C++STL——string类详解及其模拟实现
C++STL——string类
1. STL简介
STL全称
standard template libaray,译为标准模板库
- 需要注意,STL不是C++的标准库,而是C++标准库的重要组成部分
- STL是一个包含众多数据结构和算法的软件框架
下面展示STL的六大组件:

本章,我们将对STL中的容器——
string类部分常用的功能进行说明和使用,最后对string进行简单的模拟实现
本章思维导图:
 注:本章思维导图已经同步导入至资源
注:本章思维导图已经同步导入至资源
2. string类
头文件<string>
我们先来看看string类是如何被声明的:
typedef basic_string<char> string;
可以看到:
string类是被类模板basic_string用数据类型char实例化后得到的一个具体的类的别名
同时规定:
string类是一个用来表示字符串的类- 标准
string类提供的接口和许多标准容器的接口类似,但也额外提供了处理单字节字符的接口(处理字符串的常规操作)- 不能用来操作多字节或者变长字节的字符序列
需要注意:
string类是包含在C++标准库中的,因此如果要使用string:
- 一种方式:使用域作用限定符,例如
std::string。- 另一种方式:使用
using namespace std打开命名空间
2.1 成员函数
2.2.1 默认成员函数
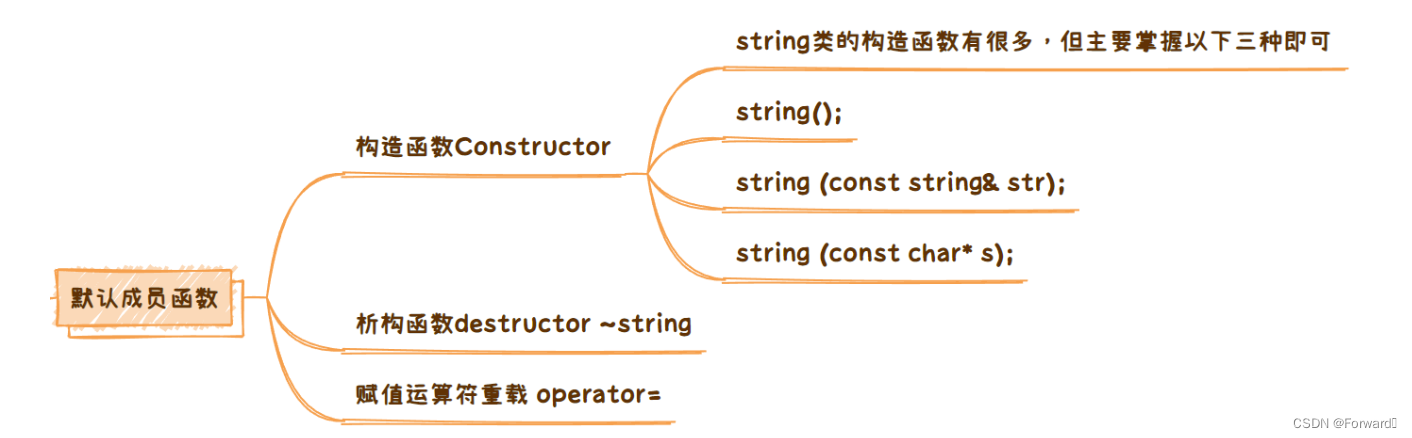
2.1.1.1 constructor——构造函数
string类的构造函数string()被重载成了许多形式,但我们只需掌握以下三种即可:
string(); //方法一:构造一个空串
string (const string& str); //方法二:拷贝构造
string (const char* s); //方法三:用一个常量字符串构造
例如:
#include <string>
#include <iostream>nt main()
{std::string s1; std::string s2("hello world");std::string s3(s2);//string类里面重载了流插入<<和流提取>>运算符std::cout << "字符串s1为:" << s1 << std::endl;std::cout << "字符串s2为:" << s2 << std::endl;std::cout << "字符串s3为:" << s3 << std::endl;return 0;
}
output:
字符串s1为:
字符串s2为:hello world
字符串s3为:hello world
2.2.1.2 operator =——赋值运算符重载
string& operator= (const string& str); //类类型之间的赋值
string& operator= (const char* s); //利用隐式类型转换,先将字符串s实例化为一个string类型对象,再进行赋值
string& operator= (char c); //和第二种方法类似
例如:
#include <string>
#include <iostream>int main()
{std::string s1, s2, s3;s1 = "hello world";s2 = 'c';s3 = s1;std::cout << "字符串s1为:" << s1 << std::endl;std::cout << "字符串s2为:" << s2 << std::endl;std::cout << "字符串s3为:" << s3 << std::endl;return 0;
}
output:
字符串s1为:hello world
字符串s2为:c
字符串s3为:hello world
2.2.2 size()/length——获取有效长度
size_t size() const;
size_t length() const;
- 这两个函数的效果是一模一样的
- 但是更建议使用函数
size() - 字符串的有效长度是不包括结束字符
‘\0’的,其结果就和C语言的strlen()函数一样
例如:
#include <string>
#include <iostream>int main()
{std::string s1;std::string s2("hello world");std::cout << "sizs of s1: " << s1.size() << std::endl;std::cout << "sizs of s2: " << s2.size() << std::endl;return 0;
}
output:
sizs of s1: 0
sizs of s2: 11
2.2.3 capacity()——获取最大容量
size_t capacity() const;
- 一般来说,这个最大容量同样指的是可以存放有效字符的最大容量,也不包括结束符
‘\0’
需要注意,由于不同平台所用的库不同,因此当用同一个字符串构造
string对象时,分配给其用来存储字符的初始空间也不一定相同(即capacity不一定相同),例如:对于相同的代码:
#include <string> #include <iostream>int main() {std::string s1;std::string s2("nice to meet you");std::cout << "capacity of s1 is: " << s1.capacity() << std::endl;std::cout << "capacity of s2 is: " << s2.capacity() << std::endl;return 0; }在VS下,output:
capacity of s1 is: 15 capacity of s2 is: 31在Linux下,output:
capacity of s1 is: 0 capacity of s2 is: 16
- 实际上,这两个平台的扩容机制也完全不同,之后我们会进行演示

2.2.4 operator []/at()——获取指定位置的字符
char& operator[] (size_t pos);
const char& operator[] (size_t pos) const;char& at (size_t pos);
const char& at (size_t pos) const;
相同点:
- 和普通的字符数组一样,
string类类型的对象也可以通过类似[下标]的方式获得指定位置的字符 - 这个函数被重载成了两份,分别给非
cosnt对象和const对象使用
不同点:
- 如果传入的
pos大于size(),那么对于operator [],则会直接报错 - 而对于
at(),则会抛出异常
有了这两个成员函数,我们就可以对string对象存储的数据进行遍历访问了:
#include <string>
#include <iostream>int main()
{std::string s1("hello world");for (int i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)std::cout << s1[i] << ' ';std::cout << std::endl;for (int i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)std::cout << s1.at(i) << ' ';std::cout << std::endl;return 0;
}
output:
h e l l o w o r l d
h e l l o w o r l d
2.2.5 iterator——迭代器
迭代器是一个用来访问容器数据的对象,其提供了统一的方式来遍历容器中的数据
- 对于
string类,我们可以将迭代器看成一个指针,其指向string对象存储的某个字符 - 我们可以通过迭代器来访问或者修改容器中的数据
- 尽管前面的
[]运算符访问和修改string存储的数据十分方便,但必须说明,在STL中,对于访问和遍历数据迭代器才是最常用的。
以下是几种获取string类型迭代器的常见方式:
2.2.5.1 begin()/end()
iterator begin();
const_iterator begin() const;
/*****************************************/iterator end();
const_iterator end() const;
begin()即返回一个指向字符序列第一个字符的迭代器;end()即返回一个指向字符序列**最后一个字符(即‘\0’)**的迭代器- 而
begin() const和end() const则是针对const对象做出的函数重载
注意:
由于
string类实际上就是存储字符序列的类,因此针对它的迭代器iterator,我们可以将其看成为一个指向char类型的指针char*;而const_iterator则对应的是const char*
- 有些小伙伴可能会疑惑:为什么
const_iterator不写成const iterator- 首先我们要清楚对于
const对象,其返回的迭代器应该具有这样的功能:允许访问(遍历)数据,但不允许修改数据- 而
const iterator本质上修饰的是迭代器iterator本身,我们可以看作是char* const,这样子的效果是不能改变迭代器指向,但是可以改变迭代器指向数据的内容,这显然是不符合要求的- 但**
const_iterator本质上修饰的就是迭代器指向的数据**,我们可以看作是const char*,这样就可以符合要求
示例:
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello world");string::iterator it = s1.begin();//对每个字符进行+1操作再进行打印while (it != s1.end()){(*it)++;cout << *it << ' ';it++;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
output:
i f m m p ! x p s m e
2.2.5.2 rbegin()/ rend()
reverse_iterator rbegin();
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const;
/*****************************************/reverse_iterator rend();
const_reverse_iterator rend() const;
- 和
begin()/end()类似,只是返回的是反向迭代器 - 所谓的反向迭代器即
rbegin()返回一个指向字符序列最后一个有效字符的迭代器;rend()返回一个指向字符序列**第一个字符之前的字符(被认为是反向末端)**的迭代器 - 如果反向迭代器的指向可以修改,那么例如对于
rbegin()的返回结果进行+1操作,就会使迭代器指向倒数第二个字符 - 反向迭代器和正向迭代器的返回类型原理类似,故不作赘述
例如:
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello world");string::reverse_iterator it = s1.rbegin();while (it != s1.rend()){cout << *it << ' ';it++;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
output:
d l r o w o l l e h
2.2.6 容量管理

2.2.6.1 reserve
void reserve (size_t n = 0);
reserve成员函数会将string的最大容量capacity扩展为n- 需要注意,由于不同平台依赖的库不同,所以
reserve最终的效果也会不同,但是无论如何,reserve()绝不会影响到存储的数据
下面就来看看在VS和Linux两个平台上reserve()函数的不同之处:
对于同样一份代码:
#include <string> #include <iostream> using namespace std;int main() {string s1("hello world");string s2 = s1;cout << "the capacity of s1 is " << s1.capacity() << endl;s1.reserve(100);cout << "after reserve(100), the capacity of s1 is " << s1.capacity() << endl;s1.reserve(50);cout << "after reserve(50), the capacity of s1 is " << s1.capacity() << endl << endl;cout << "the capacity of s2 is " << s2.capacity() << endl;s2.reserve(1);cout << "after reserve(1), the capacity of s2 is " << s2.capacity() << endl;return 0; }VS:
output:
the capacity of s1 is 15 after reserve(100), the capacity of s1 is 111 after reserve(50), the capacity of s1 is 111the capacity of s2 is 15 after reserve(1), the capacity of s2 is 15Linux:
output:
the capacity of s1 is 11 after reserve(100), the capacity of s1 is 100 after reserve(50), the capacity of s1 is 50the capacity of s2 is 11 after reserve(1), the capacity of s2 is 11可以总结出二者的不同:
- VS分配空间时,总会比给定值多几个空间;而Linux则是给多少开多少
- VS的
reserve()函数不能缩小空间,只能扩大空间;而Linux的reserve函数可以缩小空间同时它们也有一个共同点:
- 无论给定值再怎么小,
reserve()都不会影响到原来的数据
2.2.6.2 resize()
void resize (size_t n);
void resize (size_t n, char c);
resize()函数也是对最大容量的管理。但是它既可以缩小容量,同时也能影响到原有数据- 同时,这个函数还有初始化的功能:
- 如果传入的
n大于size小于capacity,那么如果字符c被指明,那么剩余的空间就会被字符c填充;如果字符c没被指明,那么剩余的空间就会被空字符‘\0’填充 - 如果传入的
n大于capacity,那么就会在扩容之后进行跟上面一样的初始化(填充)操作
- 如果传入的
例如:
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello");string s2 = s1;cout << "the capacity of s1 is " << s1.capacity() << endl;s1.resize(s1.capacity(), 'c');cout << s1 << endl << endl;cout << "the capacity of s2 is " << s2.capacity() << endl;s2.resize(100);cout << s2 << endl;cout << "the capacity of s2 is " << s2.capacity() << endl;cout << "the size of s2 is " << s2.size() << endl;return 0;
}
output:
the capacity of s1 is 15
helloccccccccccthe capacity of s2 is 15
hello
the capacity of s2 is 111
the size of s2 is 100
2.2.7 增 operator +=
注:本篇只讲最常用的string添加字符/字符串的方法。其他方法还有如
-
👉append
-
👉push_back
-
👉insert
string& operator+= (const string& str);
string& operator+= (const char* s);
string& operator+= (char c);
例如:
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1;string s2;string s3;s1 += "hello world";s2 += s1;s3 += 'c';cout << s1 << endl;cout << s2 << endl;cout << s3 << endl;return 0;
}
output:
hello world
hello world
c
2.2.8 删 erase
string& erase (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);
-
即删除从
pos位置开始的len个字符 -
注意:
npos为string里面定义的一个const静态全局变量const static size_t npos = -1; -
无符号整形
npos的值为-1,因此它的实际值为unsigned int的最大值 -
如果
npos用来表示一个长度,那么它通常用来说明直到字符串的尾 -
如果
npos用来表示一个返回值,那么它通常用来说明没有找到目标
例如:
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello world");s1.erase(2, 2);cout << s1 << endl;s1.erase(1);cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}
output:
heo world
h
2.2.9 查 find/rfind
注:本篇只讲述最常用的find和rfind。其他方法还有如:
- 👉find_first_of
- 👉find_last_of
- 👉find_first_not_of
- 👉find_last_not_of
size_t find (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const;
size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
size_t find (char c, size_t pos = 0) const;
-
即从
pos位置开始,寻找目标出现的下标 -
rfind()和find()使用类似,故不作赘述
例如:
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello world !!!");size_t pos1 = s1.find("ld");size_t pos2 = s1.find("l", 6);size_t pos3 = s1.find("nice");size_t pos4 = s1.rfind("!");cout << "pos1 = " << pos1 << endl;cout << "pos2 = " << pos2 << endl;cout << "pos3 = " << pos3 << endl;cout << "pos4 = " << pos4 << endl;return 0;
}
output:
pos1 = 9
pos2 = 9
pos3 = 4294967295
pos4 = 14
2.2.10 改
注:虽然string类有专门用于修改字符串的函数👉replace,但是由于效率原因并不常用。
实际使用中,一般都是用[]下标访问和迭代器访问来修改数据
2.2.11 c_str——获得C语言类型的字符串
const char* c_str() const;
例如:
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello world");const char* str = s1.c_str();cout << str << endl;return 0;
}
output:
hello world
2.2.12 substr——获得子串
string substr (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const;
- 获得从
pos位置开始,长度为len的子串 - 同时将这个子串存储到
string类中并进行返回
例如:
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello world");string s2 = s1.substr(0, 5); //hellostring s3 = s1.substr(5); //worldcout << s2 << s3 << endl;return 0;
}
output:
hello world
2.2 非成员函数
2.2.1 operator <</operator >>——流插入/流提取运算符重载
- 有了
<<流插入运算符重载,我们就可以利用std::cout来向屏幕打印string存储的字符序列 - 有了
>>流提取运算符重载,我们就可以用std::cin向string类的数据 - 注意:
cin类似于C语言的scanf,如果碰到空白字符就会停止读取。因此cin只能用于读取不带空格的字符序列。- 原来的数据会被输入端新字符给覆盖
- 如果输入的字符长度大于
capacity,那么就会对这个string对象进行扩容,直到可以存储输入的字符序列。
例如:
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1, s2;cin >> s1;cin >> s2;cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;return 0;
}
input:
hello
nice to meet you
output:
s1 = hello
s2 = nice
2.2.2 getline——输入字符串
istream& getline (istream& is, string& str);
- 同样是从标准输入流向
string对象输入数据 - 原来的数据会被输入端新字符给覆盖
getline()类似于C语言的gets(),只有遇到换行才会停止读取。因此可以读取带空格的字符序列- 如果输入的字符长度大于
capacity,那么就会对这个string对象进行扩容,直到可以存储输入的字符序列。
例如:
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1;getline(cin, s1);cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}
output:
hello world
2.2.3 relational operators——关系运算符重载
(1) bool operator== (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);
bool operator== (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);
bool operator== (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);(2) bool operator!= (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);
bool operator!= (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);
bool operator!= (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);(3) bool operator< (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);
bool operator< (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);
bool operator< (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);(4) bool operator<= (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);
bool operator<= (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);
bool operator<= (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);(5) bool operator> (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);
bool operator> (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);
bool operator> (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);(6) bool operator>= (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);
bool operator>= (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);
bool operator>= (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);- C++
string类关系运算符的逻辑与C语言字符串比较函数strcmp的逻辑类似,故不再赘述
3. string类简单模拟实现
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>namespace TESY
{class string{public://构造函数string(const char* str = ""):_capacity(strlen(str)),_size(strlen(str)){assert(str); //不能传入空指针 _str = new char[_size + 1]; //特别注意,这里开空间要多开一个给结束符'\0'留空间strcpy(_str, str);}//拷贝构造(深拷贝)string(const string& str){char* temp = new char[str._capacity + 1];strcpy(temp, str._str);_str = temp;_capacity = str._capacity;_size = str._size; }//赋值运算符重载(深拷贝)string& operator=(const string& str){if (this != &str){char* temp = new char[str._capacity + 1];strcpy(temp, str._str);delete[] _str;_str = temp;_capacity = str._capacity;_size = str._size;}return *this;}//尾插一个字符串void append(const char* str){int len = strlen(str);//检查容量if (_size + len > _capacity){reserve(_size + len);}strcpy(_str + _size, str);_size += len;}//尾插一个字符void push_back(const char c){//检查容量if (_size >= _capacity){size_t newCapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity;reserve(newCapacity);}_str[_size] = c;_size++;_str[_size] = '\0';}//尾插string& operator+=(char c){push_back(c);return *this;}string& operator+=(const char* str){append(str);return *this;}string& operator+=(const string& str){append(str._str);return *this;}//清空void clear(){delete[] _str;_size = _capacity = 0;_str = new char[1];_str[0] = '\0';}//交换两个string类的内容void swap(string& s){std::swap(_str, s._str);std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);std::swap(_size, s._size);}//返回C类型的字符串const char* c_str()const{return _str;}//返回长度size_t size()const{return _size;}//返回最大容量size_t capacity()const{return _capacity;}//判空bool empty()const{return _size == 0;}//修改容量void resize(size_t n, char c = '\0'){char* temp = new char[n + 1];int len = strlen(_str);if (n < len){strncpy(temp, _str, n);temp[n] = '\0';}else{strncpy(temp, _str, len);for (int i = 0; i < n - len; i++)temp[len + i] = c;temp[n] = '\0';}delete[] _str;_str = temp;_size = n;_capacity = n;}//扩容void reserve(size_t n){if (n > _capacity){char* temp = new char[n + 1];strcpy(temp, _str);delete[] _str;_str = temp;_capacity = n;}}//下标访问char& operator[](size_t index){assert(index <= _size);return _str[index];}const char& operator[](size_t index)const{assert(index <= _size);return _str[index];}//迭代器访问typedef char* iterator;typedef const char* const_iterator;iterator string::begin(){return _str;}iterator string::end(){return _str + _size;}const_iterator string::begin()const{return _str;}const_iterator string::end()const{return _str + _size;}//关系运算符重载friend bool operator<(const string& lhs, const string& rhs){return strcmp(lhs._str, rhs._str) < 0;}friend bool operator<=(const string& lhs, const string& rhs){return !(strcmp(lhs._str, rhs._str) > 0);}friend bool operator>(const string& lhs, const string& rhs){return strcmp(lhs._str, rhs._str) > 0;}friend bool operator>=(const string& lhs, const string& rhs){return (strcmp(lhs._str, rhs._str) < 0);}friend bool operator==(const string& lhs, const string& rhs){return strcmp(lhs._str, rhs._str) == 0;}friend bool operator!=(const string& lhs, const string& rhs){return strcmp(lhs._str, rhs._str) != 0;}// 返回c在string中第一次出现的位置size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0) const{for (int i = pos; i < size(); i++){if ((*this)[i] == c)return i;}return npos;}// 返回子串s在string中第一次出现的位置size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const{char* ret = strstr(_str + pos, s);if (ret == nullptr)return npos;elsereturn ret - _str;}// 在pos位置上插入字符c/字符串strstring& insert(size_t pos, char c){assert(pos <= _size);//检查容量if (_size >= _capacity){size_t newCapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity;reserve(newCapacity);}//挪动数据size_t end = _size + 1;while (end > pos){_str[end] = _str[end - 1];end--;}_str[pos] = c;_size++;return *this;}string& insert(size_t pos, const char* str){assert(pos <= _size);//检查容量int len = strlen(str);if (_size + len > _capacity){reserve(_size + len);}//挪动数据size_t end = _size + len;while (end > pos){_str[end] = _str[end - len];end--;}strncpy(_str + pos, str, len);_size += len;return *this;}//从pos位置开始删除len个字符string& erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos){assert(pos < _size);if (len == npos || pos + len >= _size){_str[pos] = '\0';_size = pos;}else{strcpy(_str + pos, _str + pos + len);_size -= len;}return *this;}//返回以从pos位置开始,长度为len的子串为内容的string对象string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const{assert(pos < _size);string temp;size_t end = pos + len;if (len == npos || len + pos > _size)end = _size;temp.reserve(end - pos);temp._size = end - pos;strncpy(temp._str, _str + pos, end - pos);temp[end - pos] = '\0';return temp;}//析构~string(){delete[] _str;_capacity = _size = 0;}//流插入friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& cout, const string& str){cout << str._str;}private:char* _str;size_t _capacity;size_t _size;static const size_t npos = -1;};std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& cout, const string& str);bool operator<(const string& lhs, const string& rhs);bool operator<=(const string& lhs, const string& rhs);bool operator>(const string& lhs, const string& rhs);bool operator>=(const string& lhs, const string& rhs);bool operator==(const string& lhs, const string& rhs);bool operator!=(const string& lhs, const string& rhs);
};
本章完
如果本篇有任何错误或讲述不清的地方,欢迎各位在评论区讨论并指出
下一篇,我们将继续STL的学习——vector

相关文章:

C++STL——string类详解及其模拟实现
CSTL——string类 1. STL简介 STL全称standard template libaray,译为标准模板库 需要注意,STL不是C的标准库,而是C标准库的重要组成部分STL是一个包含众多数据结构和算法的软件框架 下面展示STL的六大组件: 本章,我…...
使用Three.js创建导航立方体
什么是导航立方体? 导航立方体是一个交互式的3D控件,它允许用户通过点击和拖动立方体的各个面来改变3D视图的方向。这是一种非常直观的方式,让用户能够轻松地在3D空间中导航。 创建导航立方体 下面是一个基本的步骤,说明如何使用Three.js创建一个导航立方体: // 创建场景…...
C++初识类和对象
前言 上一期我们介绍了一些C入门的基础知识,本期我们来介绍面向对象。初步认识一下面向对象和面向过程、类、以及封装! 本期内容介绍 面向过程和面向对象 类的引入 类的定义 类的访问限定符和封装 类的作用域 类的实例化 类对象模型 this指针 一、面向…...
MYSQL where 子句
文章目录 前言MySQL where 子句语法 从命令提示符中读取数据使用PHP脚本读取数据后言 前言 hello world欢迎来到前端的新世界 😜当前文章系列专栏:Mysql 🐱👓博主在前端领域还有很多知识和技术需要掌握,正在不断努力…...
系列十六、Spring IOC容器的扩展点
一、概述 Spring IOC容器的扩展点是指在IOC加载的过程中,如何对即将要创建的bean进行扩展。 二、扩展点 2.1、BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 2.1.1、概述 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是bean定义的后置处理器,在BeanDefinition加载后&a…...
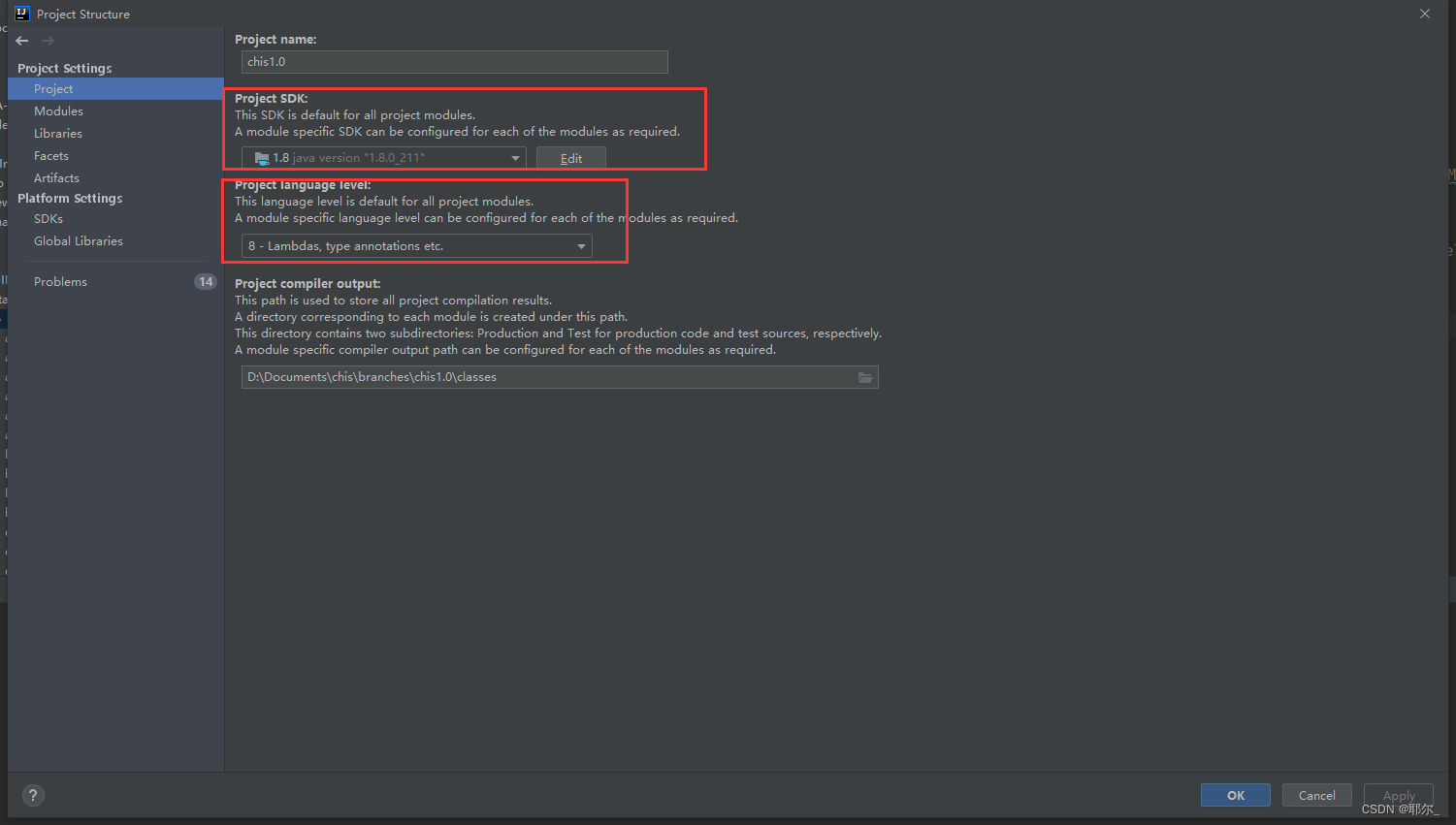
eclipse项目移到idea上部署运行
1.配置web模块 另外,模块这里,也要加上Spring 2.配置Artifact (用于tomcat) 就是从上面配置的web模块,产生的工件 3.添加lib 一般是在web-inf/lib , 遇到的坑: jdk版本问题,这里…...
支持向量机的算法原理
支持向量机(Support Vector Machine,简称SVM)是机器学习领域中一种常用的分类算法,它基于统计学习理论和结构风险最小化原则,具有很强的理论基础和良好的分类性能。本文将详细介绍支持向量机的算法原理,并解…...
)
gitlab 12升级14(解决各种报错问题)
1.这里是从自己公司的源下载的rpm包,需要换成自己的 2.从12的最后一个版本升级到14的最后一个版本 # 停服务 [rootdocker test]# gitlab-ctl stop puma && gitlab-ctl stop sidekiq && gitlab-ctl stop nginx && gitlab-ctl status# 进入…...

给element plus中动态form-item增加校验的可行方法
element plus中的form组件自带校验机制。在常规使用场景中,表单项是固定的、明确的,且数量不会太多。校验规则的使用也如下: <template><div class"edit-page"><el-form :model"formModel" ref"for…...

C++学习之值传递
c/c中存在三种传值方式,在局部函数中,对这三种传值方式传入的参数进行修改,会得到不同的结果。具体见下例: #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h>static int dummny 10000;// 传值(传过来的是原始值的副本&#…...

网络视频播放卡顿原因分析
一、问题描述 某项目通过拉摄像机rtsp流转rtmp/http-flv/ws-flv的方案,使用户可以在网页中观看摄像机的视频画面。在 观看视频时偶发出现卡顿现象。 二、卡顿现象分析和解决 此问题涉及的原因较多,所以得考虑各环节的问题可能性,并根据现场实…...

Android 相机库CameraView源码解析 (二) : 拍照
1. 前言 这段时间,在使用 natario1/CameraView 来实现带滤镜的预览、拍照、录像功能。 由于CameraView封装的比较到位,在项目前期,的确为我们节省了不少时间。 但随着项目持续深入,对于CameraView的使用进入深水区,逐…...
计算机缺少d3dx9_43.dll怎么办?5个方法快速修复d3dx9_43.dll文件
在计算机使用过程中,我们常常会遇到一些错误提示,其中之一就是“d3dx9_43.dll丢失”。这个问题可能会影响到我们的游戏体验或者软件运行。为了解决这个问题,我查阅了一些资料并尝试了多种方法。在这里,我想分享一下我对d3dx9_43.d…...
2023亚太杯数学建模C题思路分析 - 我国新能源电动汽车的发展趋势
1 赛题 问题C 我国新能源电动汽车的发展趋势 新能源汽车是指以先进技术原理、新技术、新结构的非常规汽车燃料为动力来源( 非常规汽车燃料指汽油、柴油以外的燃料),将先进技术进行汽车动力控制和驱动相结 合的汽车。新能源汽车主要包括四种类型&#x…...

c语言新龟兔赛跑
以下是一个使用C语言编写的新的龟兔赛跑游戏: #include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <time.h>int main() { int distance, turtle_speed, rabbit_speed, turtle_time, rabbit_time, rabbit_lead; srand(time(NULL)); // 随机数种…...
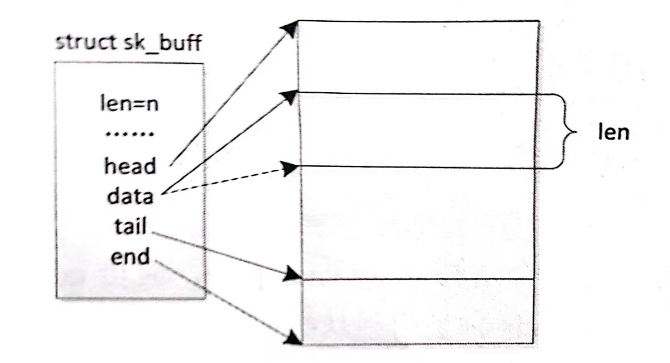
Linux驱动开发——网络设备驱动(理论篇)
目录 一、前言 二、网络层次结构 三、网络设备驱动核心数据结构和函数 一、前言 网络设备驱动是 Linux 的第三大类驱动,也是我们学习的最后一类 Linux 驱动。这里我们首先简单学习一下网络协议层次结构,然后简单讨论 Linux 内核中网络实现的层次结构。…...

simulink仿真
1)系统问题 连续系统,离散系统(采样周期问题) 系统分析问题 2)求解器问题 变步长,定步长,步长时间与采样周期问题、 3)积分器问题 连续积分,离散积分问题ÿ…...
PC端页面进去先出现加载效果
自定义指令v-loading,只需要绑定Boolean即可 v-loading“loading” <el-table :data"list" border style"width: 100%" v-loading"loading"><el-table-column align"center" label"序号" width"5…...
磁盘清理在哪里?学会这4个方法,快速清理内存!
“在使用电脑的过程中,我可能经常会保存一些文件到电脑上,这也导致电脑经常出现内存不足的情况。我想问问磁盘清理在哪里呀?我应该如何打开呢?” 随着使用电脑的时间增长,用户可能经常会遇到磁盘空间不足的情况&#x…...
Error opening terminal: xterm.”的解决方法
主要是看下面这两个变量是否设置正确 $ echo $TERM $ echo $TERMINFO 通常TERM的默认值为xterm-265color, 要查看支持的term,可以ls -al /lib/terminfo/x/ 如果TERM是xterm-265color的话,TERMINFO设置为/usr/lib/terminfo make menuconfig时提示“Err…...

KubeSphere 容器平台高可用:环境搭建与可视化操作指南
Linux_k8s篇 欢迎来到Linux的世界,看笔记好好学多敲多打,每个人都是大神! 题目:KubeSphere 容器平台高可用:环境搭建与可视化操作指南 版本号: 1.0,0 作者: 老王要学习 日期: 2025.06.05 适用环境: Ubuntu22 文档说…...
)
浏览器访问 AWS ECS 上部署的 Docker 容器(监听 80 端口)
✅ 一、ECS 服务配置 Dockerfile 确保监听 80 端口 EXPOSE 80 CMD ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]或 EXPOSE 80 CMD ["python3", "-m", "http.server", "80"]任务定义(Task Definition&…...

《Qt C++ 与 OpenCV:解锁视频播放程序设计的奥秘》
引言:探索视频播放程序设计之旅 在当今数字化时代,多媒体应用已渗透到我们生活的方方面面,从日常的视频娱乐到专业的视频监控、视频会议系统,视频播放程序作为多媒体应用的核心组成部分,扮演着至关重要的角色。无论是在个人电脑、移动设备还是智能电视等平台上,用户都期望…...

Qt Widget类解析与代码注释
#include "widget.h" #include "ui_widget.h"Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent): QWidget(parent), ui(new Ui::Widget) {ui->setupUi(this); }Widget::~Widget() {delete ui; }//解释这串代码,写上注释 当然可以!这段代码是 Qt …...

1688商品列表API与其他数据源的对接思路
将1688商品列表API与其他数据源对接时,需结合业务场景设计数据流转链路,重点关注数据格式兼容性、接口调用频率控制及数据一致性维护。以下是具体对接思路及关键技术点: 一、核心对接场景与目标 商品数据同步 场景:将1688商品信息…...

条件运算符
C中的三目运算符(也称条件运算符,英文:ternary operator)是一种简洁的条件选择语句,语法如下: 条件表达式 ? 表达式1 : 表达式2• 如果“条件表达式”为true,则整个表达式的结果为“表达式1”…...

el-switch文字内置
el-switch文字内置 效果 vue <div style"color:#ffffff;font-size:14px;float:left;margin-bottom:5px;margin-right:5px;">自动加载</div> <el-switch v-model"value" active-color"#3E99FB" inactive-color"#DCDFE6"…...

MVC 数据库
MVC 数据库 引言 在软件开发领域,Model-View-Controller(MVC)是一种流行的软件架构模式,它将应用程序分为三个核心组件:模型(Model)、视图(View)和控制器(Controller)。这种模式有助于提高代码的可维护性和可扩展性。本文将深入探讨MVC架构与数据库之间的关系,以…...

【android bluetooth 框架分析 04】【bt-framework 层详解 1】【BluetoothProperties介绍】
1. BluetoothProperties介绍 libsysprop/srcs/android/sysprop/BluetoothProperties.sysprop BluetoothProperties.sysprop 是 Android AOSP 中的一种 系统属性定义文件(System Property Definition File),用于声明和管理 Bluetooth 模块相…...
Springboot社区养老保险系统小程序
一、前言 随着我国经济迅速发展,人们对手机的需求越来越大,各种手机软件也都在被广泛应用,但是对于手机进行数据信息管理,对于手机的各种软件也是备受用户的喜爱,社区养老保险系统小程序被用户普遍使用,为方…...
