spring-boot-starter-data-redis2.X连接redis7
由于redis7引入了acl机制,可以配置用户权限,
比如配置了一个普通用户 test,权限为 test_ 前缀的key可操作
springboot想要连接,并没有设置用户名的地方,
跟了源码,jedis客户端是支持的,但是springboot自动配置类并没有用用户名去连接,因此需要手动覆盖一些源码去实现该功能;可能高版本springboot没这个问题,但由于项目用的1.8,高版本需要升级jdk,不可能的;
以下实现方式纯属跟代码去改造的,可能还有其他方式,但是我在网上也没有搜到解决办法
我的项目使用的是jedis,lettuce我没看
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId><version>2.3.7.RELEASE</version><exclusions><exclusion><groupId>io.lettuce</groupId><artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId></exclusion></exclusions></dependency><dependency><groupId>redis.clients</groupId><artifactId>jedis</artifactId><version>3.3.0</version></dependency>springboot通过用户名连接单机版redis7,
连接配置如下
spring:redis:host: ipport: 6379# 密码user: testpassword: test@123只需要覆盖一个文件
新建包目录 redis.clients.jedis
新建类BinaryClient.java
package redis.clients.jedis;import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import redis.clients.jedis.Protocol.Keyword;
import redis.clients.jedis.params.*;
import redis.clients.jedis.util.SafeEncoder;import javax.net.ssl.HostnameVerifier;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLParameters;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;import static redis.clients.jedis.Protocol.Command.EXISTS;
import static redis.clients.jedis.Protocol.Command.GET;
import static redis.clients.jedis.Protocol.Command.KEYS;
import static redis.clients.jedis.Protocol.Command.PING;
import static redis.clients.jedis.Protocol.Command.PSUBSCRIBE;
import static redis.clients.jedis.Protocol.Command.PUNSUBSCRIBE;
import static redis.clients.jedis.Protocol.Command.SET;
import static redis.clients.jedis.Protocol.Command.SUBSCRIBE;
import static redis.clients.jedis.Protocol.Command.TIME;
import static redis.clients.jedis.Protocol.Command.UNSUBSCRIBE;
import static redis.clients.jedis.Protocol.Command.*;
import static redis.clients.jedis.Protocol.Keyword.*;
import static redis.clients.jedis.Protocol.toByteArray;public class BinaryClient extends Connection {private boolean isInMulti;private String user;private String password;private int db;private boolean isInWatch;{String user = SpringUtils.getApplicationContext().getEnvironment().getProperty("spring.redis.user");if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(user)){this.user = user;}}public BinaryClient() {super();}public BinaryClient(final String host) {super(host);}public BinaryClient(final String host, final int port) {super(host, port);}public BinaryClient(final String host, final int port, final boolean ssl) {super(host, port, ssl);}public BinaryClient(final String host, final int port, final boolean ssl,final SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory, final SSLParameters sslParameters,final HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier) {super(host, port, ssl, sslSocketFactory, sslParameters, hostnameVerifier);}public BinaryClient(final JedisSocketFactory jedisSocketFactory) {super(jedisSocketFactory);}public boolean isInMulti() {return isInMulti;}public boolean isInWatch() {return isInWatch;}private byte[][] joinParameters(byte[] first, byte[][] rest) {byte[][] result = new byte[rest.length + 1][];result[0] = first;System.arraycopy(rest, 0, result, 1, rest.length);return result;}private byte[][] joinParameters(byte[] first, byte[] second, byte[][] rest) {byte[][] result = new byte[rest.length + 2][];result[0] = first;result[1] = second;System.arraycopy(rest, 0, result, 2, rest.length);return result;}public void setUser(final String user) { this.user = user; }public void setPassword(final String password) {this.password = password;}public void setDb(int db) {this.db = db;}@Overridepublic void connect() {if (!isConnected()) {super.connect();if (user != null&&password !=null) {auth(user, password);getStatusCodeReply();} else if (password != null) {auth(password);getStatusCodeReply();}if (db > 0) {select(db);getStatusCodeReply();}}}public void ping() {sendCommand(PING);}public void ping(final byte[] message) {sendCommand(PING, message);}public void set(final byte[] key, final byte[] value) {sendCommand(SET, key, value);}public void set(final byte[] key, final byte[] value, final SetParams params) {sendCommand(SET, params.getByteParams(key, value));}public void get(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(GET, key);}public void quit() {db = 0;sendCommand(QUIT);}public void exists(final byte[]... keys) {sendCommand(EXISTS, keys);}public void del(final byte[]... keys) {sendCommand(DEL, keys);}public void unlink(final byte[]... keys) {sendCommand(UNLINK, keys);}public void type(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(TYPE, key);}public void flushDB() {sendCommand(FLUSHDB);}public void keys(final byte[] pattern) {sendCommand(KEYS, pattern);}public void randomKey() {sendCommand(RANDOMKEY);}public void rename(final byte[] oldkey, final byte[] newkey) {sendCommand(RENAME, oldkey, newkey);}public void renamenx(final byte[] oldkey, final byte[] newkey) {sendCommand(RENAMENX, oldkey, newkey);}public void dbSize() {sendCommand(DBSIZE);}public void expire(final byte[] key, final int seconds) {sendCommand(EXPIRE, key, toByteArray(seconds));}public void expireAt(final byte[] key, final long unixTime) {sendCommand(EXPIREAT, key, toByteArray(unixTime));}public void ttl(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(TTL, key);}public void touch(final byte[]... keys) {sendCommand(TOUCH, keys);}public void select(final int index) {sendCommand(SELECT, toByteArray(index));}public void swapDB(final int index1, final int index2) {sendCommand(SWAPDB, toByteArray(index1), toByteArray(index2));}public void move(final byte[] key, final int dbIndex) {sendCommand(MOVE, key, toByteArray(dbIndex));}public void flushAll() {sendCommand(FLUSHALL);}public void getSet(final byte[] key, final byte[] value) {sendCommand(GETSET, key, value);}public void mget(final byte[]... keys) {sendCommand(MGET, keys);}public void setnx(final byte[] key, final byte[] value) {sendCommand(SETNX, key, value);}public void setex(final byte[] key, final int seconds, final byte[] value) {sendCommand(SETEX, key, toByteArray(seconds), value);}public void mset(final byte[]... keysvalues) {sendCommand(MSET, keysvalues);}public void msetnx(final byte[]... keysvalues) {sendCommand(MSETNX, keysvalues);}public void decrBy(final byte[] key, final long decrement) {sendCommand(DECRBY, key, toByteArray(decrement));}public void decr(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(DECR, key);}public void incrBy(final byte[] key, final long increment) {sendCommand(INCRBY, key, toByteArray(increment));}public void incrByFloat(final byte[] key, final double increment) {sendCommand(INCRBYFLOAT, key, toByteArray(increment));}public void incr(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(INCR, key);}public void append(final byte[] key, final byte[] value) {sendCommand(APPEND, key, value);}public void substr(final byte[] key, final int start, final int end) {sendCommand(SUBSTR, key, toByteArray(start), toByteArray(end));}public void hset(final byte[] key, final byte[] field, final byte[] value) {sendCommand(HSET, key, field, value);}public void hset(final byte[] key, final Map<byte[], byte[]> hash) {final byte[][] params = new byte[1 + hash.size() * 2][];int index = 0;params[index++] = key;for (final Entry<byte[], byte[]> entry : hash.entrySet()) {params[index++] = entry.getKey();params[index++] = entry.getValue();}sendCommand(HSET, params);}public void hget(final byte[] key, final byte[] field) {sendCommand(HGET, key, field);}public void hsetnx(final byte[] key, final byte[] field, final byte[] value) {sendCommand(HSETNX, key, field, value);}public void hmset(final byte[] key, final Map<byte[], byte[]> hash) {final List<byte[]> params = new ArrayList<>();params.add(key);for (final Entry<byte[], byte[]> entry : hash.entrySet()) {params.add(entry.getKey());params.add(entry.getValue());}sendCommand(HMSET, params.toArray(new byte[params.size()][]));}public void hmget(final byte[] key, final byte[]... fields) {sendCommand(HMGET, joinParameters(key, fields));}public void hincrBy(final byte[] key, final byte[] field, final long value) {sendCommand(HINCRBY, key, field, toByteArray(value));}public void hexists(final byte[] key, final byte[] field) {sendCommand(HEXISTS, key, field);}public void hdel(final byte[] key, final byte[]... fields) {sendCommand(HDEL, joinParameters(key, fields));}public void hlen(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(HLEN, key);}public void hkeys(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(HKEYS, key);}public void hvals(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(HVALS, key);}public void hgetAll(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(HGETALL, key);}public void rpush(final byte[] key, final byte[]... strings) {sendCommand(RPUSH, joinParameters(key, strings));}public void lpush(final byte[] key, final byte[]... strings) {sendCommand(LPUSH, joinParameters(key, strings));}public void llen(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(LLEN, key);}public void lrange(final byte[] key, final long start, final long stop) {sendCommand(LRANGE, key, toByteArray(start), toByteArray(stop));}public void ltrim(final byte[] key, final long start, final long stop) {sendCommand(LTRIM, key, toByteArray(start), toByteArray(stop));}public void lindex(final byte[] key, final long index) {sendCommand(LINDEX, key, toByteArray(index));}public void lset(final byte[] key, final long index, final byte[] value) {sendCommand(LSET, key, toByteArray(index), value);}public void lrem(final byte[] key, final long count, final byte[] value) {sendCommand(LREM, key, toByteArray(count), value);}public void lpop(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(LPOP, key);}public void rpop(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(RPOP, key);}public void rpoplpush(final byte[] srckey, final byte[] dstkey) {sendCommand(RPOPLPUSH, srckey, dstkey);}public void sadd(final byte[] key, final byte[]... members) {sendCommand(SADD, joinParameters(key, members));}public void smembers(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(SMEMBERS, key);}public void srem(final byte[] key, final byte[]... members) {sendCommand(SREM, joinParameters(key, members));}public void spop(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(SPOP, key);}public void spop(final byte[] key, final long count) {sendCommand(SPOP, key, toByteArray(count));}public void smove(final byte[] srckey, final byte[] dstkey, final byte[] member) {sendCommand(SMOVE, srckey, dstkey, member);}public void scard(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(SCARD, key);}public void sismember(final byte[] key, final byte[] member) {sendCommand(SISMEMBER, key, member);}public void sinter(final byte[]... keys) {sendCommand(SINTER, keys);}public void sinterstore(final byte[] dstkey, final byte[]... keys) {sendCommand(SINTERSTORE, joinParameters(dstkey, keys));}public void sunion(final byte[]... keys) {sendCommand(SUNION, keys);}public void sunionstore(final byte[] dstkey, final byte[]... keys) {sendCommand(SUNIONSTORE, joinParameters(dstkey, keys));}public void sdiff(final byte[]... keys) {sendCommand(SDIFF, keys);}public void sdiffstore(final byte[] dstkey, final byte[]... keys) {sendCommand(SDIFFSTORE, joinParameters(dstkey, keys));}public void srandmember(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(SRANDMEMBER, key);}public void zadd(final byte[] key, final double score, final byte[] member) {sendCommand(ZADD, key, toByteArray(score), member);}public void zadd(final byte[] key, final double score, final byte[] member,final ZAddParams params) {sendCommand(ZADD, params.getByteParams(key, toByteArray(score), member));}public void zadd(final byte[] key, final Map<byte[], Double> scoreMembers) {ArrayList<byte[]> args = new ArrayList<>(scoreMembers.size() * 2 + 1);args.add(key);args.addAll(convertScoreMembersToByteArrays(scoreMembers));byte[][] argsArray = new byte[args.size()][];args.toArray(argsArray);sendCommand(ZADD, argsArray);}public void zadd(final byte[] key, final Map<byte[], Double> scoreMembers, final ZAddParams params) {ArrayList<byte[]> args = convertScoreMembersToByteArrays(scoreMembers);byte[][] argsArray = new byte[args.size()][];args.toArray(argsArray);sendCommand(ZADD, params.getByteParams(key, argsArray));}public void zrange(final byte[] key, final long start, final long stop) {sendCommand(ZRANGE, key, toByteArray(start), toByteArray(stop));}public void zrem(final byte[] key, final byte[]... members) {sendCommand(ZREM, joinParameters(key, members));}public void zincrby(final byte[] key, final double increment, final byte[] member) {sendCommand(ZINCRBY, key, toByteArray(increment), member);}public void zincrby(final byte[] key, final double increment, final byte[] member,final ZIncrByParams params) {// Note that it actually calls ZADD with INCR option, so it requires Redis 3.0.2 or upper.sendCommand(ZADD, params.getByteParams(key, toByteArray(increment), member));}public void zrank(final byte[] key, final byte[] member) {sendCommand(ZRANK, key, member);}public void zrevrank(final byte[] key, final byte[] member) {sendCommand(ZREVRANK, key, member);}public void zrevrange(final byte[] key, final long start, final long stop) {sendCommand(ZREVRANGE, key, toByteArray(start), toByteArray(stop));}public void zrangeWithScores(final byte[] key, final long start, final long stop) {sendCommand(ZRANGE, key, toByteArray(start), toByteArray(stop), WITHSCORES.raw);}public void zrevrangeWithScores(final byte[] key, final long start, final long stop) {sendCommand(ZREVRANGE, key, toByteArray(start), toByteArray(stop), WITHSCORES.raw);}public void zcard(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(ZCARD, key);}public void zscore(final byte[] key, final byte[] member) {sendCommand(ZSCORE, key, member);}public void zpopmax(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(ZPOPMAX, key);}public void zpopmax(final byte[] key, final int count) {sendCommand(ZPOPMAX, key, toByteArray(count));}public void zpopmin(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(ZPOPMIN, key);}public void zpopmin(final byte[] key, final long count) {sendCommand(ZPOPMIN, key, toByteArray(count));}public void multi() {sendCommand(MULTI);isInMulti = true;}public void discard() {sendCommand(DISCARD);isInMulti = false;isInWatch = false;}public void exec() {sendCommand(EXEC);isInMulti = false;isInWatch = false;}public void watch(final byte[]... keys) {sendCommand(WATCH, keys);isInWatch = true;}public void unwatch() {sendCommand(UNWATCH);isInWatch = false;}public void sort(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(SORT, key);}public void sort(final byte[] key, final SortingParams sortingParameters) {final List<byte[]> args = new ArrayList<>();args.add(key);args.addAll(sortingParameters.getParams());sendCommand(SORT, args.toArray(new byte[args.size()][]));}public void blpop(final byte[][] args) {sendCommand(BLPOP, args);}public void blpop(final int timeout, final byte[]... keys) {final List<byte[]> args = new ArrayList<>();for (final byte[] arg : keys) {args.add(arg);}args.add(Protocol.toByteArray(timeout));blpop(args.toArray(new byte[args.size()][]));}public void sort(final byte[] key, final SortingParams sortingParameters, final byte[] dstkey) {final List<byte[]> args = new ArrayList<>();args.add(key);args.addAll(sortingParameters.getParams());args.add(STORE.raw);args.add(dstkey);sendCommand(SORT, args.toArray(new byte[args.size()][]));}public void sort(final byte[] key, final byte[] dstkey) {sendCommand(SORT, key, STORE.raw, dstkey);}public void brpop(final byte[][] args) {sendCommand(BRPOP, args);}public void brpop(final int timeout, final byte[]... keys) {final List<byte[]> args = new ArrayList<>();for (final byte[] arg : keys) {args.add(arg);}args.add(Protocol.toByteArray(timeout));brpop(args.toArray(new byte[args.size()][]));}public void auth(final String password) {setPassword(password);sendCommand(AUTH, password);}public void auth(final String user, final String password) {setUser(user);setPassword(password);sendCommand(AUTH, user, password);}public void subscribe(final byte[]... channels) {sendCommand(SUBSCRIBE, channels);}public void publish(final byte[] channel, final byte[] message) {sendCommand(PUBLISH, channel, message);}public void unsubscribe() {sendCommand(UNSUBSCRIBE);}public void unsubscribe(final byte[]... channels) {sendCommand(UNSUBSCRIBE, channels);}public void psubscribe(final byte[]... patterns) {sendCommand(PSUBSCRIBE, patterns);}public void punsubscribe() {sendCommand(PUNSUBSCRIBE);}public void punsubscribe(final byte[]... patterns) {sendCommand(PUNSUBSCRIBE, patterns);}public void pubsub(final byte[]... args) {sendCommand(PUBSUB, args);}public void zcount(final byte[] key, final double min, final double max) {sendCommand(ZCOUNT, key, toByteArray(min), toByteArray(max));}public void zcount(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max) {sendCommand(ZCOUNT, key, min, max);}public void zrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final double min, final double max) {sendCommand(ZRANGEBYSCORE, key, toByteArray(min), toByteArray(max));}public void zrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max) {sendCommand(ZRANGEBYSCORE, key, min, max);}public void zrevrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final double max, final double min) {sendCommand(ZREVRANGEBYSCORE, key, toByteArray(max), toByteArray(min));}public void zrevrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final byte[] max, final byte[] min) {sendCommand(ZREVRANGEBYSCORE, key, max, min);}public void zrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final double min, final double max, final int offset,final int count) {sendCommand(ZRANGEBYSCORE, key, toByteArray(min), toByteArray(max), LIMIT.raw, toByteArray(offset),toByteArray(count));}public void zrevrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final double max, final double min,final int offset, final int count) {sendCommand(ZREVRANGEBYSCORE, key, toByteArray(max), toByteArray(min), LIMIT.raw, toByteArray(offset),toByteArray(count));}public void zrangeByScoreWithScores(final byte[] key, final double min, final double max) {sendCommand(ZRANGEBYSCORE, key, toByteArray(min), toByteArray(max), WITHSCORES.raw);}public void zrevrangeByScoreWithScores(final byte[] key, final double max, final double min) {sendCommand(ZREVRANGEBYSCORE, key, toByteArray(max), toByteArray(min), WITHSCORES.raw);}public void zrangeByScoreWithScores(final byte[] key, final double min, final double max,final int offset, final int count) {sendCommand(ZRANGEBYSCORE, key, toByteArray(min), toByteArray(max), LIMIT.raw, toByteArray(offset),toByteArray(count), WITHSCORES.raw);}public void zrevrangeByScoreWithScores(final byte[] key, final double max, final double min,final int offset, final int count) {sendCommand(ZREVRANGEBYSCORE, key, toByteArray(max), toByteArray(min), LIMIT.raw, toByteArray(offset),toByteArray(count), WITHSCORES.raw);}public void zrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max, final int offset,final int count) {sendCommand(ZRANGEBYSCORE, key, min, max, LIMIT.raw, toByteArray(offset), toByteArray(count));}public void zrevrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final byte[] max, final byte[] min,final int offset, final int count) {sendCommand(ZREVRANGEBYSCORE, key, max, min, LIMIT.raw, toByteArray(offset), toByteArray(count));}public void zrangeByScoreWithScores(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max) {sendCommand(ZRANGEBYSCORE, key, min, max, WITHSCORES.raw);}public void zrevrangeByScoreWithScores(final byte[] key, final byte[] max, final byte[] min) {sendCommand(ZREVRANGEBYSCORE, key, max, min, WITHSCORES.raw);}public void zrangeByScoreWithScores(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max,final int offset, final int count) {sendCommand(ZRANGEBYSCORE, key, min, max, LIMIT.raw, toByteArray(offset), toByteArray(count),WITHSCORES.raw);}public void zrevrangeByScoreWithScores(final byte[] key, final byte[] max, final byte[] min,final int offset, final int count) {sendCommand(ZREVRANGEBYSCORE, key, max, min, LIMIT.raw, toByteArray(offset),toByteArray(count), WITHSCORES.raw);}public void zremrangeByRank(final byte[] key, final long start, final long stop) {sendCommand(ZREMRANGEBYRANK, key, toByteArray(start), toByteArray(stop));}public void zremrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final double min, final double max) {sendCommand(ZREMRANGEBYSCORE, key, toByteArray(min), toByteArray(max));}public void zremrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max) {sendCommand(ZREMRANGEBYSCORE, key, min, max);}public void zunionstore(final byte[] dstkey, final byte[]... sets) {sendCommand(ZUNIONSTORE, joinParameters(dstkey, toByteArray(sets.length), sets));}public void zunionstore(final byte[] dstkey, final ZParams params, final byte[]... sets) {final List<byte[]> args = new ArrayList<>();args.add(dstkey);args.add(Protocol.toByteArray(sets.length));for (final byte[] set : sets) {args.add(set);}args.addAll(params.getParams());sendCommand(ZUNIONSTORE, args.toArray(new byte[args.size()][]));}public void zinterstore(final byte[] dstkey, final byte[]... sets) {sendCommand(ZINTERSTORE, joinParameters(dstkey, Protocol.toByteArray(sets.length), sets));}public void zinterstore(final byte[] dstkey, final ZParams params, final byte[]... sets) {final List<byte[]> args = new ArrayList<>();args.add(dstkey);args.add(Protocol.toByteArray(sets.length));for (final byte[] set : sets) {args.add(set);}args.addAll(params.getParams());sendCommand(ZINTERSTORE, args.toArray(new byte[args.size()][]));}public void zlexcount(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max) {sendCommand(ZLEXCOUNT, key, min, max);}public void zrangeByLex(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max) {sendCommand(ZRANGEBYLEX, key, min, max);}public void zrangeByLex(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max, final int offset,final int count) {sendCommand(ZRANGEBYLEX, key, min, max, LIMIT.raw, toByteArray(offset), toByteArray(count));}public void zrevrangeByLex(final byte[] key, final byte[] max, final byte[] min) {sendCommand(ZREVRANGEBYLEX, key, max, min);}public void zrevrangeByLex(final byte[] key, final byte[] max, final byte[] min,final int offset, final int count) {sendCommand(ZREVRANGEBYLEX, key, max, min, LIMIT.raw, toByteArray(offset), toByteArray(count));}public void zremrangeByLex(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max) {sendCommand(ZREMRANGEBYLEX, key, min, max);}public void save() {sendCommand(SAVE);}public void bgsave() {sendCommand(BGSAVE);}public void bgrewriteaof() {sendCommand(BGREWRITEAOF);}public void lastsave() {sendCommand(LASTSAVE);}public void shutdown() {sendCommand(SHUTDOWN);}public void info() {sendCommand(INFO);}public void info(final String section) {sendCommand(INFO, section);}public void monitor() {sendCommand(MONITOR);}public void slaveof(final String host, final int port) {sendCommand(SLAVEOF, host, String.valueOf(port));}public void slaveofNoOne() {sendCommand(SLAVEOF, NO.raw, ONE.raw);}public void configGet(final byte[] pattern) {sendCommand(CONFIG, Keyword.GET.raw, pattern);}public void configSet(final byte[] parameter, final byte[] value) {sendCommand(CONFIG, Keyword.SET.raw, parameter, value);}public void strlen(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(STRLEN, key);}public void sync() {sendCommand(SYNC);}public void lpushx(final byte[] key, final byte[]... string) {sendCommand(LPUSHX, joinParameters(key, string));}public void persist(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(PERSIST, key);}public void rpushx(final byte[] key, final byte[]... string) {sendCommand(RPUSHX, joinParameters(key, string));}public void echo(final byte[] string) {sendCommand(ECHO, string);}public void linsert(final byte[] key, final ListPosition where, final byte[] pivot,final byte[] value) {sendCommand(LINSERT, key, where.raw, pivot, value);}public void debug(final DebugParams params) {sendCommand(DEBUG, params.getCommand());}public void brpoplpush(final byte[] source, final byte[] destination, final int timeout) {sendCommand(BRPOPLPUSH, source, destination, toByteArray(timeout));}public void configResetStat() {sendCommand(CONFIG, Keyword.RESETSTAT.raw);}public void configRewrite() {sendCommand(CONFIG, Keyword.REWRITE.raw);}public void setbit(final byte[] key, final long offset, final byte[] value) {sendCommand(SETBIT, key, toByteArray(offset), value);}public void setbit(final byte[] key, final long offset, final boolean value) {sendCommand(SETBIT, key, toByteArray(offset), toByteArray(value));}public void getbit(final byte[] key, final long offset) {sendCommand(GETBIT, key, toByteArray(offset));}public void bitpos(final byte[] key, final boolean value, final BitPosParams params) {final List<byte[]> args = new ArrayList<>();args.add(key);args.add(toByteArray(value));args.addAll(params.getParams());sendCommand(BITPOS, args.toArray(new byte[args.size()][]));}public void setrange(final byte[] key, final long offset, final byte[] value) {sendCommand(SETRANGE, key, toByteArray(offset), value);}public void getrange(final byte[] key, final long startOffset, final long endOffset) {sendCommand(GETRANGE, key, toByteArray(startOffset), toByteArray(endOffset));}public int getDB() {return db;}@Overridepublic void disconnect() {db = 0;super.disconnect();}@Overridepublic void close() {db = 0;super.close();}public void resetState() {if (isInWatch()) {unwatch();getStatusCodeReply();}}public void eval(final byte[] script, final byte[] keyCount, final byte[][] params) {sendCommand(EVAL, joinParameters(script, keyCount, params));}public void eval(final byte[] script, final int keyCount, final byte[]... params) {sendCommand(EVAL, joinParameters(script, toByteArray(keyCount), params));}public void evalsha(final byte[] sha1, final byte[] keyCount, final byte[]... params) {sendCommand(EVALSHA, joinParameters(sha1, keyCount, params));}public void evalsha(final byte[] sha1, final int keyCount, final byte[]... params) {sendCommand(EVALSHA, joinParameters(sha1, toByteArray(keyCount), params));}public void scriptFlush() {sendCommand(SCRIPT, Keyword.FLUSH.raw);}public void scriptExists(final byte[]... sha1) {sendCommand(SCRIPT, joinParameters(Keyword.EXISTS.raw, sha1));}public void scriptLoad(final byte[] script) {sendCommand(SCRIPT, Keyword.LOAD.raw, script);}public void scriptKill() {sendCommand(SCRIPT, Keyword.KILL.raw);}public void slowlogGet() {sendCommand(SLOWLOG, Keyword.GET.raw);}public void slowlogGet(final long entries) {sendCommand(SLOWLOG, Keyword.GET.raw, toByteArray(entries));}public void slowlogReset() {sendCommand(SLOWLOG, RESET.raw);}public void slowlogLen() {sendCommand(SLOWLOG, LEN.raw);}public void objectRefcount(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(OBJECT, REFCOUNT.raw, key);}public void objectIdletime(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(OBJECT, IDLETIME.raw, key);}public void objectEncoding(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(OBJECT, ENCODING.raw, key);}public void objectHelp() {sendCommand(OBJECT, HELP.raw);}public void objectFreq(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(OBJECT, FREQ.raw, key);}public void bitcount(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(BITCOUNT, key);}public void bitcount(final byte[] key, final long start, final long end) {sendCommand(BITCOUNT, key, toByteArray(start), toByteArray(end));}public void bitop(final BitOP op, final byte[] destKey, final byte[]... srcKeys) {sendCommand(BITOP, joinParameters(op.raw, destKey, srcKeys));}public void sentinel(final byte[]... args) {sendCommand(SENTINEL, args);}public void dump(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(DUMP, key);}public void restore(final byte[] key, final int ttl, final byte[] serializedValue) {sendCommand(RESTORE, key, toByteArray(ttl), serializedValue);}public void restoreReplace(final byte[] key, final int ttl, final byte[] serializedValue) {sendCommand(RESTORE, key, toByteArray(ttl), serializedValue, Keyword.REPLACE.raw);}public void pexpire(final byte[] key, final long milliseconds) {sendCommand(PEXPIRE, key, toByteArray(milliseconds));}public void pexpireAt(final byte[] key, final long millisecondsTimestamp) {sendCommand(PEXPIREAT, key, toByteArray(millisecondsTimestamp));}public void pttl(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(PTTL, key);}public void psetex(final byte[] key, final long milliseconds, final byte[] value) {sendCommand(PSETEX, key, toByteArray(milliseconds), value);}public void srandmember(final byte[] key, final int count) {sendCommand(SRANDMEMBER, key, toByteArray(count));}public void memoryDoctor() {sendCommand(MEMORY, Keyword.DOCTOR.raw);}public void clientKill(final byte[] ipPort) {sendCommand(CLIENT, Keyword.KILL.raw, ipPort);}public void clientKill(final String ip, final int port) {sendCommand(CLIENT, Keyword.KILL.name(), ip + ':' + port);}public void clientKill(ClientKillParams params) {sendCommand(CLIENT, joinParameters(Keyword.KILL.raw, params.getByteParams()));}public void clientGetname() {sendCommand(CLIENT, Keyword.GETNAME.raw);}public void clientList() {sendCommand(CLIENT, Keyword.LIST.raw);}public void clientSetname(final byte[] name) {sendCommand(CLIENT, Keyword.SETNAME.raw, name);}public void clientPause(final long timeout) {sendCommand(CLIENT, Keyword.PAUSE.raw, toByteArray(timeout));}public void time() {sendCommand(TIME);}public void migrate(final String host, final int port, final byte[] key, final int destinationDb,final int timeout) {sendCommand(MIGRATE, SafeEncoder.encode(host), toByteArray(port), key,toByteArray(destinationDb), toByteArray(timeout));}public void migrate(final String host, final int port, final int destinationDB,final int timeout, final MigrateParams params, final byte[]... keys) {byte[][] bparams = params.getByteParams();int len = 5 + bparams.length + 1 + keys.length;byte[][] args = new byte[len][];int i = 0;args[i++] = SafeEncoder.encode(host);args[i++] = toByteArray(port);args[i++] = new byte[0];args[i++] = toByteArray(destinationDB);args[i++] = toByteArray(timeout);System.arraycopy(bparams, 0, args, i, bparams.length);i += bparams.length;args[i++] = Keyword.KEYS.raw;System.arraycopy(keys, 0, args, i, keys.length);sendCommand(MIGRATE, args);}public void hincrByFloat(final byte[] key, final byte[] field, final double increment) {sendCommand(HINCRBYFLOAT, key, field, toByteArray(increment));}public void scan(final byte[] cursor, final ScanParams params) {final List<byte[]> args = new ArrayList<>();args.add(cursor);args.addAll(params.getParams());sendCommand(SCAN, args.toArray(new byte[args.size()][]));}public void hscan(final byte[] key, final byte[] cursor, final ScanParams params) {final List<byte[]> args = new ArrayList<>();args.add(key);args.add(cursor);args.addAll(params.getParams());sendCommand(HSCAN, args.toArray(new byte[args.size()][]));}public void sscan(final byte[] key, final byte[] cursor, final ScanParams params) {final List<byte[]> args = new ArrayList<>();args.add(key);args.add(cursor);args.addAll(params.getParams());sendCommand(SSCAN, args.toArray(new byte[args.size()][]));}public void zscan(final byte[] key, final byte[] cursor, final ScanParams params) {final List<byte[]> args = new ArrayList<>();args.add(key);args.add(cursor);args.addAll(params.getParams());sendCommand(ZSCAN, args.toArray(new byte[args.size()][]));}public void waitReplicas(final int replicas, final long timeout) {sendCommand(WAIT, toByteArray(replicas), toByteArray(timeout));}public void cluster(final byte[]... args) {sendCommand(CLUSTER, args);}public void asking() {sendCommand(ASKING);}public void pfadd(final byte[] key, final byte[]... elements) {sendCommand(PFADD, joinParameters(key, elements));}public void pfcount(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(PFCOUNT, key);}public void pfcount(final byte[]... keys) {sendCommand(PFCOUNT, keys);}public void pfmerge(final byte[] destkey, final byte[]... sourcekeys) {sendCommand(PFMERGE, joinParameters(destkey, sourcekeys));}public void readonly() {sendCommand(READONLY);}public void geoadd(final byte[] key, final double longitude, final double latitude, final byte[] member) {sendCommand(GEOADD, key, toByteArray(longitude), toByteArray(latitude), member);}public void geoadd(final byte[] key, final Map<byte[], GeoCoordinate> memberCoordinateMap) {List<byte[]> args = new ArrayList<>(memberCoordinateMap.size() * 3 + 1);args.add(key);args.addAll(convertGeoCoordinateMapToByteArrays(memberCoordinateMap));byte[][] argsArray = new byte[args.size()][];args.toArray(argsArray);sendCommand(GEOADD, argsArray);}public void geodist(final byte[] key, final byte[] member1, final byte[] member2) {sendCommand(GEODIST, key, member1, member2);}public void geodist(final byte[] key, final byte[] member1, final byte[] member2, final GeoUnit unit) {sendCommand(GEODIST, key, member1, member2, unit.raw);}public void geohash(final byte[] key, final byte[]... members) {sendCommand(GEOHASH, joinParameters(key, members));}public void geopos(final byte[] key, final byte[][] members) {sendCommand(GEOPOS, joinParameters(key, members));}public void georadius(final byte[] key, final double longitude, final double latitude, final double radius, final GeoUnit unit) {sendCommand(GEORADIUS, key, toByteArray(longitude), toByteArray(latitude), toByteArray(radius),unit.raw);}public void georadiusReadonly(final byte[] key, final double longitude, final double latitude, final double radius, final GeoUnit unit) {sendCommand(GEORADIUS_RO, key, toByteArray(longitude), toByteArray(latitude), toByteArray(radius),unit.raw);}public void georadius(final byte[] key, final double longitude, final double latitude, final double radius, final GeoUnit unit,final GeoRadiusParam param) {sendCommand(GEORADIUS, param.getByteParams(key, toByteArray(longitude), toByteArray(latitude),toByteArray(radius), unit.raw));}public void georadiusReadonly(final byte[] key, final double longitude, final double latitude, final double radius, final GeoUnit unit,final GeoRadiusParam param) {sendCommand(GEORADIUS_RO, param.getByteParams(key, toByteArray(longitude), toByteArray(latitude),toByteArray(radius), unit.raw));}public void georadiusByMember(final byte[] key, final byte[] member, final double radius, final GeoUnit unit) {sendCommand(GEORADIUSBYMEMBER, key, member, toByteArray(radius), unit.raw);}public void georadiusByMemberReadonly(final byte[] key, final byte[] member, final double radius, final GeoUnit unit) {sendCommand(GEORADIUSBYMEMBER_RO, key, member, toByteArray(radius), unit.raw);}public void georadiusByMember(final byte[] key, final byte[] member, final double radius, final GeoUnit unit,final GeoRadiusParam param) {sendCommand(GEORADIUSBYMEMBER, param.getByteParams(key, member, toByteArray(radius), unit.raw));}public void georadiusByMemberReadonly(final byte[] key, final byte[] member, final double radius, final GeoUnit unit,final GeoRadiusParam param) {sendCommand(GEORADIUSBYMEMBER_RO, param.getByteParams(key, member, toByteArray(radius), unit.raw));}public void moduleLoad(final byte[] path) {sendCommand(MODULE, Keyword.LOAD.raw, path);}public void moduleList() {sendCommand(MODULE, Keyword.LIST.raw);}public void moduleUnload(final byte[] name) {sendCommand(MODULE, Keyword.UNLOAD.raw, name);}private ArrayList<byte[]> convertScoreMembersToByteArrays(final Map<byte[], Double> scoreMembers) {ArrayList<byte[]> args = new ArrayList<>(scoreMembers.size() * 2);for (Entry<byte[], Double> entry : scoreMembers.entrySet()) {args.add(toByteArray(entry.getValue()));args.add(entry.getKey());}return args;}public void aclWhoAmI() { sendCommand(ACL, Keyword.WHOAMI.raw); }public void aclGenPass() { sendCommand(ACL, Keyword.GENPASS.raw); }public void aclList() { sendCommand(ACL, Keyword.LIST.raw); }public void aclUsers() { sendCommand(ACL, Keyword.USERS.raw); }public void aclCat() { sendCommand(ACL, Keyword.CAT.raw); }public void aclCat(final byte[] category) {sendCommand(ACL, Keyword.CAT.raw, category);}public void aclSetUser(final byte[] name) {sendCommand(ACL, Keyword.SETUSER.raw, name);}public void aclGetUser(final byte[] name) {sendCommand(ACL, Keyword.GETUSER.raw, name);}public void aclSetUser(final byte[] name, byte[][] parameters) {sendCommand(ACL, joinParameters(Keyword.SETUSER.raw,name, parameters));}public void aclDelUser(final byte[] name) {sendCommand(ACL, Keyword.DELUSER.raw, name);}private List<byte[]> convertGeoCoordinateMapToByteArrays(final Map<byte[], GeoCoordinate> memberCoordinateMap) {List<byte[]> args = new ArrayList<>(memberCoordinateMap.size() * 3);for (Entry<byte[], GeoCoordinate> entry : memberCoordinateMap.entrySet()) {GeoCoordinate coordinate = entry.getValue();args.add(toByteArray(coordinate.getLongitude()));args.add(toByteArray(coordinate.getLatitude()));args.add(entry.getKey());}return args;}public void bitfield(final byte[] key, final byte[]... value) {sendCommand(BITFIELD, joinParameters(key, value));}public void bitfieldReadonly(final byte[] key, final byte[]... arguments) {sendCommand(BITFIELD_RO, joinParameters(key, arguments));}public void hstrlen(final byte[] key, final byte[] field) {sendCommand(HSTRLEN, key, field);}public void xadd(final byte[] key, final byte[] id, final Map<byte[], byte[]> hash, long maxLen, boolean approximateLength) {int maxLexArgs = 0;if(maxLen < Long.MAX_VALUE) { // optional argumentsif(approximateLength) {maxLexArgs = 3; // e.g. MAXLEN ~ 1000} else {maxLexArgs = 2; // e.g. MAXLEN 1000}}final byte[][] params = new byte[2 + maxLexArgs + hash.size() * 2][];int index = 0;params[index++] = key;if(maxLen < Long.MAX_VALUE) {params[index++] = Keyword.MAXLEN.raw;if(approximateLength) {params[index++] = Protocol.BYTES_TILDE;}params[index++] = toByteArray(maxLen);}params[index++] = id;for (final Entry<byte[], byte[]> entry : hash.entrySet()) {params[index++] = entry.getKey();params[index++] = entry.getValue();}sendCommand(XADD, params);}public void xlen(final byte[] key) {sendCommand(XLEN, key);}public void xrange(final byte[] key, final byte[] start, final byte[] end, final long count) {sendCommand(XRANGE, key, start, end, Keyword.COUNT.raw, toByteArray(count));}public void xrevrange(final byte[] key, final byte[] end, final byte[] start, final int count) {sendCommand(XREVRANGE, key, end, start, Keyword.COUNT.raw, toByteArray(count));}public void xread(final int count, final long block, final Map<byte[], byte[]> streams) {final byte[][] params = new byte[3 + streams.size() * 2 + (block > 0 ? 2 : 0)][];int streamsIndex = 0;params[streamsIndex++] = Keyword.COUNT.raw;params[streamsIndex++] = toByteArray(count);if(block > 0) {params[streamsIndex++] = Keyword.BLOCK.raw;params[streamsIndex++] = toByteArray(block);}params[streamsIndex++] = Keyword.STREAMS.raw;int idsIndex = streamsIndex + streams.size();for (final Entry<byte[], byte[]> entry : streams.entrySet()) {params[streamsIndex++] = entry.getKey();params[idsIndex++] = entry.getValue();}sendCommand(XREAD, params);}public void xack(final byte[] key, final byte[] group, final byte[]... ids) {final byte[][] params = new byte[2 + ids.length][];int index = 0;params[index++] = key;params[index++] = group;for (final byte[] id : ids) {params[index++] = id;}sendCommand(XACK, params);}public void xgroupCreate(final byte[] key, final byte[] groupname, final byte[] id, boolean makeStream) {if(makeStream) {sendCommand(XGROUP, Keyword.CREATE.raw, key, groupname, id, Keyword.MKSTREAM.raw);} else {sendCommand(XGROUP, Keyword.CREATE.raw, key, groupname, id);}}public void xgroupSetID(final byte[] key, final byte[] groupname, final byte[] id) {sendCommand(XGROUP, Keyword.SETID.raw, key, groupname, id);}public void xgroupDestroy(final byte[] key, final byte[] groupname) {sendCommand(XGROUP, Keyword.DESTROY.raw, key, groupname);}public void xgroupDelConsumer(final byte[] key, final byte[] groupname, final byte[] consumerName) {sendCommand(XGROUP, Keyword.DELCONSUMER.raw, key, groupname, consumerName);}public void xdel(final byte[] key, final byte[]... ids) {final byte[][] params = new byte[1 + ids.length][];int index = 0;params[index++] = key;for (final byte[] id : ids) {params[index++] = id;}sendCommand(XDEL, params);}public void xtrim(byte[] key, long maxLen, boolean approximateLength) {if(approximateLength) {sendCommand(XTRIM, key, Keyword.MAXLEN.raw, Protocol.BYTES_TILDE ,toByteArray(maxLen));} else {sendCommand(XTRIM, key, Keyword.MAXLEN.raw, toByteArray(maxLen));}}public void xreadGroup(byte[] groupname, byte[] consumer, int count, long block, boolean noAck, Map<byte[], byte[]> streams) {int optional = 0;if(count>0) {optional += 2;}if(block > 0) {optional += 2;}if(noAck) {optional += 1;}final byte[][] params = new byte[4 + optional + streams.size() * 2][];int streamsIndex = 0;params[streamsIndex++] = Keyword.GROUP.raw;params[streamsIndex++] = groupname;params[streamsIndex++] = consumer;if(count>0) {params[streamsIndex++] = Keyword.COUNT.raw;params[streamsIndex++] = toByteArray(count);}if(block > 0) {params[streamsIndex++] = Keyword.BLOCK.raw;params[streamsIndex++] = toByteArray(block);}if(noAck) {params[streamsIndex++] = Keyword.NOACK.raw;}params[streamsIndex++] = Keyword.STREAMS.raw;int idsIndex = streamsIndex + streams.size();for (final Entry<byte[], byte[]> entry : streams.entrySet()) {params[streamsIndex++] = entry.getKey();params[idsIndex++] = entry.getValue();}sendCommand(XREADGROUP, params);}public void xpending(byte[] key, byte[] groupname, byte[] start, byte[] end, int count, byte[] consumername) {if(consumername == null) {sendCommand(XPENDING, key, groupname, start, end, toByteArray(count));} else {sendCommand(XPENDING, key, groupname, start, end, toByteArray(count), consumername);}}public void xclaim(byte[] key, byte[] groupname, byte[] consumername, long minIdleTime, long newIdleTime, int retries, boolean force, byte[][] ids) {ArrayList<byte[]> arguments = new ArrayList<>(10 + ids.length);arguments.add(key);arguments.add(groupname);arguments.add(consumername);arguments.add(toByteArray(minIdleTime));for(byte[] id : ids) {arguments.add(id);}if(newIdleTime > 0) {arguments.add(Keyword.IDLE.raw);arguments.add(toByteArray(newIdleTime));}if(retries > 0) {arguments.add(Keyword.RETRYCOUNT.raw);arguments.add(toByteArray(retries));}if(force) {arguments.add(Keyword.FORCE.raw);}sendCommand(XCLAIM, arguments.toArray(new byte[arguments.size()][]));}public void xinfoStream(byte[] key) {sendCommand(XINFO,Keyword.STREAM.raw,key);}public void xinfoGroup(byte[] key) {sendCommand(XINFO,Keyword.GROUPS.raw,key);}public void xinfoConsumers (byte[] key, byte[] group) {sendCommand(XINFO,Keyword.CONSUMERS.raw,key,group);}}
springboot通过用户名连接redis-cluster redis7,
连接配置如下
spring:redis:cluster:# 集群节点nodes: 172.4.2.65:30001,172.4.2.65:30002,172.4.2.65:30003,172.4.2.65:30004,172.4.2.65:30005,172.4.2.65:30006# 最大重定向次数max-redirects: 5# 密码user: testpassword: test@123多覆盖一个文件
新建包目录 redis.clients.jedis
新建类BinaryJedis.java
package redis.clients.jedis;import static redis.clients.jedis.Protocol.toByteArray;import java.io.Closeable;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.AbstractMap;
import java.util.AbstractSet;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;import javax.net.ssl.HostnameVerifier;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLParameters;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import redis.clients.jedis.commands.AdvancedBinaryJedisCommands;
import redis.clients.jedis.commands.BasicCommands;
import redis.clients.jedis.commands.BinaryJedisCommands;
import redis.clients.jedis.commands.BinaryScriptingCommands;
import redis.clients.jedis.commands.MultiKeyBinaryCommands;
import redis.clients.jedis.commands.ProtocolCommand;
import redis.clients.jedis.exceptions.InvalidURIException;
import redis.clients.jedis.exceptions.JedisDataException;
import redis.clients.jedis.exceptions.JedisException;
import redis.clients.jedis.params.ClientKillParams;
import redis.clients.jedis.params.GeoRadiusParam;
import redis.clients.jedis.params.MigrateParams;
import redis.clients.jedis.params.SetParams;
import redis.clients.jedis.params.ZAddParams;
import redis.clients.jedis.params.ZIncrByParams;
import redis.clients.jedis.util.JedisByteHashMap;
import redis.clients.jedis.util.JedisURIHelper;public class BinaryJedis implements BasicCommands, BinaryJedisCommands, MultiKeyBinaryCommands,AdvancedBinaryJedisCommands, BinaryScriptingCommands, Closeable {protected Client client = null;protected Transaction transaction = null;protected Pipeline pipeline = null;private final byte[][] dummyArray = new byte[0][];private String user;{String user = SpringUtils.getApplicationContext().getEnvironment().getProperty("spring.redis.user");if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(user)){this.user = user;}}public BinaryJedis() {client = new Client();}public BinaryJedis(final String host) {URI uri = URI.create(host);if (JedisURIHelper.isValid(uri)) {initializeClientFromURI(uri);} else {client = new Client(host);}}public BinaryJedis(final HostAndPort hp) {this(hp.getHost(), hp.getPort());}public BinaryJedis(final String host, final int port) {client = new Client(host, port);}public BinaryJedis(final String host, final int port, final boolean ssl) {client = new Client(host, port, ssl);}public BinaryJedis(final String host, final int port, final boolean ssl,final SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory, final SSLParameters sslParameters,final HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier) {client = new Client(host, port, ssl, sslSocketFactory, sslParameters, hostnameVerifier);}public BinaryJedis(final String host, final int port, final int timeout) {this(host, port, timeout, timeout);}public BinaryJedis(final String host, final int port, final int timeout, final boolean ssl) {this(host, port, timeout, timeout, ssl);}public BinaryJedis(final String host, final int port, final int timeout, final boolean ssl,final SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory, final SSLParameters sslParameters,final HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier) {this(host, port, timeout, timeout, ssl, sslSocketFactory, sslParameters, hostnameVerifier);}public BinaryJedis(final String host, final int port, final int connectionTimeout,final int soTimeout) {client = new Client(host, port);client.setConnectionTimeout(connectionTimeout);client.setSoTimeout(soTimeout);}public BinaryJedis(final String host, final int port, final int connectionTimeout,final int soTimeout, final boolean ssl) {client = new Client(host, port, ssl);client.setConnectionTimeout(connectionTimeout);client.setSoTimeout(soTimeout);}public BinaryJedis(final String host, final int port, final int connectionTimeout,final int soTimeout, final boolean ssl, final SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory,final SSLParameters sslParameters, final HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier) {client = new Client(host, port, ssl, sslSocketFactory, sslParameters, hostnameVerifier);client.setConnectionTimeout(connectionTimeout);client.setSoTimeout(soTimeout);}public BinaryJedis(final JedisShardInfo shardInfo) {client = new Client(shardInfo.getHost(), shardInfo.getPort(), shardInfo.getSsl(),shardInfo.getSslSocketFactory(), shardInfo.getSslParameters(),shardInfo.getHostnameVerifier());client.setConnectionTimeout(shardInfo.getConnectionTimeout());client.setSoTimeout(shardInfo.getSoTimeout());client.setUser(shardInfo.getUser());client.setPassword(shardInfo.getPassword());client.setDb(shardInfo.getDb());}public BinaryJedis(URI uri) {initializeClientFromURI(uri);}public BinaryJedis(URI uri, final SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory,final SSLParameters sslParameters, final HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier) {initializeClientFromURI(uri, sslSocketFactory, sslParameters, hostnameVerifier);}public BinaryJedis(final URI uri, final int timeout) {this(uri, timeout, timeout);}public BinaryJedis(final URI uri, final int timeout, final SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory,final SSLParameters sslParameters, final HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier) {this(uri, timeout, timeout, sslSocketFactory, sslParameters, hostnameVerifier);}public BinaryJedis(final URI uri, final int connectionTimeout, final int soTimeout) {initializeClientFromURI(uri);client.setConnectionTimeout(connectionTimeout);client.setSoTimeout(soTimeout);}public BinaryJedis(final URI uri, final int connectionTimeout, final int soTimeout,final SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory,final SSLParameters sslParameters,final HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier) {initializeClientFromURI(uri, sslSocketFactory, sslParameters, hostnameVerifier);client.setConnectionTimeout(connectionTimeout);client.setSoTimeout(soTimeout);}public BinaryJedis(final JedisSocketFactory jedisSocketFactory) {client = new Client(jedisSocketFactory);}private void initializeClientFromURI(URI uri) {initializeClientFromURI(uri, null, null, null);}private void initializeClientFromURI(URI uri, final SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory,final SSLParameters sslParameters, final HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier) {if (!JedisURIHelper.isValid(uri)) {throw new InvalidURIException(String.format("Cannot open Redis connection due invalid URI. %s", uri.toString()));}client = new Client(uri.getHost(), uri.getPort(), JedisURIHelper.isRedisSSLScheme(uri),sslSocketFactory, sslParameters, hostnameVerifier);String password = JedisURIHelper.getPassword(uri);if (password != null) {String user = JedisURIHelper.getUser(uri);if (user == null) {client.auth(password);} else {client.auth(user, password);}client.getStatusCodeReply();}int dbIndex = JedisURIHelper.getDBIndex(uri);if (dbIndex > 0) {client.select(dbIndex);client.getStatusCodeReply();client.setDb(dbIndex);}}@Overridepublic String ping() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.ping();return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Works same as <tt>ping()</tt> but returns argument message instead of <tt>PONG</tt>.* @param message* @return message*/public byte[] ping(final byte[] message) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.ping(message);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}/*** Set the string value as value of the key. The string can't be longer than 1073741824 bytes (1* GB).* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @param key* @param value* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic String set(final byte[] key, final byte[] value) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.set(key, value);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Set the string value as value of the key. The string can't be longer than 1073741824 bytes (1* GB).* @param key* @param value* @param params* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic String set(final byte[] key, final byte[] value, final SetParams params) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.set(key, value, params);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Get the value of the specified key. If the key does not exist the special value 'nil' is* returned. If the value stored at key is not a string an error is returned because GET can only* handle string values.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @param key* @return Bulk reply*/@Overridepublic byte[] get(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.get(key);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}/*** Ask the server to silently close the connection.*/@Overridepublic String quit() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.quit();String quitReturn = client.getStatusCodeReply();client.disconnect();return quitReturn;}/*** Test if the specified keys exist. The command returns the number of keys exist.* Time complexity: O(N)* @param keys* @return Integer reply, specifically: an integer greater than 0 if one or more keys exist,* 0 if none of the specified keys exist.*/@Overridepublic Long exists(final byte[]... keys) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.exists(keys);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Test if the specified key exists. The command returns true if the key exists, otherwise false is* returned. Note that even keys set with an empty string as value will return true. Time* complexity: O(1)* @param key* @return Boolean reply, true if the key exists, otherwise false*/@Overridepublic Boolean exists(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.exists(key);return client.getIntegerReply() == 1;}/*** Remove the specified keys. If a given key does not exist no operation is performed for this* key. The command returns the number of keys removed. Time complexity: O(1)* @param keys* @return Integer reply, specifically: an integer greater than 0 if one or more keys were removed* 0 if none of the specified key existed*/@Overridepublic Long del(final byte[]... keys) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.del(keys);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long del(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.del(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** This command is very similar to DEL: it removes the specified keys. Just like DEL a key is* ignored if it does not exist. However the command performs the actual memory reclaiming in a* different thread, so it is not blocking, while DEL is. This is where the command name comes* from: the command just unlinks the keys from the keyspace. The actual removal will happen later* asynchronously.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1) for each key removed regardless of its size. Then the command does O(N)* work in a different thread in order to reclaim memory, where N is the number of allocations the* deleted objects where composed of.* @param keys* @return Integer reply: The number of keys that were unlinked*/@Overridepublic Long unlink(final byte[]... keys) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.unlink(keys);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long unlink(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.unlink(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Return the type of the value stored at key in form of a string. The type can be one of "none",* "string", "list", "set". "none" is returned if the key does not exist. Time complexity: O(1)* @param key* @return Status code reply, specifically: "none" if the key does not exist "string" if the key* contains a String value "list" if the key contains a List value "set" if the key* contains a Set value "zset" if the key contains a Sorted Set value "hash" if the key* contains a Hash value*/@Overridepublic String type(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.type(key);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Delete all the keys of the currently selected DB. This command never fails.* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic String flushDB() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.flushDB();return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Returns all the keys matching the glob-style pattern as space separated strings. For example if* you have in the database the keys "foo" and "foobar" the command "KEYS foo*" will return* "foo foobar".* <p>* Note that while the time complexity for this operation is O(n) the constant times are pretty* low. For example Redis running on an entry level laptop can scan a 1 million keys database in* 40 milliseconds. <b>Still it's better to consider this one of the slow commands that may ruin* the DB performance if not used with care.</b>* <p>* In other words this command is intended only for debugging and special operations like creating* a script to change the DB schema. Don't use it in your normal code. Use Redis Sets in order to* group together a subset of objects.* <p>* Glob style patterns examples:* <ul>* <li>h?llo will match hello hallo hhllo* <li>h*llo will match hllo heeeello* <li>h[ae]llo will match hello and hallo, but not hillo* </ul>* <p>* Use \ to escape special chars if you want to match them verbatim.* <p>* Time complexity: O(n) (with n being the number of keys in the DB, and assuming keys and pattern* of limited length)* @param pattern* @return Multi bulk reply*/@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> keys(final byte[] pattern) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.keys(pattern);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}/*** Return a randomly selected key from the currently selected DB.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @return Single line reply, specifically the randomly selected key or an empty string is the* database is empty*/@Overridepublic byte[] randomBinaryKey() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.randomKey();return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}/*** Atomically renames the key oldkey to newkey. If the source and destination name are the same an* error is returned. If newkey already exists it is overwritten.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @param oldkey* @param newkey* @return Status code repy*/@Overridepublic String rename(final byte[] oldkey, final byte[] newkey) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.rename(oldkey, newkey);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Rename oldkey into newkey but fails if the destination key newkey already exists.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @param oldkey* @param newkey* @return Integer reply, specifically: 1 if the key was renamed 0 if the target key already exist*/@Overridepublic Long renamenx(final byte[] oldkey, final byte[] newkey) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.renamenx(oldkey, newkey);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Return the number of keys in the currently selected database.* @return Integer reply*/@Overridepublic Long dbSize() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.dbSize();return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Set a timeout on the specified key. After the timeout the key will be automatically deleted by* the server. A key with an associated timeout is said to be volatile in Redis terminology.* <p>* Volatile keys are stored on disk like the other keys, the timeout is persistent too like all the* other aspects of the dataset. Saving a dataset containing expires and stopping the server does* not stop the flow of time as Redis stores on disk the time when the key will no longer be* available as Unix time, and not the remaining seconds.* <p>* Since Redis 2.1.3 you can update the value of the timeout of a key already having an expire* set. It is also possible to undo the expire at all turning the key into a normal key using the* {@link #persist(byte[]) PERSIST} command.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @see <a href="http://redis.io/commands/expire">Expire Command</a>* @param key* @param seconds* @return Integer reply, specifically: 1: the timeout was set. 0: the timeout was not set since* the key already has an associated timeout (this may happen only in Redis versions <* 2.1.3, Redis >= 2.1.3 will happily update the timeout), or the key does not exist.*/@Overridepublic Long expire(final byte[] key, final int seconds) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.expire(key, seconds);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** EXPIREAT works exactly like {@link #expire(byte[], int) EXPIRE} but instead to get the number of* seconds representing the Time To Live of the key as a second argument (that is a relative way* of specifying the TTL), it takes an absolute one in the form of a UNIX timestamp (Number of* seconds elapsed since 1 Gen 1970).* <p>* EXPIREAT was introduced in order to implement the Append Only File persistence mode so that* EXPIRE commands are automatically translated into EXPIREAT commands for the append only file.* Of course EXPIREAT can also used by programmers that need a way to simply specify that a given* key should expire at a given time in the future.* <p>* Since Redis 2.1.3 you can update the value of the timeout of a key already having an expire* set. It is also possible to undo the expire at all turning the key into a normal key using the* {@link #persist(byte[]) PERSIST} command.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @see <a href="http://redis.io/commands/expire">Expire Command</a>* @param key* @param unixTime* @return Integer reply, specifically: 1: the timeout was set. 0: the timeout was not set since* the key already has an associated timeout (this may happen only in Redis versions <* 2.1.3, Redis >= 2.1.3 will happily update the timeout), or the key does not exist.*/@Overridepublic Long expireAt(final byte[] key, final long unixTime) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.expireAt(key, unixTime);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** The TTL command returns the remaining time to live in seconds of a key that has an* {@link #expire(byte[], int) EXPIRE} set. This introspection capability allows a Redis client to* check how many seconds a given key will continue to be part of the dataset.* @param key* @return Integer reply, returns the remaining time to live in seconds of a key that has an* EXPIRE. If the Key does not exists or does not have an associated expire, -1 is* returned.*/@Overridepublic Long ttl(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.ttl(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Alters the last access time of a key(s). A key is ignored if it does not exist.* Time complexity: O(N) where N is the number of keys that will be touched.* @param keys* @return Integer reply: The number of keys that were touched.*/@Overridepublic Long touch(final byte[]... keys) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.touch(keys);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long touch(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.touch(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Select the DB with having the specified zero-based numeric index. For default every new client* connection is automatically selected to DB 0.* @param index* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic String select(final int index) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.select(index);String statusCodeReply = client.getStatusCodeReply();client.setDb(index);return statusCodeReply;}@Overridepublic String swapDB(final int index1, final int index2) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.swapDB(index1, index2);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Move the specified key from the currently selected DB to the specified destination DB. Note* that this command returns 1 only if the key was successfully moved, and 0 if the target key was* already there or if the source key was not found at all, so it is possible to use MOVE as a* locking primitive.* @param key* @param dbIndex* @return Integer reply, specifically: 1 if the key was moved 0 if the key was not moved because* already present on the target DB or was not found in the current DB.*/@Overridepublic Long move(final byte[] key, final int dbIndex) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.move(key, dbIndex);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Delete all the keys of all the existing databases, not just the currently selected one. This* command never fails.* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic String flushAll() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.flushAll();return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** GETSET is an atomic set this value and return the old value command. Set key to the string* value and return the old value stored at key. The string can't be longer than 1073741824 bytes* (1 GB).* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @param key* @param value* @return Bulk reply*/@Overridepublic byte[] getSet(final byte[] key, final byte[] value) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.getSet(key, value);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}/*** Get the values of all the specified keys. If one or more keys don't exist or is not of type* String, a 'nil' value is returned instead of the value of the specified key, but the operation* never fails.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1) for every key* @param keys* @return Multi bulk reply*/@Overridepublic List<byte[]> mget(final byte[]... keys) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.mget(keys);return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}/*** SETNX works exactly like {@link #set(byte[], byte[]) SET} with the only difference that if the* key already exists no operation is performed. SETNX actually means "SET if Not eXists".* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @param key* @param value* @return Integer reply, specifically: 1 if the key was set 0 if the key was not set*/@Overridepublic Long setnx(final byte[] key, final byte[] value) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.setnx(key, value);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** The command is exactly equivalent to the following group of commands:* {@link #set(byte[], byte[]) SET} + {@link #expire(byte[], int) EXPIRE}. The operation is* atomic.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @param key* @param seconds* @param value* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic String setex(final byte[] key, final int seconds, final byte[] value) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.setex(key, seconds, value);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Set the the respective keys to the respective values. MSET will replace old values with new* values, while {@link #msetnx(byte[]...) MSETNX} will not perform any operation at all even if* just a single key already exists.* <p>* Because of this semantic MSETNX can be used in order to set different keys representing* different fields of an unique logic object in a way that ensures that either all the fields or* none at all are set.* <p>* Both MSET and MSETNX are atomic operations. This means that for instance if the keys A and B* are modified, another client talking to Redis can either see the changes to both A and B at* once, or no modification at all.* @see #msetnx(byte[]...)* @param keysvalues* @return Status code reply Basically +OK as MSET can't fail*/@Overridepublic String mset(final byte[]... keysvalues) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.mset(keysvalues);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Set the the respective keys to the respective values. {@link #mset(byte[]...) MSET} will* replace old values with new values, while MSETNX will not perform any operation at all even if* just a single key already exists.* <p>* Because of this semantic MSETNX can be used in order to set different keys representing* different fields of an unique logic object in a way that ensures that either all the fields or* none at all are set.* <p>* Both MSET and MSETNX are atomic operations. This means that for instance if the keys A and B* are modified, another client talking to Redis can either see the changes to both A and B at* once, or no modification at all.* @see #mset(byte[]...)* @param keysvalues* @return Integer reply, specifically: 1 if the all the keys were set 0 if no key was set (at* least one key already existed)*/@Overridepublic Long msetnx(final byte[]... keysvalues) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.msetnx(keysvalues);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** DECRBY work just like {@link #decr(byte[]) INCR} but instead to decrement by 1 the decrement is* integer.* <p>* INCR commands are limited to 64 bit signed integers.* <p>* Note: this is actually a string operation, that is, in Redis there are not "integer" types.* Simply the string stored at the key is parsed as a base 10 64 bit signed integer, incremented,* and then converted back as a string.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @see #incr(byte[])* @see #decr(byte[])* @see #incrBy(byte[], long)* @param key* @param decrement* @return Integer reply, this commands will reply with the new value of key after the increment.*/@Overridepublic Long decrBy(final byte[] key, final long decrement) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.decrBy(key, decrement);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Decrement the number stored at key by one. If the key does not exist or contains a value of a* wrong type, set the key to the value of "0" before to perform the decrement operation.* <p>* INCR commands are limited to 64 bit signed integers.* <p>* Note: this is actually a string operation, that is, in Redis there are not "integer" types.* Simply the string stored at the key is parsed as a base 10 64 bit signed integer, incremented,* and then converted back as a string.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @see #incr(byte[])* @see #incrBy(byte[], long)* @see #decrBy(byte[], long)* @param key* @return Integer reply, this commands will reply with the new value of key after the increment.*/@Overridepublic Long decr(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.decr(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** INCRBY work just like {@link #incr(byte[]) INCR} but instead to increment by 1 the increment is* integer.* <p>* INCR commands are limited to 64 bit signed integers.* <p>* Note: this is actually a string operation, that is, in Redis there are not "integer" types.* Simply the string stored at the key is parsed as a base 10 64 bit signed integer, incremented,* and then converted back as a string.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @see #incr(byte[])* @see #decr(byte[])* @see #decrBy(byte[], long)* @param key* @param increment* @return Integer reply, this commands will reply with the new value of key after the increment.*/@Overridepublic Long incrBy(final byte[] key, final long increment) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.incrBy(key, increment);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** INCRBYFLOAT work just like {@link #incrBy(byte[], long)} INCRBY} but increments by floats* instead of integers.* <p>* INCRBYFLOAT commands are limited to double precision floating point values.* <p>* Note: this is actually a string operation, that is, in Redis there are not "double" types.* Simply the string stored at the key is parsed as a base double precision floating point value,* incremented, and then converted back as a string. There is no DECRYBYFLOAT but providing a* negative value will work as expected.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @see #incr(byte[])* @see #decr(byte[])* @see #decrBy(byte[], long)* @param key the key to increment* @param increment the value to increment by* @return Integer reply, this commands will reply with the new value of key after the increment.*/@Overridepublic Double incrByFloat(final byte[] key, final double increment) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.incrByFloat(key, increment);String dval = client.getBulkReply();return (dval != null ? new Double(dval) : null);}/*** Increment the number stored at key by one. If the key does not exist or contains a value of a* wrong type, set the key to the value of "0" before to perform the increment operation.* <p>* INCR commands are limited to 64 bit signed integers.* <p>* Note: this is actually a string operation, that is, in Redis there are not "integer" types.* Simply the string stored at the key is parsed as a base 10 64 bit signed integer, incremented,* and then converted back as a string.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @see #incrBy(byte[], long)* @see #decr(byte[])* @see #decrBy(byte[], long)* @param key* @return Integer reply, this commands will reply with the new value of key after the increment.*/@Overridepublic Long incr(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.incr(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** If the key already exists and is a string, this command appends the provided value at the end* of the string. If the key does not exist it is created and set as an empty string, so APPEND* will be very similar to SET in this special case.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1). The amortized time complexity is O(1) assuming the appended value is* small and the already present value is of any size, since the dynamic string library used by* Redis will double the free space available on every reallocation.* @param key* @param value* @return Integer reply, specifically the total length of the string after the append operation.*/@Overridepublic Long append(final byte[] key, final byte[] value) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.append(key, value);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Return a subset of the string from offset start to offset end (both offsets are inclusive).* Negative offsets can be used in order to provide an offset starting from the end of the string.* So -1 means the last char, -2 the penultimate and so forth.* <p>* The function handles out of range requests without raising an error, but just limiting the* resulting range to the actual length of the string.* <p>* Time complexity: O(start+n) (with start being the start index and n the total length of the* requested range). Note that the lookup part of this command is O(1) so for small strings this* is actually an O(1) command.* @param key* @param start* @param end* @return Bulk reply*/@Overridepublic byte[] substr(final byte[] key, final int start, final int end) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.substr(key, start, end);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}/*** Set the specified hash field to the specified value.* <p>* If key does not exist, a new key holding a hash is created.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b> O(1)* @param key* @param field* @param value* @return If the field already exists, and the HSET just produced an update of the value, 0 is* returned, otherwise if a new field is created 1 is returned.*/@Overridepublic Long hset(final byte[] key, final byte[] field, final byte[] value) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.hset(key, field, value);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long hset(final byte[] key, final Map<byte[], byte[]> hash) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.hset(key, hash);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** If key holds a hash, retrieve the value associated to the specified field.* <p>* If the field is not found or the key does not exist, a special 'nil' value is returned.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b> O(1)* @param key* @param field* @return Bulk reply*/@Overridepublic byte[] hget(final byte[] key, final byte[] field) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.hget(key, field);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}/*** Set the specified hash field to the specified value if the field not exists. <b>Time* complexity:</b> O(1)* @param key* @param field* @param value* @return If the field already exists, 0 is returned, otherwise if a new field is created 1 is* returned.*/@Overridepublic Long hsetnx(final byte[] key, final byte[] field, final byte[] value) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.hsetnx(key, field, value);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Set the respective fields to the respective values. HMSET replaces old values with new values.* <p>* If key does not exist, a new key holding a hash is created.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b> O(N) (with N being the number of fields)* @param key* @param hash* @return Always OK because HMSET can't fail*/@Overridepublic String hmset(final byte[] key, final Map<byte[], byte[]> hash) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.hmset(key, hash);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Retrieve the values associated to the specified fields.* <p>* If some of the specified fields do not exist, nil values are returned. Non existing keys are* considered like empty hashes.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b> O(N) (with N being the number of fields)* @param key* @param fields* @return Multi Bulk Reply specifically a list of all the values associated with the specified* fields, in the same order of the request.*/@Overridepublic List<byte[]> hmget(final byte[] key, final byte[]... fields) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.hmget(key, fields);return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}/*** Increment the number stored at field in the hash at key by value. If key does not exist, a new* key holding a hash is created. If field does not exist or holds a string, the value is set to 0* before applying the operation. Since the value argument is signed you can use this command to* perform both increments and decrements.* <p>* The range of values supported by HINCRBY is limited to 64 bit signed integers.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b> O(1)* @param key* @param field* @param value* @return Integer reply The new value at field after the increment operation.*/@Overridepublic Long hincrBy(final byte[] key, final byte[] field, final long value) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.hincrBy(key, field, value);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Increment the number stored at field in the hash at key by a double precision floating point* value. If key does not exist, a new key holding a hash is created. If field does not exist or* holds a string, the value is set to 0 before applying the operation. Since the value argument* is signed you can use this command to perform both increments and decrements.* <p>* The range of values supported by HINCRBYFLOAT is limited to double precision floating point* values.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b> O(1)* @param key* @param field* @param value* @return Double precision floating point reply The new value at field after the increment* operation.*/@Overridepublic Double hincrByFloat(final byte[] key, final byte[] field, final double value) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.hincrByFloat(key, field, value);final String dval = client.getBulkReply();return (dval != null ? new Double(dval) : null);}/*** Test for existence of a specified field in a hash. <b>Time complexity:</b> O(1)* @param key* @param field* @return Return true if the hash stored at key contains the specified field. Return false if the key is* not found or the field is not present.*/@Overridepublic Boolean hexists(final byte[] key, final byte[] field) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.hexists(key, field);return client.getIntegerReply() == 1;}/*** Remove the specified field from an hash stored at key.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b> O(1)* @param key* @param fields* @return If the field was present in the hash it is deleted and 1 is returned, otherwise 0 is* returned and no operation is performed.*/@Overridepublic Long hdel(final byte[] key, final byte[]... fields) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.hdel(key, fields);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Return the number of items in a hash.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b> O(1)* @param key* @return The number of entries (fields) contained in the hash stored at key. If the specified* key does not exist, 0 is returned assuming an empty hash.*/@Overridepublic Long hlen(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.hlen(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Return all the fields in a hash.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b> O(N), where N is the total number of entries* @param key* @return All the fields names contained into a hash.*/@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> hkeys(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.hkeys(key);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}/*** Return all the values in a hash.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b> O(N), where N is the total number of entries* @param key* @return All the fields values contained into a hash.*/@Overridepublic List<byte[]> hvals(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.hvals(key);return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}/*** Return all the fields and associated values in a hash.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b> O(N), where N is the total number of entries* @param key* @return All the fields and values contained into a hash.*/@Overridepublic Map<byte[], byte[]> hgetAll(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.hgetAll(key);final List<byte[]> flatHash = client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();final Map<byte[], byte[]> hash = new JedisByteHashMap();final Iterator<byte[]> iterator = flatHash.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {hash.put(iterator.next(), iterator.next());}return hash;}/*** Add the string value to the head (LPUSH) or tail (RPUSH) of the list stored at key. If the key* does not exist an empty list is created just before the append operation. If the key exists but* is not a List an error is returned.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @see BinaryJedis#rpush(byte[], byte[]...)* @param key* @param strings* @return Integer reply, specifically, the number of elements inside the list after the push* operation.*/@Overridepublic Long rpush(final byte[] key, final byte[]... strings) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.rpush(key, strings);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Add the string value to the head (LPUSH) or tail (RPUSH) of the list stored at key. If the key* does not exist an empty list is created just before the append operation. If the key exists but* is not a List an error is returned.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @see BinaryJedis#rpush(byte[], byte[]...)* @param key* @param strings* @return Integer reply, specifically, the number of elements inside the list after the push* operation.*/@Overridepublic Long lpush(final byte[] key, final byte[]... strings) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.lpush(key, strings);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Return the length of the list stored at the specified key. If the key does not exist zero is* returned (the same behaviour as for empty lists). If the value stored at key is not a list an* error is returned.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @param key* @return The length of the list.*/@Overridepublic Long llen(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.llen(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Return the specified elements of the list stored at the specified key. Start and end are* zero-based indexes. 0 is the first element of the list (the list head), 1 the next element and* so on.* <p>* For example LRANGE foobar 0 2 will return the first three elements of the list.* <p>* start and end can also be negative numbers indicating offsets from the end of the list. For* example -1 is the last element of the list, -2 the penultimate element and so on.* <p>* <b>Consistency with range functions in various programming languages</b>* <p>* Note that if you have a list of numbers from 0 to 100, LRANGE 0 10 will return 11 elements,* that is, rightmost item is included. This may or may not be consistent with behavior of* range-related functions in your programming language of choice (think Ruby's Range.new,* Array#slice or Python's range() function).* <p>* LRANGE behavior is consistent with one of Tcl.* <p>* <b>Out-of-range indexes</b>* <p>* Indexes out of range will not produce an error: if start is over the end of the list, or start* > end, an empty list is returned. If end is over the end of the list Redis will threat it* just like the last element of the list.* <p>* Time complexity: O(start+n) (with n being the length of the range and start being the start* offset)* @param key* @param start* @param stop* @return Multi bulk reply, specifically a list of elements in the specified range.*/@Overridepublic List<byte[]> lrange(final byte[] key, final long start, final long stop) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.lrange(key, start, stop);return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}/*** Trim an existing list so that it will contain only the specified range of elements specified.* Start and end are zero-based indexes. 0 is the first element of the list (the list head), 1 the* next element and so on.* <p>* For example LTRIM foobar 0 2 will modify the list stored at foobar key so that only the first* three elements of the list will remain.* <p>* start and end can also be negative numbers indicating offsets from the end of the list. For* example -1 is the last element of the list, -2 the penultimate element and so on.* <p>* Indexes out of range will not produce an error: if start is over the end of the list, or start* > end, an empty list is left as value. If end over the end of the list Redis will threat it* just like the last element of the list.* <p>* Hint: the obvious use of LTRIM is together with LPUSH/RPUSH. For example:* <p>* {@code lpush("mylist", "someelement"); ltrim("mylist", 0, 99); * }* <p>* The above two commands will push elements in the list taking care that the list will not grow* without limits. This is very useful when using Redis to store logs for example. It is important* to note that when used in this way LTRIM is an O(1) operation because in the average case just* one element is removed from the tail of the list.* <p>* Time complexity: O(n) (with n being len of list - len of range)* @param key* @param start* @param stop* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic String ltrim(final byte[] key, final long start, final long stop) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.ltrim(key, start, stop);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Return the specified element of the list stored at the specified key. 0 is the first element, 1* the second and so on. Negative indexes are supported, for example -1 is the last element, -2* the penultimate and so on.* <p>* If the value stored at key is not of list type an error is returned. If the index is out of* range a 'nil' reply is returned.* <p>* Note that even if the average time complexity is O(n) asking for the first or the last element* of the list is O(1).* <p>* Time complexity: O(n) (with n being the length of the list)* @param key* @param index* @return Bulk reply, specifically the requested element*/@Overridepublic byte[] lindex(final byte[] key, final long index) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.lindex(key, index);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}/*** Set a new value as the element at index position of the List at key.* <p>* Out of range indexes will generate an error.* <p>* Similarly to other list commands accepting indexes, the index can be negative to access* elements starting from the end of the list. So -1 is the last element, -2 is the penultimate,* and so forth.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b>* <p>* O(N) (with N being the length of the list), setting the first or last elements of the list is* O(1).* @see #lindex(byte[], long)* @param key* @param index* @param value* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic String lset(final byte[] key, final long index, final byte[] value) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.lset(key, index, value);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Remove the first count occurrences of the value element from the list. If count is zero all the* elements are removed. If count is negative elements are removed from tail to head, instead to* go from head to tail that is the normal behaviour. So for example LREM with count -2 and hello* as value to remove against the list (a,b,c,hello,x,hello,hello) will leave the list* (a,b,c,hello,x). The number of removed elements is returned as an integer, see below for more* information about the returned value. Note that non existing keys are considered like empty* lists by LREM, so LREM against non existing keys will always return 0.* <p>* Time complexity: O(N) (with N being the length of the list)* @param key* @param count* @param value* @return Integer Reply, specifically: The number of removed elements if the operation succeeded*/@Overridepublic Long lrem(final byte[] key, final long count, final byte[] value) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.lrem(key, count, value);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Atomically return and remove the first (LPOP) or last (RPOP) element of the list. For example* if the list contains the elements "a","b","c" LPOP will return "a" and the list will become* "b","c".* <p>* If the key does not exist or the list is already empty the special value 'nil' is returned.* @see #rpop(byte[])* @param key* @return Bulk reply*/@Overridepublic byte[] lpop(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.lpop(key);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}/*** Atomically return and remove the first (LPOP) or last (RPOP) element of the list. For example* if the list contains the elements "a","b","c" LPOP will return "a" and the list will become* "b","c".* <p>* If the key does not exist or the list is already empty the special value 'nil' is returned.* @see #lpop(byte[])* @param key* @return Bulk reply*/@Overridepublic byte[] rpop(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.rpop(key);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}/*** Atomically return and remove the last (tail) element of the srckey list, and push the element* as the first (head) element of the dstkey list. For example if the source list contains the* elements "a","b","c" and the destination list contains the elements "foo","bar" after an* RPOPLPUSH command the content of the two lists will be "a","b" and "c","foo","bar".* <p>* If the key does not exist or the list is already empty the special value 'nil' is returned. If* the srckey and dstkey are the same the operation is equivalent to removing the last element* from the list and pushing it as first element of the list, so it's a "list rotation" command.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @param srckey* @param dstkey* @return Bulk reply*/@Overridepublic byte[] rpoplpush(final byte[] srckey, final byte[] dstkey) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.rpoplpush(srckey, dstkey);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}/*** Add the specified member to the set value stored at key. If member is already a member of the* set no operation is performed. If key does not exist a new set with the specified member as* sole member is created. If the key exists but does not hold a set value an error is returned.* <p>* Time complexity O(1)* @param key* @param members* @return Integer reply, specifically: 1 if the new element was added 0 if the element was* already a member of the set*/@Overridepublic Long sadd(final byte[] key, final byte[]... members) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.sadd(key, members);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Return all the members (elements) of the set value stored at key. This is just syntax glue for* {@link #sinter(byte[]...)} SINTER}.* <p>* Time complexity O(N)* @param key the key of the set* @return Multi bulk reply*/@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> smembers(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.smembers(key);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}/*** Remove the specified member from the set value stored at key. If member was not a member of the* set no operation is performed. If key does not hold a set value an error is returned.* <p>* Time complexity O(1)* @param key the key of the set* @param member the set member to remove* @return Integer reply, specifically: 1 if the new element was removed 0 if the new element was* not a member of the set*/@Overridepublic Long srem(final byte[] key, final byte[]... member) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.srem(key, member);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Remove a random element from a Set returning it as return value. If the Set is empty or the key* does not exist, a nil object is returned.* <p>* The {@link #srandmember(byte[])} command does a similar work but the returned element is not* removed from the Set.* <p>* Time complexity O(1)* @param key* @return Bulk reply*/@Overridepublic byte[] spop(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.spop(key);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> spop(final byte[] key, final long count) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.spop(key, count);List<byte[]> members = client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();if (members == null) return null;return SetFromList.of(members);}/*** Move the specified member from the set at srckey to the set at dstkey. This operation is* atomic, in every given moment the element will appear to be in the source or destination set* for accessing clients.* <p>* If the source set does not exist or does not contain the specified element no operation is* performed and zero is returned, otherwise the element is removed from the source set and added* to the destination set. On success one is returned, even if the element was already present in* the destination set.* <p>* An error is raised if the source or destination keys contain a non Set value.* <p>* Time complexity O(1)* @param srckey* @param dstkey* @param member* @return Integer reply, specifically: 1 if the element was moved 0 if the element was not found* on the first set and no operation was performed*/@Overridepublic Long smove(final byte[] srckey, final byte[] dstkey, final byte[] member) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.smove(srckey, dstkey, member);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Return the set cardinality (number of elements). If the key does not exist 0 is returned, like* for empty sets.* @param key* @return Integer reply, specifically: the cardinality (number of elements) of the set as an* integer.*/@Overridepublic Long scard(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.scard(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Return true if member is a member of the set stored at key, otherwise false is returned.* <p>* Time complexity O(1)* @param key* @param member* @return Boolean reply, specifically: true if the element is a member of the set false if the element* is not a member of the set OR if the key does not exist*/@Overridepublic Boolean sismember(final byte[] key, final byte[] member) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.sismember(key, member);return client.getIntegerReply() == 1;}/*** Return the members of a set resulting from the intersection of all the sets hold at the* specified keys. Like in {@link #lrange(byte[], long, long)} LRANGE} the result is sent to the* client as a multi-bulk reply (see the protocol specification for more information). If just a* single key is specified, then this command produces the same result as* {@link #smembers(byte[]) SMEMBERS}. Actually SMEMBERS is just syntax sugar for SINTER.* <p>* Non existing keys are considered like empty sets, so if one of the keys is missing an empty set* is returned (since the intersection with an empty set always is an empty set).* <p>* Time complexity O(N*M) worst case where N is the cardinality of the smallest set and M the* number of sets* @param keys* @return Multi bulk reply, specifically the list of common elements.*/@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> sinter(final byte[]... keys) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.sinter(keys);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}/*** This commanad works exactly like {@link #sinter(byte[]...) SINTER} but instead of being returned* the resulting set is stored as dstkey.* <p>* Time complexity O(N*M) worst case where N is the cardinality of the smallest set and M the* number of sets* @param dstkey* @param keys* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic Long sinterstore(final byte[] dstkey, final byte[]... keys) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.sinterstore(dstkey, keys);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Return the members of a set resulting from the union of all the sets hold at the specified* keys. Like in {@link #lrange(byte[], long, long)} LRANGE} the result is sent to the client as a* multi-bulk reply (see the protocol specification for more information). If just a single key is* specified, then this command produces the same result as {@link #smembers(byte[]) SMEMBERS}.* <p>* Non existing keys are considered like empty sets.* <p>* Time complexity O(N) where N is the total number of elements in all the provided sets* @param keys* @return Multi bulk reply, specifically the list of common elements.*/@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> sunion(final byte[]... keys) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.sunion(keys);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}/*** This command works exactly like {@link #sunion(byte[]...) SUNION} but instead of being returned* the resulting set is stored as dstkey. Any existing value in dstkey will be over-written.* <p>* Time complexity O(N) where N is the total number of elements in all the provided sets* @param dstkey* @param keys* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic Long sunionstore(final byte[] dstkey, final byte[]... keys) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.sunionstore(dstkey, keys);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Return the difference between the Set stored at key1 and all the Sets key2, ..., keyN* <p>* <b>Example:</b>** <pre>* key1 = [x, a, b, c]* key2 = [c]* key3 = [a, d]* SDIFF key1,key2,key3 => [x, b]* </pre>** Non existing keys are considered like empty sets.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b>* <p>* O(N) with N being the total number of elements of all the sets* @param keys* @return Return the members of a set resulting from the difference between the first set* provided and all the successive sets.*/@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> sdiff(final byte[]... keys) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.sdiff(keys);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}/*** This command works exactly like {@link #sdiff(byte[]...) SDIFF} but instead of being returned* the resulting set is stored in dstkey.* @param dstkey* @param keys* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic Long sdiffstore(final byte[] dstkey, final byte[]... keys) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.sdiffstore(dstkey, keys);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Return a random element from a Set, without removing the element. If the Set is empty or the* key does not exist, a nil object is returned.* <p>* The SPOP command does a similar work but the returned element is popped (removed) from the Set.* <p>* Time complexity O(1)* @param key* @return Bulk reply*/@Overridepublic byte[] srandmember(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.srandmember(key);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}@Overridepublic List<byte[]> srandmember(final byte[] key, final int count) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.srandmember(key, count);return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}/*** Add the specified member having the specified score to the sorted set stored at key. If member* is already a member of the sorted set the score is updated, and the element reinserted in the* right position to ensure sorting. If key does not exist a new sorted set with the specified* member as sole member is created. If the key exists but does not hold a sorted set value an* error is returned.* <p>* The score value can be the string representation of a double precision floating point number.* <p>* Time complexity O(log(N)) with N being the number of elements in the sorted set* @param key* @param score* @param member* @return Integer reply, specifically: 1 if the new element was added 0 if the element was* already a member of the sorted set and the score was updated*/@Overridepublic Long zadd(final byte[] key, final double score, final byte[] member) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zadd(key, score, member);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long zadd(final byte[] key, final double score, final byte[] member, final ZAddParams params) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zadd(key, score, member, params);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long zadd(final byte[] key, final Map<byte[], Double> scoreMembers) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zadd(key, scoreMembers);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long zadd(final byte[] key, final Map<byte[], Double> scoreMembers, final ZAddParams params) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zadd(key, scoreMembers, params);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> zrange(final byte[] key, final long start, final long stop) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrange(key, start, stop);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}/*** Remove the specified member from the sorted set value stored at key. If member was not a member* of the set no operation is performed. If key does not not hold a set value an error is* returned.* <p>* Time complexity O(log(N)) with N being the number of elements in the sorted set* @param key* @param members* @return Integer reply, specifically: 1 if the new element was removed 0 if the new element was* not a member of the set*/@Overridepublic Long zrem(final byte[] key, final byte[]... members) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrem(key, members);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** If member already exists in the sorted set adds the increment to its score and updates the* position of the element in the sorted set accordingly. If member does not already exist in the* sorted set it is added with increment as score (that is, like if the previous score was* virtually zero). If key does not exist a new sorted set with the specified member as sole* member is created. If the key exists but does not hold a sorted set value an error is returned.* <p>* The score value can be the string representation of a double precision floating point number.* It's possible to provide a negative value to perform a decrement.* <p>* For an introduction to sorted sets check the Introduction to Redis data types page.* <p>* Time complexity O(log(N)) with N being the number of elements in the sorted set* @param key* @param increment* @param member* @return The new score*/@Overridepublic Double zincrby(final byte[] key, final double increment, final byte[] member) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zincrby(key, increment, member);return BuilderFactory.DOUBLE.build(client.getOne());}@Overridepublic Double zincrby(final byte[] key, final double increment, final byte[] member, final ZIncrByParams params) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zincrby(key, increment, member, params);return BuilderFactory.DOUBLE.build(client.getOne());}/*** Return the rank (or index) or member in the sorted set at key, with scores being ordered from* low to high.* <p>* When the given member does not exist in the sorted set, the special value 'nil' is returned.* The returned rank (or index) of the member is 0-based for both commands.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b>* <p>* O(log(N))* @see #zrevrank(byte[], byte[])* @param key* @param member* @return Integer reply or a nil bulk reply, specifically: the rank of the element as an integer* reply if the element exists. A nil bulk reply if there is no such element.*/@Overridepublic Long zrank(final byte[] key, final byte[] member) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrank(key, member);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Return the rank (or index) or member in the sorted set at key, with scores being ordered from* high to low.* <p>* When the given member does not exist in the sorted set, the special value 'nil' is returned.* The returned rank (or index) of the member is 0-based for both commands.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b>* <p>* O(log(N))* @see #zrank(byte[], byte[])* @param key* @param member* @return Integer reply or a nil bulk reply, specifically: the rank of the element as an integer* reply if the element exists. A nil bulk reply if there is no such element.*/@Overridepublic Long zrevrank(final byte[] key, final byte[] member) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrevrank(key, member);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> zrevrange(final byte[] key, final long start, final long stop) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrevrange(key, start, stop);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic Set<Tuple> zrangeWithScores(final byte[] key, final long start, final long stop) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrangeWithScores(key, start, stop);return getTupledSet();}@Overridepublic Set<Tuple> zrevrangeWithScores(final byte[] key, final long start, final long stop) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrevrangeWithScores(key, start, stop);return getTupledSet();}/*** Return the sorted set cardinality (number of elements). If the key does not exist 0 is* returned, like for empty sorted sets.* <p>* Time complexity O(1)* @param key* @return the cardinality (number of elements) of the set as an integer.*/@Overridepublic Long zcard(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zcard(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Return the score of the specified element of the sorted set at key. If the specified element* does not exist in the sorted set, or the key does not exist at all, a special 'nil' value is* returned.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b> O(1)* @param key* @param member* @return the score*/@Overridepublic Double zscore(final byte[] key, final byte[] member) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zscore(key, member);final String score = client.getBulkReply();return (score != null ? new Double(score) : null);}@Overridepublic Tuple zpopmax(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zpopmax(key);return BuilderFactory.TUPLE.build(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic Set<Tuple> zpopmax(final byte[] key, final int count) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zpopmax(key, count);return getTupledSet();}@Overridepublic Tuple zpopmin(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zpopmin(key);return BuilderFactory.TUPLE.build(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic Set<Tuple> zpopmin(final byte[] key, final int count) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zpopmin(key, count);return getTupledSet();}public Transaction multi() {client.multi();client.getOne(); // expected OKtransaction = new Transaction(client);return transaction;}protected void checkIsInMultiOrPipeline() {if (client.isInMulti()) {throw new JedisDataException("Cannot use Jedis when in Multi. Please use Transaction or reset jedis state.");} else if (pipeline != null && pipeline.hasPipelinedResponse()) {throw new JedisDataException("Cannot use Jedis when in Pipeline. Please use Pipeline or reset jedis state .");}}public void connect() {client.connect();}public void disconnect() {client.disconnect();}public void resetState() {if (client.isConnected()) {if (transaction != null) {transaction.close();}if (pipeline != null) {pipeline.close();}client.resetState();}transaction = null;pipeline = null;}@Overridepublic String watch(final byte[]... keys) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.watch(keys);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}@Overridepublic String unwatch() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.unwatch();return client.getStatusCodeReply();}@Overridepublic void close() {client.close();}/*** Sort a Set or a List.* <p>* Sort the elements contained in the List, Set, or Sorted Set value at key. By default sorting is* numeric with elements being compared as double precision floating point numbers. This is the* simplest form of SORT.* @see #sort(byte[], byte[])* @see #sort(byte[], SortingParams)* @see #sort(byte[], SortingParams, byte[])* @param key* @return Assuming the Set/List at key contains a list of numbers, the return value will be the* list of numbers ordered from the smallest to the biggest number.*/@Overridepublic List<byte[]> sort(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.sort(key);return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}/*** Sort a Set or a List accordingly to the specified parameters.* <p>* <b>examples:</b>* <p>* Given are the following sets and key/values:** <pre>* x = [1, 2, 3]* y = [a, b, c]** k1 = z* k2 = y* k3 = x** w1 = 9* w2 = 8* w3 = 7* </pre>** Sort Order:** <pre>* sort(x) or sort(x, sp.asc())* -> [1, 2, 3]** sort(x, sp.desc())* -> [3, 2, 1]** sort(y)* -> [c, a, b]** sort(y, sp.alpha())* -> [a, b, c]** sort(y, sp.alpha().desc())* -> [c, a, b]* </pre>** Limit (e.g. for Pagination):** <pre>* sort(x, sp.limit(0, 2))* -> [1, 2]** sort(y, sp.alpha().desc().limit(1, 2))* -> [b, a]* </pre>** Sorting by external keys:** <pre>* sort(x, sb.by(w*))* -> [3, 2, 1]** sort(x, sb.by(w*).desc())* -> [1, 2, 3]* </pre>** Getting external keys:** <pre>* sort(x, sp.by(w*).get(k*))* -> [x, y, z]** sort(x, sp.by(w*).get(#).get(k*))* -> [3, x, 2, y, 1, z]* </pre>* @see #sort(byte[])* @see #sort(byte[], SortingParams, byte[])* @param key* @param sortingParameters* @return a list of sorted elements.*/@Overridepublic List<byte[]> sort(final byte[] key, final SortingParams sortingParameters) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.sort(key, sortingParameters);return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}/*** BLPOP (and BRPOP) is a blocking list pop primitive. You can see this commands as blocking* versions of LPOP and RPOP able to block if the specified keys don't exist or contain empty* lists.* <p>* The following is a description of the exact semantic. We describe BLPOP but the two commands* are identical, the only difference is that BLPOP pops the element from the left (head) of the* list, and BRPOP pops from the right (tail).* <p>* <b>Non blocking behavior</b>* <p>* When BLPOP is called, if at least one of the specified keys contain a non empty list, an* element is popped from the head of the list and returned to the caller together with the name* of the key (BLPOP returns a two elements array, the first element is the key, the second the* popped value).* <p>* Keys are scanned from left to right, so for instance if you issue BLPOP list1 list2 list3 0* against a dataset where list1 does not exist but list2 and list3 contain non empty lists, BLPOP* guarantees to return an element from the list stored at list2 (since it is the first non empty* list starting from the left).* <p>* <b>Blocking behavior</b>* <p>* If none of the specified keys exist or contain non empty lists, BLPOP blocks until some other* client performs a LPUSH or an RPUSH operation against one of the lists.* <p>* Once new data is present on one of the lists, the client finally returns with the name of the* key unblocking it and the popped value.* <p>* When blocking, if a non-zero timeout is specified, the client will unblock returning a nil* special value if the specified amount of seconds passed without a push operation against at* least one of the specified keys.* <p>* The timeout argument is interpreted as an integer value. A timeout of zero means instead to* block forever.* <p>* <b>Multiple clients blocking for the same keys</b>* <p>* Multiple clients can block for the same key. They are put into a queue, so the first to be* served will be the one that started to wait earlier, in a first-blpopping first-served fashion.* <p>* <b>blocking POP inside a MULTI/EXEC transaction</b>* <p>* BLPOP and BRPOP can be used with pipelining (sending multiple commands and reading the replies* in batch), but it does not make sense to use BLPOP or BRPOP inside a MULTI/EXEC block (a Redis* transaction).* <p>* The behavior of BLPOP inside MULTI/EXEC when the list is empty is to return a multi-bulk nil* reply, exactly what happens when the timeout is reached. If you like science fiction, think at* it like if inside MULTI/EXEC the time will flow at infinite speed :)* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @see #brpop(int, byte[]...)* @param timeout* @param keys* @return BLPOP returns a two-elements array via a multi bulk reply in order to return both the* unblocking key and the popped value.* <p>* When a non-zero timeout is specified, and the BLPOP operation timed out, the return* value is a nil multi bulk reply. Most client values will return false or nil* accordingly to the programming language used.*/@Overridepublic List<byte[]> blpop(final int timeout, final byte[]... keys) {return blpop(getArgsAddTimeout(timeout, keys));}private byte[][] getArgsAddTimeout(int timeout, byte[][] keys) {int size = keys.length;final byte[][] args = new byte[size + 1][];for (int at = 0; at != size; ++at) {args[at] = keys[at];}args[size] = Protocol.toByteArray(timeout);return args;}/*** Sort a Set or a List accordingly to the specified parameters and store the result at dstkey.* @see #sort(byte[], SortingParams)* @see #sort(byte[])* @see #sort(byte[], byte[])* @param key* @param sortingParameters* @param dstkey* @return The number of elements of the list at dstkey.*/@Overridepublic Long sort(final byte[] key, final SortingParams sortingParameters, final byte[] dstkey) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.sort(key, sortingParameters, dstkey);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Sort a Set or a List and Store the Result at dstkey.* <p>* Sort the elements contained in the List, Set, or Sorted Set value at key and store the result* at dstkey. By default sorting is numeric with elements being compared as double precision* floating point numbers. This is the simplest form of SORT.* @see #sort(byte[])* @see #sort(byte[], SortingParams)* @see #sort(byte[], SortingParams, byte[])* @param key* @param dstkey* @return The number of elements of the list at dstkey.*/@Overridepublic Long sort(final byte[] key, final byte[] dstkey) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.sort(key, dstkey);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** BLPOP (and BRPOP) is a blocking list pop primitive. You can see this commands as blocking* versions of LPOP and RPOP able to block if the specified keys don't exist or contain empty* lists.* <p>* The following is a description of the exact semantic. We describe BLPOP but the two commands* are identical, the only difference is that BLPOP pops the element from the left (head) of the* list, and BRPOP pops from the right (tail).* <p>* <b>Non blocking behavior</b>* <p>* When BLPOP is called, if at least one of the specified keys contain a non empty list, an* element is popped from the head of the list and returned to the caller together with the name* of the key (BLPOP returns a two elements array, the first element is the key, the second the* popped value).* <p>* Keys are scanned from left to right, so for instance if you issue BLPOP list1 list2 list3 0* against a dataset where list1 does not exist but list2 and list3 contain non empty lists, BLPOP* guarantees to return an element from the list stored at list2 (since it is the first non empty* list starting from the left).* <p>* <b>Blocking behavior</b>* <p>* If none of the specified keys exist or contain non empty lists, BLPOP blocks until some other* client performs a LPUSH or an RPUSH operation against one of the lists.* <p>* Once new data is present on one of the lists, the client finally returns with the name of the* key unblocking it and the popped value.* <p>* When blocking, if a non-zero timeout is specified, the client will unblock returning a nil* special value if the specified amount of seconds passed without a push operation against at* least one of the specified keys.* <p>* The timeout argument is interpreted as an integer value. A timeout of zero means instead to* block forever.* <p>* <b>Multiple clients blocking for the same keys</b>* <p>* Multiple clients can block for the same key. They are put into a queue, so the first to be* served will be the one that started to wait earlier, in a first-blpopping first-served fashion.* <p>* <b>blocking POP inside a MULTI/EXEC transaction</b>* <p>* BLPOP and BRPOP can be used with pipelining (sending multiple commands and reading the replies* in batch), but it does not make sense to use BLPOP or BRPOP inside a MULTI/EXEC block (a Redis* transaction).* <p>* The behavior of BLPOP inside MULTI/EXEC when the list is empty is to return a multi-bulk nil* reply, exactly what happens when the timeout is reached. If you like science fiction, think at* it like if inside MULTI/EXEC the time will flow at infinite speed :)* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @see #blpop(int, byte[]...)* @param timeout* @param keys* @return BLPOP returns a two-elements array via a multi bulk reply in order to return both the* unblocking key and the popped value.* <p>* When a non-zero timeout is specified, and the BLPOP operation timed out, the return* value is a nil multi bulk reply. Most client values will return false or nil* accordingly to the programming language used.*/@Overridepublic List<byte[]> brpop(final int timeout, final byte[]... keys) {return brpop(getArgsAddTimeout(timeout, keys));}@Overridepublic List<byte[]> blpop(final byte[]... args) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.blpop(args);client.setTimeoutInfinite();try {return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();} finally {client.rollbackTimeout();}}@Overridepublic List<byte[]> brpop(final byte[]... args) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.brpop(args);client.setTimeoutInfinite();try {return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();} finally {client.rollbackTimeout();}}/*** Request for authentication in a password protected Redis server. A Redis server can be* instructed to require a password before to allow clients to issue commands. This is done using* the requirepass directive in the Redis configuration file. If the password given by the client* is correct the server replies with an OK status code reply and starts accepting commands from* the client. Otherwise an error is returned and the clients needs to try a new password. Note* that for the high performance nature of Redis it is possible to try a lot of passwords in* parallel in very short time, so make sure to generate a strong and very long password so that* this attack is infeasible.* @param password* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic String auth(final String password) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();if(StringUtils.isBlank(this.user)){client.auth(password);}else{client.auth(user,password);}return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Request for authentication with a Redis Server that is using ACL where user are authenticated with* username and password.* See https://redis.io/topics/acl* @param user* @param password* @return*/@Overridepublic String auth(final String user, final String password) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.auth(user, password);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}public Pipeline pipelined() {pipeline = new Pipeline();pipeline.setClient(client);return pipeline;}@Overridepublic Long zcount(final byte[] key, final double min, final double max) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zcount(key, min, max);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long zcount(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zcount(key, min, max);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Return the all the elements in the sorted set at key with a score between min and max* (including elements with score equal to min or max).* <p>* The elements having the same score are returned sorted lexicographically as ASCII strings (this* follows from a property of Redis sorted sets and does not involve further computation).* <p>* Using the optional {@link #zrangeByScore(byte[], double, double, int, int) LIMIT} it's possible* to get only a range of the matching elements in an SQL-alike way. Note that if offset is large* the commands needs to traverse the list for offset elements and this adds up to the O(M)* figure.* <p>* The {@link #zcount(byte[], double, double) ZCOUNT} command is similar to* {@link #zrangeByScore(byte[], double, double) ZRANGEBYSCORE} but instead of returning the* actual elements in the specified interval, it just returns the number of matching elements.* <p>* <b>Exclusive intervals and infinity</b>* <p>* min and max can be -inf and +inf, so that you are not required to know what's the greatest or* smallest element in order to take, for instance, elements "up to a given value".* <p>* Also while the interval is for default closed (inclusive) it's possible to specify open* intervals prefixing the score with a "(" character, so for instance:* <p>* {@code ZRANGEBYSCORE zset (1.3 5}* <p>* Will return all the values with score > 1.3 and <= 5, while for instance:* <p>* {@code ZRANGEBYSCORE zset (5 (10}* <p>* Will return all the values with score > 5 and < 10 (5 and 10 excluded).* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b>* <p>* O(log(N))+O(M) with N being the number of elements in the sorted set and M the number of* elements returned by the command, so if M is constant (for instance you always ask for the* first ten elements with LIMIT) you can consider it O(log(N))* @see #zrangeByScore(byte[], double, double)* @see #zrangeByScore(byte[], double, double, int, int)* @see #zrangeByScoreWithScores(byte[], double, double)* @see #zrangeByScoreWithScores(byte[], double, double, int, int)* @see #zcount(byte[], double, double)* @param key* @param min* @param max* @return Multi bulk reply specifically a list of elements in the specified score range.*/@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> zrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final double min, final double max) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrangeByScore(key, min, max);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> zrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrangeByScore(key, min, max);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}/*** Return the all the elements in the sorted set at key with a score between min and max* (including elements with score equal to min or max).* <p>* The elements having the same score are returned sorted lexicographically as ASCII strings (this* follows from a property of Redis sorted sets and does not involve further computation).* <p>* Using the optional {@link #zrangeByScore(byte[], double, double, int, int) LIMIT} it's possible* to get only a range of the matching elements in an SQL-alike way. Note that if offset is large* the commands needs to traverse the list for offset elements and this adds up to the O(M)* figure.* <p>* The {@link #zcount(byte[], double, double) ZCOUNT} command is similar to* {@link #zrangeByScore(byte[], double, double) ZRANGEBYSCORE} but instead of returning the* actual elements in the specified interval, it just returns the number of matching elements.* <p>* <b>Exclusive intervals and infinity</b>* <p>* min and max can be -inf and +inf, so that you are not required to know what's the greatest or* smallest element in order to take, for instance, elements "up to a given value".* <p>* Also while the interval is for default closed (inclusive) it's possible to specify open* intervals prefixing the score with a "(" character, so for instance:* <p>* {@code ZRANGEBYSCORE zset (1.3 5}* <p>* Will return all the values with score > 1.3 and <= 5, while for instance:* <p>* {@code ZRANGEBYSCORE zset (5 (10}* <p>* Will return all the values with score > 5 and < 10 (5 and 10 excluded).* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b>* <p>* O(log(N))+O(M) with N being the number of elements in the sorted set and M the number of* elements returned by the command, so if M is constant (for instance you always ask for the* first ten elements with LIMIT) you can consider it O(log(N))* @see #zrangeByScore(byte[], double, double)* @see #zrangeByScore(byte[], double, double, int, int)* @see #zrangeByScoreWithScores(byte[], double, double)* @see #zrangeByScoreWithScores(byte[], double, double, int, int)* @see #zcount(byte[], double, double)* @param key* @param min* @param max* @param offset* @param count* @return Multi bulk reply specifically a list of elements in the specified score range.*/@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> zrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final double min, final double max,final int offset, final int count) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrangeByScore(key, min, max, offset, count);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> zrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max,final int offset, final int count) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrangeByScore(key, min, max, offset, count);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}/*** Return the all the elements in the sorted set at key with a score between min and max* (including elements with score equal to min or max).* <p>* The elements having the same score are returned sorted lexicographically as ASCII strings (this* follows from a property of Redis sorted sets and does not involve further computation).* <p>* Using the optional {@link #zrangeByScore(byte[], double, double, int, int) LIMIT} it's possible* to get only a range of the matching elements in an SQL-alike way. Note that if offset is large* the commands needs to traverse the list for offset elements and this adds up to the O(M)* figure.* <p>* The {@link #zcount(byte[], double, double) ZCOUNT} command is similar to* {@link #zrangeByScore(byte[], double, double) ZRANGEBYSCORE} but instead of returning the* actual elements in the specified interval, it just returns the number of matching elements.* <p>* <b>Exclusive intervals and infinity</b>* <p>* min and max can be -inf and +inf, so that you are not required to know what's the greatest or* smallest element in order to take, for instance, elements "up to a given value".* <p>* Also while the interval is for default closed (inclusive) it's possible to specify open* intervals prefixing the score with a "(" character, so for instance:* <p>* {@code ZRANGEBYSCORE zset (1.3 5}* <p>* Will return all the values with score > 1.3 and <= 5, while for instance:* <p>* {@code ZRANGEBYSCORE zset (5 (10}* <p>* Will return all the values with score > 5 and < 10 (5 and 10 excluded).* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b>* <p>* O(log(N))+O(M) with N being the number of elements in the sorted set and M the number of* elements returned by the command, so if M is constant (for instance you always ask for the* first ten elements with LIMIT) you can consider it O(log(N))* @see #zrangeByScore(byte[], double, double)* @see #zrangeByScore(byte[], double, double, int, int)* @see #zrangeByScoreWithScores(byte[], double, double)* @see #zrangeByScoreWithScores(byte[], double, double, int, int)* @see #zcount(byte[], double, double)* @param key* @param min* @param max* @return Multi bulk reply specifically a list of elements in the specified score range.*/@Overridepublic Set<Tuple> zrangeByScoreWithScores(final byte[] key, final double min, final double max) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrangeByScoreWithScores(key, min, max);return getTupledSet();}@Overridepublic Set<Tuple> zrangeByScoreWithScores(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrangeByScoreWithScores(key, min, max);return getTupledSet();}/*** Return the all the elements in the sorted set at key with a score between min and max* (including elements with score equal to min or max).* <p>* The elements having the same score are returned sorted lexicographically as ASCII strings (this* follows from a property of Redis sorted sets and does not involve further computation).* <p>* Using the optional {@link #zrangeByScore(byte[], double, double, int, int) LIMIT} it's possible* to get only a range of the matching elements in an SQL-alike way. Note that if offset is large* the commands needs to traverse the list for offset elements and this adds up to the O(M)* figure.* <p>* The {@link #zcount(byte[], double, double) ZCOUNT} command is similar to* {@link #zrangeByScore(byte[], double, double) ZRANGEBYSCORE} but instead of returning the* actual elements in the specified interval, it just returns the number of matching elements.* <p>* <b>Exclusive intervals and infinity</b>* <p>* min and max can be -inf and +inf, so that you are not required to know what's the greatest or* smallest element in order to take, for instance, elements "up to a given value".* <p>* Also while the interval is for default closed (inclusive) it's possible to specify open* intervals prefixing the score with a "(" character, so for instance:* <p>* {@code ZRANGEBYSCORE zset (1.3 5}* <p>* Will return all the values with score > 1.3 and <= 5, while for instance:* <p>* {@code ZRANGEBYSCORE zset (5 (10}* <p>* Will return all the values with score > 5 and < 10 (5 and 10 excluded).* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b>* <p>* O(log(N))+O(M) with N being the number of elements in the sorted set and M the number of* elements returned by the command, so if M is constant (for instance you always ask for the* first ten elements with LIMIT) you can consider it O(log(N))* @see #zrangeByScore(byte[], double, double)* @see #zrangeByScore(byte[], double, double, int, int)* @see #zrangeByScoreWithScores(byte[], double, double)* @see #zrangeByScoreWithScores(byte[], double, double, int, int)* @see #zcount(byte[], double, double)* @param key* @param min* @param max* @param offset* @param count* @return Multi bulk reply specifically a list of elements in the specified score range.*/@Overridepublic Set<Tuple> zrangeByScoreWithScores(final byte[] key, final double min, final double max,final int offset, final int count) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrangeByScoreWithScores(key, min, max, offset, count);return getTupledSet();}@Overridepublic Set<Tuple> zrangeByScoreWithScores(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max,final int offset, final int count) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrangeByScoreWithScores(key, min, max, offset, count);return getTupledSet();}protected Set<Tuple> getTupledSet() {List<byte[]> membersWithScores = client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();if (membersWithScores.isEmpty()) {return Collections.emptySet();}Set<Tuple> set = new LinkedHashSet<>(membersWithScores.size() / 2, 1.0f);Iterator<byte[]> iterator = membersWithScores.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {set.add(new Tuple(iterator.next(), BuilderFactory.DOUBLE.build(iterator.next())));}return set;}@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> zrevrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final double max, final double min) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrevrangeByScore(key, max, min);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> zrevrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final byte[] max, final byte[] min) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrevrangeByScore(key, max, min);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> zrevrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final double max, final double min,final int offset, final int count) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrevrangeByScore(key, max, min, offset, count);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> zrevrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final byte[] max, final byte[] min,final int offset, final int count) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrevrangeByScore(key, max, min, offset, count);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic Set<Tuple> zrevrangeByScoreWithScores(final byte[] key, final double max, final double min) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrevrangeByScoreWithScores(key, max, min);return getTupledSet();}@Overridepublic Set<Tuple> zrevrangeByScoreWithScores(final byte[] key, final double max,final double min, final int offset, final int count) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrevrangeByScoreWithScores(key, max, min, offset, count);return getTupledSet();}@Overridepublic Set<Tuple> zrevrangeByScoreWithScores(final byte[] key, final byte[] max, final byte[] min) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrevrangeByScoreWithScores(key, max, min);return getTupledSet();}@Overridepublic Set<Tuple> zrevrangeByScoreWithScores(final byte[] key, final byte[] max,final byte[] min, final int offset, final int count) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrevrangeByScoreWithScores(key, max, min, offset, count);return getTupledSet();}/*** Remove all elements in the sorted set at key with rank between start and end. Start and end are* 0-based with rank 0 being the element with the lowest score. Both start and end can be negative* numbers, where they indicate offsets starting at the element with the highest rank. For* example: -1 is the element with the highest score, -2 the element with the second highest score* and so forth.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b> O(log(N))+O(M) with N being the number of elements in the sorted set* and M the number of elements removed by the operation* @param key* @param start* @param stop* @return*/@Overridepublic Long zremrangeByRank(final byte[] key, final long start, final long stop) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zremrangeByRank(key, start, stop);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Remove all the elements in the sorted set at key with a score between min and max (including* elements with score equal to min or max).* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b>* <p>* O(log(N))+O(M) with N being the number of elements in the sorted set and M the number of* elements removed by the operation* @param key* @param min* @param max* @return Integer reply, specifically the number of elements removed.*/@Overridepublic Long zremrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final double min, final double max) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zremrangeByScore(key, min, max);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long zremrangeByScore(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zremrangeByScore(key, min, max);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Creates a union or intersection of N sorted sets given by keys k1 through kN, and stores it at* dstkey. It is mandatory to provide the number of input keys N, before passing the input keys* and the other (optional) arguments.* <p>* As the terms imply, the {@link #zinterstore(byte[], byte[]...)} ZINTERSTORE} command requires* an element to be present in each of the given inputs to be inserted in the result. The {@link* #zunionstore(byte[], byte[]...)} command inserts all elements across all inputs.* <p>* Using the WEIGHTS option, it is possible to add weight to each input sorted set. This means* that the score of each element in the sorted set is first multiplied by this weight before* being passed to the aggregation. When this option is not given, all weights default to 1.* <p>* With the AGGREGATE option, it's possible to specify how the results of the union or* intersection are aggregated. This option defaults to SUM, where the score of an element is* summed across the inputs where it exists. When this option is set to be either MIN or MAX, the* resulting set will contain the minimum or maximum score of an element across the inputs where* it exists.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b> O(N) + O(M log(M)) with N being the sum of the sizes of the input* sorted sets, and M being the number of elements in the resulting sorted set* @see #zunionstore(byte[], byte[]...)* @see #zunionstore(byte[], ZParams, byte[]...)* @see #zinterstore(byte[], byte[]...)* @see #zinterstore(byte[], ZParams, byte[]...)* @param dstkey* @param sets* @return Integer reply, specifically the number of elements in the sorted set at dstkey*/@Overridepublic Long zunionstore(final byte[] dstkey, final byte[]... sets) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zunionstore(dstkey, sets);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Creates a union or intersection of N sorted sets given by keys k1 through kN, and stores it at* dstkey. It is mandatory to provide the number of input keys N, before passing the input keys* and the other (optional) arguments.* <p>* As the terms imply, the {@link #zinterstore(byte[], byte[]...) ZINTERSTORE} command requires an* element to be present in each of the given inputs to be inserted in the result. The {@link* #zunionstore(byte[], byte[]...) ZUNIONSTORE} command inserts all elements across all inputs.* <p>* Using the WEIGHTS option, it is possible to add weight to each input sorted set. This means* that the score of each element in the sorted set is first multiplied by this weight before* being passed to the aggregation. When this option is not given, all weights default to 1.* <p>* With the AGGREGATE option, it's possible to specify how the results of the union or* intersection are aggregated. This option defaults to SUM, where the score of an element is* summed across the inputs where it exists. When this option is set to be either MIN or MAX, the* resulting set will contain the minimum or maximum score of an element across the inputs where* it exists.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b> O(N) + O(M log(M)) with N being the sum of the sizes of the input* sorted sets, and M being the number of elements in the resulting sorted set* @see #zunionstore(byte[], byte[]...)* @see #zunionstore(byte[], ZParams, byte[]...)* @see #zinterstore(byte[], byte[]...)* @see #zinterstore(byte[], ZParams, byte[]...)* @param dstkey* @param sets* @param params* @return Integer reply, specifically the number of elements in the sorted set at dstkey*/@Overridepublic Long zunionstore(final byte[] dstkey, final ZParams params, final byte[]... sets) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zunionstore(dstkey, params, sets);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Creates a union or intersection of N sorted sets given by keys k1 through kN, and stores it at* dstkey. It is mandatory to provide the number of input keys N, before passing the input keys* and the other (optional) arguments.* <p>* As the terms imply, the {@link #zinterstore(byte[], byte[]...) ZINTERSTORE} command requires an* element to be present in each of the given inputs to be inserted in the result. The {@link* #zunionstore(byte[], byte[]...) ZUNIONSTORE} command inserts all elements across all inputs.* <p>* Using the WEIGHTS option, it is possible to add weight to each input sorted set. This means* that the score of each element in the sorted set is first multiplied by this weight before* being passed to the aggregation. When this option is not given, all weights default to 1.* <p>* With the AGGREGATE option, it's possible to specify how the results of the union or* intersection are aggregated. This option defaults to SUM, where the score of an element is* summed across the inputs where it exists. When this option is set to be either MIN or MAX, the* resulting set will contain the minimum or maximum score of an element across the inputs where* it exists.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b> O(N) + O(M log(M)) with N being the sum of the sizes of the input* sorted sets, and M being the number of elements in the resulting sorted set* @see #zunionstore(byte[], byte[]...)* @see #zunionstore(byte[], ZParams, byte[]...)* @see #zinterstore(byte[], byte[]...)* @see #zinterstore(byte[], ZParams, byte[]...)* @param dstkey* @param sets* @return Integer reply, specifically the number of elements in the sorted set at dstkey*/@Overridepublic Long zinterstore(final byte[] dstkey, final byte[]... sets) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zinterstore(dstkey, sets);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Creates a union or intersection of N sorted sets given by keys k1 through kN, and stores it at* dstkey. It is mandatory to provide the number of input keys N, before passing the input keys* and the other (optional) arguments.* <p>* As the terms imply, the {@link #zinterstore(byte[], byte[]...) ZINTERSTORE} command requires an* element to be present in each of the given inputs to be inserted in the result. The {@link* #zunionstore(byte[], byte[]...) ZUNIONSTORE} command inserts all elements across all inputs.* <p>* Using the WEIGHTS option, it is possible to add weight to each input sorted set. This means* that the score of each element in the sorted set is first multiplied by this weight before* being passed to the aggregation. When this option is not given, all weights default to 1.* <p>* With the AGGREGATE option, it's possible to specify how the results of the union or* intersection are aggregated. This option defaults to SUM, where the score of an element is* summed across the inputs where it exists. When this option is set to be either MIN or MAX, the* resulting set will contain the minimum or maximum score of an element across the inputs where* it exists.* <p>* <b>Time complexity:</b> O(N) + O(M log(M)) with N being the sum of the sizes of the input* sorted sets, and M being the number of elements in the resulting sorted set* @see #zunionstore(byte[], byte[]...)* @see #zunionstore(byte[], ZParams, byte[]...)* @see #zinterstore(byte[], byte[]...)* @see #zinterstore(byte[], ZParams, byte[]...)* @param dstkey* @param sets* @param params* @return Integer reply, specifically the number of elements in the sorted set at dstkey*/@Overridepublic Long zinterstore(final byte[] dstkey, final ZParams params, final byte[]... sets) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zinterstore(dstkey, params, sets);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long zlexcount(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zlexcount(key, min, max);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> zrangeByLex(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrangeByLex(key, min, max);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> zrangeByLex(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max,final int offset, final int count) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrangeByLex(key, min, max, offset, count);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> zrevrangeByLex(final byte[] key, final byte[] max, final byte[] min) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrevrangeByLex(key, max, min);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic Set<byte[]> zrevrangeByLex(final byte[] key, final byte[] max, final byte[] min, final int offset, final int count) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zrevrangeByLex(key, max, min, offset, count);return SetFromList.of(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic Long zremrangeByLex(final byte[] key, final byte[] min, final byte[] max) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zremrangeByLex(key, min, max);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Synchronously save the DB on disk.* <p>* Save the whole dataset on disk (this means that all the databases are saved, as well as keys* with an EXPIRE set (the expire is preserved). The server hangs while the saving is not* completed, no connection is served in the meanwhile. An OK code is returned when the DB was* fully stored in disk.* <p>* The background variant of this command is {@link #bgsave() BGSAVE} that is able to perform the* saving in the background while the server continues serving other clients.* <p>* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic String save() {client.save();return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Asynchronously save the DB on disk.* <p>* Save the DB in background. The OK code is immediately returned. Redis forks, the parent* continues to server the clients, the child saves the DB on disk then exit. A client my be able* to check if the operation succeeded using the LASTSAVE command.* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic String bgsave() {client.bgsave();return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Rewrite the append only file in background when it gets too big. Please for detailed* information about the Redis Append Only File check the <a* href="http://redis.io/topics/persistence#append-only-file">Append Only File Howto</a>.* <p>* BGREWRITEAOF rewrites the Append Only File in background when it gets too big. The Redis Append* Only File is a Journal, so every operation modifying the dataset is logged in the Append Only* File (and replayed at startup). This means that the Append Only File always grows. In order to* rebuild its content the BGREWRITEAOF creates a new version of the append only file starting* directly form the dataset in memory in order to guarantee the generation of the minimal number* of commands needed to rebuild the database.* <p>* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic String bgrewriteaof() {client.bgrewriteaof();return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Return the UNIX time stamp of the last successfully saving of the dataset on disk.* <p>* Return the UNIX TIME of the last DB save executed with success. A client may check if a* {@link #bgsave() BGSAVE} command succeeded reading the LASTSAVE value, then issuing a BGSAVE* command and checking at regular intervals every N seconds if LASTSAVE changed.* @return Integer reply, specifically an UNIX time stamp.*/@Overridepublic Long lastsave() {client.lastsave();return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Synchronously save the DB on disk, then shutdown the server.* <p>* Stop all the clients, save the DB, then quit the server. This commands makes sure that the DB* is switched off without the lost of any data. This is not guaranteed if the client uses simply* {@link #save() SAVE} and then {@link #quit() QUIT} because other clients may alter the DB data* between the two commands.* @return Status code reply on error. On success nothing is returned since the server quits and* the connection is closed.*/@Overridepublic String shutdown() {client.shutdown();String status;try {status = client.getStatusCodeReply();} catch (JedisException ex) {status = null;}return status;}/*** Provide information and statistics about the server.* <p>* The info command returns different information and statistics about the server in an format* that's simple to parse by computers and easy to read by humans.* <p>* <b>Format of the returned String:</b>* <p>* All the fields are in the form field:value** <pre>* edis_version:0.07* connected_clients:1* connected_slaves:0* used_memory:3187* changes_since_last_save:0* last_save_time:1237655729* total_connections_received:1* total_commands_processed:1* uptime_in_seconds:25* uptime_in_days:0* </pre>** <b>Notes</b>* <p>* used_memory is returned in bytes, and is the total number of bytes allocated by the program* using malloc.* <p>* uptime_in_days is redundant since the uptime in seconds contains already the full uptime* information, this field is only mainly present for humans.* <p>* changes_since_last_save does not refer to the number of key changes, but to the number of* operations that produced some kind of change in the dataset.* <p>* @return Bulk reply*/@Overridepublic String info() {client.info();return client.getBulkReply();}@Overridepublic String info(final String section) {client.info(section);return client.getBulkReply();}/*** Dump all the received requests in real time.* <p>* MONITOR is a debugging command that outputs the whole sequence of commands received by the* Redis server. is very handy in order to understand what is happening into the database. This* command is used directly via telnet.* @param jedisMonitor*/public void monitor(final JedisMonitor jedisMonitor) {client.monitor();client.getStatusCodeReply();jedisMonitor.proceed(client);}/*** Change the replication settings.* <p>* The SLAVEOF command can change the replication settings of a slave on the fly. If a Redis* server is already acting as slave, the command SLAVEOF NO ONE will turn off the replication* turning the Redis server into a MASTER. In the proper form SLAVEOF hostname port will make the* server a slave of the specific server listening at the specified hostname and port.* <p>* If a server is already a slave of some master, SLAVEOF hostname port will stop the replication* against the old server and start the synchronization against the new one discarding the old* dataset.* <p>* The form SLAVEOF no one will stop replication turning the server into a MASTER but will not* discard the replication. So if the old master stop working it is possible to turn the slave* into a master and set the application to use the new master in read/write. Later when the other* Redis server will be fixed it can be configured in order to work as slave.* <p>* @param host* @param port* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic String slaveof(final String host, final int port) {client.slaveof(host, port);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}@Overridepublic String slaveofNoOne() {client.slaveofNoOne();return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Retrieve the configuration of a running Redis server. Not all the configuration parameters are* supported.* <p>* CONFIG GET returns the current configuration parameters. This sub command only accepts a single* argument, that is glob style pattern. All the configuration parameters matching this parameter* are reported as a list of key-value pairs.* <p>* <b>Example:</b>** <pre>* $ redis-cli config get '*'* 1. "dbfilename"* 2. "dump.rdb"* 3. "requirepass"* 4. (nil)* 5. "masterauth"* 6. (nil)* 7. "maxmemory"* 8. "0\n"* 9. "appendfsync"* 10. "everysec"* 11. "save"* 12. "3600 1 300 100 60 10000"** $ redis-cli config get 'm*'* 1. "masterauth"* 2. (nil)* 3. "maxmemory"* 4. "0\n"* </pre>* @param pattern* @return Bulk reply.*/@Overridepublic List<byte[]> configGet(final byte[] pattern) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.configGet(pattern);return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}/*** Reset the stats returned by INFO* @return*/@Overridepublic String configResetStat() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.configResetStat();return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** The CONFIG REWRITE command rewrites the redis.conf file the server was started with, applying* the minimal changes needed to make it reflect the configuration currently used by the server,* which may be different compared to the original one because of the use of the CONFIG SET command.** The rewrite is performed in a very conservative way:* <ul>* <li>Comments and the overall structure of the original redis.conf are preserved as much as possible.</li>* <li>If an option already exists in the old redis.conf file, it will be rewritten at the same position (line number).</li>* <li>If an option was not already present, but it is set to its default value, it is not added by the rewrite process.</li>* <li>If an option was not already present, but it is set to a non-default value, it is appended at the end of the file.</li>* <li>Non used lines are blanked. For instance if you used to have multiple save directives, but* the current configuration has fewer or none as you disabled RDB persistence, all the lines will be blanked.</li>* </ul>** CONFIG REWRITE is also able to rewrite the configuration file from scratch if the original one* no longer exists for some reason. However if the server was started without a configuration* file at all, the CONFIG REWRITE will just return an error.* @return OK when the configuration was rewritten properly. Otherwise an error is returned.*/@Overridepublic String configRewrite() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.configRewrite();return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Alter the configuration of a running Redis server. Not all the configuration parameters are* supported.* <p>* The list of configuration parameters supported by CONFIG SET can be obtained issuing a* {@link #configGet(byte[]) CONFIG GET *} command.* <p>* The configuration set using CONFIG SET is immediately loaded by the Redis server that will* start acting as specified starting from the next command.* <p>* <b>Parameters value format</b>* <p>* The value of the configuration parameter is the same as the one of the same parameter in the* Redis configuration file, with the following exceptions:* <p>* <ul>* <li>The save parameter is a list of space-separated integers. Every pair of integers specify the* time and number of changes limit to trigger a save. For instance the command CONFIG SET save* "3600 10 60 10000" will configure the server to issue a background saving of the RDB file every* 3600 seconds if there are at least 10 changes in the dataset, and every 60 seconds if there are* at least 10000 changes. To completely disable automatic snapshots just set the parameter as an* empty string.* <li>All the integer parameters representing memory are returned and accepted only using bytes* as unit.* </ul>* @param parameter* @param value* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic byte[] configSet(final byte[] parameter, final byte[] value) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.configSet(parameter, value);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}public boolean isConnected() {return client.isConnected();}@Overridepublic Long strlen(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.strlen(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}public void sync() {client.sync();}@Overridepublic Long lpushx(final byte[] key, final byte[]... string) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.lpushx(key, string);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** Undo a {@link #expire(byte[], int) expire} at turning the expire key into a normal key.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @param key* @return Integer reply, specifically: 1: the key is now persist. 0: the key is not persist (only* happens when key not set).*/@Overridepublic Long persist(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.persist(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long rpushx(final byte[] key, final byte[]... string) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.rpushx(key, string);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic byte[] echo(final byte[] string) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.echo(string);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}@Overridepublic Long linsert(final byte[] key, final ListPosition where, final byte[] pivot,final byte[] value) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.linsert(key, where, pivot, value);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic String debug(final DebugParams params) {client.debug(params);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}public Client getClient() {return client;}/*** Pop a value from a list, push it to another list and return it; or block until one is available* @param source* @param destination* @param timeout* @return the element*/@Overridepublic byte[] brpoplpush(final byte[] source, final byte[] destination, final int timeout) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.brpoplpush(source, destination, timeout);client.setTimeoutInfinite();try {return client.getBinaryBulkReply();} finally {client.rollbackTimeout();}}/*** Sets or clears the bit at offset in the string value stored at key* @param key* @param offset* @param value* @return*/@Overridepublic Boolean setbit(final byte[] key, final long offset, final boolean value) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.setbit(key, offset, value);return client.getIntegerReply() == 1;}@Overridepublic Boolean setbit(final byte[] key, final long offset, final byte[] value) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.setbit(key, offset, value);return client.getIntegerReply() == 1;}/*** Returns the bit value at offset in the string value stored at key* @param key* @param offset* @return*/@Overridepublic Boolean getbit(final byte[] key, final long offset) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.getbit(key, offset);return client.getIntegerReply() == 1;}public Long bitpos(final byte[] key, final boolean value) {return bitpos(key, value, new BitPosParams());}public Long bitpos(final byte[] key, final boolean value, final BitPosParams params) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.bitpos(key, value, params);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long setrange(final byte[] key, final long offset, final byte[] value) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.setrange(key, offset, value);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic byte[] getrange(final byte[] key, final long startOffset, final long endOffset) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.getrange(key, startOffset, endOffset);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}@Overridepublic Long publish(final byte[] channel, final byte[] message) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.publish(channel, message);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic void subscribe(BinaryJedisPubSub jedisPubSub, final byte[]... channels) {client.setTimeoutInfinite();try {jedisPubSub.proceed(client, channels);} finally {client.rollbackTimeout();}}@Overridepublic void psubscribe(BinaryJedisPubSub jedisPubSub, final byte[]... patterns) {client.setTimeoutInfinite();try {jedisPubSub.proceedWithPatterns(client, patterns);} finally {client.rollbackTimeout();}}@Overridepublic int getDB() {return client.getDB();}/*** Evaluates scripts using the Lua interpreter built into Redis starting from version 2.6.0.* <p>* @param script* @param keys* @param args* @return Script result*/@Overridepublic Object eval(final byte[] script, final List<byte[]> keys, final List<byte[]> args) {return eval(script, toByteArray(keys.size()), getParamsWithBinary(keys, args));}protected static byte[][] getParamsWithBinary(List<byte[]> keys, List<byte[]> args) {final int keyCount = keys.size();final int argCount = args.size();byte[][] params = new byte[keyCount + argCount][];for (int i = 0; i < keyCount; i++)params[i] = keys.get(i);for (int i = 0; i < argCount; i++)params[keyCount + i] = args.get(i);return params;}@Overridepublic Object eval(final byte[] script, final byte[] keyCount, final byte[]... params) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.eval(script, keyCount, params);client.setTimeoutInfinite();try {return client.getOne();} finally {client.rollbackTimeout();}}@Overridepublic Object eval(final byte[] script, final int keyCount, final byte[]... params) {return eval(script, toByteArray(keyCount), params);}@Overridepublic Object eval(final byte[] script) {return eval(script, 0);}@Overridepublic Object evalsha(final byte[] sha1) {return evalsha(sha1, 0);}@Overridepublic Object evalsha(final byte[] sha1, final List<byte[]> keys, final List<byte[]> args) {return evalsha(sha1, keys.size(), getParamsWithBinary(keys, args));}@Overridepublic Object evalsha(final byte[] sha1, final int keyCount, final byte[]... params) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.evalsha(sha1, keyCount, params);client.setTimeoutInfinite();try {return client.getOne();} finally {client.rollbackTimeout();}}@Overridepublic String scriptFlush() {client.scriptFlush();return client.getStatusCodeReply();}public Long scriptExists(final byte[] sha1) {byte[][] a = new byte[1][];a[0] = sha1;return scriptExists(a).get(0);}@Overridepublic List<Long> scriptExists(final byte[]... sha1) {client.scriptExists(sha1);return client.getIntegerMultiBulkReply();}@Overridepublic byte[] scriptLoad(final byte[] script) {client.scriptLoad(script);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}@Overridepublic String scriptKill() {client.scriptKill();return client.getStatusCodeReply();}@Overridepublic String slowlogReset() {client.slowlogReset();return client.getBulkReply();}@Overridepublic Long slowlogLen() {client.slowlogLen();return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic List<byte[]> slowlogGetBinary() {client.slowlogGet();return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}@Overridepublic List<byte[]> slowlogGetBinary(final long entries) {client.slowlogGet(entries);return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}@Overridepublic Long objectRefcount(final byte[] key) {client.objectRefcount(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic byte[] objectEncoding(final byte[] key) {client.objectEncoding(key);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}@Overridepublic Long objectIdletime(final byte[] key) {client.objectIdletime(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic List<byte[]> objectHelpBinary() {client.objectHelp();return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}@Overridepublic Long objectFreq(final byte[] key) {client.objectFreq(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long bitcount(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.bitcount(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long bitcount(final byte[] key, final long start, final long end) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.bitcount(key, start, end);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long bitop(final BitOP op, final byte[] destKey, final byte[]... srcKeys) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.bitop(op, destKey, srcKeys);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic byte[] dump(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.dump(key);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}@Overridepublic String restore(final byte[] key, final int ttl, final byte[] serializedValue) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.restore(key, ttl, serializedValue);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}@Overridepublic String restoreReplace(final byte[] key, final int ttl, final byte[] serializedValue) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.restoreReplace(key, ttl, serializedValue);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Set a timeout on the specified key. After the timeout the key will be automatically deleted by* the server. A key with an associated timeout is said to be volatile in Redis terminology.* <p>* Volatile keys are stored on disk like the other keys, the timeout is persistent too like all the* other aspects of the dataset. Saving a dataset containing expires and stopping the server does* not stop the flow of time as Redis stores on disk the time when the key will no longer be* available as Unix time, and not the remaining milliseconds.* <p>* Since Redis 2.1.3 you can update the value of the timeout of a key already having an expire* set. It is also possible to undo the expire at all turning the key into a normal key using the* {@link #persist(byte[]) PERSIST} command.* <p>* Time complexity: O(1)* @see <a href="http://redis.io/commands/pexpire">PEXPIRE Command</a>* @param key* @param milliseconds* @return Integer reply, specifically: 1: the timeout was set. 0: the timeout was not set since* the key already has an associated timeout (this may happen only in Redis versions <* 2.1.3, Redis >= 2.1.3 will happily update the timeout), or the key does not exist.*/@Overridepublic Long pexpire(final byte[] key, final long milliseconds) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.pexpire(key, milliseconds);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long pexpireAt(final byte[] key, final long millisecondsTimestamp) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.pexpireAt(key, millisecondsTimestamp);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long pttl(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.pttl(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}/*** PSETEX works exactly like {@link #setex(byte[], int, byte[])} with the sole difference that the* expire time is specified in milliseconds instead of seconds. Time complexity: O(1)* @param key* @param milliseconds* @param value* @return Status code reply*/@Overridepublic String psetex(final byte[] key, final long milliseconds, final byte[] value) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.psetex(key, milliseconds, value);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}@Overridepublic byte[] memoryDoctorBinary() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.memoryDoctor();return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}@Overridepublic byte[] aclWhoAmIBinary() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.aclWhoAmI();return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}@Overridepublic byte[] aclGenPassBinary() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.aclGenPass();return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}@Overridepublic List<byte[]> aclListBinary() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.aclList();return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}@Overridepublic List<byte[]> aclUsersBinary() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.aclUsers();return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}@Overridepublic AccessControlUser aclGetUser(byte[] name) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.aclGetUser(name);return BuilderFactory.ACCESS_CONTROL_USER.build(client.getObjectMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic String aclSetUser(byte[] name) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.aclSetUser(name);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}@Overridepublic String aclSetUser(byte[] name, byte[]... keys) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.aclSetUser(name, keys);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}@Overridepublic Long aclDelUser(byte[] name) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.aclDelUser(name);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic List<byte[]> aclCatBinary() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.aclCat();return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}@Overridepublic List<byte[]> aclCat(byte[] category) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.aclCat(category);return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}@Overridepublic String clientKill(final byte[] ipPort) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();this.client.clientKill(ipPort);return this.client.getStatusCodeReply();}@Overridepublic String clientKill(final String ip, final int port) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();this.client.clientKill(ip, port);return this.client.getStatusCodeReply();}@Overridepublic Long clientKill(ClientKillParams params) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();this.client.clientKill(params);return this.client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic byte[] clientGetnameBinary() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.clientGetname();return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}@Overridepublic byte[] clientListBinary() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.clientList();return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}@Overridepublic String clientSetname(final byte[] name) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.clientSetname(name);return client.getBulkReply();}public String clientPause(final long timeout) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.clientPause(timeout);return client.getBulkReply();}public List<String> time() {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.time();return client.getMultiBulkReply();}@Overridepublic String migrate(final String host, final int port, final byte[] key,final int destinationDb, final int timeout) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.migrate(host, port, key, destinationDb, timeout);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}@Overridepublic String migrate(final String host, final int port, final int destinationDB,final int timeout, final MigrateParams params, final byte[]... keys) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.migrate(host, port, destinationDB, timeout, params, keys);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}/*** Syncrhonous replication of Redis as described here: http://antirez.com/news/66 Since Java* Object class has implemented "wait" method, we cannot use it, so I had to change the name of* the method. Sorry :S*/@Overridepublic Long waitReplicas(final int replicas, final long timeout) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.waitReplicas(replicas, timeout);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long pfadd(final byte[] key, final byte[]... elements) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.pfadd(key, elements);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic long pfcount(final byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.pfcount(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic String pfmerge(final byte[] destkey, final byte[]... sourcekeys) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.pfmerge(destkey, sourcekeys);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}@Overridepublic Long pfcount(final byte[]... keys) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.pfcount(keys);return client.getIntegerReply();}public ScanResult<byte[]> scan(final byte[] cursor) {return scan(cursor, new ScanParams());}public ScanResult<byte[]> scan(final byte[] cursor, final ScanParams params) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.scan(cursor, params);List<Object> result = client.getObjectMultiBulkReply();byte[] newcursor = (byte[]) result.get(0);List<byte[]> rawResults = (List<byte[]>) result.get(1);return new ScanResult<>(newcursor, rawResults);}@Overridepublic ScanResult<Map.Entry<byte[], byte[]>> hscan(final byte[] key, final byte[] cursor) {return hscan(key, cursor, new ScanParams());}@Overridepublic ScanResult<Map.Entry<byte[], byte[]>> hscan(final byte[] key, final byte[] cursor,final ScanParams params) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.hscan(key, cursor, params);List<Object> result = client.getObjectMultiBulkReply();byte[] newcursor = (byte[]) result.get(0);List<Map.Entry<byte[], byte[]>> results = new ArrayList<>();List<byte[]> rawResults = (List<byte[]>) result.get(1);Iterator<byte[]> iterator = rawResults.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {results.add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<byte[], byte[]>(iterator.next(), iterator.next()));}return new ScanResult<>(newcursor, results);}@Overridepublic ScanResult<byte[]> sscan(final byte[] key, final byte[] cursor) {return sscan(key, cursor, new ScanParams());}@Overridepublic ScanResult<byte[]> sscan(final byte[] key, final byte[] cursor, final ScanParams params) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.sscan(key, cursor, params);List<Object> result = client.getObjectMultiBulkReply();byte[] newcursor = (byte[]) result.get(0);List<byte[]> rawResults = (List<byte[]>) result.get(1);return new ScanResult<>(newcursor, rawResults);}@Overridepublic ScanResult<Tuple> zscan(final byte[] key, final byte[] cursor) {return zscan(key, cursor, new ScanParams());}@Overridepublic ScanResult<Tuple> zscan(final byte[] key, final byte[] cursor, final ScanParams params) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.zscan(key, cursor, params);List<Object> result = client.getObjectMultiBulkReply();byte[] newcursor = (byte[]) result.get(0);List<Tuple> results = new ArrayList<>();List<byte[]> rawResults = (List<byte[]>) result.get(1);Iterator<byte[]> iterator = rawResults.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {results.add(new Tuple(iterator.next(), BuilderFactory.DOUBLE.build(iterator.next())));}return new ScanResult<>(newcursor, results);}@Overridepublic Long geoadd(final byte[] key, final double longitude, final double latitude, final byte[] member) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.geoadd(key, longitude, latitude, member);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long geoadd(final byte[] key, final Map<byte[], GeoCoordinate> memberCoordinateMap) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.geoadd(key, memberCoordinateMap);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Double geodist(final byte[] key, final byte[] member1, final byte[] member2) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.geodist(key, member1, member2);String dval = client.getBulkReply();return (dval != null ? new Double(dval) : null);}@Overridepublic Double geodist(final byte[] key, final byte[] member1, final byte[] member2, final GeoUnit unit) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.geodist(key, member1, member2, unit);String dval = client.getBulkReply();return (dval != null ? new Double(dval) : null);}@Overridepublic List<byte[]> geohash(final byte[] key, final byte[]... members) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.geohash(key, members);return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}@Overridepublic List<GeoCoordinate> geopos(final byte[] key, final byte[]... members) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.geopos(key, members);return BuilderFactory.GEO_COORDINATE_LIST.build(client.getObjectMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic List<GeoRadiusResponse> georadius(final byte[] key, final double longitude, final double latitude,final double radius, final GeoUnit unit) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.georadius(key, longitude, latitude, radius, unit);return BuilderFactory.GEORADIUS_WITH_PARAMS_RESULT.build(client.getObjectMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic List<GeoRadiusResponse> georadiusReadonly(final byte[] key, final double longitude, final double latitude,final double radius, final GeoUnit unit) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.georadiusReadonly(key, longitude, latitude, radius, unit);return BuilderFactory.GEORADIUS_WITH_PARAMS_RESULT.build(client.getObjectMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic List<GeoRadiusResponse> georadius(final byte[] key, final double longitude, final double latitude,final double radius, final GeoUnit unit, final GeoRadiusParam param) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.georadius(key, longitude, latitude, radius, unit, param);return BuilderFactory.GEORADIUS_WITH_PARAMS_RESULT.build(client.getObjectMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic List<GeoRadiusResponse> georadiusReadonly(final byte[] key, final double longitude, final double latitude,final double radius, final GeoUnit unit, final GeoRadiusParam param) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.georadiusReadonly(key, longitude, latitude, radius, unit, param);return BuilderFactory.GEORADIUS_WITH_PARAMS_RESULT.build(client.getObjectMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic List<GeoRadiusResponse> georadiusByMember(final byte[] key, final byte[] member, final double radius,final GeoUnit unit) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.georadiusByMember(key, member, radius, unit);return BuilderFactory.GEORADIUS_WITH_PARAMS_RESULT.build(client.getObjectMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic List<GeoRadiusResponse> georadiusByMemberReadonly(final byte[] key, final byte[] member, final double radius,final GeoUnit unit) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.georadiusByMemberReadonly(key, member, radius, unit);return BuilderFactory.GEORADIUS_WITH_PARAMS_RESULT.build(client.getObjectMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic List<GeoRadiusResponse> georadiusByMember(final byte[] key, final byte[] member, final double radius,final GeoUnit unit, final GeoRadiusParam param) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.georadiusByMember(key, member, radius, unit, param);return BuilderFactory.GEORADIUS_WITH_PARAMS_RESULT.build(client.getObjectMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic List<GeoRadiusResponse> georadiusByMemberReadonly(final byte[] key, final byte[] member, final double radius,final GeoUnit unit, final GeoRadiusParam param) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.georadiusByMemberReadonly(key, member, radius, unit, param);return BuilderFactory.GEORADIUS_WITH_PARAMS_RESULT.build(client.getObjectMultiBulkReply());}/*** A decorator to implement Set from List. Assume that given List do not contains duplicated* values. The resulting set displays the same ordering, concurrency, and performance* characteristics as the backing list. This class should be used only for Redis commands which* return Set result.* @param <E>*/protected static class SetFromList<E> extends AbstractSet<E> implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = -2850347066962734052L;private final List<E> list;private SetFromList(List<E> list) {if (list == null) {throw new NullPointerException("list");}this.list = list;}@Overridepublic void clear() {list.clear();}@Overridepublic int size() {return list.size();}@Overridepublic boolean isEmpty() {return list.isEmpty();}@Overridepublic boolean contains(Object o) {return list.contains(o);}@Overridepublic boolean remove(Object o) {return list.remove(o);}@Overridepublic boolean add(E e) {return !contains(e) && list.add(e);}@Overridepublic Iterator<E> iterator() {return list.iterator();}@Overridepublic Object[] toArray() {return list.toArray();}@Overridepublic <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {return list.toArray(a);}@Overridepublic String toString() {return list.toString();}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return list.hashCode();}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (o == null) return false;if (o == this) return true;if (!(o instanceof Set)) return false;Collection<?> c = (Collection<?>) o;if (c.size() != size()) {return false;}return containsAll(c);}@Overridepublic boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {return list.containsAll(c);}@Overridepublic boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {return list.removeAll(c);}@Overridepublic boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {return list.retainAll(c);}protected static <E> SetFromList<E> of(List<E> list) {return new SetFromList<>(list);}}@Overridepublic List<Long> bitfield(final byte[] key, final byte[]... arguments) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.bitfield(key, arguments);return client.getIntegerMultiBulkReply();}@Overridepublic List<Long> bitfieldReadonly(byte[] key, final byte[]... arguments) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.bitfieldReadonly(key, arguments);return client.getIntegerMultiBulkReply();}@Overridepublic Long hstrlen(final byte[] key, final byte[] field) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.hstrlen(key, field);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic List<byte[]> xread(int count, long block, Map<byte[], byte[]> streams) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xread(count, block, streams);client.setTimeoutInfinite();try {return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();} finally {client.rollbackTimeout();}}@Overridepublic List<byte[]> xreadGroup(byte[] groupname, byte[] consumer, int count, long block, boolean noAck,Map<byte[], byte[]> streams) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xreadGroup(groupname, consumer, count, block, noAck, streams);client.setTimeoutInfinite();try {return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();} finally {client.rollbackTimeout();}}@Overridepublic byte[] xadd(byte[] key, byte[] id, Map<byte[], byte[]> hash, long maxLen, boolean approximateLength) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xadd(key, id, hash, maxLen, approximateLength);return client.getBinaryBulkReply();}@Overridepublic Long xlen(byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xlen(key);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic List<byte[]> xrange(byte[] key, byte[] start, byte[] end, long count) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xrange(key, start, end, count);return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}@Overridepublic List<byte[]> xrevrange(byte[] key, byte[] end, byte[] start, int count) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xrevrange(key, end, start, count);return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}@Overridepublic Long xack(byte[] key, byte[] group, byte[]... ids) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xack(key, group, ids);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic String xgroupCreate(byte[] key, byte[] consumer, byte[] id, boolean makeStream) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xgroupCreate(key, consumer, id, makeStream);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}@Overridepublic String xgroupSetID(byte[] key, byte[] consumer, byte[] id) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xgroupSetID(key, consumer, id);return client.getStatusCodeReply();}@Overridepublic Long xgroupDestroy(byte[] key, byte[] consumer) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xgroupDestroy(key, consumer);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long xgroupDelConsumer(byte[] key, byte[] consumer, byte[] consumerName) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xgroupDelConsumer(key, consumer, consumerName);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long xdel(byte[] key, byte[]... ids) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xdel(key, ids);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic Long xtrim(byte[] key, long maxLen, boolean approximateLength) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xtrim(key, maxLen, approximateLength);return client.getIntegerReply();}@Overridepublic List<byte[]> xpending(byte[] key, byte[] groupname, byte[] start, byte[] end, int count, byte[] consumername) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xpending(key, groupname, start, end, count, consumername);return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply(); }@Overridepublic List<byte[]> xclaim(byte[] key, byte[] groupname, byte[] consumername, long minIdleTime, long newIdleTime, int retries, boolean force, byte[][] ids){checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xclaim(key, groupname, consumername, minIdleTime, newIdleTime, retries, force, ids);return client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply();}public Object sendCommand(ProtocolCommand cmd, byte[]... args) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.sendCommand(cmd, args);return client.getOne();}@Overridepublic StreamInfo xinfoStream(byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xinfoStream(key);return BuilderFactory.STREAM_INFO.build(client.getOne());}@Overridepublic List<StreamGroupInfo> xinfoGroup (byte[] key) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xinfoGroup(key);return BuilderFactory.STREAM_GROUP_INFO_LIST.build(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}@Overridepublic List<StreamConsumersInfo> xinfoConsumers (byte[] key, byte[] group) {checkIsInMultiOrPipeline();client.xinfoConsumers(key,group);return BuilderFactory.STREAM_CONSUMERS_INFO_LIST.build(client.getBinaryMultiBulkReply());}public Object sendCommand(ProtocolCommand cmd) {return sendCommand(cmd, dummyArray);}
}
遇到的问题
连接不上cluster,报错,
检查 cluster slots 查看redis集群信息,是否展示的是服务器ip,不可以是127.0.0.1
修改redis集群配置重启,ok
相关文章:

spring-boot-starter-data-redis2.X连接redis7
由于redis7引入了acl机制,可以配置用户权限, 比如配置了一个普通用户 test,权限为 test_ 前缀的key可操作 springboot想要连接,并没有设置用户名的地方, 跟了源码,jedis客户端是支持的,但是s…...
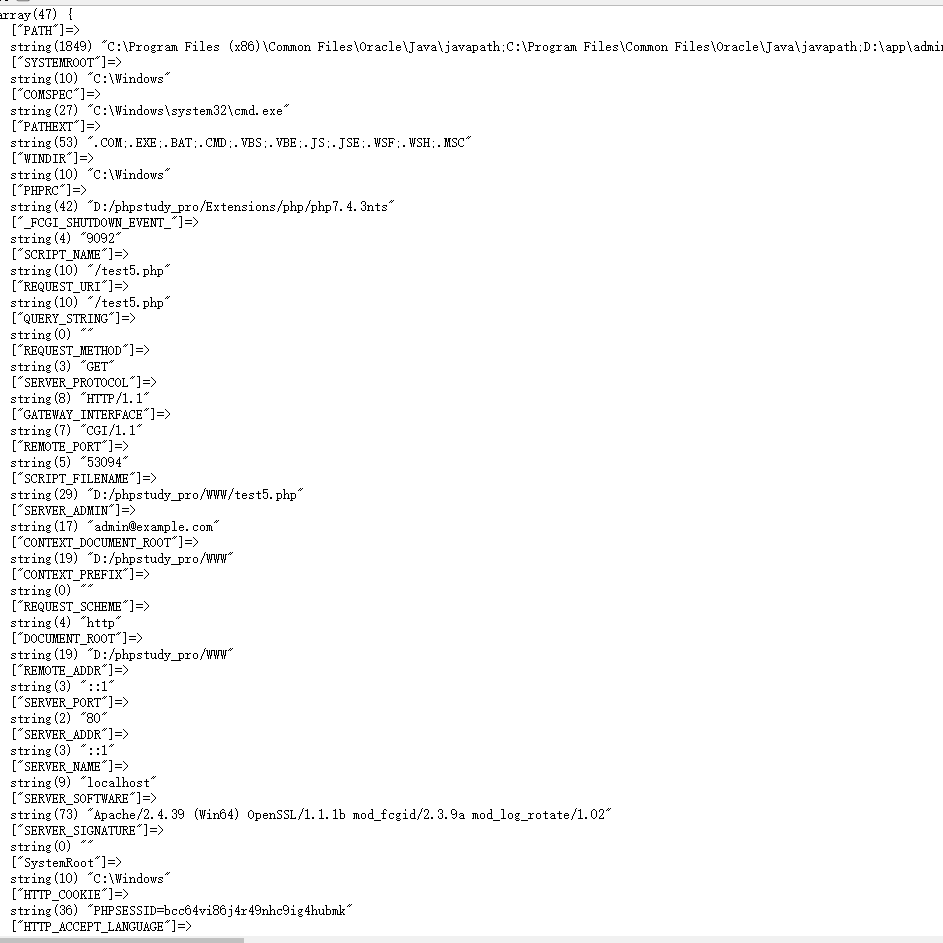
PHP中$_SERVER全局变量
在PHP中,$_SERVER 是一个全局数组变量,它包含了有关服务器和当前脚本的信息。$_SERVER 数组中的每个元素都是服务器环境的一个参数,如请求的方法、请求的 URI、客户端 IP 地址等。 PATH 系统环境变量的值,包含了多个目录的路径…...
【ML】欠拟合和过拟合的一些判别和优化方法(吴恩达机器学习笔记)
吴恩达老师的机器学习教程笔记 减少误差的一些方法 获得更多的训练实例——解决高方差尝试减少特征的数量——解决高方差尝试获得更多的特征——解决高偏差尝试增加多项式特征——解决高偏差尝试减少正则化程度 λ——解决高偏差尝试增加正则化程度 λ——解决高方差 什么是…...

服务器数据恢复—服务器发生故障导致数据丢失如何恢复服务器数据?
服务器常见故障: 硬件故障:磁盘、板卡、电源故障等。 软件故障:操作系统崩溃、程序运行错误等。 入侵破坏:加密、删除服务数据等。 不可控力:浸水、火烧、倒塌等。 误操作:格式化、删除、覆盖等。 如何减少…...

SLAM中提到的相机位姿到底指什么?
不小心又绕进去了,所以掰一下。 以我个人最直观的理解,假设无旋转,相机在世界坐标系的(5,0,0)^T的位置上,所谓“位姿”,应该反映相机的位置,所以相机位姿应该如下: Eigen::Matrix4d T Eigen::M…...
《视觉SLAM十四讲》-- 后端 1(上)
文章目录 08 后端 18.1 概述8.1.1 状态估计的概率解释8.1.2 线性系统和卡尔曼滤波(KF)8.1.3 非线性系统和扩展卡尔曼滤波(EKF)8.1.4 小结 08 后端 1 前端视觉里程计可以给出一个短时间内的轨迹和地图,但由于不可避免的…...

南昌市西湖区棒球特色规划
西湖区棒球特色学校打造方案 一、项目背景 南昌市西湖区作为江西省的教育强区,一直致力于发展特色教育。近年来,棒球运动逐渐受到广泛关注,西湖区决定将棒球运动作为特色项目,打造一所具有国际水平的棒球特色学校。 二、目标与…...
nginx启动命令
普通启动 切换到nginx安装目录的sbin目录下,执行:./nginx 通过配置文件启动 ./nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf 其中-c是指定配置文件,而且配置文件路径必须指定绝对路…...

防爆五参数气象仪的科技力量
WX-FBQ2 随着科技的不断进步,气象监测设备也在不断升级和完善。 防爆五参数气象仪是一种可以同时监测温度、湿度、压力、风速和风向五个基本气象参数的仪器。它采用了气象监测技术,不仅可以实时监测气象数据,还可以对数据进行分析和处理。 …...
J. Chem. Theory Comput. | AI驱动的柔性蛋白-小分子复合物建模
今天为大家介绍的是来自陈语谦教授团队发表在Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation的论文,“Equivariant Flexible Modeling of the Protein−Ligand Binding Pose with Geometric Deep Learning”,博士生董铁君为第一作者。该文提出了一种新的AI…...
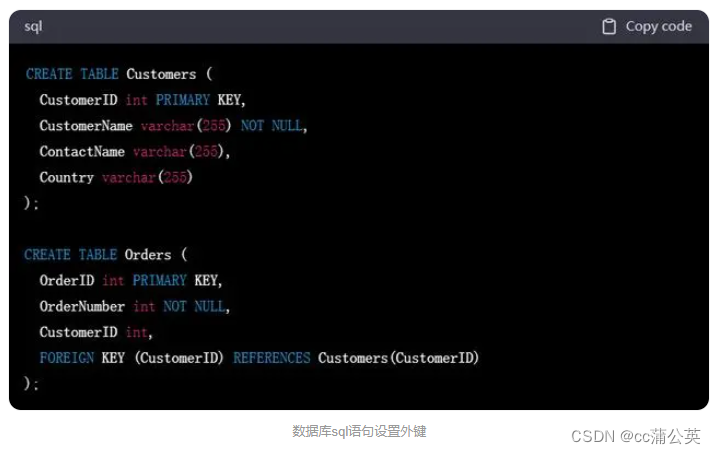
数据库sql语句设置外键
当我们需要在数据库表之间建立关联关系时,可以使用外键(Foreign Key)来实现。在 SQL 中,外键可以用来保持数据的完整性,并帮助我们更有效地管理数据。以下是设置外键的步骤: 1.在创建表时,需要…...
excel在函数中插入函数
例如,要计算RAND()1的值,其中RAND()表示取0~1之间的随机数。 插入-》函数: 选SUM函数: 点击“继续”: 将光标先放在数字1中的输入框中,然后在左边过滤出RAND函数,并且点击继续࿱…...

保姆级前端翻牌效果(CSS)
效果 翻牌效果 hover 时候 代码直接上 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang"en"> <head><meta charset"UTF-8"><meta name"viewport" content"widthdevice-width, initial-scale1.0"><title>Document<…...

Mac环境配置的相关知识
Mac中配置环境的三个途径: 1.open/vim /etc/profile (建议不修改这个文件)全局(公有)配置,不管是哪个用户,登录时都会读取该文件(一般在这个文件中添加系统级环境变量) 2./etc/bashrc全局(公有)配置,bash shell执行时࿰…...

业务连续性:确保稳健运营的关键战略
在今天的快节奏商业环境中,保障业务连续性是企业成功的重要保障。业务连续性不仅仅是关于应对自然灾害或技术故障,更是一项战略,涉及组织的整体准备、规划和应对能力,以确保在各种情况下业务的稳健运营。 一、业务连续性的定义 业…...

【Pytorch和深度学习】栏目导读
一、栏目说明 本栏目《pytorch实践》是为初学者入门深度学习准备的。本文是该栏目的导读部分,因为计划本栏目在明年完成,因此,导读部分,即本文也在持续更新中。 本栏目设计目标是将深度学习全面用pytorch实践一遍,由浅…...

sklearn笔记:neighbors.NearestNeighbors
1 最近邻 class sklearn.neighbors.NearestNeighbors(*, n_neighbors5, radius1.0, algorithmauto, leaf_size30, metricminkowski, p2, metric_paramsNone, n_jobsNone)邻居搜索算法的选择通过关键字 algorithm 控制,它必须是 [auto, ball_tree, kd_tree, brute] …...

V-for中 key 值的作用,如何选择key
Vue.js 中的 v-for 指令是一个强大的工具,可以用于循环渲染列表数据。在使用 v-for 指令时,我们经常需要为每个循环项指定一个 key 值。本文将深入探讨 key 值的作用,并为您提供如何选择 key 值的建议和指导。 开始 在开始之前,让…...

linux内核驱动开发
系列文章目录 主要介绍linux系统下的驱动开发 文章目录 系列文章目录 文章目录 前言 一、驱动是什么? 二、主要分类 2.读入数据 3.代码示例 总结 前言 对设备驱动最通俗的解释就是“驱使硬件设备行动”。驱动与底层硬件直接打交道,按照硬件设备的具体工作方式,读写…...

2.3.5 交换机的VRRP技术
实验2.3.5 交换机的VRRP技术 一、任务描述二、任务分析三、具体要求四、实验拓扑五、任务实施1.交换机的基本配置 六、任务验收七、任务小结 一、任务描述 某公司的网络核心层原来采用一台三层交换机,随着网络应用的日益增多,对网络的可靠性也提出了越来…...
详解)
后进先出(LIFO)详解
LIFO 是 Last In, First Out 的缩写,中文译为后进先出。这是一种数据结构的工作原则,类似于一摞盘子或一叠书本: 最后放进去的元素最先出来 -想象往筒状容器里放盘子: (1)你放进的最后一个盘子(…...
C++ 求圆面积的程序(Program to find area of a circle)
给定半径r,求圆的面积。圆的面积应精确到小数点后5位。 例子: 输入:r 5 输出:78.53982 解释:由于面积 PI * r * r 3.14159265358979323846 * 5 * 5 78.53982,因为我们只保留小数点后 5 位数字。 输…...

Go 语言并发编程基础:无缓冲与有缓冲通道
在上一章节中,我们了解了 Channel 的基本用法。本章将重点分析 Go 中通道的两种类型 —— 无缓冲通道与有缓冲通道,它们在并发编程中各具特点和应用场景。 一、通道的基本分类 类型定义形式特点无缓冲通道make(chan T)发送和接收都必须准备好࿰…...

A2A JS SDK 完整教程:快速入门指南
目录 什么是 A2A JS SDK?A2A JS 安装与设置A2A JS 核心概念创建你的第一个 A2A JS 代理A2A JS 服务端开发A2A JS 客户端使用A2A JS 高级特性A2A JS 最佳实践A2A JS 故障排除 什么是 A2A JS SDK? A2A JS SDK 是一个专为 JavaScript/TypeScript 开发者设计的强大库ÿ…...
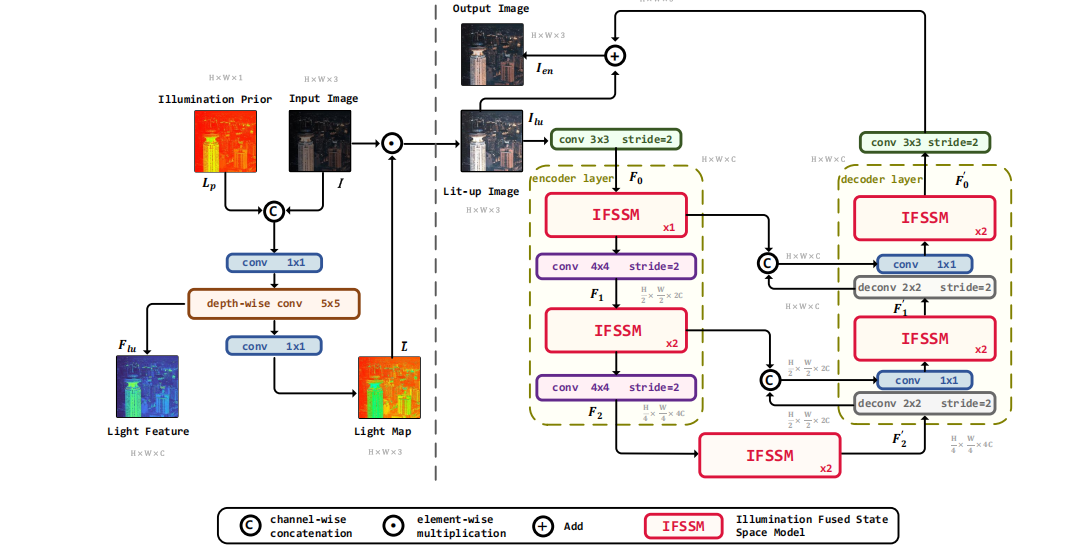
深度学习水论文:mamba+图像增强
🧀当前视觉领域对高效长序列建模需求激增,对Mamba图像增强这方向的研究自然也逐渐火热。原因在于其高效长程建模,以及动态计算优势,在图像质量提升和细节恢复方面有难以替代的作用。 🧀因此短时间内,就有不…...
: 一刀斩断视频片头广告)
快刀集(1): 一刀斩断视频片头广告
一刀流:用一个简单脚本,秒杀视频片头广告,还你清爽观影体验。 1. 引子 作为一个爱生活、爱学习、爱收藏高清资源的老码农,平时写代码之余看看电影、补补片,是再正常不过的事。 电影嘛,要沉浸,…...
FFmpeg:Windows系统小白安装及其使用
一、安装 1.访问官网 Download FFmpeg 2.点击版本目录 3.选择版本点击安装 注意这里选择的是【release buids】,注意左上角标题 例如我安装在目录 F:\FFmpeg 4.解压 5.添加环境变量 把你解压后的bin目录(即exe所在文件夹)加入系统变量…...

LOOI机器人的技术实现解析:从手势识别到边缘检测
LOOI机器人作为一款创新的AI硬件产品,通过将智能手机转变为具有情感交互能力的桌面机器人,展示了前沿AI技术与传统硬件设计的完美结合。作为AI与玩具领域的专家,我将全面解析LOOI的技术实现架构,特别是其手势识别、物体识别和环境…...
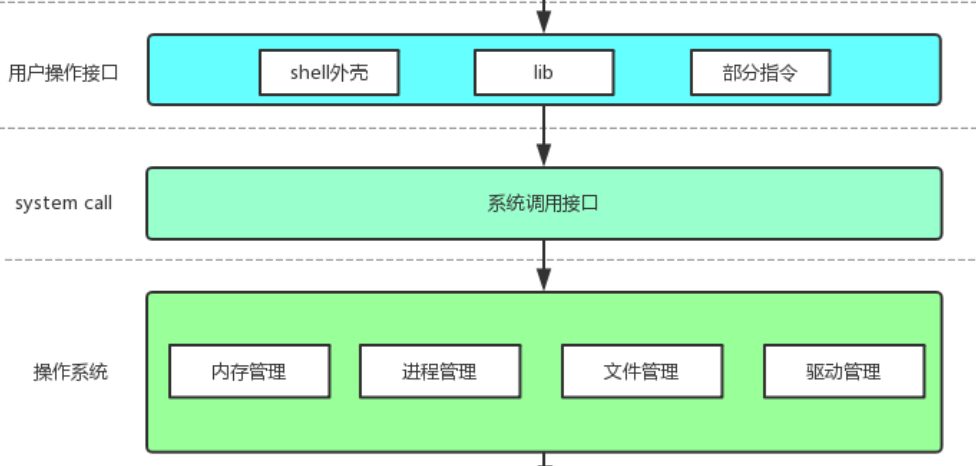
【Linux手册】探秘系统世界:从用户交互到硬件底层的全链路工作之旅
目录 前言 操作系统与驱动程序 是什么,为什么 怎么做 system call 用户操作接口 总结 前言 日常生活中,我们在使用电子设备时,我们所输入执行的每一条指令最终大多都会作用到硬件上,比如下载一款软件最终会下载到硬盘上&am…...

git: early EOF
macOS报错: Initialized empty Git repository in /usr/local/Homebrew/Library/Taps/homebrew/homebrew-core/.git/ remote: Enumerating objects: 2691797, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (1760/1760), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (636/636…...
