使用RedisCacheWriter#clean在线异步地批量扫描匹配删除缓存数据-spring-data-redis
1.背景
生产环境,某云的某个业务Redis实例,触发内存使用率,连续 3 次 平均值 >= 85 %告警。
运维同学告知,看看需要怎么优化或者升级配置?分享了其实例RDB的内存剖析链接。
通过内存剖析详情发现,存在某类未设置过期时间且无用的keys,其内存占用约3.8GB,内存占比25%。
内存占比挺大,有确定的成本经济收益。
做事有动力啦!
Redis实例信息
某云Redis实例的基本信息
- 实例规格:16G主从版
- 版本:Redis 2.8(兼容3.0特性)

某云的Redis RDB内存剖析
- 基本信息
- 分析方法:使用已有备份集 (选择的备份文件:完成于)
- 详情
- Key内存占有情况
- Key数量分布情况
- Elements内存占用情况
- Elements数量分布情况
- Key过期时间分布 (内存)
- Key过期时间分布 (数量)

2.目标
- 在线异步地删除缓存数据
- 不影响线上业务,不确定的风险可控(风险紧急预案)
3.结论先行
- 在线清理了
5GB+内存 - 已使用内存总量,15.5GB -> 10.2GB
4.技术方案
变更三板斧:可灰度、可观测/可监控、可回滚
使用spring-data-redis提供的RedisCacheWriter#clean开源解决方案,在其基础上加入异步和并发控制。
- 【批量策略】在线异步地批量扫描匹配删除,每批10/20个key
- 先SCAN匹配,再批量DEL
- SCAN(keyPattern) + DEL(allMatchKeys)
- 【执行策略】预发环境,业务低峰时期执行
- 【可观测】Redis实例性能监控,业务监控
- 【风险紧急预案-兜底方案】删除容器实例,kill杀掉异步守护线程,停止执行(可回滚)
spring-boot版本
- spring-data-redis-2.7.16
- spring-boot-starter-data-redis-2.7.16
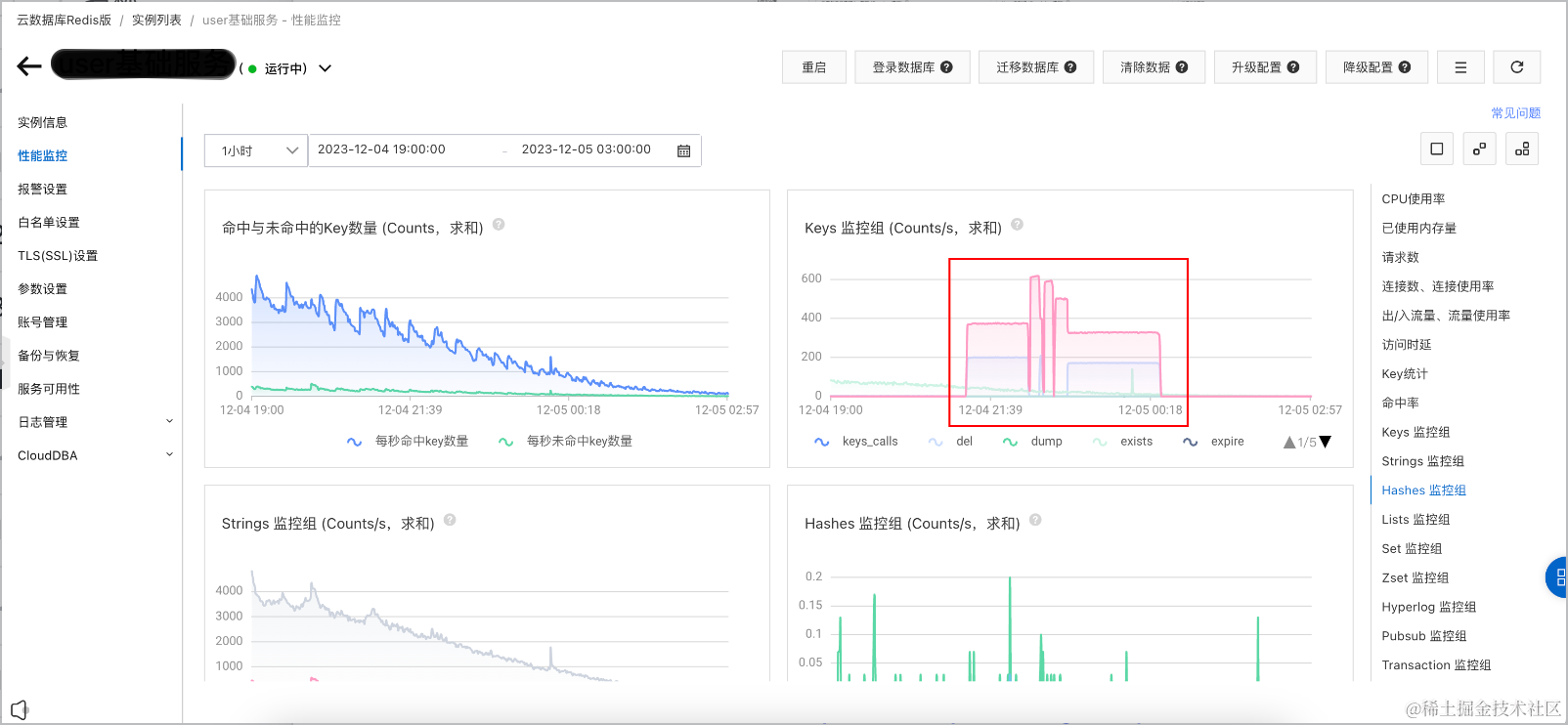
可观测-Redis实例性能监控
- key模式: “message:queue:*_lock”
- 清理时间: [2023-12-04 21:15:39.405, 2023-12-05 00:28:24.21]
清理途中,觉得每批10个key有些慢,调整到每批20个key。
【注意】应用重启后,会重新从头开始扫描,存在一段时间未删除keys,需要等一会才能看到删除效果。
不建议中途调整每批key数量!
CPU使用率 (%,平均值)
CPU使用率,增长
1~3%
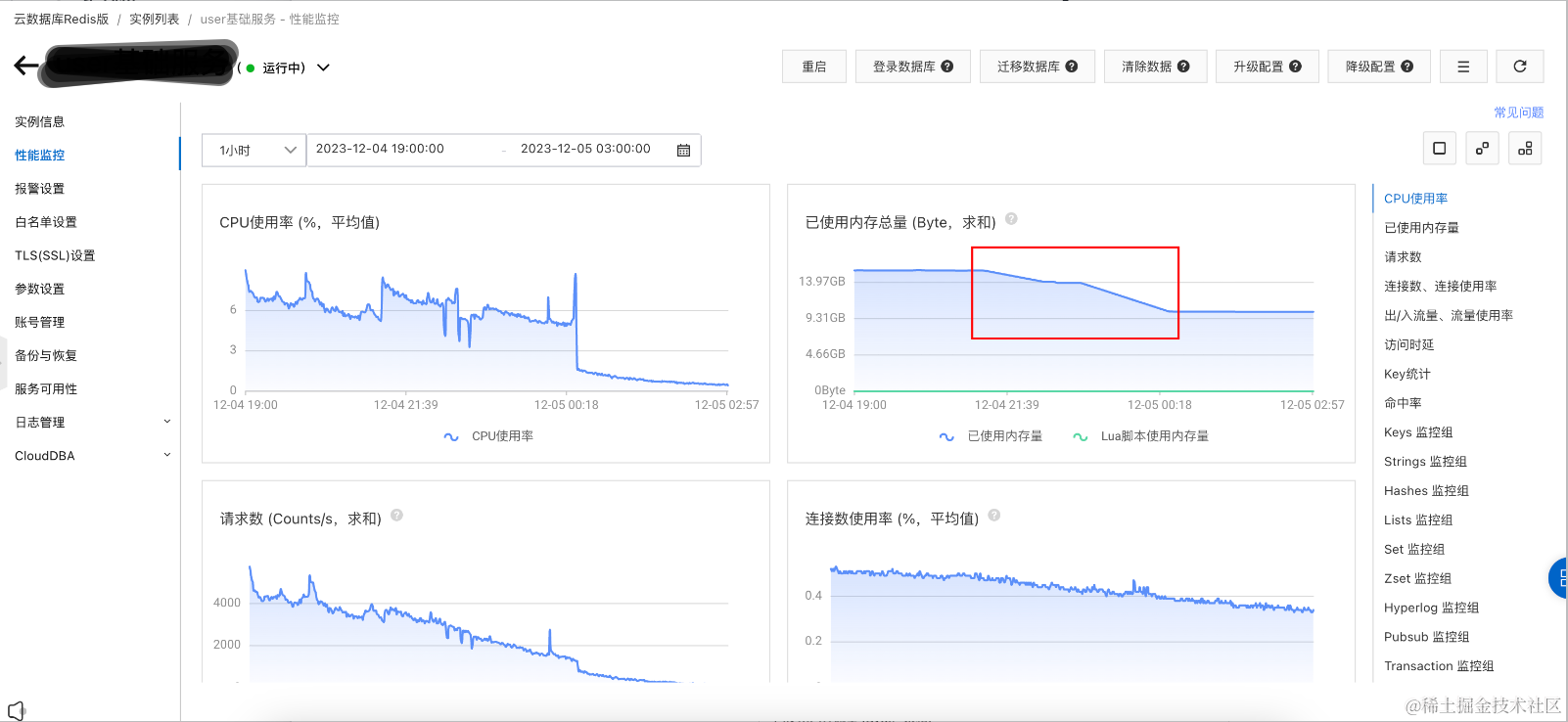
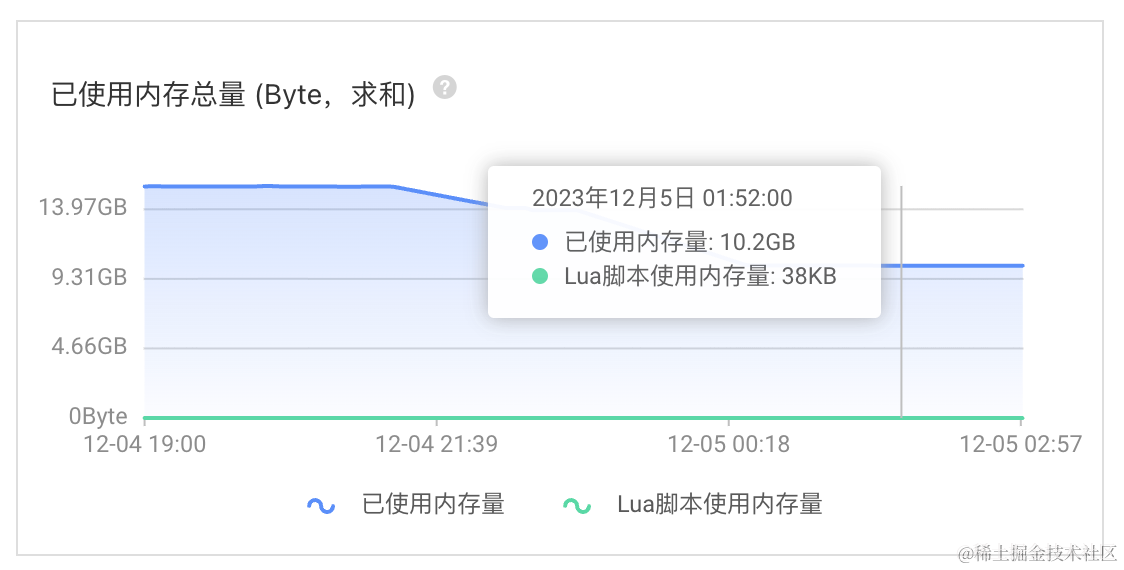
已使用内存总量 (Byte,求和)
已使用内存总量,15.5GB -> 10.22GB

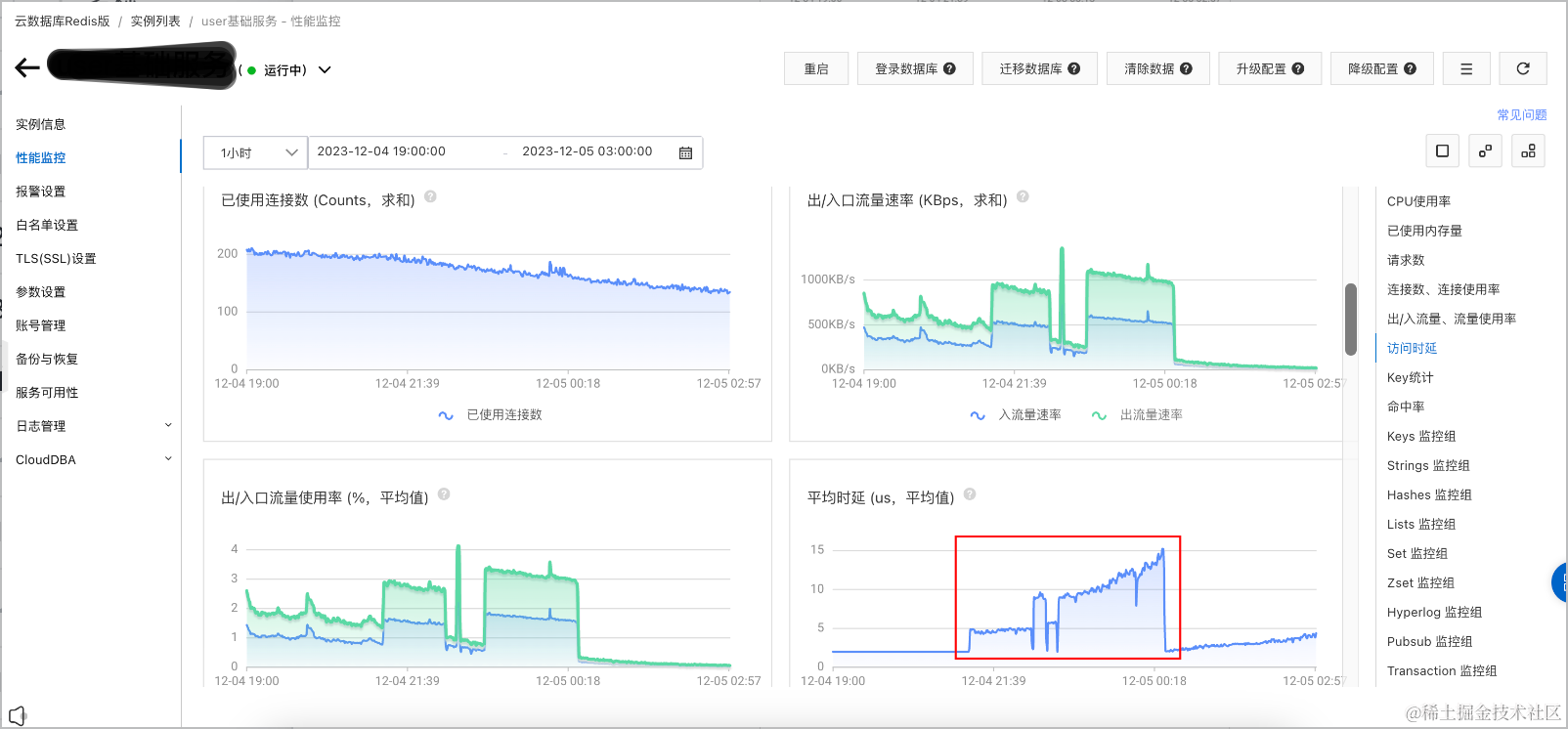
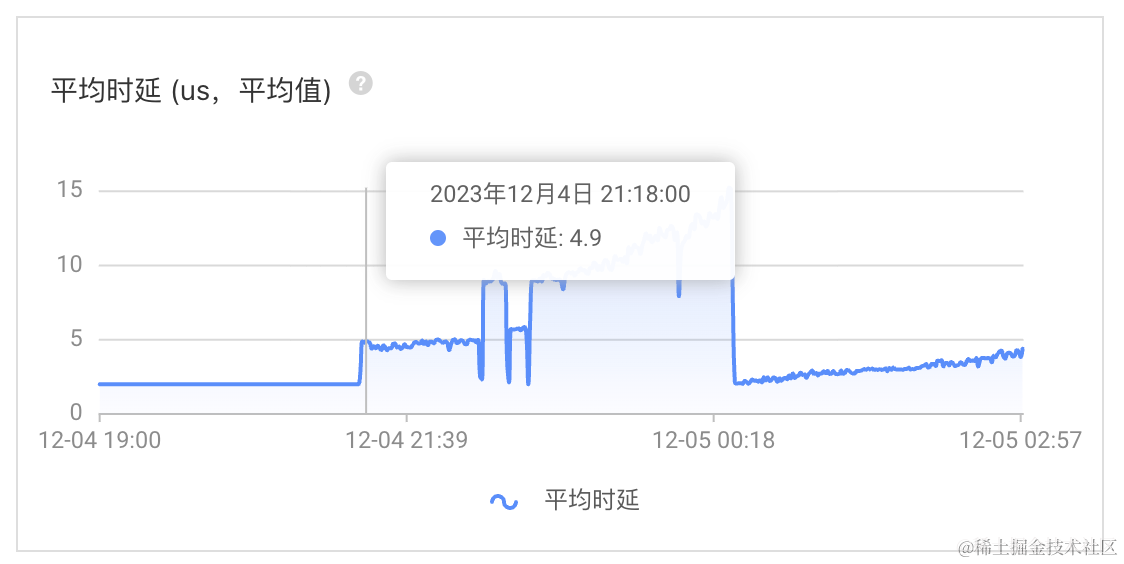
平均时延 (us,平均值)
每批10个key,时延增长
2~3微秒每批20个key,时延增长
7~13微秒
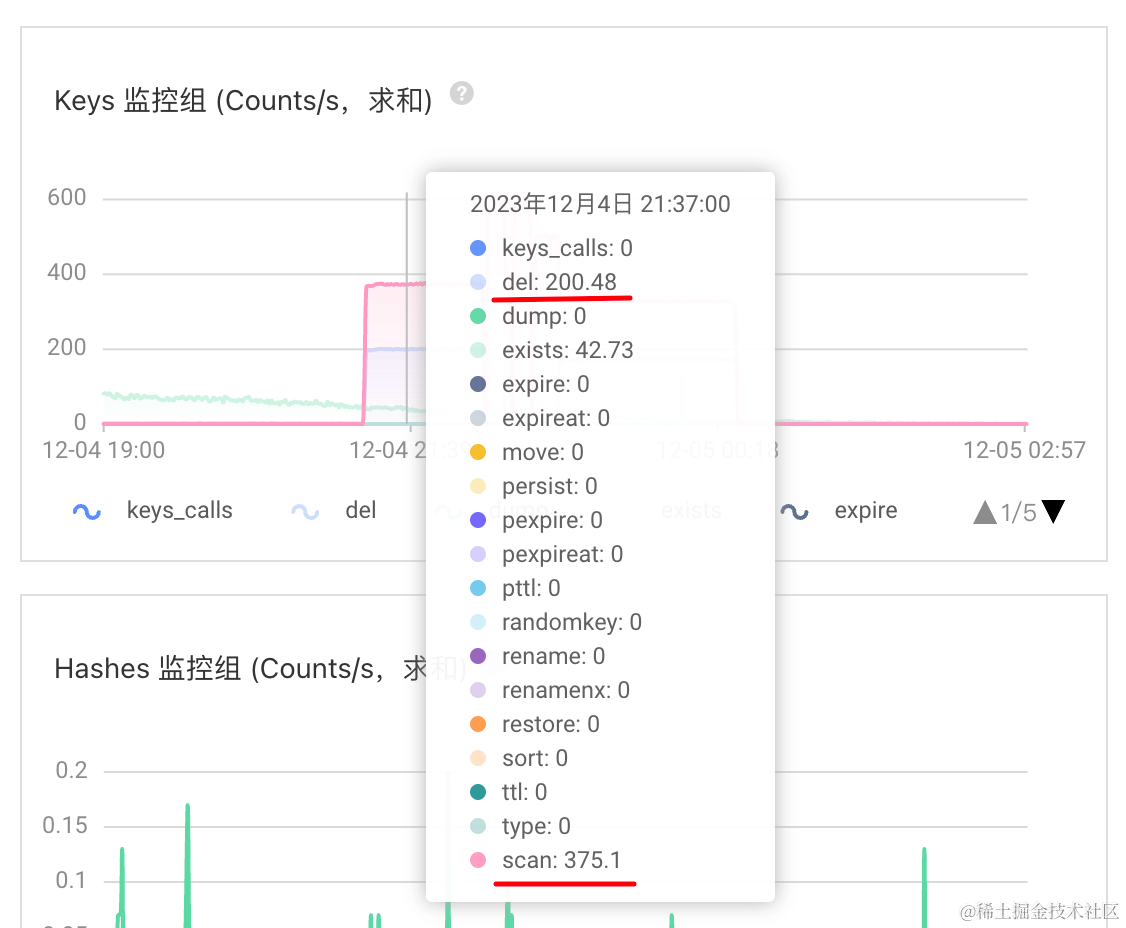
Keys 监控组 (Counts/s,求和)
del: 200
scan: 375
具体实现
scan批量策略,先批量扫描匹配,再批量删除,每批10/20个key,不断地迭代以上操作,直到数据被全部清理。
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;import cn.hutool.core.thread.ThreadFactoryBuilder;
import com.spring.boot.redis.example.model.CacheKey;
import com.spring.boot.redis.example.service.CacheService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.BatchStrategies;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheWriter;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.StopWatch;/*** 缓存服务实现** @author guang.yi* @since 2023/7/30*/
@Slf4j
@Service("cacheService")
public class CacheServiceImpl implements CacheService {/*** 并发开关*/private final ConcurrentMap<String, Boolean> concurrentSwitch = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);private final ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 5L, TimeUnit.MINUTES,new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1),new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNamePrefix("cache-clean-").setDaemon(true).build());private final RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory;public CacheServiceImpl(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {this.redisConnectionFactory = redisConnectionFactory;log.info("create CacheServiceImpl");}@Overridepublic boolean cleanCache(CacheKey cacheKey) {String keyPattern = cacheKey.getKeyPattern();// 避免多次重复地操作if (concurrentSwitch.putIfAbsent(keyPattern, Boolean.TRUE) == null) {// 异步地执行executorService.execute(() -> this.clean(cacheKey));return true;}return false;}private void clean(CacheKey cacheKey) {log.info("cleanCache start, cacheKey={}", cacheKey);StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch("cleanCache");stopWatch.start();this.clean(cacheKey.getCacheName(), cacheKey.getKeyPattern());stopWatch.stop();log.info("cleanCache end, cacheKey={}, stopWatch={}", cacheKey, stopWatch);}/*** 缓存Redis的历史数据清理* <pre>* 【批量策略】在线异步地批量扫描匹配删除,每批10个key* 先SCAN,再批量DEL* 【执行策略】预发环境,业务低峰时期* </pre>** @see org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheWriter#clean* @see org.springframework.data.redis.cache.DefaultRedisCacheWriter#clean*/private void clean(String cacheName, String keyPattern) {// 【批量策略】SCAN,每批10个keyRedisCacheWriter redisCacheWriter = RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(redisConnectionFactory, BatchStrategies.scan(10));// 先SCAN,再批量DELredisCacheWriter.clean(cacheName, keyPattern.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));}}
# .A.1. Core Properties
spring:# RedisPropertiesredis:database: 0host: "localhost"port: 6379timeout: 1sconnect-timeout: 300ms
# client-name: "user-cache"
# client-type: lettuce
# sentinel:
# master: ""
# nodes: "host:port"
# cluster:
# nodes: "host:port"
# max-redirects: 3
# jedis:
# pool:
# enabled: true
# max-idle: 8
# min-idle: 0
# max-active: 8
# max-wait: 300ms
# time-between-eviction-runs: 5mlettuce:shutdown-timeout: 100mspool:enabled: truemax-idle: 8min-idle: 0max-active: 8max-wait: -1time-between-eviction-runs: 5m开源解决方案有哪些坑?
深入源代码,深究实现细节,趴开裤子看看底细。
源代码做了简化
开源解决方案结论
深入源代码看,scan批量策略的实现方案靠谱。keys批量策略存在大坑,不靠谱。
scan批量策略,先批量扫描匹配,再批量删除,每批10/20个key,不断地迭代以上操作,直到数据被全部清理。
RedisCacheWriter#clean
org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheWriter#clean
BatchStrategy批量策略,有keys和scan两种,分别对应Redis的KEYS和SCAN命令。
批量策略默认使用keys,对于真实业务使用场景,一点都不实用。
因为KEYS命令会先收集所有满足匹配条件的keys,等所有都收集好了,再一次性全量DEL删除命令。
对于大量的keys需要删除时,其操作可能夯住线上Redis实例,存在严重影响Redis实例干活的风险。
package org.springframework.data.redis.cache;import java.time.Duration;import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;/*** {@link RedisCacheWriter} provides low level access to Redis commands ({@code SET, SETNX, GET, EXPIRE,...}) used for* caching. <br />* The {@link RedisCacheWriter} may be shared by multiple cache implementations and is responsible for writing / reading* binary data to / from Redis. The implementation honors potential cache lock flags that might be set.* <p>* The default {@link RedisCacheWriter} implementation can be customized with {@link BatchStrategy} to tune performance* behavior.** @author Christoph Strobl* @author Mark Paluch* @since 2.0*/
public interface RedisCacheWriter extends CacheStatisticsProvider {/*** Create new {@link RedisCacheWriter} without locking behavior.** @param connectionFactory must not be {@literal null}.* @return new instance of {@link DefaultRedisCacheWriter}.*/static RedisCacheWriter nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {return nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(connectionFactory, BatchStrategies.keys());}/*** Create new {@link RedisCacheWriter} without locking behavior.** @param connectionFactory must not be {@literal null}.* @param batchStrategy must not be {@literal null}.* @return new instance of {@link DefaultRedisCacheWriter}.* @since 2.6*/static RedisCacheWriter nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory,BatchStrategy batchStrategy) {Assert.notNull(connectionFactory, "ConnectionFactory must not be null!");Assert.notNull(batchStrategy, "BatchStrategy must not be null!");return new DefaultRedisCacheWriter(connectionFactory, batchStrategy);}/*** Remove all keys following the given pattern.* 按照给定模式删除所有键。** @param name The cache name must not be {@literal null}.* @param pattern The pattern for the keys to remove. Must not be {@literal null}.*/void clean(String name, byte[] pattern);}DefaultRedisCacheWriter#clean
源代码做了简化
RedisCacheWriter#clean默认实现是org.springframework.data.redis.cache.DefaultRedisCacheWriter#clean
通过批量策略清理缓存数据batchStrategy.cleanCache(connection, name, pattern)
package org.springframework.data.redis.cache;import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Function;import org.springframework.dao.PessimisticLockingFailureException;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnection;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisStringCommands.SetOption;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.types.Expiration;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;/*** {@link RedisCacheWriter} implementation capable of reading/writing binary data from/to Redis in {@literal standalone}* and {@literal cluster} environments. Works upon a given {@link RedisConnectionFactory} to obtain the actual* {@link RedisConnection}. <br />* {@link DefaultRedisCacheWriter} can be used in* {@link RedisCacheWriter#lockingRedisCacheWriter(RedisConnectionFactory) locking} or* {@link RedisCacheWriter#nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(RedisConnectionFactory) non-locking} mode. While* {@literal non-locking} aims for maximum performance it may result in overlapping, non atomic, command execution for* operations spanning multiple Redis interactions like {@code putIfAbsent}. The {@literal locking} counterpart prevents* command overlap by setting an explicit lock key and checking against presence of this key which leads to additional* requests and potential command wait times.** @author Christoph Strobl* @author Mark Paluch* @author André Prata* @since 2.0*/
class DefaultRedisCacheWriter implements RedisCacheWriter {private final RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory;private final Duration sleepTime;private final CacheStatisticsCollector statistics;private final BatchStrategy batchStrategy;/** (non-Javadoc)* @see org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheWriter#clean(java.lang.String, byte[])*/@Overridepublic void clean(String name, byte[] pattern) {Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null!");Assert.notNull(pattern, "Pattern must not be null!");execute(name, connection -> {boolean wasLocked = false;try {if (isLockingCacheWriter()) {doLock(name, connection);wasLocked = true;}// 通过批量策略清理缓存数据long deleteCount = batchStrategy.cleanCache(connection, name, pattern);while (deleteCount > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {statistics.incDeletesBy(name, Integer.MAX_VALUE);deleteCount -= Integer.MAX_VALUE;}statistics.incDeletesBy(name, (int) deleteCount);} finally {if (wasLocked && isLockingCacheWriter()) {doUnlock(name, connection);}}return "OK";});}}BatchStrategy批量策略
org.springframework.data.redis.cache.BatchStrategy
package org.springframework.data.redis.cache;import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnection;/*** A {@link BatchStrategy} to be used with {@link RedisCacheWriter}.* <p>* Mainly used to clear the cache.* <p>* Predefined strategies using the {@link BatchStrategies#keys() KEYS} or {@link BatchStrategies#scan(int) SCAN}* commands can be found in {@link BatchStrategies}.** @author Mark Paluch* @author Christoph Strobl* @since 2.6*/
public interface BatchStrategy {/*** Remove all keys following the given pattern.** @param connection the connection to use. Must not be {@literal null}.* @param name The cache name. Must not be {@literal null}.* @param pattern The pattern for the keys to remove. Must not be {@literal null}.* @return number of removed keys.*/long cleanCache(RedisConnection connection, String name, byte[] pattern);}BatchStrategies批量策略实现
org.springframework.data.redis.cache.BatchStrategies
BatchStrategy批量策略,有keys和scan两种,分别对应Redis的KEYS和SCAN命令。
scan批量策略,先批量扫描匹配,再批量删除,每批10/20个key,不断地迭代以上操作,直到数据被全部清理。
keys批量策略,对于真实业务使用场景,一点都不实用。
因为KEYS命令会先收集所有满足匹配条件的keys,等所有都收集好了,再一次性全量DEL删除命令。
对于大量的keys需要删除时,其操作可能夯住线上Redis实例,存在严重影响Redis实例干活的风险。
package org.springframework.data.redis.cache;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
import java.util.Optional;import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnection;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.Cursor;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ScanOptions;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;/*** A collection of predefined {@link BatchStrategy} implementations using {@code KEYS} or {@code SCAN} command.** @author Mark Paluch* @author Christoph Strobl* @since 2.6*/
public abstract class BatchStrategies {private BatchStrategies() {// can't touch this - oh-oh oh oh oh-oh-oh}/*** A {@link BatchStrategy} using a single {@code KEYS} and {@code DEL} command to remove all matching keys.* {@code KEYS} scans the entire keyspace of the Redis database and can block the Redis worker thread for a long time* on large keyspaces.* <p>* {@code KEYS} is supported for standalone and clustered (sharded) Redis operation modes.** @return batching strategy using {@code KEYS}.*/public static BatchStrategy keys() {return Keys.INSTANCE;}/*** A {@link BatchStrategy} using a {@code SCAN} cursors and potentially multiple {@code DEL} commands to remove all* matching keys. This strategy allows a configurable batch size to optimize for scan batching.* <p>* Note that using the {@code SCAN} strategy might be not supported on all drivers and Redis operation modes.** @return batching strategy using {@code SCAN}.*/public static BatchStrategy scan(int batchSize) {Assert.isTrue(batchSize > 0, "Batch size must be greater than zero!");return new Scan(batchSize);}/*** {@link BatchStrategy} using {@code KEYS}.*/static class Keys implements BatchStrategy {static Keys INSTANCE = new Keys();@Overridepublic long cleanCache(RedisConnection connection, String name, byte[] pattern) {// `KEYS`命令会先收集所有满足匹配条件的keys,等所有都收集好了,再一次性全量`DEL`删除命令byte[][] keys = Optional.ofNullable(connection.keys(pattern)).orElse(Collections.emptySet()).toArray(new byte[0][]);if (keys.length > 0) {connection.del(keys);}return keys.length;}}/*** {@link BatchStrategy} using {@code SCAN}.*/static class Scan implements BatchStrategy {private final int batchSize;Scan(int batchSize) {this.batchSize = batchSize;}@Overridepublic long cleanCache(RedisConnection connection, String name, byte[] pattern) {// 批量扫描匹配删除,每批10/20个key// 先SCAN匹配,再批量DEL// SCAN(keyPattern, match, batchSize) + DEL(allMatchKeys, batchSize)Cursor<byte[]> cursor = connection.scan(ScanOptions.scanOptions().count(batchSize).match(pattern).build());long count = 0;PartitionIterator<byte[]> partitions = new PartitionIterator<>(cursor, batchSize);while (partitions.hasNext()) {List<byte[]> keys = partitions.next();count += keys.size();if (keys.size() > 0) {connection.del(keys.toArray(new byte[0][]));}}return count;}}/*** Utility to split and buffer outcome from a {@link Iterator} into {@link List lists} of {@code T} with a maximum* chunks {@code size}.** @param <T>*/static class PartitionIterator<T> implements Iterator<List<T>> {private final Iterator<T> iterator;private final int size;PartitionIterator(Iterator<T> iterator, int size) {this.iterator = iterator;this.size = size;}@Overridepublic boolean hasNext() {return iterator.hasNext();}@Overridepublic List<T> next() {if (!hasNext()) {throw new NoSuchElementException();}List<T> list = new ArrayList<>(size);while (list.size() < size && iterator.hasNext()) {list.add(iterator.next());}return list;}}
}5.参考引用
- Spring Data Redis / Redis / Redis Cache
- redis-spring-boot-starter-example
献给杭州2023年的第一场雪❄️
2023.12.18
相关文章:

使用RedisCacheWriter#clean在线异步地批量扫描匹配删除缓存数据-spring-data-redis
1.背景 生产环境,某云的某个业务Redis实例,触发内存使用率,连续 3 次 平均值 > 85 %告警。 运维同学告知,看看需要怎么优化或者升级配置?分享了其实例RDB的内存剖析链接。 通过内存剖析详情发现,存在某…...
机器视觉:AI赋能缺陷检测,铸就芯片产品的大算力与高能效
导言:近年来,国内芯片行业快速发展,市场对芯片需求的不断增大,芯片的缺陷检测压力也越来越大。芯片产品在生产制造过程中,需要经历数道工序,每个生产环节的材料、环境、工艺参数等都有可能造成产品缺陷。不…...
(9)Linux Git的介绍以及缓冲区
💭 前言 本章我们先对缓冲区的概念进行一个详细的探究,之后会带着大家一步步去编写一个简陋的 "进度条" 小程序。最后我们来介绍一下 Git,着重讲解一下 Git 三板斧,一般只要掌握三板斧就基本够用了。 缓冲区ÿ…...
华为云之ECS云产品快速入门
华为云之ECS云产品快速入门 一、ECS云服务器介绍二、本次实践目标三、创建虚拟私有云VPC1.虚拟私有云VPC介绍2.进入虚拟私有云VPC管理页面3.创建虚拟私有云4.查看创建的VPC 四、创建弹性云服务器ECS——Linux1.进入ECS购买界面2.创建弹性云服务器(Linux)——基础配置步骤3.创建…...

tcp 的限制 (TCP_WRAPPERS)
#江南的江 #每日鸡汤:青春是打开了就合不上的书,人生是踏上了就回不了头的路,爱情是扔出了就收不回的赌注。 #初心和目标:拿到高级网络工程师 TCP_WRAPPERs Tcp_wrappers 对于七层模型中是位于第四层的安全工具,他…...

如何保证架构的质量
1. 如何保证架构的质量: ①. 稳定性、健壮性(1). 系统稳定性: ①. 定义:a. 当一个实际的系统处于一个平衡的状态时,如果受到外来作用的影响时,系统经过一个过渡过程仍然能够回到原来的平衡状态.b. 可以说这个系统是稳定的,否则系统不稳定c. 如一根绳子绑着小球,处于垂直状态,…...
JavaWeb笔记之前端开发JavaScript
一、引言 1.1 简介 JavaScript一种解释性脚本语言,是一种动态类型、弱类型、基于原型继承的语言,内置支持类型。 它的解释器被称为JavaScript引擎,作为浏览器的一部分,广泛用于客户端的脚本语言,用来给HTML网页增加…...

SCAU:18063 圈中的游戏
18063 圈中的游戏 时间限制:1000MS 代码长度限制:10KB 提交次数:0 通过次数:0 题型: 编程题 语言: G;GCC;VC Description 有n个人围成一圈,从第1个人开始报数1、2、3,每报到3的人退出圈子。编程使用链表找出最后留下的人。输入格式 输入一个数n&a…...

.NET Core中鉴权 Authentication Authorization
Authentication: 鉴定身份信息,例如用户有没有登录,用户基本信息 Authorization: 判定用户有没有权限 使用框架提供的Cookie鉴权方式 1.首先在服务容器注入鉴权服务和Cookie服务支持 services.AddAuthentication(options > {options.DefaultAuthe…...

PyTorch深度学习实战(26)——卷积自编码器(Convolutional Autoencoder)
PyTorch深度学习实战(26)——卷积自编码器 0. 前言1. 卷积自编码器2. 使用 t-SNE 对相似图像进行分组小结系列链接 0. 前言 我们已经学习了自编码器 (AutoEncoder) 的原理,并使用 PyTorch 搭建了全连接自编码器,但我们使用的数据…...

Milvus实战:构建QA系统及推荐系统
Milvus简介 全民AI的时代已经在趋势之中,各类应用层出不穷,而想要构建一个完善的AI应用/系统,底层存储是不可缺少的一个组件。 与传统数据库或大数据存储不同的是,这种场景下则需要选择向量数据库,是专门用来存储和查…...
使用Docker部署Nexus Maven私有仓库并结合Cpolar实现远程访问
文章目录 1. Docker安装Nexus2. 本地访问Nexus3. Linux安装Cpolar4. 配置Nexus界面公网地址5. 远程访问 Nexus界面6. 固定Nexus公网地址7. 固定地址访问Nexus Nexus是一个仓库管理工具,用于管理和组织软件构建过程中的依赖项和构件。它与Maven密切相关,可…...

GEE-Sentinel-2月度时间序列数据合成并导出
系列文章目录 第一章:时间序列数据合成 文章目录 系列文章目录前言时间序列数据合成总结 前言 利用每个月可获取植被指数数据取均值,合成月度平均植被指数,然后将12个月中的数据合成一个12波段的时间数据合成数据。 时间序列数据合成 代码…...

【深度学习】语言模型与注意力机制以及Bert实战指引之二
文章目录 前言 前言 这一篇是bert实战的完结篇,准备中。...
计算机网络 网络层下 | IPv6 路由选择协议,P多播,虚拟专用网络VPN,MPLS多协议标签
文章目录 5 IPv65.1 组成5.2 IPv6地址5.3 从IPv4向IPv6过渡5.3.1 双协议栈5.3.2 隧道技术 6 因特网的路由选择协议6.1 内部网关协议RIP6.2 内部网关协议 OSPF基本特点 6.3 外部网关协议 BGP6.3.1 路由选择 6.4 路由器组成6.4.1 基本了解6.4.2 结构 7 IP多播7.1 硬件多播7.2 IP多…...
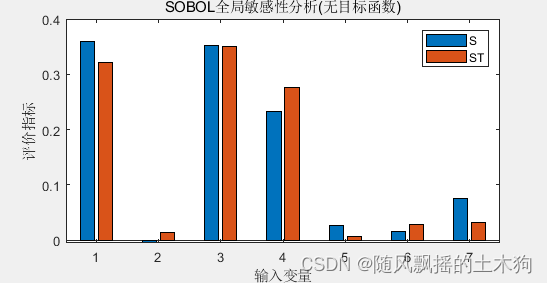
【MATLAB第83期】基于MATLAB的LSTM代理模型的SOBOL全局敏感性运用
【MATLAB第83期】基于MATLAB的LSTM代理模型的SOBOL全局敏感性运用 引言 在前面几期,介绍了敏感性分析法,本期来介绍lstm作为代理模型的sobol全局敏感性分析模型。 【MATLAB第31期】基于MATLAB的降维/全局敏感性分析/特征排序/数据处理回归问题MATLAB代…...
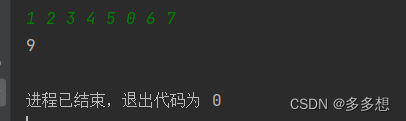
求奇数的和 C语言xdoj147
题目描述:计算给定一组整数中奇数的和,直到遇到0时结束。 输入格式:共一行,输入一组整数,以空格分隔 输出格式:输出一个整数 示例: 输入:1 2 3 4 5 0 6 7 输出:9 #inclu…...

全链路压力测试:解析其主要特点
随着信息技术的飞速发展和云计算的普及,全链路压力测试作为一种关键的质量保障手段,在软件开发和系统部署中扮演着至关重要的角色。全链路压力测试以模拟真实生产环境的压力和负载,对整个业务流程进行全面测试,具有以下主要特点&a…...

算法基础之约数个数
约数个数 核心思想: 用哈希表存每个质因数的指数 然后套公式 #include <iostream>#include <algorithm>#include <unordered_map>#include <vector>using namespace std;const int N 110 , mod 1e9 7;typedef long long LL; //long l…...
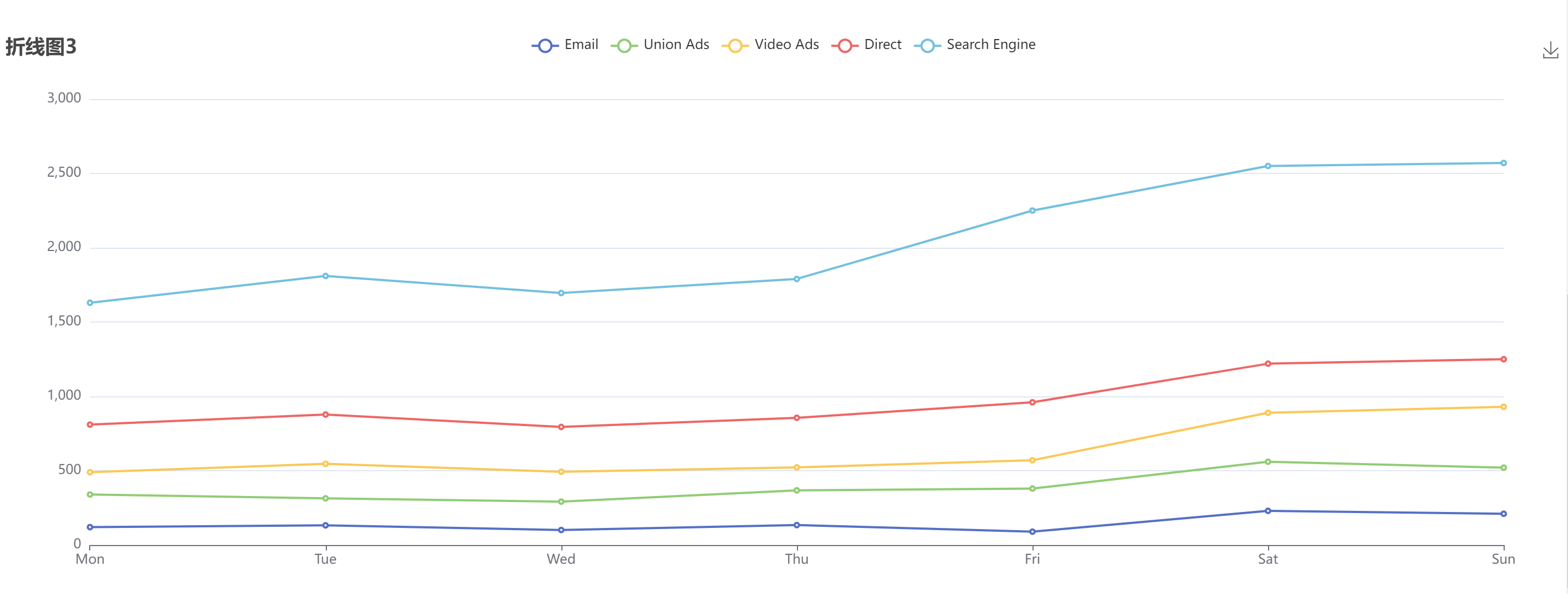
【ECharts】折线图
文章目录 折线图1折线图2折线图3示例 参考: Echarts官网 Echarts 配置项 折线图1 带X轴、Y轴标记线,其中X轴是’category’ 类目轴,适用于离散的类目数据。 let myChart echarts.init(this.$refs.line_chart2); let yList [400, 500, 6…...

国防科技大学计算机基础课程笔记02信息编码
1.机内码和国标码 国标码就是我们非常熟悉的这个GB2312,但是因为都是16进制,因此这个了16进制的数据既可以翻译成为这个机器码,也可以翻译成为这个国标码,所以这个时候很容易会出现这个歧义的情况; 因此,我们的这个国…...
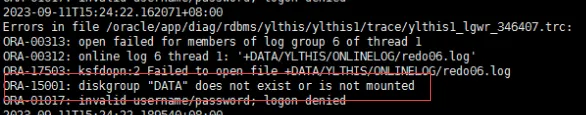
19c补丁后oracle属主变化,导致不能识别磁盘组
补丁后服务器重启,数据库再次无法启动 ORA01017: invalid username/password; logon denied Oracle 19c 在打上 19.23 或以上补丁版本后,存在与用户组权限相关的问题。具体表现为,Oracle 实例的运行用户(oracle)和集…...
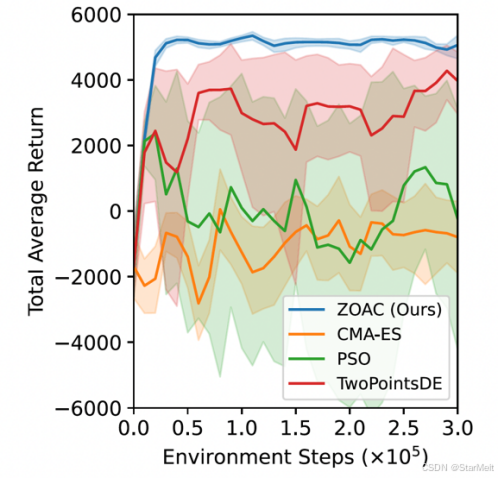
突破不可导策略的训练难题:零阶优化与强化学习的深度嵌合
强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)是工业领域智能控制的重要方法。它的基本原理是将最优控制问题建模为马尔可夫决策过程,然后使用强化学习的Actor-Critic机制(中文译作“知行互动”机制),逐步迭代求解…...

Admin.Net中的消息通信SignalR解释
定义集线器接口 IOnlineUserHub public interface IOnlineUserHub {/// 在线用户列表Task OnlineUserList(OnlineUserList context);/// 强制下线Task ForceOffline(object context);/// 发布站内消息Task PublicNotice(SysNotice context);/// 接收消息Task ReceiveMessage(…...
【网络安全产品大调研系列】2. 体验漏洞扫描
前言 2023 年漏洞扫描服务市场规模预计为 3.06(十亿美元)。漏洞扫描服务市场行业预计将从 2024 年的 3.48(十亿美元)增长到 2032 年的 9.54(十亿美元)。预测期内漏洞扫描服务市场 CAGR(增长率&…...

深入理解JavaScript设计模式之单例模式
目录 什么是单例模式为什么需要单例模式常见应用场景包括 单例模式实现透明单例模式实现不透明单例模式用代理实现单例模式javaScript中的单例模式使用命名空间使用闭包封装私有变量 惰性单例通用的惰性单例 结语 什么是单例模式 单例模式(Singleton Pattern&#…...
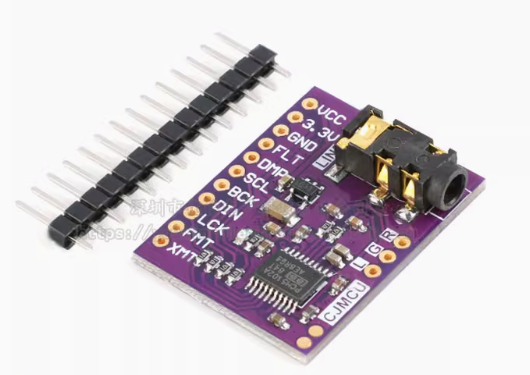
ESP32 I2S音频总线学习笔记(四): INMP441采集音频并实时播放
简介 前面两期文章我们介绍了I2S的读取和写入,一个是通过INMP441麦克风模块采集音频,一个是通过PCM5102A模块播放音频,那如果我们将两者结合起来,将麦克风采集到的音频通过PCM5102A播放,是不是就可以做一个扩音器了呢…...

多模态大语言模型arxiv论文略读(108)
CROME: Cross-Modal Adapters for Efficient Multimodal LLM ➡️ 论文标题:CROME: Cross-Modal Adapters for Efficient Multimodal LLM ➡️ 论文作者:Sayna Ebrahimi, Sercan O. Arik, Tejas Nama, Tomas Pfister ➡️ 研究机构: Google Cloud AI Re…...

Vue 模板语句的数据来源
🧩 Vue 模板语句的数据来源:全方位解析 Vue 模板(<template> 部分)中的表达式、指令绑定(如 v-bind, v-on)和插值({{ }})都在一个特定的作用域内求值。这个作用域由当前 组件…...

AT模式下的全局锁冲突如何解决?
一、全局锁冲突解决方案 1. 业务层重试机制(推荐方案) Service public class OrderService {GlobalTransactionalRetryable(maxAttempts 3, backoff Backoff(delay 100))public void createOrder(OrderDTO order) {// 库存扣减(自动加全…...
