()const{return _head->_prev->_val;}void push_back(const T& val) {insert(end(), val); }void pop_back() { erase(--end()); }void push_front(const T& val) { insert(begin(), val); }void pop_front() { erase(begin()); }// 在pos位置前插入值为val的节点iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val){Node* newnode = new Node(val);Node* node_pos = pos.Node;Node* prev = node_pos->_prev;Node* next = node_pos->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;return newnode;}// 删除pos位置的节点,返回该节点的下一个位置iterator erase(iterator pos){Node* node_pos = pos.Node;Node* node_next = pos.Node->_next;node_pos->_prev->_next = node_pos->_next;node_next->_prev = node_pos->_prev;delete node_pos;return iterator(node_next);}void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){erase(it);}_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;}void test(){Node* tmp = _head->_next;while (tmp != _head){cout << tmp->_val << endl;tmp = tmp->_next;}}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};
}

相关文章:

C++系列之list的模拟实现
💗 💗 博客:小怡同学 💗 💗 个人简介:编程小萌新 💗 💗 如果博客对大家有用的话,请点赞关注再收藏 🌞 list的节点类 template struct list_Node { public: list_Node* _prev; list_…...
?)
什么情况下你会使用AI工具(chatgpt、bard)?
在当今数字化和智能化的时代,AI工具已成为许多领域的常见工具。在本文中,我将探讨什么情况下会使用AI工具。前言 – 人工智能教程 ChatGPT是一款由OpenAI开发的大型语言模型,可以生成文本、翻译语言、编写不同类型的创意内容,并以…...
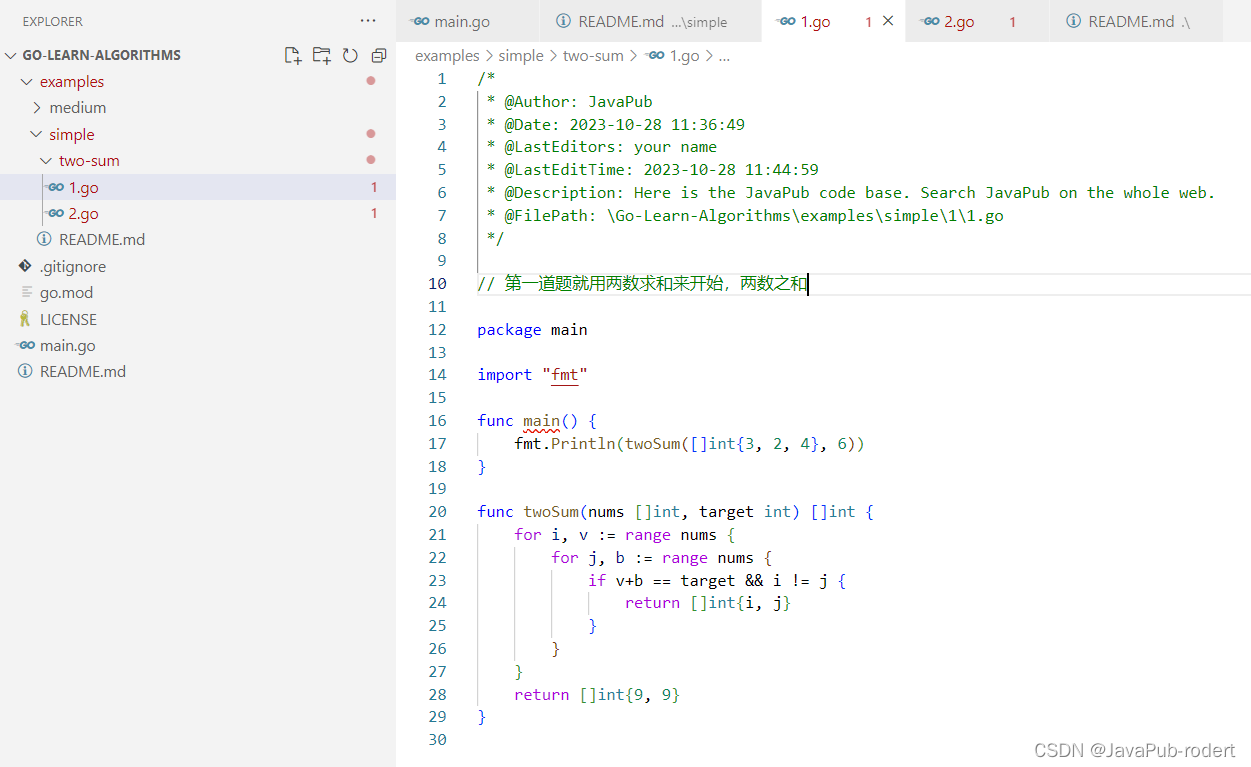
【go】两数求和
文章目录 题目代码解法2 代码仓库 题目 给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。 你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案…...

软考高项-成本管理
工具和技术 三点估算 通过考虑估算中的不确定性与风险,使用3种估算值来界定活动成本的近似区间,可以提高活动成本估算的准确性; 储备分析 为应对成本的不确定性,成本估算中可以包括应急储备。应急储备的管理方法: 将…...

24年FRM备考知识点以及一级公式表
FRM一级公示表以及备考知识点 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/17RpFF9OyfRk7FGtEQrxf3A?pwd1234 提取码:1234 FRM二级公示表以及备考知识点 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/175D05wV1p94dIfBZThutCQ?pwd1234 提取码:1234...
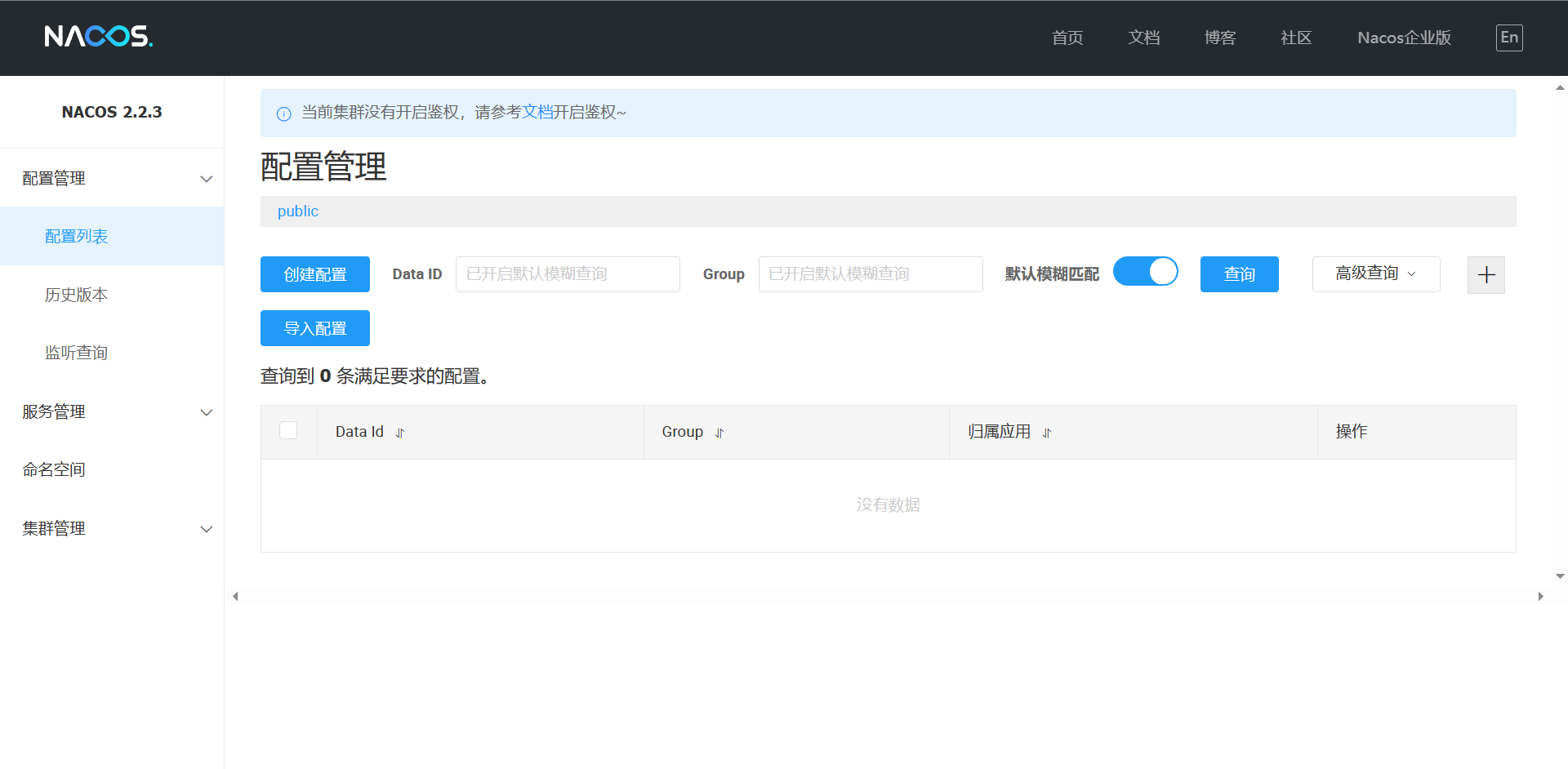
Spring Cloud学习:二【详细】
目录 Nacos的配置 Nacos的单机启动 服务注册 Nacos服务分级存储模型 优先访问同集群的服务 根据权重负载均衡 环境隔离Namespace Nacos调用流程 Nacos与Eureka注册对比 Nacos与Eureka的共同点 Nacos与Eureka的区别 Nacos配置管理 统一配置 配置自动刷新 多环境配…...

Unity的live2dgalgame多语言可配置剧情框架
这段代码用于读取表格 using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; using OfficeOpenXml; using System.IO; using UnityEngine.Networking; using UnityEngine.UI; using Random UnityEngine.Random;public class Plots…...

再畅通工程(最小生成树)
题目描述:还是畅通工程 某省调查乡村交通状况,得到的统计表中列出了任意两村庄间的距离。省政府“畅通工程”的目标是使全省任何两个村庄间都可以实现公路交通(但不一定有直接的公路相连,只要能间接通过公路可达即可)&…...
前后端分离不可忽视的陷阱,深入剖析挑战,分享解决方案,助你顺利实施分离开发。
不管你设计的系统架构是怎么样,最后都是你的组织内的沟通结构胜出。这个观点一直在组织内不断地被证明,但也不断地被忽略。 前后端分离的利与弊 近几年,随着微服务架构风格的引入、前后端生态的快速发展、多端产品化的出现,前后…...
(四)库存超卖案例实战——优化redis分布式锁
前言 在上一节内容中,我们已经实现了使用redis分布式锁解决商品“超卖”的问题,本节内容是对redis分布式锁的优化。在上一节的redis分布式锁中,我们的锁有俩个可以优化的问题。第一,锁需要实现可重入,同一个线程不用重…...
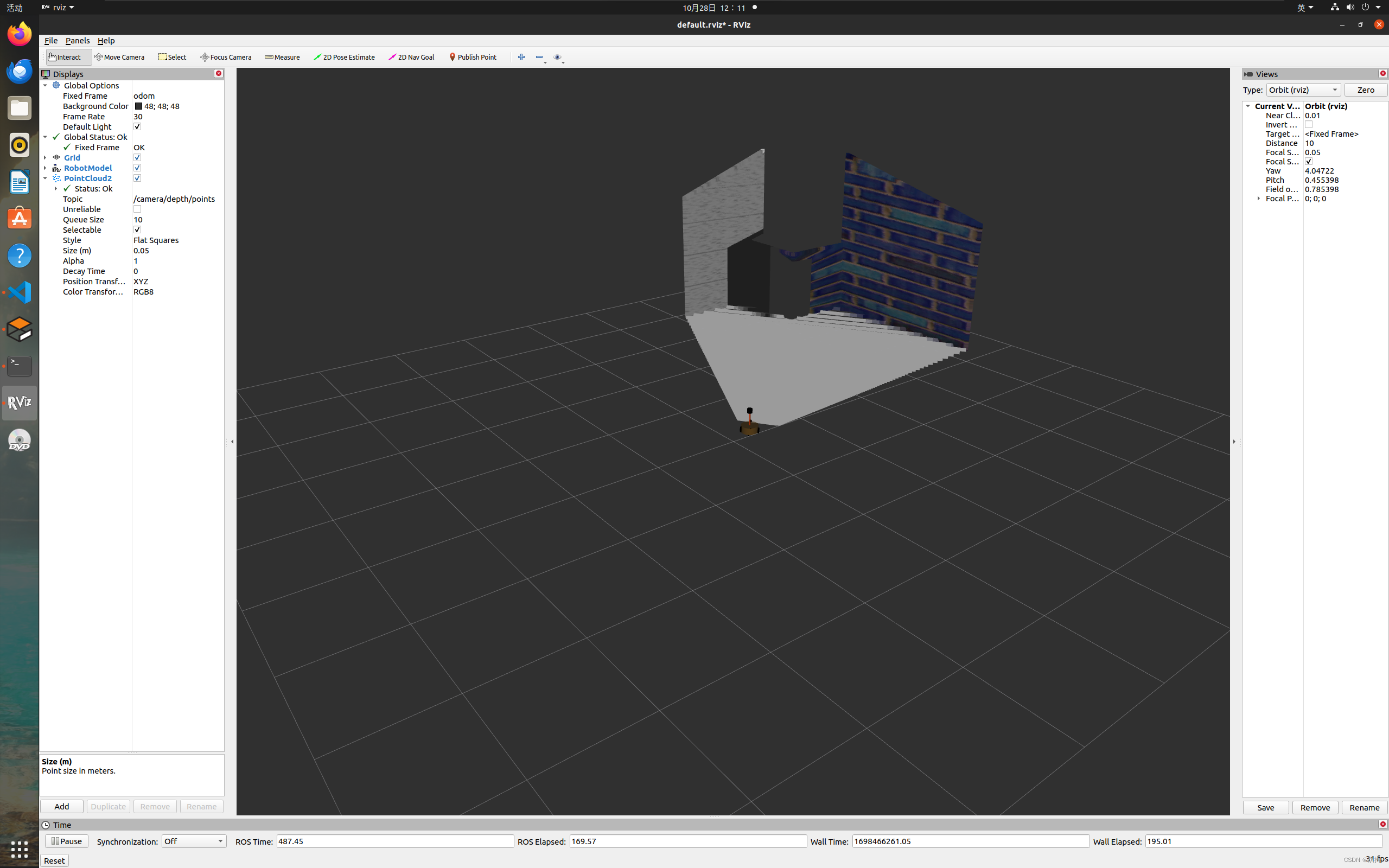
【ROS入门】雷达、摄像头及kinect信息仿真以及显示
文章结构 雷达信息仿真以及显示Gazebo仿真雷达配置雷达传感器信息xacro文件集成启动仿真环境 Rviz显示雷达数据 摄像头信息仿真以及显示Gazebo仿真摄像头新建xacro文件,配置摄像头传感器信息xacro文件集成启动仿真环境 Rviz显示摄像头数据 kinect信息仿真以及显示Ga…...
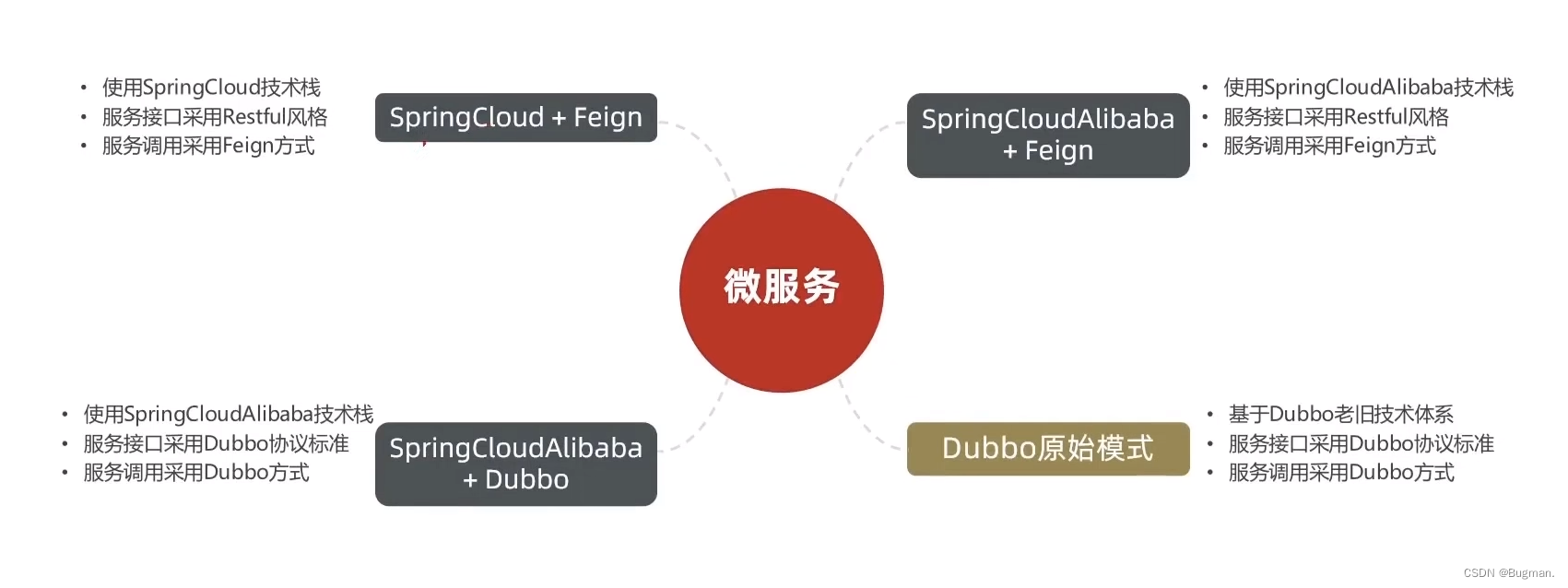
实用篇-认识微服务
一、服务架构演变 1. 单体架构 单体架构:将业务的所有功能集中在一个项目中开发,打成一个包部署 单体架构的优点: 架构简单部署成本低 单体架构的缺点: 耦合度高 2. 分布式架构 分布式架构: 根据业务功能对系…...

【产品运营】产品需求应该如何管理
产品项目在进行时经常会有一些需求需要实现,需求是产品更新迭代的动力,需求也是从用户诉求转化而来;在做需求管理时,我们需要判断一个需求的优先级等方面,对产品进行优化; 目录: 一、 为什么要…...
Linux 系统调用IO口,利用光标偏移实现文件复制
用系统调用IO函数实现从一个文件读取最后2KB数据并复制到另一个文件中,源文件以只读方式打开,目标文件以只写的方式打开,若目标文件不存在,可以创建并设置初始值为0664,写出相应代码,要对出错情况有一定的处…...

【原创】指针变量作为函数参数要点注意
指针变量作为函数参数要点注意(已写至笔记) 1传参指针不加*(main中函数) 2收参指针要加*(被main调用的函数) 3传参指针名可与收参指针名不同,不影响 4【问】如何看主函数中指针所指内容是否改变…...
SpringMVC Day 04 : 数据绑定
前言 SpringMVC是一个非常流行的Java Web框架,它提供了很多方便的功能和工具来帮助我们构建高效、灵活的Web应用程序。其中,数据绑定就是SpringMVC中非常重要的一部分,它可以帮助我们方便地将请求参数绑定到Java对象上,从而简化了…...

2.3.1 协程设计原理与汇编实现
1.为什么要有协程? 同步的编程方式,异步的性能。同步编程时,我们需要等待io就绪。但是在协程这里,我们使用一种机制,当io需要等待时,就切到下一个io,之后当之前的io就绪时,再切换回来…...
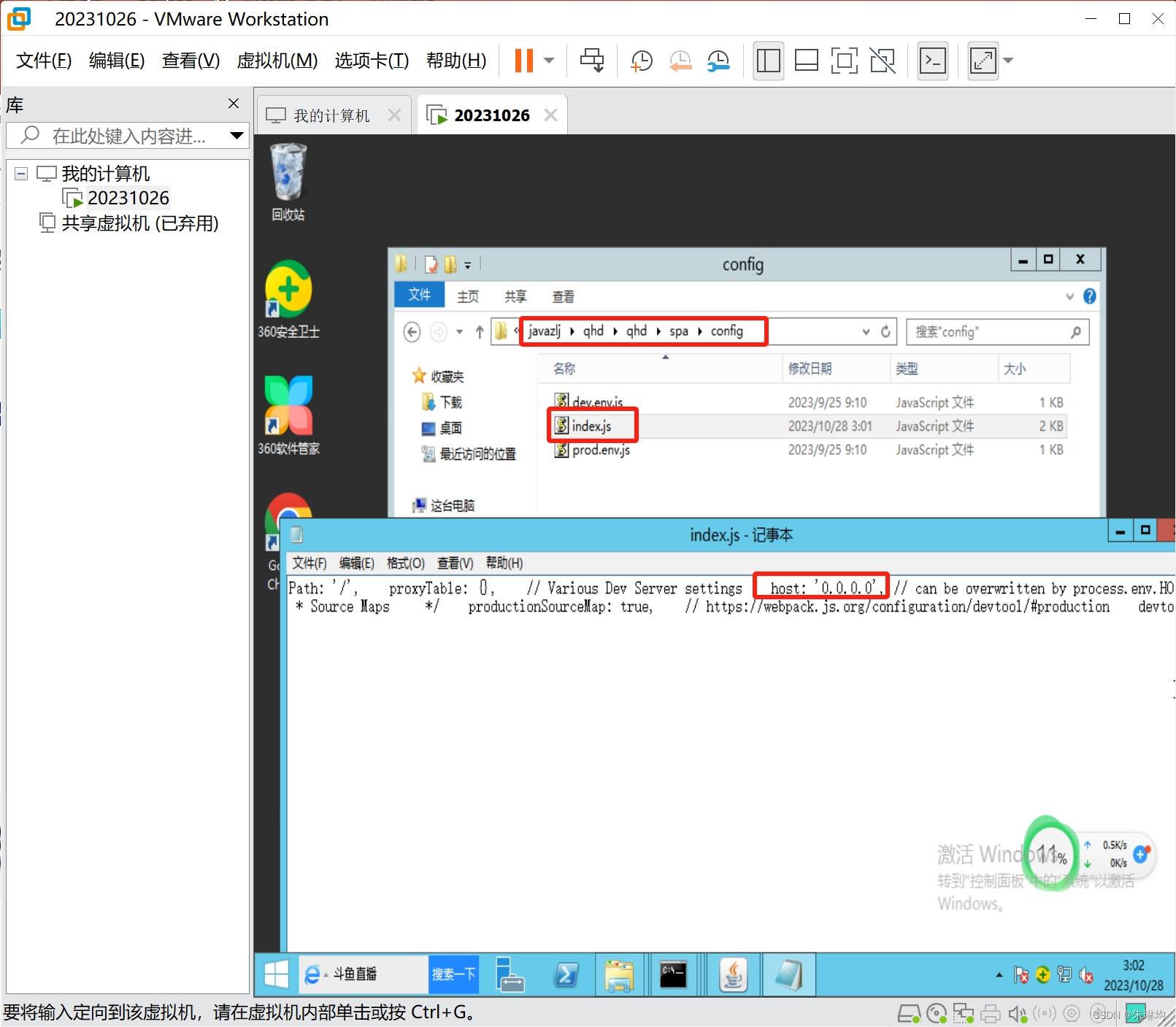
J2EE项目部署与发布(Windows版本)->会议OA单体项目Windows部署,spa前后端分离项目Windows部署
会议OA单体项目Windows部署spa前后端分离项目Windows部署 1.会议OA单体项目Windows部署(以实施的角度) 将项目放入webapp,项目能够访问: 首先拿到war包和数据库脚本,并检查是否有什么问题。 如何查看项目报错信息(当你…...

Lua脚本语言
1. 概念 Lua(发音为"loo-ah",葡萄牙语中的"lua"意为月亮)是一种轻量级的、高效的、可嵌入的脚本编程语言。官网Lua最初由巴西计算机科学家Roberto Ierusalimschy、Waldemar Celes和Luiz Henrique de Figueiredo于1993年开…...
函数和print()函数的区别)
cat()函数和print()函数的区别
目录 区别一: 区别二: cat、print函数都是输出函数。 区别一: cat()函数不能赋值; print()函数可以赋值。 x<-cat("hello world") //赋值 hello world x //cat函数无返回值 NULLy<-print("hello …...
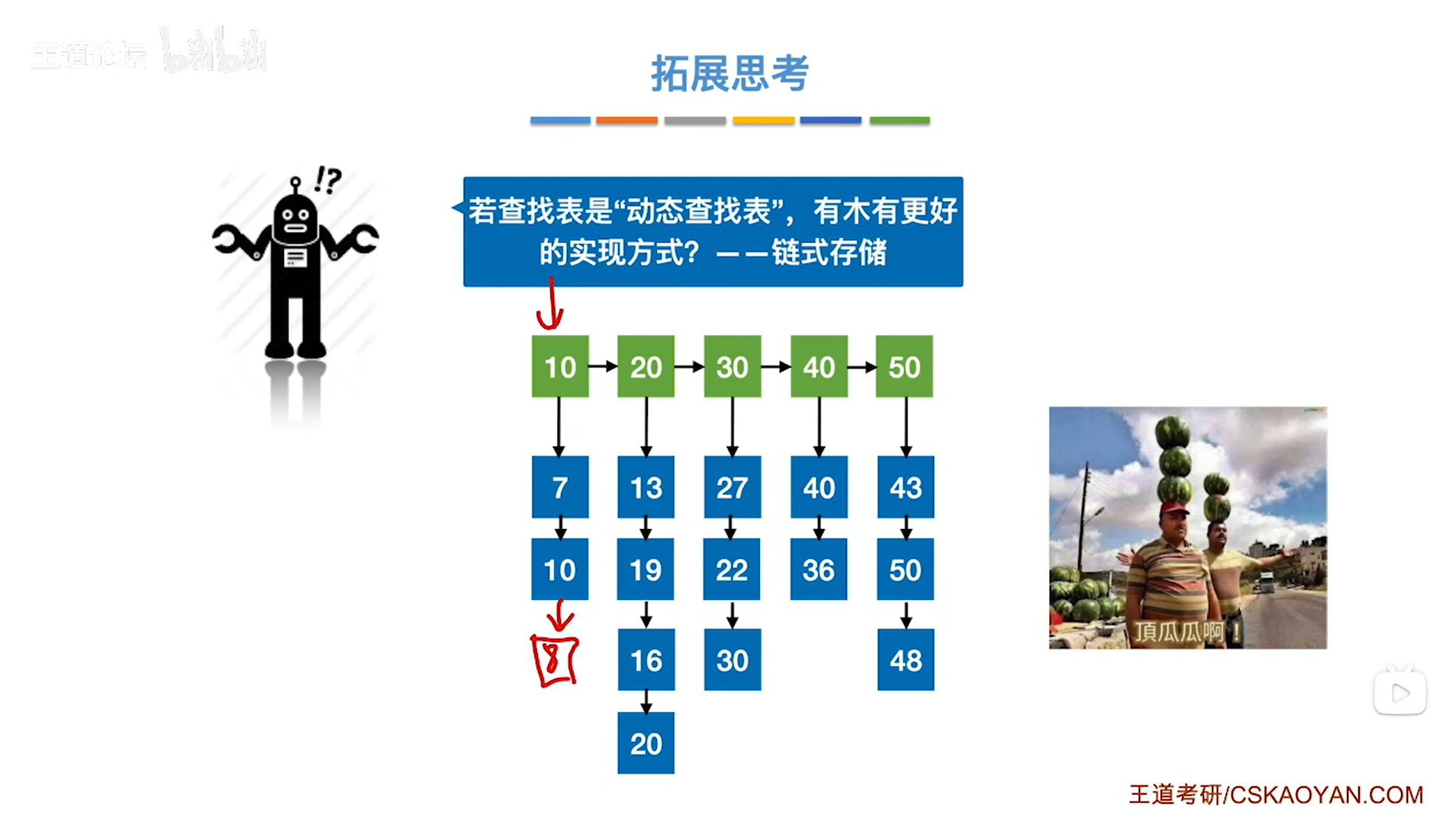
7.4.分块查找
一.分块查找的算法思想: 1.实例: 以上述图片的顺序表为例, 该顺序表的数据元素从整体来看是乱序的,但如果把这些数据元素分成一块一块的小区间, 第一个区间[0,1]索引上的数据元素都是小于等于10的, 第二…...
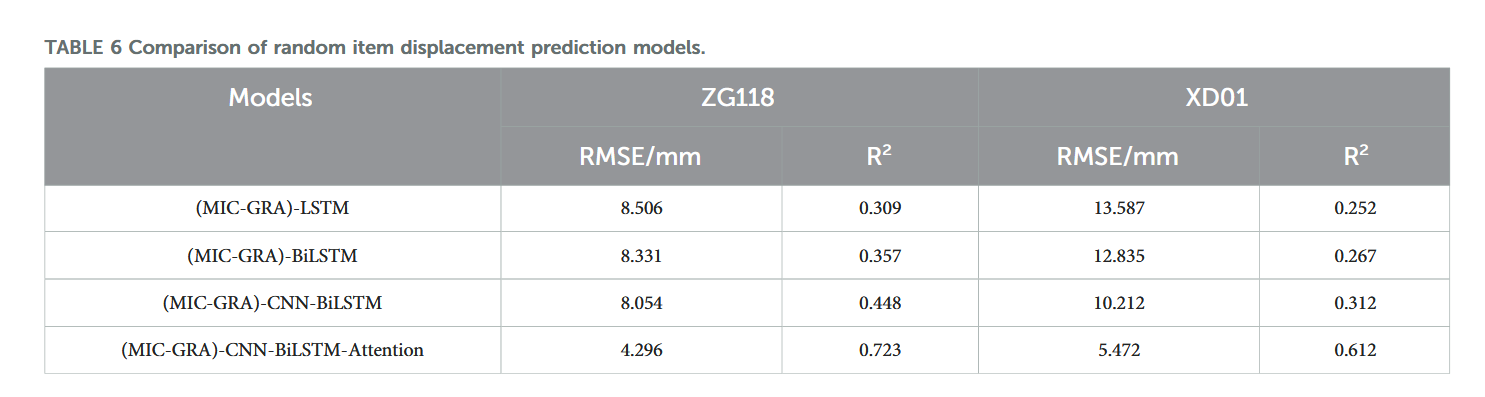
【论文阅读28】-CNN-BiLSTM-Attention-(2024)
本文把滑坡位移序列拆开、筛优质因子,再用 CNN-BiLSTM-Attention 来动态预测每个子序列,最后重构出总位移,预测效果超越传统模型。 文章目录 1 引言2 方法2.1 位移时间序列加性模型2.2 变分模态分解 (VMD) 具体步骤2.3.1 样本熵(S…...
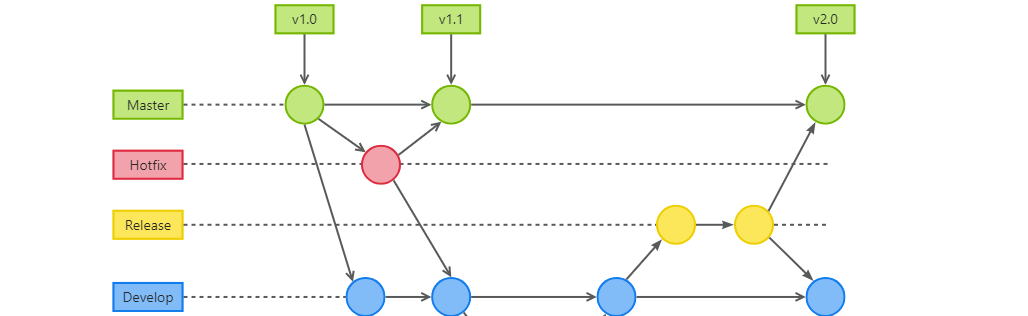
GitFlow 工作模式(详解)
今天再学项目的过程中遇到使用gitflow模式管理代码,因此进行学习并且发布关于gitflow的一些思考 Git与GitFlow模式 我们在写代码的时候通常会进行网上保存,无论是github还是gittee,都是一种基于git去保存代码的形式,这样保存代码…...
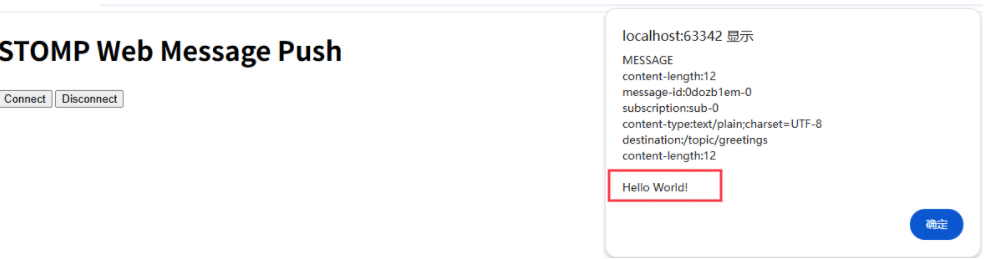
RabbitMQ入门4.1.0版本(基于java、SpringBoot操作)
RabbitMQ 一、RabbitMQ概述 RabbitMQ RabbitMQ最初由LShift和CohesiveFT于2007年开发,后来由Pivotal Software Inc.(现为VMware子公司)接管。RabbitMQ 是一个开源的消息代理和队列服务器,用 Erlang 语言编写。广泛应用于各种分布…...

GraphRAG优化新思路-开源的ROGRAG框架
目前的如微软开源的GraphRAG的工作流程都较为复杂,难以孤立地评估各个组件的贡献,传统的检索方法在处理复杂推理任务时可能不够有效,特别是在需要理解实体间关系或多跳知识的情况下。先说结论,看完后感觉这个框架性能上不会比Grap…...
Android屏幕刷新率与FPS(Frames Per Second) 120hz
Android屏幕刷新率与FPS(Frames Per Second) 120hz 屏幕刷新率是屏幕每秒钟刷新显示内容的次数,单位是赫兹(Hz)。 60Hz 屏幕:每秒刷新 60 次,每次刷新间隔约 16.67ms 90Hz 屏幕:每秒刷新 90 次,…...

JavaScript 标签加载
目录 JavaScript 标签加载script 标签的 async 和 defer 属性,分别代表什么,有什么区别1. 普通 script 标签2. async 属性3. defer 属性4. type"module"5. 各种加载方式的对比6. 使用建议 JavaScript 标签加载 script 标签的 async 和 defer …...

python基础语法Ⅰ
python基础语法Ⅰ 常量和表达式变量是什么变量的语法1.定义变量使用变量 变量的类型1.整数2.浮点数(小数)3.字符串4.布尔5.其他 动态类型特征注释注释是什么注释的语法1.行注释2.文档字符串 注释的规范 常量和表达式 我们可以把python当作一个计算器,来进行一些算术…...

使用homeassistant 插件将tasmota 接入到米家
我写一个一个 将本地tasmoat的的设备同通过ha集成到小爱同学的功能,利用了巴法接入小爱的功能,将本地mqtt转发给巴法以实现小爱控制的功能,前提条件。1需要tasmota 设备, 2.在本地搭建了mqtt服务可, 3.搭建了ha 4.在h…...
无头浏览器技术:Python爬虫如何精准模拟搜索点击
1. 无头浏览器技术概述 1.1 什么是无头浏览器? 无头浏览器是一种没有图形用户界面(GUI)的浏览器,它通过程序控制浏览器内核(如Chromium、Firefox)执行页面加载、JavaScript渲染、表单提交等操作。由于不渲…...
