【C++期末编程题题库】代码+详解18道

适合期末复习c++看,或者刚入门c++的小白看,有的题会补充知识点,期末复习题的代码一般比较简单,所以语法上没那么严谨。本文所有题目要求全在代码块的最上面。
目录
1、设计复数类
2、设计Computer类
3、实现相加的函数模板
4、圆类的设计
5、学生类设计
6、求圆与直线位置关系
7、家庭账户共享
8、栈类的设计
9、主人召唤宠物
10、点圆圆柱单继承
11、点长方形长方体单继承
12、点圆球体运行时多态
13、学生数据写入文件和读取
14、图形抽象类派生具体类求多个图形面积
15、 除数为0的异常处理
16、学生数据修改【文件操作】
17、分数的加减
18、统计字符数组中某个字符出现次数
1、设计复数类
//设计复数类Complex和友元运算符重载>>及<<实现复数类对象的标准输入和输出
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Complex
{
private:double real, imag;
public:Complex(double r = 0, double i = 0){real = r;imag = i;}//下面是友元的声明,所以函数参数只写类型是可以的friend istream& operator>>(istream&, Complex&);friend ostream& operator<<(ostream&, Complex&);
};
istream& operator>>(istream& input, Complex& c)
{//输入实部和虚部input >> c.real >> c.imag;return input;//返回istream,符合operator>>的实现
}ostream& operator<<(ostream& output, Complex& c)
{if (c.imag > 0)output << c.real << "i+" << c.imag;else if (c.imag < 0)output << c.real << "i" << c.imag;elseoutput << c.real << "i";return output;
}int main()
{Complex c;cin >> c;cout << c;return 0;
}

2、设计Computer类
//计算机Computer的属性包括型号、生产厂家和价格,用文件流中write()函数将若干
//计算机中的信息写入文件Computer.dat中,然后用read()函数将Computer.dat中所有数据读出。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;//涉及文件读写操作了,肯定要访问成员变量,用struct即可
struct Computer
{int id;string manufacter;double price;
};int main()
{Computer c;cout << "Please input the id, manufacter and price of Computer:";cin >> c.id >> c.manufacter >> c.price;ofstream out("Computer.dat", ios::binary | ios::out);if (!out.is_open())//如果文件打开不成功//也可写为if(!out){cout << "fail to open the file\n" << endl;exit(-1);}out.write((const char*)&c, sizeof(c));//写入是const char*out.close();ifstream in("Computer.dat", ios::binary | ios::in);if (!in){cout << "fail to open the file\n" << endl;exit(-1);}in.read((char*)&c, sizeof(c));//读取是char*in.close();cout << "the data of Computer is:" << endl;cout << c.id << " " << c.manufacter << " " << c.price << endl;return 0;
}
3、实现相加的函数模板
//编写两个相长度数值型一维数组对应元素相加的函数模板
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;template<class T>
void add(T a[], T b[], T c[], int n)
{for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)c[i] = a[i] + b[i];
}int main()
{int a[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };int b[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };int c[5];add(a, b, c, 5);for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) cout << c[i] << " ";cout << endl;return 0;
}
4、圆类的设计
//1、圆类的设计:设计一个圆类,计算出它的周长,面积,
//并有圆心移动和半径移动(就是变化的意思)的操作,并打印出数据
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;//这里最好不要用float,除非你写为3.14f,因为你写一个小数3.14默认为double
//如果你用float,这里就会发生截断,因为是从double到float
const double pi = 3.14;class Circle
{
public://也可采用c++11的初始化列表方式/*Circle(int x = 0, int y = 0, int r = 0):_x(x),_y(y),_r(r){}*/Circle(double x = 0, double y = 0, double r = 0){_x = x; _y = y; _r = r;}double circum(){return 2 * pi * _r;}double area(){return pi * _r * _r;}void movep(double x, double y){_x += x; _y += y;}void mover(double r){_r += r;}void show(){cout << "圆心:(" << _x << "," << _y << ") 半径:" << _r << endl;}private:double _x, _y, _r;
};int main()
{Circle c(1.2, 1.3, 2.1);c.show();cout << "circum:" << c.circum() << " " << "area:" << c.area() << endl;c.movep(1.1, 2.2);c.show();c.mover(1.2);c.show();return 0;
}
5、学生类设计
//学生类设计求学生最高分最低分和平均分,并打印出学生信息
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;class Student
{
private:int _id;string _name;double _score;public:Student(int id = 0, string name = "", double score = 0.0){_id = id;_name = name;_score = score;}void input(int id, string name, double score){_id = id;_name = name;_score = score;}double Getscore(){return _score;}void show(){cout << "id:" << _id << " " << "name:" << _name << " " << "score:" << _score << endl;}
};double maxscore(Student stu[], int n)
{double maximum = 0.0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)if (maximum < stu[i].Getscore()) maximum = stu[i].Getscore();return maximum;
}double minscore(Student stu[], int n)
{double minimum = 100;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)if (minimum > stu[i].Getscore()) minimum = stu[i].Getscore();return minimum;
}double averscore(Student stu[], int n)
{double sum = 0.0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)sum += stu[i].Getscore();return sum / n;
}int main()
{Student stu[3];int id; string name; double score;for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){cin >> id >> name >> score;stu[i].input(id, name, score);}for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) stu[i].show();cout << "maxscore:" << maxscore(stu, 3) << endl;cout << "minscore:" << minscore(stu, 3) << endl;cout << "averscore:" << averscore(stu, 3) << endl;return 0;
}
6、求圆与直线位置关系
//定义直线类和圆类,求两者位置关系(相切、相交或相离)
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;//直线:ax + by + c = 0
class Circle;//必须先声明Circle类,不然友元函数找不到Circle
class Line
{
private:double _a, _b, _c;
public:Line(double a = 0, double b = 0, double c = 0){_a = a;_b = b;_c = c;}//这里不用友元也可以,你可以用一个geta等等来获取私有成员,对于圆类同理friend int position_relation(const Line&, const Circle&);
};class Circle
{
private:double _x, _y, _r;//圆心和半径
public:Circle(double x = 0, double y = 0, double r = 0){_x = x;_y = y;_r = r;}friend int position_relation(const Line&, const Circle&);
};//圆与直线位置关系公式:d=ax+by+c/根号下a*a+b*b【其中abc均为直线的,x和y是圆的圆心】
//如果d>r:相离 d==r:相切 d<r:相交
int position_relation(const Line& l, const Circle& c)
{double d = l._a * c._x + l._b * c._y + l._c / sqrt(l._a * l._a + l._b * l._b);//因为d是算出来的,浮点数会有精度损失,所以比较的时候要靠精度来比if (fabs(d - c._r) > 0.000001) return -1; //相离else if (fabs(d - c._r) < 0.000001) return 1; //相交else return 0; //相切
}int main()
{Line l(2.1, 2.2, 2.3);Circle c(1.1, 1.2, 1.3);int ret = position_relation(l, c);if (ret == -1) cout << "相离" << endl;else if (ret == 1) cout << "相交" << endl;else cout << "相切" << endl;return 0;
}
回顾友元:
在C++中,友元函数(Friend Function)是一种特殊的函数,它可以访问并操作类的私有成员,即使它不是类的成员函数。通过友元函数,我们可以实现对类的私有成员的非成员函数访问权限。友元提供了一种突破封装的方式。友元函数提供了一种在需要时访问类的私有成员的机制,但应该慎重使用,因为过多的友元函数可能破坏类的封装性。
友元函数特性:
- (1) 友元函数可以访问类的私有和保护成员,但不是类的成员函数。
- (2) 友元函数不能被const修饰。由于友元函数不属于任何类的成员函数,它们无法被 const 修饰。
- (3) 友元函数可以在类定义的任何地方声明,不受类访问限定符限制。
- (4) 一个函数可以是多个类的友元函数。
- (5) 友元函数的调用与普通函数的调用和原理相同。
- (6)友元函数/友元类是单向的,A在B类中被声明为友元函数/友元类,表示A是B的友元函数/友元类,但B不是A的友元类函数/友元类;
- (7)友元函数在类中声明时用friend修饰,但是在定义时不需要用friend修饰;
- (8)友元函数不能被继承:父类的友元函数,继承后并不会成为子类的友元函数;
- (9)友元函数不具有传递性:A类和B类都是C类的友元类,但是A类和B类并不是友元类;
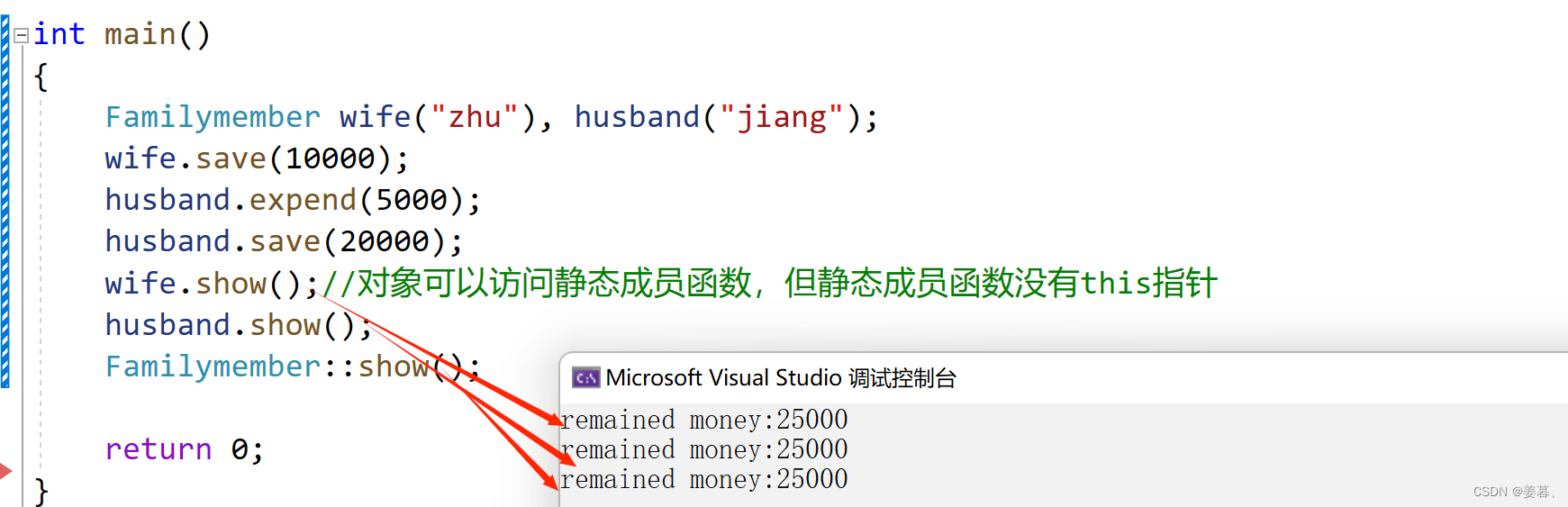
7、家庭账户共享
//家庭银行账户共享,即一个家庭几个成员共享财产,设计一个Familymember类
//实现钱财的支出和存钱,并显示剩余钱额【定义静态成员实现】
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;class Familymember
{
private:string _name;
public:Familymember(string name = "");static double money;static void save(double m);static void expend(double m);static void show();
};
//类外初始化静态成员变量不要加static
double Familymember::money = 0;//类內声明,类外定义Familymember::Familymember(string name)
{//类內声明已经有默认参数,类外就不能给了,否则就重定义默认参数了_name = name;
}
//类外定义静态成员函数不能加static
void Familymember:: save(double m)
{money += m;
}void Familymember::expend(double m)
{money -= m;
}void Familymember::show()
{cout << "remained money:" << money << endl;
}int main()
{Familymember wife("zhu"), husband("jiang");wife.save(10000);husband.expend(5000);husband.save(20000);wife.show();//对象可以访问静态成员函数,但静态成员函数没有this指针husband.show();Familymember::show();return 0;
}
8、栈类的设计
//设计一个静态栈类,内有构造函数,且有压栈和入栈操作,并返回栈顶元素,输入数据
//以0表示结束
//学校期末要求不高,我以前的博客写过动态栈,想了解的可以看看
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;//这里不要定义为size,因为size是一个关键字,用于定义类型大小,如果你这里
//常量名称定义为size就会冲突!但是在devc++就能跑过去,可能dev不严谨,vs下是过不去的
const int stackSize = 100;class Stack
{
private:int sta[stackSize];int _top;//栈顶public:Stack();int push(int x);//入栈int pop();//出栈
};Stack::Stack()
{//直接置空即可_top = 0;
}int Stack::push(int x)
{if (_top == stackSize)return 0;//栈满返回0sta[_top++] = x;return x;
}int Stack::pop()
{if (_top == 0)return 0;//栈空返回0//返回删除之后的栈顶return sta[--_top];
}int main()
{Stack s;int x;cout << "Please input pushed data:" << endl;cin >> x;while (x && s.push(x)){cout << "Please input pushed data:" << endl;cin >> x;}while (x = s.pop())cout << "the poped data is :" << x << endl;return 0;
}
9、主人召唤宠物
//主人召唤宠物,宠物有名字和应答语,主人也有名字,他可以召唤宠物,看召唤名字与宠物
//的名字是否一致,若一致,宠物就会回应应答语
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Pet
{
private:string _name;string _ans;public:Pet(string name = "", string ans = ""){_name = name;_ans = ans;}void answer(string name) const{if (name == _name)//调用string的operator==cout << _ans << endl;elsecout << "dear host, you are not calling me!" << endl;}
};class Host
{
private:string _name;public:Host(string name = ""){_name = name;}void call(const Pet& p, string name){p.answer(name);}
};int main()
{Host h("MeiZhu");Pet dog("huihui", "wangwang");Pet cat("huahua", "miaomiao~");h.call(dog, "huihui");h.call(cat, "huahuaya");return 0;
}
10、点圆圆柱单继承
//点圆圆柱单继承,即圆类继承点【圆心】类,再由圆柱类继承圆类,求出面积和体积
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;const double pi = 3.14;class Point
{
private://private即可,圆类求面积和体积用不到圆心double _x, _y;
public:Point(double x = 0, double y = 0){_x = x;_y = y;}double area(){return 0.0;}double volume(){return 0.0;}
};class Circle : public Point
{
protected://这里若用private的话,Cylinder求面积和体积就无法使用了double _r;public:Circle(double r = 0.0, double x = 0.0, double y = 0.0):Point(x, y){_r = r;}double area(){return pi * _r * _r;}double volume(){return 0.0;}
};class Cylinder : public Circle
{
private:double _h;public:Cylinder(double x = 0.0, double y = 0.0, double r = 0.0, double h = 0.0):Circle(r, x, y){_h = h;}double area(){ //上下底圆的面积+侧面积:长方形面积return 2 * pi * _r * _r + 2 * pi * _r * _h;}double volume(){ //圆柱体积为底面积*高return Circle::area() * _h;}
};int main()
{Circle cir(2.1, 1.1, 2.2);Cylinder cy(2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 1.2);cout << cir.area() << " " << cir.volume() << endl;cout << cy.area() << " " << cy.volume() << endl;return 0;
}
11、点长方形长方体单继承
//点长方形长方体单继承,长方形继承点类,长方体继承长方形类,求面积和体积
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Point
{
private:double _x, _y;public:Point(double x = 0.0, double y = 0.0){_x = x;_y = y;}double area(){return 0.0;}double volume(){return 0.0;}
};
//长方形
class Rectangle : public Point
{
protected://不能设为private,不然长方体类中用不了了double _length, _width;public:Rectangle(double x = 0.0, double y = 0.0, double l = 0.0, double w = 0.0):Point(x, y){_length = l;_width = w;}double area(){return _length * _width;}double volume(){return 0.0;}
};
//长方体
class Cuboid : public Rectangle
{
private:double _h;public:Cuboid(double x, double y, double l, double w, double h):Rectangle(x, y, l, w){_h = h; }double area(){//长方体表面积:2长*宽+2长*高+2宽*高return 2 * _length * _width + 2 * _length * _h + 2 * _width * _h;}double volume(){//长方体体积:底面积*高return _length * _width * _h;}
};int main()
{Rectangle rec(1.1, 2.0, 2.3, 2.4);Cuboid cub(1.2, 2.2, 2.4, 4.5, 1.1);cout << "area of rectangle is :" << rec.area() << "\t" << "volume of rectangle is:" << rec.volume() << endl;cout << "area of cuboid is :" << cub.area() << "\t" << "volume of cuboid is:" << cub.volume() << endl;return 0;
}
12、点圆球体运行时多态
//点圆球体运行时多态:由圆类继承点类,球类继承圆类,实现求面积和体积,要求多态实现
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;const double pi = 3.14;class Point
{
private:double _x, _y;
public:Point(const double& x, const double& y){//这种加const写法的才是最标准的,因为应付期末,没有那么高的要求的_x = x;_y = y;}virtual double area() = 0;virtual double volume() = 0;
};class Circle : public Point
{
protected:double _r;
public:Circle(double x, double y, double r):Point(x, y){_r = r; }virtual double area(){ //圆的面积:π*r*rreturn pi * _r * _r;}virtual double volume(){return 0.0;}
};
//球体类
class Sphere : public Circle
{
private:double _z; //因为球体的是三维的,所以它的圆心应该再增加一个维度
public:Sphere(double x, double y, double r, double z):Circle(x, y, r){_z = z;}double area(){return 4 * pi * _r * _r;}double volume(){ //V=(4/3)πr^3return 4 * pi * _r * _r * _r / 3;}
};int main()
{Point* p;Circle c(1.1, 1.2, 1.3);Sphere s(1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5);p = &c;cout << " circle: " << p->area() << "\t\t" << p->volume() << endl;p = &s;cout << " sphere: " << p->area() << "\t" << p->volume() << endl;return 0;
}
13、学生数据写入文件和读取
//学生数据写入文件,并读取文件数据到程序中【使用read和write实现】
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;struct Student
{char name[20];int id;int age;char gender[5];
};int main()
{//创建一个输出流对象,并打开文件,以二进制的方式写//写法1://ofstream outfile;//outfile.open("test.txt", ios::binary | ios::trunc);//trunc:如果文件存在先删除,再创建【一般是不用的】//写法2:更简洁!ofstream outfile("test.txt", ios::binary | ios::trunc);if (!outfile)//或写为if(!outfile.is_open()){//判断文件是否打开成功cout << "file open error!" << endl;exit(1);//exit(非0)都代表异常退出}Student stu[3];cout << "Please input the data of 3 students" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){cin >> stu[i].name >> stu[i].id >> stu[i].age >> stu[i].gender;//写入文件,以二进制形式写入outfile.write((const char*)&stu[i], sizeof(stu[i]));}outfile.close();//关闭文件以便以下一次的读出数据//再把学生数据读出Student tmp[3];//保存从文件中读出的数据ifstream infile("test.txt", ios::binary);//读取方法一:直接读取整个数组的数据中//infile.read((char*)tmp, sizeof(tmp));//或写为infile.read((char*)&tmp[0], sizeof(tmp));//因为都是首元素的地址,读取的是一整个数组cout << "The Student data read from file is:" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){//读取方法二:读取数据一个一个数组元素来读取infile.read((char*)&tmp[i], sizeof(tmp[i]));cout << tmp[i].name << " " << tmp[i].id << " " << tmp[i].age<< " " << tmp[i].gender << endl;}infile.close();return 0;
}测试结果如下:

此时打开test.txt文件可以看出是二进制的形式,我们看不懂,但是从文件中读入到程序当中就能看出来了,主要是因为这种二进制读写方式很方便

14、图形抽象类派生具体类求多个图形面积
//用图形类派生圆类和三角形类,分别求面积,并求出面积之和【多态实现】
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;const double pi = 3.14;class Graph
{
public:virtual double area() = 0;
};class Circle : public Graph
{
private:double _x, _y, _r;
public:Circle(const double& x, const double& y, const double& r):_x(x),_y(y),_r(r){}double area(){return pi * _r * _r;}
};class Triangle : public Graph
{
private:double _bottom, _h;
public:Triangle(const double& bottom, const double& h):_bottom(bottom),_h(h){}double area(){return 0.5 * _bottom * _h;}
};double sumarea(Graph* g[], int n)
{double sum = 0.0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)sum += g[i]->area();return sum;
}int main()
{Circle c1(1.1, 1.2, 1.3), c2(1.2, 1.3, 1.4);Triangle t1(2.1, 3.1), t2(1.1, 3.4);Graph* g[4] = { &c1, &c2, &t1, &t2 };cout << sumarea(g, 4) << endl;return 0;
}
15、 除数为0的异常处理
建议先看我写过的异常文章:【C++】异常【完整版】-CSDN博客
//写一个实现除法的函数,主函数利用异常处理除数为0的情况
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;//division:除法,dividend:被除数,divisor:除数
double division(double x, double y)
{if (y == 0){//我们不建议写为throw 0.0, 因为这种处理方式和之前讲的错误码一样,没什么意义//不如直接用错误码了throw string("发生除0错误!");}return x / y;
}int main()
{try{double x, y;cin >> x >> y;cout << "x / y = " << division(x, y) << endl;cin >> x >> y;cout << "x / y = " << division(x, y) << endl;}catch (const string& err){cout << err << endl;}//下面用基类捕获的方式,若除数为0,会直接报错!//但有时如出现数组越界问题等,会直接打印出错误信息//catch (exception& e)//{// cout << e.what() << endl;//}return 0;
}
16、学生数据修改【文件操作】
//建立学生类,将学生数据写入文件,然后读取回程序中,并修改第3个学生的信息,然后写入文件
//然后再读取到程序中并打印【要求:read和write实现,并使用文件指针定位的seekp和seekg】
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;struct Stu
{int id;char name[20];//不能用string,不然会报错:读取访问权限冲突,除非用c_str,原因下面解释double score;
};int main()
{Stu stu[20];//为什么要用fstream呢?因为下面有读指针和写指针操作同时进行的,这里定义fstream对象//既可以读又可以写,很方便,省得下面你又得关闭文件,然后又打开文件...fstream io("stu.txt", ios::binary | ios::out | ios::in);if (!io){cout << "Fail to open the file!" << endl;exit(-1);}cout << "Please input the datas of students:" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)cin >> stu[i].id >> stu[i].name >> stu[i].score;io.write((const char*)stu, sizeof(stu));//一次性把整个数组全都写入文件中io.close();io.open("stu.txt", ios::binary | ios::in | ios::out);if (!io){cout << "Fail to open the file!" << endl;exit(-1);}Stu tmp;cout << "Please input the updated datas of the third student:" << endl;cin >> tmp.id >> tmp.name >> tmp.score;io.seekp(2 * sizeof(tmp), ios::beg);//写文件指针定位,从原来第3个学生的位置开始io.write((const char*)&tmp, sizeof(tmp));//把修改后的数据放回文件中第3个学生的位置io.close();io.open("stu.txt", ios::binary | ios::out | ios::in);io.read((char*)stu, sizeof(stu));//修改完第3个学生数据后读回数组中io.close();//一定要关闭文件!cout << "The students' datas read from file are:" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)cout << stu[i].id << " " << stu[i].name << " " << stu[i].score << endl;return 0;
}

问题①、C++中文件读写类对象时,如果类对象中有string类型的成员变量,如何处理?
在C++中,对于类对象的二进制读写,涉及到对象的内存布局和成员变量的特性。而对于`string`这样的对象,它的内部实现复杂,包括指针指向堆上的动态内存,涉及到分配和释放内存等操作。因此,直接进行二进制读写可能会导致读取权限冲突。当你尝试将包含`string`成员变量的对象写入文件时,实际上只会将指针的值写入文件,而不是字符串的内容。而在读取文件时,再次加载这个对象,那个指针就指向了一个无效的内存地址。这会导致访问非法内存,进而出现读取权限冲突。为了避免这个问题,你可以考虑使用序列化和反序列化来实现文件的读写操作。序列化是指将对象转换为序列化的字节流,而反序列化则是将字节流重新转换为对象。通过序列化和反序列化操作,可以确保对象的完整性和正确性。你可以使用C++的一些库(如Boost.Serialization、Protocol Buffers)来实现对象的序列化和反序列化。这些库提供了易于使用和强大的功能,让你可以方便地进行对象的读写操作,而不会发生读取权限冲突的问题。
在C++中,文件读写类对象时,是可以包含string类型的成员变量的。C++的文件读写操作对于大多数基本类型和标准库类型(包括string)都有支持。当你将一个自定义的类对象写入文件时,包含了string类型成员变量的类实例将被完整地写入文件中。但需要注意的是,string对象的存储是动态的,所以仅将类对象的二进制数据写入文件是不够的,还需要将string的内容一并写入文件,并在读取时进行相应处理。你可以使用C++标准库中的fstream类进行文件读写操作。例如,可以使用ofstream类对象将类对象写入文件,再使用ifstream类对象从文件中读取类对象。在写入时,可以使用成员函数c_str()将string类型转换为C风格字符串,并使用成员函数write()写入文件;在读取时,可以使用成员函数getline()读取文件中的字符串,并重新构造string对象。
注意,在进行文件读写操作时,需要保证文件的打开和关闭操作正确执行,并处理可能出现的异常情况,以确保数据的完整性与安全性。同时,为了确保跨平台的文件读写兼容性,建议在二进制读写时使用文本模式(例如使用"rb"和"wb"参数)。
以下是一个简单的示例代码,演示了如何进行文件读写操作:
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>class MyClass {
public:std::string name;int age;
};int main() {MyClass obj;obj.name = "Alice";obj.age = 20;std::ofstream outfile("data.txt", std::ios::binary);if (outfile.is_open()) {outfile.write(obj.name.c_str(), obj.name.length() + 1);outfile.write(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&obj.age), sizeof(obj.age));outfile.close();std::cout << "对象写入文件成功" << std::endl;} else {std::cout << "打开文件失败" << std::endl;return 1;}std::ifstream infile("data.txt", std::ios::binary);if (infile.is_open()) {std::string name;std::getline(infile, name, '\0');obj.name = name;infile.read(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&obj.age), sizeof(obj.age));infile.close();std::cout << "从文件中读取的对象:" << std::endl;std::cout << "name: " << obj.name << std::endl;std::cout << "age: " << obj.age << std::endl;} else {std::cout << "打开文件失败" << std::endl;return 1;}return 0;
}该示例中,定义了一个包含string类型成员变量的MyClass类,通过ofstream对象将类的实例写入文件,再通过ifstream对象从文件中读取类对象。在写入时,使用了成员函数c_str()获取string对象的C风格字符串;在读取时,使用了成员函数getline()读取字符串,并重新构造了string对象。最后,将读取到的类对象的成员变量输出到控制台。
问题②、c++中,在文件操作中,为什么读取完数据后,要关闭文件,才能写入数据到文件?
在C++中,关闭文件的目的不是为了读取完数据后才能写入数据到文件,而是为了确保对文件进行完整的操作并释放相关资源。
文件在被打开后会占用一些系统资源,如文件描述符等。当读取完数据后,如果不关闭文件,文件依然保持打开状态,此时其他程序可能无法对该文件进行操作或者文件的状态可能不会及时更新。此外,一些操作系统可能会限制同时打开的文件数量,如果不关闭文件,可能会达到限制而导致其他文件无法正常打开。最重要的是,关闭文件还可以确保数据的完整性和正确性。在写入数据时,操作系统会将数据缓存到内存中,然后根据一定的策略将数据写入到文件中,这个过程是异步的。如果在写入数据的过程中突然关闭文件,可能会导致数据丢失或不完整。
因此,为了保证文件操作的正确性和系统资源的释放,我们通常会在读取完数据后关闭文件,然后再进行写入操作。这样可以确保文件的状态正确、数据的完整性并释放相关的资源。
17、分数的加减

//定义分数类,内有构造函数和显示分数的show函数,并利用友元函数实现分数的加减
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Fraction
{
private:double dividend, divisor;//dividend:被除数,即分子 divisor:除数,即分母
public:Fraction(const double& divid = 0.0, const double& divir = 0.0):dividend(divid),divisor(divir){}void show(){cout << dividend << "/" << divisor << endl;}friend Fraction operator+(const Fraction&, const Fraction&);friend Fraction operator-(const Fraction&, const Fraction&);
};Fraction operator+(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2)
{return Fraction(f1.dividend * f2.divisor + f1.divisor * f2.dividend, f1.divisor * f2.divisor);
}Fraction operator-(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2)
{return Fraction(f1.dividend * f2.divisor - f1.divisor * f2.dividend, f1.divisor * f2.divisor);
}int main()
{Fraction f1(2, 3), f2(1, 2), f3;f3 = f1 + f2;f3.show();f3 = f1 - f2;f3.show();return 0;
}
18、统计字符数组中某个字符出现次数
//定义求一个字符数组中某字符有多少个的函数sum(),用c++实现
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int sum(char* arr, char target)
{int cnt = 0;int i = 0;while (arr[i] != '\0'){if (arr[i] == target)cnt++;i++;}return cnt;
}int main()
{char arr[] = "hello world!";char target = 'o';int ret = sum(arr, target);cout << target << "出现了:" << ret << "次" << endl;return 0;
}
相关文章:

【C++期末编程题题库】代码+详解18道
适合期末复习c看,或者刚入门c的小白看,有的题会补充知识点,期末复习题的代码一般比较简单,所以语法上没那么严谨。本文所有题目要求全在代码块的最上面。 目录 1、设计复数类 2、设计Computer类 3、实现相加的函数模板 4、圆类…...

一种DevOpts的实现方式:基于gitlab的CICD(一)
写在之前 笔者最近准备开始入坑CNCF毕业的开源项目,看到其中有一组开源项目的分类就是DevOpts。这个领域内比较出名的项目是Argocd,Argo CD 是一个用于 Kubernetes 的持续交付 (Continuous Delivery) 工具,它以声明式的方式实现了应用程序的…...

nodejs和vuejs的区别
一、vue项目开发中,两个经常混合使用。 不同: 1、概念不同: 一个是前端框架,一个是服务端语言。 Node.js 是一个基于 Chrome V8 引擎的 JavaScript 运行环境。 Node.js 使用了一个事件驱动、非阻塞式 I/O 的模型,使…...

16、Kubernetes核心技术 - 节点选择器、亲和和反亲和
目录 一、概述 二、节点名称 - nodeName 二、节点选择器 - nodeSelector 三、节点亲和性和反亲和性 3.1、亲和性和反亲和性 3.2、节点硬亲和性 3.3、节点软亲和性 3.4、节点反亲和性 3.5、注意点 四、Pod亲和性和反亲和性 4.1、亲和性和反亲和性 4.2、Pod亲和性/反…...
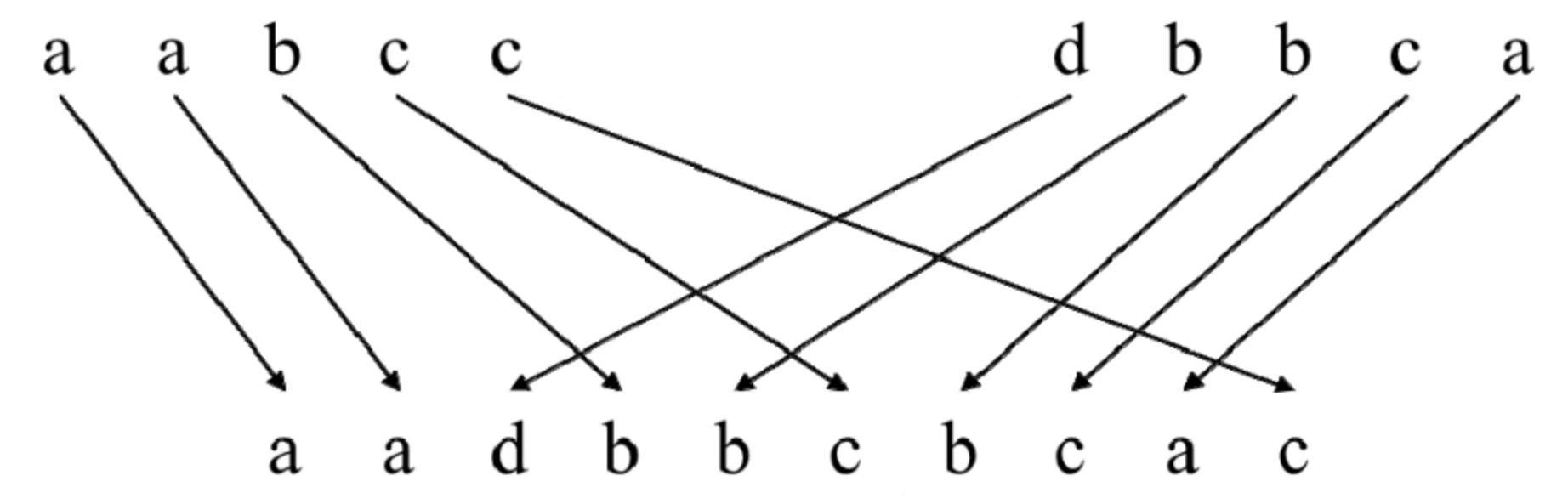
面试算法96:字符串交织
题目 输入3个字符串s1、s2和s3,请判断字符串s3能不能由字符串s1和s2交织而成,即字符串s3的所有字符都是字符串s1或s2中的字符,字符串s1和s2中的字符都将出现在字符串s3中且相对位置不变。例如,字符串"aadbbcbcac"可以由…...
?如何实现数据的双向绑定?)
什么是Vue.js的响应式系统(reactivity system)?如何实现数据的双向绑定?
Vue.js的响应式系统是指一种能够跟踪数据变化并实时更新相关界面的机制。它是Vue.js框架的核心特性之一。 在Vue.js中,你可以使用数据绑定语法将数据绑定到DOM元素上。当绑定的数据发生变化时,Vue.js会自动监听这些变化并更新相关的DOM元素。 Vue.js实…...

力扣labuladong一刷day52天LRU算法
力扣labuladong一刷day52天LRU算法 文章目录 力扣labuladong一刷day52天LRU算法概念一、146. LRU 缓存思路一:使用双向链表加map来手动实现。思路二:使用LinkedHashMap 概念 LRU的全称为Least Recently Used,翻译出来就是最近最少使用的意思…...
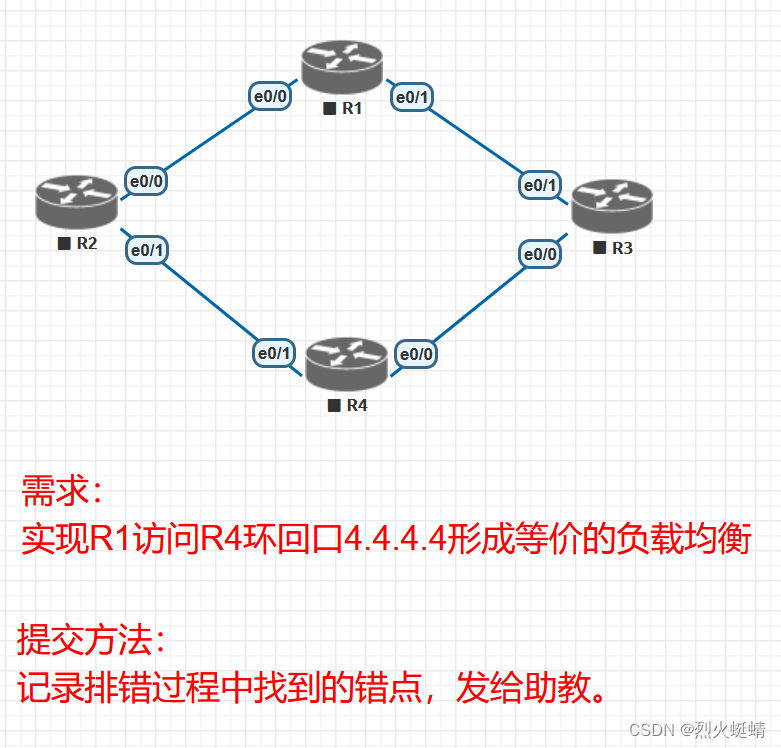
CCNP课程实验-06-EIGRP-Trouble-Shooting
目录 实验条件网络拓朴 环境配置开始排错错误1:没有配置IP地址,IP地址宣告有误错误2:R3配置了与R1不同的K值报错了。错误3:R4上的AS号配置错,不是1234错误4:R2上配置的Key-chain的R4上配置的Key-chain不一致…...
判断完全数-第11届蓝桥杯省赛Python真题精选
[导读]:超平老师的Scratch蓝桥杯真题解读系列在推出之后,受到了广大老师和家长的好评,非常感谢各位的认可和厚爱。作为回馈,超平老师计划推出《Python蓝桥杯真题解析100讲》,这是解读系列的第27讲。 判断完全数&#…...

【Bootstrap5学习 day12】
Bootstrap5 导航 Bootstrap5提供了一种简单快捷的方法来创建基本导航,它提供了非常灵活和优雅的选项卡和Pills等组件。Bootstrap5的所有导航组件,包括选项卡和Pillss,都通过基本的.nav类共享相同的基本标记和样式。 创建基本导航 要创建简单…...

算法训练第五十九天|503. 下一个更大元素 II、42. 接雨水
503. 下一个更大元素 II: 题目链接 给定一个循环数组 nums ( nums[nums.length - 1] 的下一个元素是 nums[0] ),返回 nums 中每个元素的 下一个更大元素 。 数字 x 的 下一个更大的元素 是按数组遍历顺序,这个数字之…...
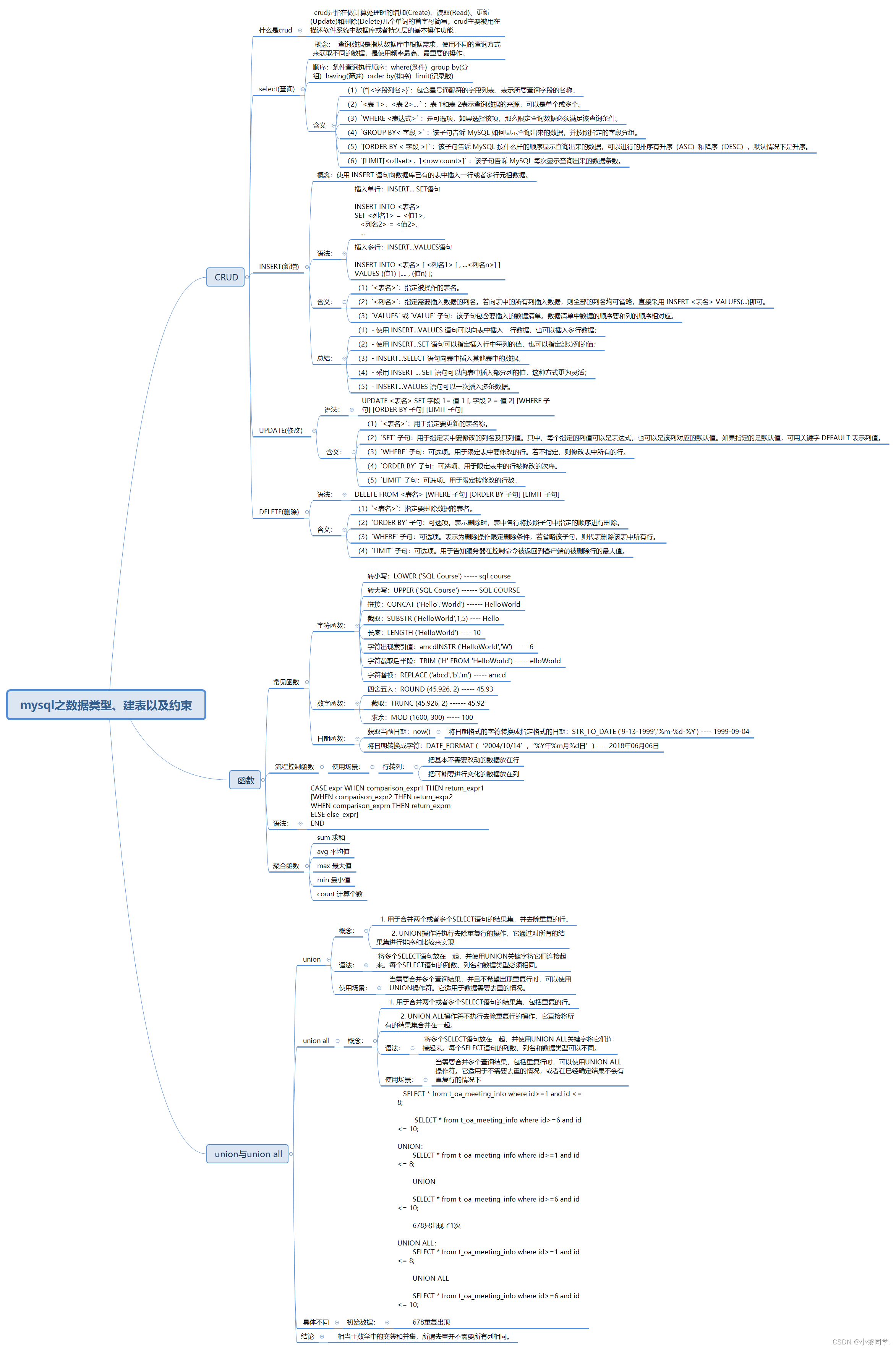
mysql之数据类型、建表以及约束
目录 一. CRUD 1.1 什么是crud 1.2 select(查询) 1.3 INSERT(新增) 1.4 UPDATE(修改) 1.5 DELETE(删除) 二. 函数 2.1 常见函数 2.2 流程控制函数 2.3聚合函数 三. union与union all 3.1 union 3.2 union all 3.3 具体不同 3.4 结论 四、思维导图 一. CRUD 1.1…...
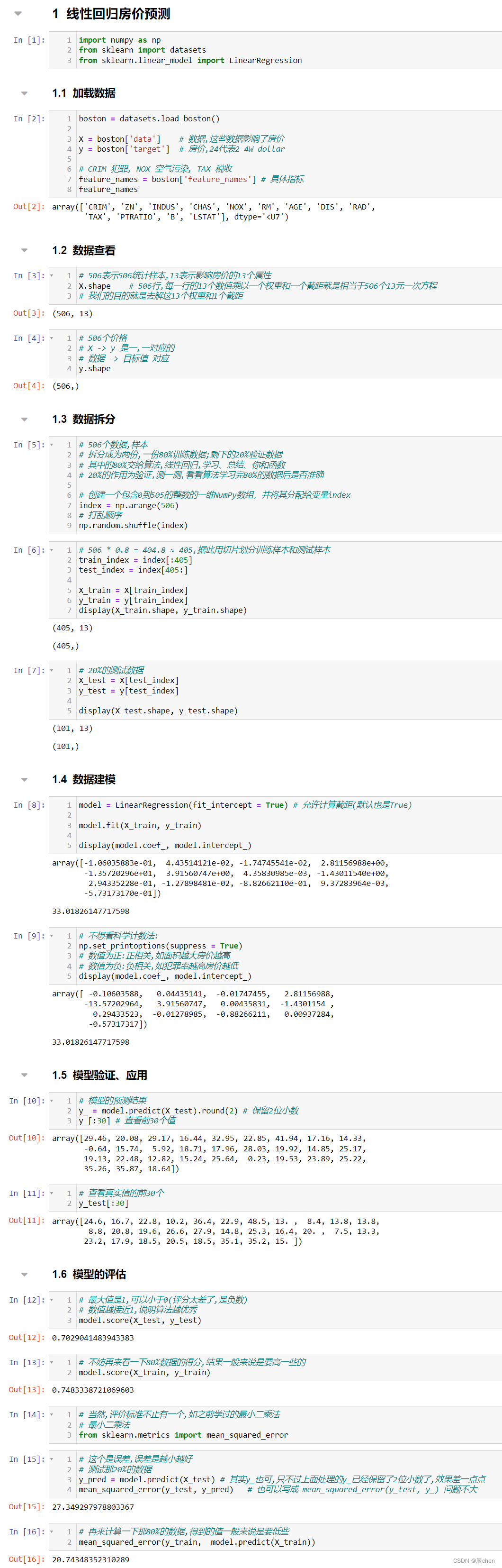
复试 || 就业day04(2024.01.05)项目一
文章目录 前言线性回归房价预测加载数据数据查看数据拆分数据建模模型的验证、应用模型的评估 总结 前言 💫你好,我是辰chen,本文旨在准备考研复试或就业 💫本文内容来自某机构网课,是我为复试准备的第一个项目 &#…...
)
华为机试真题实战应用【赛题代码篇】-最小传输时延(附python、C++和JAVA代码实现)
目录 问题描述 输入描述: 输出描述: 知识储备 解题思路 思路一...

C++ 运算符重载
(Operator) 加分 减法 []的重载 #include <iostream> using namespace std;class time1 {public:time1(){shi0;fen0;miao0;}time1(int shi, int fen, int miao){this->shi shi;this->fen fen;this->miao miao;}time1 operator (ti…...
vue3学习 【2】vite起步和开发工具基本配置
vite的简介 官方文档 刚起步学习,所以我们只需要按照官方文档的入门流程即可。推荐阅读一下官网的为什么使用vite vite目前需要的node版本是18,可以参考上一篇文章的安装nvm,用来进行多版本的node管理。 vite安装与使用 npm create vitela…...
计算机创新协会冬令营——暴力枚举题目06
我给大家第一阶段的最后一道题就到这里了,下次得过段时间了。所以这道题简单一点。但是足够经典 下述题目描述和示例均来自力扣:两数之和 题目描述 给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target …...

单片机快速入门
参考连接: 安装MinGW-64(在win10上搭建C/C开发环境)https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/85429160MinGW-64; 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1oE1FmjyK7aJPnDC8vASmCg?pwdy1mz 提取码:y1mz --来自百度网盘超级会员V7的分享C…...
)
Eureka相关问题及答案(2024)
1、什么是Eureka? Eureka是一个由Netflix开发的服务发现(Service Discovery)工具,它是Spring Cloud生态系统中的一个关键组件。服务发现是微服务架构中的一个重要概念,它允许服务实例在启动时注册自己,以便…...

Django 7 实现Web便签
一、效果图 二、会用到的知识 目录结构与URL路由注册request与response对象模板基础与模板继承ORM查询后台管理 三、实现步骤 1. terminal 输入 django-admin startapp the_10回车 2. 注册, 在 tutorial子文件夹settings.py INSTALLED_APPS 中括号添加 "the…...
UE5 学习系列(二)用户操作界面及介绍
这篇博客是 UE5 学习系列博客的第二篇,在第一篇的基础上展开这篇内容。博客参考的 B 站视频资料和第一篇的链接如下: 【Note】:如果你已经完成安装等操作,可以只执行第一篇博客中 2. 新建一个空白游戏项目 章节操作,重…...

Chapter03-Authentication vulnerabilities
文章目录 1. 身份验证简介1.1 What is authentication1.2 difference between authentication and authorization1.3 身份验证机制失效的原因1.4 身份验证机制失效的影响 2. 基于登录功能的漏洞2.1 密码爆破2.2 用户名枚举2.3 有缺陷的暴力破解防护2.3.1 如果用户登录尝试失败次…...
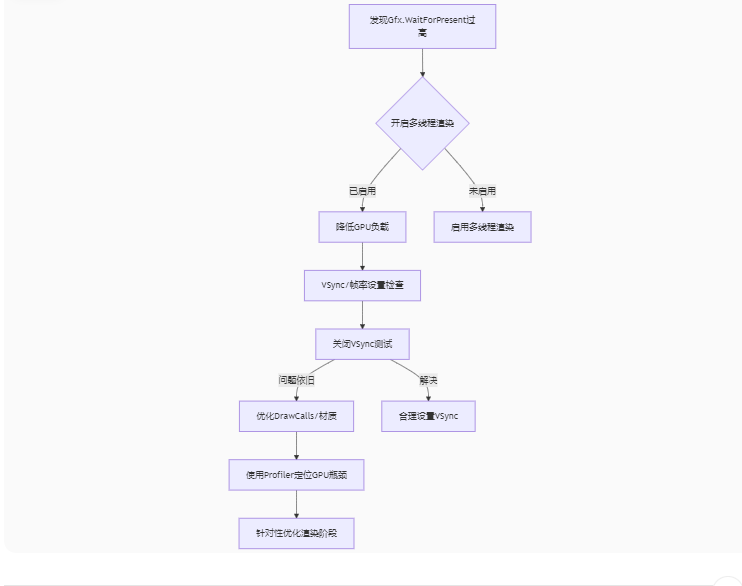
Unity3D中Gfx.WaitForPresent优化方案
前言 在Unity中,Gfx.WaitForPresent占用CPU过高通常表示主线程在等待GPU完成渲染(即CPU被阻塞),这表明存在GPU瓶颈或垂直同步/帧率设置问题。以下是系统的优化方案: 对惹,这里有一个游戏开发交流小组&…...

《Qt C++ 与 OpenCV:解锁视频播放程序设计的奥秘》
引言:探索视频播放程序设计之旅 在当今数字化时代,多媒体应用已渗透到我们生活的方方面面,从日常的视频娱乐到专业的视频监控、视频会议系统,视频播放程序作为多媒体应用的核心组成部分,扮演着至关重要的角色。无论是在个人电脑、移动设备还是智能电视等平台上,用户都期望…...

NFT模式:数字资产确权与链游经济系统构建
NFT模式:数字资产确权与链游经济系统构建 ——从技术架构到可持续生态的范式革命 一、确权技术革新:构建可信数字资产基石 1. 区块链底层架构的进化 跨链互操作协议:基于LayerZero协议实现以太坊、Solana等公链资产互通,通过零知…...
AI书签管理工具开发全记录(十九):嵌入资源处理
1.前言 📝 在上一篇文章中,我们完成了书签的导入导出功能。本篇文章我们研究如何处理嵌入资源,方便后续将资源打包到一个可执行文件中。 2.embed介绍 🎯 Go 1.16 引入了革命性的 embed 包,彻底改变了静态资源管理的…...

服务器--宝塔命令
一、宝塔面板安装命令 ⚠️ 必须使用 root 用户 或 sudo 权限执行! sudo su - 1. CentOS 系统: yum install -y wget && wget -O install.sh http://download.bt.cn/install/install_6.0.sh && sh install.sh2. Ubuntu / Debian 系统…...

安全突围:重塑内生安全体系:齐向东在2025年BCS大会的演讲
文章目录 前言第一部分:体系力量是突围之钥第一重困境是体系思想落地不畅。第二重困境是大小体系融合瓶颈。第三重困境是“小体系”运营梗阻。 第二部分:体系矛盾是突围之障一是数据孤岛的障碍。二是投入不足的障碍。三是新旧兼容难的障碍。 第三部分&am…...

SQL慢可能是触发了ring buffer
简介 最近在进行 postgresql 性能排查的时候,发现 PG 在某一个时间并行执行的 SQL 变得特别慢。最后通过监控监观察到并行发起得时间 buffers_alloc 就急速上升,且低水位伴随在整个慢 SQL,一直是 buferIO 的等待事件,此时也没有其他会话的争抢。SQL 虽然不是高效 SQL ,但…...

xmind转换为markdown
文章目录 解锁思维导图新姿势:将XMind转为结构化Markdown 一、认识Xmind结构二、核心转换流程详解1.解压XMind文件(ZIP处理)2.解析JSON数据结构3:递归转换树形结构4:Markdown层级生成逻辑 三、完整代码 解锁思维导图新…...
